Аддитивное производство и численное моделирование полимерных стентов
Автор: Спорышева Д.И., Хайрулин А.Р.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 4 (106) т.28, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Биоразлагаемые стенты – это одно из перспективных направлений в кардиологии, имеющее ряд преимуществ перед металлическими. Исследования показывают, что эти стенты могут эффективно восстанавливать просвет сосудов и одновременно органично растворяться в тканях организма, минимизируя риск осложнений. Производство биоразлагаемых стентов методом FDM-печати позволяет разнообразить типы изготавливаемых конструкций, а также является экономически выгодным решением. Было произведено численное моделирование процесса расширения 6 геометрий стен-тов. В качестве материала стента использовался биоразлагаемый полимер – полилактид (PLA). Максимального расширения на концах достиг стент № 2 с пятиэлементными распорками. Однако в центральной области наилучшее расширение получает стент № 4, состоя-щий из девятиэлементных распорок. Минимальные и максимальные напряжения конструкций равны соответственно 77,1 и 83,1 МПа. Во всех стентах после разгрузки был выявлен переход в зону пластических деформаций в областях коронок и звеньев (max = 0,65, min = 0,1). По результатам моделирования были рассчитаны коэффициенты радиальной упругости, укорочения и неравномерности раскрытия стентов. Также был произведен сравнительный анализ влияния толщины стенки стента на его способность расширяться и сохранять свое напряженно-деформированное состояние, который показал, что стенты с толщиной 0,4 мм, в отличие от толщины 0,2 мм, лучше расширяются и сохраняют значительное раскрытие после снятия нагрузки со стента.
Стент, PLA, аддитивное производство, численное моделирование
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146283001
IDR: 146283001 | УДК: 531/534: [57+61] | DOI: 10.15593/RZhBiomeh/2024.4.08
Текст научной статьи Аддитивное производство и численное моделирование полимерных стентов
RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF BIOMECHANICS
В последнее время численное моделирование расширения стентов приобрело ключевое значение в процессе разработки и оптимизации данных медицинских устройств. Данный метод позволяет исследователям не только улучшить характеристики стентов, но и повысить их общую эффективность и безопасность.
Важность численного моделирования в этой области можно обосновать несколькими основными аспектами.
Во-первых, численное моделирование служит мощным инструментом для оптимизации дизайна стентов. С его помощью возможно исследование множества конструктивных вариантов, включая различные формы и геометрические характеристики, что в конечном счете способствует достижению наилучших результатов восстановления сосудистого просвета. Например, в исследованиях [1; 2] были рассмотрены различные геометрические формы стентов, представленных на рынке. А в статье [3] оценивалось влияние толщины и ширины распорок на расширение.
0000-0002-7506-5568


Эта статья доступна в соответствии с условиями лицензии Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
License (CC BY-NC 4.0)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0)
Использование численного моделирования дало возможность выявить оптимальные параметры стента, которые минимизируют риск повреждения сосудистой стенки.
Во-вторых, метод позволяет прогнозировать поведение стента в различных условиях, включая меняющееся давление, деформацию сосудистой стенки и динамику потока крови. Это критически важно для предварительной оценки эффективности и безопасности стента до его клинического применения. Например, в работе [1] представлена МКЭ-модель, которая позволяет оценить механическую нагрузку на сосудистую стенку. В работе [4] рассматриваются этапы установки стентов в артерию с бляшкой, а статья [5] рассказывает о гидродинамических показателях при проектировании стентов.
В-третьих, численные модели предоставляют возможность подробно оценить материалы, используемые для изготовления стентов. На сегодняшний день активно развивается направление биосовмести-мых стентов, которые активно сравнивают с уже используемыми на практике металлическими аналогами [6].
Наконец, применение численного моделирования значительно экономит время и ресурсы. Оно позволяет провести большое количество виртуальных экспериментов за короткий промежуток времени, что, в свою очередь, ведет к сокращению затрат, связанных с созданием и тестированием физических прототипов стентов.
Следующим этапом сознания коронарных стентов является их производство, которое производится различными способами в зависимости от материала и конструкционных особенностей. Традиционные методы изготовления стентов включают травление [7], микроэлектроразрядную обработку [8], гальванопластику [9], литье под давлением [10] и лазерную резку [11]. Однако данные технологии имеют ряд ограничений [12], значительно влияющих на ограничения по размерам и выбор типа и сложности конструкции.
В отличие от традиционных методов, аддитивное производство ( AM ), открывает новые горизонты для создания высококачественных медицинских изделий, предоставляя ряд преимуществ [13–16]. Он позволяет одновременно снизить стоимость стента и, благодаря сочетанию с 3 D - и численным моделированием, учесть анатомические особенности конкретного пациента [17; 18].
Наиболее популярным является метод постойного наплавления материала (FDM) Принтеры, использующие FDM, функционируют на основе пошагового создания трехмерных объектов, нанося каждый слой материала сверху вниз посредством нагрева и выдавливания термопластичных нитей. Обычно экструдер перемещается по осям x и y для формирования очередного слоя, в то время как перемещение по оси z позволяет создавать новые слои.
Применения методов аддитивных технологий сделало возможным создание биоразлагаемых стентов из полимеров. Данное решение представляет собой инновационное направление в кардиологии, обладающее значительным потенциалом для улучшения медицинских показателей и исходов лечения пациентов. Данные стенты имеют способность растворяться в организме до естественных побочных продуктов после восстановления просвета артерии [19; 20], что уменьшает проблемы наличия инородного тела в кровотоке [21], а также уменьшает возможность гиперплазии тканей и дает возможность проведения повторной безопасной процедуры стентирования при рестенозе [22–26]. Еще одно важное преимущество биоразлагаемости таких полимерных стентов – использование их для лечения педиатрических пациентов, когда стент необходимо поставить ненадолго из-за быстрого роста ребенка [27–29].
Недавние обзоры состояния аддитивных технологий в производстве биоразлагаемых стентов продемонстрировали активный интерес к применению полилактида ( PLA ), который выступает в роли одного из основных биосовместимых и биоразлагаемых пластиков для 3 D -печати [26; 30–38]. Данный полимера характеризуется высокой биосовместимостью и возможностью варьирования времени разложения в пределах от 6 до 12 месяцев с последующим выведением из организма в виде естественных побочных продуктов.
