Binder properties for zol-silicate paint
Автор: Yulia A. Sokolova, Valentina I. Loganina
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: Construction materials science
Статья в выпуске: 5 Vol.14, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. The binder for sol-silicate paints is made on the basis of a polysilicate solution obtained on the basis of liquid glass and silicic acid sol. The technological process of creating a polysilicate binder is complex and it is not always possible to achieve the required characteristics. In this regard, the development of a polysilicate binder and the creation of a sol-silicate paint based on it are relevant. Materials and methods. Silicic acid sols Nanosil 20 and Nanosil 30 produced by PK Promsteklotsentr were used in the work. We used sodium liquid glass with a modulus of M = 2.78, potassium liquid glass with a modulus of M = 3.29 (GOST 13078). The conditional viscosity of paints and varnishes was determined using a VZ-4 viscometer according to GOST 8420-74. “Paint materials. Methods for determining the conditional viscosity. Tensile strength (cohesive strength) was determined according to GOST 18299-72* “Paint and varnish materials. Method for determination of tensile strength, elongation at break and modulus of elasticity” on the tensile testing machine IR 5057-50. The silicate modulus of liquid glass was determined according to the method described in GOST 13078-81. The molybdate method was used to study the composition of liquid glasses and polysilicate solutions. Results and discussions. It was revealed that liquid glass and polysilicate solution are typical pseudoplastic bodies. The addition of a sol (an increase in the silicate modulus) promotes an increase in the proportion of high-polymer fractions of siliconoxygen anions (SCA), and with an increase in the sol content, the proportion of the polymeric form of silica increases. It has been established that there is a correlation between the content of silica in the polymer form and the tensile strength of the films, which means that with an increase in the content of silica in the polymer form, an increase in the tensile strength of the films is observed. Conclusions. It has been established that with an increase in the amount of silicic acid sol introduced, a decrease in the pH of solutions is observed at a constant alkali concentration. The introduction of a sol of silicic acid leads to a change in the viscosity of the solutions. The introduction of a sol of silicic acid into liquid glass promotes an increase in the proportion of high-polymer fractions of silicon-oxygen anions. Films based on polysilicate solutions are characterized by faster curing and higher tensile strength compared to films based on liquid glasses.
Sol-silicate paint, polysilicate mortar, curing kinetics, cohesive strength
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142235382
IDR: 142235382 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2022-14-5-363-372
Текст научной статьи Binder properties for zol-silicate paint
Original article
For finishing the facades of buildings, paints and varnishes are widely used. Sol-silicate paints are gaining popularity in the paint and varnish market “Histolith Sol-Silikat” manufactured by “Caparol” (Germany), “Alligator” (Germany)[1,2]. Since 2015, the German company KEIM has been known on the paint and varnish market, producing one-pack sol-silicate paint KEIM Soldalit [3]. KEIM Soldalit paint can be applied not only on mineral, but also on numerous organic substrates. Among
the domestic manufacturers of sol-silicate paint is the St. Petersburg company Friedlander, which produces the Prochnin paint [4].
The binder for sol-silicate paints is made on the basis of a proven combination of kieselsol and liquid glass binders. The polysilicate solution formed by adding liquid glass to the silicic acid sol consists of particles of the initial sol reduced in size and a highly dispersed phase of hydrated silica with particle sizes not exceeding 5–7 nm. The technological process of creating a polysilicate binder based on liquid glass is complicated and it is not always possible
BUILDING MATERIALS SCIENCE to achieve the required characteristics [5]. In this regard, the development of a polysilicate binder and the creation of a sol-silicate paint based on it are relevant.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Silicic acid sols Nanosil 20 and Nanosil 30 produced by PK Promsteklotsentr were used in the work. We used sodium liquid glass with a modulus of M = 2.78, potassium liquid glass with a modulus of M = 3.29 (GOST 13078).
