Development of a management and monitoring system for a city farm
Автор: Blinov Andrey V., Hollay Aleksandr V., Zakharov Vadim V.
Рубрика: Краткие сообщения
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.22, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
For any manager of an agro-industrial enterprise, the use of resources is used for the efficient use of resources: labor, land, working capital and other. For this reason, the production processes of agriculture are already almost completely mechanized around the world, which is the productivity of an enterprise. The next logical step in increasing the productivity of agricultural enterprises is the automation and digitalization of agricultural production. Therefore, in order to remain competitive with the world leaders in agricultural production, it is necessary to integrate IoT technologies. It is predicted that the introduction of modern automation technologies in the agro-industrial complex will increase yields more than the inventions of the tractor, herbicides and GMOs. City farming is gradually becoming such a solution. In some megacities, urban farms are built on the rooftops of buildings, and in some places there are entire skyscrapers with vertical farms. Experts say that the quality and environmental friendliness of products grown in this way is much higher than that of counterparts grown in a traditional way. In this regard, the relevance in creating an application for a smart farm has been identified. Such an application will allow you to be more attentive to all parameters of plant growth thanks to sensors for humidity, light, temperature and other data that can be transmitted to a smartphone. The purpose of the study is to develop a management and monitoring system for a city farm. Materials and methods. The mobile application is implemented using the Xamarin framework in C# and JavaScript. The firmware for the microcontroller is written in C. Results. The paper provides an overview of management and monitoring systems for smart farms, a methodological comparison of advantages and disadvantages. The architecture of the control and monitoring system was also discovered. Implemented a mobile application and software. The functionality and design of the mobile application has been tested on various devices. Conclusion. The city farm management and monitoring system has been successfully developed. As further scientific work, it is planned to develop a mathematical model for more optimal farm management. This work can be useful in the field of decentralized agriculture.
Information systems, technologies, management, monitoring, city-farming
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147236509
IDR: 147236509 | УДК: 681.58 | DOI: 10.14529/ctcr220112
Текст краткого сообщения Development of a management and monitoring system for a city farm
Today, the rapid growth of the Earth's population and the even more active urbanization of the population requires quick food decisions. City farming is gradually becoming such a solution. In some megacities, urban farms are built on the rooftops of buildings, and in some places, there are entire skyscrapers with vertical farms [1].
Experts say that the quality and environmental friendliness of products grown in this way is much higher than that of counterparts grown in a traditional way [2]. Some of this evidence is showing that еhe heavy metal concentrations in irrigation water and soils did not exceed the recommended maximum limits (RMLs). Moreover, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni and Zn concentrations in all analysed vegetables were lower than the RML standards. In contrast, Pb concentrations were 1.4–3.9 times higher. Results of twoway ANOVA test showed that variation in metals concentrations were significant (p< 0.001) across farming site, vegetable type and site x vegetable interaction [3].
In this regard, it is important to create a city farm management system. Such a system will make it possible to be more attentive to all parameters of plant growth using sensors for humidity, light, temperature and other data that can be transmitted to a smartphone.
The Internet of Things includes several concepts:
-
• the devices themselves, connected to the network;
-
• an autonomous way of connecting M2M, that is, a machine to a machine without the participation of a living being;
-
• Big Data, that is, big data that smart devices can generate and which then need to be analyzed and systematized [4].
When connected to the Internet of Things, each device must identify itself. For this, barcodes and QR codes (Matrix codes), RFID (radio frequency identification), RTLS (Coordinate determination method) are used. The identifier must be unique. At the moment, most often the MAC address of the network adapter is used for these purposes. This symbolic combination is assigned to the manufactured device at the factory [5].
City farming is one of the most promising areas of agriculture, which implies the organization of farms for growing crops and animals in an urban setting. For the convenience of urban farmers, it is necessary to implement automated farm operation. The installation should perform the following functions:
-
1) transfer data from environmental sensors to a smartphone to track the state of plants;
-
2) control several types of LED strips to simulate daylight hours;
-
3) turn on the pump at low soil moisture.
Air humidity plays an important role in the life of the plant world. Low air humidity accelerates the evaporation of water from the soil, which leads to drying out of plants; therefore, air humidity and air temperature sensors are needed [6]. Plants need carbon dioxide, so you need to monitor its concentration in the air with a carbon dioxide sensor.
The water level in the tank must not be below a certain value, otherwise the pump will fail, as it will capture air instead of water. The water level sensor solves this problem.
