Биодеструкция смоляных кислот - доминирующих токсичных соединений в отходах целлюлозно-бумажной промышленности
Автор: Черемных Ксения Михайловна
Журнал: Вестник Пермского университета. Серия: Биология @vestnik-psu-bio
Рубрика: Биотехнология
Статья в выпуске: 3, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Смоляные кислоты относятся к группе дитерпеновых карбоновых кислот и составляют большую долю экотоксичных веществ в сточных водах целлюлозно-бумажной промышленности. Попадание этих высокостабильных и токсичных экополлютантов в окружающую среду крайне нежелательно (даже в низких концентрациях), ибо последствия их воздействия на живые организмы могут быть непредсказуемыми. В связи с этим актуален поиск экологически обоснованных способов нейтрализации и выведения смоляных кислот из окружающей среды с помощью инновационных технологий с использованием микроорганизмов. При этом перспективным является не только поиск эффективных технологий утилизации смоляных кислот, но и получение на их основе новых биологически активных соединений, пригодных в качестве интермедиатов синтеза лекарственных препаратов.
Смоляные кислоты, биодеградация, биотрансформация, отходы целлюлозно-бумажной промышленности
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147204687
IDR: 147204687 | УДК: 579.22+579.66
Текст научной статьи Биодеструкция смоляных кислот - доминирующих токсичных соединений в отходах целлюлозно-бумажной промышленности
Значительная часть токсичных веществ в жидких отходах целлюлозно-бумажной промышленности приходится на смоляные кислоты, представляющие собой трициклические дитерпеноиды [Walden, Howard, 1977; Kovacs, Voss 1992; Pulp bleaching ..., 1993; Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997]. Смоляные кислоты - это группа экстрактивных веществ, обычно встречающихся в живице хвойных деревьев (сосна, ель, пихта). Они составляют до 0.2-0.8% от общей массы древесины. [Fengel, Wegner, 1985; Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997]. В процессе химического и механического воздействия на древесину для получения целлюлозы, смоляные кислоты высвобождаются и в дальнейшем через сточные воды попадают в окружающую среду.
При попадании в открытые экосистемы данные вещества аккумулируются и могут оказывать токсическое действие на живые организмы [Bicho, Martin, Saddler, 1995; Zheng, Nicholson, 1998; Leppanen, Oikari, 1999]. В качестве эффективного способа снижения концентрации смоляных кислот признаны биотехнологические методы с использованием микроорганизмов [Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997]. Данные методы не требуют применения агрессивных реагентов и позволяют осуществлять
максимальное извлечение смоляных кислот в «мягких» условиях при физиологических температурах, нормальном давлении и нейтральных значениях pH среды.
Поскольку смоляные кислоты широко распространены в окружающей среде в микроколичествах, существует большое число грибов и бактерий, способных частично или полностью деградировать смоляные кислоты [Mohn, 1995; Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997; Martin, Yu, Mohn, 1999; Morgan, Wyndham, 2002]. В настоящее время перспективным является получение на основе смоляных кислот биологически активных соединений, пригодных в качестве интермедиатов синтеза лекарственных средств.
Химические свойства и токсичность смоляных кислот
Смоляные кислоты представляют собой природные дитерпеновые трициклические карбоновые кислоты [Scientific ..., 1988; Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997]. Они подразделяются на смоляные кислоты абиетанового и пимаранового типа. Кислоты абиетанового типа имеют изопропильную группу у С-13 атома углерода, в то время как смоляные кислоты пимаранового типа имеют в этом положе- ный [Mutton, 1962; Stoltes, Zinkel, 1989]. Тишиными представителями дитерпеновых кислот абиетанового типа, содержащихся в отходах бумажной промышленности, являются (АК) абиетиновая, (ДАК) дегидроабиетиновая, (НАК) неоа- биетиновая и (J1L1K) левопимаровая кислоты (ри-сунок). Смоляные кислоты пимаранового типа включают изопимаровую (ИНК), (ПК) пимаровую и сандаракопимаровую (СПК) кислоты [Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997].
