Значимость различных критериев оценки стопы в диагностике плоскостопия у детей
Автор: Сертакова А.В., Рубашкин С.А., Тимаев М.Х., Дохов М.М., Коршунова Г.А., Зверева К.П., Агафонова Н.Ю.
Журнал: Саратовский научно-медицинский журнал @ssmj
Рубрика: Травматология и ортопедия
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.16, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Цель: проанализировать совокупность разносторонних критериев оценки плоской стопы (ПС) у детей и выделить наиболее значимые для диагностики заболевания. Материал и методы. Проведено одномоментное исследование, включавшее 150 пациентов с диагнозом ПС (средний возраст 9,5±0,8 года) и 50 пациентов с нейтральной стопой (средний возраст 10,1 ±1,3 года). Обследование детей осуществлялось при помощи совокупности методов: клинического, метода анкетирования для определения качества жизни, рентгенологического и метода компьютерной томографии, биомеханического и электронейромиографии (ЭНМГ). Проводилась кластеризация и математическое моделирование полученных результатов стандартных диагностических тестов. Результаты. Статистически значимыми для диагностики нарушений при ПС являются рентгенологические показатели: таранно-горизонтальный угол (р
Детский возраст, критерии диагностики, плоская стопа
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149135613
IDR: 149135613 | УДК: 617.586-007.58-053.2
Текст научной статьи Значимость различных критериев оценки стопы в диагностике плоскостопия у детей
1Введение. Плоская стопа (ПС) у детей — группа патологических состояний, характеризующаяся нарушением взаимоотношений в суставах стопы по-лиэтиологичного характера, приводящих к снижению высоты медиального продольного свода и ее биомеханической функции [1, 2]. Истинная распространенность и масштаб проблемы в настоящее время оценить невозможно из-за отсутствия согласованности диагностических критериев заболевания, а также малого количества публикаций и наблюдений, посвященных ПС детского возраста [3–5]. Принятая мировым сообществом ортопедов классификация ПС у детей с делением на мобильную и ригидную формы слишком условна и проста [6]. Она включает в себя абсолютно разнородные факторы, определяющие заболевание. Приблизительная распространенность мобильной ПС составляет 35-65% в детской популяции, ригидной формы — 5-10%, без акцента на половую принадлежность [7]. На наш взгляд, именно эта классификация дала толчок к неопределенности как клинической картины, так и диагностики лечения, а также его тактике. Например, некоторые авторы определяют мобильную форму ПС как «физиологическую» из-за малосимптомного течения [7, 8], хотя ряд исследований биомеханической функции подобной стопы демонстрировали значимые отклонения при ходьбе [6, 9]. Отмечены следующие варианты анатомо-биомеханических нарушений при ПС, причем даже мобильной ее формы: вальгусное положение заднего отдела стопы по отношению к другим, подошвенное сгибание и медиальная девиация таранной кости, наружная ротация пяточной кости, тяжелая подтаранная эверсия и супинация переднего отдела стопы [9–11]. Разнятся мнения ортопедов и в отношении степени тяжести деформации, лечебной тактике, сроках проведения и показаниях для оперативного лечения по ее коррекции. Несмотря на совокупность инструментов диагностики, практически отсутствуют четко определенные критерии, которые служили бы опорными точками для решения проблемы. Кроме того, в мировой литературе имеются единичные сообщения в отношении качества жизни маленьких пациентов и данных клинических функциональных тестов [12].
Цель: проанализировать совокупность разносторонних критериев оценки ПС у детей, и выделить наиболее значимые для диагностики заболевания.
Материал и методы.
