Balinese historian chatbot using full-text search and artificial intelligence markup language method
Автор: Kadek Teguh Wirawan, I. Made Sukarsa, I. Putu Agung Bayupati
Журнал: International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications @ijisa
Статья в выпуске: 8 vol.11, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In the era of technology, various information could be obtained quickly and easily. The history of Bali is one of the information that could be obtained. Balinese have known their history through Babad and stories which are told through generations. Babad is traditional-historical writing which tells important event that has happened. As technology evolves, Balinese’s interest in studying their own history has been decreased. It is caused by people interest in studying history books and chronicles tend to decrease over time. Therefore, an innovation of technology, which able to convert historical data from printed media to digital media, is needed. The technology that could be used is Chatbot technology; a computer program that could carry out conversations. Chatbot technology is used to make people learning history easily by using Instant Messenger LINE as a platform to communicate. This Chatbot uses two methods, namely the Artificial Intelligence Markup Language method and the Full-Text Search method. The Artificial Intelligence Markup Language method is used as the process of making characteristic of questions and answers. The Full-Text Search method is the process of matching answers based on user input. This chatbot only uses Indonesian to communicate. The results of this study are a Chatbot that could be accessed by using Instant Messenger LINE and could communicate like historian expert.
Balinese History, Chatbot, Full-Text Search, Artificial Intelligence Markup Language, Instant Messenger LINE
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15016613
IDR: 15016613 | DOI: 10.5815/ijisa.2019.08.03
Текст научной статьи Balinese historian chatbot using full-text search and artificial intelligence markup language method
Published Online August 2019 in MECS
Information is an important part of life, which is expected to be obtained faster [1]. Various types of information could be obtained relatively quick and easy today; one of them is information about the history of Bali. Balinese had known their traditional history (Babad) which generally talks about certain clan (Soroh) and is decorated with mystical things.
Babad is traditional-historical writing that tells important event that has happened. In addition of Babad , the existence of history books of Bali could help to increase knowledge into history that has ever existed in Bali; but in this modern era, Balinese’s understanding of its history is still lacking.
The decreased understanding is caused by the lack of interest in learning about Balinese from Babad and other Bali historical-related books. Lontar expert and founder of the Hanacaraka Society, Sugi Lanus, stated that most Balinese had knowledge derived from Ancient Indian, but many of them could not read lontar and do not understand the meaning of Sanskrit. Lontar is traditional writing with palm leaves as a medium containing mantra, tradition, or summary of important events. He also added that the lontar in Bali that now still existed was not fully explained because there were missing pages or the transfer of knowledge was inadequate and the language itself is an obstacle. Asep Kembali, history and culture observant, explained awareness level of Indonesian to know and love their own history and culture have faded. There are many factors in society that caused this, such as the attitude of individuals in knowing history and culture, how to behave and how to respect and act on history itself. Based on these problems, an innovation that is able to convert historical data from printed media into digital media, that could be accessed anytime and anywhere, is needed.
One new innovation to get information is Chatbot technology. Chatbot technology is a form of Natural
Language Processing application that studies communication between human and computer through natural language. Chatbot will provide information about Balinese history from ancient Bali to the time of Dutch colonialism using LINE's instant messaging service. This Chatbot uses two methods, namely the Artificial Intelligence Markup Language method and the Full-Text Search method. The Artificial Intelligence Markup Language method is used as the process of making characteristic of questions and answers. The Full-Text Search method is the process of matching answers based on user input. The results of this study are a Chatbot that could be accessed by using Instant Messenger LINE and could communicate like historian expert.
The paper is organized as follows. In section 2, related work is described. Section 3 describes the research method by applying the system development life cycle method. The SDLC method that is applied is the waterfall model that starts from the study of literature, system design, system implementation, trials, discussions and improvements. Section 4 describes the method implementation in detail and also analyzes how the chatbot works from incoming messages to the answer search process. The analysis is done in 3 different scenarios with different messages that produce different answers. Finally, in section 5, the conclusions are drawn.
-
II. Related Works
Previous research related to the use of Chatbot as a communication medium and the use of the Full Text Search method and Artificial Intelligence Markup Language including Sam Goundar [2] revealed that the use of cellphones for accessing information would be more efficient and preferred for students, because students would prefer accessing information from home or place which they consider comfortable and do not need to go around only to find the desired information. This study concluded that the use of cell phones in the learning process may provide convenience for students and giving benefits to the school.
Haller and Rebedea [3] built a Chatbot application using a chat script. Chatscript uses rules or arrangement that contain labels, patterns, and outputs. The pattern is a condition that is used to filter input or question given according to the template in the database and if the question has been found then the next answer or output will be given in accordance with the knowledge that has been implanted. The results achieved in this journal, the chat script method used could work well by utilizing patterns and knowledge from Wikipedia and DBpedia .
Naem, Khalid and Hassan [4] revealed that Full-Text Search has several functions, namely Natural Language Full Text Search, Boolean Full-Text Search, Full-Text Search with Query Expansions, and others. The FTS algorithm consists of several steps, namely database initialization, connecting databases that include connecting strings with tables in the database, indexing FTS in tables and specifying indexes for FTS, and the latter matching text with the FTS index table so as to provide relevant results. The MySQL database supports Full-Text Searching by using two functions, namely MATCH and AGAINST.
Research conducted by Shah, Lahoti, and Lavanya [5] built a Chatbot application by modeling the bot-making process in several stages. The first stage is creating a database of all knowledge about general education. The second is making the same word cluster and frequently-used groups of words. The third is the use of Natural Language Processing (NLP) to interpret inputs and respond to questions given. Inputs are processed with simple steps such as dividing and sorting words and counting the number of searches for each word. The answer that is appropriate for the user is obtained by ranking and looking for the similarity of the score between the word and dataset in the database with NGram. After the answer is found, it will be given to the user. If the answer is less-expected than what the user wants, the bot could learn from the answers that have been modified by the user. This study concludes that the use of NLP and self-learning techniques could be good additional features to make Chatbot technology more human-like and also tend to provide promising results.
Khanna [6] revealed that Artificial Intelligence (AI) could create machines that could simulate human intelligence. This study shows how the current approach to AI; one typical example of an AI system is Chatbot. Chatbot has a separate section that is in charge of managing the transfer and understanding of messages between users (humans) and the AI system, there are also parts that hold keys/points during discussions, and there are parts in charge of handling errors. This research concludes that artificial intelligence could solve some of the main problems for humanity and artificial intelligence will be integrated with everyday human life.
Research conducted by Mhatre [7] applies web-based Chatbots as personal assistants from users who could manage user meetings with their clients via email. This research makes a program that is able to extract incoming e-mails in the user's account automatically by matching several keywords from the e-mail content and subject. Furthermore, the e-mail is read with the help of an algorithm such as pattern matching. The program will check it's user's schedule on a specific date and time from Google Calendar. Pattern matching is done with the O-Program which is part of Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning (AIML) which could be used in the Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP) programming language and uses the MySQL database to store Chatbot information, including AIML files used to store responses from Chatbots. This study concludes that by using the pattern matching algorithm, a system could act as a virtual personal assistant who could plan user work and schedule meetings.