The conditional viscosity of paints and varnishes was determined using a VZ-4 viscometer according to GOST 8420-74. “Paint materials. Methods for determining the conditional viscosity”. The dynamic viscosity of the compositions was determined in accordance with the formula:
η 2 / η 1 = t 2 ρ 2 / t 1 ρ 1 , (1)
where η 2 is the dynamic viscosity of the test solution, Pa s;
-
η 1 is dynamic viscosity of water, Pa s;
-
t 2 is the outflow time of the test solution, s;
-
t 1 is water outflow time, s;
-
ρ 2 is the density of the test solution, g/cm3.
-
ρ 1 is the density of water, g/cm3.
Kinematic viscosity was determined by the formula:
-
ν = µ / ρ. (2)
The silicate modulus of liquid glass was determined according to the method described in GOST 13078-81. The total silica content in the binders was estimated using a UNICO 2100 spectrophotometer. To study the composition of liquid glasses and polysilicate solutions, the molybdate method was used, based on different rates of interaction of monomeric, oligomeric, and polymeric anions (SOA) with molybdic acid [6–8]. Additionally, to study the composition of polysilicate solutions, we used the total internal reflection violation method, which provides the study of samples with a high absorption coefficient. We used the IR spectrum of FSM 1201 TIR (multiple violation of total internal reflection) in the spectral range 750–4350 cm–1 [9].
Hardness ( H ), arbitrary units, was calculated by the formula
H = t / t 1 , (3)
where t is the decay time of the pendulum oscillations from 5о to 2о on the tested paintwork, s;
-
t 1 is the damping time of pendulum oscillations from 5° to 2° on a glass plate (“glass number”), s.
Tensile strength (cohesive strength) was determined according to GOST 18299-72* “Paint and varnish materi-
als. Method for determination of tensile strength, elongation at break and modulus of elasticity” on the tensile testing machine IR 5057-50.
RESULTS
It has been established that the introduction of silica sol to liquid glass with a density of 1460 kg/m3 causes gelation over time. So, with the introduction of the sol in an amount of 5% by weight of liquid glass, the onset of gelation was observed after five days, and with the addition of 3%, after 7 days of storage [10–13].
Analysis of the data (Fig. 1) indicates that with an increase in the sol content, a decrease in the viscosity of the solution occurs, apparently caused by the introduction of an additional amount of water contained in the sol (Fig. 1, curve 1). However, after 1 day of storage, there is some increase in the viscosity of the polysilicate solution. With a sol content of 7% by weight of liquid glass, an increase in viscosity occurs after three days of storage (Fig. 1, curve 3). At the age of more than four days of storage, an increase in viscosity is observed at a sol content of 1% (Fig. 1, curve 4.5).
To ensure the stability of the polysilicate solution, lithium hydroxide was added to liquid glass.
The use of sol in an amount of 10–15% by weight of liquid glass with a modulus of M = 2.78 makes it possible to obtain polysilicate solutions with a modulus of M = 4.25–5.29 [14]. Additionally, the value of dynamic and kinematic viscosity of polysilicate solutions was determined. The results are shown in Table 1.
Analysis of the data given in Table 1 shows that the addition of 15% Nanosil 20 silicic acid sol to the composition of water glass leads to a decrease in dynamic viscosity by 13%.
It has been established that with an increase in the amount of silicic acid sol introduced, a decrease in the pH of polysilicate solutions is observed at a constant alkali concentration. So, when the content of silicic acid sol is 5% by weight of potassium liquid glass, the pH is 11.41, and when the content of silicic acid sol is 15%, it is 10.97, while in the control composition (without adding sol) – pH = 12.68. Similar regularities are also characteristic of sodium liquid glass.
It has been established that the pH of the solution with the addition of silicic acid sol is continuously changing (Fig. 2). After mixing water glass and silica sol, the pH is higher than in the later stages. The steady state of the solution corresponds to 27–30 hours.
The rheological properties of polysilicate solutions were also evaluated in terms of ultimate shear stress using the Reotest-2 instrument. The research results are shown in Fig. 3.