Дизайн исследования. Проведено ретроспективное аналитическое исследование, включавшее пациентов с диагнозом «плоскостопие» (группа исследования) и пациентов с нейтральной стопой (группа контроля), стратификация которых проводилась по возрасту (вариационный ряд: 7–14 лет) на основании формирования «зрелого» скелета стопы. Обследование детей осуществлялось при помощи совокупности методов, используемых в диагностике плоской стопы: клинического, метода анкетирования по шкале Oxford Ankle Foot Questionnaire (OAFQPro) и KiddyKINDL для определения качества жизни (КЖ), рентгенологического и метода компьютерной томографии (при подозрении на аномалии развития костей стопы в виде тарзальных коалиций), биомеханического и ЭНМГ. При интервьюировании пациентов использовали только детские вариан-
ты опросников (версии для 7–13 лет). Опрос был также предложен родителям, однако мы получили отказ по личным мотивам («предоставление самостоятельности решений ребенку»). Оба опросника валидны по коэффициенту α-Кронбаха и широко используются в практической деятельности. Кроме того, OAFQ специализирован в отношении оценки потенциальных расходов на лечение детей с патологией стоп и голеностопного сустава и содержит 15 вопросов (версия Pro), отражающих показатели «физическое развитие», «школьная жизнь и физическая нагрузка», «эмоциональное развитие» и «проблемы с подбором обуви». Структура шкал KiddyKINDL состоит из 24 вопросов, сгруппированных по принципу оценки физического состояния, эмоционального состояния, интеллектуального самосознания, отношений в семье, отношений с друзьями, отношений в детском саду/школе. Данный опросник акцентирует внимание на психологическом состоянии ребенка. Все данные представлены в виде процентной шкалы. Клинически фиксировали следующие жалобы: боль в стопе, усталость при ходьбе и расширенной физической активности, нарушение походки, деформации всех отделов стопы, а также присутствие локальной болезненности при пальпации и омозо-лелость. К специализированным функциональным тестам оценки стопы относили тест одномоментной пассивной коррекции (врач при отсутствии нагрузки пассивно возвращает положение стопы в нейтральное), пробы Шритер 1-2-3 (при вставании пациента на носки фиксируем положение вертикальной оси пяточного бугра — ее положение до средней линии определяет положительно Шритер 1; если при подъеме на носки пяточный бугор сохраняет пронированное вальгусное положение — Шритер 2; если ребенок самостоятельно не может подняться на носки — Шритер 3), тест Jack (врач осуществляет пассивное разгибание 1-го пальца стопы, что приводит к усиленной экскавации медиального продольного свода — тест положителен), тест Thompson (выполняется пассивное тыльное разгибание в голеностопном суставе с умеренным усилием при сохранении нулевого положения стопы, если тыльное разгибание возможно только до прямого угла, констатируется укорочение ахиллова сухожилия), тест уплощения свода при нагрузке (в положении стоя у ребенка отмечается снижение высоты медиального продольного свода). Рентгенологически были измерены 18 параметров в виде парных зависимых переменных для обеих стоп. Их отбор произведен на основании анализа наиболее часто используемых показателей, поскольку нет общепринятых критериев для проведения сравнения. По стандартной методике под нагрузкой в виде собственной массы тела измеряли таранно-пяточный угол (ТПУ) в прямой (ПП) и боковой проекциях (БП); таранно-1-метатарзальный угол (Т1МУ) в ПП/БП; таранно-горизонтальный угол (ТГУ) в БП; таранно-тибиальный угол (ТТУ) в БП; угол продольного медиального свода (УПМС) и пяточной инклинации (УПИ) в БП; высоту медиального продольного свода (ПМС) в мм. Все углы образованы продольными осями костей или осью кости и касательной линией поверхности. Биомеханическое исследование регистрировало результаты (всего 13 параметров с двух стоп) временных характеристик шага (подометрии): цикл шага в с; период опоры — период переноса — период одиночной и двойной опоры в%; коэффициент ритмичности ходьбы в у. е. Среди стабилометрических показателей (регистра- ция положения и движений общего центра давления на плоскость опоры при стоянии) отмечали среднее положение ЦД (центра давления) относительно фронтальной (X) и сагиттальной (Y) плоскостей, мм (L, mm), площадь статокинезиограммы, характеризующей площадь колебаний ЦД (S, mm2), среднюю скорость колебания ЦД (характеризует величину пути, пройденную ЦД за единицу времени, V мм/сек или mm/s.); параметр LFS (отношение длины стато-кинезиограммы к ее площади, мм-1 или 1/mm). ЭНМГ проводили с регистрацией активности мышц голени и стопы, вычисляли амплитуды и частоты их разных движений, а также коэффициент активации (КА) и коэффициент реципрокности (КР). КА представляет собой отношение амплитуды в период непроизвольной активации мышцы к ее же амплитуде в режиме максимального произвольного напряжения. КР отражает степень активации мышцы в процентах по отношению к величине активности мышцы-антагониста. Регистрировали данные с мало- и большеберцового нервов с отведением М-ответов с мышц стопы и голени. Определяли следующие показатели: амплитуды М-ответа — суммарный потенциал мышечных волокон, полученных с мышцы при стимуляции иннервирующего ее нерва в динамике. Латентный период — временная задержка от момента стимуляции до возникновения М-ответа. Амплитуда F-волны – суммарный потенциал двигательного ответа мышцы на возвратный разряд, возникающий в результате антидромного раздражения мотонейрона. Латентность F-волны — показатель времени проведения импульса в обе стороны.
Критерии соответствия: для подбора однородных групп определены критерии включения, невключения в группу исследования ( n =150).
Критерии включения:
-
— возраст детей от 7 до 14 лет;
-
— наличие нейтрального положения стопы у детей (группа контроля, n=50).
Критерии невключения для обеих групп в исследовании:
-
— наличие у ребенка острого инфекционного заболевания на момент исследования;
-
— синдром дефицита внимания и гиперактивности;
-
— наличие некомпенсированной патологии органа зрения и слуха;
-
— наличие повреждений стопы на момент исследования.