Abushawar and Atwell [8] revealed that the pattern matching process uses the Artificial Intelligence Markup Language method done by matching words per word to get the most suitable pattern. This process is described in the Graphmaster rule which consists of several categories and patterns. This research builds a Java-based application that is able to form the AIML knowledge base automatically and is divided into 2 program versions. The first version is feature matching based on user input. This process begins with reading the text from the corpus and inserting it into a vector, then the pre-processing process which consists of the tokenization process (word solving), the stopword or filtering process (eliminating words that have no meaning) and stemming process (changing into word form basic), then specify the word into the pattern and template, and the last process is to save the pattern and template results into the AIML file. The second version is by making a more approach to the input from the user to get the most suitable answer. Modeling is prepared to map all traits that have the same response into one form and transfer all repetition of features with different templates into one form with a list of different responses.
Research conducted by Dole [9] implemented a webbased Chatbot application that was used as an information service for customer banks. The application uses the speech recognition method to convert voice input into a text form and the Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML) method to determine the appropriate answer. The process starts when the customer finishes giving questions through the microphone. The program carries out the speech recognition process in accordance with the input from the customer and turns it into text form. The process is continued with feature matching based on the
Nila and Afrianto [1] built a Chatbot application that is used as a medium for information on tourism objects in Bandung using the Natural Language Processing approach. This Chatbot application uses the Text Mining Method as its reasoning media. The system modeling used for this application is using the Unified Model Language (UML). This study provides three conclusions, first by using the Natural Language Processing approach in Chatbot applications, it will make conversations as if done between humans. Second, using the Text Mining Method as sentence reasoning will make it easier to search for keywords (pattern). Third, conversations conducted through Internet access will allow users to have conversations with Chatbots whenever and wherever.
The research conducted by Maskur [10] describes the making of Chatbot applications that are used as virtual assistants to make it easier for users to get information on students using the AIML method. Chatbot was created and formed through the process of supervised learning and the speech of the previous Chatbot. This research produces a system that could find answers in the ALICE database according to the questions entered by the user. The system will add new knowledge if the answer sought is not found in the ALICE database.
Azwary, Indriani and Nugrahadi [1] explained the making of Chatbot applications for media on academic information, staffing, student affairs and facilities at the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Unlam Banjarbaru using the Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML) method. The purpose of this study is to make it easier for users to find academic, staffing, student information and facilities available at the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Lambung Mangkurat University, Banjarbaru. The AIML method uses the template matching process, the process of determining answers based on certain characteristics that have been designed in the database. The design of the template begins with determining the information needed, then formed into a question that is adjusted to the shape of the pattern.
Suryani and Amalia [12] built an East Java tourist attraction information Chatbot application using a website-based Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML) method. This application aims to allow tourists to find out information about a tourist attraction in the East Java area by asking questions and answers to the system. The application consists of two interfaces, the admin interface which is used by administrators to add and process AIML data, while the user interface is used by users to communicate with the system. Determining the answer is done by matching the input from the user with the pattern in the database.
Paliwahet [13] says that matching the Full-Text Search Boolean Mode is different from ordinary matching. Matching with this method could produce the most relevant results. Patterns listed will affect the results to be issued in response. The more patterns registered, the higher the chances of finding the most relevant patterns.
Baiti and Nugroho [14] explain the making of expert system-based applications with the forward chaining method. The working system of this application is to break the order of sentences into words and then from the word by the system the keywords that make the application could answer correctly. The results of the implementation and trial concluded that the Expert System algorithm with the Forward Chaining Method is a good algorithm as the completion of the search process for answers based on keywords from user questions.
Bahartyan, Bahtiar and Waspada [15] developed a Chatbot application named EIVA (Edu4Indo Interactive Virtual Assistant) by utilizing Pandorabots' Artificial Intelligence Markup Language service. The purpose of making this application as a customer service provider for online bookstores edu4indo.com. The EIVA system consists of two interfaces namely an interface for customers and for administrators. The answer search process begins by correcting typing errors by the user using the Spellcheck function. Then use the Pandorabots function to retrieve the answer text which sometimes has a specially marked word. The word is a name to call other functions such as the Customer class to manage customer data and Prestashop classes to manage product data. The final results of the process are stored in the Response class along with inputting other answers.
Christiantho, Siswanto and Chaniago [16] developed a
Chatbot application that is used to help provide information at the Harapan Bangsa Institute of Technology on service operator services by applying the Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML) methods. The NER method is used to help recognize sentence patterns from the everyday human language which will later be used as keywords and the AIML method is used as a process of matching patterns according to the keywords found through the NER method. Knowledge-Based on this application could be added by using the Reversed AIML method which begins with preprocessing which consists of the tokenization process and spelling correction, then proceed with the process of entity classification which is the NER method to determine the words that will be used as entities (keywords). The next process is checking keywords that are found whether or not they are in knowledge-based. If it already exists, the knowledge-based will only be updated, if it does not exist, the category will be included in knowledge-based.
Dwi R [17] developed a Chatbot application called MILKI BOT that could help and facilitate UKM MINSU in increasing sales and managing their business easily. This application uses the forward chaining method so that the Chatbot will reason the input from the user before taking an answer to the conclusion. Reasoning on this application starts from the user's side from ordering to payment, followed by the administrator's side starting from order notification to assignment to courier and ending by the courier side starting from the delivery of goods to the updated shipping status.
Husaini [18] revealed that technological advances were very rapid, especially in the field of computers and information technology had a positive impact on society. The use of information technology in the education process could be developed through various ways such as designing and creating database applications, designing and creating web-based learning applications, optimizing the use of TV education and implementing systems in stages ranging from small to broad scopes so as to facilitate the management of information technology users in the education process.
Sukarsa, Darma Putra, Putra Sastra, and Lie Jasa developed a framework namely Information System on Internet Messenger (ISONER) [19]. This framework will replace every model of form-based service in website or mobile application. Through the chat service, users can perform the search function, input, edit, deletion of data and other functions such as an information system. Users can communicate using natural conversations in Indonesian language without being restricted by the use of special keywords.This model is expected to develop a low-cost access model on the side of system’s owners and users. They also developed a chatbot application act as a Sulinggih in consulting people about Balinese calendar [20]. This research used ISONER Framework that enabled two-way communication [19]. ISONER framework is modified as ESB that could communicate with various service systems based on SOA (Service Oriented Architecture). Modification done in ISONER framework developed receiver’s block in ISONER’s layer that could communicate with service of external business process that is built in programming languages including PL/SQL and Python
-
III. Methodology
In this study there are several steps to be taken by applying one of the system development life cycle methods, namely the Waterfall model illustrated in Figure 1, with the following description:
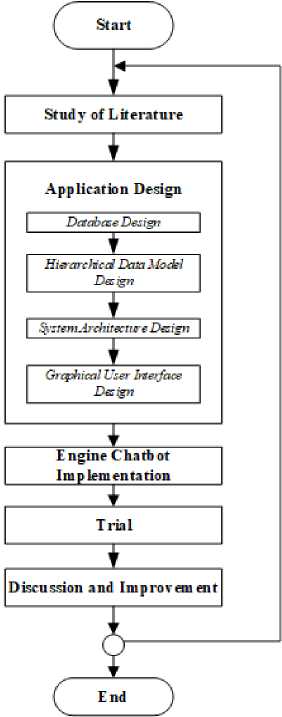
Fig.1. Research Method in Waterfall Model
-
A. Literature Study
This research was conducted to understand the various histories that have been occurred in Bali from the ancient Balinese period to the time of Dutch colonialism. Library studies are also directed to determine the dialogue model that is used to form the figure of a Balinese historian using the AIML algorithm.
