Африканские амфоры в г. Боспоре (Керчи)
Автор: Смокотина А.В.
Журнал: Краткие сообщения Института археологии @ksia-iaran
Рубрика: Древности Крыма и Тамани
Статья в выпуске: 271, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В ходе археологических исследований в Босфорском переулке г. Керчи в 2007-2009 гг. были выявлены фрагменты африканских амфор, поступавших в г. Боспор непрерывно с первой половины V до первой половины VI вв. Преобладает импорт из двух основных центров (почти 40 %): мастерских на юге провинции Бизацена (Маджура, Унка) (Keay 8B), а также мастерской Сиди Захруни в районе города Набуля в провинции Зевгитана (spatheion 1, Keay 55А, Keay 57В и некоторые другие).
Африканские амфоры, боспор, содержимое и смоление, торговля
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143182407
IDR: 143182407 | DOI: 10.25681/IARAS.0130-2620.271.138-154
Текст научной статьи Африканские амфоры в г. Боспоре (Керчи)
В Северное Причерноморье африканские товары поступали в ограниченном количестве, что объясняется, прежде всего, большой удаленностью потребителей в регионе от основных производственных центров. В боспорских комплексах выявлена продукция из северной и центральной части современного
1 Работа выполнена по проекту № 220-4556-3730 «Этнокультурные трансформации во владениях Восточной Римской империи в Крыму» при поддержке Правительства Российской Федерации: постановление от 9 апреля 2010 г. № 220 (программа «мегагрантов»).
Туниса: провинций Зевгитана ( Zeugitana ) и Бизацена ( Byzacena ) ( Bonifay , 2004. Fig. 2: 22 ). При этом импорт из других африканских регионов пока не был обнаружен. На Боспор доставлялись товары в амфорах и краснолаковая посуда, встречаются также редкие находки светильников ( Smokotina , 2014. P. 71–72).
Археологические исследования экспедиции А. И. Айбабина в Босфорском переулке г. Керчи в 2007–2009 гг. позволили получить новую комплексную информацию о типах и формах африканской керамики, оценить общие масштабы и хронологию импорта данной продукции в г. Боспоре (Пантикапей) в позднеримский и ранневизантийский периоды. На протяжении трех лет на участке исследований были открыты культурные слои с остатками хозяйственной деятельности III–VI вв., а также некрополь VII – начала VIII вв. ( Айбабин , 2019. С. 10–11; Айбабин, Хайрединова , 2018. С. 34). Одним из наиболее важных и информативных объектов исследований оказался функционировавший вплоть до второй четверти / середины VI в. рыбозасолочный комплекс из 16 цистерн разного размера ( Смокотина , 2022. С. 163–164).
Некоторые находки профильных фрагментов африканских амфор и особенности их распространения на Боспоре в сравнении с объемами и хронологией поступления краснолаковой посуды ARS ранее рассматривались в нескольких обобщающих работах, а также в отдельных публикациях автора ( Смокотина , 2011. С. 349–350; 2015. С. 316; 2018. С. 268; Smokotina , 2014. P. 71–78. Fig. 6–8). В настоящей работе представлены наиболее полные данные и систематизированы все фрагменты африканских амфор из раскопок в Босфорском переулке г. Керчи в 2007–2009 гг.
Благодаря тщательной обработке керамических материалов из раскопок в Босфорском переулке удалось зафиксировать не только профильные фрагменты, но и стенки африканских амфор. Всего за три года исследований найдено немногим более 1 тыс. фрагментов, что составило около 1 % всех обнаруженных амфор. Среди них выявлено 58 фрагментов профильных частей и один обломок стенки с отверстием от 54 амфор (рис. 1–3) 2 . Необходимо отметить, что в это число входят обломки двух амфор (5 фр.), африканское происхождение которых может быть определено предположительно (рис. 3: 53, 54 ).
В Северном Причерноморье среди опубликованного массового керамического материала фрагменты африканских амфор идентифицируются довольно редко (Smokotina, 2014. P. 71–72). Определение таких сосудов в полевых условиях осложняется малочисленностью их находок в регионе. Тем не менее они легко могут быть опознаны благодаря характерному глиняному тесту и примесям (Bonifay, 2004. P. 26. Pl. I; Smokotina, 2014. Fig. 7), учитывая типичную морфологию профильных частей сосудов. Кроме того, африканские амфоры обычно имеют характерную светлую внешнюю поверхность, полученную благодаря использованию соленой, в основном морской, воды при изготовлении керамики (Bonifay, 2004. P. 41). Нередко можно наблюдать вертикальные полосы от заглаживания поверхности сосудов, что особенно хорошо заметно в придонной части одной из найденных в г. Боспоре амфор (рис. 2: 20).
Среди находок выделяются амфоры из двух основных производственных регионов: центрального и северного Туниса.
