Complex mechanical-thermal synthesis of nanostructured calcium hydrosilicates for cement composites
Автор: Shoshin E.A., Timokhin D.K., Strakhov A.V., Kochergina M.P., Korolkov G.A.
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: Manufacturing technology for building materials and products
Статья в выпуске: 3 Vol.17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. The use of nanosized calcium hydrosilicates as additives accelerating the structure formation of cement compositions is becoming increasingly popular. The reason for this lies in their high efficiency as accelerators in the absence of a negative effect on the long-term strength and durability of cement composites. An additional advantage of nanoscale calcium hydrosilicates is the variety of existing methods for their synthesis, among which the mechanochemical method stands out due to the availability of raw materials and the simplicity of the technical design of the synthesis. Article body. The review considers a new method for the synthesis of nanostructured calcium hydrosilicates – complex mechanical-thermal synthesis, which is a combination of mechanochemical synthesis of carbohydrate-modified calcium hydrosilicates with their subsequent thermal decomposition. Modified calcium hydrosilicates , in the interlayer space of which the carbohydrate is intercalated , are capable of decomposition under conditions of low-temperature thermolysis (<150 oC ) with the formation of hydrosilicate nanoparticles, the coagulation of which leads to the formation of a nanostructured phase of calcium hydrosilicates – xerogel. A mixture of xerogel with residues of raw materials, hydrated phases that have not decomposed during thermolysis is a calcium silicate dispersion (CSD). The technological features of CSD synthesis and some properties of CSD are described. In particular, a moderate (up to 60%) acceleration of daily strength gain of CSD-modified cement mortars with a parallel increase in grade strength (17%) is revealed. A significant effect of CSD on the rheological properties of cement mixtures is noted. Conclusion. Complex mechanical-thermal synthesis is a new synthetic direction for obtaining nanosized calcium hydrosilicates. The development of this direction is far from complete and is closely related to the development of the theoretical base, in particular, the concept of non-classical nucleation as applied to hydrosilicate phases. The development of the method can be aimed at searching for new organic modifiers with the acquisition of new properties of modified hydrosilicates and products of their thermal decomposition, at improving synthesis modes in order to regulate the quantitative and qualitative parameters of the nanostructured phase, consumer properties of the CSD, and expanding the scope of its application.
Calcium hydrosilicates, nanostructure, complex mechanical-thermal synthesis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142244831
IDR: 142244831 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2025-17-3-254-272
Текст научной статьи Complex mechanical-thermal synthesis of nanostructured calcium hydrosilicates for cement composites
Review article
Шошин Е.А., Тимохин Д.К., Страхов А.В., Кочергина М.П., Корольков Г.А. Комплексный механотермический синтез нанострук-турированных гидросиликатов кальция для цементных композитов. Нанотехнологии в строительстве. 2025;17(3):254–272. – EDN: AJUNAK.
In the context of increasing requirements for accelerating additives (binders with a high degree of cement substitution, 3D printing , etc.), the efficiency of traditional accelerators is insufficient [1]. Therefore, the search for effective methods for accelerating cement hydration remains a relevant topic [2–4], and the use of nanomaterials is a new trend [5–7]. Traditional accelerating additives (nitrites, nitrates, thiocyanates , etc. [8, 9]), organic substances (formates, alkanolamines [10–11]) and their mixtures [12–13]) have a whole bunch of side effects, among which are negative changes in the phase composition of the stone, strength characteristics of the stone, and durability [1]. Against this background, nanosized calcium hydrosilicates seem to be a kind of «panacea»: having no side effects, they demonstrate a high affinity for cement gel in combination with an acceptable cost [14]. The use of nanohydrosilicates is a relatively new area, so there is a wide range of issues that need to be resolved (for example, the effect of the Ca/Si ratio of the seed and its crystallinity on the characteristics of the resulting stone). In foreign literature, nanohydrosilicates are considered primarily as accelerating agents [15], although they also have rheological activity [16, 17]. It is noteworthy that the entry into the market of a commercial accelerator based on calcium nanohydrosilicates (Basf suspension) Master X-Seed 100) does not reduce the debatability of the topic of the factors of efficiency of nanohydrosilicate accelerators, since the factors of efficiency of nanohydrosilicates, in addition to the expected concentration of nanoparticles, their size, morphology and Ca/Si ratio, mineral composition of the binder , according to [14], also include the method of obtaining the nanomaterial . The latter, in itself, clearly demonstrates the lack of clarity in the issue of the mechanisms of influence of nanohydrosilicates on the cement system.
2. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE
3. COMPLEX MECHANICAL-THERMAL SYNTHESIS
3.1. Formation of the CSH phase from the standpoint of non-classical nucleation
MECHANOCHEMICAL METHOD FOR OBTAINING NANOSIZED CALCIUM HYDROSILICATES
Direct chemical interaction of SiO2 and CaO can be carried out both under normal conditions and at elevated temperatures and pressures, for example, within the framework of mechanicochemical synthesis. Under normal conditions, the reaction parameters will be determined by the solubility of the system components in water, and the low solubility of SiO2 determines the significant duration of the process (up to a month [16]. Mechanochemical synthesis allows accelerating the pozzolanic reaction, reducing the duration of the synthesis to several hours or days [16]. The
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS accelerating effect is based on mechanical activation , an effective way to increase the activity of mineral raw materials [17–20]. Mechanochemical synthesis is carried out in the form of «wet» milling, where the liquid phase ensures better granulometry of the milling products [21] and promotes the formation of nanophases [22, 23]. At the same time, the solubility of mineral raw materials increases [24], which allows for a decrease in the water-solid ratio. The latter provides greater opportunities for controlling the Ca/Si ratio of the synthesized hydrosilicates. Perhaps the most significant advantage of mechanochemical synthesis is that the Ca/ Si ratio of the initial raw material mixture determines the Ca/Si ratio of the resulting hydrosilicates [14, 25], in addition, the method is oriented toward the use of available raw materials and a variety of milling equipment [26, 27]. At the same time, from the standpoint of application in construction, the «waste» of mechanochemical synthesis in the form of unreacted grains of raw materials can act as a useful component of raw building mixture, where the principle of polymodality of the grain mixture is decisive – and this is another non-obvious advantage of mechanochemical synthesis. However, the duration of mechanochemical synthesis remains the most «disadvantageous» side of this process. However, the solution to the problem of the duration of synthesis can be found in a comprehensive approach to the synthesis of hydrosilicate nanoparticles.
It was noted above that mechanochemical synthesis is carried out in the form of «wet» grinding, which assumes a certain sequence of heterophase processes of phase formation. It is precisely heterophase processes that are the subject of current scientific research, the results of which may have a promising continuation in relation to cement systems both in theoretical and practical terms. Familiarization with them will allow a better understanding of the features and prospects of complex mechanical-thermal synthesis (CMT-synthesis).
The complexity of the structure of C-S-H phases and the uncertainty of the mechanisms of their formation are the reason for the regular appearance of new works devoted to this topic (for example, one of the latest is [28]).
