Analysis on the agent-based Bertrand duopoly game model
Автор: Huang Xian , Hong Jia
Рубрика: Экономическая теория и мировая экономика
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.12, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The duopoly market research has a long history. Due to such reasons as material supply, product patent right and concession of the government, development of many economic industries is similar to the process of duopoly. In game theory, the Bertrand model which considers price to be a strategic variable is closer to reality and provides the market with more references, especially for retail market and electricity market, as the competitive world develops. Firstly, we analyze the classical Bertrand model and the Nash equilibrium in the model. Secondly, multi-agent technology is applied and the Bertrand duopoly game bidding process is conducted; meanwhile, in order to help agents find the optimal solutions, genetic algorithm based on multi-agent Bertrand model is chosen as the main algorithm for the research; and we finish with software implementation of the algorithm and with example analysis. In the end, oligopoly market bidding is also modelled in MATLAB simulation, which provides us with more accuracies and flexibilities. It is evidently shown in the model that when none of the two companies are able to meet all the demands in the market, the bigger the price gap, the more oscillated it is in the process; thus, the pure strategic Nash equilibrium doesn’t exist. However, when one of the two can offer the demands independently, Nash equilibrium appears and is shown as the calculated results in Bertrand-Edgeworth model where the equilibrium reaches the cost price. Further, the reason for no pure strategic Nash Equilibrium is also discussed.
Bertrand model, multi-agent, genetic algorithm, nash equilibrium
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147232343
IDR: 147232343 | УДК: 336 | DOI: 10.14529/em180201
Текст научной статьи Analysis on the agent-based Bertrand duopoly game model
The comparison between price and quantity competition has been extensively discussed in the literature. In oligopolies, it is well known that price competition is tougher, resulting in a lower level of profits between private firms, compared with quantity competition [1–4]. Bertrand competition is one of the most important models in oligopoly field, which has been intensively studied in various contexts.
Nash Equilibrium is the optimal state where each player maximizes his profit, considering other players’ strategies. Meanwhile, there are still some studies on the Nash Equilibrium under different conditions in Bertrand duopoly game [5–8]. Plenty of cases have been checked and simulated on searching the equilibrium.
However, we can deduce the equilibrium of the Bertrand model based on the game theory, but to find it that for companies whose production costs are identical, Bertrand competition leads to zero profit, with the prices set equal to the marginal cost at the equilibrium [9, 10]. Comparing with real market, no companies would do it without profits.
Meta-heuristic algorithms and especially evolutionary algorithms are used to find the equilibrium of electricity markets [9]. Numerous methods have been proposed to analyze Bertrand model, many experts study related problems via Markov Method mathematically [11, 12], moreover, quite a few people start re- searches by agent, which provide us with some enlightening approaches [13]. Simulations on the strategic interactions between market agents by applying a mean of a co-evolutionary algorithm are established [14–17]. Furthermore, agent-based modelling, market participants are modelled to maximize their profits autonomously by learning from the interactions in the markets.
It is known to us that some very fierce competitive fields, as in China, the retail markets, finance payment and the electricity market etc. are or are becoming the duopoly. It is of great use to analyze this kind of market by using agent-based model and do some market simulations, which will provide more accurate and beneficial guidance on the market strategies. In this way, the players can make out better and appropriate solutions when the similar circumstances happen.
We proposed some related analysis on how Bertrand model display itself in duopoly game [18–20], using Genetic Algorithm (GA), with the help of Matlab. Then comparisons and analysis on different cases of quantities and prices are also discussed.
Therefore, based on classic Bertrand model, different market models are established. Further, the simulations for these models
Classic Bertrand Model
French economist Joseph Bertrand proposed the Bertrand model in 1883 [16]. Unlike the Cournot model and Stackelberg model where the first two models are based on the production as the decision variables in the competitions, which is, however, Bertrand model is based where the price functions as the decision variable, which belongs to the price competition model.
As the classical Bertrand model depicts, we have, Bertrand model hypothesis:
-
(1) the oligarchs are competing with the price.
-
(2) the products produced by the oligarchs are of equal quality and can be replaced completely.