Целью данной работы является исследование биомеханического поведения полимерных биоразлагаемых стентов из PLA при дилатации для выбора рациональной конструкции, а также аддитивное производство данных имплантов методом FDM .
Материалы и методы
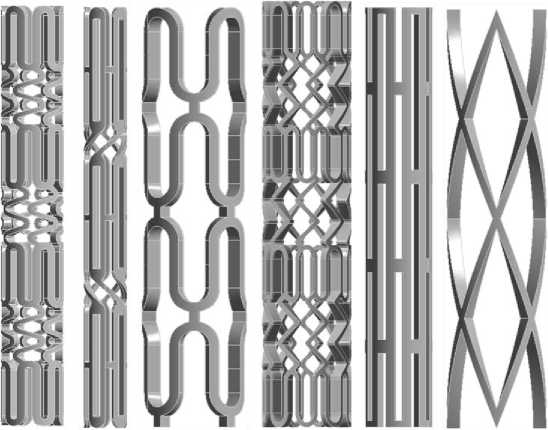
Проведен сравнительный анализ НДС 6 геометрий стентов (рис. 1), изготовленных из полилактида ( PLA ), при раскрытии в рамках операции стентирования. Геометрические параметры представлены в табл. 1.
В основе первой геометрии (рис. 1, а) лежат пятиэлементные распорки, соединенные пружинистыми элементами соединения. Вторая геометрия (рис. 1, б) представляется собой ячеистую структуру пятиэлементных распорок с соединительными элементами.
а б в г д е
Таблица 1
Геометрические параметры стентов
|
Стент |
Наружный диаметр, мм |
Толщина стенки, мм |
Длина, мм |
|
1 |
3 |
0,4 |
20,306 |
|
2 |
29,272 |
||
|
3 |
12,044 |
||
|
4 |
18,646 |
||
|
5 |
12,600 |
Рис. 1. Геометрии стентов: а – стент 1; б – стент 2; в – стент 3; г – стент 4; д – стент 5; е – стент 6
Третья геометрия (рис. 1, в ) представляет собой стент, образованный четырехэлементными распорками, соединенные между собой звеньями. Четвертая геометрия состоит из девятиэлементных распорок, соединённых пружинистыми элементами (рис. 1, г ). Пятый стент (рис. 1, д ) является ячеистым с прямыми соединяющими элементами. Шестой стент (рис. 1, е ) – сетчатая структура.
Геометрии стентов а – д были взяты c сайта Simscale , а стент е является разработкой нашей лаборатории.
В данной работе в качестве материала для стента использовался универсальный биополимер полилактид ( PLA ), мономером которого является молочная кислота. Этот материал легко синтезируется в большом количестве, поддается биологическому разложению и широко используются в биомедицине [39; 40].
В работе применялась модель материала с билинейным изотропным упрочнением (рис. 2). Значения модуля упругости, коэффициента Пуассона, предела текучести и касательного модуля представлены в табл. 2. Известно, что предел прочности на растяжение-сжатие материала PLA находится в пределах 50–80 МПа. В данной работе предел прочности материала составляет 80 МПа [41].
Для граничных условий используем тип Remote Displacement (рис. 3). Данный тип граничных условий позволяет на выбор ограничить или разрешить перемещений и поворотов относительно осей. Данное
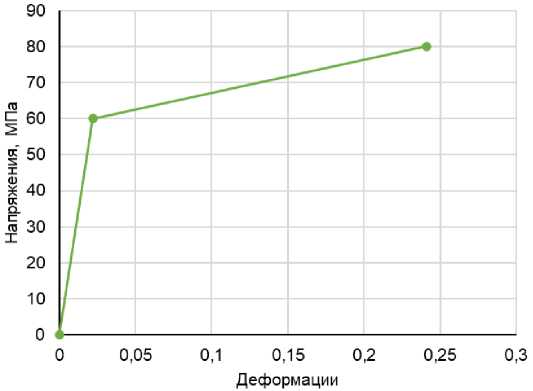
Рис. 2. Диаграмма растяжения материала с билинейным изотропным упрочнением граничное условие позволяет расширяться закрепленным концам стентов, избегая краевых эффектов, которые могут возникать при жёстком закреплении [42].
Правый край стентов закреплялся на расстоянии 15 мм от центра модели, запрещая перемещения и повороты. На левом конце разрешены перемещения вдоль продольной оси стента.
Нагружение производилось за счет приложения давления к внутренней поверхности стентов. Для всех стентов максимальное давление было установлено на уровне 0,6 МПа. Нагружение выполнялось поэтапно и включало три шага нагрузки, за которыми следовал один шаг разгрузки. Нагрузка производилась до тех пор, пока уровень напряжений не достигал 80 МПа, что соответствует пределу прочности материала.
Механические свойства PLA [41]
|
Плотность, кг/м3 |
Модуль Юнга, МПа |
Коэффициент Пуассона |
Предел текучести, МПа |
Касательный модуль, МПа |
Модель материала |
|
1250 |
3000 |
0,33 |
65 |
30 |
С билинейным изотропным упрочнением |
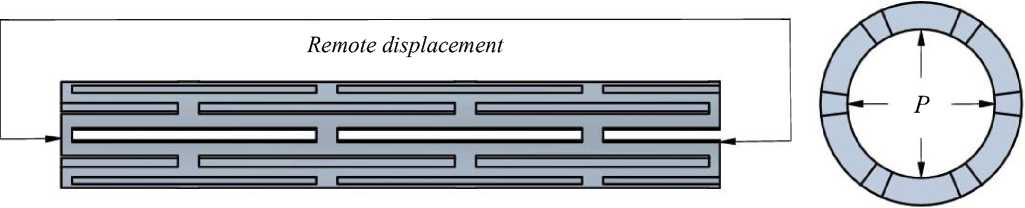
Рис. 3. Закрепление модели: граничные условия
Для описания поведения стента был выбран конечный элемент SOLID 92 ( Tet 10) c дополнительными узлами на грани. Элемент имеет 10 узлов и также хорошо подходит для описания криволинейных конструкций. Параметры сетки указаны в табл. 3.
Произведена оценка сеточной сходимости через анализ размера конечно-элементной сетки моделей. Было выявлено, что от размера элемента, равного 0,1 мм, значения радиальных перемещений менялись менее чем на 0,5 %. Таким образом, размер конечных элементов был подобран для каждого стента.