-
— наличие сопутствующей центральной неврологической патологии (церебральный
-
— паралич, агенезия мозолистого тела и др.);
-
— наличие посттравматической деформации стопы;
-
— наличие ятрогенной деформации стопы;
-
— наличие нелеченой конско-варусной косолапости или ее последствий в виде остаточных деформаций стопы.
Условия проведения. Исследование проведено на базе клинико-диагностического и детского травматолого-ортопедического отделения НИИ травматологии, ортопедии и нейрохирургии ФГБОУ ВО «Саратовский ГМУ им. В. И. Разумовского» Минздрава России. Рентгенологическое исследование проведено с помощью аппарата OPERA Swing (Италия) с дозовой нагрузкой 0,003 мЗВ. Компьютерная томография проводилась на 64-срезовом компьютерном томографе «Toshiba Aquilion Multi 64» (Япония). ЭНМГ-исследование осуществляли с помощью электромиографа «Keypoint Workstation» (Россия), а биомеханическое обследование — с помощью комплекса МБН «Биомеханика» для клинического анализа движений (Россия). Пациентам с нейтральной стопой не предлагали выполнить компьютерную томографию в связи с отсутствием показаний, остальные методы проведены в полном объеме.
Продолжительность исследования: период включения пациентов в исследование — с января 2018 г. по 31 декабря 2019 г.
Анализ в подгруппах: обследованию были подвергнуты 150 детей с ПС (группа исследования) и 50 детей с нейтральным положением стопы (группа контроля). Основными стратификационными факторами являлись возрастная периодизация — младший и старший школьные возрасты (7–14 лет) по классификации Н. П. Гундобина, поскольку в эти возрастные периоды завершены основные этапы формирования скелета стопы. Критериями «нейтральной стопы» у детей считали отсутствие жалоб родителей и детей на стопы; отрицательные функциональные тесты, отсутствие клинических признаков заболевания; нормальные рентгенологические показатели стопы у ребенка, где особенно учитывали УПМС, высоту свода и УПИ; нормальные показатели биомеханического и ЭНМГ-исследования, которые стандартизованы для детей в возрасте 7–16 лет.
Этическая экспертиза. Исследование проводилось на основании подписания пациентами (их представителями) добровольного согласия в соответствии с рекомендациями комитета по этике ФГБОУ ВО «Саратовский ГМУ им. В. И. Разумовского» Минздрава России по протоколу № 6 от 6 февраля 2018 г. НИР в рамках государственного задания Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации на 2018 г. и плановый период 2019–2020 гг. № 154018–01 «Разработка системы поддержки принятия решений при лечении статической деформации стоп у детей» (номер государственного учета НИОКТР АААА-А18-118020290180-6 от 02.02.2018 г.).
Статистический анализ.
Принципы расчета размера выборки. Размер выборки предварительно не рассчитывался и определялся имеющимся количеством больных, соответствующим установленным критериям включения, невключения и исключения.
Методы статистического анализа данных. Статистическая обработка данных выполнялась средствами программных пакетов Statistica 10 (StatSoft-Dell, USA) и Gretl (A. Cotrell, USA, freesoftware). Количественные данные имели вид многомерной выборки, где строки соответствовали пациенту, столбцы — измеренным показателям. Данные были представлены в принятых абсолютных единицах измерения, кроме того, вариативно в виде медианы (Me), стандартного отклонения (σ), интерквартильного размаха [Q1; Q3], минимумов и максимумов (min; max). Задача состояла в выявлении статистически значимых показателей и построении весового правила. Исходные данные были частично классифицированы, т. е. было известно, какие из показателей относятся к норме, а какие — к патологии. Сначала выполнен первичный анализ данных. Тесты на нормальность — ꭓ2 Пирсона, Шапиро — Уилка, Колмогорова дали отрицательный результат по показателям, кроме ЭНМГ-данных, при уровне p<0,05. Равенство средних проверялось по этой причине непараметрическим методом-тестом Вилкоксона, который показал статистически незначимое различие между сравниваемыми показателями оценки стоп (слева и справа) у детей. Корреляционный анализ (коэффициент корреляции Спирмена) выявил высокую (>0,7) коррелированность между парными показателями и корреляцию различной степени между непарными. На основании результатов первичного анализа было принято решение проводить дальнейший анализ отдельно по показателям для левой и правой нижней конечности, непарные показатели включить в анализ для каждой. Основной объем вычислений проведен для показателей правой стопы. Факторный анализ по методу главных компонент выделил факторы, от которых значимо зависит степень тяжести ПС. Значимыми согласно критерию Кайзера считались факторы с дисперсией, превышающей единицу. На основании полученных результатов была проведена кластеризация пациентов по компонентам, вошедшим в факторы. Для построения критерия отбора в каждую из выделенных групп было построена модель упорядоченной логит-регрессии, где в качестве зависимой порядковой переменной была выбрана переменная «номер кластера».
