Bioecological features and medicinal use of species of the genus Stachys L., widespread in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
Автор: Guliyeva N., Aliyev T.
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Естественные науки
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.11, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article describes the ecological characteristics of species of the genus Stachys L., common in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. It provides information on the taxonomic spectrum and use of species of the genus Stachys L. of the family Stachyceae. There are 15 species of this genus in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The species have medical significance.
Stachys l, species composition, systematics, azerbaijan
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14132552
IDR: 14132552 | УДК: 581.192.8 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/112/07
Текст научной статьи Bioecological features and medicinal use of species of the genus Stachys L., widespread in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
UDC 581.192.8
Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, located in the southwestern part of Azerbaijan, has a rich and diverse flora. The region is home to local and rare plant species, as well as vegetation adapted to various climatic conditions.
The flora of Nakhchivan is represented by various plant species of mountainous and lowland areas. Plants adapted to subtropical, temperate and mountainous climate conditions also grow in this region. The nature of Nakhchivan, the geographical location of the region and the richness of its ecosystems have given the region a unique and attractive character.
The genus Stachys L. is a genus of plants belonging to the Lamiaceae family and various species are found in the flora of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The genus Stachys consists mainly of perennial herbaceous plants, all species of which are used as medicinal plants. Species belonging to this genus are found mainly in dry and mountainous areas, meadows and forest edges.
Material and methodology of the study
The research was conducted in various areas of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic in 2023-2024. The arid and mountainous areas of the region were taken as the object of the study, and the species of the genus Stachys L. were used as the material. The definition and clarification of the names of species belonging to the genus Stachys L. are based on the Flora of Azerbaijan [13] and other works. Recent taxonomic changes were clarified using World Flora Online .
Dıscussıon and results of the study
The genus Stachys L. is a genus of plants belonging to the Lamiaceae family, and various species are found in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. There are 24 species of this genus in Azerbaijan, and 15 species in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The systematic composition, ecological groups, habitat, flowering and fruiting phases of the species included in the genus are given in the table below (Table).
Table
TAXONOMİC COMPOSİTİON OF SPECİES OF THE GENUS Stachys L.
|
Species name |
Environmental groups |
Areal class |
Flowering and fruiting phase |
|
Stachys atherocalyx C.Koch |
Xerophyte |
Asia Minor-Caucasus |
VI,VII-VII, VIII |
|
Stachys fominii Sosn. |
Xerophyte |
Atropaten |
V-VI |
|
Stachys balansae Boiss. & Kotschy |
Mesophytes |
Asia Minor mountain |
VII, VIII-VIII,IX |
|
Stachys macrostachya Briq. |
Mesophytes |
Front Asia |
VII-VIII |
|
Stachys officinalis (L.) Trevis. |
Mesophytes |
Western Palearctic |
VI-VIII |
|
Stachys pubescens Ten. |
Xerophyte |
Asia Minor-Caucasus |
VI,VII-VII, VIII |
|
Stachys setifera C.A.Mey. |
Mesophytes |
Front Asia |
VII-VIII |
|
Stachys sylvatica L |
Mesophytes |
Western Palearctic |
VI-VII |
|
Stachys macrantha (C. Koch) Stearn |
Mesophytes |
Northern Iran-Caucasus |
VI-VIII |
|
Stachys iberica Bieb. |
Xerophyte |
Asia Minor |
VI-VII |
|
Stachys lavandulifolia Vahl. |
Xerophyte |
Front Asia |
V,VII-VI, VIII |
|
Stachys germanica L . |
Mesophytes |
Western Palearctic |
VI-VII |
|
Stachys fruticulosa Bieb. |
Xerophyte |
Georgia |
VI-VII |
|
Stachys inflata Benth. |
Xerophyte |
Iran |
V-VI |
|
Stachys . stschegleewii Sosn |
Mesoxerophytes |
Iran |
VII-VIII |
During the analysis of ecological groups of species included in the genus, it was found that the ecological group xerophytes is widespread in the study area and is represented by 7 species, which is 47% of the total flora, the ecological group mesophytes The group with 7 species is 47%, and 1 species is classified as the ecological group of mesoxerophytes. It is monotypic, making up 6%.