Печать производилась на принтере Raise 3 D E 2 (рис. 4). Осуществлен подбор параметров печати для пяти геометрий стентов для PLA (табл. 3). Наибольшие сложности при печати возникали со стентом № 3, поэтому именно эта геометрия послужила основой для подбора параметров печати всех стентов. Конструкционные особенности стента № 1 (сильно изогнутые пружинистые связи) дают систематический сбой при печати. Данная проблема была решена путем варьирования скоростей, чтобы уже напечатанные элементы конструкции успевали затвердевать.
Также были проварьированы значения температуры сопла. Оптимальная температура плавления для PLA составляет 170–180 °С. Однако для нормальной склейки между слоями необходимо повышать температуру. Нами была опробована печать при 210, 215 и 220 °С. При этом обращалось внимание на количество соединительных нитей, наплыв слоев друг на друга и вид машинных дефектов печати. По результатам сравнения данных образцов был выбран режим печати при 215 °С.
Помимо вышеперечисленных параметров было выявлено, что на возможности качества печати влияет тип прилипания к столу. Было выявлено, что при типе
«кайма» образуется наилучшее прилипание стента к столу и затрачивается наименьшее количество материала и времени на печать.
Результаты
Проверка возможности расширения стентов выполняется путем численного моделирования процесса в пораженном сегменте артерии. Однако для повышения эффективности оценки этой возможности для различных геометрий и ускорения вычислений было принято решение проводить расчеты только стента без стенок сосуда, выбрать наиболее подходящие геометрии для расширения и затем моделировать поведение стентов в выбранных образцах артерий.
Стент № 1 к третьему этапу нагрузки (0,23 МПа) увеличился в диаметре до 7,56 мм в своей средней части (рис. 5, а ). Концы стента расширились до 1,12 мм в диаметре.
Диаметр стента № 2 увеличился до 6,96 мм, при этом наибольший диаметр наблюдается именно на его концах. Средняя часть стента расширилась меньше – её диаметр составил 4,2 мм (рис. 5, б ).
После трех этапов нагружения под давлением 0,44 МПа, диаметр концов стента №3 достиг 2,96 мм, а средняя часть увеличилась до 1,08 мм (рис. 5, в ).
Стент № 4 был подвергнут расширению до 0,2 МПа, в результате чего его диаметр составил 6,28 мм. Концы стента расширились до 3,72 мм в диаметре (рис. 5, г ).
Состояние стента № 5 анализировалось на трех этапах (при финальном внутреннем давлении 0,26 МПа); максимальное расширение до 6,8 мм зафиксировано на концах стента, в то время как диаметр средней части составил 3,24 мм (рис. 5, д ).
Таблица 3
Параметры сеточных моделей
|
Стент |
Размер элемента, мм |
Число элементов |
Число узлов |
|
1 |
0,15 |
94538 |
169984 |
|
2 |
0,1 |
349013 |
562134 |
|
3 |
0,1 |
98105 |
162452 |
|
4 |
0,15 |
98488 |
172956 |
|
5 |
0,1 |
70446 |
121710 |

Рис. 4. Процесс печати стентов из PLA
Таблица 4
Параметры печати стентов из PLA
|
Температура, °С |
Скорость, мм/с |
Геометрические параметры, мм |
|||
|
стола |
сопла |
охлаждения |
внешнего контура |
высота слоя |
диаметр сопла |
|
45 |
215 |
180 |
35 |
0,1 |
0,2 |
Для стента № 6 в ходе третьего этапа внутреннее давление составляло 0,36 МПа. Максимальное расширение произошло на концах стента (5,12 мм), а диаметр средней части достиг 0,7 мм (рис. 5, е ).
Для стента № 1 максимальные концентрации напряжений находятся на коронках, где они достигают своего предела в 80 МПа. В то же время минимальные значения напряжений фиксируются на средних участках распорок и составляют 0,43 МПа на третьем шаге (рис. 6, а ).
У стента № 2 максимальные напряжения (рис. 6, б ) проявляются в внутренних участках коронок и на соединительных звеньях распорок, достигая также 80 МПа, а минимальные значения (0,25 МПа) наблюдаются на центральных участках распорок.
Наибольшие напряжения у стента № 3 расположены на коронках распорок, где они достигают 80 МПа. При этом минимальные напряжения составляют 0,32 МПа в средних частях распорок (рис. 6, в ).
У стента № 4 максимальные напряжения зафиксированы на коронках и достигают значения 80 МПа, в то время как минимальные значения, равные 0,41 МПа, расположены на звеньях и средних частях распорок (рис. 6, г ).
Для стента № 5 максимальные напряжения возникают в областях, расположенных близко к соединительным звеньям распорок (рис. 6, д ), в то время как минимальные значения напряжения фиксируются на средних частях распорок и составляют 0,58 МПа.
Что касается стента № 6, то максимальные напряжения наблюдаются в участках, расположенных рядом со звеньями соединения распорок, а минимальные значения (0,09 МПа) фиксируются на внешних коронках стента (рис. 6, е ).
Согласно полученным данным, пластические деформации в стентах проявляются на более поздних этапах нагружения. Поэтому в работе представлены результаты последнего шага нагружения.
Для стента № 1 максимальные деформации достигают 0,66 и располагаются в средней части на коронках (рис. 7, а ). У стента № 2 наибольшие деформации фиксируются вблизи соединительных звеньев и составляют 0,34 (рис. 7, б ). Стент № 3 показывает пиковое значение деформации 0,11 точечно на коронках (рис. 7, в ). Для стента № 4 максимальные деформации также наблюдаются на коронках и составляют 0,39 (рис. 7, г ). У стента № 5 они возникают рядом со звеньями и на внешних коронках, достигая 0,31 (рис. 7, д ). Наконец, у стента № 6 максимальная деформация равна 0,2 и расположена на коронках (рис. 7, е ).
Анализ и обсуждение
Оценим деформационное поведение стентов на основе полученных результатов (табл. 5).
Максимального расширения достиг стент № 2 с пятиэлементными распорками, соединенными в ячейки, и соединительными элементами. Однако, если оценивать среднюю часть стента, то наилучшее расширение получает стент № 4, состоящий из девятиэлементных распорок, соединённых пружинистыми элементами.
