Determination of median lethal dose of carbamate insecticides bendiocarb and carbaryl in garden lizard, calotes versicolor
Автор: Anisha, Singh T.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Acute lethality usually determined as LD50 is defined as median dose predicted to kill 50 percent of a given test population. LD50 is a statistical estimate of the number of milligram of toxicant per kilo gram of body weight administered by any of the methods like oral, dermal, inhalation, or intravenous and is sufficient to kill 50 percent of the large population of test animals usually within certain time. Determination of LD50 has always been a much controversial subject among biologists and animal ethicists due to painful treatments on large number of animals. However, to assess the toxicity of various chemicals on different organisms Median lethal dose is still being used by toxicologists to determine acute lethality to non-target organisms. In the present study we aimed to determine the LD50 of two carbamate insecticides bendiocarb and carbaryl on a non-target species Calotes versicolor a reptilian model. An approximate LD50 was initially determined as a pilot study by a so called ‘staircase method’ using only 2 animals (for each dose) and increasing the doses of the drug. Five doses 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 mg/kg body weight for bendiocarb and 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 mg/kg body weight for carbaryl were chosen for determination of LD50 starting from no death to 100% mortality. Intraperitoneal LD50 value calculated by regression analysis is 15.57 and 64.97 mg/kg body weight for bendiocarb and carbaryl respectively in male Calotes versicolor. The result confirms that bendiocarb is more potent than carbaryl in Calotes suggesting that bendiocarb may cause death even at smaller doses in comparison to carbaryl. Our results will help in adding to the fact sheet related to carbamate toxicity in reptiles.
Carbamate, bendiocarb, carbaryl, ld50, lizard
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143183431
IDR: 143183431
Текст научной статьи Determination of median lethal dose of carbamate insecticides bendiocarb and carbaryl in garden lizard, calotes versicolor
Median lethal dose abbreviated as LD 50 is a statistical estimate of the number of milligram of toxicant per kilo gram of body weight administered by any of the methods like oral, dermal, inhalation, or intravenous and is sufficient to kill 50% of the large population of test animals usually within certain time. Determination of LD 50 is an initial screening step in the assessment and evaluation of the toxic characteristic of a chemical. It is essential for toxicologist to correlate, identify and estimate the toxicity of any chemical substance (Akhila et al. , 2007; Arya and Bist, 2022). This is useful to measure the acute toxicity of drugs, food poisonings and accidental domestic poisoning cases. In this chemical era it is very important to know the LD 50 of the pesticide before using it in the fields as excessive dose of pesticide may cause acute toxicity. This test examines the relationship between dose and the most extreme response death. The route of exposure also determines how much of the chemical substance enters or absorbs into the test animal and which organs are initially exposed. In general, the smaller the LD 50 value, the more toxic the substance is and vice versa. The information gained from dose response studies in animals is also used to set standards for human exposure (Rajawat et al. , 2015).
It is a fact that different species within the same taxonomic class can vary considerably, e.g. one or two orders of magnitude, in susceptibility to a given toxicant, so selection of representative test species for the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) standard testing protocols is important (Wu et al. , 2007; Calleja et al. , 1994). However, a comparison of LD/LC 50 values for a range of insecticides tested on the same species provides a practical way of assessing the relative potency of such chemicals to the taxon they represent. Often a given insecticide has been tested on several species of the same taxonomic group, thus providing a range of LD/LC 50 for that taxon and, therefore, more certainty about the hazards posed by the insecticide to that particular group of non-target organisms (Spurgeon et al. , 2020).
The LD 50 is determined by any accepted method, e.g. Bliss (1934), Miller and Tainter (1944), Thompson (1947), Litchfield and Wilcoxon (1949), Weil (1951) and Finney (1971). These published works suggest the use of probit analysis for determination of LD 50 . Probit analysis is used in many kinds of dose-response or binomial response experiments in toxicology to determine the relative toxicity of chemicals to living organisms. This is done by testing the response of an organism under various concentrations of each of the chemicals in question and then comparing the concentrations at which one encounters a response. The response is always binomial (e.g. death/no death) and the relationship between the response and various concentrations is always sigmoid. Probit analysis acts as a transformation from sigmoid to linear and then runs a regression on the relationship.
