Численное исследование механического поведения тазобедренного сустава при терапевтическом акустическом воздействии
Автор: Еремина Г.М., Смолин А.Ю.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 1 (99) т.27, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Дегенеративно-дистрофические заболевания являются одной из главных причин нетрудоспособности населения среднего и старшего возраста. Одними из самых распространённых заболеваний такого типа являются остеопороз и остеонекроз головки бедренной кости. Для профилактики и лечения остеопороза, остеопении и остеонекроза применяют внешнюю механическую стимуляцию, основанную на локальном ультразвуковом или ударно-волновом воздействии в области патологии. Эффект внешнего механического воздействия основан на механобиологических принципах, суть которых заключается в том, что определённый уровень давления (механического напряжения) и деформаций приводит к росту и дифференцировке разного типа биологической ткани. Для получения терапевтического эффекта необходимо правильно выбирать параметры воздействия и место его приложения. Обычно эти задачи решаются эмпирическим путём. В данной работе численно исследована возможность создания условий для регенерации костной ткани при внешнем акустическом воздействии на здоровый тазобедренный сустав и сустав, поражённый остеонекрозом. Исследование выполнено с помощью метода подвижных клеточных автоматов. Полученные результаты показали эффективность применения средне- и высокоинтенсивного ультразвукового воздействия для профилактики остеопении и остеопороза. При воздействии ультразвуком на сустав с остеонекрозом головки создание условий для остеогенеза и хондрогенеза в поражённой области наблюдаются только при высокоинтенсивном нагружении. Таким образом, была подтверждена гипотеза о том, что низкоинтенсивная ультразвуковая терапия эффективна только в сочетании с другими методами лечения. Было установлено, что ударно-волновое воздействие малой интенсивности способствует делению биологических клеток и их переносу, создавая тем самым условия для регенерации костных тканей. Данный вывод согласуется с результатами большинства экспериментальных работ.
Ударно-волновая терапия, ультразвуковая терапия, тазобедренный сустав, численное моделирование, метод подвижных клеточных автоматов
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146282686
IDR: 146282686 | УДК: 531/534: | DOI: 10.15593/RZhBiomeh/2023.1.04
Текст научной статьи Численное исследование механического поведения тазобедренного сустава при терапевтическом акустическом воздействии
Дегенеративные заболевания тазобедренного сустава (ТБС) значительно снижают качество жизни человека. Одним из самых распространённых заболеваний этого сустава является остеонекроз головки бедренной кости [16]. Наиболее часто остеонекроз поражает достаточно молодых людей трудоспособного возраста. Средний возраст начала дегенеративных заболеваний данного типа приходится на 45 лет, что приводит к инвалидизации значительной части работающего населения [11; 32; 48]. Остеонекроз происходит по причине нарушения подачи питательных веществ в головку бедренной кости, вследствие чего образуется область с некрозом тканей, далее эта область обрастает склеротическим кольцом. Таким образом, при остеонекрозе отмечаются области некроза с пониженными механическими характеристиками костных тканей и окружающие его воспалённые (склеротические) участки с повышенными механическими характеристиками. Участки некроза тканей вследствие избыточного давления со стороны склеротических участков подвержены резорбции.
При начальных стадиях заболевания применяют медикаментозную терапию и терапию, основанную на внешнем механическом воздействии [8]. На последних стадиях необходимо эндопротезировании ТБС.
Терапевтический эффект внешнего механического воздействия основан на механобиологических принципах, суть которых заключается в том, что определённый уровень давления (механического напряжения) и деформаций приводит к росту и дифференцировке определённого типа биологической ткани [1–3]. Так, регенерации костной ткани способствуют напряжения с амплитудой ниже 0,15 МПа. Регенерации хрящевой ткани способствуют сжимающие напряжения с амплитудой от 0,15 до 2 МПа (разрастание хондроцитов). Отмечено, что при напряжениях ниже 0,003 МПа хондрогенеза и остеогенеза не возникает, а напряжения сжатия порядка 0,7-0,8 МПа наиболее благоприятны для образования хрящевой ткани. Оптимальным для миграции живых клеток является давление жидкости в порах в диапазоне от 20 кПа до 2 МПа (наиболее благоприятное значение - 68 кПа) [21]. Одним из параметров, благоприятствующих дифференцировке хрящевой и фиброзной ткани, является величина деформации в диапазоне от 0,05 до 1,1 % [54; 67].
Ультразвуковое действие (УЗВ) бывает двух типов: низкоинтенсивное (с удельной мощностью на единицу поверхности до 3 Вт/см2) и высокоинтенсивное (более 3 Вт/см2). В свою очередь низкоинтенсивное воздействие подразделяется на низкодозированную нагрузку (<1 Вт/см2), среднедозированную нагрузку (1-2 Вт/см2) и высокодозированную нагрузку (2-3 Вт/см2). Для диагностических исследований и терапии по регенерации тканей опорно-двигательного аппарата человека преимущественно используется малоинтенсивное воздействие, для лечения раковых и других видов опухолей - среднеинтенсивное, для хирургических целей - высокоинтенсив- ное УЗВ [71]. Частота УЗВ, наиболее часто используемая в терапевтических целях, соответствует 1,5 МГц [23].
Ударно-волновое (УВ) воздействие терапевтического спектра отличается от ударных волн разрушительного характера амплитудой положительного давления до 100 МПа, а также малым временем фазы сжатия (менее 1 мкс) [33]. Плотность потока энергии ( energy flux density - EFD ) является основной характеристикой ударноволнового процесса для медицинских целей [4]. УВ-воздействие в медицине подразделяется на низкоинтенсивное (<0,27 мДж/мм2), среднеинтенсивное (0,270,59 мДж/мм2) и высокоинтенсивное (>0,60 мДж/мм2) [5].
Далее низкоинтенсивное ультразвуковое и ударноволновое механическое воздействие, используемое в терапевтических целях, будем называть акустическим. Нагрузка при внешнем акустическом воздействии задаётся через металлические и керамические пластины (аппликаторы) различной формы, она имеет определённый уровень плотности потока энергии, который рассчитывается, исходя из параметров пластин. Особенности физиологического состояния (возраст, болезни, травмы) пациента требуют индивидуального подбора параметров акустического воздействия. В настоящее время ведутся активные исследования по определению оптимальных параметров нагрузки, способствующих регенерации костной и хрящевой ткани. Очевидно, что подбор таких параметров экспериментальными методами является дорогостоящим и длительным процессом, поэтому эффективным подходом в решении этой сложной задачи может стать использование средств компьютерного моделирования. Однако используемые при этом модели должны быть надёжными и в достаточной степени адекватными.
В основном моделирование акустического воздействия на трубчатые кости направлено на исследование возможностей применения ультразвуковой диагностики для определения состояния тканей. Для этого рассматривались здоровые и остеопорозные ткани, а для описания распространения в них ультразвука использовалась преимущественно пороупругая модель Био, реализованная в программных пакетах ANSYS и ABAQUS на основе метода конечных элементов [14; 29; 49; 51], а также вязкоупругая модель [30]. Изучение влияния ультразвукового воздействия на регенерацию костных тканей с помощью компьютерного моделирования началось относительно недавно, и в литературе пока мало данных о подобных исследованиях бедренного сустава. Численные исследования на основе пороупругой модели с помощью двухмерного конечно-разностного метода влияния ультразвуковых волн на регенерацию костных тканей в дентальной области при установке импланта приведены в работе [39]. Трёхмерное конечно-элементное моделирование на основе упругой модели образцов элементарной геометрической формы рассмотрено в [58]. На основе двухмерных расчётов в рамках вязкоупругости [45] исследовано влияние низко-интенсивного ультразвукового воздействия на кортикальную ткань трубчатых костей.
Многомасштабная численная модель ультразвукового воздействия на бедренную кость представлена работах [9; 28]. Исследовано влияние низкоинтенсивного (30 мВт/см2) ультразвукового воздействия на условия регенерации костной ткани на основе двухмерных расчётов. Геометрически модель представлена фрагментами элементарной формы, включающей в себя слой мягких тканей и кортикальной ткани, а также трансдуктор диаметром 2 см. Установлено, что проницаемость значительно влияет на распределение сдвиговых напряжений, поэтому для исследования влияния акустического воздействия на условия регенерации костных тканей необходимо использовать модель пороупругой среды. Двухмерная пороупругая конечно-элементная модель заживления перелома трубчатой кости при переломе представлена в работе [22]. Моделировалось воздействие ультразвуком при естественных физиологических условиях. Однако данных о параметрах УЗВ в статье не представлено. Численное исследование ударно-волнового воздействия на костные ткани представлено в работе [68]. Здесь на основе двухмерной конечно-элементной упругой модели исследовано УВ-воздействие с максимальным пиковым давлением 50 МПа. В работе [38] с помощью вязкоупругой трёхмерной модели исследовано влияние способа приложения радиальных ударных волн на их распространение через кожные покровы и мышцы в области межпозвоночного диска.
