Численная оценка механического поведения локтевой кости у собак при использовании внутримозгового штифта
Автор: Дуарте Р.Х., Маркес А.С., Рамос А., Няшин Ю.И., Менар М.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 2 (42) т.20, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Главная цель исследования заключается в численной оценке с помощью метода конечных элементов того, как внутримозговой штифт, используемый для коррекции излома кости, влияет на поведение окружающих тканей. В процессе роста собаки могут испытывать неприятности от проксимальной лучелоктевой неконгруэнтности. Это в сочетании с фрагментацией медиального клювовидного отростка может также вызвать хрупкость передней конечности. Хирургическая процедура, используемая для лечения этой проблемы и восстановления нормальной подвижности собаки, основывается на хирургическом переломе, что позволяет восстановить правильный сустав. Были использованы три конечно-элементные модели, которые позволили проанализировать, как локтевая кость ведет себя после лечения при наличии внутримозгового стержня и после его удаления. Для этих трех моделей были проанализированы главные деформации, эквивалентные напряжения по Мизесу и перемещения. Результаты показали, что вставление внутримозгового штифта влияет на поведение кости, уменьшая минимальные главные деформации в пораженной области и, следовательно, увеличивая риск резорбции кости.
Конечно-элементные модели, фрагментация медиального клювовидного отростка, разрушение, внутримозговой штифт, хромота, локтевая кость
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146216203
IDR: 146216203 | УДК: 531/534:[57+61]
Текст научной статьи Численная оценка механического поведения локтевой кости у собак при использовании внутримозгового штифта
Передняя конечность собаки состоит из трех костей – плечевой, лучевой и локтевой, которые образуют локтевое соединение собаки.
Лучевая кость несет главную часть веса передней конечности (около 80 %), оставляя оставшиеся 20 % для локтевой кости [20]. У молодых собак имеется высокий
Дуарте Хосе де Хесус, аспирант, Бордо
Маркес Ана София, фармацевт, Коимбра
Рамос Антонио, ассистент профессора кафедры механической инженерии, Авейру
Няшин Юрий Иванович, д.т.н., профессор, научный руководитель кафедры теоретической механики и биомеханики, Пермь
Менар Мишель, профессор, институт механики и инженерии и отделение зубочелюстной ортопедии, Бордо риск развития некоторых проблем в суставе, таких как дисплазия локтевой области. Это связано с тем, что плотность кости у них меньше, чем у взрослых собак.
Предыдущие исследования показали, что локтевая дисплазия – наиболее распространенная причина хромоты передней конечности у собак [3, 15, 17]. Это состояние может быть обусловлено многими причинами, среди которых фрагментация медиального клювовидного отростка, остеохондроз, несросшийся локтевой отросток [3].
При лучелоктевой неконгруэнтности медиальный клювовидный отросток лежит на проксимальной или на дистальной стороне [21]. Так как лучевая и локтевая кости ответственны за удержание веса передней конечности, короткая лучевая кость (проксимальная лучелоктевая неконгруэнтность) может вызвать увеличение контактного давления на медиальном клювовидном отростке, что ведет к фрагментации, которая может, в свою очередь, привести к деструкции суставного хряща и вызвать хромоту [15, 22].
Лечение, предлагаемое ветеринарами, включает артроскопию сустава, чтобы сдвинуть суставные фрагменты, которые травмируют хрящ. Однако в большинстве тяжелых случаев положение компонентов сустава требует коррекции [1, 13]. В этих случаях, чтобы восстановить расположение лучевой и локтевой костей, хирурги-ветеринары должны отрезать или создать трещину (локтевой кости в случае проксимальной лучелоктевой неконгруэнтности) для исправления и восстановления локтевого сустава.
Тем не менее управление разрушением может быть трудным действием для хирургов-ветеринаров, даже если разрушения дистальной лучевой кости и локтевой кости являются третьей наиболее распространенной причиной хромоты у собак (8,5 и 17 % всех разрушений) [4].