Данные ЭНМГ были описаны с помощью дескриптивной статистики (среднее значение, стандартная ошибка) и разделением на группы нарушений клинически. Материал обработан статистически в программе MS Excel. Достоверность различий определяли по t -критерию Стьюдента. Критический уровень значимости при проверке статистических гипотез принимался равным 0,05.
Результаты. Дети с ПС при оценке КЖ демонстрировали значимые отличия по подшкалам «физическое развитие_OAFQ» и «подбор обуви_OAFQ» (64,3 [45,4; 75,3], р <0,05) в отличие от здоровых детей (89,5 [77,5; 97,4]). Имеется разница и по результатам KiddyKINDL_физическое развитие и самочувствие: 73,4 [50,5; 81,2], р <0,05 и 80,1 [78,5; 91,2] против 86,3 [80,5; 95,2] и 94,2 [89,1; 93,5] у детей без патологии стоп. В целом разница составила 15-20% по OAFQ и 10-14% по KiddyKINDL. Такие аспекты, как «эмоциональное развитие», «школа и активность», «отношения в семье/с друзьями», не отличались у пациентов с ПС и были сравнимы с показателями здоровых.
Среди предъявляемых больными жалоб лидировали боль и усталость при ходьбе свыше 700 м и расширенной физической активности (112 человек, 75%), родители детей с ПС в 100% случаев жаловались на изменение формы стопы (распластанность переднего отдела, вальгусное положение пяточной кости) и нарушение походки. Трудности с подбором обуви отмечали у 32 обследованных (48%). При клиническом осмотре у всех детей (100%) фиксировали локальную болезненность в подошвенной части среднего отдела стопы (проекция таранно-ладьевидного сочленения), признаки омозолелости и супинации переднего отдела стоп диагностировали у 8 человек (12%), вальгусное положение пяточной кости — у 64 детей (96%). Результаты функциональных нагрузочных тестов представлены на рис. 1.
Среди всех функциональных тестов в большинстве случаев позитивными оказались тест уплощения свода при нагрузке, Шритер 1, одномоментная пассивная коррекция (даже частичная) и тест Jack.
Среди протестированных по методу главных компонент (18 рентгенологических и 13 биомеханических показателей для стоп) выделены следующие факторы:
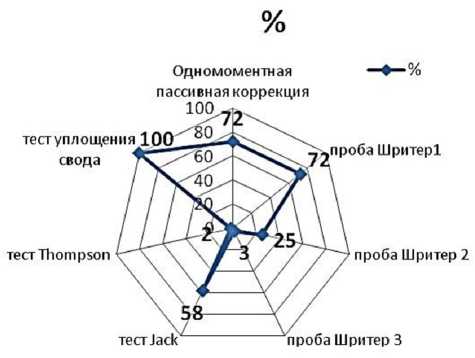
Рис. 1. Распределение функциональных нагрузочных тестов у детей с ПС ( n =150)
-
— фактор 1 «Рентгенологический показатель стопы» (УПМС, высота ПМС, УПИ — все измерения в боковой проекции);
-
— фактор 2 «Динамометрический показатель» (период общей опоры — период переноса в секунду);
-
— фактор 3 «Стабилометрический показатель» (L, mm; V, mm/s); мм, мм/сек;
-
— фактор 4 «Рентгенологический угловые показатели стопы» (ТПУ, ТГУ в боковой проекции);
-
— фактор 5 (период одиночной опоры);
— фактор 6 (ТТУ в боковой проекции).
Значимые факторы отбирались с помощью критерия Кайзера, который применяется в факторном анализе для принятия решения о вкладе фактора в общую вариабельность изучаемого признака в генеральной совокупности. Согласно этому критерию в анализе были оставлены признаки, дисперсия которых превышала единицу.
Табл. 1 демонстрирует, что наибольший вклад в дисперсию всей совокупности вносят показатели, вошедшие в первый фактор, а указанными шестью факторами можно объяснить более 72% изменений показателей в изучаемой выборке пациентов.
Выделенные показатели были подвергнуты кластерному анализу для построения весового правила разделения выборки пациентов на группы, значимо различающиеся по клиническим показателям (табл. 2).
Наиболее статистически значимым оказалось решение, в результате которого каждый из пациентов был включен только в одну из пяти групп (кластеров): 1) практически здоровые; 2) легкая степень нарушений при ПС; 3) умеренная степень нарушений при ПС; 4) средняя степень нарушений при ПС; 5) тяжелая степень нарушений при ПС. Полученные значения групп как значения переменной «номер кластера» использовались для проведения заключительного логит-анализа, в результате которого были определены коэффициенты уравнения регрессии для переменной «номер кластера», а также контрольные точки значений этой переменной для диагностики каждой группы пациентов по типу ПС.
