Biological effect of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Saccharomyces boulardii against of multidrug resistant bacteria isolated from diabetic foot infections
Автор: Mohamed Adil Hakeem, Kadium S.W.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 25, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Objective: In this study, copper oxide nanoparticles are produced using the probiotic Saccharomyces boulardii in order to assess their biological activity. The biological method of producing nanoparticles is gaining popularity due to its benefits over chemical and physical ways of synthesis in terms of affordability and environmental friendliness. Methods: To biosynthesize CuO NPs, copper sulfate was introduced at a concentration to S. boulardii’s cellfree supernatant. Results: The color change of the reaction mixture from light to dark after 150 rpm incubation, as well as the color change and antibacterial behavior, were indicators of S. bularedii’s biosynthesis of CuO NPs. The characterization completed by UV-visible spectroscopy, Atomic force microscopy, Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, Scanning Electron Microscopy, and X-ray diffraction (AFM). The CuO NP absorption spectra in the reaction mixture’s UV visible spectroscopy were (537.93 nm). The XRD showed that CuO NPs’ crystal size was (14.65 nm). The SEM was provided; the shape was uniform and spherical, and the average size (16.03 nm). EDS was used to analyze the presence of elemental CuO NPs. The CuO NPs’ three-dimensional structure was seen by the AFM, and their average diameter was (41.11 nm). The FTIR spectrum reveals a variety of functional groups that are present at various locations. Gram positive and gram negative bacteria that were isolated from diabetic foot infections were multidrug resistant (MDR), and biosynthesized CuO NPs demonstrated antibacterial action against these bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus mirabilis). In the form of biofilm using a microtiter plate.
Biosynthesis cuo nps, saccharomyces boulardii, antibiofilm, antimicrobial, antioxidant activity
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148326591
IDR: 148326591 | DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.25.3140
Текст научной статьи Biological effect of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Saccharomyces boulardii against of multidrug resistant bacteria isolated from diabetic foot infections
Adil Hakeem Mohamed, S. W.Kadium. Biological effect of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Saccharomyces boular-dii against of multidrug resistant bacteria isolated from diabetic foot infections. Cardiometry; Special issue No. 25; December 2022; p. 31-40; DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.25.3140; Available from:
EXPERIMENTAL
Preparation supernatant of S. boulardii
Saccharomyces boulardii was carefully selected from a variety of yeast species based on its resistance to extracellular synthesis of CuO NPs (supernatant) and its capacity to resist commercial CuO NPs. S. boulardii was injected into Sabouraud dextrose broth (SDB), which was then incubated for 24 hours at 37°C. To separate the S. boulardii supernatant from the culture, the centrifuge was run at 6000 rpm for 25 minutes at 4°C. In order to use cell-free supernatants in the biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles (Sahib et al 2017).
Biosynthesis of CuO NPs using cell free supernatant
S. boulardii used copper sulfate as the precursor for the production of CuO NPs. To the cell free supernatant, which had already mixed, copper sulfate was added at a concentration of 1mM. The resulting solutions were incubated for 24 hours at 37° C in a shaking incubator at 150 rpm. After incubation, the reaction mixture was centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 25 min. at 4°C to remove the supernatant. The supernatant was then replaced with deionized distill water, and the centrifugation process was repeated three more times under the same conditions to remove any remaining supernatant. The pellet-shaped collection of nanoparticles was then dried in an oven at 40°C for 18 to 24 hours. The dried powder was carefully gathered and kept in storage for additional analysis. (Harishchan-dra et al 2021).
Characterization of CuO nanoparticles
CuO NPs were characterized using X-ray diffraction and UV visible spectroscopy. In the electron microscopy unit, SEM was utilized to characterize the morphology of nanoparticles. The microscope functioned with variable magnifications, low vacuum, a spot size of 4, and working distances of 5–10 mm at an accelerated voltage of 15 KV (Shafaghat, 2015). Utilizing Bruker EDS coupled with SEM, elemental analysis 32 | Cardiometry | Issue 25. December 2022
Antibacterial activity of CuO nanoparticles
Biogenic CuO NPs’ antibacterial activity was delivered via agar well diffusion against several pathogenic, multi-drug resistant gram positive and gram negative bacteria isolated from diabetic foot infections. Each tested bacterium was suspended to the McFarland standard (0.5N) and then swabbed separately onto sterile Muller-Hinton Agar (MHA) plates. Agar was pierced with a 7 mm sterilized cork borer, and 100 l of biogenic CuO NPs were added to each well at various concentrations (50, 100, and 200 g/ml), which were then incubated for 24 hours at 37 °C. The inhibitory zones were then quantified (Rajeshkumar and Malarkodi, 2014).