LED strips should be controlled throughout the day. Early in the morning, infrared bands should be activated, which are responsible for the growth of the tops. A little later, daylight bands turn on, thanks to which the fruits ripen. During the day, ultraviolet ribbons begin to shine. After lunch, the ribbons begin to decrease the light intensity in the reverse order.
The results presented here show that the use of IoT technology can lead to significant energy savings as well as increased yields.
Methods
The choice of a development board depends on the requirements for the functionality of the board. With the right board selection, development can be dramatically accelerated. Let's compare the three most famous boards: Particle Electron, Feather Huzzah, Arduino MKR1000 (Table 1).
Table 1
Comparison of developer boards
|
Particle Electron |
Adafruit Feather Huzzah |
Arduino MKR1000 |
|
|
Clock frequency |
120 MHz |
80 MHz |
48 MHz |
|
Flash memory |
1 MB |
4 MB |
256 KB |
|
Digital lines |
14 |
9 |
12 |
|
Analog lines |
14 |
1 |
6 |
|
Antenna type |
Printed and uFI |
Printed |
Printed |
|
Support battery |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Online service |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Price |
29 $ |
16 $ |
35 $ |
Particle Electron is based on a 120MHz ARM Cortex M3 32-bit core and has a full complement of I/O pins. One of the benefits of Electron is its ability to automatically connect to the Particle web service. The firmware can be downloaded over the internet. In addition to the printed antenna, this module can be equipped with a uFl antenna to expand its wireless capabilities. Among the disadvantages of the module is a relatively high-power consumption [7].
The next stage in the development of a farm management system is the development of a mobile application. Mobile app development is the process by which apps are developed for small handheld devices such as smartphones or cell phones. These applications can be preinstalled on the device during production, downloaded by the user using various platforms to distribute software, or be web applications that are processed on the client (JavaScript) or server side [8].
The choice of technology is usually based on several factors, such as development time, product cost, and purpose. For example, for basic applications with fairly simple functionality and user interface, any solution will do. But if the product is complex, or it is expected to gradually acquire additional functions, the choice of technology must be made more carefully.
Xamarin is a cross-platform mobile application development framework based on the C# language. Leveraging the power of C# and native iOS and Android libraries allows Xamarin to make changes to the application and improve it fairly quickly throughout the project lifecycle. Most of the code is used simultaneously for several platforms, therefore, the main effort should be focused on creating the user interface for different operating systems. Since all native functions are supported by Xamarin, the result is a completely native application [9].
Using PhoneGap for application development, you can create HTML, CSS and JavaScript files in your local directory. This is more like developing a static website. Getting the user interface to look the same in the browser as native apps is not an easy task, right? Native presentation and responsiveness of the user interface is not possible on most platforms and browsers these days, even with Sencha Touch. Among other things, PhoneGap's ability to interact with other applications and device capabilities is very limited. It, in any case, will not be a cross-platform tool, since it does not have HTML5 standards, with the exception of such as geolocation, camera and local databases (Table 2).
Table 2
Comparison of development platforms
|
Criterion |
Phonegap |
Xamarin |
|
Performance |
Less productive |
Stable performance on iOS, Android and WinPhone |
|
Interface |
The user interface is common to all three platforms |
It is possible to create your own interface for each platform |
|
Start time |
Slow start |
Quick start |
|
Data volume |
Problems with displaying large amounts of data |
No problem with displaying large amounts of data |
|
Native functions |
To use additional native functionality, you must have programming skills in Objective C or Java |
Native functions can be implemented using Xamarin without using other programming languages |
The next stage of development is the hardware architecture. The basic elements of the system hardware are divided into several types: sensors, actuators, and gates.
Sensors include devices that measure the physical characteristics of objects or the environment (for example, temperature, pressure, the presence of impurities in the air, position in space, etc.) and convert it into a form that is convenient for further processing.
Actuators are designed to affect the environment, or a specific object in it. A wide variety of devices can play this role, from servos and speakers to locks with lighting fixtures.
Gates are devices that are usually assigned the logic of superficial analysis of information coming from sensors connected to them. In certain situations, data analysis may require a small amount of computational resources, so that the gates are quite capable of making some decisions on their own. Making such decisions, they send certain control commands to the actuators, which, in turn, already perform their functions.
If the processing of information is costly, or this information is subject to collection, the gates send it to the servers, where further work is done with it. Most likely the use of microcomputers or microprocessors as gates [10].