It is revealed that all systems are typical pseudoplastic bodies. In the region of slow flow, the viscosity of so-
BUILDING MATERIALS SCIENCE
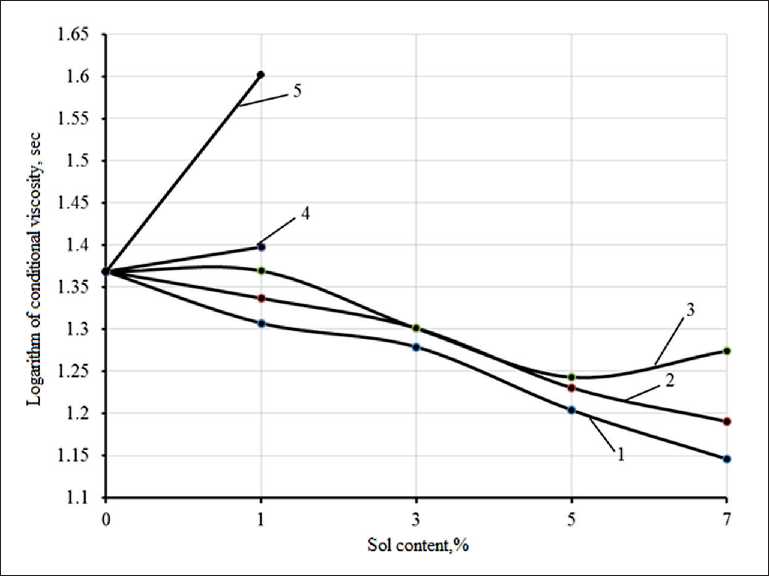
Fig. 1. Change in the viscosity of the sodium polysilicate solution depending on the content of silicic acid sol (Nanosil 20): 1 – after preparation; 2 – in a day; 3 – after 3 days;
4 – after 5 days; 5 – after 7 days
Table 1
The effect of the addition of silica sol on the rheological properties of liquid glass
Analysis of the data shown in Fig. 3 indicates that polysilicate solutions are characterized by a lower value of stress Pm , after which the solutions acquire the properties of a Newtonian fluid. So, for a sodium polysilicate solution, the voltage value Pm is Pm = 0.1 Pa•s, and for sodium liquid glass it is 0.28 Pa s. For a potassium polysilicate solution, the Pm value is Pm = 0.07 Pa•s.
BUILDING MATERIALS SCIENCE
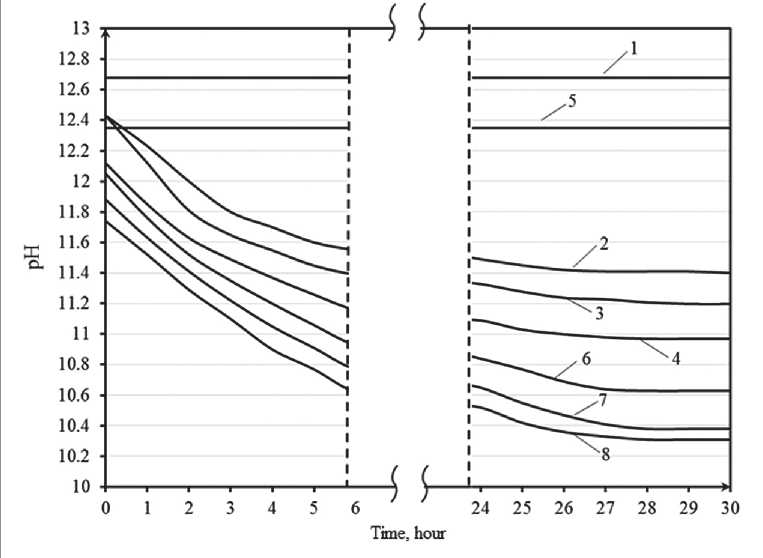
Fig. 2. The kinetics of changes in the pH of polysilicate solutions: 1 – potassium liquid glass; 2 – potassium liquid glass + 5% Nanosil 20; 3 – potassium liquid glass + 10% Nanosil 20; 4 – potassium liquid glass + 15% Nanosil 20; 5 – sodium liquid glass;
6 – sodium water glass + 5% Nanosil 20; 7 – sodium water glass +10% Nanosil 20;
8 – sodium liquid glass + 15% Nanosil 20
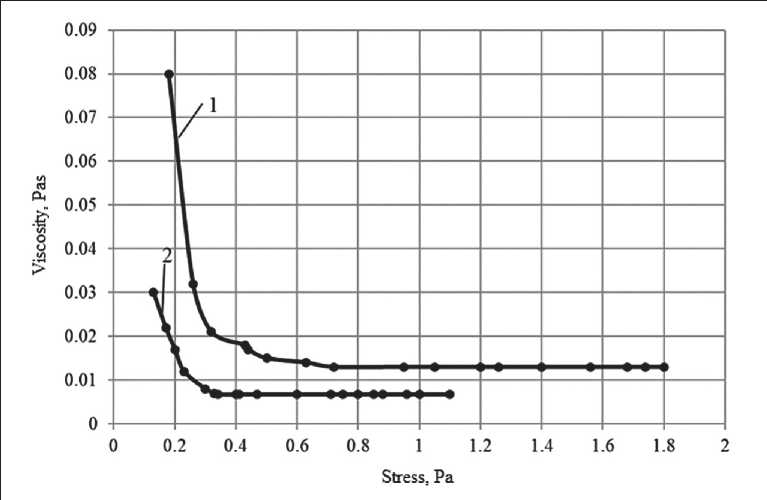
Fig. 3. Rheological flow curves of the systems under study: 1 – potassium liquid glass; 2 – potassium polysilicate solution
BUILDING MATERIALS SCIENCE
