Application of Multi-Attribute Utility Theory in a Decision Support System for Selecting the Best Budget Hotels in Samarinda
Автор: Anik Hanifatul Azizah, Heny Pratiwi, Reza Andrea, Achmad Afandi, Sri Rakhmawati, Dewi Safitriani, Nurhasanah Nurhasanah
Журнал: International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science @ijitcs
Статья в выпуске: 5 Vol. 17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This study addresses the challenge faced by tourists, companies, travel agents, and tourism agencies in selecting the ideal hotel in Samarinda, given the variety of available options. The city boasts numerous hotels with differing facilities, room types, rates, and locations, which can complicate decision-making without adequate information. To provide a solution, this research introduces a Decision Support System (DSS) that employs the Multi-Attribute Utility Theory (MAUT) method for hotel assessment. By evaluating hotels based on key attributes like price, amenities, service quality, and location, the system offers a comprehensive, objective approach to determining the best affordable hotels. The study contributes significantly to the hospitality sector by presenting a practical tool that simplifies the hotel selection process and ensures that choices align with the preferences of the visitors.
Implementation of the Multi Attribute Utility Theory (MAUT), Decision Support System, Hotel, Samarinda
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15020015
IDR: 15020015 | DOI: 10.5815/ijitcs.2025.05.03
Текст научной статьи Application of Multi-Attribute Utility Theory in a Decision Support System for Selecting the Best Budget Hotels in Samarinda
Samarinda is the capital of East Kalimantan province and stands as the largest city on Kalimantan Island, with a population of 812,597 residents [1,2]. The city's technological and infrastructure development has been accelerating rapidly, attracting numerous investors to establish businesses in Samarinda [3-10]. This growth in the economy [1,4] has been accompanied by a significant rise in the population as well [5,11-15].
Samarinda is home to a wide array of hotels, offering diverse facilities, room types, pricing, amenities, bed capacities, and locations [16-18]. This variety presents challenges for individuals, companies, travel agents, or tourism agencies who wish to choose a hotel but lack sufficient information about the available options. The selection of a hotel is heavily influenced by the visitors' specific needs and goals [6,8,19-21]. Additionally, factors such as strategic location and a comfortable environment play a crucial role in this decision-making process [21,22]. The absence of adequate information about hotels becomes a significant issue for visitors trying to determine which hotel to choose when they arrive in Samarinda.
To address this challenge, a decision support system is required to assist in selecting the most suitable hotel in Samarinda. This system applies the Multi-Attribute Utility Theory (MAUT) method [23,24] for its evaluation process. The use of MAUT in decision support systems (DSS) has been thoroughly examined in various fields, showcasing its effectiveness in managing complex decision-making situations [25]. For instance, developed a DSS for hotel selection in Samarinda using the MAUT method, emphasizing the importance of objectivity in determining criterion weights and calculating utility values to provide accurate and reliable recommendations [26-28]. This approach highlights the effectiveness of MAUT in addressing multiple criteria in the hospitality industry [29-32]. The others Research compared the MAUT method with the Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) in the context of scholarship selection, finding that MAUT offered higher accuracy in determining the best alternative, showcasing its robustness in educational decision-making [33]. Furthermore, Compared MAUT with the Multi-Factor Evaluation Process (MFEP) in employee selection, concluding that MAUT was more effective in handling complexity and subjectivity, resulting in more consistent and accountable recommendations [34]
Building upon these studies, the current research introduces novelty by applying the MAUT method in the context of selecting the best budget (cheap) hotels in Samarinda, an area that has not been extensively explored. This study focuses on local criteria such as transportation accessibility, environmental safety, and availability of public facilities, tailored to the unique characteristics of Samarinda. Additionally, the research employs web-based technology to develop a MAUT-based DSS, enabling users to access and utilize the system efficiently and effectively, thereby providing practical solutions for travelers and hotel managers in Samarinda to make better-informed decisions.