The disordered layered structure of gel phases (C-S-H-phases) is determined by the system of bridging interlayer calcium ions. This is considered to be the main factor determining the complexity of the three-dimensional structure of CSH phases [29] and has no explanation within the framework of the traditional model of solid phase formation [30], which assumes the formation and growth of critical nuclei of a new phase [31].
According to the new concept of phase formation – non-classical nucleation – the formation of a new phase begins with the formation of «subcritical clusters» («pseu-dophases», precursors of nuclei), which transform into clusters of critical sizes and grow with the formation of the final phase. The evolution of subcritical clusters of the new phase is determined by the processes of aggregation, diffusion and convection [32]. The distinctive elements of the concept of non-classical nucleation are, firstly, the absence of identity of the morphology of the precursor of nuclei of the new phase and the crystal of the final phase [33–35], and secondly, the high sensitivity of the «precursors» to the presence of organic substances in the solution, the presence of which can change the induction time, the stability of the «precursor», and change the size and shape of the crystals [36, 37].
The formation of C-S-H-phases from the standpoint of the concept of non-classical nucleation is the formation of nanosized globules (droplets, «predecessors») of amorphous calcium hydrosilicates, which then form fractal structures (Fig. 1) [31]. After 15 minutes, a core is formed in a drop of nanoaggregate, and nanofilms appear on the surface of the drop, the number of which increases as the droplets «dissolve» (Fig. 2). Within an hour, the hydrosilicate droplets are transformed into the well-known films of the C-S-H-phase.
The process of transformation of droplets into nanofilms has a certain calorimetric portrait – a sequence of endo- and exothermic effects corresponding to the formation of droplets and their transformation [31]. The presence of a polycarboxylate plasticizer promotes the stabilization of hydrosilicate droplets: their transformation into nanofilms slows down, and the beginning of the transformation process shifts towards longer times. The trajectory of droplet transformation did not change, but the calcium content in the droplet increased, and the hydrosilicate droplets themselves formed looser aggregates. That is, the influence of organic agents on the process of droplet evolution has been proven. And although this view on the processes of C-S-H-phase formation is still being debated, it is clear that the stereochemistry of organic additives is of great importance for the evolution of the silicate system. In this case, the stereochemistry of an organic molecule must correspond to the stereochemistry of both an aqueous solution and a mineral phase. And carbohydrates in this regard fully meet this requirement, which will be discussed in more detail below.
3.2. Effect of carbohydrate supplements on phase formation Ca(OH)2
The authors of [38] described the ability of sucrose to radically change the morphology of Ca(OH)2crystals. There may be several reasons for this: being a weak polybasic acid [39], sucrose can dissociate up to the fourth
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
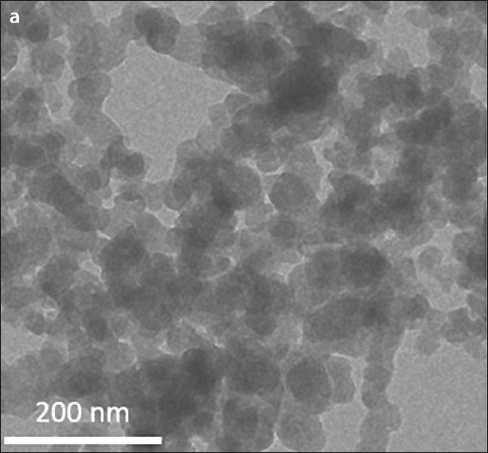
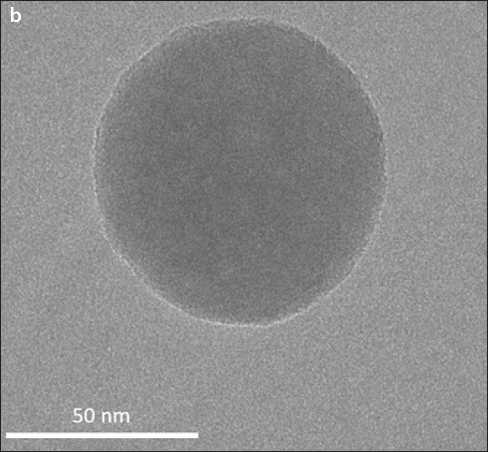
Fig. 1. Microelectron images of CSH precipitated from solutions of Ca(NO3)2 and Na2SiO3 ( 5 min): a – fractal structure of droplets (×30,000 times); b – a separate drop of calcium hydrosilicates [31]
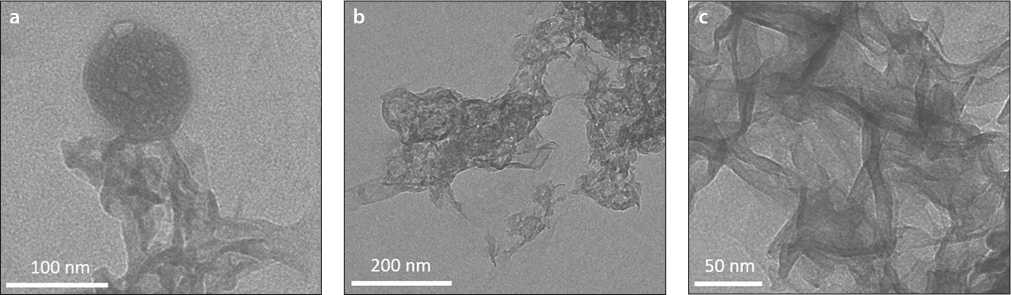
Fig. 2. Microelectron images of CSH precipitated from Ca(NO3)2solutions and Na2SiO3after: a – 15; b – 45; c – 60 minutes [31]
stage depending on the pH of the medium. Ca(OH)2 is also capable of stepwise dissociation and with increasing pH the proportion of Ca(OH)+ ions increases [40]. Under these conditions, sucrose is capable of forming a number of calcium complexes with a ratio of Ca: Sucr = 1:4 (where Sucr is sucrose) at pH>12, up to Ca: Sucr = 1:1 at pH <11 [41, 42]. The variability of the properties of sucrose depending on the pH of the solution determines its high adsorption activity, as well as high levels of supersaturation of the solution with Ca2+ . All together, this can radically change the kinetics of nucleation and affect the number of crystals formed and their sizes.
On the other hand, the stereochemistry of carbohydrates allows them to effectively replace individual water molecules in the system of hydrogen bonds of an aqueous solution [43–45], which cannot but change the conditions for the formation of nuclei according to a non-classical scheme. The latter was proven in the work [46], the authors of which revealed a chain of transformations: pre-nuclear clusters – dense liquid precursors (prenucleation stage) – amorphous Ca(OH)2– metastable nanocrystalline Ca(OH)2 . The carbohydrates studied in the work do not disrupt the sequence of transformations, but actively affect the prenucleation stage, slowing down the evolution of the precursors of the solid phase C a(OH)2. As a result, high levels of solution supersaturation are maintained while the formation of amorphous Ca(OH) 2 is slowed down. The authors [47] note an inverse relationship between the level of solution supersaturation at the beginning of nucleation and the final morphological characteristics of Ca(OH)2 , which does not correspond to the concepts of the classical theory of crystallization. In addition, additives present during nucleation are capable of influencing not only the morphology, but also
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS the properties of the resulting Ca(OH) 2 ( for example, the ability to carbonize ) [38, 48]. The importance of the fact that Ca(OH) 2is capableof evolving according to the non-classical nucleation scheme is especially increased by taking into account that, according to Taylor’s dreier-kette model (formulated in 1986, but still relevant), the formation of the C-S-H-phase begins with the formation of a Ca(OH) 2plate, on the surface of whichmonomeric or oligomeric silicon-oxygen tetrahedra are «adsorbed». Consequently, the morphology and properties of the «pri-mary» Ca(OH)2particles can determine the morphology and properties of the subsequently formed silicates.
