Abscopal effect of radiotherapy and hyperthermia: role of exosomes
Автор: Yunusova Natalia V., Fedorov Alexandr A., Startseva Zhanna A., Yeon Ju Hun
Журнал: Сибирский онкологический журнал @siboncoj
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.19, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The review presents data on the role of ionizing radiation/hyperthermia as modulating factors in exosome secretion/composition. Tumor-derived exosomes are important participants in the formation of the tumor microenvironment. They modulate the inflammatory response in the tumor, influence the capability of fibroblasts and mesenchymal cells to differentiate into myofibroblasts, trigger the angiogenic process, promote epithelial to mesenchymal transformation of tumor cells and form the pre-metastatic nisches. The review describes the mechanisms of behavior of the recipient tumor cells receiving exosomes from irradiated cells, including activation of Akt signaling, stabilization of MMP9/MMP2, and enhancement of exosome-mediated motility. In vitro models demonstrate the efficacy of exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) to modulate both direct and abscopal effects of radiation therapy/hyperthermia. Exosomes derived from MSC are the most attractive carriers for the delivery of proteins, miRNAs, drugs, and metals to the recipient tumor cells. MSC-derived exosomes potentiate the efficacy of both radiotherapy and hyperthermia in vitro studies. However, some important aspects regarding a) the most effective options for administering MSC/MSC exosomes to modulate radiotherapy/hyperthermia; b) radiation dose; c) options of hyperthermia; d) detailed mechanisms of the effect of irradiated MSC-derived exosomes on the tumor microenvironment and cancer cells, still remain poorly understood.
Radiotherapy, hyperthermia, abscopal effect, malignant tumors, extracellular vesicles, exosomes
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140254328
IDR: 140254328 | УДК: 616-006.6-091.8:615.832/.849:577.2 | DOI: 10.21294/1814-4861-2020-19-2-108-115
Текст обзорной статьи Abscopal effect of radiotherapy and hyperthermia: role of exosomes
ÀБÑÊÎПÀЛЬÍЫÉ ЭФФÅÊÒ ÐÀДИÎÒÅÐÀПИИ И ГИПÅÐÒÅÐМИИ: ÐÎЛЬ ÂÍÅÊЛÅÒÎЧÍЫÕ ÂÅЗИÊУЛ
Í.Â. Юнóñîвà1,2, À.À. Фåдîðîв1, Æ.À. Ñтàðцåвà1, J.H. Yeon3,4
Научно-исследовательский институт онкологии, Томский национальный исследовательский меди цинский центр Российской академии наук, г. Томск, Россия1
Сибирский государственный медицинский университет, г. Томск, Россия2
Россия, г. Томск, 634050, Московский тракт, 22
Center for BioMicrosystems, Brain Science Institute, Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST),
Seoul, Republic of Korea3
-
5. Hwarang-ro 14-gil, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02792, Republic of Korea3
Department of Integrative Biosciences, University of Brain Education, Cheonan, Republic of Korea4
Cheonan, 31228, Republic of Korea4
Àннîтàция
В обзоре представлены обобщенные данные о роли ионизирующего излучения/гипертермии как модулирующих факторов в секреции/составе экзосом. Опухолевые экзосомы являются важными участниками формирования микроокружения опухоли путем модуляции воспалительного ответа в опухоли, влияния на дифференцировку фибробластов и мезенхимных клеток в миофибробласты, запуска ангиогенного процесса, стимулирования эпителиально-мезенхимальной трансформации и формирования опухолевых прениш. Описаны некоторые механизмы поведения опухолевых клеток-реципиентов, получающих экзосомы от облученных клеток, включая активацию передачи сигналов Akt, стабилизацию MMP9/MMP2, усиление опосредованной экзосомами подвижности. Модели in vitro продемонстрировали эффективность экзосом из мезенхимальных стволовых клеток (МСК) для модуляции как прямого воздействия радиации/гипертермии, так и усиления абскопального эффекта. Экзосомы, полученные из MSC, являются наиболее привлекательным носителем для доставки белков, микроРНК, лекарств, металлов к опухолевым клеткам реципиента. Экзосомы MSC усиливают эффекты как лучевой терапии, так и гипертермии в экспериментальных исследованиях. Тем не менее остается ряд важных вопросов, касающихся: а) наиболее эффективных вариантов введения экзосом MSC для модуляции лучевой терапии/гипертермии; б) дозы ионизирующего излучения; в) вариантов гипертермии; г) детальных механизмов воздействия экзосом из облученных МСК на опухолевые клетки и микроокружение опухоли.
