Analysis of legal disputes arising out of advertising law violations
Автор: Kostoreva A.
Журнал: Международный журнал гуманитарных и естественных наук @intjournal
Рубрика: Юридические науки
Статья в выпуске: 9-2 (96), 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article analyzes legal disputes in advertising law violations, with a focus on significant cases in California. It examines the enforcement of consumer protection laws such as the Unfair Competition Law of California, and the so-called False Advertising Law, incorporated in the California Code Business and Professions Code («UCL» and «FAL»). The study explores notable cases, including those against Johnson & Johnson, General Motors, Juul Labs, and Bright Data. It evaluates the impact of these cases on advertising practices and regulatory compliance. The article highlights lessons for advertisers to ensure legal adherence. It discusses the role of regulatory bodies in maintaining market integrity. The findings emphasize the importance of transparency and honesty in advertising.
Advertising law, legal disputes, consumer protection, unfair competition law, false advertising law, california code business and professions code, regulatory compliance, deceptive advertising, market integrity
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170207520
IDR: 170207520 | DOI: 10.24412/2500-1000-2024-9-2-218-224
Текст научной статьи Analysis of legal disputes arising out of advertising law violations
The enforcement of advertising laws plays an important role in ensuring fair business practices and safeguarding consumer rights. California, recognized for its rigorous consumer protection regulations, has been the venue for numerous high-profile legal disputes in the realm of advertising law. The state's unique legal landscape is characterized by robust consumer rights protection and active regulatory agencies.
California's advertising laws are designed to prevent deceptive practices that can mislead consumers, ensuring transparency and honesty in commercial communications. These regulations encompass a wide range of issues, including false advertising, misleading claims, and the promotion of products in a manner that may be deemed unfair or decep- tive. The importance of these laws cannot be overstated, as they maintain market integrity and protect the public from fraudulent and harmful business practices.
This article aims to analyze the notable legal disputes in California related to advertising law infringements. This will contribute to a deeper understanding of the complexities involved in enforcing advertising laws and offer practical lessons for advertisers to ensure compliance with legal standards.
Main part
The USA advertising market is undergoing continuous development, fueled by substantial advancements in digital technologies and evolving consumer behaviors. It is projected to reach $422.3 billion in 2024 (fig. 1).
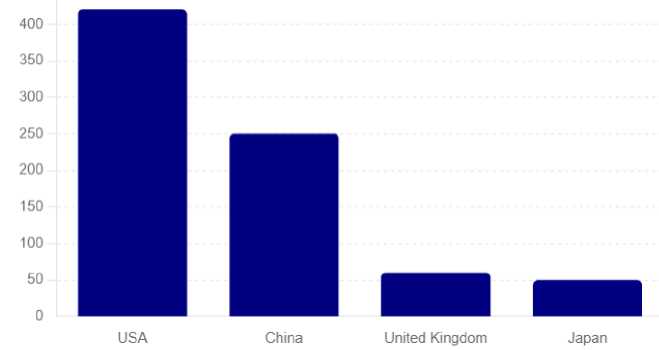
Fig. 1. Advertising spending in selected markets worldwide in 2024, billion dollars [1]
The advertising market in California constitutes a substantial portion of the overall USA advertising landscape, characterized by its unique regulatory environment and diverse consumer base. California's market is distinguished by stringent advertising regulations, which aim to protect consumers and ensure fair business practices.
Overview of advertising legislation
The legal framework governing advertising in California has significantly evolved over the past century, reflecting societal changes and advancements in media and technology [2]. The California Code Business and Professions Code serves as an important legislative framework underpinning advertising law in California. Sections 17200 and 17500 play pivotal roles in regulating commercial practices and advertising. Section 17200, known as the Unfair Competition Law of California ( UCL ), prohibits any unlawful, unfair, or fraudulent business act or practice, thereby safeguarding consumers and ensuring fair competition [3]. The UCL is comprehensive in scope, addressing not only traditional business practices but also newer, technologically driven commercial activities, thus adapting to the evolving marketplace. This section's broad definitions of «unlawful», «un-fair» and «fraudulent» conduct enable it to cover a wide range of deceptive business behaviors, offering robust consumer protection.
