Automatic Ration Material Distributions Based on GSM and RFID Technology
Автор: S.Valarmathy, R.Ramani, Fahim Akhtar, S.Selvaraju, G.Ramachandran
Журнал: International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications(IJISA) @ijisa
Статья в выпуске: 11 vol.5, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Now a day ration card is very important for every home and used for various field such as family members details, to get gas connection, it act as address proof for various purposes etc. All the people having a ration card to buy the various materials (sugar, rice, oil, kerosene, etc) from the ration shops. But in this system having two draw backs, first one is weight of the material may be inaccurate due to human mistakes and secondly, if not buy the materials at the end of the month, they will sale to others without any intimation to the government and customers. In this paper, proposed an Automatic Ration Materials Distribution Based on GSM (Global System for Mobile) and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology instead of ration cards. To get the materials in ration shops need to show the RFID tag into the RFID reader, then controller check the customer codes and details of amounts in the card. After verification, these systems show the amount details. Then customer need to enter they required materials by using keyboard, after receiving materials controller send the information to government office and customer through GSM technology. In this system provides the materials automatically without help of humans.
Microcontroller, GSM, RFID, Motor, Solenoid Control Circuits, Mechanical Part
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15010489
IDR: 15010489
Текст научной статьи Automatic Ration Material Distributions Based on GSM and RFID Technology
Published Online October 2013 in MECS
The most of the people having a ration card to buy the materials from the ration shops. When get the material from the ratio shop, first need to submit the ration card and they will put the sign in the ratio card depends on the materials. Then they will issue the materials through weighting system with help of human. But in this system having two draw backs, first one is weight of the material may be inaccurate due to human mistakes and secondly, if not buy the materials at the end of the month, they will sale to others without any intimation to the government and customers. In this paper, we have proposed an Automatic Ration Materials Distribution Based on GSM and RFID Technology to avoid the drawbacks. Today we are facing a number of transport related problems. RFID technology effectively used to solve some of them. RFID is act as ratio card and other purpose such as RC book, insurance details, service details etc. GSM used to communicate the information between the two people or more than two persons to update the information depends on the requirements.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) based accesscontrol system allows only authorized or responsible persons to get the materials from ration shops. An RFID system consists of an antenna or coil, a transceiver (with decoder) and a transponder (RF tag) electronically programmed with unique information. There are many types of RFID systems available in the market. RFID classified based on their frequency ranges. Some of the most commonly used RFID kits are low-frequency (30-500 kHz), mid-frequency (900 kHz-1500MHz) and high-frequency (2.4-2.5GHz)[1]. The passive tags are lighter and less expensive than active tags [2].
Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is a common European mobile telephone standard for a mobile cellular radio system operating at 900 MHz. In the current work, SIM300 GSM module is used. The SIM300 module is a Triband GSM/GPRS solution in a compact plug in module featuring an industry-standard interface. It delivers voice, data and fax in a small form factor with low power consumption [3, 4].
In this paper, we have designed and implemented an Automatic Ration Materials Distribution Based on
-
II. Related Works
Today mobile phone is one of the most important devices for every one that is used in communication purpose and used in embedded system to control the devices. In [5], the RFID based Bill Generation and Payment through Mobile system is implemented. In this paper, the bill generating in super market using RFID technology and payment through mobile phone. Mobile payments will become one of the most important mobile services. The most essential consideration is the security of the mobile devices and the applications along with the complexity of imbursement process. Advantages of this system, i) Increased consumer confidence, leading to increased sales. ii) Benefit for both consumers and merchants.
The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) emerges as one of the converging technologies and transportation plays a vital role in urbanization. RFID plays major role in auto ID applications like RFID contact less smart cards used by bus riders, in Super market, Textiles and logistics chain management. In [6], the RFID Based Embedded System for Vehicle Tracking and Prevention of Road Accidents system is designed and implemented. This system is may be to reduce the road accident in Indian roads.
In [7], the RFID Based Exam Hall Maintenance System presents an efficient method of examination hall management. This system is possible for a student to identify the particular exam hall from any other hall, when they swipe RFID card in a card reader located there. This helps them to identify the floor or get directions to their respective halls immediately. The card reader is provided at the entrance of the building, if the students enters wrongly a buzzer alarm sets off, otherwise the room number is displayed on the LCD, connected to controller. RFID technology is emergent technology that can be used in wide range of applications.
In today’s, power saving are very important and difficult. Even though there are many power generation methods available, but it has become very difficult to generate the power due to insufficient resources. Power saving is necessary for our society, [8] this paper discussed about the power saved in the streetlights. The key objective is to control the streetlights using Dual Tone Multi Frequency (DTMF). If any over load occurs, the connection disconnected and the information transferred to EB through Global System for Mobile communication (GSM). If it is any complaint by the consumers, they can send the information to EB through Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Reader, which is fixed in one of the street light posts and the tag provided to the all consumers. The messages send to EB server through GSM. Advantage of this system, power consumption is very less, power failure period reduced.
Motor for sugar or rice
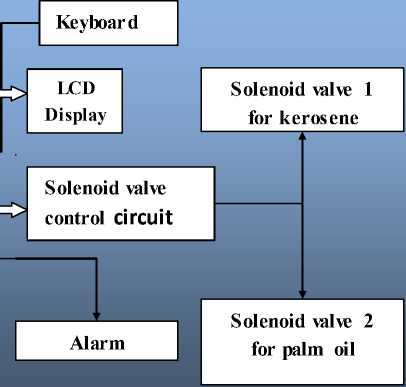
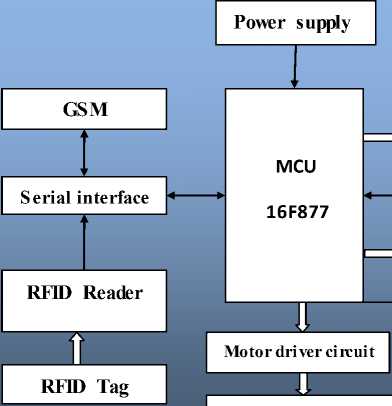
Fig. 1: Block diagram of ration materials distributions system
-
III. Proposed methods3.1 Block Diagram
-
3.2 Power Supply Circuit Diagram
-
3.3 Microcontroller Circuit
The block diagram of an Automatic Ration Materials Distribution Based on GSM and RFID Technology is shown in the Fig. 1. This system consists of various parts such as RFID, GSM, microcontroller, motor driver, solenoid control circuits and keyboard.
The power supply most important for electronic circuits, which is provide the required power to microcontroller and other electronics devices. The power supply circuit diagram is shown in the Fig. 2.
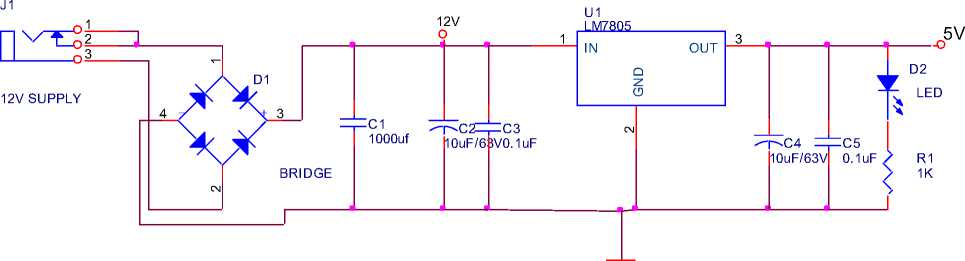
Fig. 2: Power supply
Microcontroller is the heart of the ration materials distribution system. There are used various application such as automatically controlled products, automobile engine control systems, to control medical devices, remote controls, printer, scanner, office machines, appliances, power tools, toys and other embedded systems. The size and cost of the microcontroller are less. The microcontroller circuit diagram is shown in the Fig. 3. The 12 MHz crystal oscillator is used to provide the required clock signals to the microcontroller.
5V
R2 4.7K
4 7K
J3
CON9
NP
SW1 C6
10uF/63V
5V о
U2
PIC16F877A
5V о
RA0
MCLR
RA1
RA2
RA3
RA4
RA5
RE0
RE1
RE2
CAP
RC0
RC1
RC2
RC3
Y