2. Research Method 2.1. MAUT Method
Multi-Attribute Utility Theory (MAUT) is a framework where the final evaluation, V(x), of an object × is determined by the weight assigned to a value corresponding to its specific dimension. This is commonly referred to as the utility value [23, 35]. In the MAUT method, it is essential to create a multi-attribute utility model, which involves defining the dimensions relevant to specific evaluation and decision-making issues. The MAUT method is employed to convert multiple factors into numerical values on a scale from 0 to 1, where 0 represents the least favorable option and 1 represents the best. This transformation facilitates direct comparison among different attributes [36]. The final outcome is a ranked order of alternative evaluations that mirror the preferences of the decision-maker [24,36]. The complete evaluation value can be expressed using equation (1).
Description (1):
-
V (Xj : Total utility of the 1st alternative
W j : The weight of the attribute (E w = 1)
U i : Function 1st attribute
-
i : Attributes 1, 2, 3, ..., n
-
x : Criterion i
In summary, the steps involved in the MAUT method are as follows:
-
• Decompose the decision into various dimensions.
-
• Assign relative weights to each dimension.
-
• Compile a list of all possible alternatives.
-
• Calculate the utility for each alternative based on its attributes using the formula in equation (2).
U(x) =
x-x i x + -x i
Description (2):
U (x) : Normalization of alternative weights
-
x: Alternative weights
-
x - : The worst (minimum) weight of the x-criterion
-
x + : The best (maximum) weight of the x-criteria
-
• Multiply utility by weight to find the value for each alternative using the equation.
-
2.2. Field Study
To obtain data that is used as material in data analysis activities, field study methods will be used. There are two methods of field study, namely:
-
• Interview
Interview stages are conducted to obtain more information about the hotel selection process carried out by tourists, companies, travel agents or tourism agents. Interviews conducted with tourists, companies, travel agents or tourism agents focus on the process of how to choose the desired hotel.
-
• Documentation
-
2.3. Intelligence Stage
Analyzing all documents related to how the system works, problems in the system, system input data, process and system output that will be created later.
Identification of problems
-
• This phase identifies problems that are currently being experienced, namely regarding the selection of the best cheap hotel in Samarinda City, Indonesia.
-
• Classification of Problems
-
• The problem classification above is then analyzed to determine system requirements. Analysis of the needs for this research consists of hardware requirements and software requirements, which consists of
-
2.4. Data Collection
The data used in this study are hotel data and hotel assessment criteria data. The assessment criteria are as follows:
-
• Jembatan Baru
-
• Surya Raya
-
• Bina Rahayu
-
• Bone Indah
-
• Segiri
-
2.5. Analysis System Stage
Table 1. Hotel statistics data in samarinda city
|
Classification |
amount |
|
Unstarred & Guest House |
65 |
|
Home Stay |
3 |
|
★ ☆☆☆☆ (1 Star) |
0 |
|
★ ★☆☆☆ (2 Star) |
6 |
|
★ ★★☆☆ (3 Star) |
5 |
|
★ ★★★☆ (4 Star) |
4 |
|
★ ★★★★ (5 Star) |
2 |
Source: Central Bureau of Statistics of East Kalimantan Province
The choice of a hotel is greatly impacted by the objectives and requirements of the visitors. In addition, factors such as the hotel's strategic location and a pleasant environment also play a significant role. A lack of sufficient information about hotels in Samarinda poses a challenge for visitors when they arrive in the city and try to select their preferred hotel. Based on hotel statistical data from the Central Bureau of Statistics of East Kalimantan Province in 2019, Table 1 shows the number of hotels in Samarinda is 85 hotels with various types of classifications, ranging from jasmine hotels, 1-star hotels to 4-star hotels. Statistical data for hotels in Samarinda in 2019.
This design uses a system development tool, namely a flowchart consisting of a system flowchart, a MAUT calculation flowchart and a database design.