Antibiofilm activity of CuO nanoparticles
For a quantitative evaluation of biofilm production and antibiofilm activity by nanoparticles, the Tissue Culture Plate Method or Microtiter Plate Method was employed as the gold standard test for biofilm detection. ( Barapatre et al 2016 ).
Antioxidant activity of biogeneic copper oxide nanoparticles in vitro
The ability of the extracts to scavenge free radicals was assessed using the DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl). In methanol, the DPPH solution (0.006% w/v) was created. 96-well plates are used. 200 L of freshly made DPPH solution was added to the control well, 200 L of methanol was added to the blank well, 100 L of ZnO NPs (1 mg/ml, 0.5 mg/ml, 0.25 mg/ml, 0.12 mg/ml) were added to each well’s DPPH solution, and the final volume was 200 L. After 30 minutes of incubation in the dark, discoloration was measured at 517 The control was DPPH solution.Using the following equation, the percentage of DPPH free radical scavenging was determined:
DPPH scavenging impact (%) = (Ao –A1) / Ao X 100
where A1 represents the absorbance in the presence of the CuO NPs and Ao represents the absorbance in the control. (Goyal et al 2010).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Biosynthesis of CuO NPs
The extracellular production of CuO NPs by Sac-charomyces boulardii was demonstrated utilizing cell free supernatant and zinc acetate (1Mm) as a precursor. The free cell supernatant of S. boulardii has the capacity to alter the color of the reaction mixture after 24 hours of shaking incubation at 37°C and 150rpm, which indicates as an indicator for the biosynthesis of the CuO NPs. The microbial cell secretes reductases that are used in the bio reduction of metal ions into the appropriate NPs during the extracellular creation of nanoparticles. (Ovais et al ., 2018). The antibacterial behavior and the reaction mixture’s color change from light to dark after 150 rpm incubation were indicators that S. bularedii was responsible for the CuO NPs’ biogenesis. Because of its reproducibility and adaptability, the biological technique was used. This process is quite controlled since it enables some degree of surface charge and particle size control (Yien et al., 2012). Numerous investigations have suggested that the creation of metal nanoparticles involves NADH and NA-DH-dependent enzymes. It appears that the reduction was initiated by the NADH-dependent reductase acting as an electron carrier to transfer electrons from the NADH (Ranganath et al., 2012; Joerger et al., 2000). The morphology depends on a number of chemical and physical factors, including incubation time, pH, composition of the culture medium and growth in the light or dark (Durán et al ., 2011).
UV-visible Spectroscopy
In the analysis of CuO NPs with Uv-vis spectrophotometry, absorption peak was observed at 537.93 nm wavelength, indicating the presence of CuO NPs in the reaction solution, figure (1).
Visual inspection and UV-vis spectroscopy measurements of the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) band can both attest to the biosynthesis of nanoparticles. Nanoparticles’ single SPR band demonstrates their spherical shape. (Abdulhassan, 2016).
XRD analysis of nanoparticles
The XRD showed that, S. boulardii produced CuO NPs with average crystal size 14.65 nm, Figure (2) .
X-ray diffraction pattern of CuO NPs synthesized extracellularly by S. boulardii showed intense peaks at 2θ corresponding to around the lattice planes indexes, Table (1).
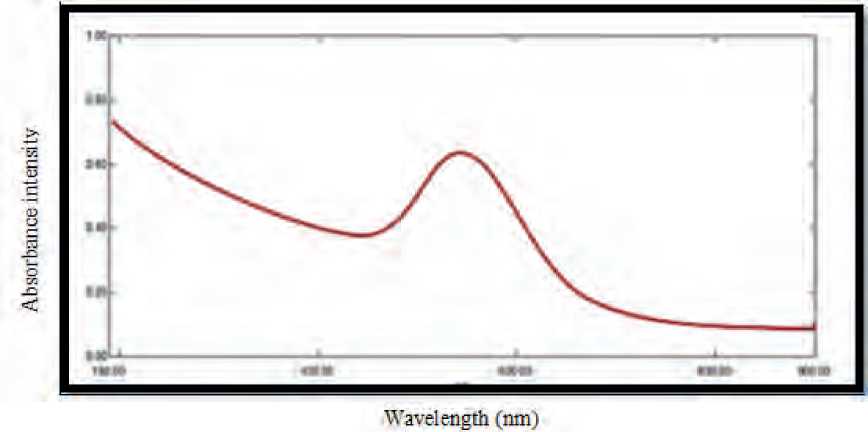
Figure (1): UV-visible spectroscopy analysis of CuO NPs synthesis by S. bularedii
Table (1
Lattice planes resulted by the CuO NPs that correspond to the Tenorite, CuO syn, Monoclinic standard card (PDF#45-0937).