-
(3) there is no formal or informal collusion between the oligarchs.
-
(4) the total market demand is constant, which is a rigid demand.
-
(5) the company with a lower price is first to obtain the market share, while the same competitive price share the common market.
In building the model, we can also find that when the other assumptions of the model are the same, the products will be changed as the products produced by the oligarch enterprises can be replaced. The price of the commodity will limit the sales, which can be obtained:
qi
if ( P i < P m )
q i = <
( 1
Q - E q j
( j = 1
qi
m
E qk k=1+1
if ( P 1 + 1 = ••• = P m - 1 = P m )
If ( P i > P m )
-
(2) the correlation coefficient of the market demand function for the product, the cost of the company i and the demand for the market Qmax .
-
(3) in the game market, the price and output of other companies are also important factors. Thus, each of the companies' profits in the market will be affected by more than three factors. It is clear that the production and price of its own are the decision variables of the company itself. The maximum profit is achieved by changing its own production and price. Moreover, when the market is determined, the correlation coefficient in the demand function becomes a fixed value. The impacts that each company imposed on the profit function makes each of them correlate, influence, and change.
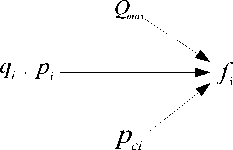
According to the multi-agent simulation technology, the associated profits of Bertrand model was shown in fig 1, it is obvious that company i can make comparison and relative study according to the game result of other companies of price and production in the last round and consider that this value will remain unchanged in the current round. Therefore, with the knowledge of this information, the company j will compare the price difference and find the critical price.
In a multi-agent system based on Bertrand model can be further improved:
q i, n - 1
q 'inn =”
i -1
Qma — E q
■^ max ^^^ j
q i, n
i + w - 1
E q k , n - 1 + q i,n
where: Q is the total market demand; Pi is the price of company i; Pm is the highest price that meets the total market demand(the critical price); while the symbol j is the index of a company whose price is less than critical price; q is the production of company i and q V is the sales of company i.
When Pi is less than Pm, the sales is equal to the production. When Pi is equal to Pm , the sales amount is equal to the average value where rest of companies separate the rest productions evenly. When Pi is greater than Pm , the sales output is 0.
Market Modeling of Bertrand Model
In the Bertrand model, the profit function of companies can be expressed as follows:
f = q i ^ ( Pi- Pd ) (2)
where: f , is profit function of company i; p , is the price of company i; q , is the production of company i; pci is the cost price of company i.
Based on Bertrand model and multi-agent, we can draw the profit figure 1, where we can obtained that, the market profits of a company will be affected by the following factors:
(1) price of a company p , and its productionq , .
if Pi, n-1< Pm, n if Pi+1, n
Pi + w - 1 P m , n
if Pi , n - 1 > P m, n
The new profit function is:
fi , n = q 'inn X ( P inn - P ci ) (0 ^ P inn ^ P m )• (4)
In the formula (4), Pl m is the price ceiling company i , Qmax is the market demand; pmn is the critical price in round n ; q ,,„ is the sale of company i in round n ; / i, nis the profit function of company i in round n ; q ‘ t is the production of company i in round n .
According to the above-mentioned analysis, in order to find out how the model works, combining with genetic algorithm (GA),we take duopoly for further study.
Nash Equilibrium in Bertrand Duopoly Model
According to the classical Bertrand model of duopoly competition, we established the market model as follows:
Actual profits Decision variables of of company i other company : price and production
Decision variables of company i : price and production
Coefficient of Optimized profits Decision variables of company i of company i other company : price and production
Decision variables of Coefficient of company i : price and company i production
qi-1 , pi-1
q + + 1 , Pu i
q 1 , p 1
q ,t , p ,t

q n , p n
f i,
q 1,t-1
q -1,t-1 q. + Lt-!