Тип абиетана Тип пимарана
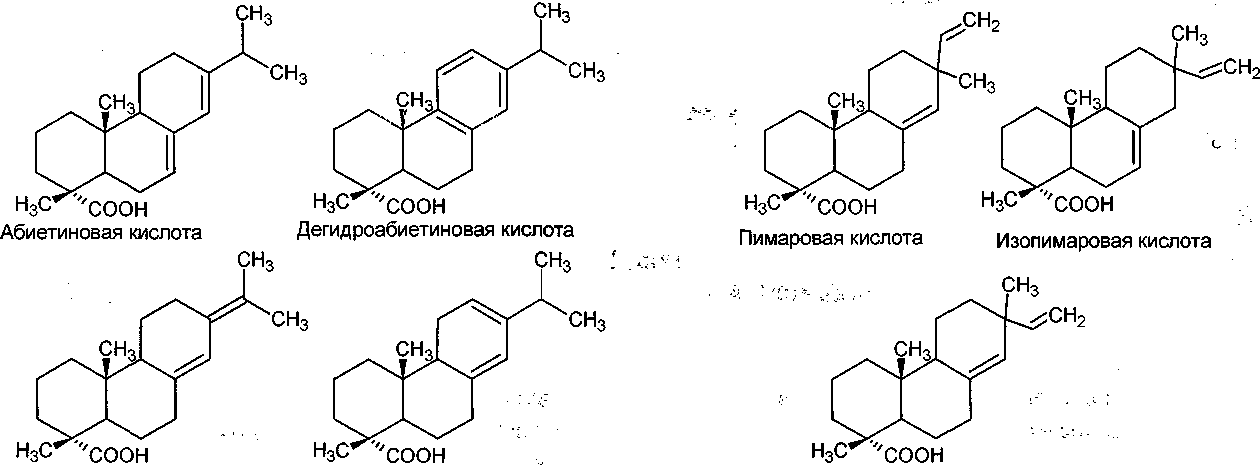
Сандаракопимаровая кислота
Неоабиетиновая кислота Левопимаровая кислота
Структурные формулы смоляных кислот абиетанового и пимаранового ряда
Смоляные кислоты являются гидрофобными соединениями, о чем свидетельствует их растворимость в водных системах. Так, растворимость АК и ДАК при кислых и нейтральных значениях pH и температуре 20°С равна 3-5 и 4-6 мг/л соответственно [Nyren, Back, 1958]. Кроме того, показано, что на растворимость данных смоляных кислот влияют значения температуры и pH среды [Nyren, Back, 1958; Zanella, 1983; Suckling, Hua, Uprichard, 1990]. Предполагается, что именно растворимость влияет на распределение смоляных кислот и транспорт через очистные фильтры [Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997].
Токсичность стоков бумажной промышленности обусловлена наличием в них смоляных кислот. Это становится очевидным при рассмотрении острой токсичности по отношению к некоторым видам рыб. Так, в исследованиях B.R. Taylor с соавт. [Scientific ..., 1988] показано, что значения острой токсичности (96 ч ЛД50) восьми смоляных кислот по отношению к нескольким видам лосося, радужной форели, гольяна распределялись от 0.5 до 1.7 мг/л, тогда как концентрация смоляных кислот в стоках может достигать до 550 мг/л [Elimination ...,2006].
Смоляные кислоты обнаружены в желчи рыб в количествах от 120 до 330 мкг/мл и от 13 до 620 мкг/г в ткани мозга рыб [Zheng, Nicholson, 1998; Leppanen, Oikari, 1999], что указывает на возможную аккумуляцию их в открытых экосистемах. Показано, что значения острой токсичности (48 ч ЛД50) смоляных кислот по отношению к Daphnia magna в 2-3 раза меньше, чем таковые по отношению к рыбам. По данным [Zanella, 1983; Identi-
|
fication ..., 1994], смоляные кислоты менее токсичны по отношению к беспозвоночным животным (табл. 1). Таблица 1 Острая токсичность смоляных кислот |
|||
|
Тестовые орга-низмы |
Смоляные кислоты, мг/л |
||
|
АК |
ДГ |
ипк |
|
|
Daphnia magna (48 ч, ЛД 50) |
19.2 |
2.5-6.4 |
1.3 |
|
Rainbow trout (96 ч, ЛД 50) |
0.7- 1.5 |
0.8- 1.7 |
0.5- 1.0 |
|
Fathead minnowe (96 ч, ЛД 50) |
0.1 |
3.2 |
0.1 |
|
Примечание. * Цит. по: Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997. |
|||
Биодеградация смоляных кислот
Наиболее эффективных способом утилизации смоляных кислот является биологическая обработка сточных вод. По данным некоторых авторов [McFarlane, Clark, 1988], применение активного ила и газированных лагун позволяет снизить уровень абиетановых смоляных кислот в стоках на 90%, при этом утилизация кислот пимаранового типа менее продуктивна и составляет 60%.