It was found that the addition of a sol (an increase in the silicate module) contributes to an increase in the proportion of high-polymer fractions of silicon-oxygen anions (SOA), and with an increase in the sol content, the proportion of the polymeric form of silica increases. So, with the introduction of Nanosil 20 silicic acid sol in an amount of 5% by weight of liquid glass, the content of the polymer form of silica γ-SiO 2 increases to 5.55%, in an amount of 15% – up to 12.1%, while in the initial composition (without sol addition) – 2.78%. In a potassium polysilicate solution, the content of the polymeric form of silica γ-SiO 2 is 19.93% with a sol content of 15% [15, 16]. The research results are shown in Table 2.
The dependence of the content of silica α-SiO 2 in the early stages of the interaction of the sol with liquid glass is extreme. The maximum content of α-SiO 2 is ob-
served after 60 minutes, depending on the type of liquid glass and the amount of sol introduced [17–19]. So, after 60 minutes, the content of silica α-SiO 2 in the sodium polysilicate solution is 18.54% with a content of 5% sol, and in the potassium polysilicate solution it is 6.97% with a content of 5% sol (Fig. 4, Table 2).
Fig. 5 shows the IR spectrum of potassium liquid glass and potassium polysilicate solution in the spectral range 750–4350 cm–1. Fig. 5 shows that the studied potassium polysilicate solution has a number of characteristic absorption bands, which in the spectral range of 1000– 1250 cm–1 correspond to vibrations of Si–O–Si bonds. The deepening