qn,t-1
, p1,t-1
, pi-1,t-1
- P i + i,t-i
, pn,t-1
Fig. 1. Associated Profit Function of Bertrand Model
It is assumed that there are two oligarchs who produce the same product: company 1 and company 2, and the price of their products are p 1 ,p2 respectively. As a result, the sales of company 1 are as follows:
|
' q i |
if p 1 |
< p 2 |
|
|
1 Q |
if p 1 |
= p 2 |
(5) |
|
1 ° |
if p 1 |
> p 2 |
The profit function of company 1 can be expressed as follows:
/ 1 = q i x ( P i - P ci ). (6)
In the same way, the profit function of company 2 is:
/ 2 = q 2 x ( P 2 - pd )• (7)
Companies in the Bertrand model bid simultaneously, it is calculated that the Nash equilibrium exists and unique in it as (p ^ , p 2 ). However, the two companies have their own products priced at cost price, namely, p ^ = p ^ = c, where there is an indeed Nash equilibrium On the basis of this price, the profits of both sides are zero. At the same time, both companies realizes that no one could benefit from raising prices. It is because that once a company rises the price, the company will lose the market shares, then the profits of the company will reduced to zero (if not, the profit is also zero because the equilibrium price equals to cost price, even the two companies share the market, no profits can be made).
There is no doubt that one of the two companies can completely reduce the price to the cost price c , and this move will directly lead to the loss of the company.
As the two manufacturers are able to meet the market demand alone, there is no absolute price advantage and turn into a "competing for a lower price" process to seize market share and gain the maximum profit. Finally, the equilibrium is achieved, but the equilibrium price is the production price.
Simulation case
Hypothesis 1 : suppose that there are only two companies produce the same product that can be substituted for each other. At the same time, the maximum production capacity of any companies cannot meet the market's total demand alone.
The two companies can be Company 1 and Company 2 respectively. Then we set the parameters for Bertrand–Edgeworth model in the market game:
Q = 5000, P max = 12, 0 < q i , q 2 < 4000, p 0 = 5. (8)
In order to gain their own maximum profits, the two companies will play a number of price games. In the first round game, the decision variables can only be randomly selected within the constraints, for the agents are not fully aware of the market environment. At the beginning of the second round game, there was a price combination in the first round of the game, and the two companies suppose that the other party would keep the first round price in the next round, which was used as a known market information to make price decisions respectively. The competitive price game in the third round is known as the result of the second round of bidding. By analogy, a multi-round game is carried out.
According to the characteristics of the model, the price strategy of Company A and Company B would reduce the price as much as possible to maximize their profits, so that they can sell the most products and maximize profits. When price is down to a critical value, a company will directly raise the price, and the other company will keep up with its own price. In order to fight for market share, the two sides will push down the price after the rising price. Then the game will go round and begin again.
This will show the periodicity. According to the characteristics of the cycle, the first part of the oscillation range is large which is recognized as the large oscillation area. The second part of the shock is relatively small, which is called a small oscillation area.
Hypothesis two : suppose that there are only two companies produce the same product that can be substituted for each other. The maximum production capacity of a company can meet the total demand of the market, and competition will lead to price reduction to the cost price of the product. The competition is the most intense at this time.
The first and second companies play a multiround game in the market according to the Bertrand Edgeworth model. The parameters are as follows:
Q = 4000, Р тах = 12, 0 < qx,q 2 < 4000, P o = 5. (9)
Discussions and Simulation Results
Simulation analysis for hypothetical one:
According to the hypothesis of the model, when the total demand Q of the market is determined, then, the two companies' maximum production capacity q 1 and q2are also set, so the profit functions of each company can be simplified as the followings:
w J f. = (Pi -5) x qi vp < p7,
1 I f 2 = ( P 2 - 5) x ( Q - q i )
• v P i = P 2
J f . = ( P i — 5) x QI 2 [ f , = ( p 2 - 5) x Q /2
w J f. = ( P i - 5) x ( Q - q 2 )
v P i > p 2 , 1
I f 2 = ( p 2 - 5) x q- 2
It is assumed that the cost of Company 1 and Company 2 is 5. The simulation results are discussed in detail.