В качестве эффективного способа утилизации смоляных кислот используются анаэробные системы. Сторонники их применения предполагают, что использование закрытых систем в процессе переработки целлюлозы существенно уменьшит объем жидких отходов и приведет к более концентрированным стокам. , . ;
жидких отходов и приведет к более концентрированным стокам.
Казалось бы, концентрированные отходы должны значительно повысить привлекательность применения анаэробных систем за счет снижения эксплуатационных затрат, в частности, снижения потребности в энергии или уменьшения формирующегося осадка [Lee, Petersen, Stickney, 1989]. Однако, по мнению отдельных авторов [Lee, Petersen, Stickney, 1989; MacClean, Vegt, Driel, 1990],
gradation ..., 1973; Morgan, Wyndham, 1996], Ar-thobacter [Levinson, Carter, Taylor, 1968], Bacillus, Escherichia, Flavobacterium [Hemingway, Greaves, 1973; Degradation ..., 1973], Cornamonas [Morgan, Wyndham, 1996], Pseudomonas [Hemingway, Greaves, 1973; Degradation ..., 1973; Wilson, Moore, Mohn, 1996], Sphingomonas, Zooglea [Mohn, 1995] способны утилизировать ДАК. Предположительно, это связано с тем, что данной смоляной кислоты в окружающей среде содержится больше. Дитерпе
данные системы менее производительны из-за наличия в концентрированных стоках ингибиторов ферментных систем анаэробных микроорганизмов.
Эффективным способом деградации отдельных смоляных кислот является применение чистых культур микроорганизмов. Бактерии, выделенные из почв, коры деревьев и природных водных систем, обладают способностью утилизировать дитерпеновые кислоты (табл. 2). Представители родов Alcaligenes, Cornamonas [Morgan, Wyndham, 1996], Pseudomonas [Wilson, Moore, Mohn, 1996], Sphingomonas, Zooglea [Mohn, 1995] способны деградировать AK. Представители значительно
ны пимаранового типа сложнее утилизировать, и на это способны лишь отдельные представители родов Cornamonas, Alcaligenes [Morgan, Wyndham, 1996] и Pseudomonas [Wilson, Moore, Mohn, 1996]. В работе P.A. Bicho, V. Martin, J.N. Saddler [1995] микроорганизмы, выделенные непосредственно из сточных вод целлюлозно-бумажных комбинатов, способны деградировать до 65% смоляных кислот абиетанового типа. По данным Т.А. Burnes, R.A. Blanchette, R.L. Farrell [2000], представители Хап-thomonas campestris и Serratia marcescens деградируют до 40% смеси смоляных кислот древесных экстрактов.