|
h k l index |
Source of CuO NPs |
|
S. boulardii |
|
|
002 |
35.091 (2θ) |
|
111 |
40.999 (2θ) |
|
020 |
53.842 (2θ) |
|
202 |
56.55 (2θ) |
|
113 |
67.945 (2θ) |
|
004 |
75.433 (2θ) |
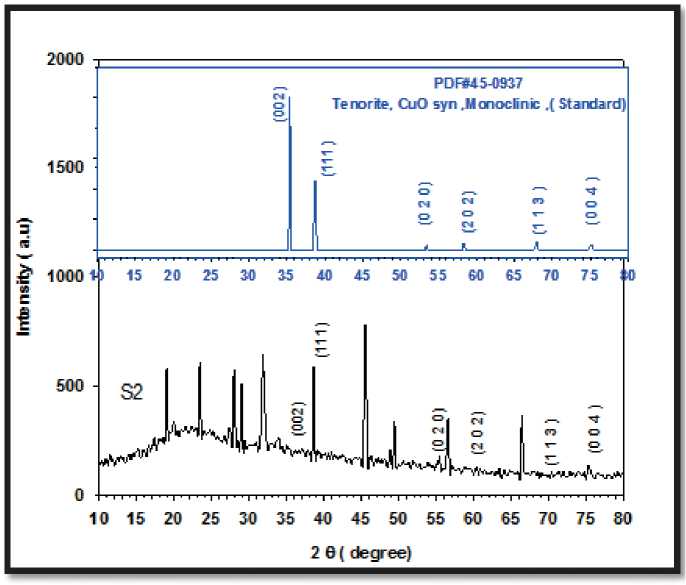
Figure (2) reveals the XRD pattern and quantitative analysis of the sample CuO NPs as synthesized by S. boulardii . The XRD of the NPs formed diffraction peaks that correspond to the Tenorite, CuO syn, Monoclinic standard card (PDF#45-0937).
Their crystalline structure is revealed by the peaks’ sharpness in the XRD spectrum (Yallappa et al 2013). Raza et al. (2016) used the concept of active facets to describe the shape-dependent antibacterial activity of nanoparticles. They discovered that facets with a high atom density, such those with a 111, have a high antibacterial activity. The outcome of the current study is in excellent accord with the nanoparticle XRD finding.
CuO NPs have a noticeable peak with 111 facets. The sample’s shaped nanoparticles have a large number of facets (111), which boosts their antibacterial activity.
SEM analysis of CuO NPs
The SEM results showed well-dispersed nanoparticles and homogenous with size average (16.03 nm) for CuO NPs, with spherical form, Figure (3).
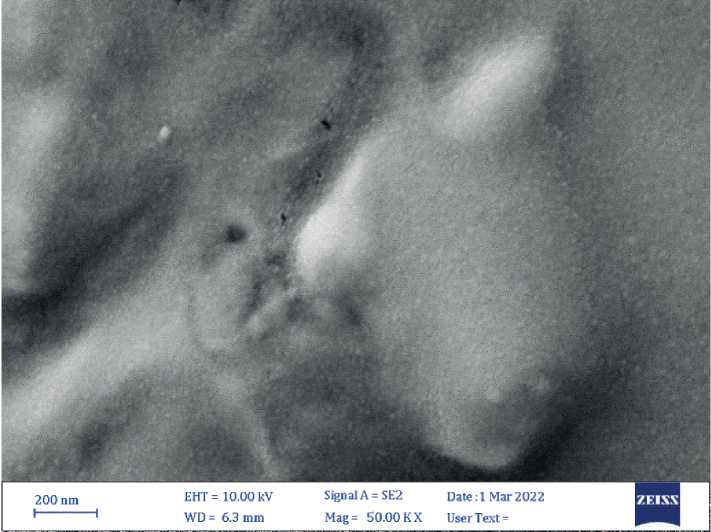
Figure (3): SEM micrograph of biogenic CuO NPs. Size average (16.03 nm) 34 | Cardiometry | Issue 25. December 2022
The SEM used to define the shape and size of biogenic nanoparticles, CuO NPs irregular tiny spherical shape, this result agreement with the results of Zhao et al (2022)
EDS analysis of nanoparticles
CuO NPs made with S. bularedii underwent EDS spectroscopy investigation, which proved the existence of elemental copper based on the signals. The nanoparticles showed a peak in the EDS spectrum as a result of the absorption of copper oxide nanocrystallites that correspond to SPR. The element that was seen was copper, and other elements including oxygen, sodium, chloride, sulfur, and carbon were also taken into consideration. This imply that they were combined precipitates from the centrifuged superna-tant/metal solution and comprise an essential component in the structural proteins of microorganisms (Bukhari et al 2021). Cu’s weight percentage of the elements was 13.9%, and oxygen’s weight percentage was 16.4%. Figure (4), Table (2).