-
B. Application Design
The application design process includes several parts such as:
-
1. The process of designing a database uses data normalization techniques and ERD (Entity
-
2. The process of designing the hierarchical data model is used to describe the relationship between data in the database. The data linkage is described in the form of a tree structure. Data depicted in the form of tree structure in the form of knowledge topics that exist in the database along with the sub topics that each topic has
-
3. The process of designing a system architecture is used to describe the application model being developed, including the integration between the Balinese historian Chatbot machine services and text-based teleconsulting services on LINE instant messenger.
-
4. The process of designing a Graphical User Interface (GUI) in LINE applications is done by adding a menu display to make it easier for users to communicate with bot services. The menu displayed is in the form of a royal list menu, a king list menu, a list of questions menu, a list of relics, a list of war menus and a help menu.
Relationship Diagram). This process is used to determine how many tables are needed as a data processing table and also as a final or temporary data store
-
C. Engine Chatbot Implementation
The implementation of the Bali Historian chatbot engine was carried out in 2 programming languages namely PL / SQL and Python. Implementation at the level of the Python programming language is carried out by the process of retrieving messages sent by the user and storing the message into a database which will then be processed using the PL / SQL programming language. In addition, the process of sending messages matching the pattern to the user is also carried out according to the user's ID. Implementation at the level of the PL / SQL programming language is done by transferring the results of the database design to the MySQL database engine. In MySQL, Full Text Search method is also applied for pattern matching.
-
D. Trial
The trial phase is carried out to ascertain whether the model design that has been applied can provide the correct results in accordance with the existing rules.
-
E. Discussion and Improvement
The discussion is useful to find out the extent to which a system that has been developed is able to solve a predetermined problem. In addition, it could also find out various errors found during testing so that system improvements could be made.
-
IV. Implementation and Analysis
-
A. Chatbot Architecture
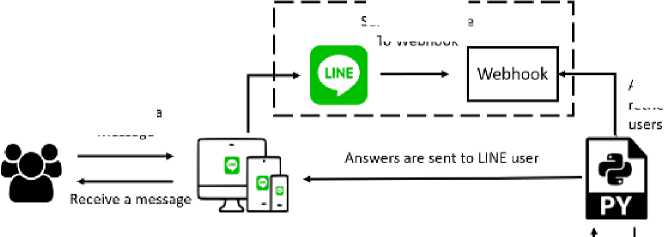
Balinese Historian Chatbot with the Full-Text Search Method and the Artificial Intelligence Markup Language is an artificial intelligence system that helps people, especially students, to know and learn about Bali's history by communicating directly through LINE's instant messaging application. The Chatbot technology that is applied is a program that could provide a smart response when communicating. Searching for answers from user questions is done by matching the knowledge traits that have been made before. The characteristic matching method used is the Full-Text Search method, which is a string matching technique that works through MySQL queries. Overall, this system works by receiving messages or questions sent via LINE application. The incoming message will be processed in several stages until it gets the appropriate answer. Answers will be sent back to the user via LINE application. The way the Balinese historian Chatbot works could be illustrated in the following Figure 2.
User Send a
Message
Sending Message To Webhook
Sending Message to LINE Server
The answer in the outbox table 1s taken by the Python engine
Access Web hook to retrieve messages from
Send messages to the database
AIMLandFull Text Search Method
Fig.2. General Illustration of the System
The following are explanations of the Chatbot flow in accordance with the general description.
-
1. Users should have a LINE account and add Bali Historian Chatbot account through LINE ID "@muu7502q".
-
2. Users who have added a Chatbot account could send questions related to the history of Bali.
-
3. LINE server is responsible for forwarding messages from users to the domain webhook that has been verified during the process of creating Chatbot on LINE Developer services. In the domain, there is a folder that is used to hold the user’s messages sent by the LINE server.
-
4. The Python Engine accesses the folder on the server to get the user’s message files in JSON form. The file will be decoded so that it gets the message content and user ID from the user. Then, the message and user ID will be saved in the database.
-
5. The MySQL engine will run the pattern matching process using the Full-Text Search method based on the knowledge pattern that has been created using AIML method. The sequence of use of AIML and Full-Text Search methods is described in Figures 3 and 4.
-
6. The Python Engine will retrieve the contents of the last table in the exit table in the form of message content and user ID. Then send the contents of the answer message to LINE users based on the user ID that was taken previously.
In the pattern matching process, the AIML method is used for pattern making and template processes, while the Full-Text Search method is used for pattern matching processes. Figures 3 and 4 are the outline of the use of the method in broad outline and in detail.
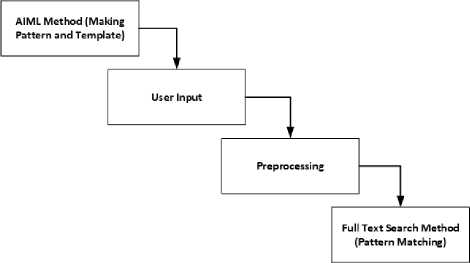
Fig.3. The flow of Methods Usage
The following are explanations of AIML dan Full-Text Search in the outline pattern recognition process.
-
1. The AIML method is used to create question characteristics (patterns) and answers to these questions (templates) based on Balinese history books that are used as a reference.
-
2. Users send messages via LINE instant messaging which are then processed in the database.
-
3. Messages that have been stored in the database will go through the preprocessing process. This process is used to find keywords from messages which are then matched with patterns in the database.
-
4. The Full-Text Search method is used for the process of matching patterns based on the set of keywords obtained from the preprocessing results.
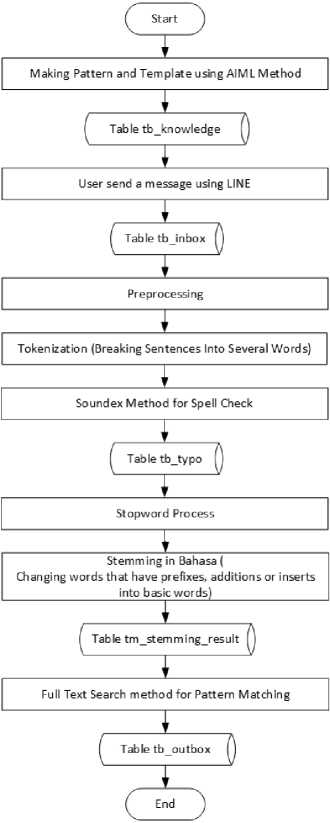
Fig.4. AIML and Full-Text Search Method Flowchart
The following are explanations of the flow of using the AIML method and Full-Text Search in the detailed pattern recognition process.