|
больших родов микроорганизмов Alcaligenes [De- Таблица 2 Микроорганизмы - деструкторы смоляных кислот |
||
|
Вид, род |
Субстрат |
Автор |
|
Бактерии |
||
|
Burkholderia sp. |
ДАК |
Physiological ..., 1999; Distinct, 2008 |
|
Cupriavidus sp. |
ДАК; AK |
Bicho, Martin, Saddler, 1995 |
|
Pseudomonas vancouverensis “Pseudomonas multiresinivorans” (Pseudomonas nitroducenf)* |
ДАК |
Physiological ..., 1999; Yu, Mohn, 1999; Wilson, Moore, Mohn, 1996 |
|
Pseudomonas reinekei, Pseudomnas moorei, Pseudomonas mohnii |
ИПК |
Pseudomonas reinekei ... , 2007 |
|
Pseudomonas sp. |
ДАК |
Wilson, Moore, Mohn, 1996; Yu, Mohn, 1999 |
|
Bacillus sp., Escherichia, Flavobacterium sp., Flavobacterium resinovorum |
ДАК |
Hemingway, Greaves, 1973; Degradation ..., 1973 |
|
Pseudomonas sp. |
ДАК; АК; ИПК |
Hemingway, Greaves, 1973; Degradation ..., 1973; Wilson, Moore, Mohn, 1996 |
|
Bacillus mycoides, Pseudomonas acidouorans, Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
ДАК |
Studies ..., 1981 |
|
Alcaligenes eutrophus |
ДАК |
Degradation ..., 1973 |
|
Arthobacter sp. |
ДАК |
Levinson, Carter, Taylor,1968 |
|
Sphingomonas sp., Zooglea sp. |
ДАК; АК |
Mohn, 1995 |
|
Cornamonas spp., Alcaligenes spp. |
ДАК; АК; НАК; ПК; ИПК; ЛК |
Morgan, Wyndham, 1996 |
|
Грибы |
||
|
Ascochyta pinodella, Aureobasidium pullulans, Cephalosporium sp., Fusarium culmorum, Lentinus lepi-deus, Mortierella isabellina, Mucor globosus, Nodulisporium sp., “Polyporus hirsutus” (Trametes hir-suta)*, Polysporus versicolor, Stereum purpureum, Trichoderma uiride |
ДАК |
Studies ..., 1981; 1982 |
Примечание. * Инвалидные виды или устаревшие названия таксонов бактерий (согласно существующим правилам) приведены прямым шрифтом и в кавычках. В скобках приведены современные названия таксонов (если таковые имеются).
Деградирующей способностью в отношении смоляных кислот также обладают грибные культуры. Например, грибы Ascochyta pinodella, Aureoba-sidium pullulans, Cephalosporium sp., Fusarium cul-morum, Lentinus lepideus, Lenzites trabea, Mortierel-la isabellina, Mucor globosus, Nodulisporium sp., “Polyporus hirsutus” (Trametes hirsuta), Polysporus versicolor, Stereum purpureum, Trichoderma uiride способны эффективно (от 60 до 90%) утилизировать ДАК [Studies ..., 1981; Biotransformation ..., 1985]. Однако применение грибов в качестве биокатализаторов процесса биодеградации смоляных кислот потенциально опасно вследствие характера их посевного материала (споры) и способности к синтезу микотоксинов, обладающих мутагенным и канцерогенным действием.
Биотрансформация смоляных кислот
В настоящее время перспективным является не только поиск новых технологий утилизации смоляных кислот, но и получение на их основе новых биологически активных соединений. Эго становится возможным благодаря применению приема микробной биотрансформации. Использование микроорганизмов в качестве биокатализаторов, в отличие от химического синтеза, не требует применения агрессивных реагентов, процесс протекает в одну технологическую стадию, и биокатализ позволяет осуществлять направленную трансформацию с высокой степенью стерео- и региоселек-тивности. Примерами таких превращений являются реакции гидроксилирования, окисления и декарбоксилирования. Гидрокси- и оксопроизводные смоляных кислот обладают выраженной биологической активностью, благодаря чему они могут использоваться в качестве интермедиатов синтеза лекарственных средств.
Наиболее эффективной признается бактериальная трансформация смоляных кислот. Однако бактериальные клетки катализируют лишь ограниченный круг реакций гидроксилирования и окисления. Так, при трансформации канифоли, которая преимущественно содержит ДАК, представителями A. oxydans и В. amyloliquefaciens детектируются в качестве продуктов 7-гидроксидегидроабиетиновая, 15-гидроксидегидроабиетиновая, 7-оксодегид-ро-абиетиновая и 15-гидрокси-7-оксодегидро-абие-тиновая кислоты [Study ..., 2008]. Образование 7-оксо и 15-гидроксипроизводных наблюдалось при трансформации ДАК клетками Rhodococcus erytro-polis [Microbial ..., 2001]. Биотрансформация данного субстрата с использованием представителей Pseudomonas sp. также приводит к образованию 7оксопроизводных [Smith, Martin, Mohn, 2004].
