Development of Blended Learning Content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha-superitem in Kelase Platform
Автор: I. Putu Wisna Ariawan, Dewa Gede Hendra Divayana, P. Wayan Arta Suyasa
Журнал: International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science @ijmecs
Статья в выпуске: 1 vol.14, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Blended learning can be carried out well if it is supported by good content. Good content consists of the subject, performance assignments, discussion forums, and quiz questions that are packaged in an interesting and structured manner. Good content must also be used to measure students’ abilities in the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. One of the efforts that can be made to realize good blended learning content is to develop content by inserting the Tri Kaya Parisudha and Superitem concepts into the Kelase platform. The Tri Kaya Parisudha concept is used as a basis for measuring students’ abilities in the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. Superitem concept is used as the basis for structured content creation (especially on quiz questions and performance tasks) starting from the lowest to the highest level of complexity. Referring to some of those things, this research aimed to provide an overview of the stages of developing blended learning content that integrated the Tri Kaya Parisudha concept and the Superitem concept in the Kelase platform (a case study of Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools in Bali). This research used the 4D method, which consists of 4 stages, including Define, Design, Develop, and Disseminate. The subjects involved in content testing were four experts. The tools used to collect data were interview guides, photo documentation, and questionnaires. The technique used to analyze the data was descriptive quantitative. The analysis technique in this research was carried out by making a comparison between the five-scale reference effectiveness standard with the percentage level of effectiveness of the blended learning content. The results showed the level of effectiveness of the blended learning content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha-Superitem in the good category with a percentage was 88.667%.
Content, Blended Learning, Tri Kaya Parisudha, Superitem, Kelase
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15018368
IDR: 15018368 | DOI: 10.5815/ijmecs.2022.01.03
Текст научной статьи Development of Blended Learning Content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha-superitem in Kelase Platform
The Covid-19 pandemic had caused various problems in various fields of life, such as health, economy, transportation, tourism, social, culture, industry, trade, and also in the field of education. If it was studied specifically in the field of education, various efforts and policies had been made by policymakers in the education sector to continue to be able to carry out the learning process during the Covid-19 pandemic.
One of the efforts that had been made was the implementation of online learning from home. Several learning models can be done online from home, including e-learning, blended learning, flipped learning, virtual learning, and others.
The learning model that is most suitable for use from these learning models is blended learning. This model can be said to be suitable for use during the Covid-19 pandemic because the learning process can still be done from home without reducing the quality of learning.
However, the implementation of blended learning from home also raises several problems. The problems intended, including 1) it is difficult to carry out the face-to-face learning process like in school because of unstable internet access,
2) it is difficult to monitor students’ learning activities as a whole because they can access online learning platforms without time restrictions, 3) it is difficult to give an honest and objective assessment of the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains because the teacher cannot see student activities at home directly.
2. Literature Review
Based on those problems, it is important to find innovations as a solution to solve them. One innovation that can be done is to develop learning material content that adopts the Tri Kaya Parisudha and Superitem concepts so that later it can be incorporated into the blended learning model through the Kelase platform.
The concept of Superitem is specifically used to evaluate the cognitive domain objectively. This is basically because the Superitem consistently presents the complexity level of the questions/assignments given to students starting from the lowest level to the highest. The Kelase platform is an online learning platform created to make it easier for teachers and students to carry out the learning process using the blended learning model. This platform provides features that make it easier for users to modify the content of the material, thus allowing learning material content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha - Superitem to be inserted into blended learning.
Based on that innovation, a question and main objective in this study arise. The question is “what are the stages of developing based blended learning based on Tri Kaya Parisudha - Superitem content in the Kelase platform?”
The main objective of this research was to determine the steps taken in the development of blended learning content based on the Tri Kaya Parisudha - Superitem which inserting into the Kelase platform.
Strengthening the innovations found in this research requires several references from the results of previous studies. The research was conducted in 2019 by Sukerti et al . [13] demonstrated the integration of the Tri Kaya Parisudha concept into a project-based learning process to improve students’ understanding of entrepreneurship. In principle, the research of Sukerti et al . has similarities with this research regarding the application of the Tri Kaya Parisudha concept to the learning process. The difference lies in the focus of the research. This research focuses more on developing blended learning content that is integrated with the Tri Kaya Parisudha and Superitem concepts. Sukerti’s research focused on integrating the Tri Kaya Parisudha concept into project-based learning.
The research was conducted in 2019 by Sudihartinih [14] showed the use of the Superitem concept to prepare questions with a tiered level of complexity. The hierarchical complexity of the questions, from easy to difficult levels, caused students to develop their thinking skills more quickly. Things that have not been raised yet in Sudihartinih’s research are questions to measure the affective and psychomotor domains.
The research was conducted in 2018 by Maftuh and Hidayat [15] showed the use of a learning model that incorporates the Superitem concept to improve student learning achievement. The thing that has not been seen yet in Maftuh and Hidayat’s research is the learning content used to measure the affective and psychomotor aspects of students.
The research was conducted in 2019 by Wu et al . [16] showed the effectiveness of using MOOC ( Massive Open Online Courses ) in combination with mixed curriculum design in the entrepreneurial learning process, to measure students’ affective abilities. The thing that has not been explained yet in the study by Wu et al . is an in-depth measurement of students’ abilities in the cognitive and psychomotor domains.
The research was conducted in 2019 by Ikawati, Majid, and Anwar [17] showed the effectiveness of implementing the Superitem learning model to improve student achievement. The limitation of Ikawati, Majid, and Anwar’s research is that it has not shown yet the learning content used to measure attainment in the affective and psychomotor domains in detail.