Êлючåвыå ñлîвà: ðàдиîтåðàпия, гипåðтåðмия, àбñêîпàльныé эффåêт, злîêàчåñтвåнныå îпóõîли, внåêлåтîчныå вåзиêóлы, эêзîñîмы.
The abscopal effect of radiation therapy (radiation therapy in combination with modifiers, in particular, with hyperthermia) is the non-targeted effect of radiation suggesting the transmission of radiation signals from irradiated to non-irradiated cells. A somewhat different interpretation of this term suggests regression of distant tumor sites after localized irradiation [1, 2]. The abscopal effect is also described for other local physical effects, for example, hyperthermia treatment [3]. It is believed that the mechanisms underlie the abscopal effect are as follows (Fig. 1):
-
1. Intercellular interaction («gap junction»), including a p53-mediated path of the damage signal.
-
2. Another mechanisms associated with the secretion of mediators into the culture medium (reactive oxygen species, cytokines, hormones, growth factors, DNA fragments, extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes).
The origin, structure and composition of exosomes
Most researchers distinguish 2 different subtypes of extracellular vesicles (EVs): microvesicles and exosomes. They differ significantly in morphology, biophysical characteristics (shape, size, optical density), biogenesis and functions. Exosomes are homogeneous group of membrane vesicles ranging in size from 30 to 100 nm with a cup-like morphology of endosomal origin secreted by all types of cells. Microvesicles, also called microparticles, are much larger extracellular particles with diameters from 100 to 1000 nm in various shapes. The composition of microvesicles is more complex and heterogeneous. Since exosomes are most reported in the context “abscopal effect”, in our review we will discuss this type of EVs. The protein ensemble of exosomes secreted by various types of cells is systematized in the ExoCarta database. Various classes of exosomal proteins have been identified: adhesion molecules (integrins), membrane transport/ transfer proteins (annexins, proteins of the Rab family), cytoskeleton proteins, tetraspanin (CD63, CD9, CD81, etc.), antigen-presenting molecules (proteins I and II histocompatibility class), enzymes (proteases, pyruvate kinase), death receptors (TNFalpha, TRAIL), cytokines, heat shock proteins and tumor antigens (CEA, HER2). The lipid composition of exosomes has been much less studied, but lipids are believed to be important for maintaining their shape, plasticity, stability and functional activity. The main lipids of EVs are sphingomyelin, phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, gangliosides and phosphatidylinositol, as well as lysobiphosphatidic acid, which determine the high stability of exosomes in the blood and other biological fluids, and also protect the contents of exosomes (functionally active miRNAs and other non-coding RNAs, proteins) from destruction [4]. The main recipients of exosomes are cells of hematopoietic origin, fibroblasts, endothelial and tumor cells [5].
The effect of ionizing radiation on the secretion of exosomes
Ionizing radiation is one of the main environmental factors that induce cellular stress. A n accumulation of reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide and cytokines can be observed as an additional mechanisms of the adverse effect of radiation. Moreover, it was shown that X-ray irradiation itself induces exosome secretion by various types of tumor cells (MCF-7, FaDu, BHY) [6, 7]. The expression level of genes including Alix, Rab27a, Rab27b, TSPA8, and CD63 as well as the protein level of CD63 in X-ray-treated MCF-7 cells increased with increasing X-ray dose ( p <0.05). In comparison with untreated cells, the total exosomal protein level, acetylcholinesterase activity, size and zeta-potential values of exosomes from irradiated cells increased ( p <0.05). Data suggest X-ray could activate exosome biogenesis and secretion in MCF-7 cells in a dose-dependent way [6].