MCLR RA0 RA1 RA2 RA3 RA4 RA5 RE0 RE1 RE2 VDD VSS
OSC1 OSC2 RC0 RC1 RC2 RC3 RD0 RD1
RB7
RB6
RB5
RB4
RB3
RB2
RB1
RB0
VDD VSS RD7 RD6 RD5 RD4 RC7 RC6 RC5 RC4 RD3 RD2
RB7
RB6
RB5
RB4
RB3
RB2
RB1
RB0
J2
J5
5V
CAP NP C9 CAP NP
C10
RD7
RD6
RD5
RD4
RC7
RC6
RC5
RC4
RD3
RD2
5V
AP
NP
C7
J4 CON9
-
Fig. 3: Microcontroller circuit
3.4 GSM and RFID Circuit
RFID stands for Radio-Frequency Identifications. The RFID is small electronic device that consist of a small chip and an antenna. The chip typically is capable of carrying 2,000 bytes of data or less. A significant advantage of RFID devices above the others devices, RFID device does not require to positioned precisely relative to the scanner. The RFID devices will work within a few feet (up to 20 feet for high-frequency devices) of the scanner. The RFID tag used to read information about the customer through RFID Reader. The GSM used to send the SMS to the customer as well as government authorized person for the verification. The circuit diagram of RFID and GSM is shown in the Fig. 4.
screen is more energy efficient than a CRT. The power consumption is very low while compare with other devices. The LCD circuit diagram is shown in the Fig. 5.
P1
О.
О—
О.
о-- о.
о— о.
о—
о.
5V
CON16
Fig. 5: LCD display circuit
10uf /35v C12
U3