-
1. The application of the AIML method is carried out in the process of making question characteristics (patterns) and answers to these features (templates). The results of making the feature and the answer are stored in the table tb_knowledge.
-
2. Then when the user sends a message, the message will be stored in the tb_inbox table. The message that has been stored in the tb_inbox table will be processed to get the response from the bot.
-
3. Processing the message begins with the preprocessing process which consists of the
-
4. The tokenization process is carried out by breaking the user's message sentence into several words while removing the punctuation in the sentence.
-
5. Before proceeding to the stopword process, the spelling results obtained from the tokenization result will be used using the Soundex method. The use of the Soundex method is done by changing the word tokenization results in a Soundex code form. Then the word that has been changed will be matched with a list of correct words that have also been changed to Soundex. The list of correct words is stored in the tb_typo table.
-
6. After the spell checking process is complete, the next step is to change the word into a basic word form if it still contains the prefix, insertion or stemming. The results of the stemming process will be stored in the tm_hasil_stemming table which will be used in the process of matching the
Table 1. Implementation of Pattern and Template Usage.
No
Pattern (Preproceesing)
Pattern
Template
1
Raja pertama raja warmadewa
Siapakah raja pertama kerajaan Warmadewa?
Raja pertama Kerajaan Warmadewa adalah Sri Kesari Warmadewa
2
Tahun kuasa raja sri ugrasena
Dari tahun berapakah berkuasa raja Sri Ugrasena ?
Raja Sri Ugrasena berkuasa dari tahun 837 Saka sampai dengan 864 Saka
3
Isi prasasti blanjong
Apa isi dari prasasti Blanjong ?
Prasasti Blanjong berisikan cikal bakal munculnya raja pertama Warmadewa yaitu Sri Kesari Warmadewa
4
Gelar raja sri ugrasena
Apa gelar dari raja Sri Ugrasena ?
Raja Sri Ugrasena memiliki gelar “Sang Ratu Sang Dewata”
5
Sebab perang puputan badung
Apa penyebab adanya perang Puputan Badung ?
Perang Puputan Badung diakibatkan oleh Belanda ingin mengambil 2 kapal miliknya dan Bali tidak menyetujuinya karena adanya hak tawan karang
matching.
-
7. The process is followed by matching the characteristics of the tb_ knowledge table. A list of stemming words will be combined into one and is considered a keyword. These keywords will be matched with the characteristics of knowledge questions in the tb_peng Knowledge table using the Full-Text Search method. The result of matching in response to the bot answer will be saved in the tb_outbox table.
-
B. Design of Artificial Intelligence Markup Language Method
tokenization process (breaking sentences into several words), stopword (deletion of words that have no meaning), and stemming (changing words that have prefixes, affixes, and endings into basic words).
The pattern formation begins with summarizing the questions and answers related to the reference book. Questions that could be summarized in the reference book include royal history, royal life, relics, people's lives, war, and terms. The pattern column alias is a summary of the questions and the answer column is the answer to the summary of the question. The summary of questions will be processed with preprocessing to discard the word stopword and change it into basic words. The pattern column (preprocessing) is the result of the preprocessing process in the alias pattern column. The pattern column (preprocessing) will be used as a character matching keyword based on user input.
C. Design of Full-Text Search Method
The use of the Full-Text Search method in the Bali Historian Chatbot lies in the pattern matching process based on user input after the pre-processing process is done. The search type used in the full-text search method is search using IN BOOLEAN MODE in certain patterns such as "King three" with "King thirteen" because it is able to add or remove one or more words to match characteristics.
The use of the Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML) method on the Bali Historian Chatbot lies in the pre-processing process which includes tokenization, stopword and stemming. The AIML method is also applied to the process of creating a knowledge base by applying patterns or shapes from a user's response and templates or forms of answers to a pattern or user response. Table 3.3 is an example of using patterns and templates that are implemented in the knowledge base.
mysql> SELECT id_pengetahuan, pertanyaan_alias,
-> MATCH(pertanyaan) AGAINST('raj a warmadewa tiga -belas'
-
-> IN BOOLEAN MODE) AS score
-
-> FROM tb_pengetahuan ORDER BY score DESC LIMIT 2;
I id I pertanyaan I skor I
I 1__L Siapakah raja ketiga Warmadewa I 5.190447 1
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Fig.5. Implementation of Full-Text Search with IN BOOLEAN MODE
-
D. Chatbot Display
The Chatbot application uses the LINE interface to communicate. The Chatbot interface makes it easy for users to interact with the Chatbot system. Interactions that could be done by Chatbot on users, namely, interaction of the search interface, welcome interface, chat interface, ambiguity interface, error handling interface and menu interface Communication could be done by adding a Chatbot account with the name ID “@muu7502q” as a friend. Figure 6 shows a Chatbot account search on the LINE application.
Fig.6. Search Interface
Fig.8. Menu Interface
LINE users type the ID name of the Chatbot in the search field to be able to communicate. Press the add button and the user could communicate with the bot.
The chat interface is the main part of the Chatbot where all text input sent by the user could be delivered to the Chatbot and the Chatbot could provide the best answer from his knowledge. Figure 7 displays communication between users and Chatbots in the chat interface.
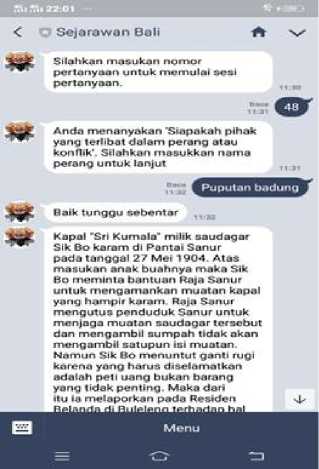
Fig.7. Chat Interface
Chatbot searches appropriate answers through hundreds of rules stored in the database. Chatbot could send text messages. Chatbot provides services in the form of a display menu containing lists of kingdoms, kings, wars and terms, relics, help, and lists of question patterns to users. This menu helps users if they want to ask something that can be found by Chatbot or add the meaning of a question that is still ambiguous. Figure 8 is a display from the interface menu.
Users could search the list of kingdoms, kings, wars and terms, relics, help and list of question patterns by pressing one of each icon.
-
E. Chatbot Tryout Result
Testing is done by giving questions related to the Balinese history module. The response given by the Chatbot to questions from users will be analyzed to find out whether the response is appropriate or not. The assessment was carried out by the recall, precision, and accuracy tests of 704 information in the database. Tests are carried out as many as 20 queries with the limit of data retrieval by the system (Threshold) as many as 10, 20 and 50 data.