We can see that when the output of the two companies can't meet the market demand alone, the two companies will game for many rounds, showing big or small oscillations. As the competition goes its way, no Nash equilibrium is found. With the help of genetic algorithm optimization analysis, we found the law in market oscillation, in the case of limited rationality.
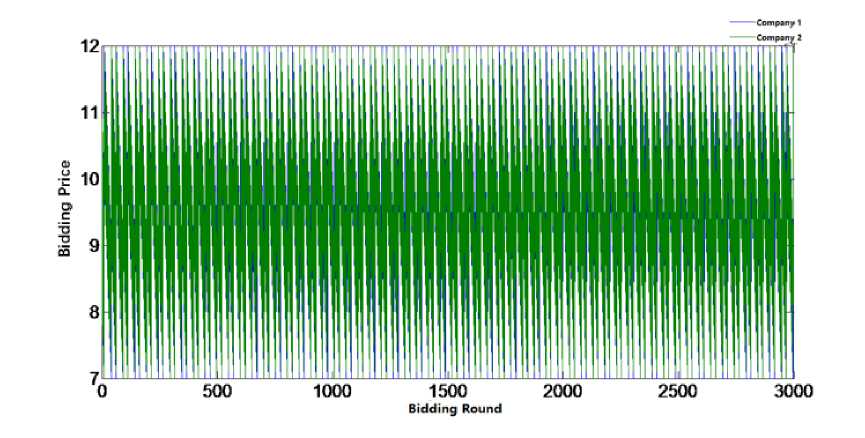
Fig. 2. Sharp Oscillation Zone of Bertrand Model
Bidding Round
Fig. 3. Small Oscillation Zone of Bertrand Model
Since its own output cannot meet the demand of the market, there are two ways to obtain the market profit: to increase market price to obtain less market share or to reduce market price to obtain a larger market share to gain a good profit. The two companies will constantly weigh the two ways in the market game. As a result, the price of a company decreases as the price of another one decreases to game for a higher market share. However, since the total output of the two manufacturers cannot meet the demand of the market alone, when the market price falls to a certain level, even if one of the company sells all the output, there will still be a surplus of market demand. Companies with limited rationality will reduce the market share by raising the price to gain the market profits. In this way, there will be a process of rising up and going down shown in the simulations. The magnitude and frequency of the shock are related to the critical price (The selling price of the same profit when one company holds the dominant price while the output is the dominant factor of another company.)
When bidding process is in sharp oscillation zone, Company 1 and Company 2 take the relatively higher or lower price in turns. And due to the characteristics of the model, company with low price will gain more market share (which is the q 1 or q2), company with higher price will get less market share (i.e. the total demand of Q minus the production of lower-price company).
When the two companies continue their bidding game in small oscillation zone, both will adjust their product prices to get bigger market share. From the figure, we can see that the price is decreasing in bidding process.
When the price of both sides game for the price, the profit will change. Because of the violent jitter of the price, the cycle will change constantly, meanwhile, it is evident that the profits of the two companies will also undergo drastic and cyclical changes. When they are competing for lower prices, profits are declining, while the price is at lower condition (we chose 6.8), suddenly there will be one choose to raise the price for profits, the other party immediately follow the price to increase profits, then once again lowered the price of competing market game. As a result of the repeated game, the profit has a periodic change. Figure 4 explains this.
The reason for the volatility in the bidding process is that:
Both of them are pursuing different bidding strategies in order to pursue maximum benefits, so that they can take advantage of production and win the most profits in the process of game. In this way, both sides will take a slightly lower price strategy, hoping to be lower than the other's offer by which way to obtain more benefits. However, in the process of bidding, there will be a distinction between the prices. The two sides' bottom line will not reach the cost price, for the maximum production capacity of each company is not enough to meet the total demand of the market independently.
On the one hand, both sides are constantly lowering their prices to get the largest market share. On the other hand, they hope to raise their prices in the next round and make profits even higher. The two companies put down their own prices alternately, and they rebounded to a high price at a certain price. And then in order to grab more market shares, they lower their prices again. The bidding process of each round is similar, so there will be an oscillation.
