Culture, synergy and balance of Northern Russia’s strategic manage-ment processes
Автор: Dmitry P. Kondral
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Social Sciences. Politology. Economics
Статья в выпуске: 17, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article briefly marks current problems of culture, synergy and balance of strategic management processes of Northern Russia. Spread of subservient culture, the need to democratize based on the culture of participation and the creation of a balanced system of strategic management is noticed.
Northern Russia, strategic management, subservient culture, the culture of participation, the synergy, balancing processes
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148319805
IDR: 148319805 | УДК: [321,02+316,42+327,82] (470.13) (045). К64
Текст научной статьи Culture, synergy and balance of Northern Russia’s strategic manage-ment processes
Strategic management of processes of Arctic and Northern Russia development is carried out under current politico-managerial relationship in the country. It is closely connected with development of subservient culture of bureaucracy and necessity of democratization of management system based on culture of participation, synergy, creation of balanced system of consideration for society, based on initiative, democracy and legitimacy.
Bureaucracy, managerial culture
Strategy of Russian Federation Arctic zone development and national security protection for the period up to 2020, programs of territorial development are to a large extent oriented to development of regional community and their adaptation to changing state goals and challenges of exploitation of the North (RFAZ — part of Northern Russia). Centrally established system of state management leads to inconspicuous involvement of government institution in organization of strategic state policy in Northern Russia [1]. It leads to inconspicuous concernment in efficiency of socio-political programs of Russian Arctic zone in northern regions of Russia strategic development realization.
It is worth noticing that high degree of political management centralization results in consolidation in the country of administrative-bureaucratic management system [2]. This system appears in development of mechanisms of subordinative management, reduction of strategic management value, group methods of management decision making and local initiatives. As a result of consolidation of political management subordinative system appeared development of subservient culture of bureaucratic management. This culture as a pattern of bureaucracy — is an accepted behavior model [3], settled in both strategic management and in innovation and scientific spheres. It at the same time decreased the value of initiative and creativity and increased formalism in problems of innovation development of Northern regions enlisted in entities of RFAZ and in the country as a whole. The pointed problem nowadays must be overviewed as an insider threat of Russian system of democratic management and civil society development together with corruption, economic depression and low social security system of country’s population.
An important consequence of formalization of innovation programs development should be considered reduction of communication, integrative and synergetic qualities and characteristics of subsystems of common strategic management system. In particular, mechanisms of intelligibility and aggregation of interests by Arctic population in the process of strengthening of administrative-bureaucratic methods and management culture [4]. As a result of the process of consolidation of subservient management culture became reduction of connecting mechanisms of bureaucratic branches and their efficiency value. As a basis of such a management becomes fear [5; 6; 7]. It is evident, that by pointed reasons of management innovation and scientific spheres will not be able to function and develop, which could lead to reduction of its efficiency.
Grade of the synergy and centeredness of management systems
By the pointed specifics of management, namely existing subordinative-bureaucratic model, subsystems of state management institutes should be overviewed as independent systems weakly interacting with each other, which could lead to reduction of adoption of the whole system of Northern Russia strategic management functioning. When appreciating the level of management systems’ synergy, based on cultures of participation or subservient, their substantial controversies should be noticed (view table 1):
Table 1
Level of interaction synergy of management system elements in dependence to the type of management culture
|
№ |
Critegia |
Types of culture |
|
|
Culture of participation |
Subservient culture |
||
|
Level of interaction |
Parts of system interact as subsystems based on mutual advantage and rivalry, drawing on common values, goals and standards |
Parts of system practically don’t interact (just officially), they are committed to set from above task. Each part of a system works as independent system and it doesn’t provide full-bodied activity of other subsystems |
|
|
Clarity |
Activity of each subsystem is open for estimates and could be examined «externally» |
Results of each subsystem’s activity could be corrected «from inside», it is difficult to get reliable information |
|
Activity base |
Initiative focused on achieving common goals and interests |
Headship fright |
|
Legitimacy |
Irreproachable posteriority of principle of legality |
Possibility to correct system’s activity for save of its stability |
|
Level of planning |
Planning according to estimate of real environment including all the factors of influence |
Planning is based on private goals and attitude of headship, who can be scientifically and ideologically «corrected» and settled down |
|
Sociability |
System is open for participation according to the principle of legality |
Real values and goals are formed behind closed doors, access to mechanisms of adoption and realization of management decisions are constrained |
|
Attraction of institutional settings to activity of the system |
Real time existing and supported by society institutions are attracted |
Loyal for headship institutions are attracted or created by the headship |
|
Direction of system’s activity |
Subsystems operate for system goals and challenges |
Each subsystem could have its own goals and challenges, being an independent control elements |
Modern systems of interregional political interaction in the Northern Russia and functional interaction of strategic planning establishments nowadays have no obliged mechanisms of joint regional interconnection which in conditions of its «close» activity lead to lost of integrative potential in problems of prospective development of Arctic territories and population. Success of the system of strategic management development in the region is predicated upon balanced functioning and cooperation of number of elements.
For increase of the system structural parts it is important to develop democratic methods of management on federal and regional levels, improve quality of communication mechanisms and interaction between subsystems of strategic management institutions.
Important problem of strategic management system efficiency, including RFAZ, is considered to be negative opportunity of its «conservation» in conditions of socio-political crisis, which could lead to its inability to educe, analyze and react to real inside and outside challenges and threats, including sanctions against Russia. To prevent this threat democratic mechanisms, oriented on initiative, creativity, legitimacy, sociability and clarity, must become the base for strategic management system.