Чтобы скорректировать эти разрушения, вставляется внутримозговой штифт [8]. Из-за своей цилиндрической геометрии штифт имеет очень большое сопротивление к изгибающим нагрузкам. Однако его низкое сопротивление к сжимающим или вращательным нагрузкам может создать нежелательные эффекты при восстановлении сустава. Единственное сопротивление вращению или аксиальной нагрузке создается трением между металлом и костью, которого в некоторых случаях недостаточно, чтобы лечение прошло благополучно, особенно на ранних стадиях после хирургической операции. При длительном лечении штифты могут привести к отрицательной динамике при движениях собаки, и некоторые ветеринары считают, что штифт должен быть удален после окончания лечения.
Однако это положение не принимается единодушно и специалисты-ветеринары обсуждают важность штифта через 8 недель после хирургической операции, так как могут наблюдаться эффект резорбции кости или расшатывания [16].
Ранее несколько исследований было посвящено этой проблеме, однако они носят общий характер и не дают ответа на вопрос, каково будет поведение кости и какие изменения будут иметь место в случаях присутствия или отсутствия внутримозгового штифта с механической точки зрения [16].
Конечно-элементные модели широко используются в различных биомеханических областях, включая такие области, как тазобедренный сустав, нижняя челюсть и кисть [10, 11, 18, 23, 24, 29].
Исследование, представленное в данной работе, следовательно, имеет цель разъяснить в терминах механики с использованием метода конечных элементов, что происходит в кости, когда внутримозговой штифт используется для коррекции разрушения, созданного при лечении лучелоктевой неконгруэнтности в локтевой кости.
Материалы и методы исследования
Геометрия локтевой кости собаки была построена с помощью компьютерной томографии собаки средних размеров (вес – 16 кг, порода дог, приблизительный возраст – 6 месяцев). Трехмерные изображения имели разрешение 0,70×0,70×1,50 мм.
На основании предыдущих исследований компьютерно-томографические изображения были построены с точностью 400–500, с шириной окна 1500 и пороговым фильтром 140–250 [11, 18].
Геометрия была затем экспортирована в систему Dassault Systems V5 и трансформирована в модель твердого тела с двумя дифференцируемыми костными структурами (кортикальная и трабекулярная кости).
Внутримозговой штифт диаметром 0,8 мм и длиной 125 мм был помещен в мозговой канал локтевой кости в соответствии с нормальной процедурой, используемой при реальной хирургической операции [8].
Три различных конечно-элементных модели были использованы для анализа здоровой локтевой кости, локтевой кости с внутримозговым штифтом и локтевой кости после удаления внутримозгового штифта.
Тест по сходимости разбиений был проведен, чтобы оценить идеальный размер сетки в наших моделях. Конечно-элементное разбиение в 1 мм было применено для каждой модели. Контакт между кортикальной и трабекулярной костями рассматривался как склеивание. В принятой модели коэффициент трения был принят равным 0,3 для контакта между внутримозговым штифтом и трабекулярной костью. Материалы считались изотропными и идеально упругими, для построения сетки использовались четырехузловые тетраэдральные конечные элементы (таблица).