По средней части стента хуже всего расширяются стент №3 и № 6 (сеточная структура).
Отметим специфику расширения двух групп стентов. В первую группу входят стенты № 1 и № 4, которые
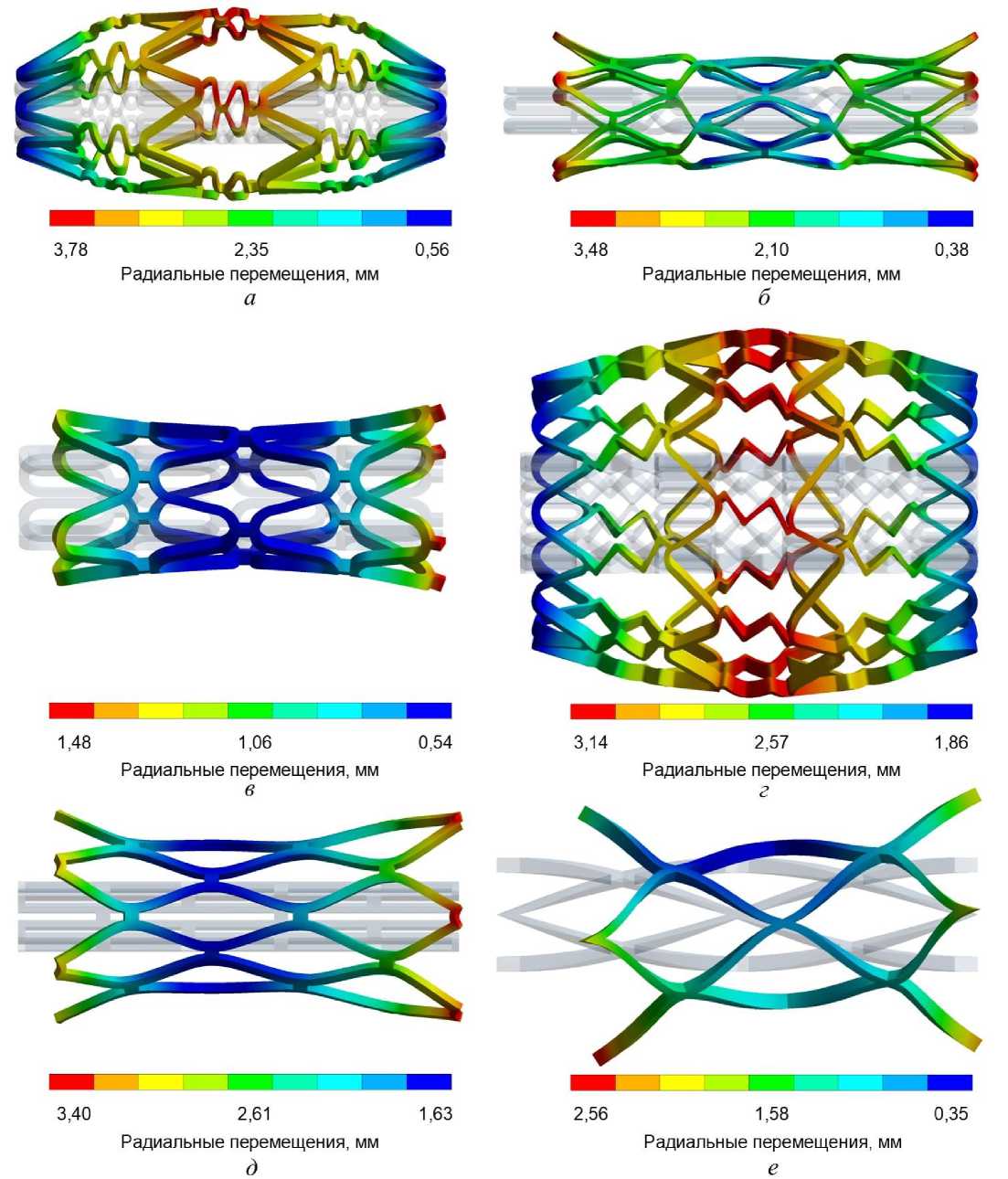
Рис. 5. Радиальные перемещения (мм) вдоль вертикальной оси:
а – стент № 1; б – стент № 2; в – стент № 3; г – стент № 4; д – стент № 5; е – стент № 6
46’4 „
Напряжения по Мизесу, МПа
а
0,43
45,5 Напряжения по Мизесу, МПа б
0,25
' ' I
43,6 Напряжения по Мизесу, МПа в
0,32
44,9 Напряжения по Мизесу, МПа г
43,3 0,58
Напряжения по Мизесу, МПа
д
Рис. 6. Напряжения по Мизесу (МПа): а – стент № г – стент № 4; д – стент № 5; е
80 43,9
Напряжения по Мизесу, МПа е
1; б – стент № 2; в – стент № 3;
– стент № 6
0,09
0,66 0,37
Пластические деформации
0,34 0,19 0
Пластические деформации
0,06
Пластические деформации
0,39
0,22 Пластические деформации г
0,38
] zzeecz^e
0,21 0
Пластические деформации д
Рис. 7. Пластические деформации: г – стент № 4; д
0,2 0,11
Пластические деформации
е а – стент № 1; б – стент № 2; в – стент № 3;
стент № 5; е – стент № 6
Финальные значения параметров математического моделирования
|
Стент |
P max , МПа |
D , мм ( D = 3 мм) конеч . , нач . |
σ , min , МПа |
σ max , МПа |
пласт ε max |
|
1 |
0,23 |
7,56 (средняя часть стента) 1,12 (концы стента) |
0,43 |
80,0 |
0,66 |
|
2 |
0,20 |
6,96 (средняя часть стента) 4,2 (концы стента) |
0,25 |
0,34 |
|
|
3 |
0,44 |
2,96 (средняя часть стента) 1,08 (концы стента) |
0,32 |
0,11 |
|
|
4 |
0,20 |
6,28 (средняя часть стента) 3,72 (концы стента) |
0,41 |
0,39 |
|
|
5 |
0,26 |
6,8 (средняя часть стента) 3,24 (концы стента) |
0,20 |
0,38 |
|
|
6 |
0,36 |
5,12 (средняя часть стента) 0,7 (концы стента) |
0,09 |
0,20 |
а б
Рис. 9. Зависимость радиальных перемещений от шага: а – толщина стенки 0,2 мм; б – толщина стенки 0,4 мм
а
б
Рис. 10. Напряжения по Мизесу от шага: а – толщина стенки 0,2 мм; б – толщина стенки 0,4 мм при расширении образуют форму бочки – раздутая центральная часть и сужения по мере приближения к краям стента. Данная специфика расширения может быть вызвана именно геометрическими особенностями.