Once a regression is run, the researcher can use the output of the probit analysis to compare the amount of chemical required to create the same response in each of the various chemicals. There are many endpoints used to compare the differing toxicities of chemicals, but the LC 50 or LD 50 are the most widely used outcomes of the modern dose-response experiments. The LC 50 /LD 50 represent the concentration (LC 50 ) or dose (LD 50 ) at which 50% of the population responds (Finney, 1971).
As reported by Weir et al., (2015; 2016) Reptiles have been understudied in ecotoxicology, which limits their consideration in Eco-toxicological risk assessments. Reptiles are usually not considered in environmental risk assessments under the assumption that the results obtained from studies on birds and mammals would be good and safe estimates for them. Nevertheless, some pesticides are more toxic to lizards than birds and mammals. Due to unique physiological and biological features of reptiles, predicting the effects of environmental contaminants on reptiles with toxicity parameters established to other vertebrates is likely to be ineffective. More toxicological data are needed to determine which pesticides provide a reasonable surrogate for reptiles. Reptiles may become vulnerable to the adverse effects of chemical pesticides as a nontarget species which is a threat to their diversity. Lizards comprise a large percentage of reptiles, their insectivore nature and the ecological niche, these are at a higher risk of pesticide exposure in agricultural farms and several species have been reported to be threatened with extinction. Lizards may be exposed to pesticides in several ways and need more attention from the scientific community (Freitas et. al. 2020). Lizards have been proposed as ideal sentinels of pollutant induced environmental changes, especially in areas where they are abundant, diverse and have a significant role in ecosystems (Lambert, 1999; 2005) however, there is dearth of information regarding ecotoxicological studies in lizards which aroused our interest to design the present work. The aim was to determine LD50 values of carbamate insecticides namely bendiocarb and carbaryl in the garden lizard Calotes versicolor so as to generate reptile toxicity data for these pesticides, and to compare our results with data available for other animals.
Bendiocarb [Chemical Name- 2,3-isopropylidenedioxyphenyl methylcarbamate, Chemical Formula- C 11 H 13 NO 4 , Water Solubility- 40 mg/L @ 20°C, Melting Point- 129 to 130°C, CAS Number: 22781-23-3, Trade names: Ficam, Dycarb, Garvox, Turcam, Niomil, Seedox, Tattoo (WHO/FAO, 1982), is a broad spectrum carbamate insecticide used against mosquitoes, flies, wasps, ants, fleas, cockroaches, silverfish, and ticks (Jankowska et al. , 2023). Bendiocarb pesticides are formulated as dusts, granules, wettable powders, pellets, and ultra-low volume (ULV) sprays (U.S. EPA, 1999; EXTOXNET, 1996). Bendiocarb exhibits its toxic effects through fast-acting, but reversible, cholinesterase inhibition. The accumulation of insecticide residues has become a chemical stressor for both invertebrates and vertebrates (Jankowska, et al. , 2023; Del Prado-Lu, 2015; Relyea, 2005), causing the decline in species biodiversity (Sánchez-Bayo and Wyckhuys , 2019).
Carbaryl [Chemical name- 1-naphthyl methylcarbamate; Molecular formula- C 12 H 11 NO 2 , Water solubility-40mg/L@ 30o, Melting point -142°C, CAS Number: 63-25-2, Trade name- Sevin (Kidd and James, 1991), is a chemical in the carbamate family used chiefly as an insecticide (Petrichev, 2022). It is a white crystalline solid, found in all types of formulations including baits, dusts, wettable powder, granules, oil, molassas, aqueous dispersions and suspensions (U.S.