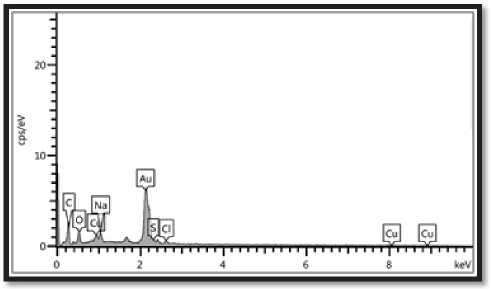
Figure (4): EDS analysis (point and mapping) of biogenic CuO NPs: the optical absorption peak of Cu was observed at 3Kev, the weight percentage of copper (13.9%) and oxygen was (16.4%).
Table (2)
Elemental analysis of CuO NPs nanocomposite
|
Elements |
Wt % |
|
C |
46.4 |
|
O |
16.4 |
|
Cu |
13.9 |
|
Na |
9.0 |
|
Cl |
8.7 |
|
S |
5.5 |
AFM analysis of nanoparticles
Atomic force microscope (AFM) analysis seemed, S. boulardii produced CuO NPs with average diameter 41.11 nm and average roughness 10.19 nm, Figures (5, 6) .
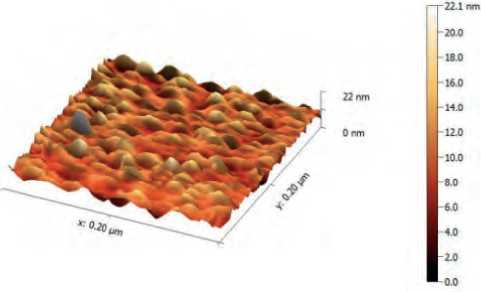
Figure (5) AFM analysis shows three-dimension image, and topography of biogenic CuO NPs synthesis by S. bularedii
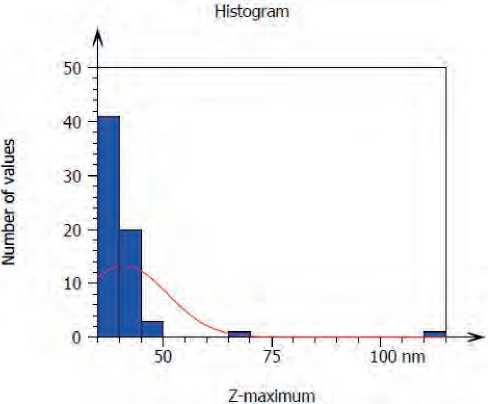
Figure (6) Granularity and accumulation distribution chart of biogenic CuO NPs synthesis by S. bularedii
CuO NPs were shown in three dimensions by AFM analysis, and the typical diameter of CuO NPs derived from S. boulardii was 41.11 nm. This result may be attributed to differences in the bio-reduction that may be return to the qualitative and quantitative of extracellular protein/enzyme and other biomolecules that offered in the culture of each microorganism, in addition to their ability of interaction with precursor for synthesized nanoparticles. Nanoparticles amalgamation was better in terms of quality; minimum size and less polydispersity, with S. bularedii (copper sulfate) (Chaudhari, et al 2012).
FTIR analysis of nanoparticles
The FTIR spectrum shows various functional groups present at different positions, the wavenumber started from 400 cm-1 to 4000 cm-1 and peaks below 1500 cm-1 called fingerprinting region, peaks above 1500 cm-1 called diagnostic region (Onysz-ko et al 2022). The CuO NPs synthesized by S. bu-
Issue 25. December 2022 | Cardiometry | 35
laredii exhibited prominent peaks at 3428 cm-1, 2933 cm-1, 1654 cm-1, indicate the presence of O-H stretching, C-H stretching vibration of alkane groups and C=C stretching (alkene) respectively, figure (7). These results agreement with (Zhao et al 2022).
Antibacterial activity
The results demonstrated that both gram positive and gram negative bacteria can grow more slowly when exposed to CuO NPs. Gram negative bacteria had a larger inhibitory zone than gram positive bacteria. At a concentration of 200 g/ml, CuO NPs produced by S. bularedii exhibited the strongest inhibition against P. mirabilis (240.8) and the lowest inhibition against S. aureus (180.4). This supports (Ali et al 2021). The investigation also revealed notable variations between the various doses at (P ≤ 0.05), Table (3).
