Biomorphological characteristics, phytochemical composition and medical significance of species belonging to the Geranium Tourn. ex L. Genus
Автор: Alibeili Khayala, Sadygov Tofig, Gafarova Mehriban, Abbasov Javid
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Биологические науки
Статья в выпуске: 10 т.8, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Geranium Tourn. ex L. is a flowering plant Genus belonging to the Geraniaceae Family. It is mainly grown as an ornamental plant in Azerbaijan. It was brought to Europe in the 17th century. Its propagation zone is South Africa. It is cultivated in many countries because it is a very valuable essential oil plant. Geranium is also successfully cultivated in Azerbaijan. Geranium essential oil is used in the perfume industry to make perfumes, soaps and face lotions. It is also used in the food industry to flavor beverages, as well as confectionery. It is also used in the preparation of medicines. Not only the leaves of the geranium plant, but also its roots, flowers and leaves are considered very good. The root of the plant contains phenols, various phenolic compounds in the upper green part, sucrose, starch and hemicellulose. The leaves and flowers are rich in phenolic carboxylic acids, vitamins, flavonoids, pigments, essential oils and carbohydrates.
Geranium, ornamental plants, analysis, flowers, flavonoids
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14125963
IDR: 14125963 | УДК: 582.998.3:577.19 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/83/04
Текст научной статьи Biomorphological characteristics, phytochemical composition and medical significance of species belonging to the Geranium Tourn. ex L. Genus
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
UDC 582.998.3:577.19
The main purpose of the article is to study the morphological features, essential oil, phytochemical composition and medical significance of some species belonging to the genus Geranium , introduced in Absheron and cultivated in cultural conditions.
The plant species of the genus Geranium consists of 422 species, including monocotyledonous, dicotyledonous and perennial species. They are mainly distributed in temperate zones, mountainous parts of tropical zones and in the east of the Mediterranean region. There are 23 species in Azerbaijan, and they are mainly cultivated as ornamental plants. It was brought to Europe in the 17th century. Its propagation zone is South Africa. The leaves of geraniums are round, narrow, with an arrow-shaped tip, plamatus (the leaves of the plant protrude from one point) — palm-shaped, the cuts can extend to the middle vein of the leaf. The leaves are divided into narrow, pointed segments in the form of palms.
The flowers are bisexual. It has 5 calyx leaves, 5 petals. The flowers are white, pink, purple or blue, and often have different veins on them. Most of the fruit has a box shape that is broken down into seeds. When the seed matures, it is divided into 5 seeds. The leaves are simple, finger-shaped, covered with hairs that secrete a little - very fragrant oil. Geranium species can grow in any soil, but the soil should not be swampy, because in this case the roots of the plant cannot receive enough oxygen. Propagation is carried out in the summer by dividing the half-ripe cuttings, seeds in the fall, and in the spring by dividing.
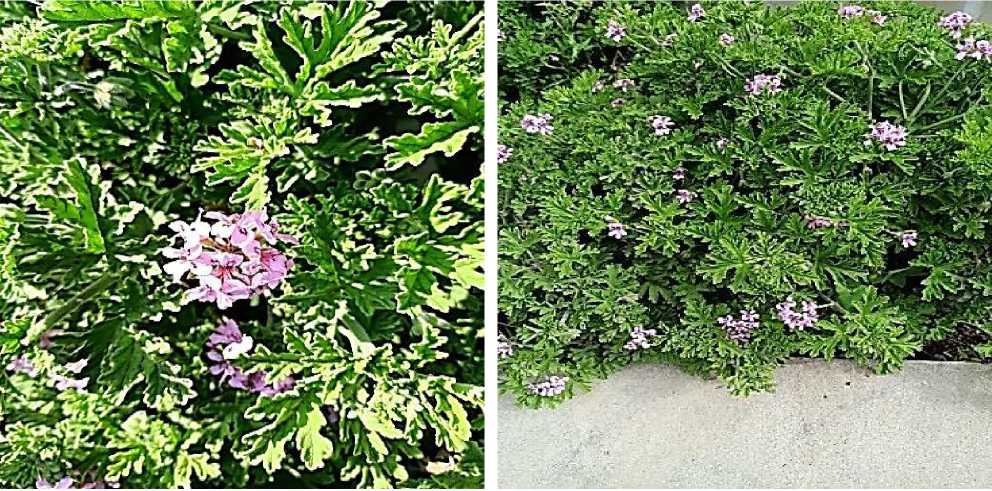

Figure 1. Geranium species
Figure 2. Leaves and flowers of Geranium species
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice Т. 8. №10. 2022
The fruit capsule consists of five cells attached to a column formed from the center. The cells form lobes of tissue in each, and these lobes gradually separate. When the fruit ripens, the beak-like stigma springs open and the seeds are scattered around.