EPA, 1987). Carbaryl has been reported to cause nausea, bronchoconstriction, blurred vision, excessive salivation, muscle twitching, cyanosis, convulsion, coma, respiratory failure and colorectal tumour in humans (Wilson et al. , 1985; Khalaf et al., 1993). Reports on carbaryl induced toxicity in reptiles are mainly confined to the studies on locomotor performance, histopathological effects in testes and digestive system (Hopkins et al. , 2005; Hopkins and Winne, 2006; DuRant et al. , 2007; Cakici, Akat, 2012a; 2012b).
The determination of LD 50 in this reptilian model will help in adding to the fact sheet related to carbamate toxicity in reptiles and also in potential non target risk assessment of these chemicals on garden lizard Calotes versicolor . Collecting sufficient data over time will help in possibly using data from other species to predict responses of other endangered reptiles.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Location and duration of study:
This study was conducted in the Department of Zoology Udai Pratap College, Varanasi (An Autonomous Institution), India. The preliminary studies standardization of experimental procedures and pilot experiment lasted for one month and the animal acclimatization and actual animal experiment lasted for a period of 12 days.
Animals:
Adult male garden lizards, Calotes versicolor were caught locally in suburbs of Varanasi (latitude 25°18’N: longitude 83°01’E). The lizards (average snout – vent length 10 ± 2 cm and body weight 30 ± 2g) were selected and housed in vivarium (wire net cages of size 18 x12x 10 inch). These were provided with food (crickets, maggots, flies) and water ad libitum . These were acclimatized for one week prior to experimentation. The guidelines of the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiment on Animals, Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation, Government of India, were followed in maintenance and sacrifice of animals. The carcasses were buried in soil after each experiment.
Test Chemical:
Bendiocarb and Carbaryl were obtained from Sigma– Aldrich India.
Experimental design:
The LD 50 value for intraperitoneal (ip) dose of bendiocarb and carbaryl was determined after slight modification from the methods described by Miller and Tainter (1944), Finney and Stevens (1948), Finney (1952) and Randhawa (2009). An approximate LD 50 was initially determined as a pilot study by a so called ‘staircase method’ using a small number of animals (2 each dose) and increasing the doses of the drug. Five doses were chosen for determination of LD 50 starting from no death to 100% mortality. A total of 100 lizards were taken for experimentation and the animals were divided into two groups of 50 each. These two groups were further divided into 5 sub- groups. The steps followed were-
Step 1 - The test animals were divided into five sub groups of 10 Calotes each for each test chemical namely bendiocarb and carbaryl.
Step 2 - Experimental animals received a fixed intraperitoneal acute dose of test compound according to the following protocol.
Group I- Bendiocarb
Sub Group I- received 10 mg/kg body weight.
Sub Group II - received 15 mg/kg body weight.
Sub Group III - received 20 mg/kg body weight.
Sub Group IV - received 25 mg/kg body weight.
Sub Group V- received 30 mg/kg body weight.
Group II- Carbaryl
Sub Group I- received 50 mg/kg body weight.
Sub Group II- received 60mg/kg body weight.
Sub Group III- received 70 mg/kg body weight.
Sub Group IV- received 80 mg/kg body weight.
Sub Group V- received 90 mg/kg body weight.
Step 3 - The observations for mortality of animals in each group were noted at regular intervals of 8 hours up to 96 hours from the first dose administered.
Step 4 - Data was presented as log of dose against probit value of % mortality in each group (Probit values were obtained from Finney’s table – Table 1, Finney, 1948).
Step 5 - MS Excel was used for Regression analysis to obtain one line fit plot for log of dose against probit and regression statistics was used to calculate LD 50 .
Step 6 - The LD 50 value was calculated from the linear equation-
Y= a+bX
Where
-
Y, a, b and x denote the following:
-
Y- Log of LD 50 dose a is coefficient of intercept b is coefficient of x variable (the slope of the line) x = 5 for 50% mortality
RESULTS
Table 1 shows the probit values of % mortality according to Finney (1948). Table 2 and 3 shows lethal doses, mortality, percent mortality, log doses and probit value of % mortality for the two carbamate compounds bendiocarb and carbaryl respectively. Figure 2 (a) and (b) shows regression plot between log doses and probit value of % mortality for bendiocarb and carbaryl respectively. Intraperitoneal LD 50 value calculated by regression analysis is 15.57 mg/kg body weight for bendiocarb and 64.97 mg/kg body weight for carbaryl in male Calotes versicolor.