C11
CAP NP
C+
10uf /35v 5
V+
C2+
C2-
R1IN R2IN
C-
V-
MAX232
R1OUT R2OUT
T2OUT
T1OUT Z о
T2IN T1IN
3 I 10uf/35v

C15
TX
RC6
RC7
GSM Interf ace P1
о.
О— о.
О—
О.
о— о.
о— о.
3.6 Motor with Driver Circuit
The motor driver circuit is used to provide proper matching between motor and circuits.
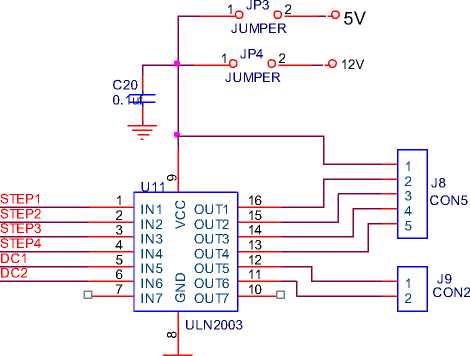
Fig. 6: Motor driver circuit
RFID Interf ace
-
Fig. 4: GSM and RFID circuit
-
3.5 LCD Display
-
3.7 Relay with Solenoid Valve
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly.
The LCD is used in a wide range of applications including computer monitors, televisions, instrument, aircraft cockpit displays, and signage. The most common in consumer devices such as video players, gaming devices, clocks, watches, calculators, and telephones, and have replaced cathode ray tube (CRT) displays in most applications. The LCD
A solenoid value is an electromechanically operated valve. The valve is controlled by an electric current through a solenoid, in the two-port valve the flow is switched on or off, in the three-port valve, the outflow is switched between the two outlet ports. Multiple solenoid valves can be placed together on a manifold. Solenoid valves are the most frequently used control elements in fluidics. Their tasks are to shut off, release, dose, distribute or mix fluids. They are found in many application areas. Solenoids offer fast and safe switching, high reliability, long service life, good medium compatibility of the materials used, low control power and compact design. The circuit diagram of the solenoid valve is shown in the Fig. 7.
12V
R21
^1K/' 2
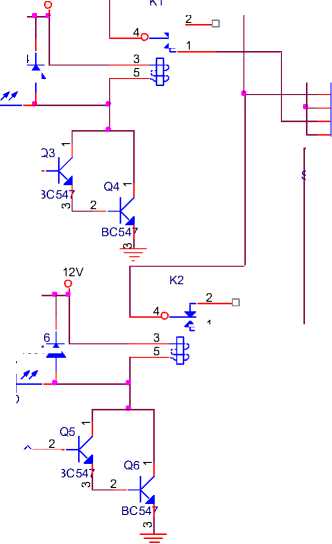
♦ 1
SOLENIID CON
R23
1K /^
-к
LED
Fig .7: Relay circuit
R20 R
D14
IN 4001
D15
-к
LED
REL1N
R22 R

