4-nitrobenzaldoxime and cynnamaldoxime structures
Автор: Sharutin V.V., Sharutina O.K.
Журнал: Вестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Химия @vestnik-susu-chemistry
Рубрика: Краткие сообщения
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The structures of 4-nitrobenzaldoxime (1) and cynnamaldoxime (2) have been determined by X-ray diffraction analysis. In the oxime molecules the distances C=N, N-O have the usual values for oximes (1.267(3), 1.403(2) Å for 1 and 1.278(4), 1.395(3) Å for 2a, 1.284(4), 1.384(3) Å for 2b). In crystals the oximes are observed as dimers: two oxime 1 molecules are interconnected by two hydrogen bonds N(1A)…H(1B) (2.12 Å), two oxime 2 molecules are interconnected by the single hydrogen bond N(1A)…H(1B) (1.66 Å).
4-nitrobenzaldoxime, cynnamaldoxime, molecular structures, x-ray analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147160323
IDR: 147160323 | УДК: 547-304.6+547.53.024+548.312.5
Текст краткого сообщения 4-nitrobenzaldoxime and cynnamaldoxime structures
Oximes are mono-, bi- and tridentate chelating ligands, which form numerous metal complexes that are well studied and find wide practical application. At the present time the crystalline and molecular structures of more than 3000 oximes are known, of which about 300 oximes are derivatives of benzaldehyde oxime [1].
Experimental
X-Ray diffraction analysis of crystals 1 and 2 was carried out on the Bruker D8 QUEST automatic four-circle diffractometer (Mo K α - emission, λ = 0.71073 Å, graphite monochromator). Using SMART and SAINT-Plus programs, data were collected, edited; unit cell parameter and absorptivity were refined [2]. All calculations needed for determination and refinement of molecular structures were done using SHELXL/PC program [3]. The structures 1 and 2 were determined using the direct method and refined with the least squares method, all non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.
Selected crystallographic data and structure refinement results are listed in Table 1, selected bond lengths and bond angles are summarized in Table 2.
Table 1
Crystallographic data, experimental and structure refinement parameters for compounds 1 – 2
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
Formula |
C 7 H 6 O 3 N 2 |
C 18 H 18 N 2 O 2 |
|
Formula weight |
166.14 |
294.34 |
|
Т , К |
296(2) |
296(2) |
|
Crystal system |
Monoclinic |
Оrthorhombic |
|
Space group |
P2 1 /c |
Pbca |
|
a , Å |
6.2548(3) |
10.2935(11) |
|
b , Å |
4.8928(2) |
7.7033(8) |
|
c, Å |
24.7226(11) |
41.297(4) |
|
α , deg |
90.00 |
90.00 |
|
β, deg |
94.536(2) |
90.00 |
|
γ , deg |
90.00 |
90.00 |
|
V , Å3 |
754.23(6) |
3274.6(6) |
|
Z |
4 |
8 |
|
ρ (calcd) , g/cm3 |
1.463 |
1.194 |
|
µ , mm–1 |
0.117 |
0.079 |
|
F (000) |
344.0 |
1248.0 |
Table 1 (end)
|
Crystal size, mm |
0.78×0.55×0.22 |
0.25×0.22×0.16 |
|
2Θ range of data collection, deg |
6.62 - 70.14° |
6.68 - 39.18° |
|
Range of refraction indices |
- 10 ≤ h ≤ 9, - 7 ≤ k ≤ 7, - 29 ≤ l ≤ 39 |
- 9 ≤ h ≤ 9, - 7 ≤ k ≤ 7, - 35 ≤ l ≤ 38 |
|
Measured reflections |
8109 |
6468 |
|
Independent reflections, R int |
3217 ( R int = 0.0274) |
1428 ( R int = 0.0475) |
|
Refinement variables |
110 |
271 |
|
GOOF |
1.140 |
1.078 |
|
R factors for F2 > 2 σ (F2) |
R 1 = 0.0855, wR 2 = 0.2119 |
R 1 = 0.0367, wR 2 = 0.0918 |
|
R factors for all reflections |
R 1 = 0.1197, wR 2 = 0.2293 |
R 1 = 0.0565, wR 2 = 0.1003 |
|
Residual electron density (min/max), e/A3 |
0.41/ - 0.34 |
0.11/ - 0.15 |
Table 2
Selected bond lengths and bond angles in the structures of compounds 1 – 2
|
Bond |
d , Å |
Angle |
ω , deg |
Bond |
d , Å |
Angle |
ω , deg |
|
1 |
2 |
||||||
|
C(4) – N(2) |
1.467(2) |
C(3)C(4)N(2) |
119.12(15) |
O(1) - N(1) |
1.395(3) |
C(9)N(1)O(1) |
111.8(3) |
|
C(4) - C(5) |
1.377(2) |
C(5)C(4)N(2) |
118.45(15) |
С(1) - C(7) |
1.452(4) |
C(8)С(7)C(1) |
128.3(3) |
|
C(1) - C(6) |
1.392(2) |
C(2)C(1)C(7) |
122.72(16) |
С(1) - C(2) |
1.390(4) |
C(7)С(8)C(9) |
123.1(4) |
|
C(1) - C(2) |
1.397(2) |
O(2)N(2)C(4) |
118.20(15) |
С(1) - C(6) |
1.382(4) |
C(12)С(11)C(16) |
119.6(3) |
|
C(1) - C(7) |
1.465(2) |
O(2)N(2)O(3) |
123.84(16) |
N(1) - C(9) |
1.278(4) |
C(15)С(11)C(12) |
118.2(3) |
|
C(3) - C(2) |
1.383(3) |
O(3)N(2)C(4) |
117.96(15) |
С(7) - C(8) |
1.324(4) |
C(15)С(11)C(16) |
122.2(3) |
|
N(2) - O(2) |
1.218(2) |
C(5)C(6)C(1) |
120.85(16) |
O(2) - N(2) |
1.384(3) |
C(17)N(2)O(2) |
111.5(3) |
|
N(2) - O(3) |
1.220(2) |
C(3)C(2)C(1) |
120.41(16) |
С(8) - C(9) |
1.441(4) |
N(2)C(17)C(10) |
128.3(4) |
|
C(6) - C(5) |
1.384(3) |
N(1)C(7)C(1) |
122.34(18) |
N(2) - C(17) |
1.284(4) |
C(16)C(10)C(17) |
123.1(4) |
|
C(7) - N(1) |
1.267(3) |
C(4)C(5)C6 |
118.41(16) |
С(17) - C(10) |
1.427(4) |
C(10)C(16)C(11) |
128.5(4) |
|
N(1) - O(1) |
1.403(2) |
C(7)N(1)O(1) |
111.08(18) |
С(10) - C(16) |
1.331(4) |
N(1)C(9)C(8) |
129.2(4) |
The full tables of atomic coordinates, bond lengths, and bond angles are deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC 1045607, 1049482; ; .