Figure 1. Chemical Structure of Bendiocarb (a) and Carbaryl (b).
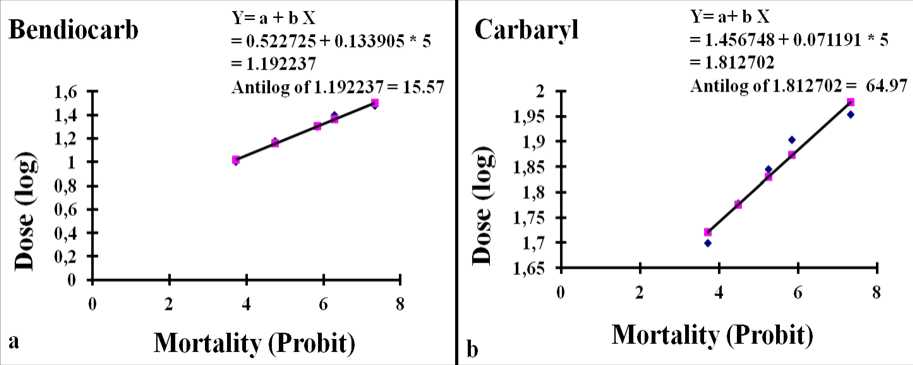
Figure: 2 Plot of log-doses versus probits from Table 2 and 3 for calculation of LD 50 of Bendiocarb (a) and Carbaryl (b) administered intraperitoneally to Calotes versicolor .
■ Estimated Variate ♦ Observed Variate
Table 1. Finney’s table (Finney, 1948).
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
|
0 |
- |
2.67 |
2.95 |
3.12 |
3.25 |
3.36 |
3.45 |
3.52 |
3.59 |
3.66 |
|
10 |
3.72 |
3.77 |
3.82 |
3.87 |
3.92 |
3.96 |
4.01 |
4.01 |
4.08 |
4.12 |
|
20 |
4.16 |
4.19 |
4.23 |
4.26 |
4.29 |
4.33 |
4.36 |
4.36 |
4.42 |
4.45 |
|
30 |
4.48 |
4.50 |
4.53 |
4.56 |
4.59 |
4.61 |
4.64 |
4.64 |
4.69 |
4.72 |
|
40 |
4.75 |
4.77 |
4.80 |
4.82 |
4.85 |
4.87 |
4.90 |
4.90 |
4.95 |
4.97 |
|
50 |
5.00 |
5.03 |
5.05 |
5.08 |
5.10 |
5.13 |
5.15 |
5.15 |
5.20 |
5.23 |
|
60 |
5.25 |
5.28 |
5.31 |
5.33 |
5.36 |
5.39 |
5.41 |
5.41 |
5.47 |
5.50 |
|
70 |
5.52 |
5.55 |
5.58 |
5.61 |
5.64 |
5.67 |
5.71 |
5.71 |
5.77 |
5.81 |
|
80 |
5.84 |
5.88 |
5.92 |
5.95 |
5.99 |
6.04 |
6.08 |
6.08 |
6.18 |
6.23 |
|
90 |
6.28 |
6.34 |
6.41 |
6.48 |
6.55 |
6.64 |
6.75 |
6.75 |
7.05 |
7.33 |
Table 2. Results of the lethal doses of Bendiocarb for the determination of LD 50 after intraperitoneal injection in Calotes versicolor.
|
Groups |
No. of animals |
Dose (mg/kg b.w.) |
Mortality (in number) |
% Mortality |
Conversion of dose in log |
Conversion of % mortality to probit |
|
1. |
10 |
50 |
1 |
10 |
1.69897 |
3.72 |
|
2. |
10 |
60 |
3 |
30 |
1.778151 |
4.48 |
|
3. |
10 |
70 |
6 |
60 |
1.845098 |
5.25 |
|
4. |
10 |
80 |
8 |
80 |
1.90309 |
5.85 |
|
5. |
10 |
90 |
10 |
100 |
1.954243 |
7.33 |
Table 3. Results of the lethal doses of Carbaryl for the determination of LD50 after intraperitoneal injection in Calotes versicolor.