The effect of ionizing radiation on the exosome сomposition
Exosomes from non-irradiated tumor and nontumor cells contain both radiosensitizing and radioresistance factors (miRNAs, proteins) [8–10]. The most complete picture of changes in the protein composition of tumor cell exosomes after exposure to ionizing radiation is provided by proteomics. The most overexpressed exosomal proteins from irradiated cells (cell cultures of HPV-negative squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) – FaDu) involved in the transcription, translation, cell division, protein folding (chaperones) and proteasome complex proteins were detected. The authors suggest that cell cycle arrest and blockade of transcription/translation are the main responses of cells to ionizing radiation. Therefore, the presence of transcription/translation/protein folding factors and proteins of ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation system in the exosome cargo secreted from irradiated cells may reflect the dynamic adapta-
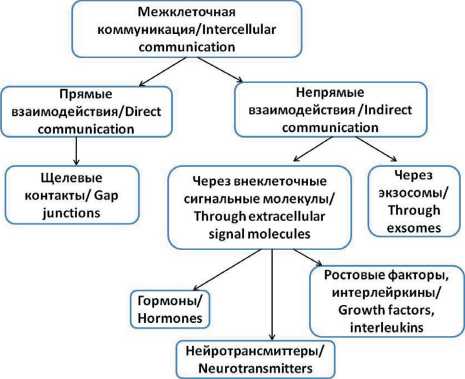
Рис.1. Механизмы межклеточной коммуникации Fig. 1. Mechanisms of intercellular communication tion of cells to stress. Perhaps through secretion of exosomes, cells try to remove excess/unnecessary components. Also, the presence of signaling factors (RABs and RASs proteins) related with GTPases in exosomes may reflect the stress-induced response triggered in cells exposed to radiation [11].
Data obtained by L. Mutschelknaus et al. (2017) on HNSCC cell cultures showed that exosomes derived from cancer cells modify the motility of tumor cells and metastasis. The authors demonstrated the association of radiation changes in exosomes with their ability to stimulate the migration of recipient HNSCC cells. Exosomes isolated from irradiated donor cells increase HNSCC BHY and FaDu cell motility. The studies revealed activation of Akt signaling in recipient cells, which manifested through increased activity of phospho-mTOR, phospho-rpS6 proteases and stability of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP2/9). The inhibition of Akt signaling at the level of internalization of exosomes by tumor recipient cells (by dynamin) blocked this effect. Thus, it can be assumed that Akt signaling is a key point in exosome-mediated migration. Proteomic analysis of exosomes isolated from irradiated and non-irradiated BHY donor cells revealed 39 elevated and 36 decreased proteins. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), heat shock proteins (HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, HSP90B1) are candidate proteins, which are upregulated in exosomes after irradiation and activate Akt signaling way, stabilize MMP2/MMP9, enhance exosome-mediated motility as well as metastasis. [11]. FGFR1 is overexpressed in 75 % of HPV-negative patients with HNSCC, correlates with poor overall, disease-free survival, and induces radiation resistance in glioblastoma cells [12, 13].
Numerous miRNAs detected in circulating exosomes before radiation therapy (miRNA-493, miR-NA-323a, miRNA-411, miRNA-494, miRNA-379, miRNA-654, miRNA-409) are associated with the effectiveness of prostate cancer radiotherapy (carbon ion radiotherapy). Repeated measurements of miRNA-654 and miRNA-379 can be used to conveniently monitor the effectiveness of radiation therapy in these patients [2, 14]. Radiation-induced miRNA-208a, a marker of the radioresistance of lung cancer and a promising therapeutic target, was detected in circulating exosomes [2].
The abscopal effect of hyperthermia: the role of extracellular vesicles/exosomes [15–18]
Many recent studies have demonstrated that combination of hyperthermia and chemotherapy enhances the anti-tumor effect of tumor-cell- and non-tumor-cell-derived exosomes [15–18]. To heat biological objects, various sources of energy, such as microwave ablation, radiofrequency ablation, laser thermal ablation, and ultrasonic ablation can be used. Microwave ablation (MVA) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) are widely used both in vivo and in vitro studies. However, these are mainly experimental studies [19].