Плечевая кость
Локтевая Лучевая
кость
кость
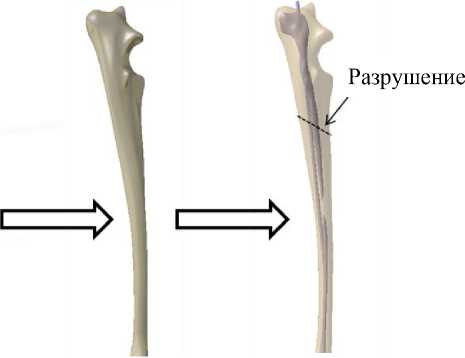
Здоровая локтевая кость
Локтевая кость с внутримозговым штифтом
Компьютерное томографическое изображение
Рис. 1. Этапы конструирования геометрических моделей
Свойства материалов [25, 26, 28]
|
Компонент |
Материал |
E , ГПa |
ν |
|
Кортикальная кость |
Кортикальная кость |
15,0 |
0,3 |
|
Трабекулярная кость |
Трабекулярная кость |
0,250 |
0,3 |
|
Хрящ |
Хрящ |
0,000625 |
0,3 |
|
Имплантат |
Титан |
110,0 |
0,3 |
а
F
б
Рис. 2. Моделирование локтевой кости: а – диаграмма левой задней конечности; б – нагрузка и ограничения, приложенные в конечно-элементных моделях
Нагрузка 250 Н была приложена в полулунной выемке (выемке головки суставного конца кости) в соответствии с предыдущими исследованиями, опубликованными в работе Gillette [9] . Было указано, что наиболее дистальная сторона локтевой кости была полностью ограничена во всех моделях (рис. 2). Конечноэлементный анализ был проведен с использованием модели CATIA V5 .
Результаты
Для того чтобы оценить, как внутримозговой штифт влияет на механическое поведение локтевой кости собаки, были созданы три конечно-элементные модели. Распределения трех главных деформаций, эквивалентного напряжения по Мизесу и перемещения кости были сравнены в каждой модели.
Приемлемая сходимость результатов была получена при разбиении с размером элемента 1 мм, что соответствует предыдущим исследованиям, опубликованным в работах Ito et al. [12].
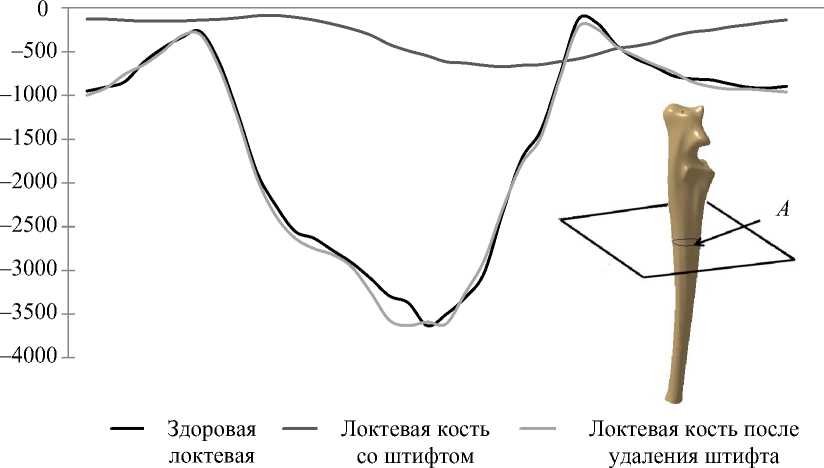
Было замечено, что вставление внутримозгового штифта в локтевую кость уменьшило минимальные главные деформации, имеющиеся в ней. Также изменился градиент распределения деформации в сравнении со здоровой костью. Как результат было отмечено, что критические деформации были локализованы у конца внутримозгового штифта (1500 микрон). Как только внутримозговой штифт был удален, деформации в кости имели то же поведение, что и в здоровой кости.
Кроме того, минимальные деформации вблизи места разрушения были оценены в соответствии с областью разрушения. Было определено, что в здоровой локтевой кости и в локтевой кости после удаления штифта распределение деформаций на наружной поверхности кости имело одинаковый характер (рис. 4). Иначе говоря, когда использовался внутримозговой штифт, распределение деформации в той же области уменьшилось на 85 % в сравнении со здоровой локтевой костью.
Эквивалентные напряжения по Мизесу были оценены в модели с внутримозговым штифтом. Было установлено, что три максимальных пика были зарегистрированы на поверхности кости (рис. 5). Наибольший пик (26 МПа) был расположен у конца внутримозгового штифта. На внешней границе максимум 102 МПа был замечен вблизи зоны разрушения кости.