Таким образом, анализ современной литературы показывает, что работ по численному исследованию влияния акустического воздействия широкого диапазона (в терапевтических дозировках) на элементы опорнодвигательного аппарата достаточно мало. В основном же рассматриваются образцы различных тканей простой геометрической формы. Полностью отсутствуют работы по моделированию такого воздействия на объекты костно-мышечного аппарата реальной формы и геометрии. Поэтому актуальным является разработка численных моделей акустического воздействия широкого спектра нагружения на крупные кости реальной геометрии, в том числе тазобедренного сустава.
Целью данной работы является разработка и исследование численной модели, описывающей механическое поведение бедренного сустава человека при малоинтенсивном акустическом воздействии. В качестве численного метода был выбран метод подвижных клеточных автоматов, который является представителем вычислительной механики частиц (дискретных элементов) и позволяет в явном виде описывать возникновение и развитие повреждений в гетерогенных материалах, в том числе насыщенных флюидом.
Материалы и методы
Для моделирования акустического воздействия на тазобедренный сустав был применён метод подвижных клеточных автоматов (ПКА), основанный на дискретном представлении материала. В ПКА моделируемый материал рассматривается как ансамбль дискретных элементов (клеточных автоматов), взаимодействующих между собой по определённым правилам, позволяющим в рамках дискретного подхода описывать его деформационное поведение как изотропного упругопластического тела [52]. Для описания механического поведения костных тканей с учётом наличия в них биологической жидкости применялась модель пороупругой среды, реализованной в методе ПКА [53]. Основу модели пороупругой среды в методе ПКА составляет декомпозиция решаемой задачи на две подзадачи: 1) описание механического поведения вмещающего твёрдого тела (каркаса) с учётом давления внутренней жидкости, и 2) описание переноса жидкости в фильтрационном объёме, представленном системой взаимосвязанных каналов, пор, трещин и т.д., рассматриваемых неявно.
В методе подвижных клеточных автоматов предполагается, что материал состоит из определённого количества элементарных объектов конечного размера (автоматов), которые вследствие взаимодействия друг с другом могут перемещаться и вращаться в пространстве, тем самым моделируя реальные процессы деформации. Движение ансамбля частиц описывается уравнениями Ньютона - Эйлера:
' d2 R mi i dt2
<
N i
= j F^ r + F ° j= i
N i
Jˆ dωi =M i dt j i
jj ’
где R i , ю i , m i и J i - радиус-вектор, скорость вращения, масса и момент инерции автомата i соответственно. F pair - парная сила механического взаимодействия автоматов i и j , F^ - объёмно-зависящая сила, действующая на автомат i и обусловленная взаимодействием его соседей с другими автоматами. В последнем уравнении M,y = q^ ( n. х F?air ) + Ky , здесь qy расстояние от центра i -го автомата до точки его взаимодействия (контакта) с j -м автоматом, n ij = ( R j - R i )/ r ij - единичный вектор ориентации пары i - j , r ij - расстояние между центрами автоматов.
Для локально изотропных сред объёмно-зависящая компонента сил может быть записана через давление P j в объёме соседних автоматов j следующим образом:
N i
F" = — A j P j S j n j , (2)
j=i где Sj - площадь контакта i-го автомата с j-м, а A - материальный параметр, связанный с его упругими характеристиками.
С другой стороны, общая сила, действующая на автомат, может быть представлена в виде суммы нормальной F n и Fz т касательной (сдвиговой) составляющих:
NL, N-
F - Ц FT" - A Fa) = 1
( FT ( h , ) — APS,} n , +F,"" ( lS" ) T ,
Ni
Ж+ft )•
j= 1
где F pair ,n нормальная, а F pair ,τ – касательная силы взаимодействия в паре, зависящие, соответственно, от межавтоматного перекрытия h ij и относительного тангенциального смещения l shear , рассчитанного с учётом вращения обоих автоматов. Отметим, что несмотря на то, что последнее выражение в уравнении (3) формально соответствует обычной записи силы взаимодействия в методе дискретных элементов, оно принципиально отличается от последнего вследствие многочастичного характера центрального взаимодействия автоматов.
С помощью процедуры осреднения для тензора напряжений в частице выражение для компонент усреднённого тензора напряжений в автомате i принимает вид:
1 Ni
° Ip = 1 q^a , , (4)
V i j= 1
где α и β обозначают оси X , Y , Z лабораторной системы координат, V i – текущий объём автомата i , n ij α – α -компонента единичного вектора n ij и F ij ,β – β -компонента полной силы, действующей в точке «контакта» между автоматами i и j .
Давление P i , или, что то же самое, среднее напряжение 5^еап в объёме автомата, может быть вычислено через компоненты тензора напряжений:
, _ 5 xx + 5 Уу + 5 =
- — —5_ —-- i mean
Знание компонент тензора напряжений позволяет вычислять все его инварианты в объёме автомата, в частности интенсивность сдвиговых напряжений
Соотношение для силы центрального взаимодействия автоматов формулируется на основе определяющего уравнения материала для диагональных компонент тензора напряжений, а сила тангенциального взаимодействия – на основе аналогичных уравнений для недиагональных компонент напряжений. При реализации линейно-упругой модели выражения для удельных значений центральной и тангенциальной сил взаимодействия автомата i с соседним автоматом j записываются следующим образом:
-д Fp^xn — 2 С д£ i, + d ^5 mean \д F^ — 2 G , Ду
где символ Δ обозначает приращение величины соответствующего параметра за шаг Δ t численной схемы интегрирования (1), Δε ij и Δγ ij – приращения сдвиговой и нормальной деформации элемента i в паре i – j , G i – модуль сдвига материала элемента i , K i – модуль всестороннего сжатия, D i = 1-2 G i / K i . Формулы (7) записаны по аналогии с выражениями для компонент тензора напряжений упругого тела, диагональных в первом выражении и недиагональных (сдвиговых) – во втором. Заметим, что индексы i и j в формулах (1)–(5) и далее обозначают номер автомата, а и ij – номера автоматов в паре, для которой рассчитывается взаимодействие, а не оси системы координат, как в обычных выражениях теории упругости. При этом все выражения здесь справедливы для любой размерности задачи.
Формулы (1) – (7) описывают механическое поведение линейно-упругого тела в рамках метода ПКА. Для численного интегрирования уравнений движения (1) можно использовать схему Верле в скоростной форме, модифицированную введением предиктора для оценки 5 ^p на текущем шаге по времени.
В связи с необходимостью выполнения третьего закона Ньютона приращения сил реакции автоматов i и j рассчитываются на основе решения следующей системы уравнений:
(напряжения по Мизесу):
Д F Pair ’" — Д ^ pair -"
5n —
(5 Xx
—
i
5 УУ
yy
—
5 Zz
zz
—
5 Xx ^
+
. (6)
R, ДЕу + RyДё^ — Д гц
Д F pair . !
Из уравнений (1), (2) и (3) следует, что выражения для вычисления F pair ,n и F pair ,τ определяют реологические свойства модельной среды.
Инварианты тензора напряжений 5^еап и 5^( используются для расчёта сил взаимодействия ( F pair ,n и F pair ,τ ) и в качестве критерия прочности межавтоматной связи (критерий локального разрушения). Компоненты осреднённого тензора деформаций ё^р рассчитываются по приращениям с использованием заданного уравнения состояния моделируемого материала и рассчитанных приращений осреднённых напряжений.
Ri Ду, + R, Ду ,i — Д IS,
где Δ r ij – изменение расстояния между центрами автоматов за шаг по времени A t , Д Г * - величина относительного сдвигового смещения взаимодействующих автоматов i и j . Система уравнений (8) после подстановки в неё выражений (7) решается относительно приращений деформаций. Это позволяет также рассчитать приращения удельных сил взаимодействия. При решении системы (8) приращения средних напряжений и значения удельных сил в правых частях соотношений берутся из предыдущего временного шага или оцениваются и уточняются в рамках схемы предиктор – корректор.
Автоматы, моделирующие флюидонасыщенный материал, рассматриваются как пористые и проницаемые. Поровое пространство такого автомата может быть насыщено жидкостью. Характеристики порового пространства учитываются неявно через заданные интегральные параметры, а именно пористость ϕ, проницаемость k , отношение a = 1 - K / K s макроскопического значения модуля всестороннего сжатия K к модулю объёмного сжатия стенок пористого скелета K s . Механическое влияние поровой жидкости на напряжения и деформации в твёрдом каркасе автомата учитывается на основе линейной модели пороупругости Био. В рамках этой модели механический отклик «сухого» автомата предполагается линейно-упругим и описывается на основе приведённых выше соотношений. Механическое воздействие поровой жидкости на поведение автомата описывается через локальное поровое давление P pore (поровое давление жидкости в объёме автомата). В модели Био поровое давление влияет только на диагональные компоненты тензора напряжений. Поэтому необходимо модифицировать только соотношения для центральных сил взаимодействия в (7):
a \P pore
AF par n = 2 G Ae —i—P— i ‘ i K
+ D Ao mean
Внутритканевая жидкость предполагается линейно сжимаемой. Значение порового давления жидкости в объёме автомата рассчитывается на основе соотношений модели пороупругости Био с использованием текущего значения порового объёма. В развитой модели жидкость полагается слабосжимаемой и описывается с помощью линейного уравнения состояния:
p ( P pore ) = p o ( 1 + ( P pore - P o ) / K, ) , (10)
где ρ и P pore – текущие значения плотности и давления жидкости; ρ 0 и P 0 – значения плотности и давления жидкости при атмосферных условиях; K fl модуль всестороннего сжатия жидкости.