Амфоры из мастерских центрального Туниса
Несколько мастерских центрального Туниса, прежде всего, вероятно Мад-жура ( Majoura ) и Унка ( Iunca ) на юге провинции Бизацена, со второй четверти / середины V в. и до первой трети / середины VI в. производили амфоры наиболее известного и широко распространенного в Восточном Средиземноморье и Причерноморье типа Keay 8B (Bonifay 38) ( Keay , 1984. P. 126–129. Fig. 47: 3, 4 ; 48: 1–3 ; Bonifay , 2004. P. 31, 132. Fig. 71: 5 – 8 . Tab. IV; Bonifay et al. , 2011. P. 244; Смокотина , 2018. С. 268). В комплексах Босфорского переулка амфоры Keay 8B являются наиболее многочисленным типом африканского производства ( Смокотина , 2011. С. 349; Smokotina , 2014. P. 78). Всего за время раскопок в 2007– 2009 гг. было найдено 13 фрагментов от 12 амфор (рис. 1: 1–12 ).
Глиняное тесто амфор Keay 8B плотное, преимущественно красное (2.5YR 5/6) 3 , с небольшим количеством светлых включений (известняк, микроокаменелости?) (рис. 1: 1–8, 12 ). При довольно большой однородности теста, у двух фрагментов прослеживается несколько цветных слоев в изломе черепка: красновато-коричневый (5YR 5/4) с коричневыми прослойками (7.5YR 5/3) (рис. 1: 9 ) и стандартный красный (2.5YR 5/6) с красновато-коричневой (5YR 5/4) прослойкой в центре (рис. 1: 11 ). Визуально они ближе глиняному тесту, характерному для производства мастерской Маджура ( Bonifay , 2004. Pl. I: 7 ). Еще один фрагмент отличается более песчанистым красным (2.5YR 5/6) со светло-коричневой сердцевиной (7.5YR 6/4) тестом (рис. 1: 10 ) и имеет сходство с амфорами из мастерской Унка (Ibid. Pl. I: 6 ). У всех амфор визуально наблюдается примесь кварцевого песка в различной концентрации, мелкие светлые включения, иногда встречаются мелкие блестящие частицы (слюда?).
Макроскопическое изучение амфор Keay 8B указывает на наличие в составе примесей небольших микроокаменелостей (Ibid. P. 31. Pl. I: 6, 7 ). Петрографические анализы выявили большое разнообразие глиняного теста, что, возможно, свидетельствует о существовании множества достаточно удаленных друг от друга мастерских, кроме двух уже известных производственных центров (Маджура и Унка) ( Capelli et al. , 2016. P. 285).
Амфоры Keay 8B из боспорских комплексов можно разделить на два основных морфолого-хронологических варианта ( Smokotina , 2014. P. 78. Fig. 8). Ранний вариант отличается близкими к подпрямоугольным пропорциями венчика (высотой 2,8–3,1 см), при этом толщина в средней и нижней частях венчика составляет больше половины от толщины в верхней части (рис. 1: 1–3 ). Такие амфоры являются переходными в эволюционной линии от типа Keay 59

Рис. 1. Африканские амфоры из г. Боспора: продукция мастерских центрального Туниса к типу Keay 8B и датируются второй четвертью или серединой V в. (Bonifay et al., 2011. P. 244. Fig. 9: 25, 26). Два фрагмента амфор раннего варианта, очевидно, являются «примесью снизу» в боспорских комплексах VI в. (рис. 1: 1, 2; табл. 1: 3, 14 (см. в конце статьи)). При этом в комплексе около середины V в. найден фрагмент венчика этого же варианта с немного меньшей толщиной в средней и нижней частях, что может указывать на дальнейшее эволюционное развитие типа в направлении визуально более вытянутых пропорций венчика (рис. 1: 3; табл. 1: 8).
Более поздний вариант амфор Keay 8B представлен 7 фрагментами (рис. 1: 4–7, 9–11 ). Венчики визуально более вытянутые, высотой 2,8–3,7 см, толщина в нижней и особенно в средней частях обычно меньше половины толщины у верхнего края. В Босфорском переулке такие амфоры были обнаружены только в комплексах не ранее VI в., преимущественно второй четверти VI в. (табл. 1: 4, 10, 11, 13 ). Отметим, что наиболее поздние амфоры этого типа М. Бонифе датировал первой третью / первой половиной VI в. ( Bonifay , 2004. P. 132. Fig. 71: 8 ).
Среди боспорских находок представляет интерес также фрагмент стенки ту-лова с остатками неопределенного граффити на плечиках (рис. 1: 8 ; табл. 1: 10 ), найденный рядом с венчиком Keay 8B (рис. 1: 7 ; табл. 1: 10 ).