а
|
Микродеформация |
Микродеформация |
Микродеформация |
|
–246 |
–164 |
–246 |
|
–491 |
–327 |
–491 |
|
–737 |
–491 |
► –737 |
|
–982 |
–654 |
–982 |
|
–1230 |
–818 |
–1230 |
|
–1470 |
–981 |
–1470 |
|
–1720 |
–1140 |
–1720 |
|
–1960 |
–1310 |
–1960 |
|
–2210 |
–1470 |
–2210 |
|
–2460 |
–1640 |
–2460 |
|
–2700 |
–1800 |
–2700 |
|
–2950 |
–1960 |
–2950 |
|
–3190 |
–2130 |
–3190 |
|
–3440 |
–2290 |
–3440 |
|
–3680 |
–2450 |
–3680 |
б
в
Рис. 3. Минимальные главные деформации внутри кортикальной кости: а – модель здоровой кости; б – с внутримозговым штифтом; в – без внутримозгового штифта
Микродеформации
кость
Рис. 4. Минимальные главные деформации вокруг локтевой кости: А – начальная точка
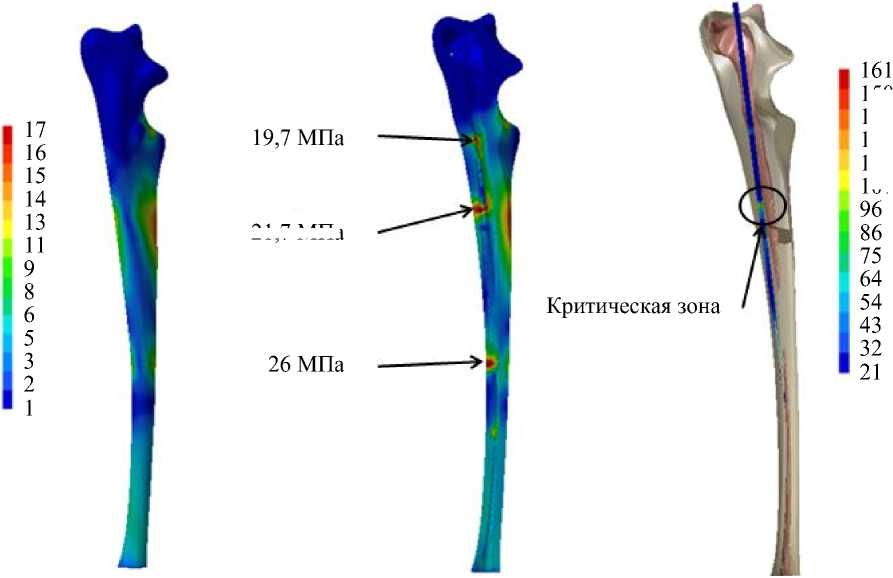
21,7 МПа
б
а
в
Рис. 5. Распределение по Мизесу (МПа) в модели с внутримозговым штифтом: а – на внешней поверхности кортикальной кости; б – внутри кортикальной кости; в – во внутримозговом штифте
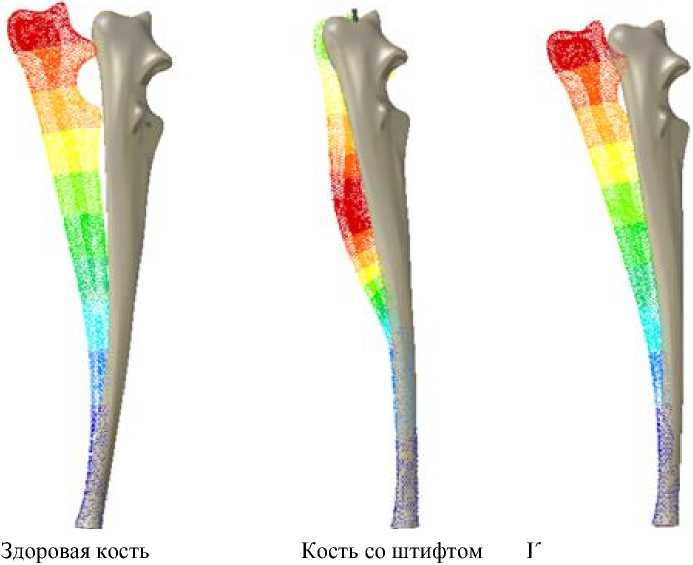
Рис. 6. Перемещения в трех различных случаях
Кость после удаления штифта
Для того чтобы понять, как введение штифта с различными механическими свойствами может изменить естественное поведение кости, были также оценены перемещения в кости. Было замечено, что модель перемещений в кости изменялась, когда внутримозговой штифт был вставлен (рис. 6). В обоих случаях без штифта наибольшие перемещения были на проксимальной стороне локтевой кости, но введение штифта изменяло перемещения около области разреза.