By way of an adsorption process, metal oxide NPs typically permeate into bacterial cells and release metal ions that cause DNA damage and produce ROS oxide NPs. As a result, the surface area of bacterial cells considerably increased and interacted with intracellular enzymes (Siddiqi & Husen 2018). According to Wang et al. (2018) and Fein et al. (2019), biopolymer comprises carboxyl and amine groups, and copper typically interacts with those functional groups on the bacterial cell surface (Sharma et al 2012). CuO NPs have strong antibacterial activity because of the ionic nature and surface charge of Cu (Azam et al. 2012), which interacts with several functional groups on the cell surface. (Shirzadi‐Ahodashti et al 2020).
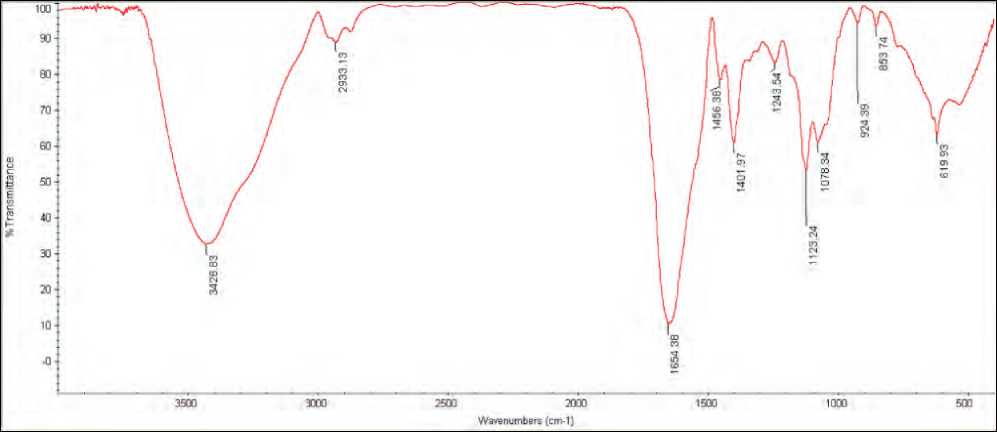
Figure (7): Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra of CuO NPs synthesized by S. bularedii
Table (3)
Antibacterial activity of the CuO NPs synthesis by S. bularedii against the tested bacteria as demonstrated by diameters of the inhibition zone (mm).
|
(A) |
(D) |
(B) (C)(µg/ml) |
Inhibition zone (mm) (Mean±S.D) |
||
|
S. bularedii |
|||||
|
50 |
100 |
200 |
|||
|
CuO NPs |
S. aureus |
16±1.6 |
17±0.4 |
18±0.4 |
|
|
E. coli |
17±1.4 |
20±0.2 |
22±1.1 |
||
|
P. aeruginosa |
10±1.0 |
18±1.1 |
23±1.6 |
||
|
K. pneumonia |
16±1.6 |
18±0.7 |
22±1.3 |
||
|
P.mirabilis |
18±1.2 |
20±1.3 |
24±0.8 |
||
LSD (O.O5)(A*B*C*D) —1*"2
A: type of nanoparticles
B: S. bularedii used for synthesized nanoparticles
C: Concentration of nanoparticles
D: pathogenic bacteria
Antibiofilm activity of copper oxide nanoparticles
The quantitative measurement of biofilm production is done using the microtiter plate method (Peer-zada et al 2022). We selected one isolate from Gram positive bacteria and one from Gram negative bacteria from earlier research since all of the isolates produced biofilm. Different doses of Biogenic CuO NPs were investigated for anti-biofilm action against two bacterial strains, including (S. aureus and P. mirabilis). Based on earlier studies (Panda et al. 2016; Sultan & Nabiel, 2019), biofilm formation was computed and classified as strong, moderate, or non/weak. In this study, the production of biofilms decreased with increasing con- Table (4)
centrations of CuO NPs, with (1024 g/ml) concentration showing the maximum inhibition and (4 g/ml) showing the lowest inhibition., Table (4,5).
Additionally, the study demonstrated that there were differences in biofilm formation caused by S. bu-laredii-produced nanoparticle concentration and their impact on S. aureus and P. mirabilis at a significant level of (P 0.05). table (6).
Nanoparticles may be altered gene the expression relating to biofilm formation, as consequence they affect on microcolony formation and biofilm maturation .This lead to nanoparticles could be used for prevention and treatment of biofilm-related infections (González et al 2015; Schmidt et al 2017; Hassan, 2018).
