A study of alfa feto protein parameter in serum and histological effects of pups liver by SEM in pregnant rats exposed to overdose of aminoglycoside antibiotics
Автор: Mohammed Ali A.R., Abdul-zahra N.I., Amer Kadhim D.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 28, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The study has been conducted in Animal House/Faculty of Sciences/University of Kufa between December 2022 and February 2022, fifteen female Albino Rats are used. Gentamicin is aminoglycoside antibiotics widely used during pregnancy for treatment the infections . The present study has been intended to show Alfa Feto Protein parameter in serum and the histological effects of gentamicin on pups liver by SEM in female Albino Rats. The females Rats are randomly divided into three main groups, comprising five rats for each group .The control group is given inta peritoneal injection of physiological normal saline and the second and third group are given inta peritoneal injection of gentamicin doses twenty, forty mg/kg/day respectively for 20 days from the first day to the end of experimental allocated for each female.The rats are sacrificed in 20 th (dpc) to study the Alfa Feto Protein parameter in serum and histological effects of gentamicin on pups liver. The physiological study show negative results in all study groups due to absent of malformations in pups and present histological effects in external architecture structure of pups liver compare with control groups. In conclusion aminoglycoside gentamicin caused histological effects on pupa liver and not absent of malformations in pups due to negative results of Alfa Feto Protein parameter
Pups, pregnant, aminoglycoside, alfa feto protein
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148327109
IDR: 148327109 | DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2023.28.4852
Текст научной статьи A study of alfa feto protein parameter in serum and histological effects of pups liver by SEM in pregnant rats exposed to overdose of aminoglycoside antibiotics
Imprint
Ashraf raoof mohammed ali, Noor I.Abdul-Zahra, Doaa Amer Kadhim. A study of Alfa Feto Protein parameter in Serum and Histological Effects of Pups Liver by SEM in Pregnant Rats Exposed to Overdose of Aminoglycoside antibiotics. Cardiometry; Issue No. 28; August 2023; p. 48-52; DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2023.28.4852; Available from:
-
I. INTRODUCTION
During pregnancy many pregnants are on medications for acute infections related with pregnancy (e.g. heart burn and morning sickness), and also utilized for chronic illness management, predating or developing during pregnancy (e.g. epilepsy, asthma, depression, psychosis, chronic hypertension and genitourinary bacterial infections), sometime a treatment is endorsed to the mother to treat fetal diseases (e.g. fetal dysrhythmia) (Yates and Thomas, 2016).Little is thought about the impacts of human fetal exposure when another medication is approved unless it is specifically prescribed for use in pregnancy, Since numerous factors may add to adverse fetal impacts, having comprehensive information about in utero exposures will enhance our capacity to make correct determinations about causality (Clemow et al., 2015).The pregnancy duration represent critical periods in which the pregnant mother is exposed to external impacts and the most likely effects are the period called the embryonic period, which extends in the human fertilized stage until the end of the eighth week of pregnancy, during this period the three germinal layers are formed which included ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm and also neural crest cells, it is known that different body organs originate from these germinal layers (Deye et al., 2016).It has been confirmed that antibiotics can damage developing fetal organs during pregnancy (Romero et al., 2007; Sachdeva et al., 2009). Placenta is permeable to the most antibiotics, for example gentamicin and cephalotin preserve in amniotic fluid and embryonic tissues in high concentration, it is worthy to note that permeability of placenta to various antibiotics varies during pregnancy, as it is reduced to Gentamicin in the last days of the pregnancy but increase under Cephalotin effect (Schuenemann, et al., 2007).Gen-tamicin is antibiotic an aminoglycoside derived from Micomono- sporapurpurea, it has a bactericidal effect
on gram-negative microorganisms by preventing the production of protein in the bacterial cell therefore it is used in the treatment of a number of infections caused by a number of bacterial species such as respiratory infection, skin, gallbladder, bile ducts, urinary tracts, meningitis, septicemia diseases (Narayana, 2008).Gentamicin is quickly absorbed after intra muscular injection and mainly diffused in extracellular fluid (peak serum levels usually reached within 30 to 90 minutes) and it accumulates in the renal proximal convoluted tubules (50 to 100 times more than that in serum). Although gentamicin passes through the placenta and is excreted in breast milk, it is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Gentamicin concentration in umbilical cord blood and the placenta reaches 50% and 8% of mother’s blood serum respectively, after 1-2 hours of intra muscular injection (Pacifici and Marchini, 2017).In mammals, the peri-implantation is considered as a developmental period, implantation and signaling for pregnancy maintenance, which are a periods for floating time after zona pellucida hatch, but the cells growth and differentiation during embryonic development (Elmetwally et al.,2019).Implantation is defined as the process by which the embryo attaches to the endometrial surface of the uterus and invades the epithelium and then the maternal circulation to form the placenta (Mesiano, 2019).