Контрольные точки являются диагностическими критериями: если вычисленное по индивидуальным показателям пациента значение переменной «номер кластера» оказывается меньше –7,20, то пациент относится к группе здоровых, значения в интервале [–7,20; –1,03] соответствуют легкой степени ПС, зна-
Таблица 1
Анализ вклада факторов в общую дисперсию совокупности показателей
|
Номер фактора |
Значение дисперсии фактора |
Доля дисперсии фактора в общей дисперсии, % |
Накопленные значения дисперсии факторов |
Накопленная доля дисперсии в общей дисперсии, % |
|
1. «Рентгенологический показатель стопы» |
3,75 |
20,83 |
3,76 |
20,88 |
|
2. «Динамометрический показатель» |
2,95 |
16,42 |
6,71 |
37,30 |
|
3. «Стабилометрический показатель» |
2,38 |
13,22 |
9,09 |
50,53 |
|
4. «Рентгенологический угловые показатели стопы» |
1,53 |
8,54 |
10,63 |
59,07 |
|
5. «Период одиночной опоры» |
1,24 |
6,92 |
11,88 |
65,99 |
|
6. «ТТУ в боковой проекции» |
1,14 |
6,34 |
13,02 |
72,33 |
Таблица 2
Коэффициенты уравнения логит-регрессии для переменной «номер кластера»
|
Показатели |
Коэффициент |
Ст. ошибка |
z |
P -значение |
|
Таранно-горизонтальный угол, боковая проекция (фактор 4) |
0,97 |
0,26 |
3,65 |
р<0,001 |
|
Угол продольного медиального свода, боковая проекция (фактор 1) |
1,12 |
0,54 |
2,07 |
р<0,05 |
|
Высота продольного медиального свода, мм (фактор 1) |
–1,14 |
0,59 |
–1,93 |
|
|
Угол пяточной инклинации, боковая проекция (фактор 1) |
–0,15 |
0,35 |
–0,42 |
р>0,05 |
|
Период опоры, с. (фактор 2) |
11,73 |
5,82 |
2,01 |
р<0,05 |
|
Период переноса, с. (фактор 2) |
11,96 |
5,87 |
2,03 |
|
|
Длина пути пробега, мм (фактор 3) |
–105,32 |
101,59 |
–1,03 |
р>0,05 |
|
Скорость пути пробега, мм/сек (фактор 4) |
112,2 |
106,1 |
1,05 |
|
|
Контрольная точка 1 |
–7,20 |
1,49 |
–4,81 |
р<0,001 |
|
Контрольная точка 2 |
–1,03 |
1,09 |
–0,94 |
р<0,05 |
|
Контрольная точка 3 |
2,21 |
1,07 |
2,07 |
|
|
Контрольная точка 4 |
4,22 |
1,14 |
3,69 |
р<0,001 |
|
Количество «корректно предсказанных» случаев = 116 (77,3%) |
||||
П р и м е ч а н и е : коэффициент — коэффициент в уравнении регрессии переменной «номер кластера» на переменные из списка, ст. ошибка — ст. ошибка коэффициента в уравнении регрессии, z — значение z-статистики, имеющей стандартное нормальное распределение, P-значение — вероятность наблюдаемого значения, если коэффициент в уравнении регрессии статистически незначимо отличается от нуля. Контрольные точки — границы интервала значений вычисленной переменной «номер кластера».
чения «номер кластера» из интервала [–1,03; 2,21] относят пациента к умеренной степени ПС, из интервала [2,21; 4,22] — к средней тяжести ПС и значения больше 4,22 относят к тяжелой форме ПС.
Угол пяточной инклинации входит в модель со значимостью р =0,67, L, мм и V , мм/сек со значимостью около 0,29, однако в их присутствии повышалась доля корректно предсказанных случаев, что объясняется клинической значимостью этих показателей и «настройкой» математической модели.
При сопоставлении ЭНМГ-данных общего мало-и большеберцового нервов и ЭМГ-показателей мышц голени детей с ПС выявлены общие закономерности и отличительные особенности, коррелируемые с рентгенологическими и биомеханическими показателями тяжести нарушений:
-
1. Независимо от тяжести деформации стопы и возраста, у всех пациентов регистрировались сниженные по амплитуде М-ответы (2,7±0,8 мкв, в норме 7,5±2,3 мкв) и нерегулярные поздние нейрональные ответы (F-волны, не более 40 мкв при норме 140 мкв) с короткого разгибателя пальцев стопы с двух сторон. Показатели М-ответов и F-волн большеберцового нерва, регистрируемые с мышц стопы, соответствовали норме (9,2±2,4 мкв).
-
2. Основные изменения ЭНМГ-данных мышечных и нейрональных ответов были отмечены при отведении с мышц голени. В большинстве случаев с икроножных мышц регистрировались высокоамплитудные М-ответы (13,4±1,6 мкв, в норме 7,7±0,8 мкв) и F-волны (1603±235,4 мкв, в норме 360±115 мкв), превышающие данные здоровых детей в 5 раз.