Effect of CuO NPs from S.bularedii on S. aureus biofilm
|
non/weak |
OD |
inhibition% |
moderate |
OD |
inhibition% |
stronge |
OD |
inhibition% |
control |
OD |
|
1024 μg/ml |
0.004 |
98.65 |
16 μg/ml |
0.177 |
33.97 |
4 μg/ml |
0.267 |
0.07 |
control |
0.268 |
|
512 μg/ml |
0.009 |
96.49 |
8 μg/ml |
0.188 |
29.93 |
2 μg/ml |
0.268 |
0.00 |
||
|
256 μg/ml |
0.015 |
94.36 |
||||||||
|
128 μg/ml |
0.039 |
85.58 |
||||||||
|
64 μg/ml |
0.054 |
80.01 |
||||||||
|
32 μg/ml |
0.09 |
66.55 |
Table (5)
Effect of CuO NPs from S.bularedii on P.mirabilis biofilm
|
non/weak |
OD |
inhibition% |
moderate |
OD |
inhibition% |
stronge |
OD |
inhibition% |
control |
OD |
|
1024 μg/ml |
0.005 |
98.14 |
64 μg/ml |
0.139 |
50.46 |
8 μg/ml |
0.276 |
1.14 |
control |
0.280 |
|
512 μg/ml |
0.006 |
97.82 |
32 μg/ml |
0.165 |
41.13 |
4 μg/ml |
0.279 |
0.29 |
||
|
256 μg/ml |
0.017 |
94.03 |
16 μg/ml |
0.190 |
32.19 |
2 μg/ml |
0.279 |
0.29 |
||
|
128 μg/ml |
0.074 |
73.71 |
||||||||
Table (6)
Prevention of multiple drug resistant bacterial biofilm formation by action of CuO NPs synthesis by S. bularedii .
|
(A) |
(B) |
Inhibition biofilm formation (%) Mean±S.D |
|
|
S. bularedii |
|||
|
(D) (C) (µg/ml) |
S. aureus |
P. mirabilis |
|
|
CuO NPs |
Control |
0.00±0.0 |
0.00±0.0 |
|
2 |
0.04±0.001 |
0.14±0.01 |
|
|
4 |
0.07±0.002 |
0.29±0.02 |
|
|
8 |
29.90±2.5 |
1.14±0.1 |
|
|
16 |
34.00±2.1 |
32.20±0.3 |
|
|
32 |
66.60±3.8 |
41.10±0.7 |
|
|
64 |
80.00±3.4 |
50.50±2.6 |
|
|
128 |
85.60±1.6 |
73.70±2.2 |
|
|
256 |
94.40±1.7 |
94.00±3.7 |
|
|
512 |
96.50±2.0 |
97.80±3.9 |
|
|
1024 |
98.70±1.3 |
98.10±4.1 |
|
LSD (O.O5)(A*B*C*D) -0'909
A: type of nanoparticles
B: S. bularedii used for synthesized nanoparticles
C: Concentration of nanoparticles
D: pathogenic bacteria
Antioxidant activity of biogenic CuO NPs
The ability of nanoparticles to scavenge DPPH free radicals was demonstrated in the study by examining the transformation of DPPH from its original (purple) hue to its current (yellow) color. With higher concentrations, CuO NPs become more effective at scavenging DPPH free radicals. The lowest inhibition was at a dosage of 0.12 mg/ml, whereas the highest inhibition was at 1 mg/ ml. Additionally, the study found that there were substantial variations in the amounts of CuO NPs produced by S. bularedii (p 0.05). According to the table (7).
Table (7)
Antioxidant activity of CuO NPs nanoparticles synthesized by S. bularedii , and influence of different concentration.
|
(A) |
(B) (C) mg /ml |
Scavenging percentage (%) Mean±S.D |
|
S. bularedii |
||
|
CuO NPs |
Control |
0.00±0.00 |
|
1 |
72.44±4.71 |
|
|
0.5 |
71.76±5.09 |
|
|
0.25 |
70.80±3.00 |
|
|
0.12 |
69.16±2.75 |
LSD (o,o5)(a.b.q =0.429
A: type of nanoparticles
B: S. bularedii used for synthesized nanoparticles
C: Concentration of nanoparticles
Inhibition titer it varies from one type of nanoparticles to another, due to a donated electron and accepts by DPPH (Kanipandian et al 2014; Bhakya et al 2015).