Based on the literature and our own field studies, it has been established that the species of the genus belong to different areal classes, which allows us to determine the migration routes of species to the territory. Based on the zonal and regional principles, it has been established that the species included in the genus are grouped into 9 areal classes. As can be seen from the table, the following areas are represented by 1 species: West Palaearctic 3, Near East 3, Asia Minor-Caucasian 2, Iranian 2, Georgian, Atropatene, Asia Minor Mountain, Asia Minor and Northern Irano-Caucasian.
Stachys L. is a perennial plant with serrated leaves. Flowers in a multi-flowered inflorescence have a bell-shaped or elongated raceme. The calyx is tubular-cylindrical, 10-veined, 5-toothed. The corolla tube is two-lipped, the lower lip is three-lobed, the upper one is curved. The stamens are arranged in pairs, close to the upper lip. There are 24 species of this genus in Azerbaijan, and 15 species in the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic.
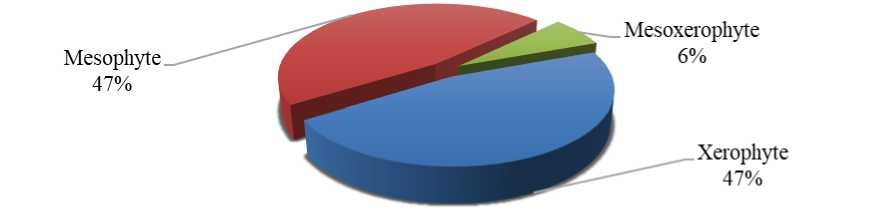
Figure 1. Ecological groups of species belonging to the genus Stachys L.
The Stachys atherocalyx plant has a variety of uses, especially in traditional medicine and herbal medicine. This species has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties and is used to treat skin inflammations and wounds. The leaves and flowers of the plant provide energy to the body, as they have a relaxing effect. The plant also contains active ingredients such as essential oils, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds, which play an important role in its antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. In some regions, S. atherocalyx infusion is used for colds and stomach problems.
Stachys fominii Sosn. It is found on rocky slopes of the middle mountain zone. The plant S. fominii is especially widely used in traditional medicine. Since the plant has anti-inflammatory properties, it is used to treat inflammatory skin diseases and inflammation in various organs. Some studies of this plant have shown that it is effective against bacteria and fungi. Therefore, it is used to treat infections, especially skin infections. St. John's wort has antioxidant properties that fight free radicals entering the body and reduce cell damage. In folk medicine, the plant is used to treat gastrointestinal diseases. An infusion of this plant is used in some regions to maintain overall health and relieve problems such as insomnia and stress.
Balansae spp. — Staceys balansius Boiss. & Kochi. It is found in meadows and shrubs of the middle mountain zone. The plant has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect in various diseases. In folk medicine, it is used to treat wounds and skin diseases, as well as various inflammatory conditions of the body. Some components of the plant relieve spasms of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system. Therefore, it is considered a useful remedy for treating abdominal pain and stomach cramps. This species is also known for its antioxidant properties.
Stachys macrostachya Brig. It is found on the rocky slopes of the middle mountain belt. S. macrostachya has anti-inflammatory properties. For this reason, it is used to treat various inflammatory diseases, especially skin inflammation and joint pain. This plant has antibacterial and antifungal properties. Infusions and extracts of the plant are used to treat skin infections and prevent fungal diseases. Large bulbs help improve the digestive system. This plant is used to combat gastrointestinal problems, abdominal pain and indigestion. It is used in traditional medicine in India and neighboring regions to maintain overall health and treat a number of diseases. Its flowers and leaves, especially in the form of infusions and extracts, are suitable for use in various diseases.
Medicinal plant — Stachys officinalis (L.) Trevis. It is found in meadows, forests and thickets of the subalpine belt. Stachys officinalis, also known as "German weed" or "royal fig", is a perennial plant. This plant is used for various medicinal purposes. The medicinal powder is mainly used for the following purposes: it is used to treat properties such as a sedative, digestive problems, muscle pain, inflammation, blood circulation and antioxidants.