All of the above species are perennials and generally winter-hardy and are usually grown for their attractive flowers and leaves. They are long-lived and most have palmate-shaped leaves. They grow both vertically and horizontally. Some species grow and spread vertically (rhizomes). They are usually grown from partial shade to full sun, in well-drained but moisture-retaining soils rich in humus from plant and animal remains. Other perennials grown for flowers and leaves include G. argenteum, G. eriostemon, G. farreri, G. nodosum, G. procurrens, G. renardii, G. traversii, G. tuberosum, G. versicolor, G. wallichianum and G. wlassovianum . Some of them are not winterhardy in cold areas and are grown in special gardens such as rock gardens. The land area in the rock gardens is distinguished by the abundance of gravel, stones and rocks.
Materials and Methods
Geranium species were taken as the object of research, from which pens were made for planting. Before planting in special greenhouses in the greenhouse of the Institute of Dendrology and in the open field, sand, soil and peat were mixed in a ratio of 1: 1: 1 and planted in special greenhouses in January-February and in the experimental field in March-April. All kinds of agro-technical care rules were shown to the plants and plant samples were collected for research. The formation of the roots of the pens was compared with the greenhouse in the open field. The collected plant samples were dried using standard methods and prepared for laboratory research. The results of the analysis are given in Table 1. Various methods were used in conducting research.
Geranium is eaten by larvae of some Lepidoptera species. Geranium is cultivated in Azerbaijan mainly as an ornamental plant. Only one type of it is used in medicine — Geranium collinum . Geranium is a perennial herb with dense hairs and fleshy roots. In the lower part of the stem, there are fruits with 5 to 7 sections, deep finger-shaped leaves, pink-red flowers, and 5-seeded fruit. The plant blooms in June-July, the fruits ripen in August [4].
It grows in the middle and upper mountainous parts of the Greater and Lesser Caucasus in Azerbaijan - in meadows, gardens and forest edges.
The hill-like geranium growing in Azerbaijan has not been studied scientifically yet. However, the hill-like geranium, which is widespread in Uzbekistan, was chemically analyzed at the Tashkent Pharmaceutical Institute and found to contain vaccines in all its parts. In addition, the leaves contain ellagic, gallic and 3-methoxygall acids, as well as flavonoids: quercetin, kaempferol, 3, 7, 8, 4-tetrahydroxyflavone, rutin, isoquercitrin and anthocyanins. Pelargonium chloride was found in the flowers.
Due to its analgesic and sedative properties, geranium oil is also used in neurology in radicular syndrome, rheumatism, arthritis.
It is prescribed for external and internal bleeding (especially gastric bleeding). The liquid extract has a stimulating effect on the nervous system. Ibn Sina reported on the antitoxic properties of this plant against snake venom.
Results and Discussion
The roots of geranium species contain vaccines. The roots of G. dissectum are used as a vegetable. The roots and leaves of G. ibericum are black, and the flowers of G. sylvaticum are blue. The leaves of G. dissectum contain from 251.1 mg% to 457.7 mg%, and G. tuberosum contains 288.4 mg% of vitamin C. Geranium species are widespread in the foothills to the alpine grasslands. Also, one of the important conditions for studying the bioecological characteristics of ornamental and
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice Т. 8. №10. 2022 economically important plants and determining their application to the economy is to determine the methods of their reproduction [5].
Due to the release of essential oil, keeping it in a room creates a pleasant aura [3]. It regulates the air in the room, produces oxygen and essential oil. The oil extracted from its flowers has a whitening and toning effect. It has a very good effect on all skin types, it improves blood circulation in the skin and gives it a healthy color. It has the ability to clean the air of the environment from germs. Geranium is an essential oil plant. Essential oil is obtained by steam distillation of the flower and green parts of the plant.