Table 2. Tryout Query
|
ID |
Query |
|
1 |
Siapakah raja pertama kerajaan Warmadewa? |
|
2 |
Dari tahun berapa Raja Sri Kesari Warmadewa berkuasa? |
|
3 |
Gelar raja |
|
4 |
Berapa umur tahun prasasti blanjong? |
|
5 |
Siapakah anak dari Raja Sri Dharmodayana Warmadewa |
|
6 |
Apa saja kebijakan yang dikeluarkan oleh Raja Anak Wungsu |
|
7 |
Apa saja nama prasasti yang dikeluarkan oleh Raja Marakatta? |
|
8 |
Siapakah raja yang berkuasa sebelumnya? |
|
9 |
Apa saja prasasti yang dikeluarkan oleh Raja Anak Wungsu? |
|
10 |
Bagaimana sejarah kemunculan suatu kerajaan? |
|
11 |
Prasasti tertua di kerajaan Warmadewa |
|
12 |
Apa itu Banjar? |
|
13 |
Raja ke3 kerajaan Warmadewa siapa? |
|
14 |
Apa gelar raja pertama Kerajaan Warmadewa? |
|
15 |
Raja terburuk di Kerajaan Warmadewa siapa? |
|
16 |
Lama berkuasa Raja Warmadewa |
|
17 |
Siapakah raja pertama kerajaan klungkung? |
|
18 |
Siapa nama ibu Sri dharma udayana warmadewa |
|
19 |
Bagaimana penyebab terjadinya perang ? |
|
20 |
Raja termuda di Kerajaan Klungkung siapa? |
TP, TN, FP, and FN are used as terms for accuracy, recall, and precision [21].
-
1. TP represents the total object that is predicted as positive and actually positive.
-
2. TN represents the total object that is predicted as negative and actually negative.
-
3. FP represents the total object that is predicted as positive but actually negative.
-
4. FN represents the total object that is predicted as negative but actually positive.
-
a. The result of Recall Test
The recall is the ability of a system to call or get back documents that are relevant or match with user's will from the database. Equation 1 is applied to get the recall score.
TP
R /PP + FN
The following is the result of the recall test based on 20 tryout queries.
Table 3. Result of Recall Test
|
ID |
Threshold = 10 |
Threshold = 20 |
Threshold = 50 |
||||||
|
TP |
FN |
R |
TP |
FN |
R |
TP |
FN |
R |
|
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
2 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
3 |
10 |
34 |
0,23 |
20 |
24 |
0,45 |
44 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
4 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
5 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
6 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
7 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
8 |
10 |
29 |
0,26 |
20 |
19 |
0,51 |
39 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
9 |
3 |
0 |
1,00 |
3 |
0 |
1,00 |
3 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
10 |
3 |
0 |
1,00 |
3 |
0 |
1,00 |
3 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
11 |
10 |
48 |
0,17 |
20 |
38 |
0,34 |
50 |
8 |
0,86 |
|
12 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
13 |
10 |
29 |
0,26 |
20 |
19 |
0,51 |
39 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
14 |
10 |
35 |
0,22 |
20 |
25 |
0,44 |
38 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
15 |
10 |
38 |
0,21 |
20 |
28 |
0,42 |
48 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
16 |
5 |
0 |
1,00 |
5 |
0 |
1,00 |
5 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
17 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
18 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
1 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
19 |
8 |
0 |
1,00 |
8 |
0 |
1,00 |
8 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
20 |
10 |
13 |
0,43 |
20 |
3 |
0,87 |
23 |
0 |
1,00 |
Based on tryout of 20 queries with 10, 20, and 50 thresholds, it could be concluded that the higher the threshold is given, the more relevant the data that possibly found by the system; recall score is increasing. It is caused by data that are actually relevant but are not able to be retrieved by the system because of the threshold amount that is given. Graphic of the recall test result is shown in figure 9.
1,2 00,,681 00,,24
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19
Threshold 10 Threshold 20 Threshold 50
-
Fig.9. Graphic of Recall Test Result
-
b. The result of the Precision Test
Precision is the ability of a system to prevent the irrelevant document from the database to be given to users. Equation 2 is applied to get the precision score.
TP
P = /TP + FP
The following is the result of the precision test based on 20 tryout queries.
Table 4. Result of Precision Test
|
ID |
Threshold = 10 |
Threshold = 20 |
Threshold = 50 |
||||||
|
TP |
FP |
P |
TP |
FP |
P |
TP |
FP |
P |
|
|
1 |
1 |
9 |
0,10 |
1 |
19 |
0,05 |
1 |
49 |
0,02 |
|
2 |
1 |
9 |
0,10 |
1 |
19 |
0,05 |
1 |
49 |
0,02 |
|
3 |
10 |
0 |
1,00 |
20 |
0 |
1,00 |
44 |
6 |
0,88 |
|
4 |
1 |
9 |
0,10 |
1 |
19 |
0,05 |
1 |
49 |
0,02 |
|
5 |
1 |
9 |
0,10 |
1 |
19 |
0,05 |
1 |
49 |
0,02 |
|
6 |
1 |
9 |
0,10 |
1 |
19 |
0,05 |
1 |
49 |
0,02 |
|
7 |
1 |
9 |
0,10 |
1 |
19 |
0,05 |
1 |
49 |
0,02 |
|
8 |
10 |
0 |
1,00 |
20 |
0 |
1,00 |
39 |
11 |
0,78 |
|
9 |
3 |
7 |
0,30 |
3 |
17 |
0,15 |
3 |
47 |
0,06 |
|
10 |
3 |
7 |
0,30 |
3 |
17 |
0,15 |
3 |
47 |
0,06 |
|
11 |
10 |
0 |
1,00 |
20 |
0 |
1,00 |
50 |
0 |
1,00 |
|
12 |
1 |
9 |
0,10 |
1 |
19 |
0,05 |
1 |
49 |
0,02 |
|
13 |
10 |
0 |
1,00 |
20 |
0 |
1,00 |
39 |
11 |
0,78 |
|
14 |
10 |
0 |
1,00 |
20 |
0 |
1,00 |
38 |
12 |
0,76 |
|
15 |
10 |
0 |
1,00 |
20 |
0 |
1,00 |
48 |
2 |
0,96 |
|
16 |
5 |
5 |
0,50 |
5 |
15 |
0,25 |
5 |
45 |
0,10 |
|
17 |
1 |
9 |
0,10 |
1 |
19 |
0,05 |
1 |
49 |
0,02 |
|
18 |
1 |
9 |
0,10 |
1 |
19 |
0,05 |
1 |
49 |
0,02 |
|
19 |
8 |
2 |
0,80 |
8 |
12 |
0,40 |
8 |
42 |
0,16 |
|
20 |
10 |
0 |
1,00 |
20 |
0 |
1,00 |
23 |
27 |
0,46 |
Based on tryout of 20 queries with 10, 20, and 50 thresholds, it could be concluded that the higher the threshold is given, the more chance of irrelevant document will be given by the system; the precision score is lowering. The cause is the given relevant data are less than the irrelevant. Graphic of the precision test result is shown in figure 10.