-
II. MATERIAL AND METHODS
-
2.1 Animal Model:
-
-
2.2 Drug used
-
2.3 Experimental croups:
This study achieved on pregnant white rat Rattus norvegicus females (15) and males(5) for mating. All rat weights ranging from 200-250 g. They should be in good health. The rats are placed in plastic cages with metal covers, 48 cm wide, 15 cm wide and 7 cm wide. The sawdust, which should be replaced three times a week, is considered in its care to clean the hatching of the special diet and plastic bottles can be used to make a watering tough with a cork equipped with metal pipes. The animals are placed under suitable laboratory conditions in terms of temperature 18-26 Cº and light/dark cycle 10/14 and ventilation rate time/hour 10-15 and also the relative humidity 30-70 (Tan and Tan, 2017).
From the ampoule of gentamicin, required dosages can be administered to animals of varying body weights as illustrated in table below:
|
Standard dose |
Stock solution |
Animals body weight (g) |
Calculated dose in mg |
Equivalent dose in ml |
|
Gentamicin, 80 mg/kg for Rats |
80 mg/2ml =40 mg/ml |
100 g |
8 mg |
0.20 ml |
|
150 g |
12 mg |
0.30 ml |
||
|
250 g |
20 mg |
0.5 ml |
Single dose= 20mg /kg/day (equivalent 0.5 ml of gentamicin).
Double dose= 40 mg /kg/day (equivalent 1 ml of gentamicin).
The average weight of animals = 250 g equivalent 0.25 kg (Erhirhie et al., 2004 ).
First: Control group: included five female rats injected by normal saline (Nacl 0.9%) intraperitoneally for seven days, the group sacrifice it in the end of experiment.,
Second: first treated group : included five female rats injected intraperitoneally by dose 20mg /kg/day of gentamicin for twenty days, the group sacrifice it in the end of experiment.
Third: second treated group : included five female rats injected intraperitoneally by dose 40mg /kg/day of gentamicin for twenty days, the group sacrifice it in the end of experiment.
-
2.4 Animals sacrifice and collection of pups liver
The experimental animals of all groups were sacrifice after general anesthesia by combination of Ketamine: Xylazine (90mg/ kg: 10mg/ kg intraperitoneal), used ketamine 0.5 ml & xylazine 0.1 ml to each 250 g of body weight for anesthesia when sacrifice the female rat from the control & treated croups, after the anesthesia the females rats put in anatomical dish and made linear incision by scissors in abdominal region for extraction the liver that contains for collected, by anatomical tools. Saved in containers contains 10% formalin (AlTameemi, 2014).
-
2.5 : Scanning Electron Microscope SEM
Procedure:
-
A. Glutelaldehyde Fixation
-
1. Prepare fixative solution and fill the scintillation vials with fixative.
-
2. Cut specimen tissue and place in tube with glute-laldehyde solution.
-
3. Place tube on its side to keep the air away from the tissue.
-
4. Incubate at 4 Cº for 12-24 hours (Overnight is good).
-
B. Osmium tetroxide fixation
-
1. The solution can be stored in the cold room or freezer for about one month. If frozen, thaw at room temperature. This solution should be straw colored. If it is purple it is no longer good.