Section 17500, often referred to as the False Advertising Law (FAL), explicitly tar- gets false advertising, prohibiting any advertisements that are misleading or untruthful. The FAL is critical in maintaining advertising integrity, ensuring that consumers receive accurate information about products and services. This section mandates that all advertising must be based on truthful and substantiated claims, thereby preventing businesses from gaining unfair advantages through deceitful marketing practices. Together, these sections form a robust legal foundation designed to protect consumers from deceptive practices and maintain integrity in the marketplace, thus promoting trust and fair competition in the business environment.
The enforcement of these laws is overseen by key regulatory bodies, including the California Department of Consumer Affairs (DCA) and the Office of the Attorney General. The DCA protects consumers by overseeing various licensing boards and ensuring adherence to advertising standards [4]. The Attorney General’s Consumer Law Section actively pursues cases of false advertising and unfair practices, leveraging the California Code Business and Professions Code to protect the public and maintain market integrity. Local district attorneys and city attorneys, particularly in larger municipalities like Los Angeles and San Francisco, also participate in enforcing these laws. California’s advertising regulations encompass a wide range of issues, reflecting the diverse and dynamic nature of the state’s market (table 1).
Table 1. Key aspects of advertising regulation in California [5, 6]
|
Aspect of regulation |
Description |
|
False advertising |
Prohibits the dissemination of false or misleading statements about products or services. |
|
Unfair competition |
Encompasses acts of fraud, deceit, and unfair business practices, aiming to protect both consumers and competitors. |
|
Health claims |
Strict guidelines on health-related claims, requiring substantial scientific evidence to support such assertions. |
|
Environmental claims |
Regulates the use of terms like «green» or «eco-friendly», requiring proof of environmental benefits to avoid misleading consumers. |
|
Alcoholic beverage advertising |
Controls advertising practices related to alcoholic beverages, including restrictions on targeting minors and false claims about the effects of consumption. |
|
Digital and social media advertising |
Mandates clear disclosure of paid endorsements and sponsored content to ensure transparency and prevent deception. |
|
Price advertising |
Requires advertised prices to be accurate and truthful, and any limitations or conditions must be clearly disclosed. |
|
Privacy and data protection |
Protects consumers' personal information collected through advertising, enforcing strict data privacy regulations. |
|
Sweepstakes and contests |
Sets rules for advertising sweepstakes and contests to prevent fraud and ensure fair play. |
|
Food and beverage marketing to children |
Restricts the advertising of unhealthy food and beverages to children to combat childhood obesity and promote healthier choices. |
|
Telemarketing regulations |
Limits the use of telemarketing practices, requiring clear identification and adherence to the «Do not call registry». |
By implementing a detailed and flexible legal framework, California addresses the complexities of modern advertising practices, ensuring business operations comply with transparency and ethical standards. The efforts of regulatory bodies in enforcing laws are essential in protecting consumer interests and maintaining the advertising industry's integrity within the state.
Legal disputes analysis
Examining legal disputes offers valuable insights into the enforcement and interpretation of advertising laws. Through rigorous examination of various cases, discernible patterns and trends in judicial decisions emerge, elucidating the practical application of specific legal provisions and assessing the efficacy of existing regulatory frameworks.
People v. General Motors LLC
General Motors (GM), a leading automotive manufacturer, faced legal action from the California Attorney General over its advertising practices related to diesel vehicles. The lawsuit alleged that GM falsely marketed its diesel engines as «clean» and environmentally friendly, despite evidence showing that these vehicles emitted higher levels of pollutants than permitted by state regulations.
The core legal issues in this case pertained to false advertising and environmental protection. The state contended that GM's marketing claims about the environmental benefits of its diesel engines were misleading and violated California's FAL and UCL. The case required the court to evaluate the accuracy of GM's advertising claims and their compliance with environmental standards.
In March 2020, GM settled the case with the California Attorney General's office, agreeing to pay $1.5 million and to cease the deceptive advertising practices. The settlement acknowledged that GM's advertisements had misled consumers regarding the environmental impact of its diesel vehicles [9]. This case underscored California's commitment to enforcing environmental claims in advertising and holding companies accountable for misleading statements about product sustainability.