Вторая группа – стенты № 2, № 3, № 5 и № 6 – седлообразные, которые имеют наибольшее расширение на краях стентов. Основной причиной данной специфики расширения также можно предположить особенности геометрии стента, так как все перечисленные стенты имеют ячеистую или сетчатую структуру.
Во всех стентах был выявлен переход в зону пластических деформаций в областях коронок и звеньях соединения распорок.
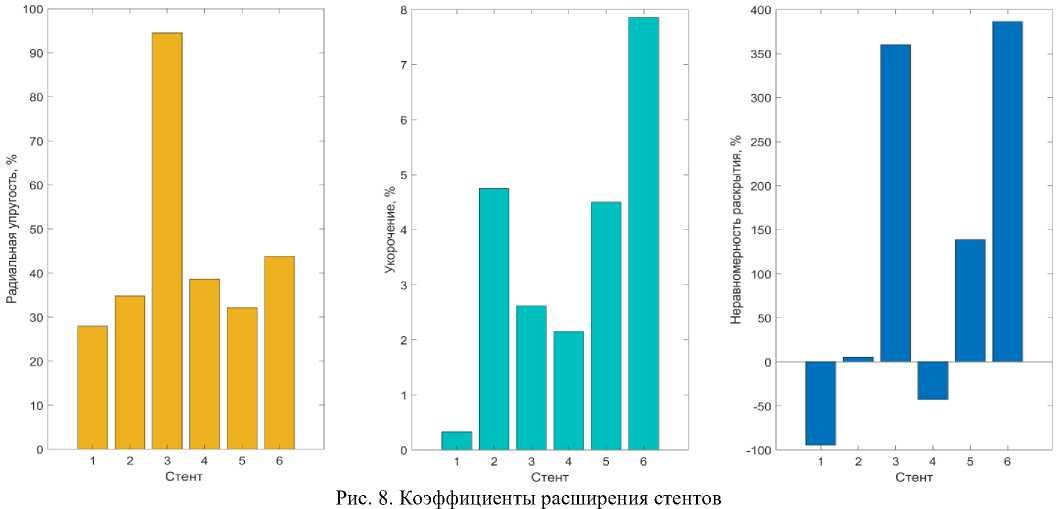
Для оценки расширения стентов часто применяются различные коэффициенты. Мы рассмотрели для данного случая наиболее известные из них – радиальную упругость, укорочение и неравномерность раскрытия (рис. 8).
Радиальная упругость (устойчивость) ( Recoiling ( R )) – это явление, которое проявляется при упругопластической деформации стента под действием давления от расширенной артерии [43; 44]. Чем выше значение этого коэффициента, тем более эффективен стент.
Коэффициент радиальной упругости (устойчивости) находится следующим образом:
нагр разгр
R = dmax d ⋅100%, нагр max
где d нагр и d разгр – средние диаметры на этапах максимальной нагрузки и разгрузки соответственно.
Коэффициент укорочения стента является лучшим
при минимальном своем значении, т.к. сохранятся охват большей площади повреждённого участка [43], и находят по формуле нач разгр
F = L - на L ч ⋅ 100% (16)
Dogboning (DB) – явление, при котором концы стента раскрываются больше, чем центральная часть (неравномерность раскрытия стента), в следствии неравномерности расширения баллона, что оказывает значительное влияние на тромбоз и гиперплазию [12; 45; 46]. При положительном значении данного коэффициента расширение концов стента превосходит расширение центральной части. При отрицательном значении наоборот, центральная часть расширяется больше, образуя подобие бочки. Значение неравномерности раскрытия считается лучшим при минимальном значении по модулю. Рассчитывается коэффициент по формуле конец середина
DB =D-D⋅100% середина где Dконец – средний диаметр на концах стента, Dсередина – средний диаметр середины стента.
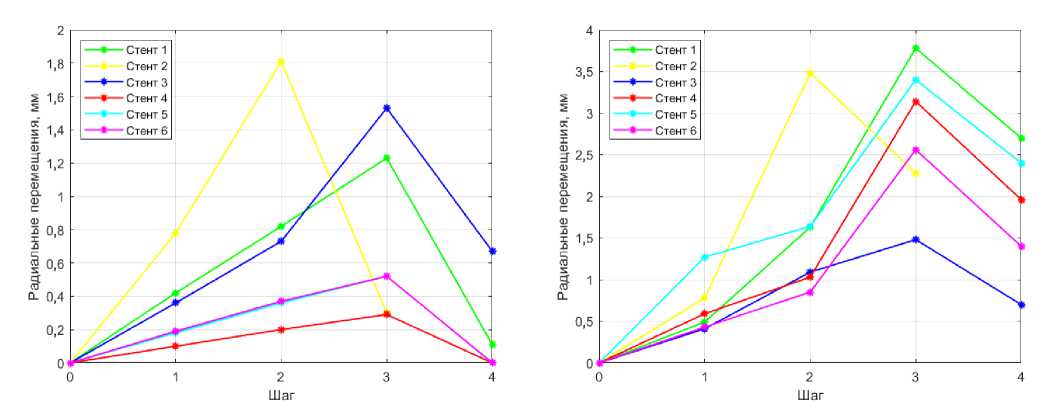
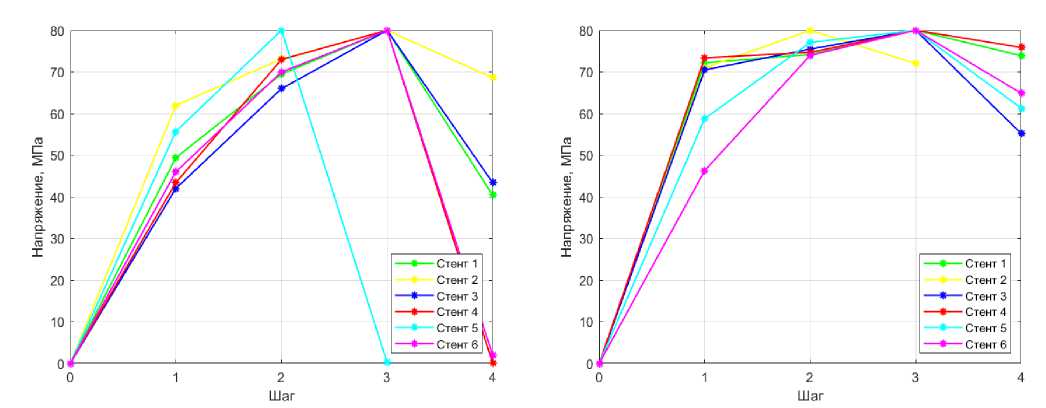
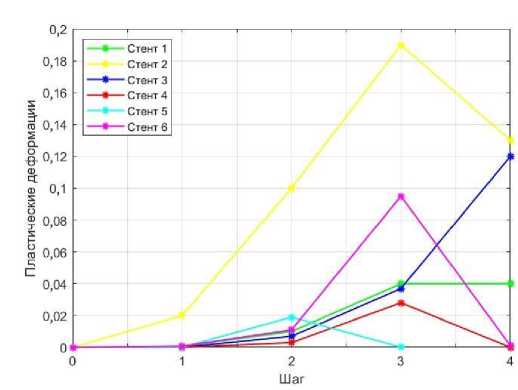
Для оценки влияния толщины стенки стентов на способность расширения и сохранения состояния после разгрузки было произведено моделирование идентичное представленному выше при толщине 0,2 мм. По результатам расчетов были построены графики зависимости параметров математического моделирования от шага нагружения (рис. 9–11).