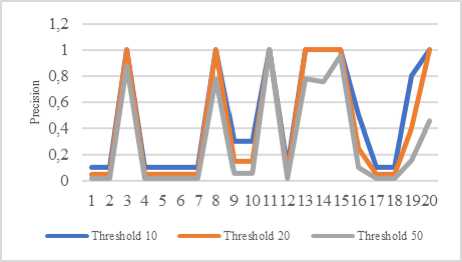
Fig.10. Graphic of Result of Precision Test
-
c. The result of the Accuracy Test
Accuracy is an exactness percentage of a system related to finding the relevant document from the database desired by the user. Equation 3 is applied to get the precision score.
TP + TN + FP + FN
The following is the result of the accuracy test based on 20 tryout queries.
Table 6. Result of Accuracy Test with Threshold = 20
|
ID |
TP |
FN |
FP |
TN |
ACC |
% |
|
1 |
1 |
19 |
0 |
684 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
2 |
1 |
19 |
0 |
684 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
3 |
20 |
0 |
24 |
660 |
0,966 |
96,59% |
|
4 |
1 |
19 |
0 |
684 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
5 |
1 |
19 |
0 |
684 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
6 |
1 |
19 |
0 |
684 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
7 |
1 |
19 |
0 |
684 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
8 |
20 |
0 |
19 |
665 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
9 |
3 |
17 |
0 |
684 |
0,976 |
97,59% |
|
10 |
3 |
17 |
0 |
684 |
0,976 |
97,59% |
|
11 |
20 |
0 |
38 |
646 |
0,946 |
94,60% |
|
12 |
1 |
19 |
0 |
684 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
13 |
20 |
0 |
19 |
665 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
14 |
20 |
0 |
25 |
659 |
0,974 |
97,44% |
|
15 |
20 |
0 |
28 |
656 |
0,960 |
96,02% |
|
16 |
5 |
15 |
0 |
684 |
0,979 |
97,87% |
|
17 |
1 |
19 |
0 |
684 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
18 |
1 |
19 |
0 |
684 |
0,973 |
97,30% |
|
19 |
8 |
12 |
0 |
684 |
0,983 |
98,30% |
|
20 |
20 |
0 |
3 |
681 |
0,996 |
99,57% |
Table 5. Result of Accuracy Test with Threshold = 10
|
ID |
TP |
FN |
FP |
TN |
ACC |
% |
|
1 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
694 |
0,987 |
98,72% |
|
2 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
694 |
0,987 |
98,72% |
|
3 |
10 |
0 |
34 |
660 |
0,952 |
95,17% |
|
4 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
694 |
0,987 |
98,72% |
|
5 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
694 |
0,987 |
98,72% |
|
6 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
694 |
0,987 |
98,72% |
|
7 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
694 |
0,987 |
98,72% |
|
8 |
10 |
0 |
29 |
665 |
0,959 |
95,88% |
|
9 |
3 |
7 |
0 |
694 |
0,990 |
99,01% |
|
10 |
3 |
7 |
0 |
694 |
0,990 |
99,01% |
|
11 |
10 |
0 |
48 |
646 |
0,932 |
93,18% |
|
12 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
694 |
0,987 |
98,72% |
|
13 |
10 |
0 |
29 |
665 |
0,959 |
95,88% |
|
14 |
10 |
0 |
35 |
659 |
0,960 |
95,03% |
|
15 |
10 |
0 |
38 |
656 |
0,946 |
94,60% |
|
16 |
5 |
5 |
0 |
694 |
0,993 |
99,29% |
|
17 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
694 |
0,987 |
98,72% |
|
18 |
1 |
9 |
0 |
694 |
0,987 |
98,72% |
|
19 |
8 |
2 |
0 |
694 |
0,997 |
99,72% |
|
20 |
10 |
0 |
13 |
681 |
0,982 |
98,15% |
Table 7. Result of Accuracy Test with Threshold = 50
|
ID |
TP |
FN |
FP |
TN |
ACC |
% |
|
1 |
1 |
49 |
0 |
654 |
0,930 |
93,04% |
|
2 |
1 |
49 |
0 |
654 |
0,930 |
93,04% |
|
3 |
44 |
6 |
0 |
654 |
0,991 |
99,15% |
|
4 |
1 |
49 |
0 |
654 |
0,930 |
93,04% |
|
5 |
1 |
49 |
0 |
654 |
0,930 |
93,04% |
|
6 |
1 |
49 |
0 |
654 |
0,930 |
93,04% |
|
7 |
1 |
49 |
0 |
654 |
0,930 |
93,04% |
|
8 |
39 |
11 |
0 |
654 |
0,984 |
98,44% |
|
9 |
3 |
47 |
0 |
654 |
0,933 |
93,32% |
|
10 |
3 |
47 |
0 |
654 |
0,933 |
93,32% |
|
11 |
50 |
0 |
8 |
646 |
0,989 |
98,86% |
|
12 |
1 |
49 |
0 |
654 |
0,930 |
93,04% |
|
13 |
39 |
11 |
0 |
654 |
0,984 |
98,44% |
|
14 |
38 |
12 |
0 |
654 |
0,983 |
98,30% |
|
15 |
48 |
2 |
0 |
654 |
0,997 |
99,72% |
|
16 |
5 |
45 |
0 |
654 |
0,936 |
93,61% |
|
17 |
1 |
49 |
0 |
654 |
0,930 |
93,04% |
|
18 |
1 |
49 |
0 |
654 |
0,930 |
93,04% |
|
19 |
8 |
42 |
0 |
654 |
0,940 |
94,03% |
|
20 |
23 |
27 |
0 |
654 |
0,962 |
96,16% |
Table 8. Comparison of Result of Accuracy Test
|
ID |
ACCURACY |
||
|
Threshold 10 |
Threshold 20 |
Threshold 50 |
|
|
1 |
98,72% |
97,30% |
93,04% |
|
2 |
98,72% |
97,30% |
93,04% |
|
3 |
95,17% |
96,59% |
99,15% |
|
4 |
98,72% |
97,30% |
93,04% |
|
5 |
98,72% |
97,30% |
93,04% |
|
6 |
98,72% |
97,30% |
93,04% |
|
7 |
98,72% |
97,30% |
93,04% |
|
8 |
95,88% |
97,30% |
98,44% |
|
9 |
99,01% |
97,59% |
93,32% |
|
10 |
99,01% |
97,59% |
93,32% |
|
11 |
93,18% |
94,60% |
98,86% |
|
12 |
98,72% |
97,30% |
93,04% |
|
13 |
95,88% |
97,30% |
98,44% |
|
14 |
95,03% |
97,44% |
98,30% |
|
15 |
94,60% |
96,02% |
99,72% |
|
16 |
99,29% |
97,87% |
93,61% |
|
17 |
98,72% |
97,30% |
93,04% |
|
18 |
98,72% |
97,30% |
93,04% |
|
19 |
99,72% |
98,30% |
94,03% |
|
20 |
98,15% |
99,57% |
96,16% |
|
AVG |
97,67% |
97,29% |
95,04% |
Based on the tryout of 20 queries with 10, 20, and 50 thresholds, it could be concluded that the higher the threshold is given, the accuracy of the system to give the relevant answer is relatively lesser. The cause is the irrelevant data are more than the relevant; it also depends on TP, FN, FP, and TN score given by the system. Graphic of the accuracy test result is shown in figure 11.