of 1095 cm–1 corresponds to Si–O–Si vibrations. The shift of the band to higher frequencies compared to liquid glass (1082 cm–1) indicates a higher degree of polymerization and an increase in the number of siloxane bonds. Reflections in the region 980–880 cm–1
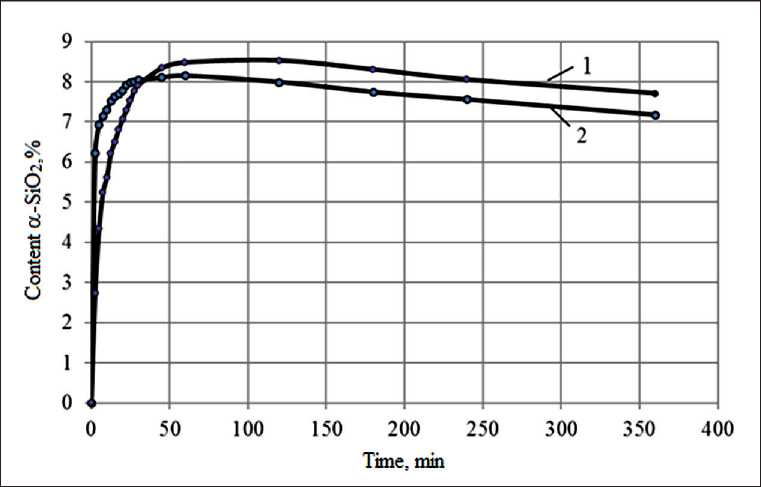
Fig. 4. Kinetics of change in the content of α-SiO2 in a potassium polysilicate solution: 1 – content of Nanosil 20 sol – 10%; 2 – Nanosil 20 sol content – 15%
Table 2
Change in the colloid-chemical state of silica depending on the content of silicic acid sol
|
Sol content, % |
Soda water glass |
Potassium liquid glass |
||||
|
General content silica SiO2, % |
Content α-SiO2 + β-SiO2, % |
Content γ-SiO2, % |
General content silica SiO2, % |
Content α-SiO2 + β-SiO2, % |
Content γ-SiO2, % |
|
|
0 |
23.72 |
20.93 |
2.78 |
21.9 |
19.38 |
2.51 |
|
5 |
25.83 |
20.28 |
5.55 |
26.21 |
18.61 |
7.6 |
|
10 |
28.12 |
19.79 |
8.33 |
30.39 |
17.71 |
12.68 |
|
15 |
30.57 |
18.83 |
12.10 |
34.93 |
15.00 |
19.93 |
BUILDING MATERIALS SCIENCE
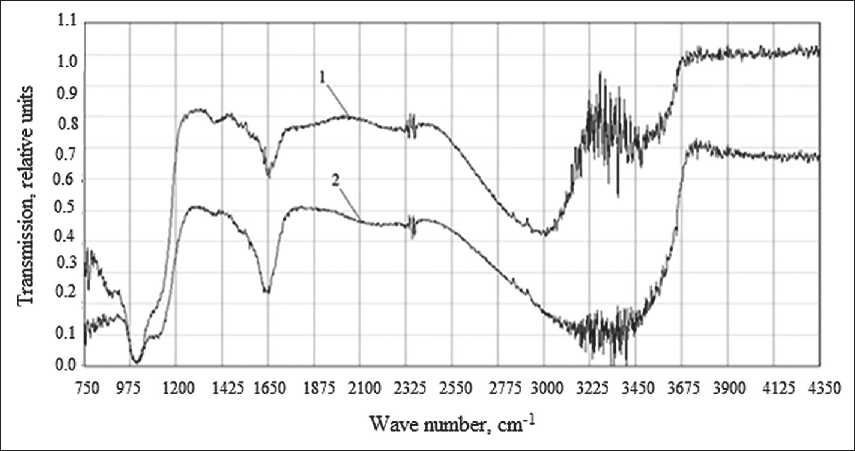
Fig. 5. IR spectra of potassium liquid glass (1) and potassium polysilicate solution (2) with a Nanosil 30 sol content of 15%
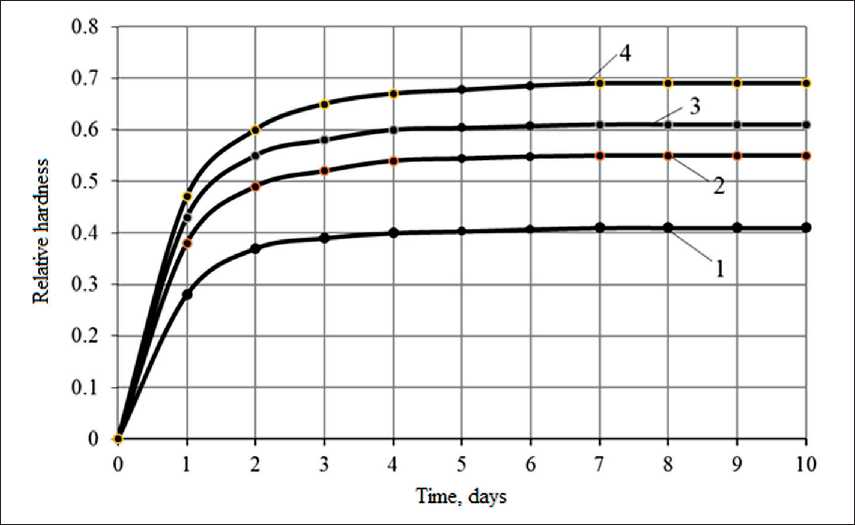
Fig. 6. Change in time of the relative hardness of films based on polysilicate solutions:
1 – potassium liquid glass; 2 – potassium liquid glass + 5% sol; 3 – potassium liquid glass + 10% sol; 4 – potassium liquid glass + 15% sol
characterize the stretching vibrations of Si–(OH) hydroxyls [16–18].