-
A. System Flowchart
The flowchart system can be seen in Fig. 1 . The system flowchart illustrates the step-by-step process for selecting the best hotel in Samarinda using the Multi-Attribute Utility Theory (MAUT) method. The flowchart begins with the Start point, followed by a Login step where the user inputs their login details. If the login credentials are correct, the system progresses to the Main Page. The flow then proceeds to several input steps, including Hotel Data Input, where hotel-related information is entered, and Input Data Criteria, where the evaluation criteria for the hotels are provided. The next step involves Inputting Hotel Value, followed by the core process of Hotel Assessment Using the MAUT Method. After assessment, the Hotel Assessment Results are generated, leading to the Finish point.
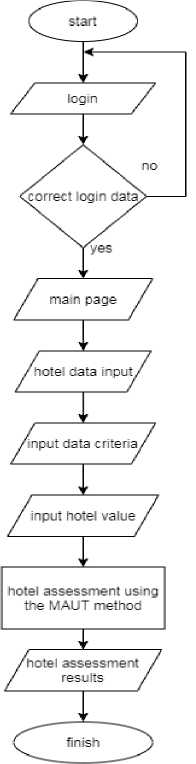
Fig.1. System flowchart
-
B. Flow Chart MAUT Calculation
-
2.6. Stage of Choice (Choice)
Flowchart system can be seen in Fig. 2. The MAUT calculation flowchart is a detailed representation of the steps involved in using the MAUT method to assess the hotels. It starts with the selection of hotel data and then uses the input criteria to evaluate each hotel based on different attributes such as price, amenities, service, and location. These attributes are weighted, and each hotel's score is calculated based on its performance across these criteria. The flowchart then leads to the calculation of the utility value for each hotel, and the final step aggregates the utility values to provide an overall assessment of the hotel.
Table 2 outlines the evaluation criteria used in the decision support system for selecting the best hotel in Samarinda, based on the Multi Attribute Utility Theory (MAUT) method. These criteria are crucial for assessing various hotel options, considering attributes that align with visitors' needs and preferences. Price, for instance, is a key factor as most visitors consider their budget when choosing accommodation. Hotels that offer affordable rates while maintaining adequate facilities are prioritized, with prices receiving higher weight to reflect its importance for most guests. Amenities also play a significant role in hotel selection, as the availability of facilities such as swimming pools, restaurants, and fitness centers contributes to guest comfort. The weight for this criterion is greater for hotels that offer a more extensive range of services. Additionally, the quality of service, including the efficiency and friendliness of the staff, affects the overall guest experience. Hotels with better quality service are rated higher.
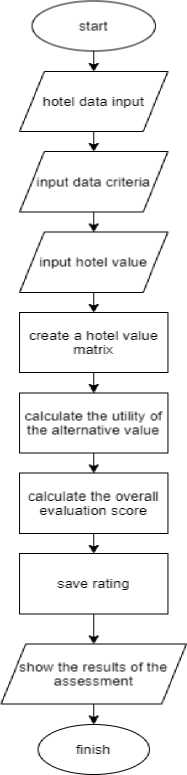
Fig.2. MAUT calculation flowchart
Table 2. Assessment criteria
|
#. |
Criteria Code |
Criteria |
Weight |
|
1 |
C01 |
Price / Tariff |
5 |
|
2 |
C02 |
Amenities |
4 |
|
3 |
C03 |
Service |
3 |
|
4 |
C04 |
Location |
2 |
The criteria above are translated into sub-criteria which have their respective weighted values. The sub-criteria data is in Table 3.
Information of Table 3:
• The facilities recorded are Hot Water, Cable TV, Free Wi-Fi, Restaurant, Swimming Pool, Fitness, Meeting Room (Source: Central Bureau of Statistics, East Kalimantan Province).
-
a. Complete, which has all recorded facilities.
-
b. Medium, namely having at least 3 to 5 facilities recorded.
-
c. Less, that is, only having 1 or 2 recorded facilities.
-
• Service
-
a. Good, namely a timely, efficient way of working, and a service attitude characterized by being friendly, welcoming, attractive and sympathetic.
-
b. Moderate, namely the low, inconsistent, disorganized way of working, but the service is characterized by being friendly, welcoming, interesting and sympathetic.
-
c. Less, namely slow, inconsistent, disorganized workmanship, and an unfriendly and unattractive attitude.