Обсуждение
Дисплазия локтевой области у собак – наиболее распространенное явление, которое влияет на их нормальное движение. Одна из проблем, связанных с дисплазией локтевой области, – проксимальная лучелоктевая неконгруэнтность сустава [14]. Она может способствовать разрушению субхондральной кости и суставного хряща, что вызывает боль и дискомфорт собак [2].
Лучелоктевая неконгруэнтность была исследована путем построения изображений с помощью радиографии и образов компьютерной томографии [19]. Лечение в этом случае также было изучено эмпирически, в основном на основе анализа клинических случаев, и поэтому механические изменения в кости не исследовались [7].
Несмотря на это, изучение биомеханики животных в основном было основано на анализе клинических случаев, но не на механических исследованиях [4, 18]. Однако, поскольку результаты исследований методом конечных элементов в других областях науки впечатляют, на наш взгляд, его полезно применить для изучения биомеханики собак.
Как ранее было упомянуто, конечно-элементные модели не часто использовались при изучении биомеханики животных, в частности при исследовании локтевой области собак. Это означает, что доступная литература по данной проблематике немногочисленна [6].
Среди работ по данной теме стоит отметить исследование Anne Polikeit et al. [20], которая пыталась подробнее изучить дисплазию локтевой области собаки, применяя метод конечных элементов. Цель ее исследования заключалась в выявлении влияния различных биомеханических параметров на передачу нагрузки у здоровых собак и при наличии патологии локтевой области.
Авторами было установлено, что при введении внутримозгового штифта распределение деформации в кости было изменено. Сравнивая различные модели, мы заметили, что результаты в проксимальной локтевой области в 10 раз больше в здоровой локтевой области, чем в локтевой области с внутримозговым штифтом. Это свидетельствует о том, что риск резорбции кости реален при использовании внутримозгового штифта.
После окончания процесса лечения внутримозговой штифт был удален, затем здоровая локтевая область была сравнена с областью без штифта. В результате было замечено, что распределение деформации было аналогичным. Это наблюдение подтверждает, что имеется уменьшение риска резорбции кости, если внутримозговой штифт не вставляется.
Сравнивая наши результаты с данными C. Coleman et al. [5], которые определили условия нагружения кости на передней конечности собаки при движении, можем утверждать, что распределение деформации в нашем исследовании очень близко к ранее полученным результатам, даже при условии, что ранее внимание было сосредоточено на лучевой кости.
При вставлении внутримозгового штифта возникает другая проблема: концентрация напряжений у конца штифта. Возникновение высоких напряжений может быть проблемой, если они достигают напряжения текучести кости. Это может вести к разрушению. В наших исследованиях было отмечено, что в этом случае разрушения кости не происходит, так как наивысшее наблюдаемое значение напряжения по Мизесу равно 26 МПа. Кроме того, при наличии штифта разрушение было невозможно, так как регистрируемое напряжение текучести было далеко от разрушения при 104–121 МПа [27].