При моделировании фильтрации используется предположение об определяющей роли градиента давления жидкости как движущей силы этого процесса. В пренебрежении гравитационными эффектами уравнение фильтрации в поровом пространстве твёрдого тела может быть записано следующим образом:
dp
ф|р = K,V kVp , d t n
d t
где η – вязкость жидкости и k – коэффициент проницаемости твёрдого каркаса, определяемый как:
k = ф d c2h , (12)
где d ch – диаметр фильтрационного канала
Уравнения (9)–(11) решаются на ансамбле дискретных элементов с использования явной разностной схемы Эйлера.
В работе использовался программный комплекс « MCA-3D » версии 3.0, разработанный в лаборатории компьютерного конструирования материалов Института физики прочности и материаловедения СО РАН. Данный комплекс позволяет решать задачи компьютерного моделирования процессов деформирования и разрушения гетерогенных материалов на различных масштабных уровнях при динамическом нагружении в трёхмерной постановке. Программный комплекс включает в себя графическое приложение для подготовки численной модели ( Preprocessor ), вычислительное ядро ( Solver ) и графическое приложение анализа полученных результатов ( Postprocessor ). Все программы работают под операционной системой Linux . Возможности комплекса позволяют реализовывать различные структурные и реологические модели гетерогенных материалов и осуществлять моделирование процессов деформирования и разрушения таких систем на различных масштабных уровнях. Важно подчеркнуть, что программа, реализующая вычислительное ядро, может применяться как на индивидуальных рабочих станциях с многоядерными процессорами, так и на высокопроизводительных кластерных системах (суперкомпьютерах) в режимах параллельных вычислений по технологии MPI + OpenMP .
Была построена оригинальная численная модель тазобедренного сустава, с реальными геометрическими параметрами (рис. 1, а ). В качестве основы использовались стандартные твердотельные CAD -модели соответствующих компонентов бедренной кости (внутренней губчатой и внешней кортикальной). На основе твердотельных моделей бедренной кости были построены сеточные модели в формате стереолитографии « stl » ( ASCI STL ), которые затем импортировались в препроцессор программного комплекса, реализующего метод ПКА, а затем к ним добавлялись модели остальных составляющих сустава (хрящи, часть тазовой кости с вертлужной впадиной, суставная капсула).
Построенная модель коленного сустава включала в себя следующие элементы: проксимальный отдел бедренной кости, часть вертлужной впадины, хрящевые пластины и аппликатор для приложения внешнего акустического воздействия. Данная модель сустава была помещена в область из двух цилиндров, имитирующую
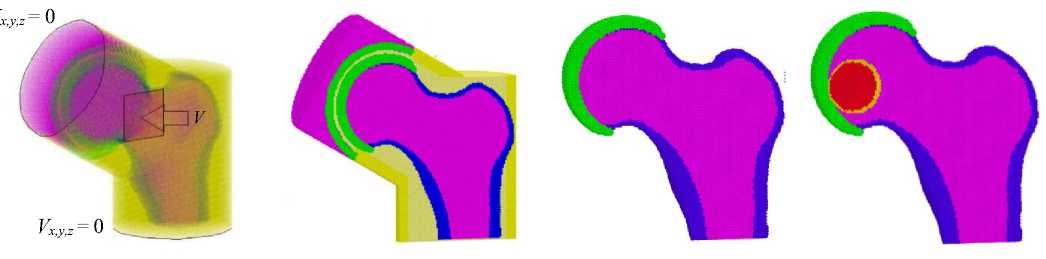
Кортикальная ткань ■ Хрящевая ткань Мышечная ткань ■ Губчатая ткань Материал синовиальной капсулы а б в г
Рис. 1. Модель бедренного сустава: а – 3 D -вид с капсулой и аппликатором (точками показаны центры автоматов); б – 3 D- вид ТБС в сечении (автоматы изображены сферами); в – срез здоровой бедренной кости; г – срез кости, поражённой остеонекрозом головки 1-й степени
а б
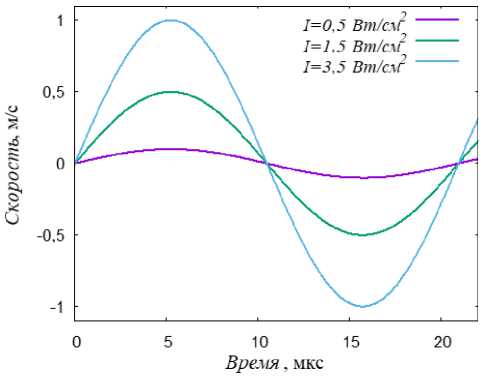
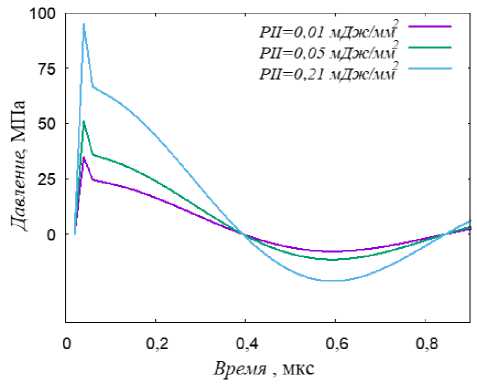
Рис. 2. Параметры акустического нагружения: а – зависимость скорости колебания частиц от времени при УЗ-нагружении; б – зависимость давления от времени при УВ-нагружении суставную (синовиальную) капсулу, состоящую из фиброзной ткани (внутренняя часть) и мышечный слой (внешняя часть капсулы) (рис. 1, б).
При моделировании внешнего акустического воздействия аппликатор рассматривался как тонкая медная пластина квадратной формы размером 20×20 мм и располагался в области шейки в случае здорового сустава и в области средней части головки при остеонекрозе (см. рис. 1). Начальные условия представляют собой равновесную конфигурацию системы автоматов (частиц) в отсутствие деформаций и напряжений (то есть все силы между автоматами равны нулю). Содержание жидкости в биологических тканях соответствует объёму пор и нулевому давлению. Температурные эффекты в расчётах не учитывались. Краевые условия соответствуют принятой схеме нагружения: нижний слой автоматов, а также крайний слой автоматов, соответствующий вер-лужной чаше модели, жёстко закреплены (их скорости задаются равными нулю, как показано на рис. 1, а), а автоматам аппликатора задаются скорости, направленные поперёк плоскости аппликатора, величина которых определяется частотой и амплитудой акустического воздействия (рис. 1, а).
Предварительные исследования по верификации разработанной модели показали, что значения её интегральной жёсткости при вертикальном сжатии достаточно быстро сходятся к величине 3,6 кН (что соответствует литературным данным [27]) при уменьшении размера подвижных клеточных автоматов от 2 до 0,75 мм (соответствующее число частиц увеличивалось от 187 388 до 1 426 328). Исходя из проведённого анализа, для дальнейших расчётов был выбран размер автоматов, равный 1 мм.
Для ультразвукового воздействия в виде плоской синусоидальной волны интенсивность ультразвука I определяется по формуле:
pv _ v 2 р c
= =
где р – амплитуда звукового давления Па; v – амплитуда колебательной скорости частиц, м/c; ρ – плотность сре- ды, кг/м3; с - скорость звука, м/с.
Из формулы (13) можно выразить скорость колебания частиц и сделать её входным параметром для численного моделирования ультразвукового воздействия на биологические ткани (рис. 2, а ):
v =
Для ударно-волнового воздействия главной характеристикой является величина плотности потока энергии ( P ц), которую, согласно работе [17], можно выразить через произведение интенсивности акустической волны ( I ) и нормализованной длительности импульса ( T ?) (англ. - normally pulse length ):
P = I ■ T p . (15)
T p согласно [36] можно определить как время состояния 90 % максимального положительного давления. В то же время интенсивность является характеристикой акустического импеданса среды и в соответствии с формулами (14) и (15) получим следующее выражение для расчёта плотности потока энергии:
P ii =
v 2p cT p
Параметр «нормализированной длительности импульса» T p определялся по графикам зависимости давления от времени расчёта (рис. 2, б).