-
3. Наиболее выраженные отклонения соотношения амплитуд F/М-волн — показателя, характеризующего уровень активности мотонейронов — отмечены у детей со средней степенью тяжести деформации (18,9% при норме не более 5-10%). У детей с тяжелым поражением уровень активности мотонейронов парадоксально снижается, но остается высоким.
При анализе показателей суммарной ЭМГ передней большеберцовой и икроножной мышц выраженных отклонений средних значений амплитуды в большинстве случаев не было выявлено. Менялись частотные характеристики ЭМГ кривых икроножных мышц в сторону повышения (433 колебания за единицу времени, в норме 284 колебания). При исследовании взаимоотношений мышц антагонистов голени путем подсчета коэффициентов активации (КА) и ре-ципрокности (КР) выявлено отклонение показателей
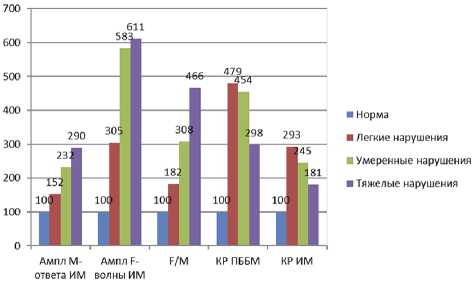
Рис. 3. Данные электронейромиографического исследования: ИМ — икроножная мышца, ПББМ — передняя большеберцовая мышца, Ампл — амплитуда. Все данные переведены в процентную шкалу в сторону повышения практически во всех случаях, но в разной степени выраженности. Наибольшие отклонения КА (100-83,7%) были отмечены у пациентов с легкой и степенью тяжести ПС по икроножной мышце, а отклонения КР (65-70%) преобладали по данным передней большеберцовой мышцы у пациентов со средней и тяжелой деформацией стоп. Таким образом, наиболее чувствительными критериями среди регистрируемых ЭНМГ-показателей являлись амплитуда М-ответа и F-волны икроножной мышцы, мкв; соотношение F/M в%; КР передней большеберцовой мышцы в%; КР икроножной мышцы в%, которые позволили в результате дескриптивного описания диагностировать клинически легкие, умеренные и тяжелые нарушения у детей с ПС (рис. 3)
Обсуждение.
Резюме основного результата исследования : проведен анализ комплексных данных 150 детей с диагнозом ПС для оценки значимости клинических и диагностических критериев отбора. Группу сравнения составили 50 детей без патологии стоп, обследованных по разработанному плану. Выделены наиболее информативные показатели, отражающие достоверные нарушения формирования стопы у ребенка. Определены числовые значения показателя (номер кластера), с помощью которого возможно отнесение пациента к одной из групп по типу степени нарушений при ПС у детей (норма, легкие, умеренные, средние, тяжелые нарушения).
Обсуждение основного результата исследования. По нашим данным, КЖ у детей с ПС отличалось от группы здоровых в пределах 10-20% по параметрам физического развития и трудности подбора обуви, однако разница не затрагивала психоэмоциональный статус ребенка и его коммуникации, а статистическая значимость расценивалась как умеренная из-за небольшого объема выборки. В литературе имеется малое количество работ, посвященных данной проблеме. Например, исследование Y. Damayanti et al., изучивших КЖ у 120 детей с помощью PedsQL (79 с нормальной стопой и 41 с ПС в возрасте 5–18 лет, средний возраст 8,7±2,5 года), показало отсутствие его снижения у детей ≥ 11 лет и умеренные нарушения в группе младше 11 лет [13]. Примечательно, что регрессионный анализ объяснял только 16-27% результатов, полученных по опроснику. Авторы связывают это с отсутствием комплексной оценки КЖ по опроснику, в частности, PedsQL не учитывает значимость образа жизни, дозирован-ности физической активности, периодов сна и ряда других критериев. Схожие результаты были получены и в работе A. Kothari et al. [14], использовавших опросники OAFQ и HRQOL. Несмотря на некоторую противоречивость данных, авторы убеждены, что экспресс-оценка с помощью опросника КЖ позволяет подвергнуть сомнению выводы о «безопасности» ПС у детей, и подтолкнуть к дальнейшему клинико-инструментальному обследованию. Только одно исследование демонстрировало корреляцию между интенсивностью боли, усталостью в нижних конечностях после нагрузки и сложности подбора обуви со степенью уплощения свода [15], но не указывало статистические основы и критерии. Важно отметить, что и у взрослых пациентов с ПС при оценке КЖ отмечали неоднородные результаты, где показатели по одним анкетам не изменялись, а по другим — коррелировали с основным диагнозом, что наглядно представлено в работе M. Gonzalez-Martin et al. [16]. Авторы изучили 835 человек с ПС в возрасте 40–64 лет и 390 старше 65 лет, учитывая коморбид-ный статус, индекс массы тела, используя опросники SF-36, FHS, FFI и другие, получив в итоге неполные сведения. Клинические данные и функциональные тесты позволили провести первичную диагностику в отношении ПС, где подтверждали качественные нарушения у детей. Это демонстрирует необходимость их применения в практике любого специалиста, как педиатра, так и детского ортопеда [16].