|
Groups |
No. of animals |
Dose (mg/kg b.w.) |
Mortality (in number) |
% Mortality |
Conversion of dose in log |
Conversion of % mortality to probit |
|
1. |
10 |
10 |
1 |
10 |
1 |
3.72 |
|
2. |
10 |
15 |
4 |
40 |
1.176091 |
4.75 |
|
3. |
10 |
20 |
8 |
80 |
1.30103 |
5.84 |
|
4. |
10 |
25 |
9 |
90 |
1.39794 |
6.28 |
|
5. |
10 |
30 |
10 |
100 |
1.477121 |
7.33 |
DISCUSSION
The potency of a toxic chemical is usually gauged by its lethal median dose (LD 50 ), median lethal concentration (LC 50 ) or median effective concentration (EC 50 ) to surrogate species belonging to common taxa, i.e. fish, mammals, birds, crustaceans, worms and bees. With the exception of insect pests, which are the target of the insecticides, all other species and taxa are considered non-target organisms. Median lethal dose (LD 50 ) has been used by toxicologists to assess the toxicity of any substance since it was launched by Trevan in 1927. LD 50 is a statistical estimate of the number of milligram of toxicant per kilo gram of body weight administered by any of the methods like oral, dermal, inhalation, or intravenous and is sufficient to kill 50% of the large population of test animals usually within certain time. Determination of LD 50 has always been a much controversial subject among biologists and animal ethicists due to painful treatments done on large number of animals (Noga et al. , 2024; Pillai et al. , 2021; Erhirhie et al. , 2018).
The acute toxicity of carbamates ranges from highly toxic to only slightly toxic or practically non-toxic (IPCS, 1986). Concerning the main carbamate insecticides in use, their relative toxic potency estimated human values, (Erdman, 2003) vary from high toxicity (LD 50 <50 mg/kg; for aldicarb, aldoxycarb, aminocarb, bendiocarb, carbofuran, dimetan, dimetilan, dioxacarb, formetanate, methiocarb, methomyl, oxamyl and propoxur), to moderate toxicity (LD 50 = 50-200 mg/kg; bufencarb, carbosulfan, pirimicarb, promecarb, thiodicarb, trimethacarb) and to low toxicity (LD 50 > 200 mg/kg; fenocarb, carbaryl, isoprocarb, meobal, metacrate, tsumacide and cosban).
Wide differences have been reported in the values for LD50 of bendiocarb in various organisms exposed orally for example 0.1 μg/bee in honey bee, 3.1 mg/kg b.w.in mallard ducks, 19 mg/kg b.w.in quail, 34 to 156 mg/kgb.w.in rats, 35 to 40 mg/kg b.w.in rabbits, and 35 mg/kg b.w. in guinea pigs. Similarly the LD50 of carbaryl also vary in various organisms exposed orally for example 1.54 – 26.5 μg/bee in honey bee (Union Carbide, 1983), 2179 mg/kg b.w.in mallard duck, 2000 mg/kg b.w.in pheasants, 2230 mg/kg b.w.in Japanese quail, 1000-3000 mg/kg b.w. in pigeons, 250 - 850 mg/kg b.w. in rats, 100 - 650 b.w. mg/kg in mice, 710 mg/kg b.w. in rabbit (Kidd and James, 1987). Moreover, there are few reports related to intraperitoneal LD50, 8mg/kg b.w.in wistar rat for bendiocarb (Sanderson 1971) and 25 mg/kg b.w.in mouse for carbaryl.