а
Рис. 11. Зависимость пластических деформаций от шага: а – толщина стенки 0,2 мм; б – толщина стенки 0,4 мм
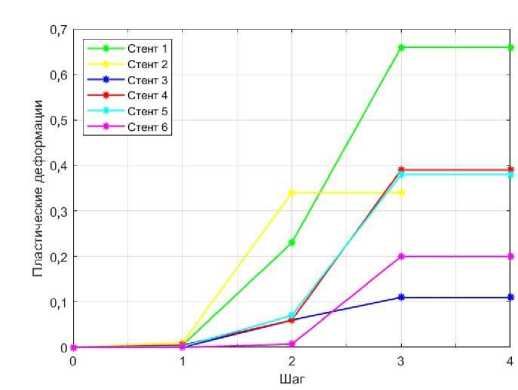
б
На рис. 9, а и б показаны зависимости радиальных перемещений для стентов с толщиной стенки 0,2 и 0,4 мм соответственно. Результаты показывают, что максимальные радиальные перемещения для стентов с толщиной 0,4 мм значительно выше, чем для стентов с толщиной 0,2 мм. Это указывает на то, что при увеличении толщины стенки стента его способность к расширению значительно улучшается, что обеспечивает более больший просвет артерии после установки стента.
На рис. 10 показаны напряжения по Мизесу для стентов с толщиной стенки 0,2 (рис. а ) и 0,4 мм (рис. б ). Максимальные значения напряжений для данных толщин стентов на каждом шаге находятся примерно в одном диапазоне. Разница напряжений для двух толщин на каждом шаге нагружения не превышает 5–7 %. Для стентов с толщиной стенки 0,2 мм была отмечена тенденция к низким остаточным напряжениям, которые в ряде случаев приближаются к нулю. Однако несмотря на то, что остаточные напряжения для стентов № 4, № 5 и № 6 практически отсутствуют, для стентов № 1, № 2 и № 3, остаточные напряжения все же имеют место. Эти значения варьируются от 40 до 69 МПа. При увеличении толщины стенки стентов до 0,4 мм наблюдается существенное увеличение остаточных напряжений. Для всех стентов величины варьируются от 55 до 78 МПа.
Для стентов с толщиной стенки 0,2 мм, как показано на рис. 11, а, наблюдаются значительные различия в поведении стентов под нагрузкой. В частности, стенты № 4, № 5 и № 6 не сохраняют свою форму после снятия нагрузки. Напротив, стенты № 1, № 2 и № 3, как показывают результаты, демонстрируют большие уровни пластических деформаций и, следовательно, лучше сохраняют свою форму после снятия нагрузки. При увеличении толщины стенки до 0,4 мм, как видно на рис. 11, б, все стенты перешли в зону пластичности после снятия нагрузки. Это означает, что такие стенты, в отличие от более тонких, способны сохранять определённую форму, что может быть положительным фактором, обеспечивающим длительную проходимость сосуда. Важно отметить, что наиболее деформируемым является стент № 1, у которого наибольшая пластическая деформация при толщине 0,4 мм.
Таким образом по результатам исследования для стентирования коронарных артерий наиболее подходят стенты с толщиной стенки 0,4 мм.
Заключение
В процессе выполнения данной работы был произведен анализ влияния геометрии на расширение стента под действием давления. Наиболее расширяемыми являются стенты № 1, № 2 и № 4.
Полученные данные о возникающих напряжениях будут в дальнейшем сравнены с результатами экспериментального изучения конструкций, на основе чего будут сделаны выводы о пределах прочности для каждой конструкции.
С помощью критериев расширения были выявлены лучшие стенты. Наибольшей радиальной упругостью (устойчивостью) обладает стент № 3. Меньшее укорочение, а следовательно, и захват большего пораженного участка, происходит для стента № 1. По критерию Dogboning лучшими свойствами обладает стент № 2, расширяющийся наиболее равномерно относительно других стентов. Суммарно по трем критериям стенты были расставлены в порядке от лучшего к худшему: стент № 4, стент № 3, стенты № 1 и № 2, стент № 5, стент № 6.
Дальнейший анализ НДС будет проводиться непосредственно в артерии, что позволит снизить неравномерного расширения стентов. В данной работе анализировалась лишь возможность геометрий стентов к расширению и определение давлений расширения каждой геометрии. Также планируется моделирование баллона и численное моделирование взаимодействия баллона со стентом.
В процессе выполнения данной работы был произведен подбор параметров 3 D -печати стентов из полилактида ( PLA ), биосовместимого и биоразлагаемого полимера. Параметры печати подобраны универсально для печати 5 разных геометрий стентов.