The mechanisms of anti-tumor activity of exosomes derived from cells undergoing hyperthermia have been poorly studied, but there is evidence that under such conditions exosomes can accumulate and transport drugs, a complex of chemokines, heat shock proteins, microRNAs that promote apoptosis, induce redistribution of lymphocyte fractions, etc. [16–18]. In addition, active endocytosis of magnetic particles packed in exosomes by a tumor cells was detected in vitro. This process accelerated tumor ablation through hyperthermia induced by an external magnetic field
-
[19] . There are sufficient data indicating the feasibility of using thermal ablation in the treatment of osteosarcomas. The abscopal antitumor effect of hyperthermia on the Walker-256 carcinosarcoma was found [3, 20].
Besides tetraspanins and integrins, the exosome membrane contains a complex of proteases. Tetraspanin-associated proteases, which mainly include ADAM10, ADAM17 and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), are important for tumor invasion, metastasis, and chemoresistance [21–25]. Overexpression of MMP2/MMP9 gelatinases after incubation of tumor recipient cells with exosomes from irradiated donor cells is considered to be one of the main mechanisms of the non-target effect of radiotherapy [11]. Secreted MMPs (MMP1, MMP13, MMP2, MMP9, MMP3, MMP10, MMP7) and membrane-bound MMPs (MMP14, MMP24, MMP25) were detected in exosomes. MMP2 and MMP9 gelatinases are the most studied enzymes. Also, EVs contain an inducer of MMPs – EMMPRIN (CD147), as well as MMPs inhibitors TIMP1, TIMP2 and TIMP3 [22–24, 26]. Both immature and mature forms of MMP2, MMP9, MMP14 with proteolytic activity were detected in EVs, including exosomes derived from from tumor-and nontumor-derived cell lines [27]. Substrates for MMPs are type IV collagen, elastin, fibronectin and laminin, as well as cell surface proteins E-cadherin, fibrin and interleukin-1. Thus, they modulate the interaction of cells and extracellular matrix. It is believed that exosomes transfer MMP2, MMP3, and MMP9 from primary tumors to the lymph nodes and lung tissue [21,
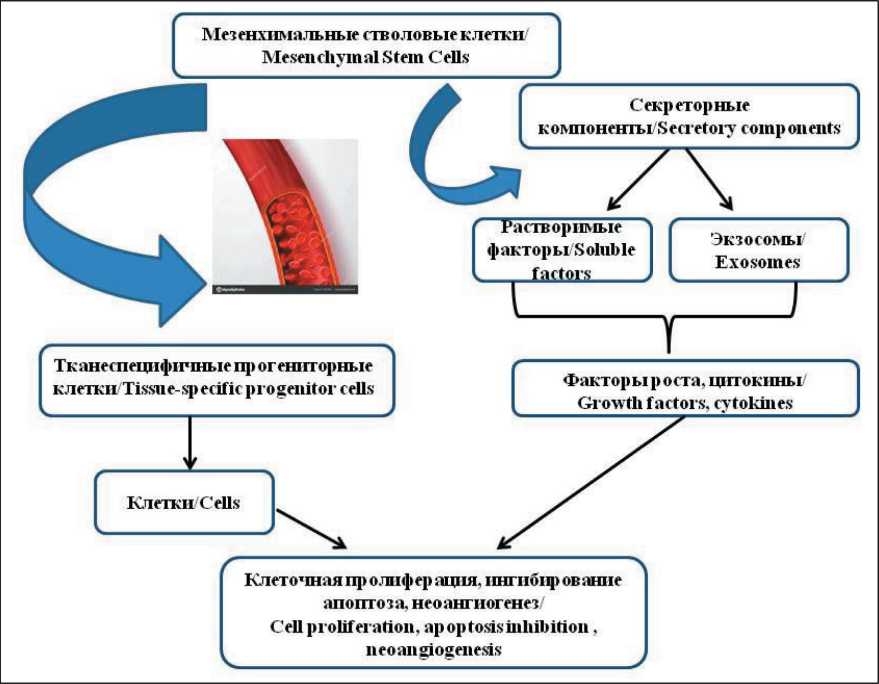
Рис. 2. Механизмы регенеративных эффектов мезенхимальных стволовых клеток
Fig. 2. Mechanisms of the regenerative effects of mesenchymal stem cells
25]; however, the role of vesicular metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the formation and progression of malignant tumors has been poorly studied. The effects of ionizing radiation and hyperthermia are practically unexplored.