-
3.3. Prerequisites for the effectiveness of combining mechanochemical synthesis and thermolysis methods in the technology of highly dispersed silicate systems
A striking illustration of the importance of the stereochemical factor are the results of the authors’ works [49, 50], where fundamental differences in the adsorption of mono- and disaccharides on the surfaces of cement clinker and hydrosilicates are shown. Sucrose, as a disaccharide, due to the spatial structure of its molecule, which is stable in an alkaline medium, forms an adsorption complex on the surface of alite with the participation of three OH groups , whereas glucose is adsorbed only by the carbonyl group in the open form [49] (Fig. 3). As a result, the surface of the silicate is blocked: according to [49], the rate of hydration of alite in the presence of sucrose decreases by 90%. At the same time, the hydration products are distinguished by greater dispersion and shape defects. Mechanical blocking of the surface, solvable [49], is the reason for the retarding effect of sucrose. But, from the point of view of the topic discussed in this paper, it is more important that the blocking of the silicate surface can be overcome by milling. In this case, the carbohydrates themselves are incorporated into the structure of the hydrated phases, changing the values of the interlayer distance in proportion to their own compatibility with the three-dimensional network of hydrogen bonds of water [51] (Fig. 4).
The latter confirms the participation of carbohydrates in the formation of modified hydrate phases, presumably at the stage of droplet formation, when nanoclusters of the new phase aggregate in an aqueous solution, where fragments of the hydrogen bond network of water are replaced by carbohydrate molecules. On the other hand, the presence of carbohydrate in the structure of the modified hydrate phase can affect its properties, in particular, the attitude of modified hydrate phases to heating and dehydration.
All these considerations formed the basis of complex mechanical-thermal synthesis, which is a two-stage process: the first stage consists of grinding mineral raw mate-
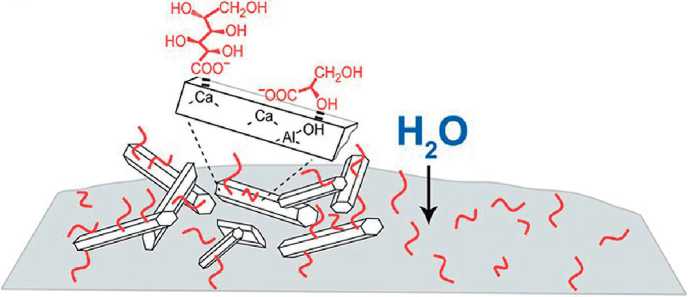
b
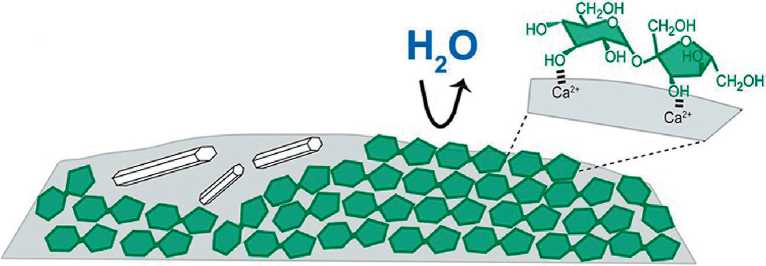
Fig. 3. Scheme of the arrangement of adsorbed carbohydrate molecules on the surface of calcium aluminate: a – glucose, b – sucrose [49]
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS

Sucrose / 0.45 nm / maximally compatible
Lactose / 0.35 nm / Maltose / 0.43 nm / least compatible moderately compatible
Fig. 4. Change in the interplanar distance of hydrate phases modified with different carbohydrates (SAED analysis, wave number 2 nm–1): carbohydrate / interplanar distance of modified hydrate phases / compatibility of carbohydrates with the three-dimensional network of hydrogen bonds of water [51]
rials in a carbohydrate solution to form sucrose-modified calcium hydrosilicates (CHS), the second stage is heat treatment of the products of mechanochemical synthesis, which results in fragmentation of CHS particles ( selfdispersion ) with the formation of a polymodal silicate powder – a calcium silicate dispersion (SCD) [52]. Polymodality is ensured by the presence of unreacted raw mineral particles (micrometer fraction) and submicrometer particles of xerogel – a loose coagulum of weakly bound calcium hydrosilicate nanoparticles (Fig. 5a). The presence of xerogel particles determines the relatively high level of specific surface area of the powders (according to BET): for example, a 1.5-hour mechanochemical synthesis of SMCH followed by heat treatment of the obtained products allows obtaining a powder with a specific surface area of 26.3 ± 0.7 m2/g with a nanophase content of 6–8% [53]. Xerogel particles are “attached” to the surface of the micrometric fraction, which facilitates the homogenization of the nanophase in the volume of the cement composition. In addition, when grinding SCD with cement, weakly bonded nanoparticles of hydrosilicates are separated from the xerogel particles and distributed over the surface of the binder particles in the form of smaller aggregates or isolated nanoparticles (Fig. 6) [54]. This morphology of the SCD nanophase forms a complex effect of SCD application: it provides pronounced waterretaining, plasticizing effects, and effects of accelerating the strength gain of cement compositions [55]. At the same time, the high content of micrometric fractions in the SCD composition (Fig. 5 b) and the presence of hydrosilicate nanoparticles in the form of a xerogel particle reduce the accelerating effect of the SCD additive and determine its high (compared to nanosuspensions [14]) dosages. On the other hand, 1.5 hours of mechanochemical synthesis (used, for example, in [52]) were prescribed in order to ensure the presence of micrometric fractions in the SCD and can be increased to change the granulometric composition of the SCD.