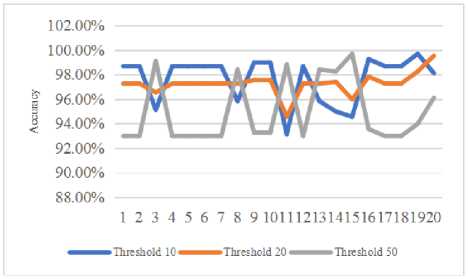
Fig.11. Graphic of Result of Accuracy Test
-
F. Analysis of Pattern Identification
Fig.12. Matching process flowchart
To understand the flow of pattern-matching based on user's input and the response given by Chatbot more, three tests are done by using the reference from the results of using AIML method as seen in table 9.
Table 9. Self-matching Tryout
-> against ( "raj a warmadewa" IN boolean MODE) AS skor
-> FROM tb_pengetahuan
-> ORDER BY Skor DESC;
-
a. First Scenario
In the first scenario, the user sent the message “Raja Warmadewa?” The following is an explanation of pattern identification in the first scenario.
-
1. The program did preprocess that begins with tokenization of "Raja Warmadewa?" into two words, namely "raja" and "warmadewa". Punctuation is also removed; that is the question mark in this case.
-
2. The process continued by erasing word that has no meaning (stopword) related with list of words -stopword in tm_stopword table, so "raja" and "warmadewa" words are gained.
-
3. The process continued again by changing the word with prefix and suffix into basic word (stemming), so "raja" and "warmadewa" words are obtained.
-
4. There are two keywords obtained after preprocessing, namely “raja” and “warmadewa” words, that later matched with keywords template in “tb_pengetahuan” using Full-Text Search method.

sri kesari warmadewa
sang ratu sri haji tabanendra warmadewa sang ratu sri janasadhu warmadewa sang ratu sri jayasingha warmadewa sri dharma udayana warmadewa
sang ratu sri haji tabanendra warmadewa|8,575| sang ratu sri janasadhu warmadewa |8,575| sang ratu sri jayasingha warmadewa 18,5751 sri dharma udayana warmadewa 18,5751
110Igelar
Iskor I
|8,575 I
18,575 I
10 row in set (0.00 sec)
Fig.13. Matching Pattern using Full-Text Search (Scenario 1)
It can be seen that the score from all templates is the same. It shows that keyword from users was not specific enough, so the bot responded that the question sent by the user is unanswerable because it is less specific.
-
b. Second Scenario
In the second scenario, the user sent the message “Berapa lama berkuasanya raja warmadewa?” The following is an explanation of pattern identification in the first scenario.
-
1. The program did preprocess that begins with tokenization of “Berapa lama berkuasanya raja warmadewa?” into five words, namely "berapa", "lama", "berkuasanya", "raja", and "warmadewa". Punctuation is also removed; that is the question mark in this case.
-
2. The process continued by erasing word that has no meaning (stopword) related with list of words stopword in tm_stopword table, so “lama”, “berkuasanya”, “raja” and “warmadewa” words are obtained.
-
3. The process continued again by changing the word with prefix and suffix into basic word (stemming), so “lama”, “kuasa”, “raja” and “warmadewa” words are gained.
-
4. There are four obtained after preprocessing, namely “lama”, “kuasa”, “raja” and “warmadewa” words, that later matched with keywords template in “tb_pengetahuan” using Full-Text Search method.
-
4. There are six keywords obtained after preprocessing, namely “lama”, “kuasa”, “raja”, “sri”, “kesari” and “warmadewa” words, that later matched with keywords template in “tb_pengetahuan” using Full-Text Search method.
mysql> SELECT id_pengetahuan AS id, pertanyaan, MATCH (pertanyaan)
-> AGAINST( ”lama kuasa raja warmadewa" IN BOOLEAN MODE) AS skor
-> FROM tb_pengetahuan
-> ORDER BY skor DESC;
mysql> SELECT id_pengetahuan AS id, pertanyaan, MATCH (pertanyaan)
-> AGAINST( "lama kuasa raja sri kesari warmadewa" IN BOOLEAN
-
- > MODE) AS skor
-
- > FROM tb_pengetahuan
-
- > ORDER BY skor DE SC;
I id|pertanyaan |skor |
|1 llama kuasa raja sri kesari warmadewa |28,59| 12 llama kuasa raja sang ratu sri haji tabanendra warmadewaI 22,111 |3 llama kuasa raja sang ratu sri janasadhu warmadewa |22, 111 14 llama kuasa raja sang ratu sri jayasingha warmadewa 122,111 15 llama kuasa raja sri dharma udayana warmadewa 122,111 |6 Igelar raja sri kesari warmadewa |19,35| 17 Igelar raja sang ratu sri haji tabanendra warmadewa 117,82 1 |8 Igelar raja sang ratu sri janasadhu warmadewa |17,82| 19 Igelar raja sang ratu sri jayasingha warmadewa 117,821 110Igelar raja sri dharma udayana warmadewa |17,82|
6 row in set (0.00 sec)
Fig.15. Matching Pattern using Full-Text Search (Scenario 3)
It can be seen that score in the first template is higher than the other template. It shows that keywords from the user are specific so all keywords from the first template suit with keywords from users.
I id|pertanyaan Iskor |
|1 llama kuasa raja sri kesari warmadewa |17,82| I 2 llama kuasa raja sang ratu sri haji tabanendra warmadewa|17,82| 13 llama kuasa raja sang ratu sri janasadhu warmadewa 117,821 14 llama kuasa raja sang ratu sri jayasingha warmadewa 117,82 1 15 llama kuasa raja sri dharma udayana warmadewa 117,821 I 6 Igelar raja sri kesari warmadewa |8,575| I 7 Igelar raja sang ratu sri haji tabanendra warmadewa |8,575| I 8 Igelar raja sang ratu sri janasadhu warmadewa |8,575| 19 Igelar raja sang ratu sri jayasingha warmadewa 18,5751 110Igelar raja sri dharma udayana warmadewa 18,5751
10 row in set (0.00 sec)
Fig.14. Matching Pattern using Full-Text Search (Scenario 2)
It can be seen that score in the first to the fifth template are the same while the sixth has the lowest score. It shows that keywords from the users are not specific enough, but could be categorized as a question related to how long a certain king held a throne. Therefore, bot sent questions in form of choices from first to fifth templates.