The research was conducted in 2019 by Rahadini and Fitriana [18] showed the use of blended learning to support the learning process effectively by providing online and offline learning facilities. Online facilities are used to make it easier to disseminate teaching materials quickly, while offline in class are used to facilitate direct discussion/interaction between educators and students. The limitation of Rahadini and Fitriana’s research is that it has not shown yet learning content with a level of complexity that is graded from low to high.
3. Method
The research approach was development research. The development stages were carried out based on the 4D model design, which consists of [19,20]: the Define stage, the Design stage, the Develop stage, and the Disseminate stage. Some of the activities carried out at the Define stage including front-end analysis, student analysis, task analysis, concept analysis, and arrangement of learning objectives. Activities carried out at the Design stage were the creations of blended learning content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha - Superitem . Activities carried out at the Develop stage, including testing of blended learning content from experts, and revising blended learning content based on expert’s input. Activities carried out at the Disseminate stage, including socialization and implementation of Blended learning content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha - Superitem in the Kelase platform.
The object of research in 2020 was blended learning content, especially for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools Mathematics which was integrated with the Tri Kaya Parisudha and Superitem concept. This content will later be inserted into the Kelase platform. The implementation of this research was carried out in several Senior High Schools/ Vocational High Schools spread over six districts in Bali province. Some of the Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools were in the districts of Tabanan, Badung, Gianyar, Buleleng, Denpasar, and Klungkung. The subjects involved in creating blended learning content were three people which included all research members. Four experts were involved in testing the blended learning content.
All data collected in this research were obtained from data collection tools in the form of questionnaires, interview guides, and photo documentation. The questionnaires were used to get the percentage of the effectiveness level of the blended learning content. Interview guidelines were used to obtain descriptive data to strengthen arguments against research findings. Documentation photos were used to obtain the Kelase platform user interface design which is used as a container for placing blended learning content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha - Superitem .
The test data analysis of the blended learning content was carried out using quantitative descriptive techniques. This analysis technique was carried out by comparing the percentage level of effectiveness of the blended learning content with the five-scale reference effectiveness standard. The calculation of the effectiveness percentage level of blended learning content follows equation (1). The equation (1) which is intended can be shown as follows [21-23].
Percentage of effectiveness = (f/N) * 100% (1)
Notes: f = total acquisition value; N = total maximum score
The five scale classification references consist of a percentage of 90-100 which means very good, a percentage of 80-89 which means good, a percentage of 65-79 which means moderate, a percentage of 40-64 which means less, and a percentage of 0- 39 which means very less.
4. Results and Discussion
-
A. Results at the Define Stage
The front-end analysis results were used to determine the problems that often occur in the implementation of blended learning of Mathematics subject for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools in several districts in Bali. Some of the problems intended can be explained as follows.
-
1) Platforms were incompatible with the blended learning model and learning support facilities implemented in schools.
-
2) The material presented in blended learning was not well structured.
-
3) Quiz questions and exercises were able to be used only limited to measure the cognitive domain.
Results of the student’s analysis were used to determine the readiness of students in participating in the Mathematics learning process using the blended learning model. The results of the student’s analysis can be described as follows:
The results of concept analysis were used to determine the content structure of Mathematics subject matter, quiz questions, questions for discussion forums in the blended learning platform. The structure of Mathematics subject material content for 10 grade Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools in Bali can be seen in Table 1, Quiz questions in Table 2, performance questions in Table 3, and discussion forum questions in Table 4.
Table 1. Content Structure of Mathematics Subjects for 10 grade Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools in Bali
|
Matrial Code |
Material Content |
|
M1 |
Equations and inequalities of linear absolute value for one variable |
|
M2 |
Linear equation system for three variables |
|
M3 |
Function |
|
M4 |
Trigonometry |
Table 2. Quiz Questions
|
Material Code |
No |
Quiz Questions |
|
M1 |
1. |
The solution set for |2x + 3| = |x + 6| is ...
|
|
2. |
The solution set for |2x - 7| = 5 is ...
|
|
|
3. |
The solution set for |2x - 5| ≤ 9 is ...
|
|
|
M2 |
4. |
If x : y : z = 2 : 1 : 3 and x + y - 2z = -6, so the value x – y + z = ⋯
|
|
5. |
If x : y = 5 : 3, while y : z = 4 : 5. if 2(x+y+z) = 94, so the value 3y = …
|
|
M3 |
6. |
Function f : R → R, and g : R → R. If f(x) = 2x – 3 and g(x) = x2 + 2x – 3 the value of (fog)(2) = ...
C. 1 D. 11 E. 0 |
|
7. |
Function f : R → R and g : R → R If f(x) = x + 3 and (fog)(x) = x2 + 6x + 7, then g(x) = ...
|
|
|
8. |
Function f : R → R, and g : R → R. If f(x) = x + 3 and g(x) = x2 – 2, then (gof)(x) = ...