It is used in folk medicine for diarrhea, dysentery, kidney, rheumatism, gout. The plant is placed on the stumps and used to treat them. In folk medicine, tea is brewed from the dried surface of the hill-like geranium, and it is used as an astringent and antiseptic in diarrhea and dysentery in gastrointestinal diseases. In addition, it is taken to prevent bloody sputum from the chest in lung disease. Geranium, native to South Africa, was brought to Europe as an ornamental plant. The leaves contain large amounts of essential oils. The flower, leaves and root are very good. As you rub the leaves of the geranium, you get a strange and pleasant aroma, reminiscent of the combined aroma of lemon, apple and mint. Essential oils derived from it are widely used in aromatherapy. It should also be noted that the house with geraniums does not contain moths, ticks, lice, fleas and other insects. Geranium is very useful in otitis media, laryngitis, stimulation of blood circulation, regulation of heart rhythm and heart muscle function, headaches [1]. It is possible to normalize blood pressure by placing geranium leaves on the heart [2]. An ointment made from the leaves is an excellent remedy for colds, coughs, angina and colds.
As a result of our scientific research, 2.5 mg of geranium oil was extracted from the 500 g of wet leaves grown in greenhouse at lab conditions. The composition of the obtained oils was checked on a chromatograph and given in the Table. As a result of the research, we come to the conclusion that we offer the obtained essential oils for use in the production of perfumes, creams, and various medicinal soaps.
Table THE RESULTS OF THE ANALYSIS OF THE ESSENTIAL OIL OBTAINED FROM THE LEAVES OF THE Geranium SPECIES IN CRYSTALL-2000M GAS-LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY
|
Component |
Percentage |
Component |
Percentage |
|
Alpha-Pinene |
1.144 |
Estragole |
2.833 |
|
Beta-Pinen e |
0.044 |
Myrtenol |
0.769 |
|
Carene-3 |
0.303 |
Nerol |
0.206 |
|
Alfa-Terpinen |
0.439 |
Geraniol |
40.769 |
|
1,8-Cineol (Eucalyptol) |
4.557 |
Myrtenyl Acetate |
0.502 |
|
gamma – Terpinen e |
0.237 |
Citronellyl butyrate |
0.970 |
|
Tetrahydro-2-H-Pyran |
0.019 |
Geranyl Oleate |
0.609 |
|
Terpinolen e |
0.303 |
neryl acetate |
0.306 |
|
Cyclohexanone-5-m-2(1-m e), -cis |
6.174 |
Citronellyl tiglate |
0.212 |
|
Linalool |
8.154 |
Geranil acetate |
0.047 |
|
Caryophyllene |
2.995 |
Geranyl tiglate |
0.722 |
|
Terpinen-4-ol |
7.684 |
Cedrol |
0.093 |
|
Citronellol |
3.181 |
2-phenylethyl tiglate |
0.735 |
Т. 8. №10. 2022
Отчет хроматограммы
Паспорт хроматограммы
|
Проект: |
полатв |
Колонка: |
|
|
Название метода: |
Efir |
Проба: |
Etjrshah_Yeni_1 |
|
Дата и время: |
20 08 2021 10 07 38 |
Метод расчета: |
Абсолютная градуировка |
|
Амали хХромвтограмма: |
502 |
Объем, мкл: |
1 |
|
Оператор: |
Разведение: |
1 |
|
|
Источник: |
|||
Расчет по компонентам
|
Время, мин |
Компонент |
Группа |
Площадь |
Высота |
Площадь. % |
Концентрация |
Ед. концентрации |
Детектор |
|
8 593 alia Р.пеп |
1512 007 491 142 |
1 144 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
9 077 |
294 15 0 96 046 |
0 222 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
9.347 |
beta-PInen |
58 040 21.266 |
0.044 |
пиД-1 |
||||
|
9.430 |
282 974 59 811 |
0.214 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
9 712 |
Cwene-3 |
<00 151 113 361 |
0 303 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
9 919 |
56 5 10 3 189 099 |
0 427 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
10.064 |
101 753 35.221 |
0 077 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
10 270 |
аМа-Тегрюел |
580 253 181 720 |
0 439 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
10.435 |
1.B-Clneol (Evkaliptol) |
6024 842 1040 356 |
4.557 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
10.576 |
210 549 71 933 |