Грибы способны катализировать больше разнообразных реакций по сравнению с бактериями.
Например, гидроксилирование абиетановых смоляных кислот с использованием отдельных представителей грибов чаще всего происходит только в определенных положениях, в частности Corticum sasaki (С-3), Fomes annosus (С-1, С-15 и С-16), Mucor circinelloides (С-2) или Mortierella isabellina (С2, С-15 и С-16). Представители Chaetomium coch-lioides трансформируют ДАК с образованием 15,16-дигидрокси-8,11,13 -абиетатриен-18-оновой кислоты [Biotransformation ...,1985; Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997; Regio- and stereo-selective ..., 2005]. Использование иммобилизованных и покоящихся клеток Mortierella isabellina позволяет получать 15- и 16-гидрокси-8,9,11,12-тетрадегидро-7,8-дигидроабие-тиновую кислоты из ДАК практически при полной (94%) её биоконверсии [Biotransformation ..., 1985]. Представители Moraxella sp. катализируют образование 3,7-диоксидегидро-абиетина из ДАК [Regio- and stereo-selective ..., 2005], а представители Fusarium oxysporum и F. moniliforme катализируют образование 1-гидроксипроизводных. При биотрансформации ДАК с использованием микроскопических грибов A. niger обнаружено образование 1р,7[3-дигидрокси-производных [ lb,7b-Dihydroxydehydroabietic ..., 2004]. Уровень биотрансформирующей активности у грибов в отношении ДАК может достигать 75%.
По данным многочисленных исследований [Wilson, Moore, Mohn, 1996; Liss, Bicho, Saddler, 1997; Martin, Yu, Mohn, 1999], смоляные кислоты пимаранового типа более устойчивы к биотрансформации. Это объясняется тем, что данные дитерпены не имеют сопряженных двойных связей и поэтому устойчивы к воздействию микроорганизмов.
Заключение
Смоляные кислоты являются одной из приоритетных групп экотоксикантов сточных вод целлюлозно-бумажной промышленности. Данные соединения способны оказывать токсическое воздействие на живые организмы. Современные методы утилизации смоляных кислот включают применение микробиологической обработки. Благодаря распространению смоляных кислот в окружающей среде, существует широкий круг грибов и бактерий, способных деградировать смоляные кислоты в той или иной степени. Однако наиболее эффективным способом деградации в настоящее время считается применение активного ила и газированных лагун. Использование микроорганизмов позволяет не только снизить уровень токсичных смоляных кислот, но и получать на их основе биологически активные соединения, перспективные в качестве интермедиатов для тонкого органического синтеза. Получаемые в процессе биокатализа абиетановых кислот гидрокси- и оксо-продукты обладают выраженной противоопухолевой и противовирусной активностью. Анализ литературных данных свидетельствует о том, что примеры биотрансформации смоляных кислот пимаранового типа пока немногочисленны и связаны преимущественно с использованием эукариотов, в частности представителей грибов Aspergillus, Mortierella. Необходимо отметить, что использование грибов в качестве биокатализаторов процесса биотрансформации смоляных кислот нетехнологично и даже потенциально опасно.
Проведенный анализ литературных данных показал, что смоляные кислоты обладают значительным потенциалом модификации в биологически активные соединения. В последние годы наблюдается повышенный интерес к продуктам, образующимся в результате биотрансформации смоляных кислот и обладающих выраженной противоопухолевой и противовирусной активностью. Наиболее перспективным является использование бактериальных биокатализаторов вследствие специфики их многоцелевых ферментных систем и устойчивой активности в экстремальных условиях внешней среды.