Results and Discussion
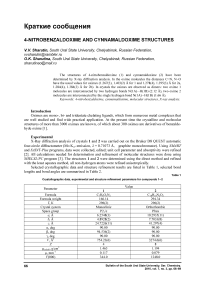
Oximes in the crystalline state exist as dimmers, in which oxime molecules are interconnected by two intermolecular hydrogen bonds N ⋅⋅⋅ H. For example, in the 4-dimethylaminobenzaldoxime dimer (Fig. 1) intermolecular hydrogen bonds N ⋅⋅⋅ H are equal to 2.09 Å [4] (the sum of Van der Waals radiuses of the said elements is equal to 2.70 Å [5]).
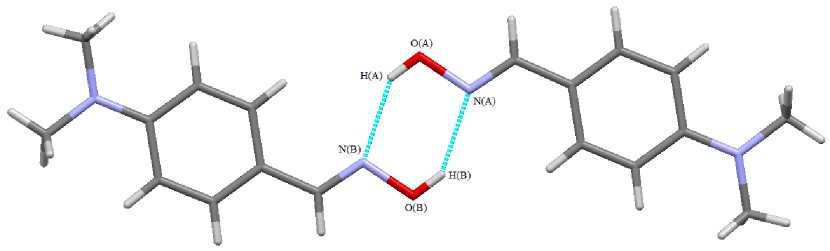
Fig. 1. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds in 4-dimethylaminobenzaldoxime crystal
Краткие сообщения
We have found that such intermolecular hydrogen bonds exist in 4-nitrobezaldoxime crystal (1) , too (Fig. 2).
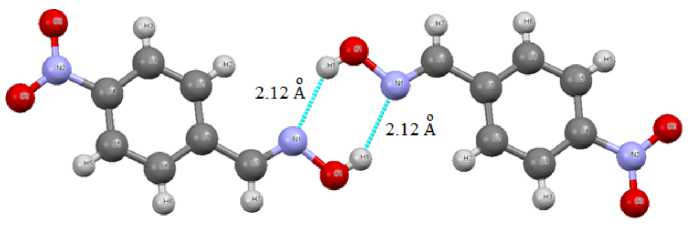
Fig. 2. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds N ⋅⋅⋅ H in 4-nitrobezaldoxime crystal (1)
We have also found that in the cynnamaldoxime crystal (2) two oxime molecules are connected in the dimer by only one abnormally short (1.66 Å) intermolecular hydrogen bond (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Intermolecular hydrogen bond N(A) ⋅⋅⋅ H(B) in cynnamaldoxime dimer (2)
In oxime molecules the distances C=N, N - O have the usual values for oximes (1.267(3), 1.403(2) Å for 1 and 1.278(4), 1.395(3) Å for 2а , 1.284(4), 1.384(3) Å for 2b ). Note the unusual linkage of two oxime molecules 2 into the dimer by only one intermolecular hydrogen bond, which is not typical for the most oximes [1].
Conclusion
Thus, 4-nitrobezaldoxime and cynnamaldoxime crystals exist as dimers interconnected by two or one intermolecular hydrogen bonds N ⋅⋅⋅ H, respectively.
Список литературы 4-nitrobenzaldoxime and cynnamaldoxime structures
- Cambridge Crystallografic Database. Release 2015. Cambridge.
- Bruker (2000) SMART. Bruker Molecular Analysis Research Tool, Versions 5.625 Bruker AXS, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2000) SAINTPlus Data Reduction and Correction Program Versions 6.02a, Bruker AXS, Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Шарутин, В.В. Кристаллическая и молекулярная структура 4-диметил¬аминобензальдоксима/В.В. Шарутин//Бутлеровские сообщения. 2014. Т. 39. № 7. С. 163-164.
- Бацанов, С.С. Атомные радиусы элементов/С.С. Бацанов//Журн. неорган. химии. 1991. Т. 36. № 12. С. 3015-3037.