0.159 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
10 755 |
155 272 51 385 |
0 11В |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
11 061 |
qamma-Terpinen |
312 941| 105 426 |
0 237 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
11.209 |
151 433 50 230 |
0.115 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
11 442 |
33 977 12 241 |
0 02€ |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
11 769 |
16 998 7 181 |
0 013 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
11.56€ |
T etrahydro-2-H-Pyran |
24 604 10.070 |
0.019 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
12.012 |
925 585 302 478 |
0 700 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
12 232 |
311581 91042 |
0 236 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
12 913 |
26 050 10 515 |
0 020 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
13.096 |
Tefplnoten |
400 695 125.531 |
0 303 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
13 361 |
84 571 19 565 |
0 064 |
ПИД 1 |
|||||
|
13 455 |
77 854 27.34 9 |
0 069 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
13.626 |
373 767 118 909 |
0.283 |
пид-1 |
|||||
|
14 016 |
Cyclohexanone 5m 2 (1m a),-cis |
8162 932 2181 843 |
€.174 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
14 165 |
linaool |
10781 05 7 3133 941 |
8 154 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
14 286 |
416 912 135 746 |
0 315 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
14.445 |
Cariophyttene |
3959 363 1115 481 |
2.995 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
14 000 |
62 078 20 523 |
0 047 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
14 811 |
132 902 29 094 |
0 101 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
14.967 |
171 09 9 46.224 |
0.129 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
15 045 |
137 997 40 249 |
0 104 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
15140 |
390 109 159 086 |
0 295 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
15 234 |
7 erplnen-4-ct |
10158 440 2753 696 |
7.084 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
15.321 |
Citronellol |
4206 040 1220.959 |
3.181 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
15 405 |
240 767 84 373 |
0 182 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
15.561 |
160 301 49 019 |
0.121 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
15.636 |
440 308 152.132 |
0 333 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
15 739 |
104 525 30 308 |
0 079 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
15 943 |
12В 767 33 771 |
0.097 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
16.011 |
268 090 78.411 |
0.203 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
16.197 |
Estragole |
3745 818 009 796 |
2 033 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
16 394 |
mirtenol |
1016 132 185 632 |
0 769 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
16.507 |
NMOt |
272 943 70.156 |
0 206 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
16 833 |
1275 497 242 498 |
0 865 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
16.061 |
geraniol |
53900 832 9681 062 |
40 769 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
17.101 |
Mirtenilacetate |
564 200 117.347 |
0 502 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
17 252 |
Cilronelly butyrate |
1281 86 8 385 539 |
0 970 |
пид-1 |
||||
|
17 345 |
95 141 31 730 |
0 072 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
17.453 |
590 099 191 398 |
0 446 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
17.742 |
11052 975 3036 532 |
а 360 |
ПИД-1 |
|||||
|
17 913 |
75 325 19 713 |
0 057 |
пид-1___ пид-1 |
|||||
|
17.996 |
118 149 22 660 |
0 089 |
||||||
|
18 273 |
Geranyl Oleate |
004 707 254 089 |
0 ВО9 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
10.812 |
77 090 |
27.065 |
0 058 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