|
|
|
M4 |
9. |
For 0° ≤ x ≤ 360° find the set of solutions for cos x =½ A. The solution set = {-60o,120o} B. The solution set = {30o,120o}
|
|
10. |
Find a value for x that fulfill the equation 2 sin x = 1 where 0o ≤ x ≤ 360o
|
Table 3. Performance Questions
|
Material Cdoe |
No |
Performance Questions |
|
M1 |
1. |
The normal hemoglobin level in adult male blood is between 13 and 16 grams per deciliter (g/dL). Find the hemoglobin level which represents the abnormal hemoglobin level for an adult male! |
|
M2 |
2. |
Find a linear equation system for three variable that represents the mathematical model of the real problems in your environment. Describe the process of finding the mathematical model and solve it as a solution to the problem. Make a report on your work! |
|
M3 |
3. |
One of the income sources earned by soccer clubs in the sale of spectator tickets when the team is playing. The amount of funds obtained depends on the number of spectators who watch the match. A club provides information that the amount of revenue the club gets from ticket sales of spectators follows the function f (x) = 500 x + 20,000, where x is the number of spectators who watch the match. If in a match, the club receives IDR 5,000,000 from the sale of spectators’ tickets, how many spectators will watch the match? |
|
M4 |
4. |
Two teachers of the same height, namely 170 cm, were standing looking at the top of the flagpole at their school. The first teacher stands exactly 10 m in front of the second teacher. If the elevation angle of the first teacher is 60o and the second teacher is 30o can you calculate the height of the flagpole? |
Table 4. Discussion from Questions
|
Material Code |
No |
Discussion Questions |
|
M1 |
1. |
Please discuss the following problems to find a solution! The normal water level of the Petanu River is 140 cm. The water level of the Petanu River can change during the dry season or the rainy season. If the deviation from the river water level is less than 12 cm, so the interval for the height of the Petanu River is …? |
|
M2 |
2. |
Please respond to the following questions! If the price of 4 kg of bark, 1 kg of guava, and 2 kg of longan is IDR 55,000. The price of 1 kg of salak, 2 kg of guava, and 2 kg of longan is IDR 45,000. The price of 3 kg of salak, 1 kg of guava, and 1 kg of longan is IDR 38,850.00. The price of 1 kg of guava is ⋯? |
|
M3 |
3. |
Provide solutions to the following questions! Jacky takes math lessons with a compulsory monthly fee of IDR 120,000 plus a meeting fee of IDR 55,000. If Jacky attended 4 meetings for a month, so the tutoring fees that must pay by Jacky is ... |
|
M4 |
4. |
Please solve the following cases! Rina’s tall is 152 cm. She stands at a distance of 12 m from the flagpole. She saw the top of the flagpole with an elevation angle of 45 0 . The flagpole’s height is ⋯⋅? |
The learning objectives were used to determine the extent to which the success of the learning process had been achieved. The objectives of learning Mathematics for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools in Bali can be explained as follows.
-
1) Students can understand and solve problems related to equations and inequalities of the absolute linear value for one variable.
-
2) Students can understand and solve problems related to the Linear Equation System for Three Variable.
-
3) Students can understand and solve problems related to function both theoretically and practically in everyday life.
-
4) Students can understand and solve problems related to trigonometry both theoretically and practically in everyday life.
-
B. Results at the Design Stage
Based on the problems shown in the results of the front-end analysis and student analysis, innovation was needed to solve those problems. Referring to the results of task analysis, concept analysis, and learning objectives, the problem was able to be solved at the design stage by presenting blended learning content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha - Superitem which is applied in the Kelase platform. The display of that content can be seen in Figure 1 to Figure 6.
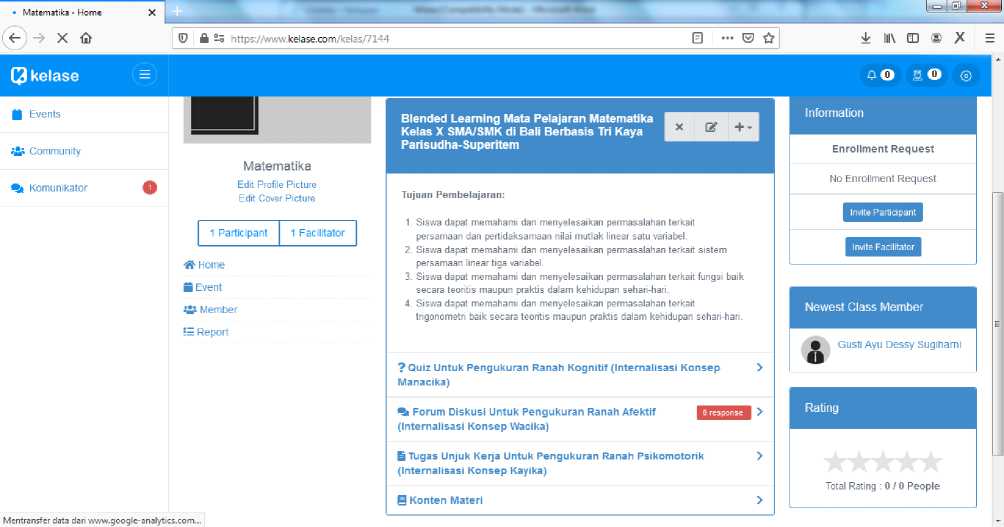
Fig. 1. Display of the main page of Blended Learning for Mathematics Subjects based on Tri Kaya Parisudha-Superitem
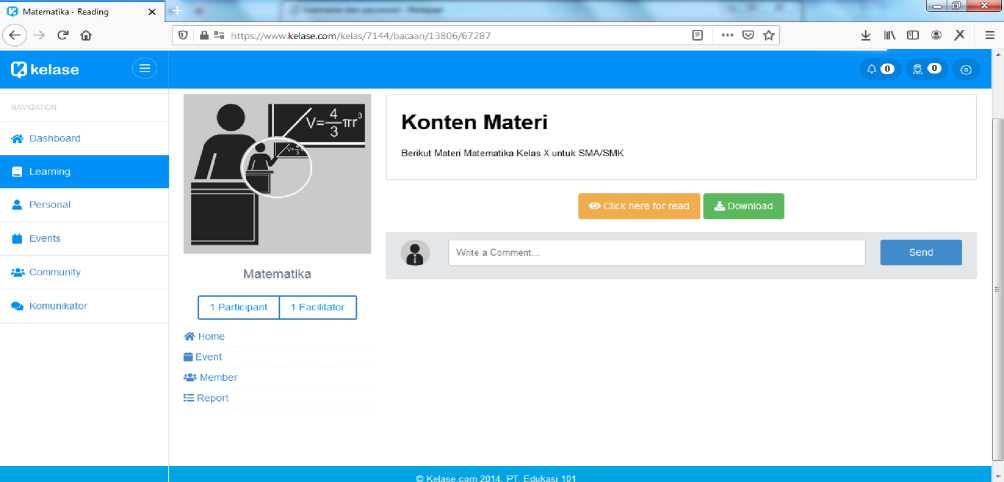
Fig. 2. Display of Page for Material Content Download
Figure 2 shows a blended learning page that functions to provide facilities to download structured mathematics subject material for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools. On the page, there are two-button, included: orange button and green buttons. The orange button (“ click here for reading ” button) is used to display Mathematics subject material directly in digital book format on a web page. The display of digital books can be seen more clearly in Figure 3. The green button (“ download ” button) is used to download Mathematics subject materials in .pdf format.