Ключевые выводы:
-
1. Рассмотрено 6 стентов разной геометрии, произведено их численное моделирование и 3 D -печать;
-
2. Не все стенты возможно напечатать методом FDM без дополнительного оснащения: стент № 4 не был напечатан в силу конструкционных особенностей;
Список литературы Аддитивное производство и численное моделирование полимерных стентов
- Lally, C. Cardiovascular stent design and vessel stresses: a fi-nite element analysis / C. Lally, F. Dolan, P.J. Prendergast // J Biomech. – 2005. – Vol. 38, no. 8. – P. 1574–81.
- Finite element analysis of the mechanical performances of 8 marketed aortic stent-grafts / N. Demanget, A. Duprey, P. Badel, L. Orgéas, S. Avril, C. Geindreau, J.N. Albertini, J.P. Favre // J Endovasc Ther. – 2013. – Vol. 20, no. 4. – P. 523–35.
- Wang, W. Finite element analysis of the expansion behavior of coronary stents / W. Wang, D. Yang, M. Qi // Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. – 2006. – Vol. 23, no. 6. – P. 1258–62, 1266.
- Рововой, Э.Ю. Математическое моделирование поведе-ния биодеградируемых коронарных стентов из полимер-ных материалов / Э.Ю. Рововой, О.В. Антонова // Россий-ский журнал биомеханики. – 2024. – Т. 28, № 1. – С. 23–39.
- Frank, A.O. Computational fluid dynamics and stent design / A.O. Frank, P.W. Walsh, J.E. Moore Jr. // Artif Organs. – 2002. – Vol. 26, no. 7. – P. 614–21.
- Mechanical behavior of polymer-based vs. metallic-based bi-oresorbable stents / H.Y. Ang, Y.Y. Huang, S.T. Lim, P. Wong, M. Joner, N. Foin // J Thorac Dis. – 2017. – Vol. 8. – P. S923–S934.
- Chemical etching of nitinol stents / B. Katona, E. Bognár, B. Berta, P. Nagy, K. Hirschberg // Acta Bioeng Biomech. – 2013. – Vol. 15, no. 4. – P. 3–8.
- Lappin, D. An experimental study of electrochemical polish-ing for micro-electro- discharge-machined stainless-steel stents / D. Lappin, A.R. Mohammadi, K. Takahata // J Mater Sci Mater Med. – 2012. – Vol. 23, no. 2. – P. 349–56.
- Electroforming as a new method for fabricating degradable pure iron stent / A. Purnama, A. Mostavan, C. Paternoster, D. Mantovani // Advances in Metallic Biomaterials. – 2015. – P. 85–100.
- Özarslan, S. Microstructure, mechanical and corrosion prop-erties of novel Mg-Sn-Ce alloys produced by high pressure die casting / S. Özarslan, H. Şevik, İ. Sorar // Materials Sci-ence and Engineering C. – 2019. – Vol. 105. – P. 110064.
- Fu, C.H. Statistical characteristics of surface integrity by fiber laser cutting of Nitinol vascular stents / C.H. Fu, J.F. Liu, A. Guo // Appl Surf Sci. – 2015. – Vol. 353. – P. 291–299.
- Evaluation of coronary stents: A review of types, materials, processing techniques, design, and problems / F. Ahadi, M. Azadi, M. Biglari, M. Bodaghi, A. Khaleghian // Heliyon. – 2023. Vol. 9, no. 2. – P. e13575.
- Ali, M.A. Additive manufacturing potential for medical de-vices and technology / M.A. Ali, M. Rajabi, S. Sudhir Sali // Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering. – 2020. – Vol. 28. – P. 127–133.
- In vivo evaluation and characterization of a bio-absorbable drug-coated stent fabricated using a 3D-printing system / S.A. Park, S.J. Lee, K.S. Lim, I.H. Bae, J.H. Lee, W.D. Kim, M.H. Jeong, J.-K. Park // Materials Letters. – 2015. – Vol. 141. – P. 355–358.
- Mechanical properties and shape memory effect of 3D-printed PLA-based porous scaffolds / F.S. Senatov, K.V. Niaza, M.Y. Zadorozhnyy, A.V. Maksimkin, S.D. Kaloshkin, Y.Z. Estrin // J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. – 2016. – Vol. 57. – P. 139–48.
- 4D printing of shape memory-based personalized endolumi-nal medical devices / M. Zarek, N. Mansour, S. Shapira, D. Cohn // Macromol Rapid Commun. – 2017. – Vol. 38, iss. 2. – P. 1600628.
- Advancements and limitations in 3D printing materials and technologies: a critical review / S.F. Iftekar, A. Aabid, A. Amir, M. Baig // Polymers. – 2023. – Vol. 15, no. 11. – P. 2519.
- Design and fabrication of novel polymeric biodegradable stents for small caliber blood vessels by computer-aided wet-spinning / D. Puppi, A. Pirosa, G. Lupi, P.A. Erba, G. Giachi, F. Chiellini // Biomedical Materials (Bristol). – 2017. – Vol. 12, no. 3. – P. 035011.
- Cardiovascular stents: overview, evolution, and next genera-tion / S. Borhani, S. Hassanajili, S.H. Ahmadi Tafti, S. Rabbani // Progress in Biomaterials. – 2018. – Vol. 7, no. 3. – P. 175–205.
- The development of design and manufacture techniques for bioresorbable coronary artery stents / L. Wang, L. Jiao, S. Pang, P. Yan, X. Wang, T. Qiu // Micromachines (Basel). – 2021. – Vol. 12, no. 8. – P. 990.
- Advances in the development of biodegradable coronary stents: A translational perspective / J. Zong, Q. He, Y. Liu, M. Qiu, J. Wu, B. Hu // Materials Today Bio. – 2022. – Vol. 16. – P. 100368.
- A review of material degradation modelling for the analysis and design of bioabsorbable stents / E.L. Boland, C.J. Shine, N. Kelly, C.A. Sweeney, P.E. McHugh // Annals of Biomed-ical Engineering. – 2016. – Vol. 44, no. 2. – P. 341–56.
- Enhancing flexibility and strength-to-weight ratio of poly-meric stents: A new variable-thickness design approach / M. Khatami, A. Doniavi, A.M. Abazari, M. Fotouhi // J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. – 2024. – Vol. 150. – P. 106262.