-
2. Dilute to a 1% solution in 25 mM phosphate buffer.
-
3. Pour off fixative and add the 1% osmium tetroxide solution.
-
4. Incubate in the cold room overnight to several days. The osmium turns black.
-
C. Dehydration of tissue
-
1. Pour off osmium solution and rinse 3 times with 25mM phosphate buffer.
-
2. Put tissue through an alcohol series. 15 to 30 minutes each step.
-
1: Alfa Feto Protein parameter
The physiological measurement of Alfa Feto Protein in all expimental groups show negative results due to absent of malformations in pups and this agreement with may studies.The biological role of this major embryonic serum protein is unknown although numerous speculations have been made. We have used gene targeting to show that AFP is not required for embryonic development (Gabant et al.,2002). The developed methods incorporating panning and multiparametric FACS to enrich for fetal hepatoblasts. The procedures yielded predominantly single cells with greater than 90% viability, and at E15,95% of the whole organ weight was recovered in the final cell preparation. The panning procedures removed 84% of the total cells, reduced the hemopoietic and endothelial cell fraction from greater than 90% to approximately 70% and enriched hepatoblasts by greater than fivefold. The increase in the parenchyma-specific gene expression of albumin and AFP was illustrated by Northern-blot analysis of the cells before and after panning. In addition, the procedure’s specificity was demonstrated by analysis of the adherent cells,which contained negligible amounts of albumin and AFP mRNA. Cell enrich-
ment was further confirmed by in vitro studies, which revealed a dramatic increase in the number of parenchymal cell colonies compared with the original suspension. The plating efficiency after panning was significantly higher (up to 60%) compared with previous studies, in which it ranged from 6% to 10% (Sigal et al.,1994)
Table (1-1)
The results of Alfa Feto Protein in all study groups.
|
Study Groups |
(Alfa Feto Protein)nn/ml Results positive or negative |
||
|
Control group |
negative |
negative |
negative |
|
20mg/kg/day of gentamicin |
negative |
negative |
negative |
|
40mg/kg/day of gentamicin |
negative |
negative |
negative |
-
2: Histological Study of pups liver by SEM
Scanning electron micrographs results in pups liver in control groups showed normal external architecture structures of hepatocytes figure (1), while in treated by doses20+40mg/kg/day of gentamicin show changes in external architecture structures but in treated by dose 40mg/kg/day of gentamicin show severely effects they showed deformation of hepatocytes and high fenestrae figure (2). In scanning electron microscope, the impacts of the aminoglycoside antimicrobials are generally restricted to the apical surface of the cell, poly-l-lysine induces complete necrosis of the cell, qualitative assessment of apical surface damage allows the antibiotics to be ranked in the following order: neomycin, gentamicin, dihydrostreptomycin, neamine, amikacin, and spectinomy-cin (Hobbie et al.,2008).Liver plays an important role in the detoxification and metabolic elimination of various drugs and harmful substances, Its exposure to hazardous compounds and toxins could lead to injury and reduced function (Arjinajarn et al.,2017). The tumor necrosis factor elevated due to inflammation of liver and apoptosis were observed in gentamicin treated rats lead to deformation of hepatocytes (Arjinajarn et al.,2017).Gentamicin has actuated histological modifications of hepatocytes including hydropic degeneration of hepatocytes, fatty changes, inflammatory cell infiltration and congestion of portal vein (Galaly et al.,2014).
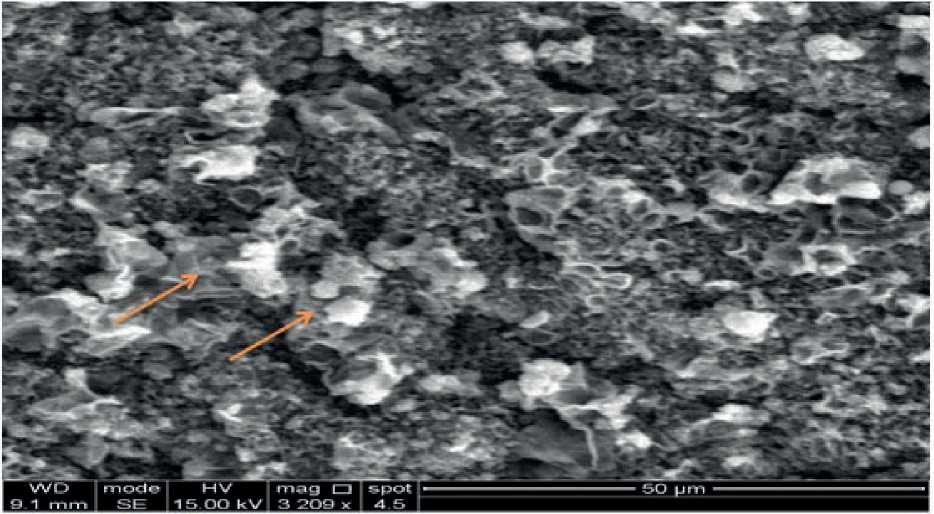

Figure (1): Scanning electron micrograph of pups liver control group show a normal architecture of parenchyma (hepatocytes) ( ).