Список литературы Biological effect of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Saccharomyces boulardii against of multidrug resistant bacteria isolated from diabetic foot infections
- Abdulhassan, A. J. (2016). Effect of Silver and Titanium Nanoparticles Synthesized by Lactobacillus as Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Some Physiological Parameters (Doctoral dissertation, Master Thesis. University of Kufa, Faculty of Science–Iraq).
- Ali, E. M., Rasool, K. H., Abad, W. K., & Abd, A. N. (2021, July). Green Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial activity of CuO nanoparticles (NPs) Derived from Hibiscus sabdariffa a plant and CuCl. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1963, No. 1, p. 012092). IOP Publishing.
- Azam, A., Ahmed, A. S., Oves, M., Khan, M. S., & Memic, A. (2012). Size-dependent antimicrobial properties of CuO nanoparticles against Gram-positive and-negative bacterial strains. International journal of nanomedicine, 7, 3527.
- Barapatre, A., Aadil, K. R., & Jha, H. (2016). Synergistic antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized by lignin-degrading fungus. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 3(1), 1-13.
- Begum, S. J., Pratibha, S., Rawat, J. M., Venugopal, D., Sahu, P., Gowda, A., ... & Jaremko, M. (2022). Recent Advances in Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Bioactive Metallic Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals, 15(4), 455.
- Bhakya, S.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Sukumaran, M. and Muthukumar, M.(2015). Biogenic synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Appl Nanosci., 6 (5):755–766.
- Bukhari, S. I., Hamed, M. M., Al-Agamy, M. H., Gazwi, H. S., Radwan, H. H., & Youssif, A. M. (2021). Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Streptomyces MHM38 and its biological applications. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2021.
- Chaudhari, P. R., Masurkar, S. A., Shidore, V. B., & Kamble, S. P. (2012). Antimicrobial activity of extracellularly synthesized silver nanoparticles using Lactobacillus species obtained from VIZYLAC capsule. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, (Issue), 25-29.
- Dahiya, D., & Nigam, P. S. (2022). The Gut Microbiota Influenced by the Intake of Probiotics and Functional Foods with Prebiotics Can Sustain Wellness and Alleviate Certain Ailments like Gut-Inflammation and Colon-Cancer. Microorganisms, 10(3), 665.
- Durán, N., Marcato, P.D., Durán, M., Yadav, A., Gade, A., Rai, M.; Mechanistic aspects in the biogenic synthesis of extracellular metal nanoparticles by peptides, bacteria, fungi, and plants; Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol, 2011; 90: 1609‐1624.
- Fein, J. B., Yu, Q., Nam, J., & Yee, N. (2019). Bacterial cell envelope and extracellular sulfhydryl binding sites: their roles in metal binding and bioavailability. Chemical Geology, 521, 28-38.
- González, A.G.; Mombo, S.; Leflaive, J.; Lamy, A.; Pokrovsky, O.S. and Rols, J.L. (2015). Silver nanoparticles impact phototrophic biofilm communities to a considerably higher degree than ionic silver. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 22(11):8412-24.
- Goyal, A. K., Middha, S. K., & Sen, A. (2010). Evaluation of the DPPHradical scavenging activity, total phenols and antioxidant activities in Indian wild Bambusa vulgaris” Vittata” methanolic leaf extract. Journal of Natural Pharmaceuticals, 1(1).
- Harishchandra, B. D., Pappuswamy, M., Antony, P. U., Shama, G., Pragatheesh, A., Arumugam, V. A., ... & Sundaram, R. (2020). Copper nanoparticles: a review on synthesis, characterization and applications. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Biology, 5(4), 201-210.
- Hassan, H. H. (2018). Biosynthesis and characterization of Ag Nanoparticles from Klebsiella pneumonia (Doctoral dissertation, University of Kufa).
- Joerger R, Klaus T, Granqvist CG. Biologically produced silver carbon composite materials for optically functional thin-film coatings. Adv Mater, 2000; 12: 407–409
- Kanipandian, N., Kannan, S., Ramesh, R., Subramanian, P., & Thirumurugan, R. (2014). Characterization, antioxidant and cytotoxicity evaluation of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Cleistanthus collinus extract as surface modifier. Materials Research Bulletin, 49, 494-502.
- Onyszko, M., Markowska-Szczupak, A., Rakoczy, R., Paszkiewicz, O., Janusz, J., Gorgon-Kuza, A., ... & Mijowska, E. (2022). The cellulose fibers functionalized with star-like zinc oxide nanoparticles with boosted antibacterial performance for hygienic products. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 1-13.
- Ovais, M., Khalil, A. T., Ayaz, M., Ahmad, I., Nethi, S. K., & Mukherjee, S. (2018). Biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles via microbial enzymes: a mechanistic approach. International journal of molecular sciences, 19(12), 4100.