При остеонекрозе механические свойства сегмента головки бедренной кости существенно меняются. Согласно данным [7; 30; 38; 41; 59; 65], при некрозе существенно падает значение модуля упругости, также отмечается значительное повышение пористости; диапазон разброса значения упругого модуля у разных авторов от 300 МПа до 12 ГПа. Более низкие значения модуля упругости соответствуют более поздним стадиям остеонекроза. Так для, третей стадии остеонекроза модуль упругости колеблется в диапазоне 600-1000 МПа [20]. Кроме того, при остеонекрозе ТБС область с некрозом костных тканей зачастую соседствует с локальными областями склероза тканей, при котором отмечается недостаток переноса питательных веществ, вызванный уменьшением пористости и проницаемости [63; 76]. Известно, что на начальных стадиях вокруг области с некрозом формируется «кольцо» из склеротической ткани по свойствам, близким к гранулированной среде [13], а проницаемость падает [18]. В нашем исследовании рассматриваются ранние стадии остеонекроза, когда неинвазивное лечение может оказаться эффективным [64].
Упругие и пороупругие свойства тканей здорового тазобедренного сустава и тканей в области некроза
[12; 19; 76] приведены в таблице.
Для определения модуля упругости на макроуровне использовались данные [74; 76; 77]. Для определения модуля на микроуровне (структура ткани) использовались данные статьи [64]. Проницаемость определялась в соответствии с зависимостью проницаемости от модуля упругости, представленной в работах [34; 35]. Пористость 9 рассчитывалась из соотношения [10]: 9 = 1 - VB/VT , где VB/VT - объёмная доля трабекулярной кости в соответствии с экспериментальными данными [63]. Внешней оболочкой имитировали слой мышечной ткани с пороупругими характеристиками из работы [55]. Явным учётом геометрических параметров подвздошно-бедренной связки и кожных покровов пренебрегали.
Биологическая жидкость, находящаяся внутри тканей в данной модели, имеет свойства физиологического раствора: модуль объёмного сжатия K f = 2,4 ГПа, плотность р f = 1000 кг/м3, вязкость n f = 1 мПа^с. Для описания механического поведения медных пластин аппликатора используется модель упругого тела с параметрами: плотность р = 8950 кг/м3, модуль объёмного сжатия K = 115 ГПа, модуль сдвига G = 41,6 ГПа [26].
Результаты
Различные авторы сообщают о регенеративном эффекте ультразвукового воздействия на бедренный сустав с небольшой степенью остеопении и без дегенеративных изменений, если интенсивность этого воздействия находится в диапазоне от 10 мВт/см2 до 5 Вт/см2 [57]. В данной работе исследовалось низкоинтенсивное акустическое воздействие в диапазоне от 0,1 до 3 Вт/см2 и частотой f = 1,5 МГц.
Поля гидростатического давления (рис. 3, а , в ) показывают, что при интенсивности воздействия более 1 Вт/см2 наблюдаются участки с напряжениями всестороннего сжатия и растяжения выше минимально необходимых для остеогенеза значений амплитуды (3 кПа) и не достигают пороговых значений, при которых происходит дифференцировка клеток хряща или фиброзной ткани (менее 0,15 МПа).
Из анализа полей распределения давления биологической жидкости (рис. 3, б , г ) установлено, что при интенсивности воздействия менее 3 Вт/см2 условия для переноса остеоцитов или хондроцитов отсутствуют. При нагрузке интенсивностью более 3 Вт/см2 в локальных областях наблюдается необходимый уровень давления внутритканевой жидкости для запуска процессов переноса биологических клеток.
Этот результат согласуется с экспериментальными
Упругие и пороупругие свойства тканей ТБС, поражённого остеонекрозом головки
|
Тип ткани |
Плотность матрикса ρ, кг/м3 |
Модуль сдвига матрикса G , ГПа |
Модуль объёмного сжатия матрикса K , ГПа |
Пористость θ |
Проницаемость k , м2 |
|
Кортикальная |
1850 |
5,55 |
14,0 |
0,04 |
3,6 10-15 |
|
Губчатая |
700 |
1,30 |
3,3 |
0,70 |
1,0 10-11 |
|
Губчатая (некроз) |
600 |
1,15 |
2,5 |
0,80 |
2,0 10-10 |
|
Губчатая (склероз) |
800 |
1,84 |
4,0 |
0,60 |
1,0 10-12 |
|
Хрящевая |
800 |
0,0043 |
0,0416 |
0,80 |
4,8 10-18 |
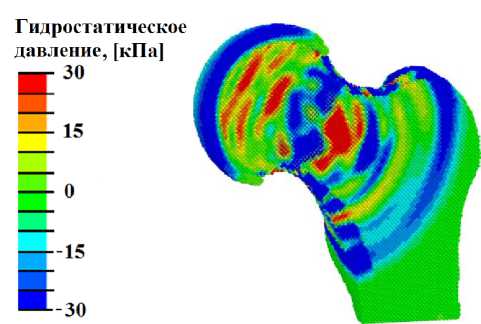
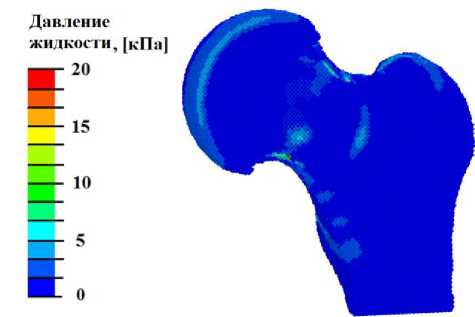
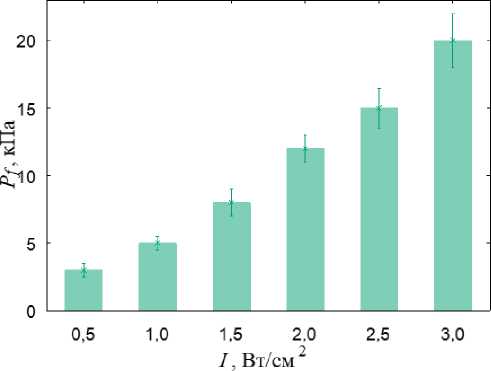
б
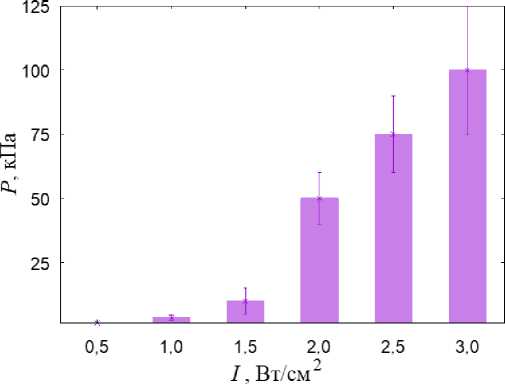
Рис. 3. Результаты моделирования УЗВ на здоровый сустав: а – распределение гидростатического давления (кПa) при УЗВ 3 Вт/см2; б – распределение давления флюида в порах (кПa) при УЗВ 3 Вт/см2; в – гистограммы зависимости максимальной амплитуды гидростатического давления от интенсивности УЗВ; г – гистограммы зависимости максимальной амплитуды давления флюида в порах от интенсивности УЗВ
данными [6; 42; 43], где при интенсивностях выше
2 Вт/см2 отмечается регенерация костной ткани.
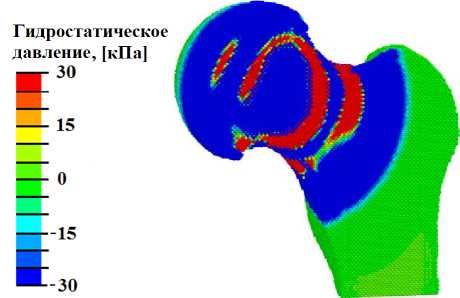
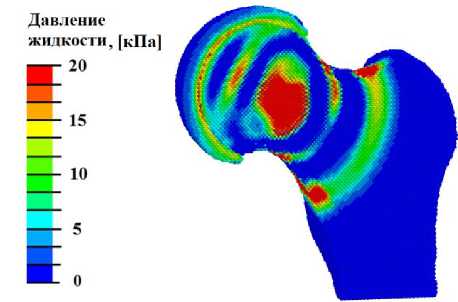
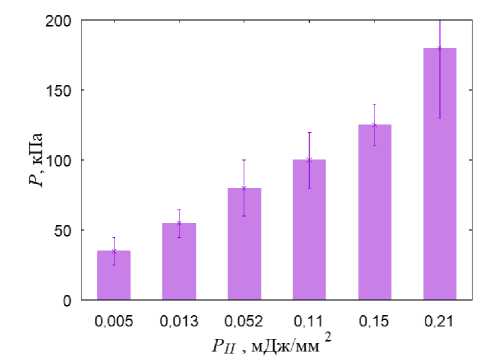
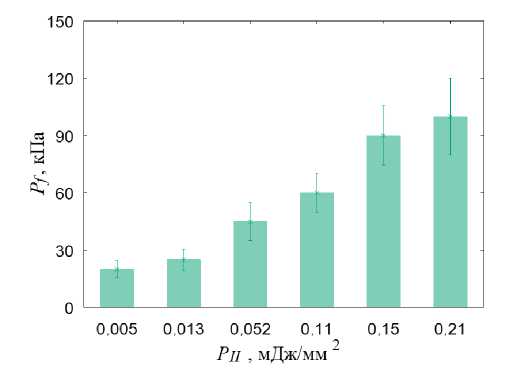
В литературе [61] сообщается о терапевтическом эффекте ударно-волнового нагружения с плотностью потока энергии в диапазоне от 0,01 до 1 мДж/мм2. При анализе полученных в наших расчётах полей распределения гидростатического давления было обнаружено, что при начала процесса остеогенеза и хондрогенеза (гидростатическое давление выше 3 кПа) (рис. 4, а ). Картина распределения давления жидкости в порах свидетельствует о создании условий для переноса биологических клеток в области шейки при плотности потока энергии более 0,01 мДж/мм2 , значения этого параметра должны лежать в диапазоне от 20 кПа до 2 МПа, при плотности потока энергии более 0,05 мДж/мм2 в области головки под хрящевой пластинкой создаются условия для перераспределения биологических клеток (рис. 4, в ).