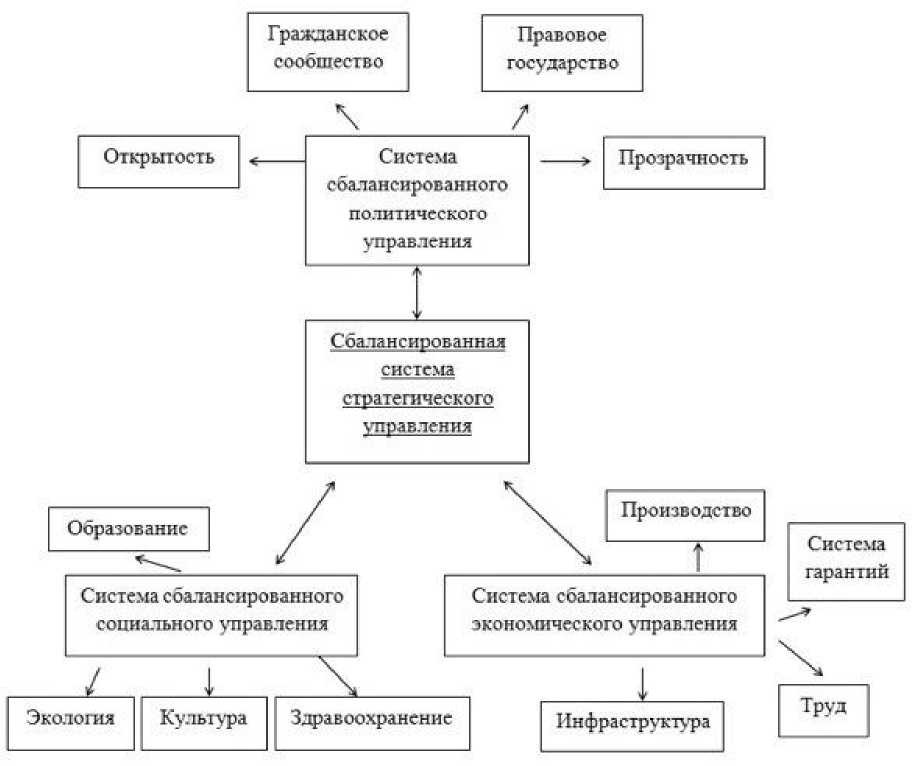
Picture 1. Model of a balanced system of Arctic process development strategic management (author’s view) URL:
Conclusion
It is worth noticing that main foreign principle of strategic management is considered to be the widening of living space of the territory [8], and domestic political principle must become principle of creation and support of balanced system of national interests consideration of the state, society and person, based on initiative, democracy and legitimacy; creation of effective management system based on culture of participation, synergy, activity of persons and civil society. Pointed problems in this article are extensively investigated in monographs and other articles of the author.
Список литературы Culture, synergy and balance of Northern Russia’s strategic manage-ment processes
- Кondral D.P., Morozov N.A. Strategicheskoye upravleniye processami prostranstvennoterritorial’nogo vzaimodeystviya Severa Rossii: problemy i perspectivy [Strategic management of Northern Russia regional-territorial development processes: problems and perspectives]. Syktyvkar, publ. Syktyvkar State university, 2014, 96 p.
- Rimsky V.L. Byurokratiya, klientelism i korrupciya v Rossii [Bureaucracy, clienteling and corruption in Russia]. Politiya. Analyz. Chronika. Prognoz. No. 1(44), 2007, pp. 65—84.
- Feodorchenko S.N. Poddanicheskaya politicheskya kul’tura kak matrica sovetskoy i sovremennoy rossiyskoy byurokratii [Subservient political culture as matrix of soviet and current Russian bureaucracy]. Rossiya v mire: gumanitarnoye, politicheskoye i ekonomicheskoye izmereniye. Materialy Vserossiyskoy nauchnoy konferencii v presidium RAN [Russia in the world: humanitarian, political and economic dimension. Materials of Russian scientific conference in Presidium of RAS]. Moscow, Nauchniy expert, 2010 (in Russian).
- Kondral D.P. Social’no-politicheskiye faktory strategicheskogo razvitiya Severa Rossii [Sociopolitical factors of Northern Russia strategic development]. Sovremenniye nauchniye issledovaniya i innovacii [Modern scientific researches and innovations]. 2014, no 4. URL: http:// web.snauka.ru/issues/2014/04/32776 (accessed 16.10.2014).
- Zevina O.G., Makarenko B.I. Ob osobennostyah politicheskoy kultury sovremennoy Rossii [On specialties of modern Russian political culture]. Polis, 2010, no. 3, pp. 114—131.
- Rozov N.S. Rossiyskiy mentalitet: naibolee konstruktivniye koncepcii i ih kritica [Russian mentality: more constructive concepts and its criticism]. Mir Rossii, 2011, no 2, pp. 100—112.
- Titov V.V. Rossiyskaya model upravleniya: opyt geopoliticheskogo i sociokulturnogo analiza [Russian model of managements: practice of geopolitical and socio-cultural analysis]. Chelovek, Soobshchestvo. Upravleniye [Person. Society. Management]. 2004, no 3—4, pp. 143—150.
- Haushofer K. O geopolitike. Raboty raznyh let [On geopolitics. Works of different years]. Moscow, Mysl’ publ., 2001, 426 p.