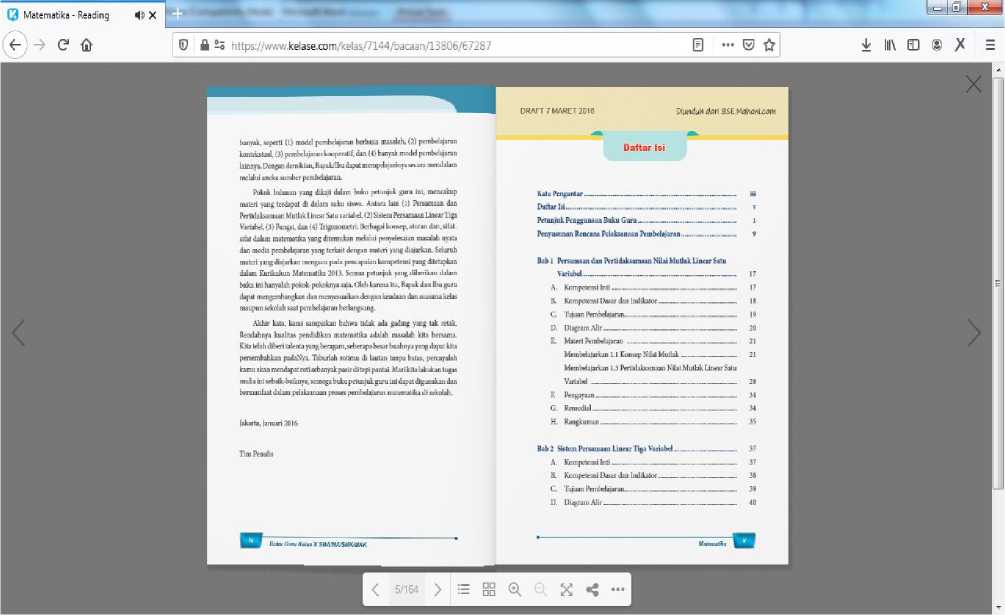
Fig. 3. Display of Structured Material Content Pages in the Form of Digital Books
Figure 3 shows the display of structured Mathematics subject content in the form of a digital book for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools. The digital book is structured, equipped with a cover, introduction, table of contents, material content, summary, practice questions, and references.
Preview Question
Preview Question
Preview Question
Preview Question
Preview Question
Tentukan nilai x yang memenuhi persamaan 2 sin x = 1 , dengan Oo s. x £ 360o ...
Mentransfer data dari id..,
Fig. 4. Display of Question Quiz Settings Page
|
ykelase |
oo so |
® |
|
|
Question |
1 |
||
|
И No Question |
Type Answer Score |
Himpunan penyelesaian dari persamaan |2x + 3| = |x + 6| adalah
Himpunan penyelesaian dari |2x - 7| = 5 adalah.....
Himpunan penyelesaian dari |2x - 51 £ 9 adalah......
Diketahui x у = 5 : J, sedangkan у : z - 4 : 5. Jika 2(x+y+z) = 94, maka nilai Jy
Fungsi f: R -> R, dan g : R -> R Diketahui f(x) - 2x - 3 dan g(x) = x2 + 2x
Dari fungsi f: R—> R dan g : R->R diketahui bahwa f(x) = x 4 3 dan (fog)(x} = x2 4
Diketahui fungsi f: R - > R, dan g : R-> R, dengan f(x) - x 4 3 dan g(x) = x2 - 2.
Preview Question
Figure 4 shows the page for setting Quiz questions on the Kelase platform that can be done by teachers. The teacher can arrange the question form, answer key, score, and time for solving the questions. Through this page, teachers can also randomize, edit, and delete quiz questions. Quiz questions are made in a structured manner starting from the lowest difficulty level to the highest by internalizing the Superitem concept. This quiz question is used to measure a student’s cognitive abilities. Student cognitive assessment is carried out by referring to the Tri Kaya Parisudha component, especially in the Manacika section.
Л Events
2. Silahkan tanggapi pertanyaan berikut!
;Д; community
Matematika
О
% Komunikator
Edit Profile Picture
Edit Cover Picture
Ketinggian normal permukaan air Sungai Petanu adalah 140 cm. Ketinggian permukaan air Sungai Petanu dapat berubah-ubah pada musim kemarau atau musim penghujan. Jika penyimpangan ketinggian permukaan air sungai tersebut kurang dari 12 cm, maka interval ketinggian Sungai Petanu adalah ...