Амфоры из мастерских северного Туниса
Во время раскопок 2007–2009 гг. в Босфорском переулке г. Керчи были обнаружены 12 фрагментов от 11 амфор, произведенных в мастерских провинции Зевгитана на севере современного Туниса (рис. 2: 13–23 ). В мастерской Сиди Захруни ( Sidi Zahruni ) были изготовлены 10 фрагментов от 9 амфор (рис. 2: 13– 21 ) и 2 фрагмента от 2 амфор происходят из неизвестной мастерской северного Туниса, расположенной, возможно, в долине реки Меджерды (рис. 2: 22, 23 ).
Вторым по численности центром, откуда на Боспор поступали африканские амфоры, является район города Набуля ( Nabeul ), расположенного на юге полуострова Бон, на берегу залива Хаммамет (Ibid. P. 37–39. Fig. 2). В мастерской Сиди Захруни, по-видимому, были изготовлены амфоры типов spatheion 1/ Bonifay 31 (рис. 2: 13 ), Keay 55А/Bonifay 44 (рис. 2: 14, 15 ), Keay 57В/Bonifay 42 (рис. 2: 16, 17 ), типологически неопределенные (рис. 2: 18–21 ), всего 10 фрагментов от 9 сосудов.
Глиняное тесто таких амфор достаточно плотное, с характерными мелкими включениями железистых частиц и минералов кварцевого песчаника (Ibid. P. 29, 39. Fig. 12b. Pl. I: 20, 21 ). Черепок найденных в Босфорском переулке фрагментов обычно красный (2.5YR 5/6) (рис. 2: 13–19 ). Немного более насыщенный оттенок красного характерен для глиняного теста дна с небольшой ножкой (рис. 2: 20 ) – 10R 4/6 и керамического кружка (рис. 2: 21 ) – 2.5YR 4/6, с темным красновато-серым (5YR 4/2) слоем у поверхности.
Мастерская действовала в основном в V–VII вв. (Ibid. P. 37). В г. Боспор поступала продукция V – первой половины VI вв., найденная обычно в более поздних слоях (табл. 1: 1, 3, 4, 20). Наиболее ранней можно считать находку фрагмента амфоры типа spatheion 1 первой половины – середины V в. (рис. 2: 13) (Bonifay, д/1,2 см д 14,5 см
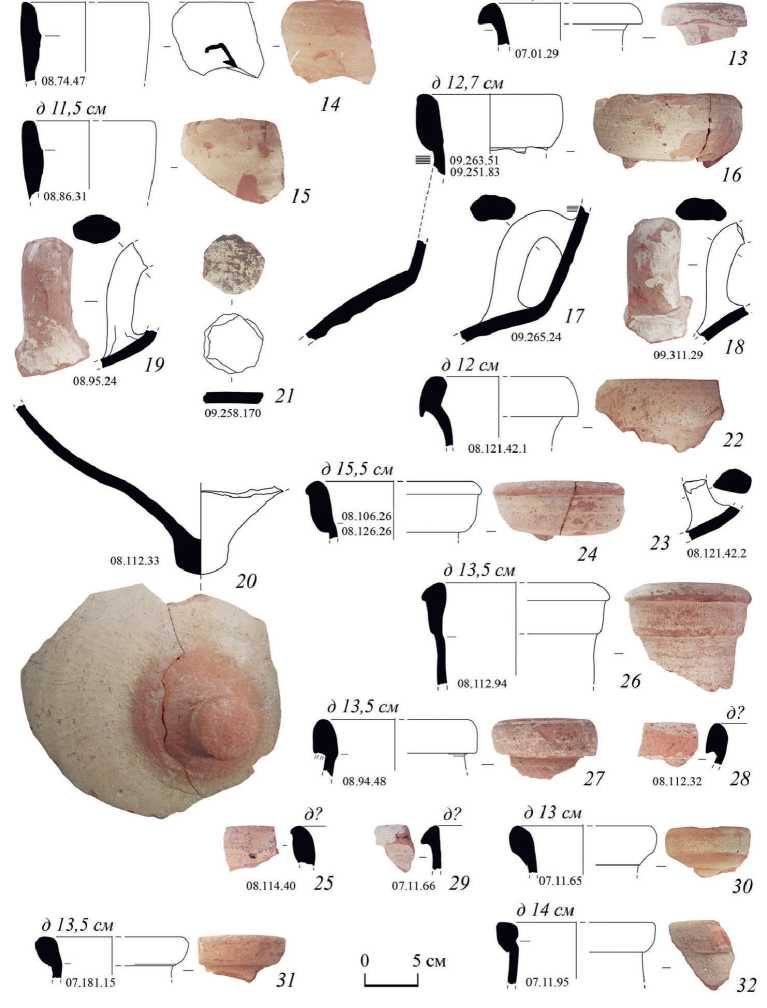
Рис. 2. Африканские амфоры из г. Боспора: продукция мастерских северного Туниса ( 13–23 ), неопределенных центров ( 24–32 )
2004. P. 125. Fig. 67). Во второй половине V в. изготавливались амфоры с вытянутым венчиком и врезным гребенчатым поясом на горле типа Keay 57В (рис. 2: 16, 17 ) (Ibid. P. 135, 137. Fig. 73). В конце V – первой половине VI вв. производились амфоры с закраиной на внутренней стороне венчика типа Keay 55А (рис. 2: 14, 15 ) (Ibid.).