The difference in the amplitude of the oscillation is that in each bidding process, the rise and decline of the price are related to the price of the two parties at the beginning of the game. When the difference between the quotations is relatively large, there is a big oscillation area.
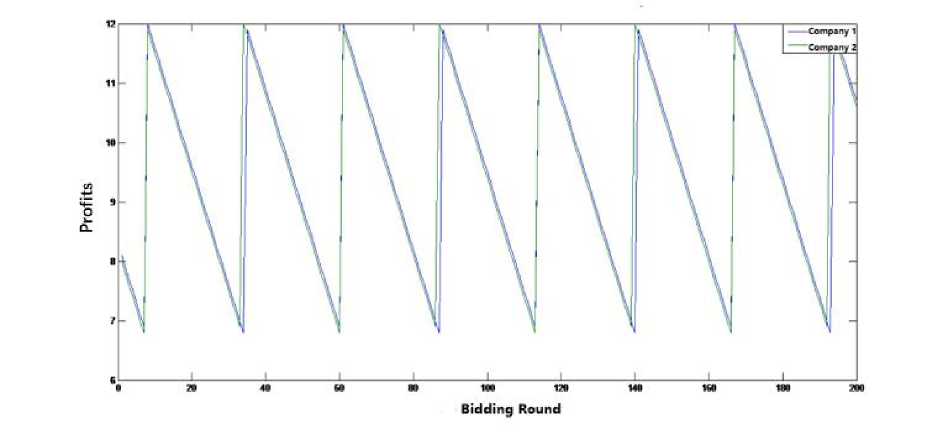
Fig. 4. Profit Changes of Company 1 and Company 2
Unit price of the two players is decreasing slowly during the slight fluctuation. When companies reach the lowest acceptable price, the lower price company will abandon the low price but to rise the price to get a bigger profit, so the price will rise.
Therefore, the conclusion can be obtained according to the Bertrand Edgeworth model, when production capacity is limited, it is difficult to predict the duopoly market price, there is no pure strategy Nash equilibrium.
For the analysis of the simulation results of hypothesis two: as the price of either side of the two sides can meet the market demand, the simulation results are shown in Figure 5.
It can be obtained that when the two sides com- pete in the 60th round, the price of both sides is basically adjusted to the cost.
Conclusion
It is evidently shown in the model that when none of the two companies are able to meet all the demands in the market, the bigger the price gap, the more oscillated it is in the process, thus, it doesn’t exist the pure strategic Nash equilibrium. However, when one of the two can offer the demands independently, Nash equilibrium appears and is shown as the calculated results in Bertrand-Edgeworth model where the equilibrium reaches the cost price.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor Huang Xian for his careful and patient guidance.
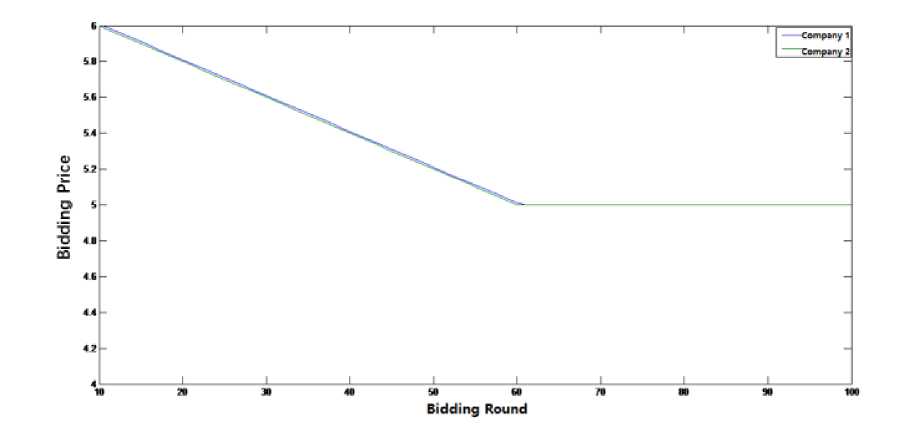
Fig. 5. Competitive Price Simulation of Company 1 and Company 2
Список литературы Analysis on the agent-based Bertrand duopoly game model
- Hirata D., Matsumura T. On the Uniqueness of Bertrand Equilibrium // Operations Research Letters, 2010, 38(6):533-535. DOI: 10.1016/j.orl.2010.08.010
- Dastidar K.G. On the existence of pure strategy Bertrand equilibrium // Economic Theory 5 (1) (1995) 19-32. DOI: 10.1007/BF01213642
- Liang Xiaoying, Xie, et al. Bertrand competition with intermediation // Economics Letters, 2012, 116(1):112-114. DOI: 10.1016/j.econlet.2012.01.019
- Nijs R.D. Further results on the Bertrand game with different marginal costs // Economics Letters, 2012, 116(3):502-503. DOI: 10.1016/j.econlet.2012.04.055
- Anderson S.P., de Palma A., Thisse J.-F., 1997. Privatization and efficiency in a differentiated industry // Eur. Econ. Rev. 41 (9), 1635-1654. DOI: 10.1016/S0014-2921(97)00086-X
- Froeba L., Tschantzb S., Crookeb P., 2013. Bertrand competition with capacity constraints: mergers among parking lots // Journal of Econometrics, 113(1):49-67.