- Panda, P. S., Chaudhary, U., & Dube, S. K. (2016). Comparison of four different methods for detection of biofilm formation by uropathogens. Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology, 59(2), 177.
- Peerzada, Z., Kanhed, A. M., & Desai, K. B. (2022). Effects of active compounds from Cassia fistula on quorum sensing mediated virulence and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. RSC Advances, 12(24), 15196-15214.
- Rajeshkumar, S., Malarkodi, C.; In Vitro Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles against Foodborne Pathogens; Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications, 2014; 10.
- Ranganath, E., Rathod, V.,Banu, A.; Screening of Lactobacillus spp, for mediating the biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from silver nitrate; Journal of Pharmacy, 2012; 2(2): 237-241.
- Raza, M. A., Kanwal, Z., Rauf, A., Sabri, A. N., Riaz, S., & Naseem, S. (2016). Size-and shape-dependent antibacterial studies of silver nanoparticles synthesized by wet chemical routes. Nanomaterials, 6(4), 74.
- Sahib, F. H., Aldujaili, N. H., & Alrufae, M. M. (2017). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Saccharomyces boulardii and study their biological activities. European journal of pharmaceutical and medical research, 4(9), 65-74.
- Schmidt, H.; Thom, M.; Madzgalla, M.; Gerbersdorf, S.U.; Metreveli, Gand Manz, W. (2017). Exposure to Silver Nanoparticles Affects Biofilm Structure and Adhesiveness. J Aquat Pollut Toxicol. 1(2):9.
- Shafaghat, A. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles by phytosynthesis method and their biological activity. Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic, Metal-Organic, and Nano-Metal Chemistry, 45(3), 381-387.
- Sharma, A., Kumar Arya, D., Dua, M., Chhatwal, G. S., & Johri, A. K. (2012). Nano-technology for targeted drug delivery to combat antibiotic resistance. Expert opinion on drug delivery, 9(11), 1325-1332.
- Shirley, B., & Jarochowska, E. (2022). Chemical characterisation is rough: the impact of topography and measurement parameters on energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy in biominerals. Facies, 68(2), 1-15.
- Shirzadi‐Ahodashti, M., Ebrahimzadeh, M. A., Ghoreishi, S. M., Naghizadeh, A., & Mortazavi‐Derazkola, S. (2020). Facile and eco‐benign synthesis of a novel MnFe2O4@ SiO2@ Au magnetic nanocomposite with antibacterial properties and enhanced photocatalytic activity under UV and visible‐light irradiations. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 34(5), e5614.
- Siddiqi, K. S., & Husen, A. (2018). Properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their activity against microbes. Nanoscale research letters, 13(1), 1-13.
- Singh, N., Armstrong, D. G., & Lipsky, B. A. (2005). Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Jama, 293(2), 217-228.
- Sultan, A. M., & Nabiel, Y. (2019). Tube method and Congo red agar versus tissue culture plate method for detection of biofilm production by uropathogens isolated from midstream urine: Which one could be better?. African Journal of Clinical and Experimental Microbiology, 20(1), 60-66.
- Veve, M. P., Mercuro, N. J., Sangiovanni, R. J., Santarossa, M., & Patel, N. (2022, June). Prevalence and Predictors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa among Hospitalized Patients with Diabetic Foot Infections. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases.
- Wang, B. B., Liu, X. T., Chen, J. M., Peng, D. C., & He, F. (2018). Composition and functional group characterization of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in activated sludge: the impacts of polymerization degree of proteinaceous substrates. Water research, 129, 133-142.
- Yallappa, S., Manjanna, J., Sindhe, M. A., Satyanarayan, N. D., Pramod, S. N., & Nagaraja, K. (2013). Microwave assisted rapid synthesis and biological evaluation of stable copper nanoparticles using T. arjuna bark extract. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 110, 108-115.
- Yien, L., Zin, N. M., Sarwar, A., and Katas, H. (2012). Antifungal activity of chitosan nanoparticles and correlation with their physical properties. International Journal of Biomaterials, 2012.
- Zhang, S., Lin, L., Huang, X., Lu, Y. G., Zheng, D. L., & Feng, Y. (2022). Antimicrobial Properties of Metal Nanoparticles and Their Oxide Materials and Their Applications in Oral Biology. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2022.
- Zhao, H., Maruthupandy, M., Al-mekhlafi, F. A., Chackaravarthi, G., Ramachandran, G., & Chelliah, C. K. (2022). Biological synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using marine endophytic actinomycetes and evaluation of biofilm producing bacteria and A549 lung cancer cells. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 34(3), 101866.