Еще на заре XX в. рентгенологи вводили критерии оценки ПС у детей [17], оценивая свод стопы. В настоящий момент единой рентгенологической классификации педиатрической стопы не существует, однако предложены различные методы анализа рентгенограмм с измерением угловых и линейных параметров взаиморасположения костно-суставных образований во всех отделах стопы [18, 19]. Большинство ортопедов западных стран в основе оценке ПС используют данные R. Vanderwilde et al. [20], предложивших 11 наиболее оптимальных критериев детской ПС по анализу 74 рентгенограмм детей. В России ортопеды широко использую критерии Ф. Р. Богданова, К. К. Жоха. В целом наиболее значимые рентгенологические показатели получили широкое использование во многих современных работах, но их статистическая значимость и валидность не определена, также многие указывают на слишком широкий диапазон значений, что конфликтует со статистическими законами. В нашей работе из 18 проанализированных параметров выделено 4 значимых критерия (ТГУ, УПМС, высота свода и УПИ), совокупность подсчета которых подтверждает свыше 75% случаев ПС. В ходе исследования выявлены некоторые интересные факты. Так, часто используемые в оценке ПС значения ТПУ не могут быть интерпретированы в практике клинициста только лишь по числовым значениям, поскольку необходимо точно знать анатомическое положение пяточной кости по отношению к горизонтальной поверхности нагрузки стопы. УПИ статистически не обладает высокой точностью, но его суммирование к другим параметрам увеличивает точность определения отклонений ПС. По биомеханическим параметрам наибольшие изменения демонстрировали показатели статической педографии (величина скорости и пути пробега в поперечной плоскости), а также значимое увеличение опорного периода с сокращением периода переноса при регистрации цикла шага. Полученные данные соответствуют опыту других исследований. Например, C. M. Kerr et al. [11] у пациентов с ПС отмечают из- мененные хаотичные движения стоп в поперечной поверхности в статике, замедление шага, а также нарушения гониометрии в тазобедренном, коленном и голеностопных суставах. В других работах тоже были выявлены качественные отклонения толчковой функции стопы (момент «опора — толчок» пятки и носка) в сторону замедления и несовершенного момента, пропульсивные движения [11–15]. ЭНМГ-показатели демонстрировали значимые нарушения иннервации и работы мышц голени, в частности передней большеберцовой, икроножной, что выражалось в увеличении амплитуд М-ответов, показателей F-волн и соотношения F/M, КР Полученная нами картина констатировала изменения, характерные для поражения руброспинального тракта (проекционный путь экстрапирамидной системы), отвечающего за регуляцию взаимных позных движений, их целенаправленность и корректировку. Возможно, именно картина ЭНМГ-нарушений может внести весомый вклад в сторону выбора хирургической тактики лечения ПС, поскольку выявленные изменения в возрасте 7–14 лет практически не поддаются коррекции. К сожалению, мы встретили только единичные работы, посвященные состоянию нейромышечного аппарата при плоскостопии у детей, что не позволяет составить целостную картину. В настоящее время проблема ПС детского возраста актуальна во многих аспектах. Так, отсутствуют данные о распространенности патологии в популяции в связи с неточными классификационными критериями. Не унифицированы критерии диагностики, применяемые методы лечения ПС — спорны. В нашем исследовании дан анализ существующих разноплановых критериев оценки ПС у детей с акцентом на статистическую достоверность. Подобная проверка позволила выделить ядро наиболее чувствительных показателей, исключить незначимые или ухудшающие картину. Особое внимание уделено ЭНМГ-анализу, который демонстрировал качественные изменения нисходящих проводящих путей головного мозга, отвечающих за контроль поперечнополосатой мускулатуры. В дальнейшем для достоверности полученных результатов и практического их применения планируется создание базы выделенных параметров стопы у детей, как плоской, так и нейтральной (здоровой), по типу нейронной сети, что значительно облегчит оценку тяжести изменений при ПС и позволит выбрать метод лечения у ребенка.
Ограничения исследования. Основным ограничением исследования, способным повлиять на его результаты, является средний размер выборки пациентов.
Заключение. Таким образом, благодаря статистическому анализу была создана выборка наиболее значимых критериев верификации плоской стопы у детей. Сочетание выбранных критериев уникально и позволяет определить патологию стопы более чем в 70% случаев. Создание подобной диагностической базы необходимо, поскольку стандарты диагностики плоской стопы у детей не разработаны ни в одной ортопедической школе мирового сообщества, существует только разнородная группа методов, которыми хирурги-ортопеды пользуются на свое усмотрение.