Судя по макроскопическим характеристикам глиняного теста в мастерских Сиди Захруни были изготовлены еще несколько фрагментов амфор неопределенных типов (рис. 2: 18–20 ). Возможно, амфоре типа Keay 55 или Keay 56 конца V – первой половины VI вв. принадлежит фрагмент дна с небольшой ножкой со светлой внешней поверхностью и характерными вертикальными полосами заглаживания в придонной части (рис. 2: 20 ; табл. 1: 4 ) (Ibid. P. 135–137. Fig. 73: 6 ).
Представляет интерес также находка керамического кружка из заполнения боспорской рыбозасолочной цистерны II-10 (рис. 2: 21 ; табл. 1: 20 ). Кружки из обломков стенок сосудов, аккуратно отбитые по краям, использовались как один из способов запечатывания африканских амфор (Ibid. P. 467. Fig. 263). В основном они были характерны для амфор Africana I и некоторых более поздних типов, таких как Keay 62Q/Albenga 11-12 ( Bonifay , 2021. P. 286). Однако диаметр нашей находки (около 5,0 × 5,3 см) заметно меньше диаметра горла основных известных типов африканских амфор из этой мастерской и, например, диаметра между 8 и 9 см, характерного для крышек из кораблекрушения в бухте Ла-Палюд ( de la Palud ) у острова Порт-Крос на юге Франции ( Long, Volpe , 1998. P. 332, Fig. 296; 297). Следы возможной известняковой обмазки или смолы у боспорской находки, которые могли бы пролить свет на ее предназначение, визуально не прослеживаются.
Два фрагмента амфор Keay 40/41 из боспорского слоя второй четверти VI в. были изготовлены в неизвестной мастерской северного Туниса, вероятно, в долине реки Меджерды около середины / второй половины V в. (рис. 2: 22, 23 ; табл. 1: 4 ) ( Bonifay , 2016. P. 515; Remolà Vallverdù , 2000. P. 154). Обломок венчика морфологически наиболее близок типу Keay 40 (рис. 2: 22 ) ( Keay , 1984. P. 250, 252. Fig. 108: 1, 3–5 ). Обе находки имеют визуально близкую, хотя и не идентичную структуру глиняного теста с многочисленными включениями кварцевого песка и песчанистых частиц, которая немного отличается от других типичных африканских образцов. По описаниям такое тесто более характерно для амфор Keay 41 ( Capelli et al. , 2016. P. 289). Черепок боспорских находок двухцветный: плавно переходит от красновато-коричневого (5YR 5/4) у внутренней к красному (2.5YR 5/6) у внешней поверхности (рис. 2: 22 ) или красный (2.5YR 5/6) с узкой светло-коричневой (7.5YR 6/6) прослойкой у внешней стороны (рис. 2: 23 ).
Амфоры неопределенных африканских центров
В комплексах Босфорского переулка г. Керчи были обнаружены фрагменты амфор африканского производства, типологическая принадлежность которых не определена по причине, главным образом, фрагментированности и плохой сохранности профильных фрагментов (рис. 2: 24 – 32 ; 3: 33 – 52 ). Кроме того,