-
c. Third Scenario
In the third scenario, the user sent message “Berapa lama berkuasanya raja sri kesari warmadewa?” The following is explanation of pattern identification in the first scenario
-
1. The program did preprocess that begins with tokenization of “Berapa lama berkuasanya raja sri kesari warmadewa?” into seven words, namely “berapa”, “lama”, “berkuasanya”, “raja”, “sri”, “kesari” and “warmadewa”.
-
2. The process continued by erasing word that has no meaning (stopword) related with list of words stopword in tm_stopword table, so “lama”, “berkuasanya”, “raja”, “sri”, “kesari” and “warmadewa” words are gained.
-
3. The process continued again by changing the word with prefix and suffix into basic word (stemming), so “lama”, “kuasa”, “raja”, “sri”, “kesari” and “warmadewa” words are gained.
V. Conclusion
Bali Historian Chatbot with Full-Text Search Method and Artificial Intelligence Markup Language could provide information related with Balinese history from ancient Bali, Bali during the Middle Ages (XIV to XVIII century), and Bali during Dutch colonialism. LINE instant messaging users can add Balinese Historian Chatbot as a friend in order to communicate with the bot that feels like communicating directly with historians.
Список литературы Balinese historian chatbot using full-text search and artificial intelligence markup language method
- E. Nila S C P and I. Afrianto, “Build a Tourist Information Chatbot Application in Bandung City with Natural Language Processing Approach (In Indonesia Rancang Bangun Aplikasi Chatbot Informasi Objek Wisata Kota Bandung dengan Pendekatan Natural Language Processing,” KOMPUTA, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 49–54, 2015.
- S. Goundar, “What is the Potential Impact of Using Mobile Devices in Education ?,” in Shanghai: Proceedings of SIG GlobDev Fourth Annual Workshop, 2015, pp. 1–30.
- E. Haller and T. Rebedea, “Designing a Chat-bot that Simulates an Historical Figure,” in 19th International Conference on Control Systems and Computer Science., 2014, pp. 1–8.
- N. Muhammad, Z. U. Hassan, M. Naeem, and M. Khalid, “Proposed Generic Full Text Searching Algorithm : A Database Approach Proposed,” International Journal of Computer., vol. 22, pp. 2–4, 2015.
- R. Shah, S. Lahoti, and L. K, “An Intelligent Chat-bot using Natural Language Processing,” International Journal of Engineering Research, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 281–286, 2017.
- A. Khanna, B. Pandey, K. Vashishta, and K. Kalia, “A Study of Tod ay ’ s A . I . through Chatbots and Rediscovery of Machine Intelligence,” International Journal of u- and e- Service, Science and Technology, vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 277–284, 2015.
- N. Mhatre, K. Motani, M. Shah, and S. Mali, “Donna Interactive Chat-bot acting as a Personal Assistant,” International Journal of Computer Applications., vol. 140, no. 10, pp. 6–11, 2016.
- B. Abushawar and E. Atwell, “ALICE Chatbot : Trials and Outputs,” Computacion y Sistemas, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 625–632, 2015.
- A. Dole, H. Sansare, R. Harekar, and S. Athalye, “Intelligent Chat Bot for Banking System,” International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS), vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 49–51, 2015.
- Maskur, “Designing Chatbot Student Information Center Using AIML As a Web-Based Virtual Assistant (In Indonesia Perancangan Chatbot Pusat Informasi Mahasiswa Menggunakan AIML Sebagai Virtual Assistant Berbasis Web),” KINETIK, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 123–128, 2016.
- F. Azwary, F. Indriani, and D. T. Nugrahadi, “Question Answering System Based On Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (In Indonesia Question Answering System Berbasis Artificial Intelligence Markup Language),” Kumpulan jurnaL Ilmu Komputer (KLIK), vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 48–60, 2016.
- D. Suryani and E. L. Amalia, “Chatbot Application for East Java Tourism Objects Based on AIML (In Indonesia Aplikasi Chatbot Objek Wisata Jawa Timur Berbasis AIML),” SMARTICS Journal., vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 47–54, 2017.
- I. N. S. Paliwahet, I. M. Sukarsa, and I. K. G. Darma Putra, “Bali Tourism Information Search application uses Chatbot Technology (In Indonesia Pencarian Informasi Wisata Daerah Bali menggunakan Teknologi Chatbot),” LONTAR Komputer, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 144–153, 2017.
- Z. N. Baiti and F. Nugroho, “"MI3" Chatbot Application for Information Informatics Engineering Department using Forward Chaining Methods (In Indonesia Aplikasi Chatbot ‘MI3’ untuk Informasi Jurusan Teknik Informatika Berbasis Sistem Pakar menggunakan Metode Forward Chaining,” MATICS, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 178–183, 2013.
- E. Bahartyan, N. Bahtiar, and I. Waspada, “AIML Based Chatbot Integration On E-Commerce Website as Virtual Assistant in Product Search and Reservation (Case Study on Edu4indo.Com Online Book) (In Indonesia Integrasi Chatbot Berbasis AIML pada Website E-Commerce Sebagai Virtual Assistant dalam Pencarian dan Pemesanan Produk (Studi Kasus Toko Buku Online Edu4indo.Com)),” Jurnal Masyarakat Informatika., vol. 5, no. 10, pp. 34–43, 2014.
- D. Christianto, E. Siswanto, and R. Chaniago, “Use of Entity Recognition Named and Artificial Intelligence Markup Language for Text-Based Chatbot Application (In Indonesia Penggunaan Named Entity Recognition dan Artificial Intelligence Markup Language untuk Penerapan Chatbot Berbasis Teks),” J. Telemat., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 61–68, 2015.
- A. Dwi R, F. Imamah, Y. M. Andre, and Ardiansyah, “The Integrated Chatbot Application (MILKI Bot) with Web CMS for Customer Service in MINSU SMEs (In Indonesia Aplikasi Chatbot ( MILKI Bot ) yang Terintegrasi dengan Web CMS untuk Customer Service pada UKM MINSU,” Jurnal Cendikia, vol. XVI, pp. 100–106, 2018.
- M. Husaini, “Utilization of Information Technology in Education Fields (E-Education) (In Indonesia Pemanfaatan Teknologi Informasi dalam Bidang Pendidikan (E-Education)),” Jurnal Mikrotik, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1–5, 2014.
- I. M. Sukarsa, I. K. Gede, D. Putra, N. P. Sastra, and L. Jasa, “A New Framework for Information System Development on Instant Messaging for Low Cost Solution,” TELKOMNIKA, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 2799–2808, 2018.
- I. M. Sukarsa, I. K. Gede, D. Putra, N. P. Sastra, and L. Jasa, “Modification of ISONER Framework as Enterprise Service Bus to Build Consultation Robot Using External Engine,” International Journal of Engineering and Emerging Technology, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 123–128, 2018.
- J. Sujatha, “Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms in the Classification of Parkinson Disease Using Voice Attributes,” International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, vol. 12, no. 21, pp. 10669–10675, 2017.