3.4. Technique for carrying out mechanochemical synthesis
Carrying out mechanochemical synthesis of sucrose-modified calcium hydrosilicates – SMCH – is possible
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
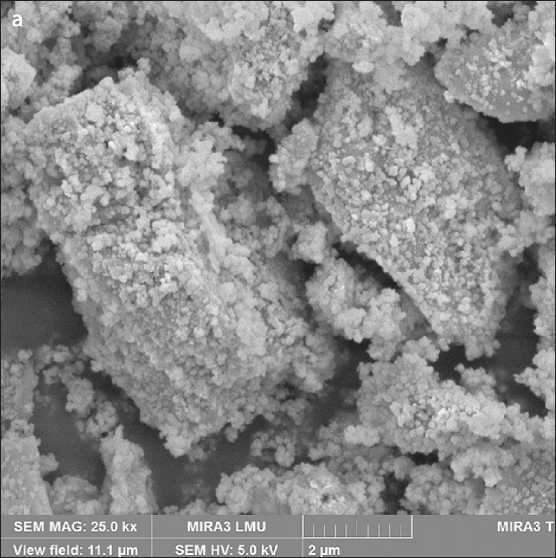
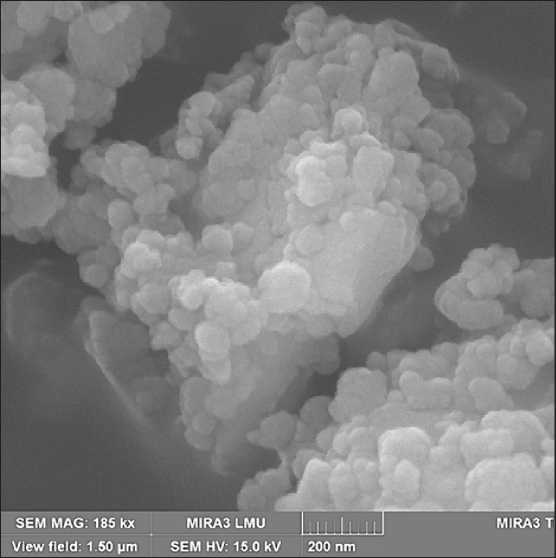


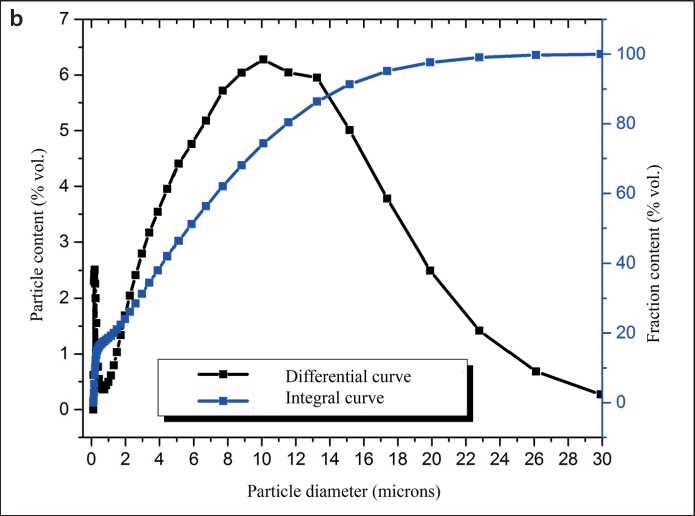
Fig. 5. Morphology of SCD (a) and particle size distribution curves of SCD (b), modifying carbohydrate sucrose. Duration of mechanochemical synthesis is 1.5 hours [53]
using a planetary mill with adjustable grinding intensity (e.g., [52, 53]). This is especially convenient when conducting exploratory studies. For industrial adaptation of the technology, it is more efficient to use inertial-type vibration mills: they have a simple design and are adapted for «wet» grinding. Under steady-state operating conditions of the vibration mill, the depth of mechanochemical synthesis is regulated by the grinding duration .
Products of various origins can be used as mineral raw material components, for example, a mixture of siliceous rock and quicklime. Opoka, microsilica , slag and even quartz sand can act as siliceous rock. The differences between them are only in the nature of the crystal lattice and the level of dispersion: with increasing crystallinity, the chemical activity of the raw material naturally decreases, which will require an increase in the duration of mechanochemical synthesis.
Portland cement can be used as a mineral raw material, the cost of which is significantly lower than the cost of commercial quicklime. Moreover, both low-grade and stale cements with reduced hydration activity are suitable for use. High hydration activity of cement allows minimizing the time of mechanochemical synthesis.
It should be noted that the use of clinker minerals of cement in the mechanochemical synthesis of nano-hydrosilicates is well known [56, 57], the disadvantage of this option is the need to «wash out» the excess free Ca(OH)2formed during the hydration of alite. In the case of complex mechanical-thermal synthesis, the excess free Ca(OH)2 can be «utilized» by introducing an additional
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
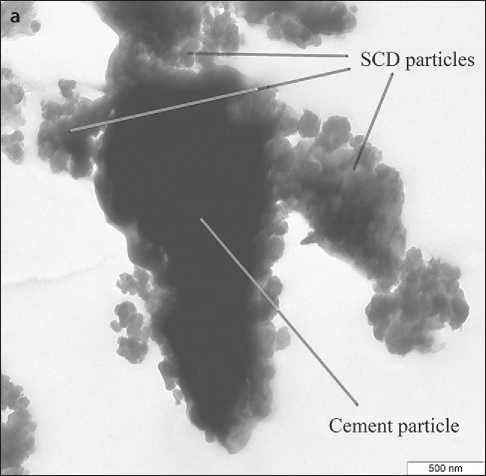
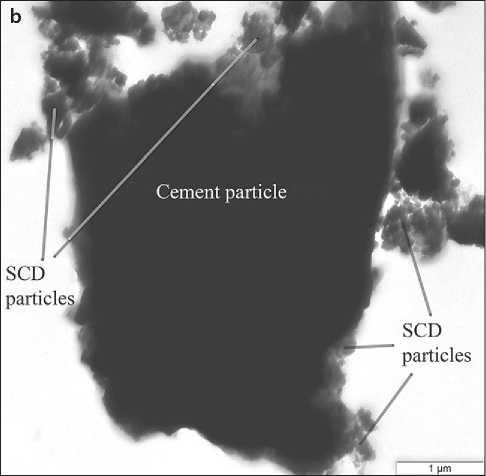
Fig. 6. The nature of the interaction of SCD particles with cement clinker particles (C+SCD (15%)) after ultrasonic treatment of the sample in absolute ethanol [54]
amount of pozzolana into the grinding mixture. Thus, cements, including substandard ones, as mineral raw materials for the mechanochemical synthesis of SMCH have a number of advantages that ensure their relatively high competitiveness.
3.5. Technique for carrying out thermolysis of SMCH
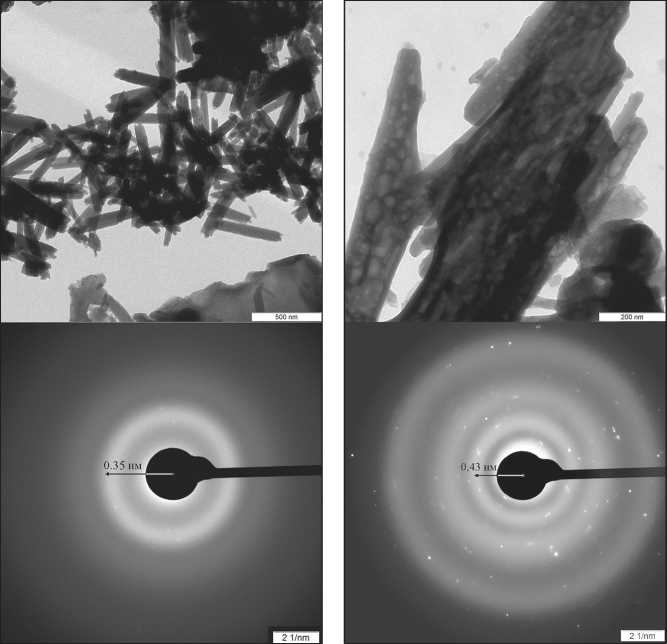
The purpose of SMCH thermolysis is the dehydration of hydrosilicates. The thermolysis conditions are mild enough (up to 150 °C ) to prevent thermal oxidation of carbohydrates. Presumably, the restructuring of the hydrogen bond system in the «silicate–carbohydrate» system is the cause of the destruction of the array of modified hydrosilicate phases and the formation of hydrosilicate nanoparticles (the self-dispersion process) [52]. In this case, to minimize the effects of nanoparticle compaction , the synthesis temperature should be reduced [ 58 ], which in turn can be achieved by reducing the partial pressure of water vapor during thermolysis, for example, by vacuuming the system and / or using water absorbers . When using vacuum, the optimal temperature range of thermolysis is 120–130 °C [51]. The resulting self-dispersion Calcium hydrosilicate nanoparticles are characterized by variable composition and cryptocrystalline structure (Fig. 7).