Coatings based on polysilicate solutions are characterized by faster curing. Figure 6 shows the curing kinetics of a coating, which is characterized by a change in relative hardness. At the age of 24 hours, the relative hardness of the film based on the control composition (without sol)
is 0.28, and with the addition of Nanosil 20 sol in the amount of 5, 10, 15% by weight of liquid glass, respectively, 0.38; 0.43, 0.47. The curing process ends after 7 days.
Films based on polysilicate solutions are characterized by the manifestation of a scale factor [20]. With an increase in the thickness of the coating, a decrease in relative hardness is observed (Fig. 7).
BUILDING MATERIALS SCIENCE
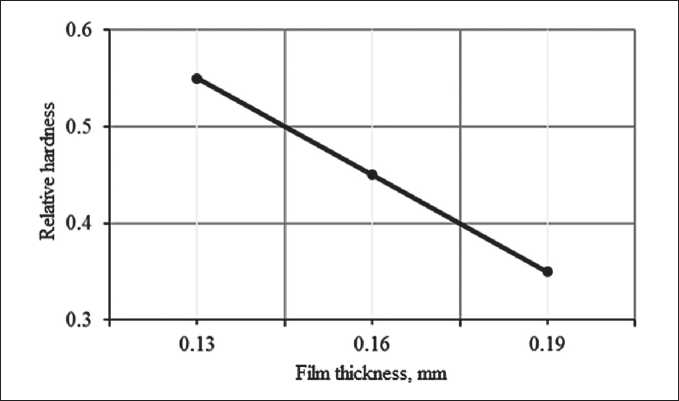
Fig.7. Influence of the coating thickness on the change in the relative hardness of the films
As can be seen from the obtained experimental data, with an increase in the thickness of the polymer coating from 0.1 to 0.3 mm, the relative hardness decreases from 0.6 to 0.48 MPa. There is a manifestation of the scale factor. An analysis of the obtained dependence of the relative hardness of coatings on their thickness shows that the relative hardness decreases linearly with an increase in the thickness of the polymer coating. The resulting dependence is described by the equation:
y = a + bx , (4)
where a , b are material constants.
The calculated dependence of the relative hardness of films based on a polysilicate solution on their thickness is obtained, which has the form:
y = 0.983–3.333 x . (5)
To assess the strength characteristics, free films were studied. It has been established that films based on polysilicate solutions have a higher cohesive strength. It was found that the tensile strength of a film based on potassium liquid glass is Rp = 0.39 MPa, and the tensile strength of a film based on a polysilicate solution (15% Nanosil 20) is 1.14 MPa (Fig. 8). Increase in strength,
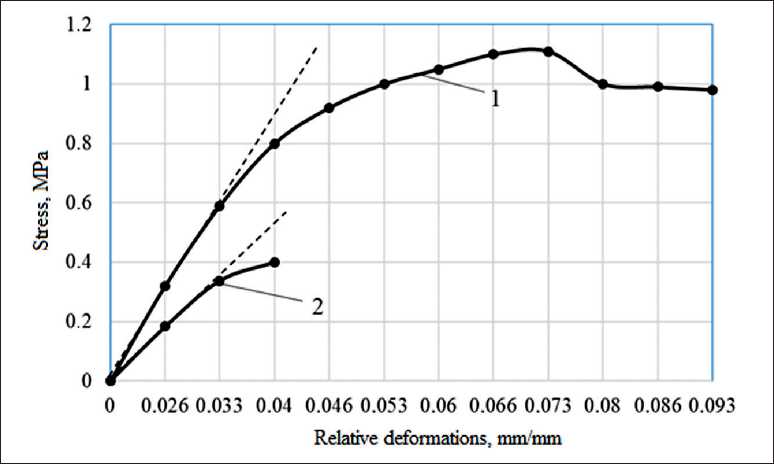
Fig. 8. Change in relative strain during stretching of films: 1 – liquid glass with 15% content of Nanosil 30; 2 – liquid glass
BUILDING MATERIALS SCIENCE
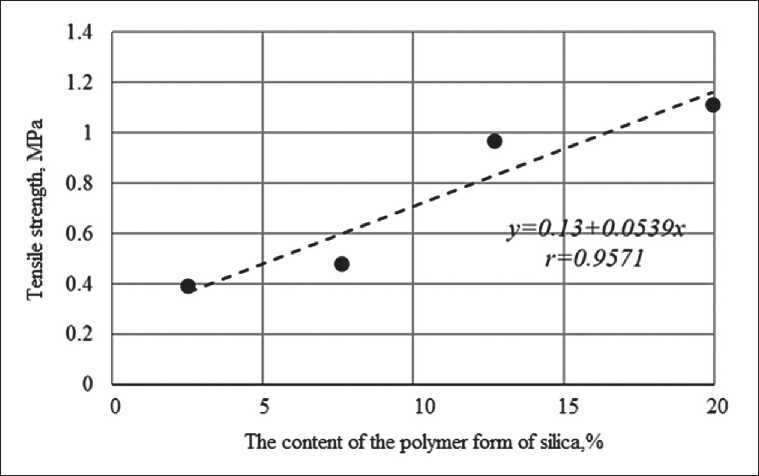
Fig. 9. Dependence of the tensile strength of films based on potassium polysilicate solution on the content of silicic acid in the polymer form γ -SiO2