Stachys pubescens Ten. It is found on the rocky slopes of the middle mountain belt. Stachys pubescens has anti-inflammatory properties and is used to treat various inflammatory diseases. It helps to reduce pain and swelling, especially in inflammation of the skin and joints. The species has antibacterial and antifungal properties. For this reason, it is used to treat skin infections and fungal diseases. The natural ingredients of the plant help prevent and treat infections. Hairy leek is important for improving the digestive system. This plant is used as a natural remedy for stomach pain, gastrointestinal discomfort, and digestive disorders.
Hairy sedge — Stachys setifera C.A.Mey. It is common along river banks and in humid areas of the middle mountain zone. Stachys setifera has anti-inflammatory properties and this plant is used to treat inflammatory diseases. It helps to reduce pain and swelling, especially in inflammation of the skin and joints. The plant has antibacterial and antifungal properties. The species has a special function of improving the digestive system. This plant is used as an important remedy for stomach pain, gastrointestinal discomfort and digestive disorders. Hairy leek is used to treat many diseases such as colds, coughs, headaches, general fatigue and digestive problems.
Wood buckthorn — Stachys sylvatica L. It is found in forests and subalpine meadows of the middle mountain and subalpine zones. Stachys sylvestris has antibacterial and antifungal properties. This species helps regulate the digestive system. It is used as a natural remedy for abdominal pain, gastrointestinal discomfort and indigestion. The plant contains various compounds that calm the nervous system. This type is especially effective in relieving headaches, colds and general fatigue.
Large-flowered cornflower — Stachys macrantha (C. Koch) Stearn. It is common in the meadows of the subalpine and alpine belts. Large-flowered leek is an important plant used for various purposes. In medicine, the flowers and leaves of the plant are used, in particular. Local people believe that this plant has anti-inflammatory properties, regulates blood pressure, has antimicrobial, sedative effects, and is also good for treating stomach and digestive diseases.
Georgian spirea — Stachys iberica Bieb. It is common on rocky, grassy and shrubby slopes of the mid-mountain and subalpine belts. Siberian anthracnose has anti-inflammatory properties and is used to treat various inflammatory diseases, especially skin diseases and problems associated with joint pain. The plant has antibacterial and antifungal properties, so it is used to treat skin infections and fungal diseases. Georgian parsley has properties that regulate the digestive system. Its infusion or other preparations are used for stomach pain, stomach upset and intestinal problems. This plant contains antioxidant substances and prevents damage to the body's cells, reducing the damage caused by free radicals. At the same time, this species has properties that calm the nervous system. It is used to relieve stress, eliminate sleep problems and nervous tension. In many regions of the Caucasus, the plant is used in folk medicine to relieve colds, coughs, headaches and general fatigue. Its flowers and leaves are used, especially in the form of infusions and extracts.
Lavender leaf — Stachys lavandulifolia Vahl. It is common in rocky and stony areas of the middle mountain zone. S. lavandulifolia has anti-inflammatory properties and can be used to treat inflammatory diseases. This plant is especially useful for reducing skin inflammation, joint pain and swelling. This plant has antibacterial and antifungal properties. S. lavandulifolia is used to treat skin infections and prevent fungal diseases. This species relieves stress by calming the nervous system and helps treat insomnia. It has a soft calming effect, relieves tension and anxiety. Lavender leaves have antioxidant properties. It helps the body fight free radicals and reduces cell damage, which slows down the aging process of the body and improves overall health. This species is used in traditional medicine to improve overall health and treat various diseases. It is especially useful for colds, headaches and general fatigue.
Stachys germanica L. It is found in forests and subalpine meadows of the mid-mountain and subalpine zones. Chamomile is used for various medicinal purposes. This plant has mainly antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and mild analgesic properties.
Stachys stschegleewii has anti-inflammatory properties. This plant is used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. This type is considered useful for skin inflammation, swelling and joint pain. The plant has antibacterial and antifungal properties, so it is used in the treatment and prevention of skin infections and fungal diseases. Taking infusions and extracts of S. stschegleewii is considered useful for improving the digestive system. It is used to relieve abdominal pain, digestive problems and intestinal problems.