Наблюдая результаты по перемещениям кости во всех моделях, мы заключаем, что нормальное перемещение изменялось, когда внутримозговой штифт был вставлен. В этом случае наибольшее перемещение было сконцентрировано в области, где разрушение было индуцировано. В процессе выздоровления лапы собаки должны быть «защищены» и нагрузка на них должна быть минимальна, особенно в первые пять недель. Силы, которые действуют на локтевую кость, будут меньше при условии исключения нагружения весом тела собаки. После выздоровления лапы собаки подвергаются нормальной нагрузке, выдерживая ее вес. Когда внутримозговой штифт остается внутри локтевой кости, нормальное перемещение под действием веса собаки создает наибольшее перемещение в области разрушения, что может привести к новому разрушению в случае увеличения нагрузки.
Выводы
Использование внутримозгового штифта для управления и фиксации двух половин кости после операции не является общепризнанным. В зависимости от возраста животного или при хороших признаках перемещений после хирургической операции некоторые ветеринары выбирают вариант, при котором штифт остается внутри лапы собаки в течение времени восстановления после операции.
В соответствии с нашими результатами внутримозговой штифт изменяет механическое поведение кости. Хорошо известно, что сразу после операции он обусловливает ее положительный исход. Однако если после периода восстановления штифт не извлекается, то поведение локтевой кости не становится таким же, каким оно было до установки хирургического штифта.
Список литературы Численная оценка механического поведения локтевой кости у собак при использовании внутримозгового штифта
- Adams J.E., Merten S.M., Steinmann S.P. Arthroscopic-assisted treatment of coronoid fractures//Arthroscopy. -2007. -Vol. 23, № 10. -P. 1060-1065.
- Boulay J.P. Fragmented medial coronoid process of the ulna in the dog//Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice. -1998. -Vol. 28. -P. 51-74.
- Breit S., Pfeiffer K., Pichler R. Use of a 3D laser scan technique to compare the surface geometry of the medial coronoid process in dogs affected with medial compartment disease with unaffected controls//The Veterinary Journal. -2010. -Vol. 185, № 3. -P. 285-291.
- Brianza S.Z.M., Delise M., Maddalena M., Amelio P.D., Botti P. Cross-sectional geometrical properties of distal radius and ulna in large, medium and toy breed dogs//Journal of Biomechanics. -2006. -Vol. 39. -P. 302-311.
- Coleman J.C., Hart R.T., Burr D.B. Reconstructed bone end loads on the canine forelimb during gait//Journal of Biomechanics. -2003. -Vol. 36. -P. 1837-1844.
- Coleman J.C., Hart R.T., Owan I., Tankano Y., Burr D.B. Characterization of dynamic three-dimensional strain fields in the canine radius//Journal of Biomechanics. -2002. -Vol. 35. -P. 1677-1683.
- Fitzpatrick N., Yeadon R., Smith T., Schulz K. Techniques of application and initial clinical experience with sliding humeral osteotomy for treatment of medial compartment disease of the canine elbow//Vet. Surg. -2009. -Vol. 38. -P. 261-278.
- Fossum T.W., Duprey L.P., O’Connor D. (Eds.). Small animal surgery. -3th ed. -St. Louis: Elsevier, 2007. -1610 p.
- Gillette R.L., Angle T.C. Recent developments in canine locomotor analysis: a review//The Veterinary Journal. -2008. -Vol. 178, № 2. -P. 165-176.
- Gislason M.K., Stansfield B., Nash D.H. Finite element model creation and stability considerations of complex biological articulation: the human wrist joint//Medical Engineering & Physics. -2010. -Vol. 32, № 5. -P. 523-531.
- Hathcock J.T., Stickle R.L. Principles and concepts of computed tomography//Veterinary Clinics of North America Small Animal Practice. -1993. -Vol. 23. -P. 399-415.
- Ito Y., Corey Shum P., Shih A.M., Soni B.K., Nakahashi K. Robust generation of high-quality unstructured meshes on realistic biomedical geometry//International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering. -2006. -Vol. 65, № 6. -P. 943-973.