Exosomes from multipotent mesenchymal stem cells potentiate the effect of both radiotherapy and hyperthermia
Exosomes derived from multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are the most attractive carriers for delivery of proteins, miRNAs, drugs, metals to recipient tumor cells due to effective biocompatibility, reduced immunogenicity (reduced expression of MHI I and II), small size and ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. In addition, methods for culturing human MSCs from various sources (bone marrow, adipose tissue) and isolating exosomes from cell cultures are well established. It has long been shown that MSCs from various sources stimulate tissue regeneration, including bone, skeletal muscle, myocardium, liver, and nervous tissue. The mechanisms of this effect are presented in Fig. 2. They include:
-
1. Integration of transplanted MSCs into recipient tissues with the formation of progenitor tissue-specific stem cells.
-
2. Secretory activity of MSCs, including the secretion of both soluble factors and factors in the composition of EVs/exosomes.
Among the growth factors mediated by MSCs, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), nerve growth factor (NGF), glial cell neurotrophic factor (GCNF), platelet growth factor (PDGF-BB), TGFbeta and others factors were identified [28]. Exosomes derived from MSCs will have a trophic effect and stimulate proliferation and angiogenesis [29]. Thus, exosomes obtained by culturing MSCs from bone marrow attenuated radiation-induced bone loss in a rat model that was similar to transplantation of MSCs. Among the mechanisms that explain this phenomenon, the contribution of exosomes to the antioxidant status, restoration of DNA damage, proliferation and aging of recipient cells, as well as induction of angiogenesis was described. The positive effect of exosomes on the differentiation potential of irradiated MSCs with the predominance of their osteogenic differentiation in experiments both in vitro and in rat models was also revealed [30].
Both MSCs and cancer cells, including cancer stem cells, can secrete EVs with a mutual metabolic effect on oncogenesis, as a result of which exosomes from heterogeneous MSCs of various origins contain various unique factors with different effects on tumor cells [28]. A number of studies indicate the tumorstimulating effect of exosomes from MSCs. On the other hand, human umbilical cord MSC-derived exosomes protected against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and stimulated cell proliferation [31]. A good antitumor effect of MSC exosomes after incubation with taxol was shown. Taxol-loaded exosomes were isolated and incubated with various highly metastatic human cell lines. Although the control MSC exosomes almost did not inhibit tumor growth, exposure to taxol-loaded exosomes was associated with cytotoxicity reaching 80–90 %, indicating a specific and more effective targeting of the tumor. Systemic intravenous use of MSC-derived exosomes loaded with taxol revealed a decrease in subcutaneous primary tumors of more than 60 %, as well as a significant reduction in metastases of MDA-hyb1 in the lungs, liver, spleen and kidneys. The effect of MSC exosomes was similar to that observed for taxol, although the concentration of taxol in exosomes was approximately 1000 times lower [28]. V.A. Farias et al. (2018) revealed a significant reduction in both the primary tumor and metastatic foci of subcutaneous xenografts of A375 human melanoma (NOD/SCID-gamma mice) treated with combination of MSC and radiation therapy. The most significant antitumor/antimetastatic effect was observed when MSC was used before radiation therapy or simultaneously with radiation therapy. The authors suggested that this effect might be due to exosomes secreted by MSC. To simulate this effect in vitro, a comparative proteomic analysis of exosomes from unirradiated and irradiated at a dose of 2 Gy MSC was performed. Among the most representative clusters of exosomes originating from irradiated MSC, clusters of cell adhesion of leukocytes and cell localization were identified. Proteins typical for these clusters included annexins and integrins such as ANXA1, ANAX2, ITGB1, ITGA3, FN1, CTNNB1, APOH, which can activate the adhesion of exosomes and leukocytes to tumor cells, thus leading to inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis [32]. The use of iron oxide-associated exosomes from MSCs of various origins (adipose tissue, bone marrow, dental pulp, human umbilical cord cells) is promising for ablation of tumor cells using magnetic hyperthermia [18].