Possessing excess surface energy, nanoparticles actively coagulate and form a coagulum – loose xerogel particles, the structure of which is largely determined by the type of modifying carbohydrate [53].
Thus, the content of the nanostructured phase – xerogel – in the composition of the SCD is determined by the volume of the synthesized SMCH, i.e. the duration of the mechanochemical synthesis, the structure of the xerogel – by the type of carbohydrate and the thermolysis parameters.
4. TECHNOLOGICAL FEATURES OF CMT SYNTHESIS
4.1. Ripening effect
After milling, raw material suspensions must be subjected to maturation without air access. This is due to the presence of a prolonged action of mechanochemical synthesis [22], i.e. the continuation of phase processes for 24 hours after the cessation of milling. The maturation of suspensions is accompanied by water separation and gelatinization until complete loss of mobility. The amount of water separation (according to GOST 310.62020) decreases with increasing milling duration (Fig. 8), which characterizes the increase in the content of highly dispersed phases in the suspension.
4.2. Rheology of grinding suspensions
The content of the highly dispersed phase is the main factor in the rheology of grinding suspensions, but the carbohydrate content also has an effect on it (Fig. 9) [59]. The presence of sucrose slightly increases the relative viscosity of the initial water-cement suspension, which is most likely explained by the ability of sucrose to form polymolecular adsorption sandwich structures on the surface of the silicate (in the presence of Ca(OH)2) from alternating sucrose molecules and chelated Ca2+ ions [60].
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
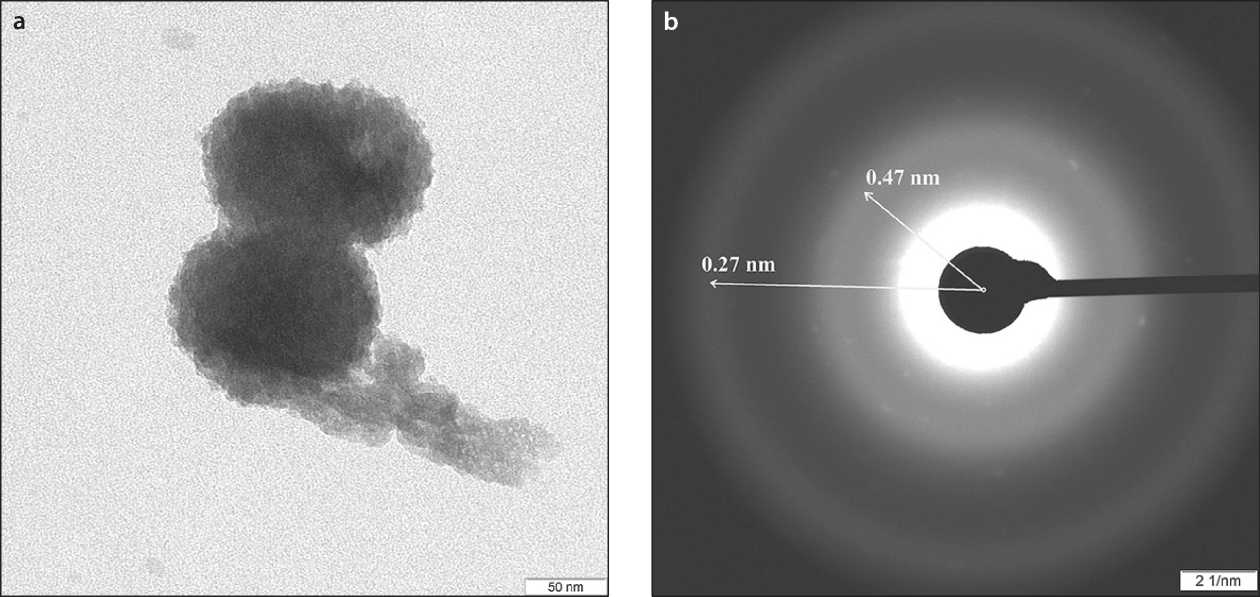

Fig. 7. SAED analysis of SMCH thermolysis products: a – aggregated particle in the composition of SCD xerogel; b – diffraction pattern of the aggregated particle [52]
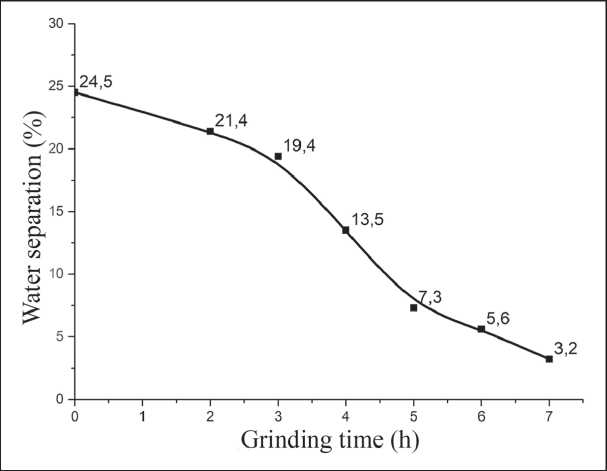
Fig. 8. Change in water separation during the maturation of the SMCH suspension depending on the duration of grinding
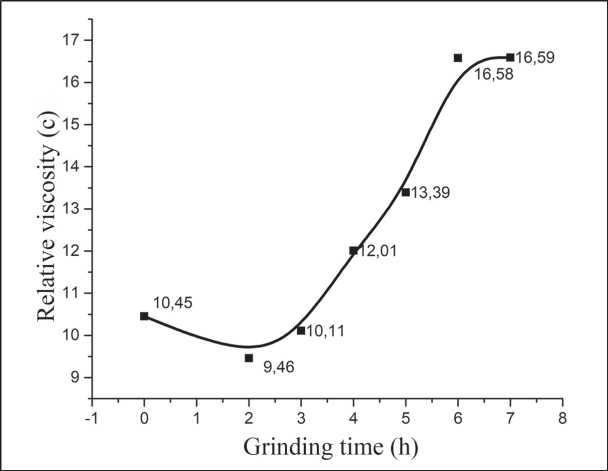
Fig. 9. Change in the relative viscosity of the SMCH suspension (according to VZ-4) from the duration of grinding [59]
Sucrose is actively involved both in the composition of polymolecular adsorption shells and in the interlayer space of the synthesized hydrosilicate phases [51]. The question of the relationship between the adsorbed and absorbed forms of carbohydrate remains open and requires further study, but the fact of a decrease in the equilibrium concentration of sucrose in the liquid phase of the suspension after 3 hours of milling from 1.48% to 0.07% indicates the effectiveness of the processes of carbohydrate absorption by silicate phases. Stabilization of the relative viscosity of the milled suspension after 6 hours of milling can be considered as a sign of the end of synthesis.