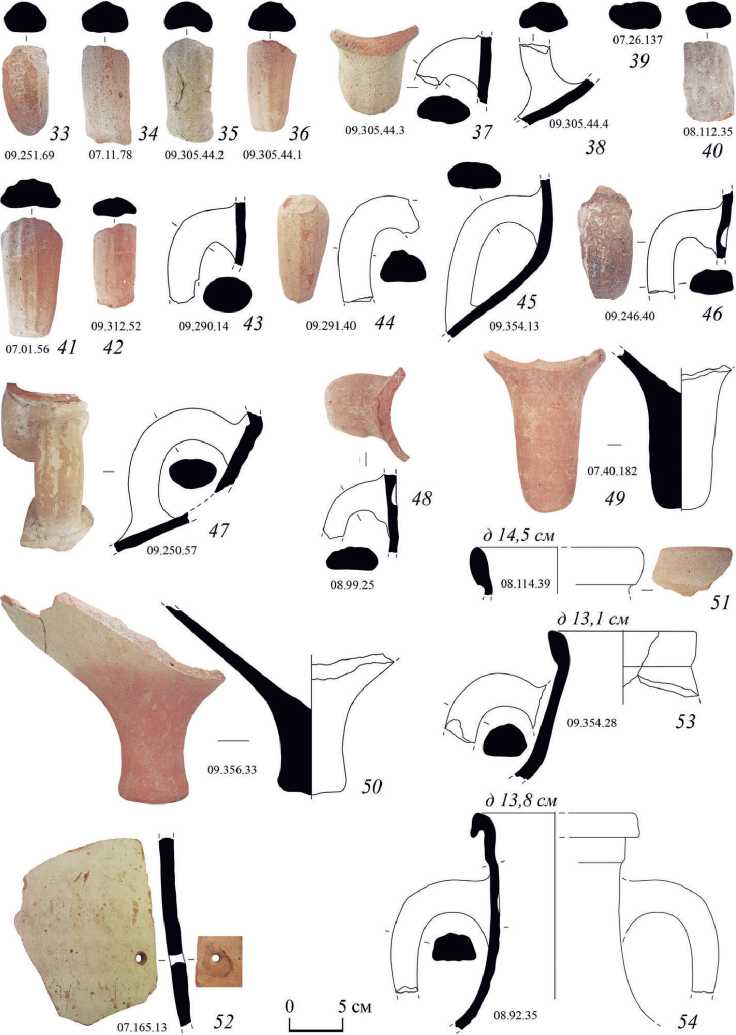
Рис. 3. Африканские амфоры из г. Боспора: продукция мастерских неопределенных центров обнаружены обломки двух амфор, африканское происхождение которых предположительно (рис. 3: 53, 54).
Фрагменты вытянутых венчиков амфор с клювовидным верхним краем из глиняного теста красного (2.5YR 5/6) (рис. 2: 24 ), двухцветного красного (2.5YR 5/6) и светлого красновато-коричневого (5YR 6/4) (рис. 2: 25 ), красновато-коричневого (5YR 5/4) с темной красновато-серой (5YR 4/2) сердцевиной (рис. 2: 26 ), могут принадлежать типу Keay 62Q (Albenga 11-12) (рис. 2: 24–2 6; табл. 1: 4, 9 ). Такие амфоры достаточно разнородны и сформованы из нескольких групп глиняного теста (Ibid.). Предположительно они производились в северной части современного Туниса в последней трети V – первой половине VI вв. ( Bonifay , 2004. P. 137. Fig. 74; Bonifay et al. , 2011. P. 244; Capelli et al. , 2016. P. 290).
Другим вариантам амфор Keay 62 VI в. могут принадлежать также два фрагмента клювовидных венчиков (рис. 2: 27, 28 ; табл. 1: 4, 10 ) ( Bonifay , 2004. P. 137, 140. Fig. 74). Они изготовлены из красновато-коричневого (5YR 5/4) глиняного теста (рис. 2: 27 ), а также красного (2.5YR 5/6) у внутренней и красновато-желтого (5YR 6/6) у внешней поверхности (рис. 2: 28 ).
Фрагмент амфоры с подтреугольным клювовидным венчиком (рис. 2: 29 ; табл. 1: 3 ) отличается от продукции мастерских Сиди Захруни более песчанистым красным (2.5YR 5/6) с коричневой сердцевиной (7.5YR 5/4) тестом. Размеры венчика миниатюрнее, чем у широко распространенных в западном Средиземноморье в течение первых двух третей V в. амфор Keay 35В (Ibid. P. 134–135. Fig. 72).
Обломки амфор из глиняного теста красного (2.5YR 5/6) (рис. 2: 30, 31 ; 3: 51 ) и красновато-коричневого (5YR 5/4) с коричневатой (7.5YR 5/3, 5YR 4/3) прослойкой (рис. 3: 32 ), вероятно, принадлежат разным типам амфор (табл. 1: 4, 6 ). Два фрагмента, возможно, относятся к амфорам Keay 3 “similis” конца IV – первой половины V вв. (рис. 2: 31, 32 ) (Ibid. P. 129. Fig. 70: 2 ).
Все найденные в боспорских комплексах фрагменты амфор с сохранившимися прилепами ручек к стенкам принадлежат второй типологической линии африканских амфор с креплением ручек к горлу (рис. 3: 37, 38, 43–48 ) (Ibid. P. 89. Fig. 46: 2 ). Выявлено также восемь ручек неопределенных амфор (рис. 3: 33–36, 39–42 ).
Точно установить типологическую принадлежность двух фрагментов доньев амфор с красным (2.5YR 5/6) черепком затруднительно (рис. 3: 49, 50 ; табл. 1: 4, 17 ). Они могут принадлежать различным вариантам амфор spatheion (Ibid. Fig. 67–69) или типа Keay 25 (Ibid. Fig. 64; 65).