- DOI: 10.1016/S0304-4076(02)00166-5
- Palmer I. Coalbed methane completions: a world view // International Journal of Coal Geology, 2010, vol. 82, no. 3, pp. 184-195.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2009.12.010
- Andrés J., Burriel P. Inflation and optimal monetary policy in a model with firm heterogeneity and Bertrand competition // European Economic Review, 2018, 103:18-38.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroecorev.2017.12.009
- Amir R., Evstigneev I.V. A new look at the classical Bertrand duopoly // Games & Economic Behavior, 2018, 109:99-103.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.geb.2017.12.010
- Baye, M., Kovenock, D., 2008. In: Durlauf, Steven, Blume, Lawrence (Eds.). Bertrand competition, The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd ed. Palgrave Macmillan.
- DOI: 10.1057/978-1-349-95121-5_2462-1
- Łukasz Balbus, Reffett K, Łukasz Woźny. A Constructive Study of Markov Equilibria in Stochastic Games with Strategic Complementarities // Journal of Economic Theory, 2010, 150(1).
- DOI: 10.2139/ssrn.1723038
- Algarvio H, Lopes F, Sousa J, et al. Multi-agent electricity markets: Retailer portfolio optimization using Markowitz theory // Electric Power Systems Research, 2017, 148:282-294.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.epsr.2017.02.031
- Cellini R, Lambertini L. R&D Incentives Under Bertrand Competition: A Differential Game // Japanese Economic Review, 2011, 62(3):387-400.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-5876.2011.00541.x
- Amir R., Erickson P., Jin J., 2017. On the microeconomic foundations of linear demand for differentiated products // J. Econ. Theory, 169, 641-665.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jet.2017.03.005
- Soleymani S. Bidding strategy of generation companies using PSO combined with SA method in the pay as bid markets // Int J Electr Power Energy Syst, 2011; 33(7): 1272-8.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2011.05.003
- Ladjici A.A., Boudour M. Nash cournot equilibrium of a deregulated electricity market using competitive coevolutionary algorithms // Electr Power Syst Res, 2010;81(4):958-66.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.epsr.2010.11.016
- Chen H., et al. Analyzing oligopolistic electricity market using coevolutionary computation // IEEE Transactions On Power Systems, 21 (1) (2006) 143-152.
- DOI: 10.1109/TPWRS.2005.862005
- Gwartney J.D., Stroup R., Clark J.R. Pure Competition And Monopoly // Essentials of Economics, 1985, pp. 307-332.
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-311035-0.50019-8
- Vazhayil J.P., Balasubramanian R. Optimization of India's electricity generation portfolio using intelligent Pareto-search genetic algorithm // International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2014, 55:13-20.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.08.024
- Cai J., Kim D., Jaramillo R., et al. A general multi-agent control approach for building energy system optimization // Energy & Buildings, 2016, 127:337-351.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.05.040