Options for the internalization of exosomes: as one of the reasons for the presence/absence of an abscopal effect in vitro and in vivo
Currently, several variants of the interaction of exosomes with recipient cells have been described. Exosome uptake mechanisms may include:
-
- ligand-receptor interactions without membrane fusion (antigen presentation);
-
- fusion of exosome membranes and target cells, leading to the transfer of proteins anchored in the vesicular membrane to the plasma membrane of the recipient cell;
-
- internalization of exosomes by endocytosis (all fragments of exosomes are translocated into the cell);
-
- impact of the components of exosomes on the cell after their lysis in the extracellular environment (at low pH, for example, in the tumor microenvironment) [4].
Thus, it can be assumed that the effect of exosomes at the cellular and whole body levels significantly depends on the option of internalization of exosomes. Visualization of exosome uptake by endotheliocytes, macrophages, hepatocytes, tumor and other types of cells using confocal laser microscopy is quite common. Exosomes isolated by various methods are suitable for this study. 3Ddata reconstruction allowed researchers to demonstrate EVs internalization and cellular localization. EVs internalization has been observed by means of confocal microscopy after staining with different fluorescent lipid membrane dyes including rhodamine, DiD, Dil, PKH26, PKH67. Membrane-permeable compounds are also used for EVs staining [33]. Several sub-populations of exosomes (external adherent exosomes, internalized exosomes, colocalized exosomes) can be detected using Amnis ImageStream® X Mk II, which combines the speed, sensitivity and phenotyping of flow cytometry with detailed images and the functionality of microscopy [34–36].
Conclusion
Exosomes are nanosized vesicles that can deliver bioactive cargo, including lipids, growth factors and their receptors, proteases, signaling molecules, mRNAs and miRNAs released from donor cells to recipient cells. Tumor exosomes are important participants in the formation of the tumor microenvironment by (a) modulating the inflammatory response in the tumor (b) influencing the differentiation of fibroblasts
Список литературы Abscopal effect of radiotherapy and hyperthermia: role of exosomes
- Siva S., Lobachevsky P., MacManus M.P., Kron T., Moller A., Lobb R.J., Ventura J., Best N., Smith J., Ball D., Martin O.A. Radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer induces DNA damage response in both irradiated and out-of-field normal tissues. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 1; 22(19): 48174826. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0138
- Tang Y., Cui Y., Li Z., Jiao Z., Zhang Y., He Y., Chen G., Zhou Q., Wang W., Zhou X., Luo J., Zhang S. Radiation-induced miR-208a increases the proliferation and radioresistanee by targeting p21 in human lung eaneer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 12; 35: 7. 10.1186/ s13046-016-0285-3. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-016-0285-3
- Wang H., Zhang L., Shi Y., Javidiparsijani S., Wang G., Li X., Ouyang W., Zhou J., Zhao L., Wang X., Zhang X., Gao F., Liu J., Luo J., Tang J. Oncol Lett. Abscopal antitumor immune effects of magnet-mediated hyperthermia at a high therapeutic temperature on Walker-256 carcinosarcomas in rats. Oncol. Lett. 2014 Mar; 7(3): 764770. 10.3892/ ol.2014.1803. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.1803
- Tamkovich S.N., Tutanov O.S., Laktionov P.P. Exosomes: Generation, Structure, Transport, Biological Activity, and Diagnostic Application. Biochemistry (Moscow), Supplement Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology. 2016; 10 (3): 163-173. DOI: 10.1134/S1990747816020112
- Yunusova N.V., Tugutova E.A., Tamkovich S.N., Kondakova I.V. The Role of Exosomal Tetraspanins and Proteases in Tumor Progression Biochemistry (Moscow) Supplement Series B: Biomedical Chemistry. 2018; 12(3): 191202. DOI: 10.1134/S1990750818030095