На обломке стенки амфоры из красного (2.5YR 5/6) глиняного теста с красновато-коричневой (5YR 5/4) прослойкой у поверхности сохранилось просверленное отверстие диаметром около 1,0 см (рис. 3: 52 ; табл. 1: 5 ). Такие отверстия (1–2 см диаметром) встречаются в нижней трети тулова некоторых африканских амфор и указывают на один из способов вскрытия этих контейнеров (Ibid. P. 467–468. Fig. 264: A ).
Предположительно к африканскому производству могут относиться находки фрагментов еще двух амфор: с глиняным тестом желтовато-красным (5YR 5/6) (рис. 3: 54 ; табл. 1: 12 ) и желтовато-красным (5YR 5/6) со светлой желтовато-коричневой (10YR 6/4) сердцевиной (рис. 3: 53 ; табл. 1: 15 ).
Содержимое, хронология, распространение
Во время раскопок в Босфорском переулке г. Керчи было обнаружено немногим более 1 тыс. фрагментов африканских амфор, в том числе 58 профильных частей и 1 фрагмент стенки с отверстием от 54 сосудов, что составляет около 1 % всех найденных амфор (рис. 1–3; табл. 1). Среди них 5 фрагментов от 2 сосудов определены предположительно (рис. 3: 53, 54 ). Хотя объем продукции в африканских контейнерах обычно в несколько раз больше типичного для восточносредиземноморских и понтийских амфор (Ibid. P. 446), ее доля в причерноморской торговле, очевидно, остается крайне незначительной.
В африканских амфорах перевозились различные товары: оливковое масло, вино, рыбные и некоторые другие продукты ( Bonifay , 2004. Tab. IV; Woodworth et al. , 2015. P. 42; Bonifay , 2016. Fig. 124; Bonifay , 2021. Fig. 1). На внутренней поверхности найденных в боспорских комплексах сосудов визуально не было обнаружено следов смоления. Наличие таких следов длительное время считалось признаком транспортировки вина или рыбной продукции, но не оливкового масла ( Bonifay , 2018. P. 331; 2021. P. 281). Однако в настоящее время это можно считать скорее вопросом сохранности такого покрытия. Известны примеры смоления у амфор с оливковым и, возможно, касторовым маслом ( Pecci et al. , 2010. P. 618, 619. Tab. 2; Bonifay , 2018. P. 331–332; Garnier, Pecci , 2021. P. 114). Скорее всего, внутренняя поверхность всех амфор покрывалась смолой хвойных (обычно сосновых) растений с целью гидроизоляции ( Garnier, Pecci , 2021. P. 114). В то же время хорошая визуальная сохранность такого покрытия по-прежнему может являться признаком содержимого отличного от оливкового масла, так как смола имела свойство растворяться с внутренней поверхности амфор под воздействием масла, в том числе в анаэробных контекстах ( Bonifay , 2018. P. 332; 2021. P. 288).
Предположительно оливковое масло доставлялось в амфорах Keay 8B (рис. 1: 1–12 ), а также, возможно, Keay 40/41 (рис. 2: 22, 23 ) и Keay 62Q/Albenga 11/12 (?) (рис. 2: 24–26 ); о содержимом других типов амфор, найденных в боспор-ских комплексах, пока нет достаточных данных ( Bonifay , 2021. P. 290. Fig. 1). Товары перевозившиеся в амфорах Keay 55A и Keay 57B не определены, возможно, это были вино или рыбная продукция, по крайней мере можно говорить, что сосуды Keay 55 не содержали оливкового масла (Ibid. P. 291. Fig. 1: 44–46 ). Результаты анализов и косвенные данные о продуктах в некоторых других типах амфор, например, spatheion 1, довольно противоречивы ( Bonifay , 2004. P. 473. Tab. IV; 2016. Fig. 124; Pecci et al. , 2010. P. 618. Tab. 2). Такие амфоры могли иметь взаимозаменяемое содержимое и являться многоцелевыми контейнерами, стандартизация которых упростила загрузку в трюмы кораблей ( Woodworth et al. , 2015. P. 54; Bonifay , 2021. Fig. 1: 33 ), или даже быть изначально изготовленными как инструмент оптимизации, для заполнения пространства в грузах с крупными цилиндрическими амфорами ( Bonifay , 2021. P. 92).
Анализ находок из боспорских комплексов позволяет говорить о поступлении африканских амфор в Пантикапей на протяжении приблизительно полутора столетий: с первой половины V до первой половины VI вв. При этом для профильных фрагментов от 19 амфор удалось точно установить типологическую принадлежность, а еще 8 фрагментов определены предположительно (табл. 1). В первой половине – середине V в. на Боспор, вероятно, поступали следующие типы амфор: spatheion 1 (рис. 2: 13), Keay 3 “similis” (?) (рис. 2: 31, 32), ранний вариант Keay 8B (рис. 1: 1–3). Период второй половины V в. представлен обломками сосудов Keay 57B (рис. 2: 16, 17) и Keay 40/41 (рис. 2: 22, 23). При этом наиболее многочисленными в боспорских комплексах являются находки более позднего варианта амфор Keay 8B, датирующиеся в рамках второй половины V – первой половины или первой трети VI вв. (рис. 1: 5–7, 9–11). К ним же, скорее всего, относятся и фрагменты неопределенного варианта этого типа (рис. 1: 8, 12). В третьей четверти / конце V – первой половине VI вв. в г. Боспор также поступали некоторые другие типы амфор: Keay 55A (рис. 2: 14, 15), предположительно варианты Keay 62 (рис. 2: 24–28).