Federal Trade Commission (FTC) v. Juul Labs
In 2022, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) initiated legal action against several influencers and advertisers in California for deceptive advertising practices involving Juul Labs' e-cigarettes. Juul was accused of targeting youth through misleading advertisements and failing to disclose the risks associated with their products. This legal battle highlighted the increasing regulatory scrutiny over social media endorsements, as part of a broader crackdown by the FTC and state attorneys general on misleading advertising practices, especially involving social media influencers [10].
The primary legal issues were false advertising and the failure to disclose material connections between influencers and the advertiser. The FTC's Endorsement Guides require clear disclosure of such relationships, which Juul allegedly failed to do, misleading consumers about product safety. Most lawsuits were consolidated into multi-district litigation in the Northern District of California [11]. Juul Labs agreed to a settlement of $1.2 billion to $1.7 billion with 10,000 plaintiffs in 5.000 cases, also requiring adherence to strict marketing guidelines. The court found Juul's marketing practices deceptive and harmful to minors, violating California's FAL and FTC guidelines, emphasizing the need for transparency in advertising, particularly for products with health risks.
Meta Platforms, Inc. v. Bright Data Ltd.
Meta Platforms, Inc., the parent company of Facebook and Instagram, initiated a lawsuit against Bright Data Ltd., accusing it of unauthorized data scraping activities. Bright Data, specializing in data collection and web scraping services, allegedly collected publicly available data from Facebook and Instagram and sold it as part of its data products to third parties [12]. The case, which attracted significant attention due to its implications for data privacy and legal boundaries in the digital age, revolved around whether Bright Data's actions violated California law. Meta argued that Bright Data’s actions infringed upon its terms of service and potentially violated data protection and privacy regulations.
The case was heard in the USA District Court for the Northern District of California, presided over by Judge Edward Chen. The court's evaluation focused on whether accessing and using publicly available information without authorization constituted illegal activity under California law. On January 23, 2024, the court granted summary judgment in favor of Bright Data, ruling that since the data was publicly accessible, Bright Data's activities did not constitute an illegal act under state law [13]. This decision highlighted the need for clearer regulatory guidelines on data scraping and the distinction between publicly available and private data.
Implications for advertisers
The notable legal disputes in California's advertising law landscape provide critical lessons for advertisers, underscoring the necessity of adhering to stringent regulatory standards to avoid significant legal repercussions. Advertisers must prioritize transparency and honesty in their marketing campaigns. The cases of Johnson & Johnson and General Motors illustrate the severe consequences of misleading consumers about product safety and environmental benefits. Advertisers should ensure that all claims made in their advertisements are substantiated by reliable evidence and do not exaggerate the benefits or downplay the risks associated with their products. This practice not only helps in maintaining legal compliance but also builds consumer trust and brand integrity.
To effectively comply with advertising laws, advertisers should develop and implement robust internal review processes . These processes should include thorough factchecking and legal review of all marketing materials before they are disseminated to the public. Establishing a cross-functional team involving marketing professionals, product experts, and legal advisors can help identify potential issues early and ensure that all advertising content meets regulatory standards [14]. This proactive approach can prevent costly legal disputes and protect the brand's reputation.
Legal advisors provide critical guidance on the interpretation and application of advertising laws, helping advertisers navigate complex regulatory environments. They can assist in drafting clear and compliant advertising copy, reviewing promotional materials, and advising on risk mitigation strategies.
Advertisers should stay informed about the latest regulatory changes and legal precedents in advertising law. Continuous educa- tion and awareness can help advertisers anticipate potential legal challenges and adapt their strategies accordingly [15]. Engaging in industry forums, subscribing to legal updates, and participating in professional networks are effective ways to keep abreast of evolving legal standards and enforcement trends. By integrating these lessons and strategies, advertisers can significantly reduce the risk of legal disputes and enhance their compliance with advertising regulations.
Conclusions
The analysis of legal disputes in advertising law violations reveals a multifaceted and dynamic legal landscape, particularly exemplified by the stringent regulatory environment of California. The state’s robust consumer protection laws, such as the Unfair Competition Law of California, and the so-called False Advertising Law, incorporated in the California Code Business and Professions Code, serve as pivotal frameworks for ensuring honesty and transparency in advertising. Notable cases underscore the severe consequences of deceptive advertising practices, emphasizing the importance of truthful marketing to safeguard consumer rights and maintain market integrity. These disputes highlight critical lessons for advertisers, including the necessity of substantiating all claims with reliable evidence and the implementation of comprehensive internal review processes to preemptively address potential legal issues. The continuous evolution of advertising mediums, particularly with the rise of digital and social media platforms, further complicates the regulatory landscape, necessitating ongoing vigilance and adaptation by advertisers to ensure compliance and protect their brand reputation. These legal disputes underscore the crucial role of regulatory bodies in enforcing advertising laws and the need for advertisers to prioritize ethical practices in their marketing strategies.