Diketahui harga 4 kg salak, 1 kg jambu, dan 2 kg kelengkeng adalah Rp65.000,00. Harga 1 kg salak, 2 kg jambu, dan 2 kg kelengkeng adalah Rp45.000,00. Harga 3 kg salak, 1 kg jambu, dan 1 kg kelengkeng adalah Rp38.850,00. Harga 1 kg jambu adalah
3. Berikan solusi untuk pertanyaan berikut!
| 1 Participant |
1 Facilitator
Jacky mengikuti les matematika dengan biaya wajib per bulan sebesar Rp120.000,00 ditambah biaya per pertemuan sebesar Rp55.000,00. Jika Jacky mengikuti 4 pertemuan selama sebulan, maka biaya. les yang harus dibayarkan Jacky adalah ...
•S Home
4. Silahkan dipecahkan kasus berikut!
^ Member
Seorang anakyang memiliki tinggi badan 152 cm {terukur sampai ke mata) berdiri pada jarak 12 m dari tiang bendera. la melihat puncaktiang bendera dengan sudut elevasi 45» Tinggi tiang bendera itu adalah —-
Report
+ Add Response
0 Response
I Find Response
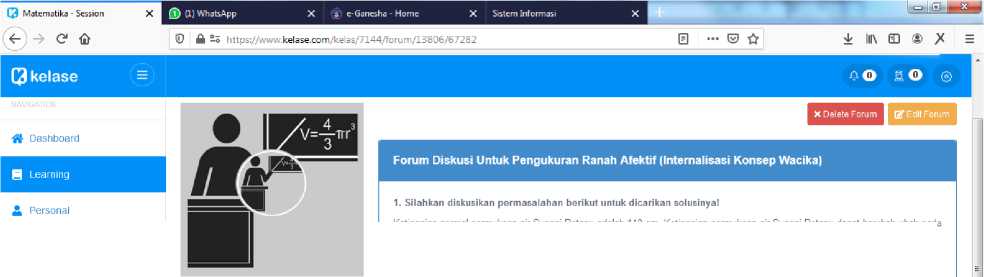
Fig. 5. Display of Discussion Forum Page
Figure 5 shows a blended learning page that functions to make it easier for teachers and students to have discussions regarding Mathematics subjects for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools. This discussion form is also used as a basis for teachers to assess student attitudes in following the learning process through blended learning. Assessment of student attitudes is carried out by referring to the Tri Kaya Parisudha component, especially in the Wacika section. On this page, there is a green button ( add response button) and a blue button ( response button). The green button is used to make it easier for students to input their responses. The blue button is used to make it easier to see the number of responses that joined into blended learning.
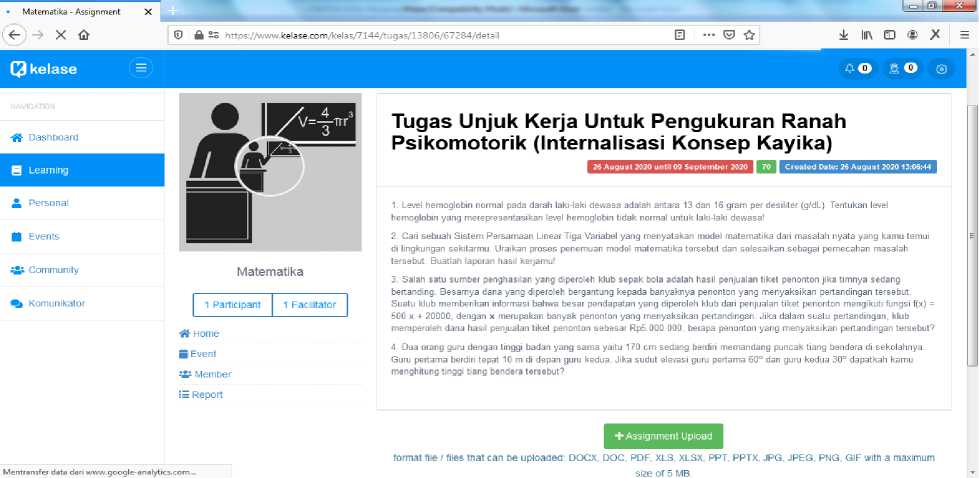
Fig. 6. Display of Performance Task Page
Figure 6 shows a blended learning page that makes it easier for teachers to provide performance assignments to students. This page is also used as a basis for conducting psychomotor assessments of students participating in the Mathematics learning process. The psychomotor assessment of students refers to the Tri Kaya Parisudha component, especially in the Kayika section. On this page, there is a green button (assignment upload) which is used to make it easier for students to upload answers to their performance assignments.
-
C. Results at the Develop Stage
The results of the blended learning content test from experts carried out at the development stage were used to determine the level of effectiveness of the blended learning content being developed. Some of the experts were involved in testing blended learning content, included: two informatics experts, and two education experts. The test results can be seen completely in Table 5.
Table 5. Test Results for Blended Learning Content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha-Superitem on the Kelase Platform
|
No |
Respondents |
Items- |
∑ |
Effectiveness Percentage (%) |
||||||||||||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
||||
|
1 |
Education Expert-1 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
65 |
86.667 |
|
2 |
Education Expert-2 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
70 |
93.333 |
|
3 |
Informatics Expert-1 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
64 |
85.333 |
|
4 |
Informatics Expert-2 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
67 |
89.333 |
|
Average |
88.667 |
|||||||||||||||||
Viewed from the results of the effectiveness percentage shown in Table 5 above, it appears that the content of blended learning based on Tri Kaya Parisudha - Superitem had been used effectively in supporting the Mathematics learning process for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools in Bali province.