При ударно-волновом нагружении с плотностью по тока энергии более 0,21 мДж/мм2 в областях хрящевых пластинок сформировались условия для регенерации хрящевой ткани [54; 67]: величина сжимающих напряжений в локальных областях превышает 0,15 МПа (рис. 4, в). На большей площади хрящевых пластин при плотности потока энергии более 0,21 мДж/мм2 создаются условия для остеогенеза и хондрогенеза. Паттерн распределения давления флюида в порах (рис. 4, г) свидетельствует, что при плотности потока энергии более 0,21 мДж/мм2 создаются условия для переноса биологических клеток в области хрящевых пластин.
Ультразвуковое воздействие различной интенсивности на бедренный сустав, поражённый остеонекрозом головки
Авторы [47; 50] сообщают о различных диапазонах значений интенсивности ультразвукового воздействия на бедренный сустав с остеонекрозом головки, при которых наблюдается регенеративный эффект (от 20 до 5 Вт/см2). В данной работе исследовалось низкоинтенсивное акустическое воздействие в диапазоне интенсивностей 0,5; 1,5; 3 Вт/см2 при частоте 1,5 МГц.
б
в г
Рис. 4. Результаты моделирования УВВ на здоровый сустав: а – распределение гидростатического давления (кПa) при УВВ 0,013мДж/мм2; б – распределение давления флюида в порах (кПa) при УВВ 0,013 мДж/мм2; в – гистограммы зависимости максимальной амплитуды гидростатического давления от интенсивности УВВ; г – гистограммы зависимости максимальной амплитуды давления флюида в порах от интенсивности УВВ
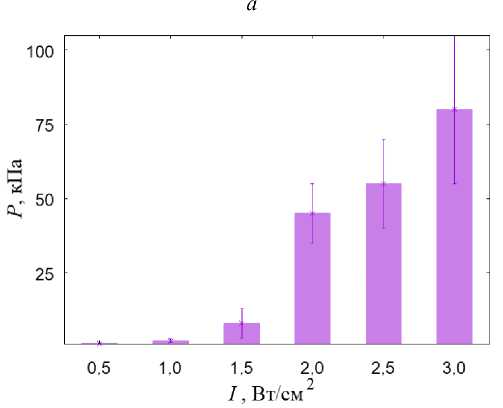
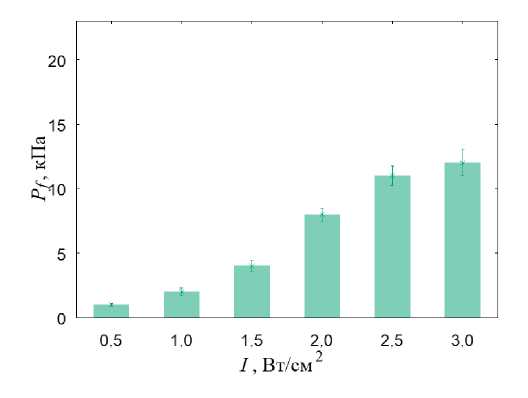
При интенсивности УЗВ менее 1 Вт/см2 во внутренней области бедренной кости наблюдаются напряжения ниже необходимого уровня для запуска процесса остеогенеза (рис. 5, в ). Условия для переноса биологических тканей при данной интенсивности воздействия также не наблюдаются (рис. 5, г ). На поверхности бедренной кости (преимущественно в кортикальной оболочке) вблизи. расположения аппликатора наблюдаются локальные области с условиями для регенерации костной ткани
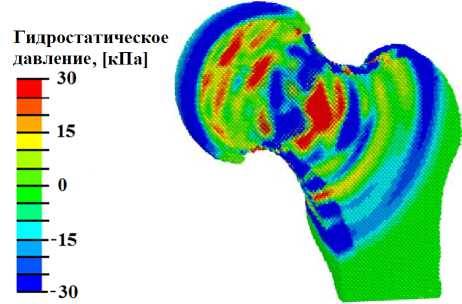
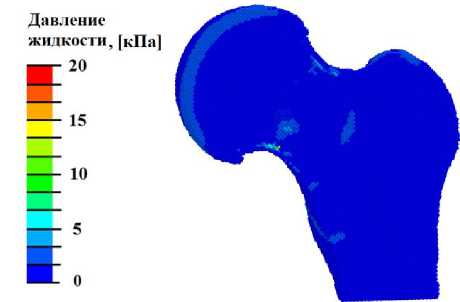
При интенсивности более 1 Вт/см2 (рис. 5, в ) наблюдаются локальные участки с напряжениями всестороннего сжатия и растяжения выше минимально необходимых значений амплитуды для остеогенеза (3 кПа). Однако в области, поражённой остеонекрозом, наблюдается недостаточный минимум гидростатического давления для запуска процесса остеогенеза. На паттерне распределения давления флюида в порах отсутствуют области с необходимой величиной данного параметра для запуска процесса переноса биологических клеток (рис. 5, г ).
Условия для начала процесса остеогенеза в области некроза наблюдаются при УЗВ интенсивностью более 2 Вт/см2. Так, в этом случае в области некроза наблю- даются растягивающие напряжения, превышающие 3 кПа (рис. 5, а). Однако на паттерне распределения давления флюида в порах отсутствуют участки с необходимым минимумом для переноса биологических клеток в области некроза и склероза (рис. 5, б).
Анализ полученных результатов моделирования свидетельствует, что УЗВ является эффективным для лечения остеонекроза головки ТБС при интенсивности более 1 Вт/см2. Однако этот тип воздействия не способствует переносу биологических клеток внутри проксимального отдела бедренной кости.
В работе [24] исследовалось влияние УВ на бедренный сустав, поражённый остеонекрозом, с плотностью потока энергии 0,12 и 0,32 мДж/мм2. В работах [31; 70] сообщается об эффективности лечения некроза при УВ-воздействии 0,474 мДж/мм2. Эффективность УВ с плотностью потока энергии 0,5 мДж/мм2 при начальных стадиях остеонекроза наблюдали в работе [60].
б
в г
Рис. 5. Результаты моделирования УЗВ на ТБС, пораженном остеонекрозом: а – распределение гидростатического давления (кПa) при УЗВ 3 Вт/см2; б – распределение давления флюида в порах (кПa) при УЗВ 3 Вт/см2;
в – гистограммы зависимости максимальной амплитуды гидростатического давления от интенсивности УЗВ;
г – гистограммы зависимости максимальной амплитуды давления флюида в порах от интенсивности УЗВ
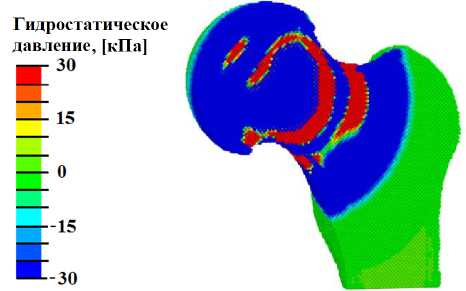
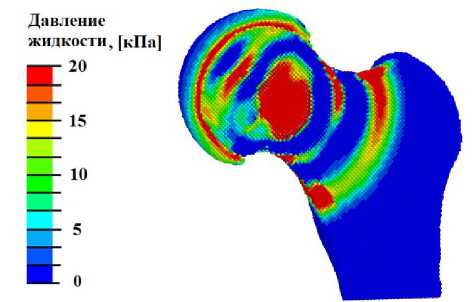
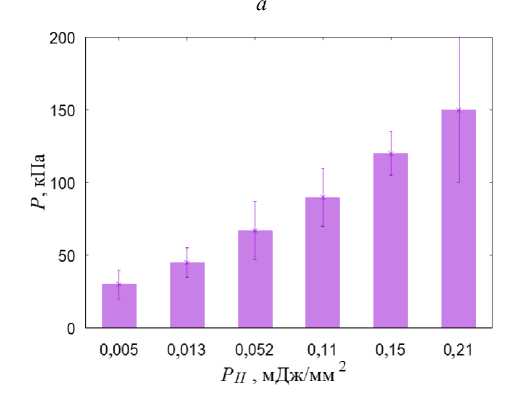
При анализе полученных в расчётах полей распределения гидростатического давления было обнаружено, что при УВ-нагружении с плотностью потока энергии выше 0,01 мДж/мм2 в области остеонекроза создаются условия для начала процесса остеогенеза и хондрогенеза (гидростатическое давление выше 3 кПа) (рис. 6, а ). Распределение давления жидкости в порах (рис. 6, б ) свидетельствует о создании условий (значения этого параметра должны лежать в диапазоне от 20 кПа до 2 МПа) для переноса биологических клеток в области склероза тканей, но фрагментарно. При УВТ с плотностью потока энергии более 0,05 мДж/мм2 в области остеонекроза присутствуют обширные участки (преимущественно в склерозном кольце, окружающем область некроза тканей) с условиями для переноса биологических клеток (рис. 6, в , б ). При плотности потока энергии более 0,2 мДж/мм2 по всей области, поражённой остеонекрозом, создаются условия для переноса биологических клеток (рис. 6, г ).