Every pesticide may vary greatly in its toxicity and persistence. The LD 50 values can be influenced by several factors such as size, nutritional status (Pal and Kushwah, 1981; Das and Garg, 1981), species specificity (Jacob et al. , 2006), animal weight (Pickering et al. , 1962), its developmental stage, time of exposure and temperature (Macek et al., 1969). It vary from species to species (Pickering et al. , 1962), capacity of the species to tolerate the pesticide (Chambers and Yarbrough, 1974), between animals of the same basic strain obtained from different suppliers (Russell and Overstreet, 1987), according to the purity of the chemical (Ho and Hoskins, 1986) and to the sex differences (Overstreet et al. , 1979).
The present work shows that bendiocarb is more potent or toxic with a lower ip LD 50 value of 15.57 mg/kg b.w. than carbaryl with a higher ip LD 50 value of 64.97 mg/kg b.w. in Calotes suggesting that bendiocarb may cause death even at smaller doses in comparison to carbaryl. The results also validate the fact that the carbamates under consideration namely, bendiocarb and carbaryl are comparatively less toxic for our experimental model Calotes in comparison to wistar rat and mice.
This data provides information on health hazards likely to arise from short-term exposure and serve as a basis for labelling and classification of the selected carbamates, bendiocarb and carbaryl in lizard. Our results will help in adding to the fact sheet related to carbamate toxicity in reptiles.
It is hereby suggested that effect of Pesticide should not be generalized from the data obtained on surrogate species or from a single group or taxon. More toxicological studies should be done on lizards and data thus obtained need to be considered in toxicological risk assessments, meaning more research needs to be done to acquire these data as only few pesticides have been studied in lizards so far.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Список литературы Determination of median lethal dose of carbamate insecticides bendiocarb and carbaryl in garden lizard, calotes versicolor
- Akhila, J. S., Shyamjith, Deepa and Alwar, M. C. (2007). Acute toxicity studies and determination of median lethal dose. Curr. Scien., 93(7): 917-920.
- Arya, J., and Bist, R. (2022). The diverse ways to determine experimental dose in animals. Hos. Pal. Med. Int. Jnl., 5(2):21-24.
- Bliss, C. I. (1934). The method of probits - A correction. Science, 7l9(2053): 409-10.
- Cakici, O. and Akat, E. (2012a). Histopathological effects of carbaryl on testes of snake-eyed lizard, Ophisops elegans. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 19: 64-71.
- Cakici, O. and Akat, E., (2012b). Histopathological Effects of Carbaryl on Digestive System of Snake-eyed Lizard, Ophisops elegans. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 88(5): 685-690.
- Calleja, M. C., Persoone, G. and Geladi, P. (1994). Comarative acute toxicity of the first 50 multicentre evaluation of in vitro cytotoxicity chemicals to aquatic non vertebrates. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 26: 69-78.
- Chambers, J. E. and Yarbrough, J. D. (1974). Parathion and methyl parathion toxicity to insecticide resistant and susceptible mosquito fish, Gambusia affinis. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination Toxicology., 11: 315.
- Das, N. and Garg, A. (1981). Effect of endosulfan in female rat grown on low protein and high protein cereal diet. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol., 5(1): 90-98.
- Del Prado-Lu, J. L. (2015). Insecticide residues in soil, water, and eggplant fruits and farmers' health effects due to exposure to pesticides. Environ. Health Prev. Med., 20(1):53.
- DuRant, S. E., Hopkins, W. A. and Talent, L. G. (2007). Impaired terrestrial and arboreal locomotor performance in the western fence lizard (Sceloporus occidentalis) after exposure to an AChE-inhibiting pesticide. Environ. Pollut., 149:18-24.
- Erdman, A. R. (2003). "Pesticides—insecticides" In: Dart RC, Medical toxicology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1487-1492.
- Erhirhie, E. O., Ihekwereme, C. P. and Ilodigwe, E. E. (2018). Advances in acute toxicity testing: strengths, weaknesses and regulatory acceptance. Interdiscip. Toxicol, 11(1):5-12.
- EXTOXNET (Extension Toxicology Network). (1996). Pesticide Information Profiles: Bendiocarb.
- Finney, D. J. (1971). Probit Analysis. 3rd ed. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Finney, D. J. and Stevens W. L. (1948). A table for the calculation of working probits and weights in probit analysis. Biometrika., 35 (1-2): 191-201.