This is evidenced by the results of the percentage level of effectiveness in the categorization that refers to the five-scale reference effectiveness standard. The percentage of effectiveness of 88.667% was included in the good category because it was in the range of percentage values between 80% and 89%. There were 15 questions used to assess blended learning content. Item-1 was related to the display of the Kelase platform design which was used as a forum for implementing blended learning. Item-2 was related to the structure of Mathematics material content. Item-3 was related to the internalization of the Tri Kaya Parisudha components (especially the Manacika concept) in the question of quizzes. Item-4 was related to the internalization of the Tri Kaya Parisudha component (especially the Wacika concept) in the discussion forum. Item-5 was related to the internalization of the Tri Kaya Parisudha component (especially the Kayika concept) in performance tasks. Item-6 was related to editing and setting material content in the Kelase platform. Item-7 was related to editing and setting quiz questions. Item-8 was related to editing and setting questions in the discussion forum. Item-9 was related to editing and setting performance tasks. Item-10 was related to the safety of Mathematics material content stored in blended learning. Item-11 was related to security regarding quizzes. Item-12 was related to the security of performance tasks. Item-13 was related to the ease for users (teachers) to upload materials and assignments into blended learning. Item-14 was related to the ease for users (students) to download material and upload answers to assignments into blended learning. Item-15 was related to access rights and security.
In addition to providing an assessment based on those 15 questions, experts also provide suggestions for improvements to the blended learning content. Some of the suggestions given by experts can be seen in Table 6.
Table 6. Suggestions from Experts
Based on some suggestions given by experts, it was necessary to revise the blended learning content. There were two revision activities carried out on blended learning content. Revision 1 was to add features for video content material that was able to be accessed via hyperlinks. Revision 2 was to add hyperlinks that contain examples of enrichment questions before working on quiz questions. The display of the feature of adding hyperlinks to access the content of Mathematics subjects for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools in video format can be seen in Figure 7. The features display for adding hyperlinks for examples of enrichment questions can be seen in Figure 8.
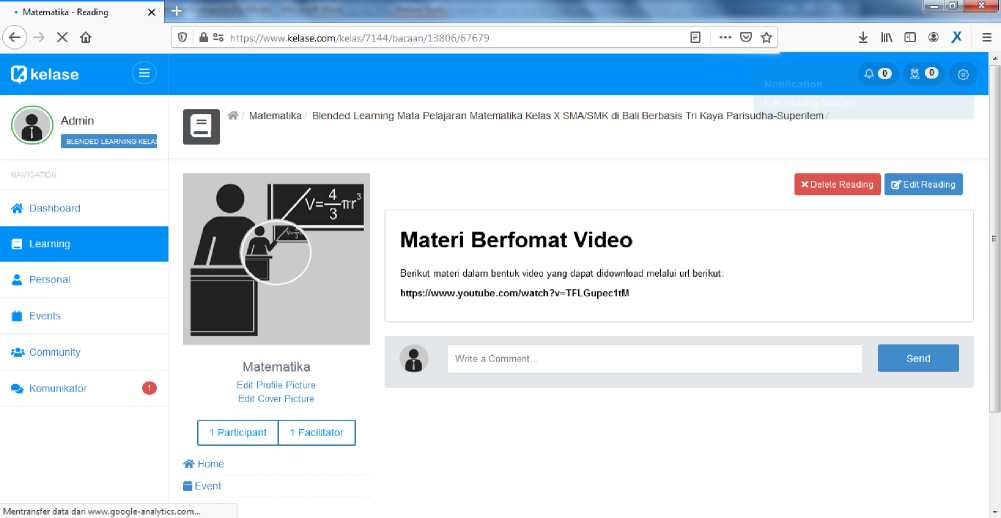
Fig. 7. Hyperlink Display for Content of Video Formatted Material
Figure 7 is a page display showing a hyperlink to the content of Mathematics subjects for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools that are packaged in video form. This hyperlink makes it easy for students to access and download material in the form of video directly.
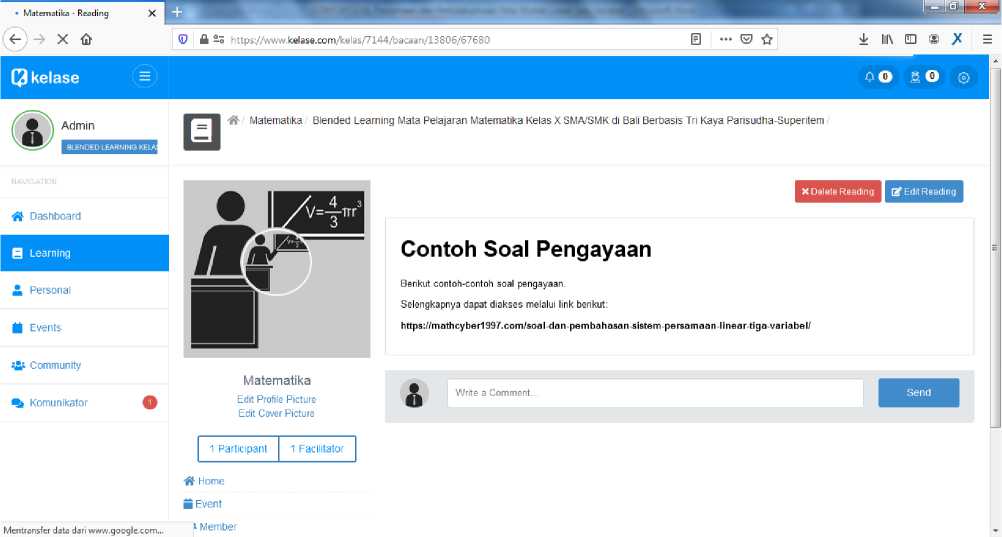
Fig. 8. The Hyperlink Display for Example of Enrichment Questions
Figure 8 is a page display showing a hyperlink about the enrichment of Mathematics content for grade 10 Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools. This hyperlink makes it easy for students to access, study, and answer enrichment questions online.