Список литературы Analysis of legal disputes arising out of advertising law violations
- Advertising spending in selected markets worldwide in 2024 / Statista. - URL: https://www.statista.com/forecasts/1380173/ad-spending-markets-worldwide (date of application: 01.06.2024).
- Tomas W.R., Diamantis M.E. A Marketing pitch for corporate criminal law // Stetson bus. L. Rev. - 2023. - T. 2. - C. 1.
- Widijowati D., Denysenko S. Securing consumer rights: Eehical and legal measures against advertisements that violate advertising procedures // Lex Publica. - 2023. - T. 10. - № 1. -C. 28-42.
- Odunaiya O.G., Nwankwo E.E., Okoye C.C., Scholastica U.C. Behavioral economics and consumer protection in the US: A review: Understanding how psychological factors shape consumer policies and regulations // International Journal of Science and Research Archive. - 2024. - T. 11. - № 1. - C. 2048-2062.
- Ko Y. Unfair Competition: Big Data and the Fight Over Data Privacy // Georgia Journal of International and Comparative Law. - 2024. - T. 52. - № 1. - C. 223-238.
- Goldenfein J., McGuigan L. Managed sovereigns: How inconsistent accounts of the human rationalize platform advertising // Journal of Law and Political Economy. - 2023. - T. 3. - № 3.
- Attorney General Becerra Secures nearly $344 Million Judgment Against Johnson & Johnson for Endangering Patients through Deceptive Marketing of Pelvic Mesh Products / State of California department of justice office of the attorney general. - URL: https://oag.ca.gov/news/press-releases/attorney-general-becerra-secures-nearly-344-million-judgment-against-johnson (date of application: 07.06.2024).
- The people of the state of California v. Johnson & Johnson / Superior Court of the State of California. - URL: https://oag.ca.gov/system/files/attachments/press-docs/Statement%20of%20Decision.pdf (date of application: 10.06.2024).
- Peeples v. General Motors, LLC / Justia Legal Resources. - URL: https://www.courthousenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/meta-platforms-v-bright-data-ruling-motion-for-summary-judgment.pdf (date of application: 13.06.2024).
- Juul Labs, Inc., Marketing, Sales Practices, and Products Liability Litigation (3:19-md-02913) / District Court, N.D. California. - URL: https://www.courtlistener.com/docket/16284915/in-re-juul-labs-inc-marketing-sales-practices-and-products-liability/?page=18 (date of application: 14.06.2024).
- Attorney General James Secures $462 Million from JUUL for Its Role in the Youth Vaping Epidemic /Office of the New York State Attorney General. - URL: https://ag.ny.gov/press-release/2023/attorney-general-james-secures-462-million-juul-its-role-youth-vaping-epidemic (date of application: 15.06.2024).
- Meta Platforms, Inc. v. Bright Data Ltd. / United States district court northern district of California. - URL: https://www.courthousenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/meta-platforms-v-bright-data-ruling-motion-for-summary-judgment.pdf (date of application: 20.06.2024).
- Court rules in favor of Bright Data in Meta v. Bright Data case reaffirming the right to collect public web data / Bright Data. - URL: https://brightdata.com/blog/web-data/court-rules-in-favor-of-bright-data-in-meta-v-bright-data-case (date of application: 05.07.2024).
- Bukhtueva I. Machine learning applications in marketing: enhancing customer segmentation and targeting // Proceedings of the XLI International Multidisciplinary Conference «Prospects and Key Tendencies of Science in Contemporary World». Bubok Publishing S.L., Madrid, Spain. 2024.
- Kendjaev A. Features of establishing foreign economic activities when entering the American market: practical steps and legal nuances // Sciences of Europe. - 2024. - № 144. - P. 8-11.