- Finney, D. J., Ed. (1952). Probit Analysis. Cambridge, England, Cambridge University Press.
- Freitas, L. M., Paranaiba, J. F. F. S., Perez, A. P. S., Machado, M. R. F. and Lima F. C. (2020). Toxicity of pesticides in lizards. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 39(5) 596-604.
- Ho, I. K. and Hoskins, B. (1986). Biochemical and pharmacological aspects of neurotoxicity from and tolerance to organophosphate cholinesterase inhibitors. In: Hand book of toxicology. Eds. Haley, T. J. and Berndt W. O. Hemisphere publishing corp. Washington.
- Hopkins, W. A. and Winne, C. T. (2006). Influence of body size on swimming performance of four species of neonatal natricine snakes acutely exposed to a cholinesterase-inhibiting pesticide. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 25(5): 1208-1213.
- Hopkins, W. A., Winne, C. T. and DuRant, S. E. (2005). Differential swimming performance of two natricine snakes exposed to a cholinesterase inhibiting pesticide. Environ. Pollut., 33: 531-540
- International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS). (1986). Environmental Health Criteria 64, Carbamate Pesticides: a General Introduction, World Health Organization, Geneva.
- Jacob, P., Nagarjuna, A., Suhasini, K., Savithri, Y., Dayanand and Rajeswar, R. M. (2006). Impact of monocrotophos on Albino Rat Neural nitric oxide synthatase activity in vivo. J. Natcon., 18(2): 305310.
- Jankowska, M., Augustyn, B., Maliszewska, J., Przezdziecka, B., Kubiak, D., Chetchowska, O., Kaczorek, J., Knop, D., Krajnik, K., Kletkiewicz, H., K^sy, J., Rogalska, J, and Stankiewicz, M. (2023). Sublethal biochemical, behavioral, and physiological toxicity of extremely low dose of bendiocarb insecticide in Periplaneta americana (Blattodea: Blattidae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 30(16): 47742-47754.
- Khalaf, K. D., Morales-Rubio, A. and de la Guardia, M. (1993). Simple and rapid flow injection spectrophotometric determination of Carbaryl after liquid-liquid extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta., 280: 231238.
- Kidd, H. and D. R. James (Eds.). (1987). The Agrochemicals Handbook, Second Edition. Royal society of Chemisty Information Services, Cambridge, UK, Carbaryl.
- Kidd, H. and James, D. R. (1991). Eds. The Agrochemicals Hand book, Third Edition Royal Society of Chemistry Information Services, Cambridge, UK. 3-11.
- Lambert, M. R. K. (1999). Lizards as bioindicators. Biologist., 46: 12-16.
- Lambert, M. R. K. (2005). Lizards used as bioindicators to monitor pesticide contamination in sub-Saharan Africa: a review. Appl. Herpetol., 2: 99-107.
- Litchfield, J. T. and Jr, Wilcoxon, F. (1949). A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 96(2), 99-113.
- Macek, K. J., Hutchinson, C., & Cope, O. B. (1969). The effects of temperature on the susceptibility of bluegills and rainbow trout to selected pesticides. Bulletin of Environmental and Contamination Toxicology, 4: 174.
- Miller, L. C. and Tainter, M. L. (1944). Estimation of LD50 and its error by means of log - Probit graph paper. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 57: 261-264.
- Noga, M., Michalska, A. and Jurowsk, K. (2024). The prediction of acute toxicity (LD50) for organophosphorus-based chemical warfare agents (V-series) using toxicology in silico methods. Archives of Toxicology, 98:267-275.
- Overstreet D. H, Russell, R. W. Helps, H. C. and Messenger, M. (1979). Selective breeding for sensitivity to the anticholinersterase DFP. Psychopharmacology, 65: 15-20.
- Pal A. K. and Kushwah, H. S. (1981). A Preliminary study on protective role of protein against endosulfan exposure. Ind. J. Biophys. Biochem., 8: 4-10.