-
2) . MAUT calculation
An example of the calculation of the MAUT method using five hotel data.
-
• Jembatan Baru
-
• Surya Raya
-
• Bina Rahayu
-
• Bone Indah
-
• Segiri
Table 3. Sub criteria
|
#. |
Criteria |
Sub Criteria Name |
Weight |
|
1 |
Price (IDR) |
<100.000 |
5 |
|
100.000-200.000 |
4 |
||
|
200.000-350.000 |
3 |
||
|
350.0000-500.000 |
2 |
||
|
> 500.000 |
1 |
||
|
2 |
Amenities |
Complete |
5 |
|
Moderate |
3 |
||
|
Less |
1 |
||
|
3 |
Service |
Good |
5 |
|
Moderate |
3 |
||
|
Less |
1 |
||
|
4 |
Location |
City center |
5 |
|
Near the tourist center |
4 |
||
|
Near the airport |
3 |
||
|
Near the Sports Center |
2 |
||
|
Near the Central Government / Offices |
1 |
The first step in the process of determining the best cheap hotel using the MAUT method is to assign a value to each alternative or hotel data. The value of each hotel in accordance with the assessment criteria can be seen in table 4.
Table 4. Hotel ratings
|
Hotel Name |
Price (IDR) |
Service |
Amenities |
Location |
Star Level |
|
Jembatan Baru |
100.000-200.000 |
Moderate |
Moderate |
City center |
Unstarred |
|
Surya Raya Hotel |
100.000-200.000 |
Less |
Less |
Near the Center for Urban Government |
Unstarred |
|
Bina Rahayu Hotel |
100.000-200.000 |
Less |
Moderate |
Near the Center for Urban Government |
Unstarred |
|
Bone Indah Hotel |
<100.000 |
Less |
Less |
Near the Center for Urban Government |
Unstarred |
|
Segiri Hotel |
100.000-200.000 |
Less |
Complete |
Navel City |
Unstarred |
The next step is to calculate the utility value with the following (1 ) , an example of calculating utility values for all alternatives or hotel data is as follows.
-
• Jembatan Baru
и 1.1= (4 - 4) - (5 - 4) =0
U 1.2= (3 - 1) - (3 - 1) =1
U 1.з= (3 - 1) - (5 - 1) =0
U 1.4= (5 - 1) - (5 - 1) =1
-
• Surya Raya
U 2.1= (4 - 4) - (5 - 4) =0
U 2.2= (1 - 1) - (3 - 1)=0
U 2.3= (1 - 1) - (5 - 1) =0
U 2.4= (1 - 1) - (5 - 1) =0
-
• Bina Rahayu
U 3.1= (4 - 4) - (5 - 4) =0
U 3.2= (1 - 1) - (3 - 1) =0
U 3.3= (3 - 1) - (5 - 1) =0
U 3.4= (1 - 1) - (5 - 1) =0
-
• Bone Indah
U 4.1= (5 - 1) - (5 - 1) =1
U 4.2= (1 - 1) - (3 - 1) =0
U 4.3= (1 - 1) - (5 - 1) =0
U 4.4= (1 - 1) - (5 - 1) =0
-
• Segiri
U 5.1= (4 - 4) - (5 - 4) =0
U 5.2= (3 - 1) - (3 - 1) =1
U 5.3= (5 - 1) - (5 - 1) =1
U 5.4= (5 - 1) - (5 - 1) =1
After calculating the utility values U for each hotel based on the defined attributes, the next step involves determining the overall value V for each alternative. The utility value U represents the normalized score for each individual attribute, showing how well a hotel performs in relation to that specific criterion
-
• Jembatan Baru
V 1.1 = w 1 U 1.1= 4 x 0= 0
V 1.2 = w 2 U 1.2= 3 x 1 =3
V 1.3 = w 3 U 1.3 = 4 x 0 =0
V 1.4 = w 4 U 1.4= 2 x 1 =2
-
• Surya Raya
V 2.1 = w 1 U 2.1= 4 x 0 =0
V 2.2 = w 2 U 2.2= 3 x 0 =0
V 2.3 = w 3 U 2.3= 4 x 0 =0
V 2.4 = w 4 U 2.4= 2 x 0 =0
-
• Bina Rahayu
V 3.1 = w 1 U 3.1= 4 x 0 =0
V 3.2 = w 2 U 3.2= 3 x 0 =0
V 3.3 = w 3 U 3.3= 4 x 0 =0
V 3.4 = w 4 U 3.4= 2 x 0 =0
-
• Bone Indah
V 4.1 = w 1 U 4.1 = 4 x 1 = 4
V 4.2 = W 2 U 4.2= 3 X 0 =0
V 4.3 = w 3 U 4.3= 4 X о =о
V 4.4 = W 4 U 4.4= 2 X 0 =0
-
• Segiri
V 5.1 = w 1 U 5.1 = 4 X0 = 0
V 5.2 = W 2 U 5.2= 3 X 1 =3
V 5.3 = w 3 U 5.3 = 4 X 1 =4
V 5.4 = W 4 U 5.4= 2 X 1 =2
The final step is to calculate the total weight of the utility value that has been calculated above for each alternative.