in our opinion, is due to an increase in the proportion of high-polymer fractions of silicon-oxygen anions (SOA) in the structure of the polysilicate binder compared to liquid glass.
The modulus of elasticity of a film based on a polysilicate solution is 0.05•104 MPa, and on the basis of liquid glass it is 0.022•104 MPa.
Fig. 9 shows the dependence of tensile strength on the content of the polymer form of silica based on a polysilicate solution. It has been established that there is a cor-
Table 3
Technological and operational properties of sol-silicate paints and coatings based on them
|
The name of indicators |
Values |
|
Viscosity according to VZ-4, s |
25–30 |
|
Density, kg/m3 |
1400 |
|
Drying time up to degree 5 at 20оС, min, no more |
41 |
|
Vapor permeability, g/(m2•day) (GOST 33355-2015) |
155 |
|
Tensile strength, MPa |
2.30 |
|
Flammability group |
Г1 |
|
Covering power, g/m2 |
186.5 |
|
Frost resistance, brand |
F35 |
relation between the content of γ-SiO 2 in the polysilicate solution and the tensile strength of the films
On the basis of a polysilicate binder, a sol-silicate paint was developed. Table 3 shows the properties of the sol-silicate paint and coatings based on it.
CONCLUSIONS
It has been established by the method of violation of total internal reflection and the molybdate method that the introduction of a silicic acid sol into liquid glass contributes to an increase in the proportion of high-polymer fractions of silicon-oxygen anions. It was revealed that the dependence of the content of silica in the monomeric form at the early stages of the interaction of the silicic acid sol with liquid glass is of an extreme nature.
It was found that films based on polysilicate solutions are characterized by faster curing. Films based on polysilicate solutions are characterized by the manifestation of a scale factor. With increasing coating thickness, a decrease in relative hardness is observed. The dependence of the relative hardness of films based on a polysilicate solution on their thickness is obtained.
It was found that films based on polysilicate solutions have a higher tensile strength compared to films based on liquid glasses. A linear relationship has been established between the tensile strength of films based on a polysilicate solution and the content of high-polymer fractions of silicon-oxygen anions γ-SiO 2 in it, due to an increase in the number of siloxane bonds.