4.3. Structural and morphological state of grinding suspensions
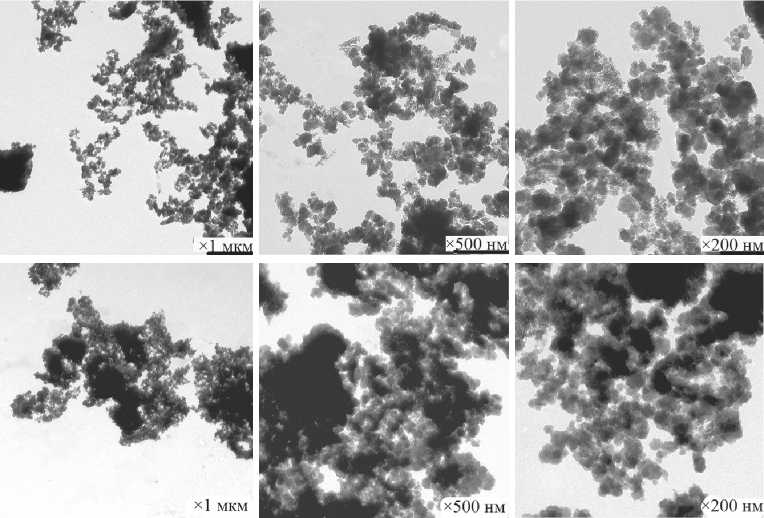
The SCDs obtained by thermolysis contain xerogel particles, the morphology of which is constant throughout the mechanochemical synthesis (Fig. 10) [59].
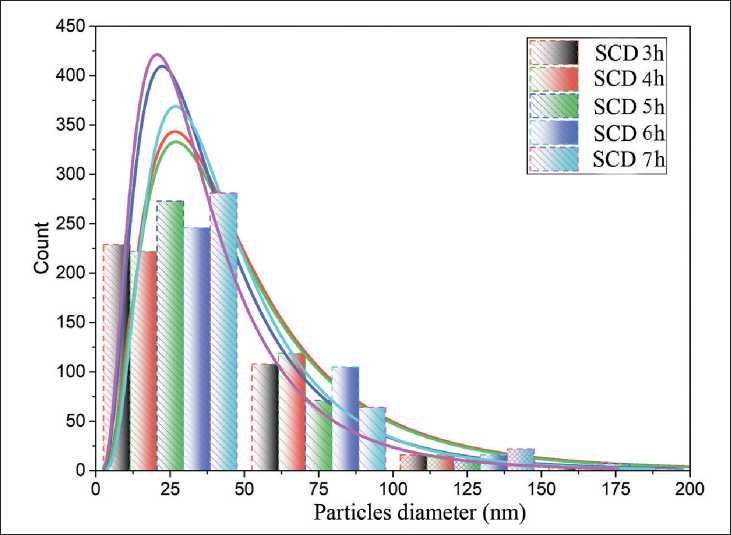
Direct measurement of the sizes of primary nanoparticles of hydrosilicates in the composition of xerogel particles showed that an increase in the duration of milling of the raw suspension changes the nature of the size distribution of the primary nanoparticles: the standard deviation is halved, a decrease (by more than 20%) is observed in
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
а
b
c
d
e
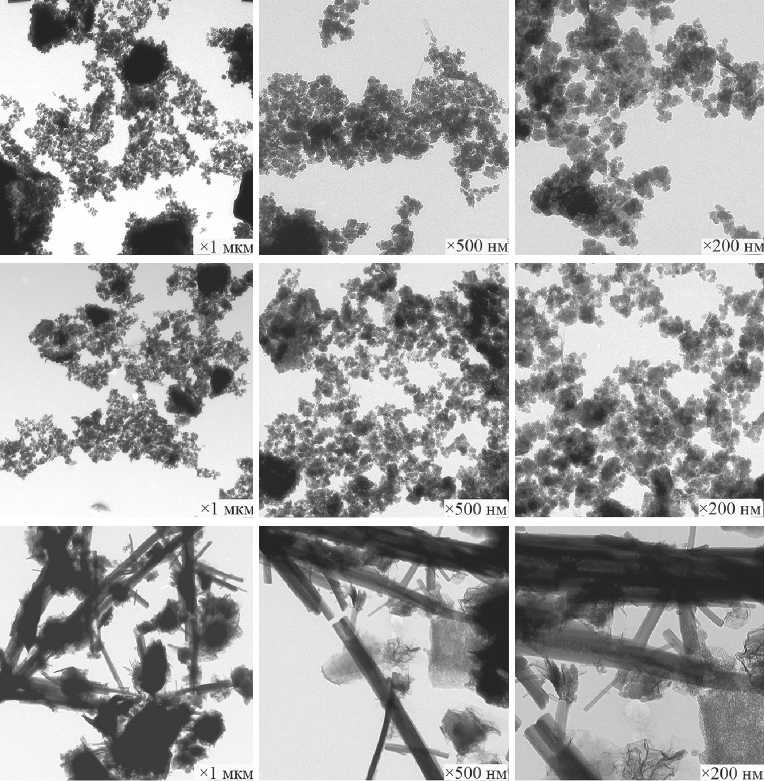
Fig. 10. Morphology of xerogel particles in the composition of SCD (milling duration): a) SCD (1.5 h); b ) SCD (3 h); c) SCD (5 h); d ) SCD (7 h). Morphology of SMCH particles – e [59]
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS the median, average diameter of nanoparticles and maximum size of primary nanoparticles of calcium hydrosilicates – degeneration effects are observed (Fig. 11) [ 59 ].
4.4. State of the modifying carbohydrate in the structure of the SCD
An increase in the duration of mechanochemical synthesis does not affect the structure of xerogel particles in the composition of the SCD, but determines their content in the SCD. The EELS spectroscopy method [61] has proven the constancy of the shape and position of the absorption bands of the excited Cπ* state of carbon and the excited Cσ* state of carbon atoms included in the carbohydrate (Fig. 12) [59] regardless of the milling duration.
-
4.5. Phase state of hydrated phases of the milling suspension in the process of mechanochemical synthesis
Qualitative X-ray phase analysis (XRD) allows monitoring the dynamics of changes in the phase composition
of the SCD based on the relative intensity of the phase signals (in relation to the intensity of the signal of the initial alite-belite phases of the cement clinker (Jabф) in the range of angles 2Θ = 32.4–32.8 degrees). The dependence of the magnitude of the signal of the relative intensity of weakly crystallized phases in the SCD composition on the duration of the mechanochemical synthesis of the corresponding SMCH is extreme in nature with an extremum at 6 hours of grinding (Table 1) [59]. The increase in the intensity of this signal is due, among other things, to the consumption of clinker phases of Portland cement in the mechanochemical synthesis (the Jabф signal is used for comparison). A 15% decrease in the intensity of the signal of cryptocrystalline phases after 6 hours of milling is due to the activation of crystallization of cryptocrystalline phases: in the corresponding SCD samples, the appearance and increase in the intensity of signals of portlandite and calcium aluminates is observed (Fig. 13) [59].