19 173 |
37 864 |
11 576 |
0 029 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
19339 |
169 667 |
М 576 |
0 128 |
пид-1 |
||||
|
19 825 |
ncnlacetai |
405 081 |
127 993 |
0 308 |
ПИД-1 |
|||
|
19.731 |
32 884 |
9 956 |
0 025 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
19 941 |
cilronelly! Ilglale |
280 389 |
5€ 274 |
0212 |
пид-1 |
|||
|
20.055 |
47 652 |
14 073 |
0 036 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
20.293 |
geranilacetat |
61 572 |
16 739 |
0.047 |
пид-1 |
|||
|
20419 |
65 756 |
22 899 |
0 042 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
20544 |
293 638 |
77 149 |
0 222 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
20.829 |
128 869 |
ЗВ 01В |
0098 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
20 772 |
Gef amyl Delate |
954 191 |
2 76 478 |
0 722 |
I ПИД-1 |
|||
|
21 063 |
28 434 |
10 529 |
0 022 |
пид-1 |
||||
|
21.231 |
160 253 |
50 320 |
0 136 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
21.531 |
Cedtol |
122 838 |
34 815 |
0 093 |
ПИД-1 |
|||
|
21.718 |
107 282 |
29 365 |
0 081 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
21.917 |
129409 |
37 909 |
0 09В |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
22 030 |
2-phorylethyl l*glale |
971 462 |
247.209 |
0 738 |
ПИД-1 |
|||
|
22 477 |
248 708 |
85 939 |
0 187 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
23839 |
44 310 |
14 276 |
0 034 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
|
24 074 |
93 798 |
22 041 |
0 071 |
ПИД-1 |
||||
Figure 2. The results of the analysis of the essential oil obtained from the leaves of the Geranium species in Crystall-2000 M gas-liquid chromatography
Хроматограммы
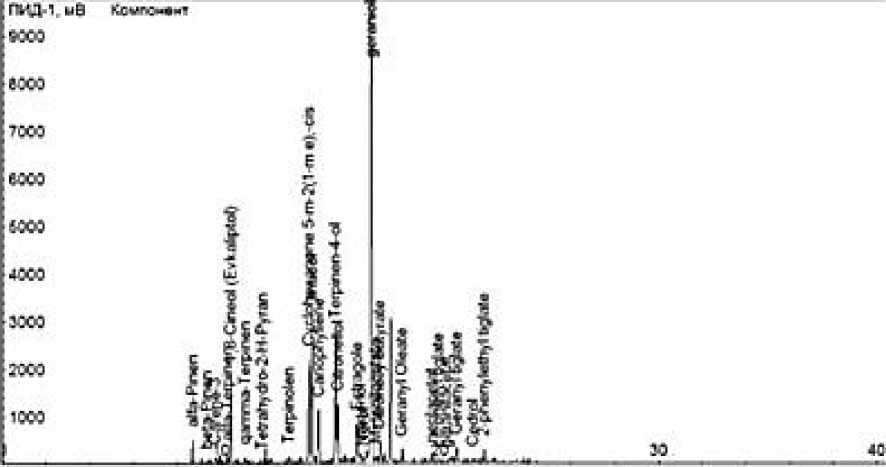
Figure 2. The results of the analysis of the essential oil obtained from the leaves of the Geranium species in Crystall-2000M gas-liquid chromatography
Conclusion
As a result of the conducted scientific research, it was found that Geranium species adapts well to local conditions. Geranium is a very productive essential oil plant. The oil was extracted from the leaves and analyzed in Crystall-2000M gas chromatography. Based on the results of the analysis, alpha-Pinene containing essential oil — 1.144%, beta-Pinene — 0.044%, Carene — 3-0.303%, alphaTerpinene — 0.4391%, 8-Cineol (Eucalyptol) — 4.557%, gamma-Terpinene — 0.237%, Tetrahydro-2-H-Pyran — 0.019%, Terpinolene — 0.303%, Cyclohexanone-5-m-2(1-m e), -cis — 6.174%, linaool — 8.154%, Cariophyliene — 2.995 %, Terpinen-4-ol — 7.684%, Citronellol — 3.181%, Estragole — 2.833%, Myrtenol — 0.769%, Nerol — 0.206%, Geraniol — 40.769%, Myrtenilacetate — 0.502%, Citronelly butyrate — 0.970%, Geranyl Oleate — 0.609%, Nerylacetate — 0.306%, citronellyt tiglate — 0.212%, geranilacetate — 0.047%, Geranyl tigrate — 0.722%, Cedrol — 0.093%, 2-phenylethyl tiglate — 0.735% substances were detected. Regarding the use, it should be noted that geranium essential oil is used in the perfumery industry as the main ingredient of perfumes, soaps and face ointments. In the food industry, it is used for flavoring alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks, as well as confectionery products. Geranium oil is also used in the preparation of a number of medicines.
Список литературы Biomorphological characteristics, phytochemical composition and medical significance of species belonging to the Geranium Tourn. ex L. Genus
- Алекбаров Р, Ибадуллаева С. Лекарственные растения (этноботаника и фитотерапия). Баку, 2013.
- Дамиров И. А., Исламова Н. А., Каримов Ч. Б., Махмудов Р. М. Лекарственные растения Азербайджана. Баку, 1988.
- Гасымов М. А. Морфология и систематика высших растений. Баку, 1959.
- Мамедов Т. С. Деревья и кустарники Апшерона. Баку, 2010.
- Taylor R. J. Sagebrush country: a wildflower sanctuary. Missoula: Mountain Press Publishing Company, 1992. P. 1-211.