Анализ полученных результатов моделирования свидетельствует, что УВТ является эффективным способом для лечения остеонекроза головки ТБС при плотности потока энергии более 0,05 мДж/мм2 .
Заключение
В рамках данного исследования были разработаны трёхмерные численные модели бедренного сустава, поражённого дегенеративными изменениями, реальной геометрии. Впервые с помощью компьютерного моделирования были проведены исследования по терапевтическому влиянию на бедренный сустав ультразвукового и ударно-волнового воздействий в широком диапазоне интенсивности. Большинство авторов считают эффективным для лечения начальных стадий остеонекроза УВТ с диапазоном нагружения от 0,18 до 0,25 мДж/мм2 [15; 62]. Существует также ряд работ, в которых говорится о перспективности использование нагружения в пределах 0,3–0,5 мДж/мм2 [25; 56; 60; 62; 72]. Наши результаты показали, что условия для начала процесса остеогенеза губчатой ткани в области остеонекроза создаются при нагружении от 0,05 мДж/мм2. Однако при таком воздействии не достигается необходимый уровень давления флюида в порах, способствующий переносу биологических клеток в область некроза через склеротическое кольцо. Необходимый уровень данного параметра наблюдается лишь при плотности потока энергии более
в
Рис. 6. Результаты моделирования УВВ на на ТБС, пораженном остеонекрозом: а – распределение гидростатического давления (кПa) при УВВ 0,013 мДж/мм2; б – распределение давления флюида в порах (кПa) при УВВ 0,013мДж/мм2; в – гистограммы зависимости максимальной амплитуды гидростатического давления от интенсивности УВВ (в области остеонекроза); г – гистограммы зависимости максимальной амплитуды давления флюида в порах от интенсивности УВВ (в области остеонекроза)
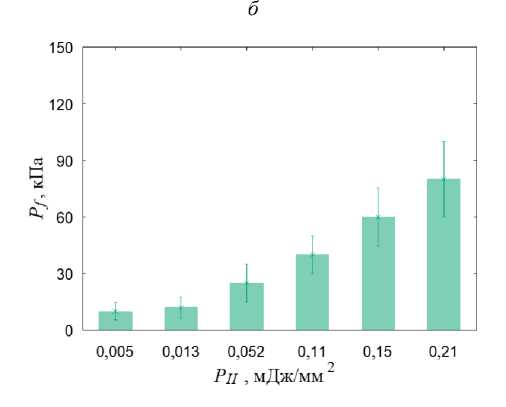
г
0,2 мДж/мм2. Таким образом, наши результаты соответствуют рекомендуемому диапазону УВТ на ТБС с остеонекрозом большинства исследований [41; 78]. Для лечения остеонекроза применяют также низкоинтенсивное ультразвуковое воздействие ( LIPUS – Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound ). Ряд авторов приводят данные о положительном эффекте УЗТ с интенсивностью менее 100 мВт/см2, преимущественно 30 мВт/см2. Однако ряд исследователей считают, что применения только низкоинтенсивного УЗ-воздействия недостаточно для остеогенеза, и данная неинвазивная методика эффективна только в сочетании с другими способами лечения. Кроме того, многие авторы отмечают, что гипотеза о том, что такая величина УЗТ считается эффективной при лечении остеонекроза, основанная на эффективности лечения переломов, неверна. В работах [43; 46] было показано, что лечение LIPUS с интенсивностью 30 мВт/см2 не способствует остеогенезу костной ткани в области некроза. Возможной причиной авторы считают отсутствие необходимого уровня давления для переноса биологических клеток, способных к делению, в область некроза. Однако использование LIPUS в сочетании с трансплантацией здоровых клеток костного мозга способствует остеогенезу. В работе [44] было показано, что УЗТ 0,30 мВт/см2 эффективна при лечении остеонекроза головки ТБС только в сочетании с методом радиоактивного облучения поражённой области.
В работе [79] на модели кролика показано, что при стероид-ассоциируемом остеонекрозе при УЗ-воздействии 200 мВт/см2 наблюдается образование новых сосудов в области некроза тканей и уменьшение жировых клеток, однако не наблюдается расширения сосудов, способствующих распространению здоровых клеток в область некроза. Авторы пришли к выводу, что такое низкоинтенсивное УЗ воздействие может быть эффек
тивно в качестве профилактики остеонекроза, а не как способ его лечения. Аналогичные выводы также были сделаны в работе [75]. Было показано, что низкоинтенсивный импульсный ультразвук усиливает остеогенную дифференцировку мезенхимальных стволовых клеток, стимулирует дифференцировку и пролиферацию остеобластов, ингибирует остеокласты, улучшает локальную перфузию крови. Однако он не способствует переносу здоровых клеток в область некроза. В работе [73] использовалась интенсивность УЗТ 200 мВт/см2 и было установлено, что само по себе УЗ-воздействие малоэффективно, и его предпочтительнее использовать вместе с другими способами регенерации костных тканей в области некроза. Наши исследования показали, что при низкоинтенсивном воздействии до 2 Вт/см2 не создаются условия для процесса остеогенеза. Анализ давление флюида в порах показал, что при низкоинтенсивном УЗ-воздействии не создаётся необходимый уровень давления для переноса биологических клеток в область некроза. Таким образом, наше исследование подтверждает гипотезу о том, что применение только низкоинтенсивной УЗТ при остеонекрозе ТБС не способствует регенерации тканей в области некроза.
Впервые на основе результатов компьютерного моделирования показано, что при малоинтенсивном УЗ-воздействии создаются условия для остеогенеза в здоровых тканях. Малоинтенсивное УЗТ может применяться для профилактики и лечения начальных стадий остеопении и остеопороза. Согласно полученным результатам, при УЗ-терапии малой интенсивности (до 1 Вт/см2) не создаются условия для регенерации костной ткани в подхрящевой области. Однако средне- и высокоинтенсивное УЗ-воздействие способствует созданию условий для остеогенеза в области некроза и склероза костных тканей.
Финансирование. Работа выполнена при финансовой поддержке РФФИ в рамках научного проекта № 20-08-00818 (результаты моделирования) и осударственного задания ИФПМ СО РАН, тема номер FWRW-2021-0009 (метод моделирования и программное обеспечение).
Список литературы Численное исследование механического поведения тазобедренного сустава при терапевтическом акустическом воздействии
- Киченко А.А. Перестройка структуры губчатой костной ткани: математическое моделирование // Российский журнал биомеханики. - 2019. - Т. 23, № 3. - С. 336-358.
- Кирпичев И.В., Коровин Д.И., Маслов Л.Б., Томин Н.Г. Математическая модель клеточных преобразований при регенерации костной ткани в условиях изменяющейся биохимической среды с возможной механорегуляцией // Российский журнал биомеханики. - 2016. - Т. 20, № 3. -С. 220-235.
- Тверье В.М. Кинетические уравнения перестройки трабекулярной костной ткани в пространстве Ильюшина // Российский журнал биомеханики. - 2019. - Т.23, no 2. -С. 293-301.
- Al-Abbad H., Allen S., Morris S., Reznik J., Biros E., Paulik B., Wright A. The effects of shockwave therapy on musculoskeletal conditions based on changes in imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression // BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. - 2020. - Vol. 21, no. 1. - Article no. 275.
- Alkhawashki H.M. Shock wave therapy of fracture nonunion // Injury. - 2015. - Vol. 46, no. 11. - P. 2248-2252.
- Ardan J.R.N.I., Janes J.M., Herrick J. Ultrasonic energy and surgically produced defects in bone // Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. - 1957. - Vol. 39. - P. 394-400.
- Bae J.Y., Kwak D.S., Park K.S., Jeon I. Finite Element Analysis of the Multiple Drilling Technique for Early Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head // Annals of Biomedical Engineering. - 2013. - Vol. 41, no. 12. - P. 2528-2537.