Ранее исследователями уже отмечался определенный количественный и хронологический дисбаланс между поставками амфор и краснолаковой керамики из Африки в Восточное Средиземноморье ( Sodini , 2000. P. 191; Bonifay , 2004. P. 463, 480–481; Reynolds , 2021. P. 342). Незначительное число находок (менее 1 % в обоих случаях) не позволяет судить о количественных диспропорциях поступления этих двух групп в г. Боспор. Абсолютное большинство краснолаковой керамики ARS из раскопок в Босфорском переулке принадлежит производству конца IV – первой половины V вв., при этом были найдены также два фрагмента сосудов VI в. (формы ARS 99B/C и 104A) ( Смокотина , 2011. С. 349. Табл. 1). Краснолаковая посуда сама являлась товаром и распространялась на восток, вероятно, в качестве дополнительного продукта вместе с зерном, что объясняет почти полное отсутствие ее поставок после вандальского завоевания Северной Африки со второй четверти и особенно во второй половине V в. ( Bonifay , 2005. P. 576–577; Смокотина , 2011. С. 350; Bonifay , 2018. P. 335–338). В отличие от краснолаковой керамики поступление на Боспор товаров в африканских амфорах со второй половины V в. только увеличивается. В целом преобладает импорт из двух основных центров, в сумме почти 40 % всех африканских амфор: в первую очередь из мастерских на юге провинции Бизацена (Маджура, Унка и, вероятно, некоторых других, всего около 22 %) (рис. 1: 1–12 ), а также из мастерской Сиди Захруни в районе города Набуля в провинции Зевгитана (рис. 2: 13–21 ).
Африканские амфоры и краснолаковая керамика второй половины / конца VI – VII вв. не были обнаружены при раскопках в Босфорском переулке г. Керчи. Вероятно, это объясняется в первую очередь стратиграфической ситуацией на участке исследований, прекращением жизнедеятельности и началом использования этой территории для захоронений уже в начале VII в. ( Айбабин, Хай-рединова , 2018. С. 34). В то же время редкие находки краснолаковой керамики ARS, известные в других районах города ( Смокотина , 2015. С. 321), свидетельствуют о том, что доставка отдельных африканских товаров в г. Боспор продолжалась вплоть до первой половины VII в.
Список литературы Африканские амфоры в г. Боспоре (Керчи)
- Айбабин А. И., 2019. Усадьба рыбака в ранневизантийском Боспоре // Проблемы истории и археологии средневекового Крыма: материалы Междунар. науч. конф., посвящ. 70-летию А. И. Айбабина / Ред.-сост. Э. А. Хайрединова. Симферополь: Антиква. С. 7–16.
- Айбабин А. И., Хайрединова Э. А., 2018. Ранневизантийский некрополь Боспора // Античная древность и средние века. Вып. 46. Екатеринбург: Уральский ун-т. С. 33–53.
- Домжальский К., Смокотина А. В., 2020. Позднеримская и ранневизантийская краснолаковая керамика Тиритаки // МАИЭТ. Вып. 25. Симферополь. С. 188–223.
- Смокотина А. В., 2011. Керамика группы «африканская краснолаковая» из раскопок в Керчи // МАИЭТ. Вып. 17. Симферополь. С. 328–362.
- Смокотина А. В., 2015. Импорт краснолаковой керамики в г. Боспор в конце IV – первой половине VII вв. // ДБ. Т. 19. М.: ИА РАН. С. 312–339.
- Смокотина А. В., 2018. Импорт товаров в амфорах и краснолаковой керамики на Боспор в конце IV – первой половине VII вв. // SP. № 4. С. 263–279.
- Смокотина А. В., 2022. Керамика ранневизантийского времени из боспорского рыбозасолочного комплекса: предварительный анализ // Византийский «круг земель». Orbis terrarum
- Byzantinus…: тез. докл. XXIII Всерос. науч. сессии византинистов РФ / Отв. ред. С. П. Карпов. Симферополь: Ариал. С. 163–164.
- Bonifay M., 2004. Études sur la céramique romaine tardive d’Afrique. Oxford: Archaeopress. 525 p. (British Archaeological Reports. International series; 1301.)