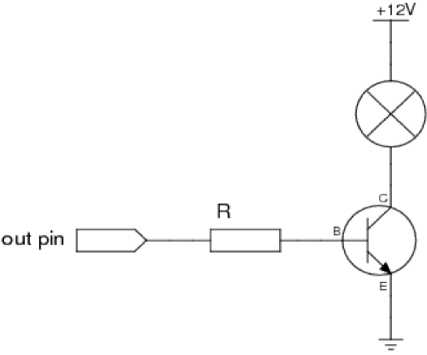
The microcontroller controls the LED strips using a transistor. From the pin of the operating device, a voltage from 0 to 3.3V is applied to the control leg of the transistor. At a certain voltage, the transistor opens with a certain ratio. In this way, the intensity of the light can be controlled (Fig. 1).
A relay is used to control the pump. A voltage of 3.3 V is applied to the control leg of the relay, thereby opening the relay. For safety reasons, the relay is used in normally closed mode. That is, in the absence of a signal, the relay is closed.
The water level sensor is digital, so the microcontroller can get values 0 (no water) and 1 (there is
Fig. 1. Lighting control water).
Soil moisture sensor, air humidity sensor, soil temperature sensor and air temperature sensor are analog, therefore fra c tional values from 0 to 3.3 V are possible.
The next stage of development is cloud configuration.
Particle cloud is an important element of the software part of the system. In addition to collecting and storing data, the cloud implements a software update function.
Firmware Updates (OTA) are a vital component of any IoT system [11]. Over-the- air firmware updates are the pra ctice of remotely updating code on an embedded device. Pa rticle's all-in- one IoT platform offers good OTA upgrade c apabilities [12].
A hybrid approach was chosen for the development of a mobile application (Fig. 2). A hybrid app is a mobile app that contains a mob ile platform WebView [13]. The main comp o nent over which the development is created with this approach is the WebView component. It can be used to embed web a pplications (sites).
In Android version 7.0 and higher, WebView uses the Chrome engine. If this c annot be done for any reason, then the System WebView is used, which appeared in Android ve r sion 5 and later. Earlier versions of Android use WebKit or Chromium for these tasks [14].
Results
Fig. 2. Mobile app
Once the smart farm management and monitoring system is develope d, it needs to be tested. One of the main tasks of a smart farm is th e constant processing of readings from environm ental sensors.
The problem of incorrect read ing of parameters may occur due to incorrect supply of voltage to the microcontroller input. Th is phe nomenon can occur due to different physical ph enomena. Therefore, in the firmware of the microcontro ller, an additional check is made that the value belongs to a certain range. For example, the temperatu re cannot go below 0 degrees and rise above 5 0 degrees. There are ranges for each sensor according to the environment in which they are located. Also, there can be no abrupt change in any parameter. Fo r this, the voltage value is read several times in a short period of time and compared with the previo us value.
This problem cannot be determined by a one -time measurement; therefore, the developed solution requires testing for a long time. The ThingSpeak service was used to visualiz e the environmental parameters (Fig. 3).
These graphs show that there are no unreasonable jumps in readings. The increases and de creases are caused by external fa ctors. For example, turning on the heating, st arting watering, and the like.
Thus, smart farm monitoring functions correctly.
To test a mobile application, it is necessary to determine the criteria by which it will be possible to evaluate the mobile application and rank them in order of importance [15].
-
1. Ease of use of the mobile application.
-
2. Design of a mobile application.
-
3. Functioning.
The mobile applicati on was t ested on an emulator, on a smartphone and on a Smart TV. Testing consisted of viewing the start page and checking these three criteria.
Usability was verified as a result of initial testing.
The next stage of testing is to check compatibility. For this task, it was necessary to check the cor rect display of the application on d ifferent screens, that is, to investigate the design of the application for adaptability. On android 4.0 and hi gher, the application is displayed correctly (Fig. 4, 5).