- Mechanical properties and degradation process of biliary self-expandable biodegradable stents / C.I. Kwon, J.S. Son, K.S. Kim, J.P. Moon, S. Park, J. Jeon, G. Kim, S.H. Choi, K.H. Ko, S. Jeong, D.H. Lee // Digestive Endoscopy. – 2021. – Vol. 33, no. 7. – P. 1158–1169.
- Prabhu, S. Modeling of degradation and drug release from a biodegradable stent coating / S. Prabhu, S. Hossainy // J Bio-med Mater Res A. – 2007. – Vol. 80, no. 3. – P. 732–41.
- Additive manufacturing of vascular stents / Y. Li, Y. Shi, Y. Lu, X. Li, J. Zhou, A.A. Zadpoor, L. Wang // Acta Bio-materialia. – 2023. – Vol. 167. – P. 16–37.
- The effects of the mechanical properties of vascular grafts and an anisotropic hyperelastic aortic model on local hemodynam-ics during modified blalock–taussig shunt operation, assessed using FSI simulation / A.G. Kuchumov, A. Khairulin, M. Shmurak, A. Porodikov, A. Merzlyakov // Materials. – 2022. – Vol. 15, no. 8. – P. 2719.
- Welch, T.R. Biodegradable stents for congenital heart disease / T.R. Welch, A.W. Nugent, S.R. Veeram Reddy // Interventional Cardiology Clinics. – 2019. – Vol. 8, no. 1. – P. 81–94.
- Bioresorbable stent to manage congenital heart defects in chil-dren / J. Wright, A. Nguyen, N. D'Souza, J.M. Forbess, A. Nugent, S.R.V. Reddy, R. Jaquiss, T.R. Welch // Materialia (Oxf). – 2021. – Vol. 16. – P. 101078.
- Jia, H. 3D printed self-expandable vascular stents from biode-gradable shape memory polymer / H. Jia, S.Y. Gu, K. Chang // Advances in Polymer Technology. – 2018. – Vol. 37, no. 8.
- Heparin coating on 3D printed poly (l-lactic acid) biodegrada-ble cardiovascular stent via mild surface modification ap-proach for coronary artery implantation / S.J. Lee, H.J. Ha, S.L. Kyung, L. Dohyung, S. Lee, S.J. Lee, D.K. Wan, H.J. Myung, Y.L. Joong, K.K. Il, J. Youngmee, K.P. Jun, A.P. Su // Chemical Engineering Journal. – 2019. – Vol. 378. – P. 122116.
- Radial compressive property and the proof-of-concept study for realizing self-expansion of 3D printing polylactic acid vas-cular stents with negative poisson’s ratio structure / Z. Wu, J. Zhao, W. Wu, P. Wang, B. Wang, G. Li, S. Zhang // Mate-rials. – 2018. – Vol. 11, no. 8. – P. 1357.
- Experimental study of polymeric stent fabrication using homemade 3D printing system / D. Zhao, R. Zhou, J. Sun, H. Li, Y. Jin // Polym Eng Sci. – 2019. – Vol. 59, no. 6.
- 4D printing of shape memory polylactic acid (PLA) / M. Mehrpouya, H. Vahabi, S. Janbaz, A. Darafsheh, T.R. Mazur, S. Ramakrishna // Polymer. – 2021. – Vol. 230. – P. 124080.
- 3D-printed PCL/PLA composite stents: Towards a new solu-tion to cardiovascular problems / A.J. Guerra, P. Cano, M. Rabionet, T. Puig, J. Ciurana // Materials. – 2018. – Vol. 11, no. 9. –P. 1679.
- 3D printing advances in the development of stents / R. Khalaj, A.G. Tabriz, M.I. Okereke, D. Douroumis // Int J Pharm. – 2021. – Vol. 609, no. 20. – P. 121153.
- Research progress of absorbable stents / Y. Song, B. Li, H. Chen, Z. Yu // International Journal of Medical Sciences. – 2024. – Vol. 21, no. 2. – P. 404–412.
- Sousa, A.M. 3D printing of polymeric bioresorbable stents: a strategy to improve both cellular compatibility and mechani-cal properties / A.M. Sousa, A.M. Amaro, A.P. Piedade // Pol-ymers. – 2022. – Vol. 14, no. 6. – P. 1099.
- Bergström, J.S. An overview of mechanical properties and material modeling of polylactide (PLA) for medical applica-tions / J.S. Bergström, D. Hayman // Ann Biomed Eng. – 2016. – Vol. 44, no. 2. – P. 330–40.
- DeStefano, V. Applications of PLA in modern medicine / V. DeStefano, S. Khan, A. Tabada // Engineered Regenera-tion. – 2020. – Vol. 1. – P. 76–87.
- Finite element analysis of the mechanical performance of a two-layer polymer composite stent structure / Ž. Donik, B. Necemer, S. Glodež, J. Kramberger // Eng Fail Anal. – 2022. – Vol. 137, no. 4. – P. 106267.
- Khairulin, A. In silico model of stent performance in multi-layered artery using 2-way fluid-structure interac-tion: Influ-ence of boundary conditions and vessel length / A. Khairulin, A.G. Kuchumov, V.V. Silberschmidt // Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine. – 2024. – Vol. 255. – P. 108327
- An experimental investigation of the mechanical performance of PLLA wire-braided stents / A. Lucchetti, C. Emonts, A. Idrissi, T. Gries, T.J. Vaughan // J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. – 2023. – Vol. 138. – P. 105568.
- Revolutionary auxetic intravascular medical stents for angio-plasty applications / M.S. Ebrahimi, M. Noruzi, R. Hamzehei, E. Etemadi, R. Hashemi // Mater Des. – 2023. – Vol. 235, no. 2. – P. 112393.
- Numerical analysis for non-uniformity of balloon-expandable stent deployment driven by dogboning and foreshortening / G.B. Rahinj, H.S. Chauhan, M. Sirivella, M.V. Satynarayana, R. Lakshminarayanan // Cardiovasc Eng Technol. – 2022. – Vol. 13, no. 2.
- Schiavone, A. Effects of material, coating, design and plaque composition on stent deployment inside a stenotic artery - Fi-nite element simulation / A. Schiavone, L.G. Zhao, A.A. Abdel-Wahab // Materials Science and Engineering C Mater Biol Appl. – 2014. – Vol. 42. – P. 479–88.