-
D. Results at the Disseminate Stage
The socialization and implementation of blended learning content on the Kelase platform were carried out by inviting grade 10 students and teachers spread across several Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools in Bali
Province to join as members of the Kelase platform. The way that teachers and students can join as members on the Kelase platform is by providing a Participant Access Code to teachers and students.
Referring to the average result of the percentage effectiveness of the blended learning content was 88.667% from this study, so the effectiveness level was relatively good. These results when compared with Khader’s research [24], it appears that in general the effectiveness level was classified as good but the percentage score of effectiveness in Khader’s research had not been shown yet explicitly.
This blended learning content inserted the Tri Kaya Parisudha concept so that it is more optimal in measuring the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains in Mathematics learning in Senior High Schools/Vocational High Schools in Bali province. Measuring the cognitive domain is done by giving quizzes to students. The quiz question arrangement is carried out using the quiz setting features on the Kelase platform shown in Figure 4. The quiz questions were arranged carefully and in stages, starting from the easiest level to the most difficult level. Arrangement of questions is carried out based on the concept of Superitem , so that students’ critical thinking skills will be raised through the complexity of the available quiz questions. The excellent ability of students in the cognitive domain can be seen from the high scores they get in answering quiz questions. It is hoped that the quality of students’ cognitive abilities has shown good internalization into the Manacika concept.
Measurement of the affective domain is carried out through checking the activeness of students in using communication media to be able to interact with the teacher. The communication feature can be done using the “ discussion forum ” feature provided in the Kelase platform which is fully shown in Figure 5. The excellent ability of students in the affective domain can be seen from the activeness of students in responding to each question in the discussion forum. It is hoped that the quality of student responses has shown good internalization into the Wacika concept.
Measurement of the psychomotor domain is carried out by checking the quality of the performance tasks that have been uploaded by students through the features provided on the Kelase platform shown in Figure 6. The excellent ability of students in the psychomotor domain can be seen from the quality of the performance tasks that have been completed by students. It is hoped that the quality of performance tasks has shown good internalization into the Kayika concept.
The results of this research have succeeded in answering the questions and research objectives by showing the stages is conducted in developing blended learning content by following the 4-D development stages.
The results of this research also have succeeded in being a solution to some of the obstacles found in previous studies. Research constraints Sudihartinih [14], Maftuh and Hidayat [15], Wu et al . [16], Ikawati, Majid, and Anwar [17] were answered through this research with the availability of blended learning content that adopts the Tri Kaya Parisudha concept in presenting quizzes, performance tasks, and discussion forums.
The constraints of Rahadini and Fitriana’s research [18] were answered through this research by the availability of structured quiz questions from the lowest to the highest level of complexity using the Superitem concept. This is reinforced by the research of Rahmawati, Priatna, and Juandi [25] and the research of Lian and Yew [26] which in principle show the use of the super-item concept to present a test that is able to measure students’ critical thinking levels from the lowest to the highest level of complexity.
Although there are advantages in the form of solutions to the constraints of previous research, this research also has constraints. The constraints of this research are no quiz questions in the form of learning video analysis questions.
5. Conclusions
The stages of developing blended learning content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha and Superitem have run well. The resulting blended learning content has been able to measure students’ abilities in the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. The ability of students in the cognitive domain is measured through the quiz question facility on the Kelase platform by applying the Superitem concept and adopting the Manacika concept. Students’ ability in the affective domain is measured through discussion forum facilities. The ability of students in the psychomotor domain is measured by performance tasks. The results of this research have contributed to the education sector by showing innovations in the form of learning resources based on a combination of the concept of local wisdom in Bali with technology that can be used to support the learning process in the cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains. Future work that needs to be done to overcome the obstacles in this research is to provide quiz questions in the form of video activities related to the subject matter topic.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the Directorate General of Research and Development, Ministry of Research and Technology of the Republic of Indonesia for providing the opportunity and funding for this research. This research funding was provided based on research contract No. 97 / UN48.16 / LT / 2020.
Список литературы Development of Blended Learning Content based on Tri Kaya Parisudha-superitem in Kelase Platform
- P.D. Rosalina, “The Implementation of Hindu Philosophy “Tri Kaya Parisudha” for Sustainable Tourism in Munduk Village, North Bali,” JUMPA, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 223–237, 2017.
- I.G.P.E.R. Dewi, and I.D.G.D. Suputra, “Philosophy Tri Kaya Parisudha as Moderators the Effect of Equity Sensitivity and Ethical Sensitivity on Auditor’s Ethical Behavior in Financial Audit Board of Republic Indonesia (BPK RI) Representatives of Bali Province,” International Journal of Research Publications, Vol. 10, No. 1, pp. 1–15, 2018.
- D.G.H. Divayana, “Development of ANEKA-Weighted Product Evaluation Model Based on Tri Kaya Parisudha in Computer Learning on Vocational School,” Cogent Engineering, Vol. 5, pp. 1–33, 2018.
- I.K. Ardhana, “Religious Teachings on Sustainability in the Context of Hinduism in Bali,” Istanbul Journal of Sociological Studies, Vol. 56, No. 2, pp. 21–41, 2017.