REL2N
D1
IN 4001
D17
-
IV. Result and discussion
The Automatic Ration Materials Distribution Based on GSM and RFID Technology used to distribute or vend the liquid or solid material, which is used for Ration materials distribution in ration shops. Initially everyone will be provided an RFID or smart Card, instead of a ration card. If the customer needs to get any ration material, the user has to show the ration RFID tag card to the RFID reader Kit, the reader that is incorporated with the project kit will recognize the RFID numbers show by the user. Each user will have a unique number, which is not visible to the user.
Once the user is identified, the microcontroller will check whether the user has already bought the ration item belongs to that month. If not then, ration items to be dispensed will be displayed on the LCD screen, the user has to feed the comments that which ration item he is going to buy. If the user, select the ration item for purchasing purposes then the controller will calculate the amount of his or her buy and check with the amount available in the RFID card. If he or she has sufficient amount to buy then the micro controller will start the solenoid and motor mechanis m to dispense the selected ration item. As the dispensing process is going on simultaneously in the controller will send a command to GSM Modem, to send the text SMS to the user about the ration item, he or she purchased. Before starting the process the amount of the item to be dispensed has to be calibrated separately then the only controller will dispense the correct quantity of ration item selected.
Table 1: Comparative study of existing and proposed locker system
|
S. No |
Existing system |
Proposed system |
|
1 |
Ration sheets used |
RFID tag act as ration card |
|
2 |
Ration materials distributed with the help of humans |
Ration materials distributed automatically without the help of humans |
|
3 |
Inaccurate |
Accurate |
Output Results
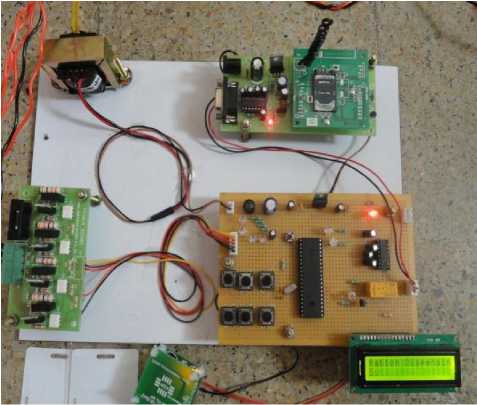
Fig. 8: Ration materials distribution kit

Fig. 9: Overall ration distribution system with mechanical parts

Fig. 10: Show your ID card
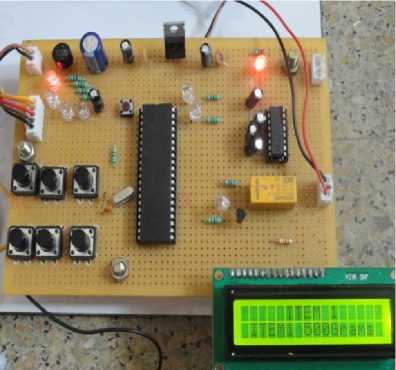
Fig. 13: 500 Grams selection
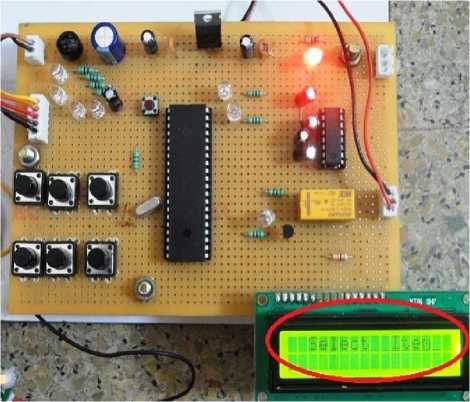
Fig .11: Items selection from system

Fig. 14: 250 Grams selection
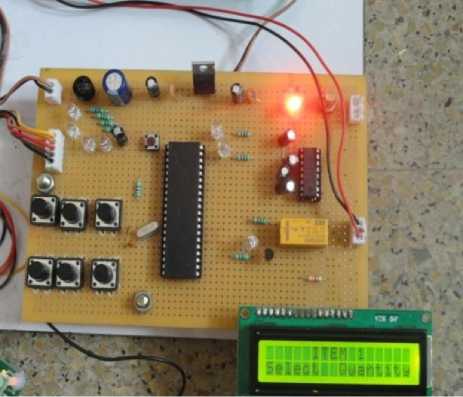
Fig. 12: Items selection
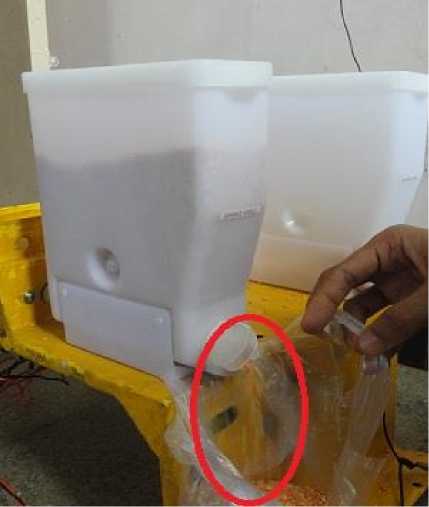