- Kang L.Q., Ding L.Q., Sha M., Hong J.Y., Chen W. A minimal invasive anterior approach to reduction and screw fixation of coronoid fractures//Journal Hand Surgery Eur. -2009. -Vol. 35, № 3. -P. 224-227.
- Kirberger R.M., Fourie S.L. Elbow dysplasia in the dog: pathophysiology, diagnosis and control//Journal of the South African Veterinary Association. -1998. -Vol. 69. -P. 43-54.
- Kramer A., Holsworth I.G., Wisner E.R., Kass P.H., Schulz K.S. Computed tomography evaluation of canine radioulnar incongruence in vivo//Veterinary Surgery. -2006. -Vol. 35, № 1. -P. 24-29.
- Kraus K.H., Toombs J.P., Ness M.G. External fixation in small animal practice. -Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, 2008. -240 p.
- Morgan J.P., Wind A., Davidson J.P. Hereditary bone and joint disease in the dog. -Hannover: Sclutersche, 2000. -310 p.
- Ohlerth S., Scharf G. Computed tomography in small animals -Basic principles and state of the art applications//The Veterinary Journal. -2007. -Vol. 173, № 2. -P. 254-271.
- Peremans K., Vermeire S., Dobbeleir A., Gielen I., Samoy Y., Piron K., Vandermeulen E. Recognition of anatomical predilection sites in canine elbow pathology on bone scans using micro-single photon emission tomography//The Veterinary Journal. -2011. -Vol. 188, № 1. -P. 64-72.
- Polikeit A., Ferguson S.J., Schawalder P. Elbow dysplasia in the dog: finite element analysis//Biomedical Engineering. -2007. -Vol. 52, № 4. -P. 308-314.
- Presnel K.R. Surgery for fragmented medial coronoid process//Current techniques in small animal surgery/ed. M.J. Bojrab. -3rd ed. -Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1990. -P. 774-778.
- Preston C.A., Schulz K.S., Taylor K.T., Kass P.H., Hagan C.E., Stover S.M. In vitro experimental study of the effect of radial shortening and ulnar ostectomy on contact patterns in the elbow joint of dogs//American Journal of Veterinary Research. -2001. -Vol. 62. -P. 1548-1556.
- Ramos A., Completo A., Relvas C., Mesnard M., Simões J.A. Straight, semi-anatomic and anatomic TMJ implants: the influence of condylar geometry and bone fixation screws//Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery: official publication of the European Association for Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery. -2011. -Vol. 39, № 5. -P. 343-350.
- Ramos A., Simões J.A. Tetrahedral versus hexahedral finite elements in numerical modelling of the proximal femur//Medical Engineering & Physics. -2006. -Vol. 28, № 9. -P. 916-924.
- Shahar R., Banks-Sills L., Eliasy R. Stress and strain distribution in the intact canine femur: finite element analysis//Med. Eng. Phys. -2003. -Vol. 25, № 5. -P. 387-395.
- Sharir A., Israeli D., Milgram J., Currey J.D., Monsonego-Ornan E., Shahar R. The canine baculum: the structure and mechanical properties of an unusual bone//Journal of Structural Biology. -2011. -Vol. 175, № 3. -P. 451-456.
- Vahey J.W., Lewis J.L. Elastic moduli, yield stress, and ultimate stress of cancellous bone in the canine proximal femur//Journal of Biomechanics. -1987. -Vol. 20, № 1. -P. 29-33.
- Verrue V., Dermaut L., Verhegghe B. Three-dimensional finite element modelling of a dog skull for the simulation of initial orthopaedic displacements//European Journal of Orthodontics. -2001. -Vol. 23, № 5. -P. 517-527.
- Watanabe Y., Shiba N., Matsuo S., Higuchi F., Tagawa Y., Inoue A. Biomechanical study of the resurfacing hip arthroplasty: finite element analysis of the femoral component//The Journal of Arthroplasty. -2000. -Vol. 15, № 4. -P. 505-511.