- Petrichev, M. (2022). Intoxication with carbamate insecticides and toxicological risk to animals. Zhivotnovadni Nauki, 59(1), 67-74 (Bg).
- Pickering, Q. H., Henderson, C. S. and Lemke, A. E. (1962). Toxicity of organophosphorous insecticides to different species of warm water fishes. Trans. A. M. Fish. Soc., 91: 175- 184.
- Pillai, S., Kobayashi, K., Michael, M. et al (2021) John William Trevan's concept of Median Lethal Dose (LD50/LC50)- more misused than used. J. Pre. Clin. Clin. Res. 15:137-141.
- Rajawat, N. K., Verma, R. and Soni, I. (2015). Median lethal dose (LD50) estimation of p- cyfluthrin in male and female swiss albino mice. Int. J. Scientific Res. Publicat., 5(8): 1-4.
- Randhawa, M. A. (2009). Calculation of LD50 values from the method of Miller and Tainter, 1944. J. Ayub. Med. Coll. Abbottabad, 21(3):184-5.
- Relyea, R. A. (2005). The impact of insecticides and herbicides on the biodiversity and productivity of aquatic communities. Ecol. Appl., 15(2):618-627.
- Russell, R. W. and Overstreet, D. H. (1987). Mechanisms underlying sensitivity to organophosphorous anticholinesterase compounds. Progress in Neurobiology., 28: 97- 128.
- Sánchez-Bayo, F. and Wyckhuys, K. A. G. (2019). Worldwide decline of the entomofauna: a review of its drivers. Biol. Cons., 232:8-27.
- Sanderson, D. M. (1971). The toxicology of NC 6897: Acute toxicity of pure NC 6897. Report from Fisons Limited submitted to the World Health Organization by FBC Limited. (Unpublished).
- Spurgeon, D., Lahive, E., Robinson, A., Short, S. and Kille, P. (2020). Species Sensitivity to Toxic Substances: Evolution, Ecology and Applications. Front. Environ. Sci., 8:588380.
- Thompson, W. R. (1947). Use of moving averages and interpolation to estimate median-effective dose; fundamental formulas, estimation of error, and relation to other methods. Bacteriol. Rev., 11(2): 115-45.
- Trevan, J. W. (1927). The error of determination of toxicity. Proc. R. Sco. Lond. B., 101:483-514.
- U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. (1987). Office of Drinking Water. Carbaryl Health Advisory. Draft Report.
- U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. (1999). Reigart J. R., Roberts J. R. Recognition and Management of Pesticide Poisonings. Washington DC: Office of Pesticide Programs. Available from: http://www.epa.gov/oppfead1/safety/healthcare/hand book/handbook.pdf.
- Union Carbide. (1983). Data to support revised honey bee caution Sevin XLR, Vol. 169- 074 # 911691, Department of Pesticide Regulation, Sacramento, CA.
- Weil, C. S. (1951). Tables for convenient calculation of median effective dose (LD50 or ED50) and instructions in their use. Biometrics, 8(3): 249-63.
- Weir, S. M., Yu, S., Knox, A., Talent, L. G., Monks, M. J. and Salice, C. J. (2016). Acute toxicity and risk to lizards of rodenticides and herbicides commonly used in New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 40 (3): 342350.
- Weir, SM, Yu, S, Talent, LG, Maul, JD, Anderson, TA, Salice, CJ, (2015). Improving reptile ecological risk assessment: oral and dermal toxicity of pesticides to a common lizard species (Sceloporus occidentals). Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 34: 1778-1786.
- WHO/FAO (World Health Organization/Food and Agricultural Organization). (1982). Data Sheets on Pesticides. No. 52: Bendiocarb. Revision 1. Geneva.
- Wilson, G. D., d'Arcy Doherty, M. and Cohen, G. M. (1985). Selective toxicity of 1-naphthol to human colorectal tumour tissue. Br. J. Cancer., 51: 853863.
- Wu, Y., Lin, C. and Yuan, L. (2007). Characteristics of six cladocerans in relation to ecotoxicity testing. Ecol. Indicators., 7: 768-775.