Thus, 6 hours is a «turning point» in time in mechanochemical synthesis, followed by the formation of crystalline hydrate phases from the volume of weakly crystallized phases accumulated during mechanochemical synthesis.
|
Sample, duration of mechanochemical synthesis |
Number of dimensions |
Average diameter, nm |
Standard deviation |
min, nm |
Median, nm |
max, nm |
|
SCD, 3h |
369 |
54.42 |
55.96 |
7.2 |
39.6 |
576 |
|
SCD, 4h |
369 |
53.35 |
48.76 |
7.2 |
42.2 |
468 |
|
SCD, 5 h |
369 |
44.82 |
42.10 |
7.2 |
32.4 |
351 |
|
SCD, 6 h |
369 |
45.61 |
27.71 |
7.2 |
37.6 |
158 |
|
SCD, 7h |
369 |
39.44 |
28.02 |
7.2 |
32.4 |
162 |
Fig. 11. Granulometry of nanoparticles in the composition of xerogel particles [59]
Table 1. Changes in the intensity of signals of weakly crystallized phases in the composition of the SCD depending on the duration of the mechanochemical synthesis of the SMCH [59]
|
Duration of mechanochemical synthesis of SMCH, hours |
Relative intensity of the signal of weakly crystallized phases of the SCD in the range of angles 2Θ(J(2Θ)/Jabф ) |
||||
|
J (18–23) /J ABf |
J (25–38) /J ABf |
J (41–34) /J Abf |
J (49–58) /J ABf |
Total signal intensity |
|
|
3 |
- |
4.38 |
2.54 |
– |
6.93 |
|
4 |
0.98 |
3.58 |
2.09 |
2.30 |
8.96 |
|
5 |
1.16 |
4.39 |
1.58 |
1.98 |
9.01 |
|
6 |
0.88 |
5.70 |
1.85 |
2.70 |
11.14 |
|
7 |
1.03 |
5.04 |
1.03 |
2.27 |
9.38 |
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
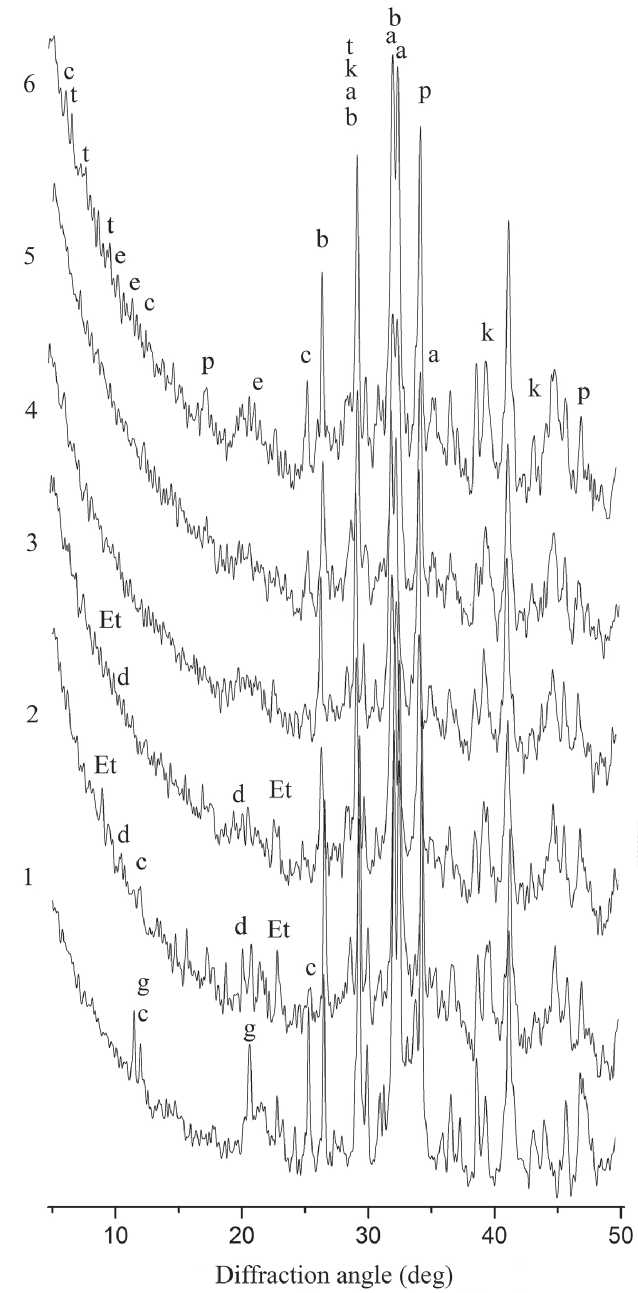
a – Alite Ca3SiO5
b – Belite γ-Ca2SiO4
c – CaOAl2O310H2O d – 3CaOAl2O36H2O e – Ca4Al2O7xH2O
Et – phases groups ettringite, in particular
Ca6Fe2(SO4)3(OH)12·25–27H2O g – CaSO42H2O k – CaCO3
p – Ca(OH)2 ( portlandite )
t – phases of the tobermorite group, in particular, 5CaO6SiO22.5H2O
Fig. 13. Diffraction patterns of the SCD obtained with different grinding durations: 1 – control (cement stone), 2–6 – SCD obtained with 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 hours of grinding, respectively [59]
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
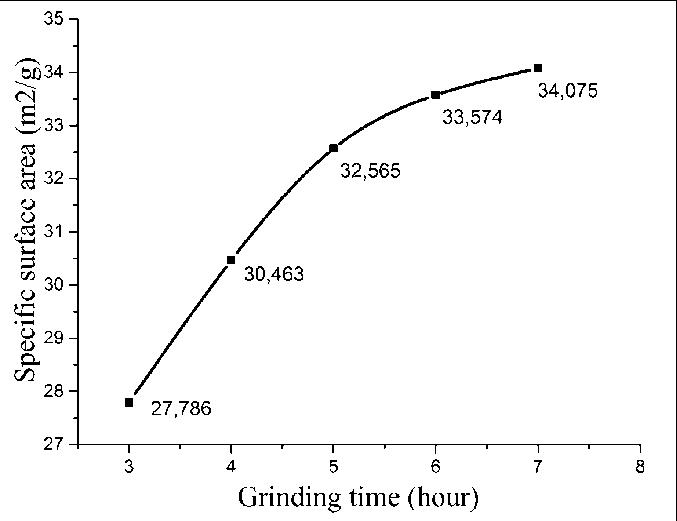
Fig. 14. Dependence of the specific surface area of the SCD (BET) on the duration of the mechanochemical synthesis of the SMCH [59]
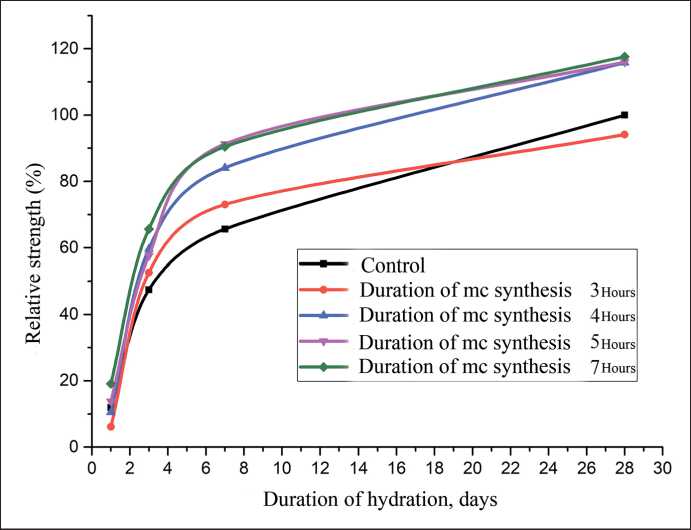
Fig. 15. Changes in the relative strength of modified cement mortars (SCD content 10%) depending on the duration of mechanochemical synthesis
Table 2. Compressive strength (MPa) of cement mortar with the addition of SCD (10%) depending on the duration of mechanochemical synthesis of SMCH
|
Duration of hydration, days |
control |
Duration of mechanochemical synthesis |
|||
|
3 o’clock |
4 o’clock |
5 o’clock |
7 o’clock |
||
|
1 |
4.99 |
2.55 |
4.39 |
5.75 |
7.97 |
|
3 |
19.79 |
21.95 |
24.88 |
24.04 |
27.36 |
|
7 |
27.36 |
30.46 |
35.17 |
38.06 |
37.73 |
|
28 |
41.71 |
39.25 |
48.30 |
48.38 |
49.06 |
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
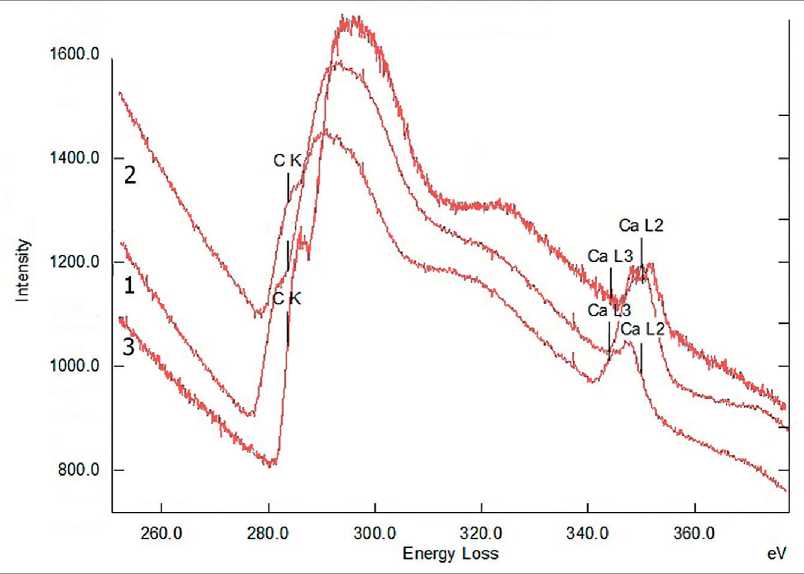
Fig. 12. EELS spectra of SCD xerogel particles for different durations of mechanochemical synthesis: 1 – 4 hours; 2 – 5 hours; 3 – 7 hours [59]
5. CHANGES IN THE PROPERTIES
OF THE SCD DEPENDING ON THE DURATION
OF MECHANOCHEMICAL SYNTHESIS
An increase in the duration of mechanochemical synthesis predictably led to an increase in the specific surface area of the SCD. At the same time, the activation of crystallization of hydrated phases after 6 hours of milling coincides with a slowdown in the growth of the specific surface area of the resulting SCD (Fig. 14). However, the role of crystallization processes of hydrated phases in slowing down the growth of the specific surface area of the SCD requires additional study.