- Baig S.A., Baig M.N. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Etiology, Investigations, and Management // Cureus. - 2018. - Vol. 10, no. 8. - Article No. e3171.
- Baron C., Hieu Nguyen V.-, Nali S., Guivier-Curien C. Interaction of ultrasound waves with bone remodelling: A mul-tiscale computational study // Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology. - 2020. - Vol. 19. - P. 1755-1764.
- Berli M., Borau C., Decco O., Adams G., Cook R.B., Aznar J.M.G., Zioupos P. Localized tissue mineralization regulated by bone remodelling: A computational approach // PLoS ONE - 2017. - Vol. 12, no. 3 - Article No. e0173228.
- Bolen J., Schieb L., Hootman J.M., Helmick C.G., Theis K., Murphy L.B., Langmaid G. Differences in the prevalence and severity of arthritis among racial/ethnic groups in the United States, National Health Interview Survey, 2002, 2003, and 2006 // Prev Chronic Dis. - 2010. - Vol. 7, no. 3. - Article No. A64.
- Carter D.R., Hayes W.C. The compressive behavior of bone as a two-phase porous structure // The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. - 1977. - Vol. 59, no. 7. - P. 954-962.
- Chan W.P., Liu Y.-J., Huang G.-S., Lin M.-F., Huang S., Chang Y.-C., Jiang C.-C. Relationship of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head to perfusion changes in the proximal femur by dynamic contrast-enhanced MRIAJR // Am. J. Roentgenol. - 2011. - Vol. 196. - P. 637-643.
- Chen H, Gilbert R.P., Guyenne P. A Biot model for the determination of material parameters of cancellous bone from acoustic measurements // Inverse Problems. - 2018. - Vol. 34, no. 8. - Article No. 0850094.
- Cheng Y. Li P. Efficacy analysis of ESWT in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. // Chinese Medical Sciences Journal. - 2015. - Vol. 5. - P. 20-26.
- Choi H.R., Steinberg M.E., Y Cheng E. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: diagnosis and classification systems // Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine. - 2015. - Vol. 8, no. 3. - P. 210-220.
- Cleveland R.O., McAteer J.A. Physics of shock-wave lithotripsy // Smith's Textbook of Endourology. - Wiley-Blackwell, 2012. - P. 527-558. DOI: 10.1002/9781444345148.ch49
- Cortet S., Paccou B., Pascart J.T., Budzik J.F. (2020). Bone perfusion and adiposity beyond the necrotic zone in femoral head osteonecrosis: A quantitative MRI study// European Journal of Radiology. - 2020. - Vol. 131. - Article No. 109206
- Cowin S.C., Doty S.B. Tissue mechanics. - NY, 2007. Feng C., Wang L., Xu P., Chu Z., Yao J., Sun W., Gong H., Zhang X., Li Z., Fan Y. Microstructural and mechanical evaluations of region segmentation methods in classifications of osteonecrosis // Journal of Biomechanics. -2021. -Vol. 119. - Article No. 110208.
- Giori N.J., Ryd L., Carter D.R. Mechanical influences on tissue differentiation at bone-cement interfaces // Journal of Arthroplasty. - 1995. - Vol. 10, no. 4. - P. 514-522.
- Grivas K.N., Vavva M.G., Polyzos D., Carlier A., Geris L., Van Oosterwyck H., Fotiadis D.I. Effect of ultrasound on bone fracture healing: A computational mechanobioregulato-ry model // The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. - 2019. - Vol. 145. - P. 1048-1059. ter
- Haar G. Therapeutic applications of ultrasound // Progress in Biophysics &Molecular Biology. - 2007. - Vol. 93. - P. 111 -129.
- Han Y., Lee J.K., Lee B.Y., Kee H.S., Jung K.I., Yoon S.R. Effectiveness of lower energy density extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the early stage of avascular necrosis of the femoral head // Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. - 2016. - Vol. 40, no. 5. - P. 871-887.
- Han Y., Lee J.-K., Lee B.-Y. Correction: effectiveness of lower energy density extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the early stage of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. // Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine. - 2017. -Vol. 41, no 2. -P. 337-338.
- He J., Zeng Z., Li H., Wang S.T. The microstructure and mechanical properties of copper in electrically assisted tension // Materials & Design. - 2020. - Vol. 196. - Article No. 109171.
- Helgason B., Gilchrist S., Ariza O. The influence of the modulus-density relationship and the material mapping method on the simulated mechanical response of the proximal femur in side-ways fall loading configuration // Medical Engineering & Physics. - 2016. - Vol. 38. - P. 679-689.
- Heriveaux Y., Nguyen V.-H., Haiat, GReflection of an ultrasonic wave on the bone-implant interface: A numerical study of the effect of the multiscale roughness // The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. - 2018. - Vol. 144, no. 1. -P. 488-499.
- Hodaei M., Rabbani V., Maghoul P. Transient acoustic wave propagation in bone-like porous materials using the theory of poroelasticity and fractional derivative: a sensitivity analysis // Acta Mechanica. - 2020. -Vol. 231, no. 1. - P. 179-203.
- Hodaei M., Maghoul P., Wu N. Three-dimensional biome-chanical modeling of cylindrical bone-like porous materials subject to acoustic waves // International Journal of Mechanical Sciences. - 2022. - Vol. 213. -P. 106835.
- Hsu S.L., Wang C.J., Lee M.S., Chan Y.S., Huang C.C., Yang K.D. Cocktail therapy for femoral head necrosis of the hip // Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery. - 2010. - Vol. 130, no. 1. - P 23-29.
- Hulshof C., Colosio C., Daams J G., Ivanov I.D., Prakash K.C., Kuijer P., Leppink N., Mandic-Rajcevic S., Masci F., van der Molen H.F., Neupane S., Nygard C.H., Oakman J., Pega F., Proper K., Pruss-Ustun A.M., Ujita Y., Frings-Dresen M. WHO/ILO work-related burden of disease and injury: Protocol for systematic reviews of exposure to occupational ergonomic risk factors and of the effect of exposure to occupational ergonomic risk factors on osteoarthritis of hip or knee and selected other musculoskeletal diseases // Environment International. - 2019. - Vol.125. - P. 554-566.
- Kertzman P., Csaszar N.B.M., Furia J.P., Schmitz C. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy is efficient and safe in the treatment of fracture nonunions of superficial bones: a retrospective case series // Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. - 2017. - Vol. 12, no. 1. - Article No. 164.
- Kohles S.S., Roberts J.B., Upton M.L., Wilson C.G., Bonas-sar L.J., Schlichting, A.L. Direct perfusion measurements of cancellous bone anisotropic permeability.// Journal of Biomechanics. - 2001. - Vol. 34, no 9. - P. 1197-1202.
- Kohles S.S., Roberts J.B. Linear poroelastic cancellous bone anisotropy: trabecular solid elastic and fluid transport properties. // Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. - 2002. - Vol. 124, no 5. - P. 521-526.
- Loske A.M. Shock waves as used in biomedical applications // Medical and Biomedical Applications of Shock Waves. -NY, 2017. - P. 19-42. DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-47570-7_3
- Liu G.B., Lu Q., Meng H.Y., Quan Q., Zhang Y.X., Li H., Ma H.Y., Zhao J., Wang P., Zhou X.F., Peng J. Three-dimensional distribution of bone-resorption lesions in oste-onecrosis of the femoral head based on the three-pillar classification // Orthopaedic Surgery. - 2021. - Vol. 13, no. 7. -P. 2043-2050.
- Liu Y., Chen X., Guo A., Liu S., Hu G. Quantitative assessments of mechanical responses upon radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy //Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany). - 2017. - Vol. 5, no 3. - Article No. 1700797.
- Mathieu V., Anagnostou F., Soffer E., Haiiat G. Numeri-calsimulation of ultrasonic wave propagation for the evaluation of dentalimplant biomechanical stability // Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. - 2011. -Vol. 129. -P. 4062-4072.
- Mei Y., Tang Q., Chen S., Chen D. Mechanical evaluation of collapse risk for osteonecrosis of femoral head post-medical treatment // Research Square. - 2021. - Artcle no. rs-138877/v1. DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-138877/v1
- Mei J., Pang L., Jiang Z. The effect of extracorporeal shock wave on osteonecrosis of femoral head: a systematic review and meta-analysis.// The Physician and Sports Medicine. -2022. - Vol. 50, no. 4. - P. 280-288.
- Mirhadi S., Ashwood N., Karagkevrekis B. Factors influencing fracture healing // Trauma. - 2013. - Vol. 15. - P. 140155.
- Mishima H., Sugaya H., Yoshioka T., Aoto K., Wada H., Akaogi H., Ochiai N. The safety and efficacy of combined autologous concentrated bone marrow grafting and low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head // European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. - 2016. - Vol. 26, no. 3. - P. 293298.
- Muramatsu K., Iwanaga R., Sakai T. III-3 low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) for the treatment of massive os-teonecrosis following carbon ion radiotherapy for malignant bone tumor //Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma. - 2019. - Vol. 33, no. 10. - Article No. S3.