Список литературы Биодеструкция смоляных кислот - доминирующих токсичных соединений в отходах целлюлозно-бумажной промышленности
- Bicho P.A., Martin V., Saddler J.N. Growth, induction, and substrate specificity of dehydroabietic aciddegrading bacteria isolated from a kraft mill effluent enrichment//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995. Vol. 61. P. 3245-3250
- Biotransformation of dehydroabietic acid with resting cell suspensions and calcium alginate-immobilized cells of Mortierella isabellina/J.P. Kutney et al.//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985. Vol. 49(1). P. 96-100
- Burnes T.A., Blanchette R.A., Farrell R.L. Patterns of bordered pit membrane attack bacterial biodegrada-tion of extractives and in pine wood//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000. Vol. 66(12). P. 5201-5205
- Degradation bacterienne de l'acide dehydroabietique Flavobacterium resinovorum/J.F. Biellmann et al.//Tetrahedron Lett. 1973. Vol. 29. P. 1227-1236
- Distinct Roles for two CYP226 family Cytochromes P450 in abietane diterpenoid catabolism by Burk-holderia xenovorans LB400/D.J. Smith et al.//J. Bacteriol. 2008. P. 1575-1583
- Elimination of resin acids by advanced oxidation processes and their impact on subsequent biode-gradation/S. Ledakowicz et al.//Water Res. 2006. Vol. 40. P. 3439-3446
- Fengel D., Wegner G. Extractives in wood chemistry, ultrastructure and reactions//Walter de Gruyter. Pub. 1985. P. 182-226
- Hemingway R. W., Greaves H. Biodegradation of resin acid sodium salts//Tappi J. 1973. Vol. 56(12). P. 189-192
- Identification of leachable toxic fractions from lodge-pole pine/S. Nelson et al.//Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Environmental Fate and Effects of Bleached Pulp Mill Effluents. 1994. Vol. 6-9. P. 34-36
- Kovacs T.G., Voss R.H. Biological and chemical characterization of newsprint/specialty mill effluents//Water Res. 1992. Vol. 26(6). P. 771-780
- Lavallk H.C., Rouisse L., Paradis R.A. Comprehensive study of the Quebec pulp and paper mill effluents as an instrument to define a strategy for abatement//J. Pulp Pap. Can. 1993. Vol. 94(11). P. 84-90
- Lee J., Petersen D., Stickney A. Anaerobic treatment of pulp and paper mill wastewaters//Tappi J. 1989. P. 473-486
- Leppanen H., Oikari A. Occurrence of retene and resin acids in sediments and fish bile from a lake receiving pulp and paper mill effluents//Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999. Vol. 18. P. 1498-1505
- Levinson A.S., Carter B.C., Taylor M.B. Microbial degradation of methyl dehydroabietate//J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1968. P. 1344-1346
- Liss N., Bicho A., Saddler N. Microbiology and biode-gradation of resin acids in pulp mill effluents: a minireview//Can. J. Microbial. 1997. Vol. 75. P. 599-611
- MacClean B., Vegt A., Driel E. Full-scale anaerobic1 aerobic treatment of TMPIBCTMP effluent at Quesnel River Pulp//Tappi J. 1990. P. 647-661
- Martin V.J., Yu Z., Mohn W.W. Recent advances in understanding resin acid biodegradation: microbial diversity and metabolism//Arch. Microbiol. 1999. Vol. 172. P. 131-138
- McFarlane P., Clark T. Metabolism of resin acids in anaerobic systems//Water Sci. Technol. 1988. Vol. 20. P. 273-276
- Microbial transformations of diterpene acids/A.V. Vorob'ev et al.//Mendeleev Commun. 2001. Vol. 11(2). P. 72-73
- Mohn W.W. Bacteria obtained from a sequencing batch reactor that are capable of growth on dehy-droabietic acid//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995. Vol. 61. P. 2145-2150
- Morgan C.A., Wyndham R.C. Isolation and characterization of resin acid degrading bacteria found in effluent from a bleached kraft pulp mill//Can. J. Microbiol. 1996. Vol. 42. P. 423-430
- Morgan C.A., Wyndham R.C. Characterization of tdt genes for the degradation of tricyclic diterpenes by Pseudomonas diterpeniphila A19-6a//Can. J. Microbiol. 2002. Vol. 48. P. 49-59
- Mutton D. Wood resins//Wood Extractives and their Effects and Significance to the pulp and paper industry/W.E. Hillis (Ed.). New York and London: Academic Press, 1962. Chapter 10. P. 331-363
- Nyren V., Back E. The ionization constant, solubility product and solubility of abietic and dehydroabie-tic acid//Acta Chem. Scand. 1958. Vol. 12(7). P. 1516-1520
- Physiological and phylogenetic diversity of bacteria growing on resin acids/W.W. Mohn et al.//System. Appl. Microbial. 1999. Vol. 22. P. 68-78.