An increase in the duration of mechanochemical synthesis is generally accompanied by an increase in the early strength of modified cement mortars (Fig. 15, Table 2). The exceptions are additives of SCD of three-hour grinding (SCD-3h) and SCD-4h: in their presence, the daily strength is reduced, which is due to the retarding effect of free sucrose in the SCD composition [62]. Additives SCD-5h and SCD-7h accelerate the gain of daily strength by 39% and 59%, respectively, which is explained, on the one hand, by the predominant accelerating effect of the nanophase in the SCD composition [55], and on the other hand, by an increase in the proportion of sucrose absorbed by hydrate phases, since the carbohydrate, firmly
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS retained by the silicate matrix, is not capable of being extracted into the mixing water and affecting the rate of strength gain.
It should be noted that the residual content of nonhydrated cement in the composition of SCD 5h and SCD 7h is a priori minimal in the series of dispersions under consideration (3h–7h), but at the same time, these SCDs demonstrate the greatest increase in the strength characteristics of mortar samples at all hydration periods. The latter means that the residual content of non-hydrated clinker in the SCD is not a factor determining the magnitude of the increase in the strength of SCD-modified cement mortar samples.
6. CONCLUSION
The technology of CMT synthesis is based on the ability of calcium hydrosilicates modified with carbohydrates (in particular, sucrose) to self-disperse during dehydration with the formation of nanostructured hydrosilicate phases. The mechanism of the self-dispersion process is under study, but its features are already clear: mild thermolysis conditions allow the nanostructured phases of SCD to be in a cryptocrystalline state; not only carbohydrates, but also other organic agents that meet a specific set of requirements for the spatial structure of the molecule can potentially be used in the mechanochemical synthesis of SMCH; it is economically feasible to use Portland cement as a mineral raw material for complex mechanical-thermal synthesis,
but it is also possible to use other silica-containing raw materials.
When using Portland cement as a mineral raw material, the optimal duration of mechanochemical synthesis is 6 hours; exceeding this value leads to a decrease in the rate of growth of the specific surface area of the final SCP.
The duration of the mechanochemical synthesis of the SMCH does not affect the morphology of the xerogel particles in the composition of the SCD, but improves the granulometric characteristics of the nanodispersed phase and increases the volume of the synthesized nanophases.
The compacted form of calcium nanohydrosilicates predetermines moderate accelerating activity of SCD in relation to the processes of hardening of cement mortars and high dosages of SCD (10%). At the same time, SCD increases the grade strength of samples, which is not typical for «CSH – seeds» additives.
Complex mechanical-thermal synthesis is a new direction in the synthesis of nanosized hydrosilicate phases based on the specific properties of calcium hydrosilicates modified by organic agents. The development of this direction is far from complete, and the solution of applied issues is closely related to the development of the theoretical base, in particular, with the application of approaches to the concept of non-classical nucleation to the formation of hydrosilicate phases. The high potential of this concept in terms of controlling the properties of the resulting hydrate phases determines the potential for the development of complex mechanical-thermal synthesis.