- A.A.I.P. Kusumawati, and I.W.E. Mahendra, “Health Student Readiness Following Interprofessional Education Based on Tri Kaya Parisudha,” Journal of Advanced Research in Dynamical and Control Systems, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 321–329, 2020.
- C. Wells, “The Structure of Observed Learning Outcomes (SOLO) Taxonomy Model: Howeffectiveis it?,” Journal of Initial Teacher Inquiry, Vol.1, pp.37–39, 2015.
- J. Apawu, N.A Owusu-Ansah, and P. Akayuure, “A Study on the Algebraic Working Processes of Senior High School Students in Ghana,” European Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, Vol.6, No.2, pp.62–68, 2018.
- E. Bijsterbosch, T. Béneker, W. Kuiper, and J.V.D. Schee, “Characteristics of Test Items Focusing on Meaningful Learning: A Case Study in Pre-Vocational Geography Education in the Netherlands,” European Journal of Geography, Vol.9, No.1, pp.62–79, 2018.
- A.F. Jamil, “Development of Student’s Worksheet to Analyze Student’s Algebraic Thinking Based on SOLO Taxonomy,” Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research, Vol.160, pp.119–122, 2017.
- E. Bijsterbosch, J.V.D. Schee, and W. Kuiper, “Meaningful Learning and Summative Assessment in Geography Education: An Analysis in Secondary Education in the Netherlands,” International Research in Geographical and Environmental Education, Vol.26, No. 1, pp.17–35, 2017.
- D.G.H. Divayana, “The Implementation of Blended Learning with Kelase Platform in the Learning of Assessment and Evaluation Course,” International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, Vol. 14, No. 17, pp. 114–132, 2019.
- I.M. Ardana, I.P.W. Ariawan, and D.G.H. Divayana, “Development of Decision Support System to Selection of the Blended Learning Platforms for Mathematics and ICT Learning at SMK TI Udayana,” International Journal of Advanced Research in Artificial Intelligence, Vol.5, No. 12, pp.15–18, 2016.
- N. W. Sukerti, A. Mukhadis, T.M. Kiranawati, H. Suswanto, and D. Nurhadi , “The Effect of Project-Based Learning which Integrates Tri Kaya Parisudha Concept and Emulation Ability on Students’ Comprehension and Formation of An Entrepreneurial Mindset ,” International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, Vol.8, No. 1, pp.324–343, 2019.
- E. Sudihartinih, “Facilitating Mathematical Understanding in Three-Dimensional Geometry using the SOLO Taxonomy,” ERUDIO: Journal of Educational Innovation, Vol.6, No. 1, pp.11–18, 2019.
- M.K. Maftuh, and D. Hidayat, “The Effect of Superitem Learning Model on Increasing Students Learning Achievements,” Journal of Innovative Mathematics Learning, Vol.1, No. 4, pp.367–373, 2018.
- W.H. Wu, H.Y. Kao, S.H. Wu, and C.W. Wei, “Development and Evaluation of Affective Domain Using Student’s Feedback in Entrepreneurial Massive Open Online Courses,” Frontiers in Psychology, Vol.10, pp.1–9, 2019.
- H.D. Ikawati, I.A. Majid, and Z. Anwar, “Effectiveness of the Superitem Learning Model on Students Learning Achievements,” International Journal for Educational and Vocational Studies, Vol.1, No.3, pp.184–188, 2019.
- A.A. Rahadini, and T.R. Fitriana, “Blended Learning on Listening Learning Based of Local Wisdom in the Javanese Language Education Study Program,” Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research, Vol. 397, pp.426–433, 2019.
- B.A. Hibra, L. Hakim, and T. Sudarwanto, “Development of Vlog Learning Media (Video Tutorial) on Student Materials Tax at SMK PGRI 1 Jombang,” International Journal of Educational Research Review, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 435–438, 2019.
- D.L. Wardani, I.N.S. Degeng, and A. Cholid, “Developing interactive multimedia model 4D for teaching natural science subject,” International Journal of Education and Research, Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 63–72, 2019.
- G.A.D. Sugiharni, “The Development of Interactive Instructional Media Oriented to Creative Problem Solving Model on Function Graphic Subject,” Journal of Educational Research and Evaluation, Vol. 2, No. 4, pp. 183–189, 2018.
- S.A. Sari, and Y.S. Rezeki, “The Development of An Ingenious Circuit Based on Chemo-Edutainment Learning,” International Journal of Educational Research Review, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 15–25, 2019.
- M.R.R. Razak, M. Dahong, J. Ahmad, H. Dema, and A. Mustanir, “The effect of siri’s marriage on government administration,” International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR), Vol. 42, No. 3, pp.171–184, 2018.
- N.S.K. Khader, “The Effectiveness of Blended Learning in Improving Students’ Achievement in Third Grade’s Science in Bani Kenana,” Journal of Education and Practice, Vol. 7, No. 35, pp. 109–116, 2016.
- D.I. Rahmawati, N. Priatna, and D. Juandi, “Algebraic Thinking Characteristics of Eighth Grade Junior High School Students Based on Superitem Test of SOLO Model,” IOP Conf. Series: Journal of Physics: Conf. Series, Vol. 1157, No. 4, pp. 1–7, March 2019 [International Conference on Mathematics and Science Education (ICMScE 2018), Bandung, Indonesia, p. 5, 2018].
- L.H. Lian, and W.T. Yew, “Development of an Assessment Literacy Super-item Test for Assessing Preservice Teachers’ Assessment Literacy,” International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, Vol.13, No.7, pp.870–889, 2020.