-
• Jembatan Baru = 0 + 3 + 2 + 2 + 0 = 7
-
• Surya Raya Hotel = 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 =0
-
• Bina Rahayu Hotel = 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 =0
-
• Bone Indah Hotel = 4 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 =4
• Segiri Hotel = 0 + 3 + 4 + 2 + 0 =9
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Main Admin Page3.2. Hotel Data Page
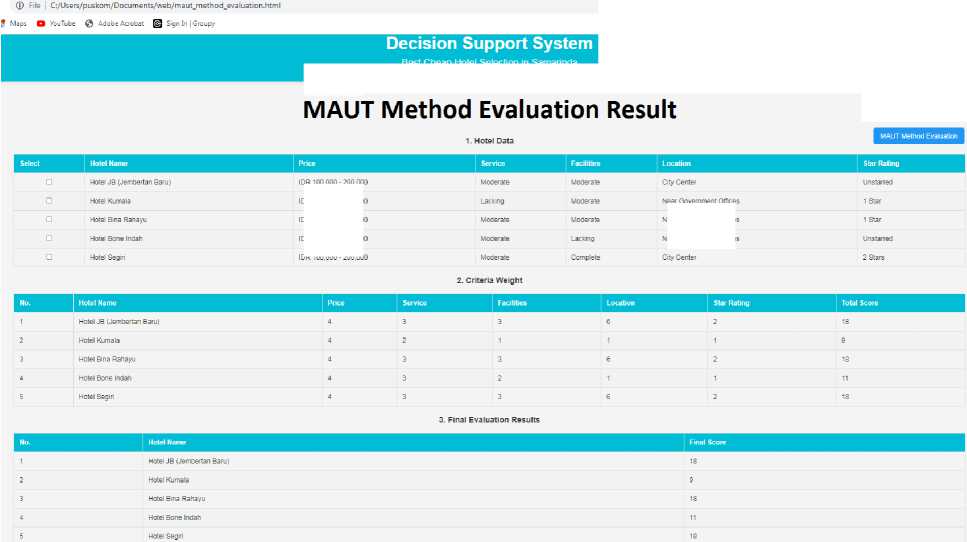
The total utility values for all the alternatives are then ranked from the highest to the lowest, and the results are presented in Table 5. In Table 5, Segiri Hotel receives a value of 9, indicating that it is more highly recommended than the other hotels (Jembatan Baru, Bone Indah Hotel, Bina Rahayu Hotel, and Surya Raya Hotel) based on the criteria of Price, Facilities, Service, and Location.
Table 5. Calculation results of MAUT
|
Ranking |
Hotel Data |
Score |
|
1 |
Segiri |
9 |
|
2 |
Jembatan Baru |
7 |
|
3 |
Bone Indah |
4 |
|
4 |
Bina Rahayu |
0 |
|
5 |
Surya Raya |
0 |
Fig.1. Main page
Admin page is a page that contains a menu list for data processing and hotel assessment as well as a brief explanation of the decision support system program for determining the best cheap hotel using the MAUT method. The menus on the main page are the home menu, hotel data, criteria data, value input, assessment, assessment results, reports and the logout menu, we can see in Fig. 1.