Список литературы Значимость различных критериев оценки стопы в диагностике плоскостопия у детей
- Costa FP, Costa G, Carvalho MS, et al. Long-term outcomes of the calcaneo-stop procedure in the treatment of flexible flatfoot in children: a retrospective study. Acta Med Port 2017; 30 (7-8): 541–5. DOI: 10.20344 / amp. 8137.
- Fyodorov МА. The current state of surgical treatment of planovalgus feet deformity in children. Issues of Reconstructive and Plastic Surgery 2016; 3 (58): 26–35. Russian (Федоров М. А. Современное состояние вопроса хирургического лечения плоско-вальгусной деформации стоп у детей. Вопросы реконструктивной и пластической хирургии 2016; 3 (58): 26–35. DOI: 10.17223 / 1814147 / 58 / 03.
- Sheikh AM, Feldman DS. Painful Flexible Flatfoot. Foot Ankle Clin 2015; 20 (4): 693–704. DOI: 10.1016 / j. fcl. 2015.07.011.
- Dare DM, Dodwell ER. Pediatric flatfoot: cause, epidemiology, assessment, and treatment. Current Opinion in Pediatrics 2014; 26 (1): 93–100. DOI: 10.1097 / MOP. 0000000000000039.
- Timaev MKh, Sertakova AV, Kurkin SA, et al. The flatfoot of children age: actual state of problem. Russian Medical Journal 2017; 23 (3): 165–8. Russian (Тимаев М. Х., Сертакова А. В., Куркин С. А. и др. Плоская стопа (pes planovalgus / flatfeet) детского возраста: современное состояние проблемы. Российский медицинский журнал 2017; 23 (3): 165–8.
- Hösl M, Bohm H, Multerer C, et al. Does excessive flatfoot deformity affect function? A comparison between symptomatic and asymptomatic flatfeet using the oxford foot model. Gait Posture 2014; 39 (1): 23–8. DOI: 10.1016 / j. gaitpost. 2013.05.017.
- Mosca VS. Flexible flatfoot in children and adolescents. J Child Orthop 2010; 4 (2): 107–21. DOI: 10.1007 / s11832‑010‑0239‑9.
- Atik A, Ozyurek S. Flexible flatfoot. North Clin Istanbul 2014; 1 (1): 57–64. DOI: 10.14744 / nci. 2014.2929.
- Kerr CM, Zavatsky AB, Theologis T, et al. Kinematic differences between neutral and flat feet with and without symptoms as measured by the Oxford foot model. Gait & Posture 2019; (67): 213–8. DOI: 10.1016 / j. gaitpost. 2018.10.015.
- Twomey DM, McIntosh AS. The effects of low arched feet on lower limb gait kinematics in children. Foot 2012; 22 (2): 60–5. DOI: 10.1016 / j. foot. 2011.11.005.
- Kerr CM, Stebbins J, Theologis T, et al. Static postural differences between neutral and flat feet in children with and without symptoms. Clin. Biomech 2015; 30 (3): 314–7. DOI: 10.1016 / j. clinbiomech. 2015.02.007.
- Kothari A, Dixon PC, Stebbins J, et al. The relationship between quality of life and foot function in children with flexible flatfeet. Gait Posture 2015; 41 (3): 786–90. DOI: 10.1016 / j. gaitpost. 2015.02.012.
- Damayanti Y, Hadisoemarto PF, Defi IR. Flatfoot decreases school functioning among children < 11 years of age. Univ Med 2018; 37 (1): 50–6. DOI: 10.18051 / UnivMed. 2018. v37.50–56.
- Kothari A, Stebbins J, Zavatsky AB, et al. Health-related quality of life in children with flexible flatfeet: A cross-sectional study. J Child Orthop 2014; (8): 489–96.
- Wilson JMM. Synopsis of causation: pes planus. UK: Ministry of Defence, 2008; 14 p.
- Gonzalez-Martin С, Pita-Fernandez S, PertegaDiaz S. Quality of life and functionality in patients with flatfoot. In: Badekas Th., ed. Update in Management of Foot and Ankle Disorders. London: Intech Open, 2018; 73–90.
- Kuslik MI. To the accurate method of flat feet degree determining. New surgery 1925; (2): 66–7. Russian (Куслик М. И. К методике точного определения степени плоскостопия. Новая хирургия 1925; (2): 66–7).
- Bourdet C, Seringe R, Adamsbaum C, et al. Flatfoot in children and adolescents Analysis of imaging findings and therapeutic implications. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2013; 99 (1): 80–7. DOI: 10.1016 / j. otsr. 2012.10.008.
- Butterworth ML, Marcoux JT (Eds). The Pediatric Foot and Ankle. Cham ZG: Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2020; 289 p.
- Vanderwilde R, Staheli LT, Chew DE, et al. Measurements on radiographs of the foot in normal infants and children. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1988; 70 (3): 407–15.