- Bonifay M., 2005. Observations sur la diffusion des céramiques africaines en Méditerranée orientale durant l’antiquité tardive // Mélanges Jean Pierre Sodini / Eds.: F. Baratte, V. Déroche, C. Jolivet-Lévy, B. Pitarakis. Paris: Association des Amis du Centre d’Histoire et Civilisation de Byzance. P. 565–581. (Travaux et mémoires; 15.)
- Bonifay M., 2016. Éléments de typologie des céramiqoues de l’Afrique Romaine // La ceramica Africana nella Sicilia romana / Eds.: D. Malfitana, M. Bonifay. Catania: Istituto per i beni archeologici e monumentali. P. 507–573.
- Bonifay M., 2018. The distribution of African pottery under the Roman Empire: evidence versus interpretation // Trade, Commerce, and the State in the Roman World / Eds.: A. Wilson, A. Bowman. Oxford: University Press. P. 327–352.
- Bonifay M., 2021. African amphora contents: an update // Roman Amphora Contents: Reflecting on the Maritime Trade of Foodstuffs in Antiquity (In honour of Miguel Beltrán Lloris) / Ed. D. Bernal-Casasola et al. Oxford: Archaeopress. P. 281–297.
- Bonifay M., Capelli C., Moliner M., 2011. Amphores Africaines de la Basilique de la Rue Malaval à Marseille (Ve siècle) // Actes du Congrès d’Arles. Marseille: Société Française d’Étude de la Céramique Antique en Gaule. P. 235–254.
- Capelli C., Bonifay M., Franco C., Huguet C., Leitch V., Mukai T., 2016. Etude archéologique et archéométrique intégrée // La ceramica africana nella Sicilia romana / Eds.: D. Malfitana, M. Bonifay. Catania: Istituto per i beni archeologici e monumentali. P. 273–351, 651–736.
- Garnier N., Pecci A., 2021. Amphorae and residue analysis: content of amphorae and organic coatings // Roman Amphora Contents: Reflecting on the Maritime Trade of Foodstuffs in Antiquity (In honour of Miguel Beltrán Lloris) / Ed.: D. Bernal-Casasola et al. Oxford: Archaeopress. P. 113–125.
- Hayes J. W., 1972. Late Roman Pottery. London: The British School at Rome. 477 p.
- Keay S. J., 1984. Late roman amphorae in the Western Mediterranean. A typology and economic study: the Catalan evidence. Oxford: British Archaeological Reports. 398 p. (British Archaeological Reports. International series; 196.)
- Long L., Volpe G., 1998. Le chargement de l’épave 1 de la Palud (VIe s.) à Port-Cros (Var). Note préliminaire // Fouilles à Marseille: les mobiliers (Ier–VIIe siècles ap. J.-C.) / Eds.: M. Bonifay, M.-B. Carre, Y. Rigoir. Paris: Errance. P. 317–342.
- Pecci A., Salvini L., Cirelli E., Augenti A., 2010. Castor oil at Classe (Ravenna – Italy): residue analysis of some Late Roman amphorae coming from the port // LRCW 3. Late Roman coarse wares, cooking wares and amphorae in the Mediterranean: archaeology and archaeometry. Comparison between western and eastern Mediterranean. Vol. II / Eds.: S. Menchelli, S. Santoro. Oxford: Archaeopress. P. 617–622.
- Remolà Vallverdù J. A., 2000. Las Anforas tardo-antiguas en Tarraco (Hispania tarraconensis). Barcelona: Universitat de Barcelona. 353 p.
- Reynolds P., 2021. The oil supply in the Roman East: identifying modes of production, containers and contents in the eastern Empire // Roman Amphora Contents: Reflecting on the Maritime Trade of Foodstuffs in Antiquity (In honour of Miguel Beltrán Lloris) / Ed. D. Bernal-Casasola et al. Oxford: Archaeopress. P. 307–354.
- Smokotina A. V., 2014. The North African red slip ware and amphorae imported into Early Byzantine Bosporus // The North African red slip ware and amphorae imported into Early Byzantine Bosporus. Bonn. P. 71–80. (Rei Cretariae Romanae Fautorum Acta; 43.)
- Sodini J.-P., 2000. Productions et échanges dans le monde protobyzantin (IVe–VIIe s.): le cas de la céramique // Byzanz als Raum: zu Methoden und Inhalten der historischen Geographie des östlichen Mittelmeerraumes. Wien: Österreichische Akademie der Wissenschaften. P. 181–208.
- Woodworth M., Bernal D., Bonifay M., De Vos D., Garnier N., Keay S., Pecci A., Poblom J., Pollard M., Richez F., Wilson A., 2015. The content of African Keay 25 / Africana 3 amphorae: initial results of the CORONAM project // ArchaeoAnalytics: chromatography and DNA analysis in archaeology / Eds.: C. Oliveira, R. Morais, Á. M. Cerdán. Esposende: Município de Esposende. P. 41–57.