Fig. 2. show a page for hotel data processing. On this page there is a description of the hotel name, hotel specifications and prices. To add new hotel data click add new button. To change hotel data click the edit button and to delete hotel data, click the delete button.
|
uh* 0 Atobe* Acrob ^ ■ Group? |
|
Decision Support System Best Cheap Hotel Selection in Samarinda |
|
Hotel Data |
|
1 No Name Address Phone Type Facilities Action |
|
1 Hotel Lambung Jalan Lambung Mangkurat No 75 0541-748745 Unstarred 2 Hotel Pirus Jalan Pirus No 30 0541-734162 Unstarred 3 Hotel Rahmat Abadi Jalan Gatot Subroto, Temindung Permai 0541-734462 Unstarred 4 Hotei Berkat Tenang Jalan Gatot Subroto No. 107 0541-735267 Unstarred 5 Hotel Harmon Indah II Jalan Awang Long 0541-735775 Unstarred
|
Fig.2. Page and hotel
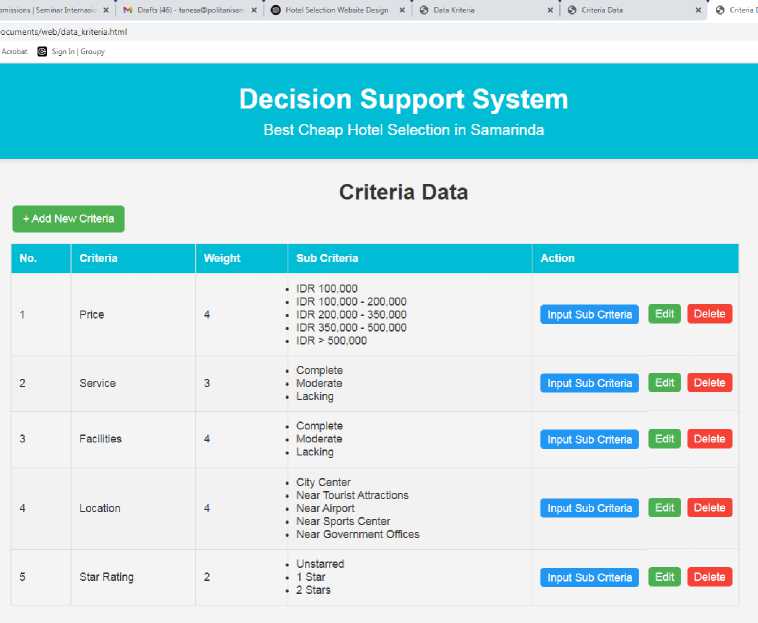
Fig.3. Assessment criteria page
-
3.3. Assessment Criteria Page
-
3.4. Assessment Page
-
3.5. Result Page
Criteria page is a page for the processing of assessment criteria data. On this page there is a description of the criteria name, weights and the names of the sub criteria. To add new criteria click add new button. To change criteria data, click the edit button and to delete criteria data, click the delete button. To add detailed sub criteria data, click the sub criteria input button then add the sub criteria details and weight the values according to the main criteria. Click the save button to save the sub criteria data in Fig. 3.
This is a page for processing hotel appraisal data using the MAUT method. This page displays all previously processed hotel value data. The admin can start the assessment process using the MAUT method by clicking the MAUT Method Assessment button, see in Fig. 4.