The Stachys inflata plant has anti-inflammatory properties and can be used to treat various inflammatory diseases. This plant helps reduce pain and swelling, especially in skin and joint inflammations. The species has antibacterial and antifungal properties. For this reason, it is also used to treat skin infections and fungal diseases. It is used as a natural remedy for abdominal pain, gastrointestinal discomfort, and digestive problems. It is also useful for improving bowel function. The plant calms the nervous system and relieves stress. This species is widely used in Chinese medicine. This plant is used to improve overall health, strengthen the immune system, and treat diseases such as colds.
Celandine has anti-inflammatory properties. For this reason, it is used to treat various inflammatory diseases, especially skin inflammation and joint pain. This plant has antibacterial and antifungal properties. Infusions and extracts of S. macrostachya are used to treat skin infections and prevent fungal diseases. S. macrostachya helps improve the functioning of the digestive system. This plant is used to combat gastrointestinal problems, abdominal pain, and digestive disorders. This species is used in traditional medicine in India and neighboring regions to maintain overall health and treat a number of ailments. Its flowers and leaves, especially in the form of infusions and extracts, are useful for a variety of ailments.
Against inflammation
Stomach and intestinal pain, joint pain Calming Tea
Figure 2. Directions for use of the genus Stachys L.
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic is a region located in the western part of Azerbaijan and is home to various biotic groups. The climatic conditions, relief and soil types of this territory influence the formation of biotic groups. Thus, the existence of various biotic groups is an indicator of the ecological diversity and natural wealth of the region. The diversity of these groups is of great importance for the protection of natural resources and biological diversity of Nakhchivan. [1, 2, 8, 10, 20-24].
Xerophytic vegetation of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, which is the study area, creates an ecosystem that ensures the sustainability of life in the dry climate of the region. These plants contribute to the stability of the ecosystem. Xerophytic plants play an important role in protecting the natural environment in drought conditions and ensuring sustainable development of agriculture. The xerophytic ecosystem of Nakhchivan is an important resource that forms the basis of both natural life and economic development [10, 22].
The interaction of herbaceous plants with plant families creates complex relationships between plants and animals in the ecosystem. Plants mainly adapt to the environment and carry out their activities at different times of the year. Each plant family has unique characteristics and adaptive abilities. Herbaceous plants are distributed mainly in grassy ecosystems, deserts, agricultural lands, etc. In general, the interaction of herbaceous plants with different species contributes to the maintenance of the ecosystem balance and the existence of various species [9, 11, 12, 15, 25].
Forest-shrub complex ecosystems are ecosystems in which both forests and shrub plants combine and interact. These complexes are observed in various climatic conditions, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. They provide a rich habitat for various plant and animal species. Forest-shrub complex ecosystems are also important in terms of providing ecosystem services, and their protection is necessary to ensure the sustainability of ecosystem functions. Thus, in the resulting phytocenoses, the dominant species are plants belonging to the families Fabaceae, Malvaceae, Rosaceae and many others [3-7, 14, 16-19, 26-28].
Thus, the above options for using species of the genus Stachys L. do not fully reflect the directions of their use. In our further studies, it seems appropriate to comprehensively study all the features of the studied species.
Conclusion
-
1. In the course of the studies, it was found that 15 species of the genus Stachys L. are found in the flora of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. It was found that all species belonging to the genus have medicinal value. 2. When analyzing the ecological groups of species included in the genus, it was found that 5 species of the genus are xerophytes, 9 species are mesophytes and 1 species is a mesoxerophyte. According to the analysis of geographic ranges, 3 species of the genus are found in the Western Palearctic, 3 species in the Middle East, 2 species in Asia Minor and the Caucasus, 2 species in Iran, 1 species in Georgia, 1 species in Atropatena, 1 species in the mountains of Asia Minor, 1 species in Asia Minor and 1 species in It is monotypic, originating from Northern Iran and the Caucasus.
Acknowledgments: We would like to express our gratitude to Professor Dashgin Ganbarov for identifying the studied species
Financing: The research it is financed and supported on the basis of the "Herbari Fund of Biology Department of Nakhchivan State University" project.