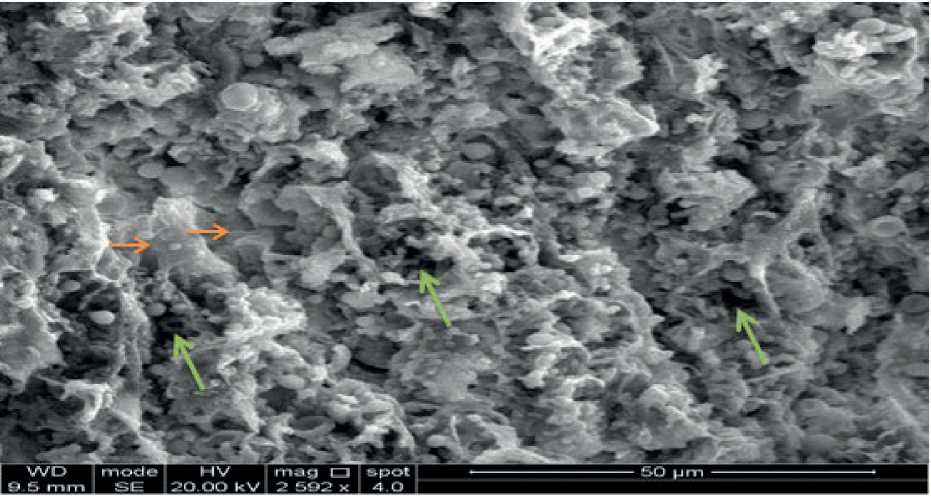
Figure (2): Scanning electron micrograph of pups liver treated by dose40mgkg day of gentamicin show deformation of hepatocytes( ■>), high fenestrae( -).
Список литературы A study of alfa feto protein parameter in serum and histological effects of pups liver by SEM in pregnant rats exposed to overdose of aminoglycoside antibiotics
- AlTameemi WTM. (2014). Immunohistochemical and molecular detection of Reg3a, Ins1, and Ins2 genes in pancreatic tissues of thymoquinon treated diabetic rats. Ph.D. Thesis. Al-qadisiyah University.
- Arjinajarn, P, et al. (2017). Anthocyanin-rich Riceberry bran extract attenuates gentamicin-induced hepatotoxicity by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy, 92, 412-420.
- de Montemor Marçal, G, et al. (2021). Association between the consumption of ultra-processed foods and the practice of breast-feeding in children under 2 years of age who are beneficiaries of the conditional cash transfer programme, Bolsa Família. Public Health Nutrition, 24(11), 3313-3321.
- Erhirhie E. Ekene N. and Ajaghaku D. (2014). Guidelines on dosage calculation and stock solution preparation in experimental animals’ studies.J. natu. Sci. R. ISSN 2224-3186.
- Gabant P, et al. (2002). Alpha-fetoprotein, the major fetal serum protein, is not essential for embryonic development but is required for female fertility. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(20), 12865-12870.
- Galaly SR, Ahmed OM and Mahmoud AM. (2014). Thymoquinone and curcumin prevent gentamicin- induced liver injury by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 65(6): 823-32.
- Hall JE. (2016). Text Book of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 1168 pp.
- Hobbie SN, et al. (2008). Genetic analysis of interactions with eukaryotic rRNA identify the mitoribosome as target in aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(52), 20888-20893.
- Sigal SH, et al. (1994). Characterization and enrichment of fetal rat hepatoblasts by immunoadsorption (“panning”) and fluorescence‐activated cell sorting. Hepatology, 19(4), 999-1006.
- Survarna SK., Lyaton C. and Bancroft JD. (2018). Bancroft,s Theory and practice of histological technique. Saven edition. Elsevier Limited.,China. 584 pp.
- Tan D. (2017). Anatomy, Physiology, and Husbandry of Laboratory Animals. Fundamentals of Laboratory Animal Science, 129-188.