BUILDING MATERIALS SCIENCE
Список литературы Binder properties for zol-silicate paint
- CAYMAN: Sol-silicate paint. Available from: http://www.alligator.spb.ru/catalog/materialy-tm-kayman/zolsilikatnaya-kraska-tm-kayman
- Histolith Sol-Silikat. Sol-silicate paint. Available from: http://www.caparol.ru/produkty/materialy-dljarestavracii-pamjatnikov-arkhitektury/histolith/histolith-silikatnaja-programma/histolith-sol-silikat
- KEIM Soldalit. Sol silicate facade paint for universal use. Available from: http://www.keim.com/ru-ru/produkcija/fasadnye-kraski/soldalit
- Prochnin. Sol silicate paint. Available from: http://www.fridlender.ru/products/solsilicate/zol-silikatnayakraska-prochnin
- Killman E. The stability of silica-aerosil-hydrosols under the influence of polymer adsorption. The effect of polymers on dispersion properties. J. Eisenlauer. Tadros.1989. Th. F. London: Academic Press; 1982.
- HDPE F 14. 1: 2: 4. 215-06 A technique for measuring the mass concentration of silicic acid (in terms of silicon) in drinking, surface and waste waters in a photometric method in the form of a yellow silica-molybdenum heteropolyacid. Center for Water Research and Control. SPb; 2006.
- Grasshoff, K. On the determination of silica in seawater. Deep-Sea Res. 1964; 11(4): 74–81.
- RD 52. 24. 433-2005. Mass concentration of silicon in surface waters of the land. MVI photometric method in the form of a yellow form of molybdosilicic acid. GU GUI; 2005.
- Loganina V.I., Kislitsyna S.N., Mazhitov Y.B. Structure and Properties of the Modified Binding for Silicate Paints. Materials Science Forum. 2018; 931: 469–474. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.931.469
- Rao I.V., Ruckenstein Е. Phase behavior of mixtures of sterically stabilized colloidal dispersions and free polymer. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 1985; 108(2): 389–402. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(85)90276-0
- Loganina V.I., Mazhitov Y.B. Estimation of Rheological Propertie of Sol Silicate Paint. Materials Science Forum. 2020; 992: 569–573. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.992.569
- Figovsky O., Borisov Yu., Beilin D. Nanostructured Binder for Acid-Resisting Building Materials. Scientific Israel–Technological Advantages. 2012; 14(1): 7–12. Available from: https://doi.org/10.17265/2159-5348/2017.03.003
- Kudryavtsev P.G., Figovsky O.L. Nanocomposite organomineral hybrid materials. Part 3. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2016;8(3): 16–49. Available from: https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2016-8-3-16-49
- Ayler R. Silica Chemistry. Part 1. M.: Mir; 1982.
- Loganina V., Mazhitov Y., Skachkov Y. Assessment of the Structure of Polysilicate Binding with Added Glycerol. Materials Science Forum. 2020; 987: 15-19. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.987.15
- Figovsky O.L., Kudryavtsev P.G. Liquid glass and aqueous solutions of silicates as a promising basis for technological processes for obtaining new nanocomposite materials. Engineering Bulletin of the Don. 2014; 2.
- Salimian S., Zadhoush A. Water-glass based silica aerogel: unique nanostructured filler for epoxy nanocomposites. Journal of Porous Materials. 2019; 26(6): 1755 – 1765. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-019-00757-3
- Mazraeh-Shahi Z.T., Shoushtari A.M., Abdouss M., Bahramian A.R. Relationship analysis of processing parameters with micro and macro structure of silica aerogel dried at ambient pressure. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids. 2013; 376: 30–37. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.04.039
- Duan Y., Jana S.C., Reinsel A.M., Lama B., Espe M.P.. Surface modification and reinforcement of silica aerogels using polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes. Langmuir. 2012; 28 (43): 15362–15371. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1021/la302945b
- Bartenev G.M., Zuev Yu.S. Strength and fracture of highly elastic materials. M., L.: Chemistry; 1964.