Fig. 15: Materials drawn from system
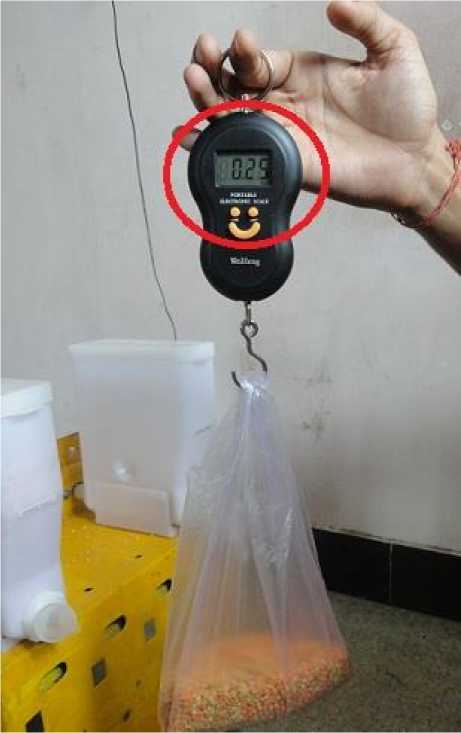

Fig. 16: Quantity verified through weight meter
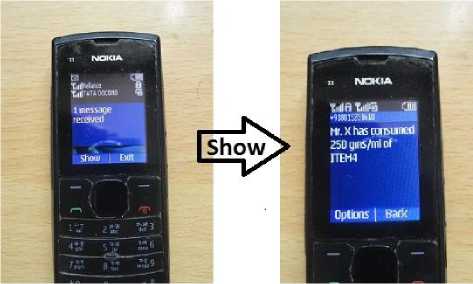
Fig. 17: Customer and Government office received Message from microcontroller after materials drawn from system
-
V. Conclusion
In this paper, we have implemented and tested an Automatic Ration Materials Distribution Based on GSM and RFID technology instead of ration cards. But in the existing system having two draw backs, first one is weight of the material may be inaccurate due to human mistakes and secondly, if not buy the materials at end of the month, they will sale to others without any intimation to the government and customers. The above drawbacks rectified by this method. In this system, ration Materials (sugar, rice, oil, kerosene, etc) distributed through automatic mechanism without any help of humans. After receiving the materials, controller sends the information to government office and customer through GSM technology. This system is very accurate, simple and low power consumption, which is used for the real time applications.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their careful reading of this paper and for their helpful comments to improve the paper.
Список литературы Automatic Ration Material Distributions Based on GSM and RFID Technology
- Parvathy A, Venkata Rohit Raj, Venumadhav, Manikanta, “RFID Based Exam Hall Maintenance System’’, IJCA Special Issue on “Artificial Intelligence Techniques - Novel Approaches & Practical Applications” AIT, 2011
- Gyanendra K Verma, Pawan Tripathi, “A Digital Security System with Door Lock System Using RFID Technology”, International Journal of Computer Applications (IJCA) (0975 – 8887), Volume 5– No.11, August 2010
- Kumar Chaturvedula .U.P, “RFID Based Embedded System for Vehicle Tracking and Prevention of Road Accidents”, International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) , Vol. 1 Issue 6, August – 2012, ISSN: 2278-0181.
- R.Ramani ,S. Selvaraju, S.Valarmathy, P.Niranjan, “Bank Locker security System Based on RFID and GSM Technology”, International Journal of Computer Applications (IJCA) (0975 – 8887) Volume 57– No.18, November 2012
- Swati R.Zope, Prof. Maruti Limkar, “RFID based Bill Generation and Payment through Mobile”, International Journal of Computer Science and Network (IJCSN) Volume 1, Issue 3, June 2012 www.ijcsn.org ISSN 2277-5420
- Kumar Chaturvedula .U.P, “RFID Based Embedded System for Vehicle Tracking and Prevention of Road Accidents”, International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) Vol. 1 Issue 6, August - 2012 ISSN: 2278-0181
- Parvathy A, Venkata Rohit Raj Gudivada, Venumadhav Reddy M, Manikanta Chaitanya.G, “RFID based exam hall maintenance system”, IJCA Special Issue on “Artificial Intelligence Techniques - Novel Approaches & Practical Applications” AIT, 2011
- Rubananth, T.Kavitha, “GSM based RFID approach to Automatic Street Lighting system”, journal of theoretical and applied information technology 30th april 2012. Vol. 38 no.2, ISSN: 1992-8645.