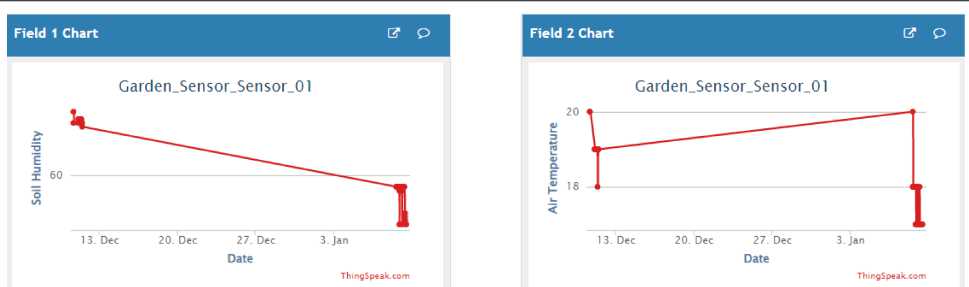
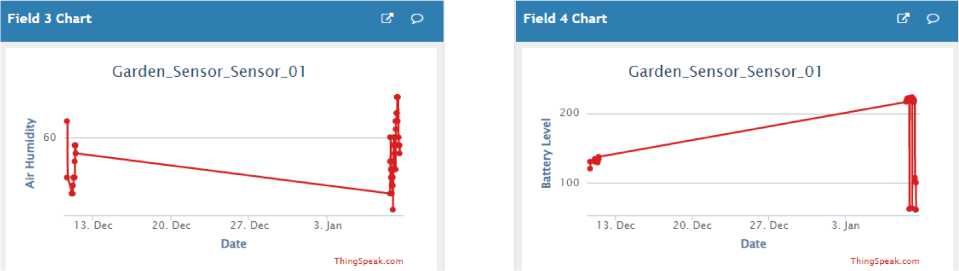
Fig. 3. ThingSpeak

Fig. 4. Displaying an app in landscape orientation

Fig. 5. Displaying an app in landscape orientation
Functional testing included checking links, animations, choosing a farm, displaying hints. As a result of this study, no problems were found.
Thus, the mobile application functions and is displayed correctly on various devices.
Discussions and Conclusions
The architecture of the software is designed in this article. The implementation of data exchange between the microcontroller and the Particle cloud is considered. Environmental monitoring is carried out correctly and stably. A mobile application for managing and monitoring a smart farm has been created. The functionality and design of the mobile application has been tested on various devices.
Thus, the city farm management and monitoring system has been successfully implemented.
As further scientific work, it is planned to develop a mathematical model for more optimal farm management.
Список литературы Development of a management and monitoring system for a city farm
- Maciaszek L.A. Practical software engineering: a case study approach. Transl. from Engl. Moscow: Binom. Laboratoriya znanii; 2013. 424 p. (In Russ.)
- Yarochkin, V.I. Informatsionnaya bezopasnost' [Information Security]. 5th ed. Moscow: Akademicheskii proekt; 2016. 544 p. (In Russ.)
- Ghezzi C., Jazayeri M., Mandrioli D. Fundamentals of software engineering. Transl. from Engl. Moscow: BHV-Petersburg; 2013. 832 p. (In Russ.)
- Zasada I., Fertner C., Piorr A., Nielsen T.S. Peri-urbanisation and multifunctional adaptation of agriculture around Copenhagen. Geografisk Tidsskrift. 2011;111(1):59–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/00167223.2011.10669522.
- Particle Documentation. Available at: https://store.particle.io/collections/electron/.
- Agurov P. C#. Sbornik retseptov [C#. Collection of recipes]. Moscow: BHV-Petersburg; 2007. 432 p. (In Russ.)
- Echmaeva, G. Informatsionnaya kul'tura organizatora fermerskogo khozyaistva [Information culture of the organizer of the farm]. Moscow: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing; 2011. 260 p. (In Russ.)
- Leventhal L. Introduction to microprocessors: software, hardware, programming. Transl. from Engl. Moscow: Energoatomizdat; 1983. 464 p. (In Russ.)
- Duvall P.M. Continuous Integration: Improving Software Quality and Reducing Risk. Transl. from Engl. Moscow: Vil'yams; 2017. 240 p. (In Russ.)
- Shangin V.F. Informatsionnaya bezopasnost' i zashchita informatsii [Information security and information protection]. Moscow: DMK Press; 2014. 702 p. (In Russ.)
- Richter J. CLR via C #. Programming on Microsoft .NET Framework 4.0 in C#. Transl. from Engl. St. Petersburg: Piter; 2013. 896 p. (In Russ.)
- Bob F. Microservices, IoT, and Azure. Apress; 2015. P. 3–27.
- Woldetsadik D., Drechsel P., Keraita B. et al. Heavy metal accumulation and health risk assessment in wastewater-irrigated urban vegetable farming sites of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. FoodContamination. 2017;4, 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40550-017-0053-y.
- Mohan S.V., Hemalatha M., Amulya K. et al. Decentralized Urban Farming Through Keyhole Garden: a Case Study with Circular Economy and Regenerative Perspective. Mater Circ Econ. 2020;2, 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42824-020-00011-1.
- Babash A.V., Baranova E.K., Mel'nikov Yu.N. Informatsionnaya bezopasnost'. Laboratornyi praktikum: ucheb. posobie [Information Security. Laboratory practice: Textbook]. Moscow: KnoRus; 2016. 136 p. (In Russ.)