- Nguyen V.H., Naili S. Ultrasonic wave propagation in visco-elastic cortical bone plate coupled with fluids: a spectral finite element study // Computer methods in biomechanics and biomedical engineering. -2013. - Vol. 16, no. 9. - P. 963974.
- Ogawa T., Ishii T., Mishima H., Nishino T., Watanabe A., Ochiai N. Is low-intensity pulsed ultrasound effective for revitalizing a severely necrotic small bone? An experimental rabbit model // Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology. - 2011. -Vol. 37, no. 12. - P. 2028-2036.
- Palanisamy P., Alam M., Li S., Chow S.K.H., Zheng Y.P. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation for bone fractures healing: A review // Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. - 2022. - Vol. 41, no. 3. - P. 547-563.
- Petek D., Hannouche D., Suva D. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: pathophysiology and current concepts of treatment // EFORT Open Reviews. - 2019. - Vol. 4, no. 3. - P. 8597.
- Pereira D., Haiat G., Fernandes J., Belanger P. Simulation of acoustic guided wave propagation in cortical bone using a semi-analytical finite element method // The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. - 2017. - Vol. 141, no 4. -P. 2538-2547.
- Romano C.L., Kirienko A., Sandrone C., Toro G., Toro A., Valente E.P., Caporale M., Imbimbo M., Falzarano G., Setti S., et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in the treatment of nonunions and fresh fractures: A case series // Trauma Care. - 2022. - Vol. 2. - P. 174-184.
- Sadouki M., Fellah M., Fellah Z., Ogam E., Depollier C. Ultrasonic propagation of reflected waves in cancellous bone: application of Biot theory // 2015 6th European symposium on ultrasonic characterization of bone, IEEE. - 2015. - P. 1-55.
- Shilko E.V., Psakhie S.G., Schmauder S., Popov V.L., Asta-furov S.V., Smolin A.Yu. Overcoming the limitations of distinct element method for multiscale modeling of materials with multimodal internal structure // Computational Materials Science. - 2015. - Vol. 102. - P. 267-285.
- Shilko E.V., Smolin A.Yu., Dimaki A.V., Eremina G.M. Particle-based approach for simulation of nonlinear material behavior in contact zone // Multiscale Biomechanics and Tribology of Inorganic and Organic Systems. - Singapore, 2021. - P. 67-89.
- Simon U., Augat P., Utz M., Claes L. A numerical model of the fracture healing process that describes tissue development and revascularization // Computer Methods in Biome-chanics and Biomedical Engineering. - 2011. - Vol. 14, no. 1. - P. 79-93.
- Sowinski D.R., McGarry M.D.J., Van Houten E.E. W., Gor-don-Wylie S., Weaver J.B., Paulsen K.D. Poroelasticity as a model of soft tissue structure: Hydraulic permeability reconstruction for magnetic resonance elastography in silico // Frontiers in Physics. - 2021. - Vol. 8. - Article No. 617582.
- Su Y., Yuyu C., Liang Y. Clinical observation of high-energy extracorporeal shock wave in the treatment of early femoral head necrosis // J. Biotechnol. World. - 2016. - Vol. 2016. - P. 87-88.
- Sun S. Sun L., Kang Y., Tang L., Qin Y.X., Ta D. Therapeutic effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats: Intensity-dependent study // Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology.- 2020. - Vol. 46, no. 1. - P. 108-121.
- Vayron R., Karasinski P., Mathieu V., Michel A., Loriot D., Richard G.,Lambert G., Ha€iat, G. Variation of the ultrasonic response of a dental implant embedded in tricalcium silicate-based cement undercyclic loading // Journal of Biome-chanics. - 2013. - Vol. 46. - P. 1162-1168.
- Volokh K.Y. Prediction of femoral head collapse in osteone-crosis // Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. - 2005. -Vol. 128, no. 3. - P. 467-470.
- Vulpiani M.C., Vetrano M., Trischitta D., Scarcello L., Chizzi F., Argento G., Saraceni V.M., Maffulli N., Ferretti A. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in early osteonecrosis of the femoral head: prospective clinical study with long-term follow-up // Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery. - 2012. - Vol. 1322, no. 4. - P. 499-508.
- Wang C.-J., Wang F.-S., Ko J.-Y., Huang H.-Y., Chen C.-J., Sun Y.-C., Yang Y.-J., Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows regeneration in hip necrosis // Rheumatology. - 2008. - Vol. 47, no. 4. - P. 542-546.
- Wang C.J., Huang C.C., Wang J.W. Long-term results of extracorporeal shockwave therapy and core decompression in osteonecrosis of the femoral head with eight- to nine-year follow-up // Biomed J. - 2012. - Vol. 35. - P. 481-485.
- Wang C., Wang X., Xu X.-l., Yuan X.-L., Gou W.-L., et al. Bone microstructure and regional distribution of osteoblast and osteoclast activity in the osteonecrotic femoral head // PLoS ONE. - 2014. - Vol. 9, no. 5. - Article No. e96361.
- Wang C., Peng J., Lu S. Summary of the various treatments for osteonecrosis of the femoral head by mechanism: A review. // Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. - 2014. -Vol. 8, no. 3. - P. 700-706.
- Wang C., Wang Y., Meng H., Gou W., Yuan X., Xu X., Lu S. Microstructure and nanomechanical properties of single trabecular bone in different regions of osteonecrosis of the femoral head // Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. - 2016. - Vol. 16, no. 3. - P. 2264-2269.
- Wang C.-J., Huang C.-C., Yip H.-K. Dosage effects of ex-tracorporeal shockwave therapy in early hip necrosis. // International Journal of Surgery. - 2016. - Vol. 35. - P. 179186.
- Wang M., Yang N., Wang X. A review of computational models of bone fracture healing // Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing. - 2017. - Vol. 55, no. 11. - P. 1895-1914.
- Wang X., Matula T.J., Ma Y., et al. Finite element modeling of acoustic wave propagation and energy deposition in bone during extracorporeal shock wave treatment // Journal of Applied Physics. - 2013. - Vol. 113. - Article No. 244901.
- Wen P.F., Guo W.S., Zhang Q.D., Gao F.Q., Yue J.A., Liu Z.H., Cheng L.M., Li Z.R. Significance of lateral pillar in osteonecrosis of femoral head: A finite element analysis // Chinese Medical Journal (Engl). - 2017. - Vol. 130, no. 21. - P. 2569-2574.
- Wong T., Wang C.J., Hsu S.L., Chou W.Y., Lin P.C., Huang 75. C.C. Cocktail therapy for hip necrosis in SARS patients // Chang Gung Medical Journal. - 2008. - Vol. 31. - P. 546553.
- Xin Z., Lin G., Lei H., Lue T.F., Guo Y. Clinical applica- 76. tions of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and its potential role in urology // Translational Andrology and Urology. - 2016. - Vol. 5, no. 2. - P. 255-266. 77.
- Xie K., Mao Y., Qu X., Dai K., Jia Q., Zhu Z., Yan M. High-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy for nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head // Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. - 2018. - Vol. 13, no. 1. - Article No. 25.
- Xu D. F., Qu G.X., Yan S.G., Cai, X. Z. Microbubble- 78. mediated ultrasound outweighs low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on osteogenesis and neovascularization in a rabbit model of steroid-associated osteonecrosis // BioMed Research International. - 2018. - Vol. 2018. - Article No. 79. 4606791.
- Xu J., Zhan S., Ling M., Jiang D., Hu H., Sheng J., Zhang C. Biomechanical analysis of fibular graft techniques for non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A finite element analysis // Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. -2020. - Vol. 15, no 1. - Article No. 335.
- Yan S. G., Huang L.Y., Cai X.Z. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound: a potential non-invasive therapy for femoral head os-teonecrosis // Medical Hypotheses. - 2011. - Vol. 76, no 1. -P. 4-7.
- Yu T., Xie L., Chu F. A sclerotic rim provides mechanical support for the femoral head in osteonecrosis // Orthopedics. - 2015. - Vol. 38, no. 5. - P. e374-e379.
- Yue Y., Yang H., Li Y., Zhong H., Tang Q., Wang J., Wang R., He H., Chen W., Chen D. Combining ultrasonic and computed tomography scanning to characterize mechanical properties of cancellous bone in necrotic human femoral heads. // Medical Engineering & Physics. - 2019. - Vol. 66. - P. 12-17.
- Zhang Q., Liu L., Sun W., Gao F., Cheng L., Li, Z. Extra-corporeal shockwave therapy in osteonecrosis of femoral head: A systematic review of now available clinical evidences // Medicine. - 2017. - Vol. 96, no. 4. - Article No. e5897.
- Zhu H., Cai X., Lin T., Shi Z., Yan S. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound enhances bone repair in a rabbit model of steroid-associated osteonecrosis // Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. - 2015. - Vol. 473, no 5. - P. 1830-1839.