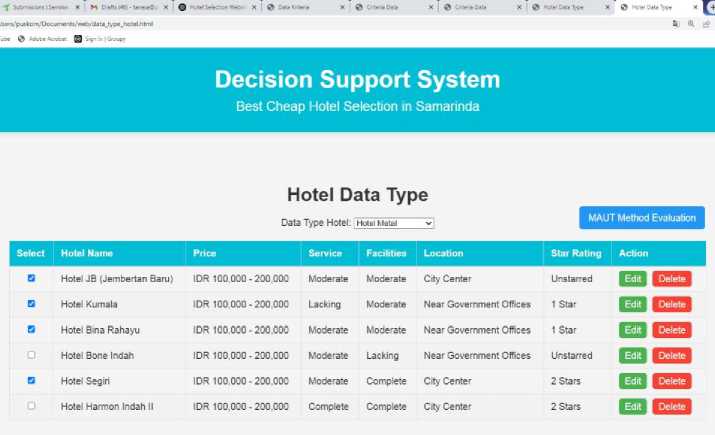
Fig.4. Assessment page
The assessment process using the MAUT method begins by displaying a list of values that have been stored for each alternative or hotel. The value data is then converted into a weighted value in accordance with the criteria that have been selected. The weighted value is then displayed in the form of a weighted value table matrix.
ф ☆
DR 100,000-200,000
Near government unices
DR 100,000 - 200,000
Fig.5. Results of hotel calculations using the lethal method
best Cheap Hotel selection in bamannaa
DR 100,000 - 200,000
DR 100,000 - 200,000
DR 100,000 - 200,000
Meat Government Offices
Чеаг Government Offices
The next process is to calculate the utility value for each of the assessment criteria. The final step is to calculate the overall evaluation value by calculating the utility value multiplied by the weighted criterion value. The multiplication result of the utility value weight is then added up according to alternative data. The sum result is the final value of the calculation process of the MAUT method. The results of hotel calculations using the MAUT method will be shown as in Fig. 5.
3.6. Report Page
4. Conclusions
Fig. 6 shows page for printing reports generated by the system. On this page there is an option to print a hotel assessment report and an assessment report for each hotel. To print the report the user can use the print preview button. The assessment report is a report that contains information about the hotel data that has been assessed. In this report, information on the name of the hotel, type, address, telephone number and value of the hotel is provided in Fig. 6.
Fig.6. Report page
Table 6 shows, the report page is a page for printing reports generated by the system. On this page there is an option to print a hotel assessment report and an assessment report for each hotel. To print the report the user can use the print preview button. The assessment report is a report that contains information about the hotel data that has been assessed. This report contains information about the hotel name, type, address, telephone number and hotel value. While the per hotel assessment report is a report that contains information about the detailed assessment results for each hotel using the MAUT method.
Table 6. Report on the results of the assessment per hotel
|
Rank |
Hotel Name |
Star |
Address |
Telephone |
MAUT Value |
|
1 |
Segiri Hotel |
Unstarred |
Jalan Pahlawan No.34 RT 31 |
0541-204198 |
9.0 |
|
2 |
JB Hotel (Jembatan Baru) |
Unstarred |
Jalan K.H. Agus Salim No. 16 |
0541-375788 |
7.0 |
|
3 |
Bone Indah Hotel |
Unstarred |
Jalan H. Juanda No.9 |
0541-353934 |
4.0 |
|
4 |
Bina Rahayu Hotel |
Unstarred |
Jalan H. Juanda RT 18 No.10 |
0541-732936 |
2.0 |
|
5 |
Kumala Hotel |
Unstarred |
Jalan H. Juanda No.165 |
0541-732875 |
0.0 |
The decision support system developed for selecting the best budget hotel in Samarinda is built using a web-based programming language. The hotel evaluation process is carried out through the MAUT calculation method. This system offers more objective evaluation results since the assessment is conducted automatically by the program. The outcomes of this evaluation can serve as a foundation for making recommendations on the best hotel choices. This system presents an alternative solution for selecting the ideal hotel based on the preferences of visitors. Future studies could explore the integration of additional criteria, such as customer reviews or real-time data, along with the application of advanced machine learning algorithms, like neural networks or reinforcement learning, to enhance the accuracy and adaptability of the evaluation process. This would lead to more personalized hotel recommendations, better decisionmaking support for users, and the ability to continuously improve the system based on evolving trends and user preferences.