- Pseudomonas reinekei sp. nov., Pseudomonas moorei sp. nov. and Pseudomonas mohnii sp. nov., novel species capable of degrading chlorosalicylates or isopimaric acid/B. Camara et al.//Int. J. System. Evol. Microbiol. 2007. Vol. 57. P. 923-931
- Pulp bleaching and the environmentthe situation/Axegard P. et al.//Nord. Pulp Pap. J. 1993. Vol. 4. P. 365-378
- Regio-and stereo-selective hydroxylation of abietic acid derivatives by Mucor circinelloides and Mor-tierella isabellina/K. Mitsukura et al.//Biotechnol. Lett. 2005. Vol. 27. P. 1305-1310
- Scientific criteria document for development of provincial water quality objectives and guidelines: resin acids/B.R. Taylor et al.//Water Res. 1988. P. 59-64
- Semizi J.A., Gordon R. W. Detoxification of TMP and CTMP effluents alternating in a pilot scale aerated lagoon//Pulp Pap. Can. 1986. Vol. 87(11). P. 404-409
- Smith D.J., Martin J.J., Mohn W.W. A Cytochrome P450 involved in the metabolism of abietane diter-penoids by Pseudomonas abietaniphila BKME-9//J. Bacteriol. 2004. Vol. 186(11). P. 3631-3639
- Stoltes E., Zinkel D. Chemistry of rosin//Naval stores: production, chemistry, utilization/D. Zin-kel, J. Russel (Ed.). New York: Pulp Chem. Assoc, 1989. P. 261 -345
- Studies related to biological detoxification of kraft pulp mill effluent. I. The biodegradation of dehy-droabietic acid with Mortierella isabellina/J.P. Kutney et al.//Can. J. Chem. 1981. Vol. 59. P. 2334-2341
- Studies related to biological detoxification of kraft pulp mill effluent. IV. The biodegradation of 14-chlorodehydroabietic acid with Mortierella isabel lina/J.P. Kutney et al.//Helv. Chim. Acta. 1982. Vol. 65. P. 1343-1350
- Study of biodeterioration of diterpenic varnishes used in art painting: colophony and venetian turpentine/J. Romero-Noguera et al.//Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008. Vol. 62. P. 427-433
- Stuthridge T.R., Tavendale M.H. Biotransformation and partitioning of resin acids in an aerated stabilization basin//Tappi Press. 1996. P. 17-30
- Suckling I.D., Hua H.L., Uprichard J.M. Factors affecting resin removal from radiata pine mechanical pulps//Appita J. 1990. Vol. 43(3). P. 217-221
- Walden C.C., Howard T.E. Toxicity of pulp and paper mill, effluents-a review of regulations and research//Tappi J. 1977. Vol. 60(1). P. 122-125
- Wilson A.J., Moore E.R.B., Mohn W.W. Isolation and characterization of isopimaric acid-degrading bacteria from a sequencing batch reactor//Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996. Vol. 62. P. 3146-3151
- Yu Z., Mohn W.W. Isolation and characterization of thermophilic bacteria capable of degrading dehy-droabietic acid//Can. J. Microbiol. 1999. Vol. 45(6). P. 513-519
- Zanella E. Effect of pH on acute toxicity of dehydroa-bietic acid and chlorinated dehydroabietic acid on fish and daphnia//Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1983. Vol. 30. P. 133-140
- Zheng J., Nicholson R.A. Action of resin acids in nerve ending fractions isolated from fish central nervous system//Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998. Vol. 17. P. 1852-1859
- 1b,7b-Dihydroxydehydroabietic acid, a new biotrans-formation product of dehydroabietic acid by As-pergillus niger/S.C. Gouiric et al.//World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004. Vol. 20. P. 281-284


