Development of transport networks of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia)
Автор: Petr I. Tarasov
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Social Sciences. Politology. Economics
Статья в выпуске: 17, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In modern conditions exploration of the Arctic is impossible without development of transport, introduction of new technologies. The author proposes the creation of a net of transport corridors in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) on the basis of existing transport nodes, in particular the port of Tiksi, and the usage of new technologies.
Arctic, transport, transport hub, port Tiksi, technology, trailer, lightweight railway
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148319806
IDR: 148319806 | УДК: 656.02/656.6/656.2/656.5
Текст научной статьи Development of transport networks of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia)
Main transport provision of industrial and social infrastructure in Arctic currently consists of chief air and marine transport. But in conditions of expansion of production it is required a systematic organisation of connections between arctic, circumpolar territories and inner regions of the country, exploitation of arctic territories by means of development of Northern sea route (NSR) and complex use of all means of transport and creation of effectively working transport networks.
Based on multiannual researches of Northern Russia author suggests to reclaim arctic and surrounding circumpolar territories of the Sakha republic (Yakutia) by the method of creation of transport corridors on the basis of biggest ports, for example Tiksi. Transport networks (arctic hubs), which holistically combine marine, vehicular, railway, river and air transport, will effectively work for speedy exploitation of already existed and search for new mineral deposits in Russian Federation Arctic zone (RFAZ).
Use of innovation technologies on the transport, different means of transport for exploitation in severe conditions of Arctic and Northern Russia: special road-trains, «Light» railway, methods of construction of automobile beds from materials, which are produced during work on di-amondiferous and other deposits are suggested.
Demands of the Sakha Republic in development of transport networks
Development of complex transport network (hubs) in the Russian Arctic is overviewed in the context of analysis of the Sakha republic (Yakutia) demands. Mineral resources potential of the republic based on estimates of the RF Ministry of Natural Resources in 2006 is 78,4 trillion rubles. Besides deposits of hydrocarbon crude, deposits of coal with book inventory 14,3 billion tones, iron stones — 5,7 billion tones, precious, rare-earth and other metals, non-metallic natural resources, as well as deposits of fresh, mineral, thermal and industrial groundwaters are explored [1].
During semicentennial preconceptual studies in Yakutia it was founded and approved more than 1500 primary and placer kimberlite deposits, which are concentrated in Yakutia diamanti-ferous province. Its square is about 900 thousand km 2 [1]. But it is just a part of great Russian Federation Arctic zone (RFAZ), which includes land territories of Murmansk region, Nenets Autonomous Area, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Area, the Chukotka Autonomous District, urban district «Vorkuta» of the Komi republic, 5 settlements (districts) of the Sakha republic (Yakutia), Norilsk and two districts of Krasnoyarsk Krai and seven municipal districts of Arkhangelsk region 1 . Nowadays in RFAZ one of the most industrially developed territories is considered to be Western Yakutia, where known reserves of kimberlite deposits spread up to the Arctic Ocean (pic. 1). In the plan of transport networks’ construction (Arctic hubs) for exploitation of new territories in Western Yakutia one of the most interesting is considered to be port Tiksi, situated on the shore of similarly named bay near the Lena river estuary, founded 1933. It is considered to be the main base of supply and provision of all the marine cabotage trade in the eastern part of Russian Arctic. Mainly food, manufactures and equipment are imported there. The only current problem of the port is shallowness; it could take only ships with draft not more than five meters. That’s why construction of different ways of carrying ships over it is important. 1987 port capacity was 850 thousand tones, to the year 2011 it reduced to 55 thousand tones. At year-end 2012 capacity of the Tiksi branch — FSI «PFM Vostochny» — arranged 358,4 thousand tones [3].
Currently Tiksi port, according to the author’s point of view, is considered to be mostly ready for exploitation of Arctic and surrounding northern territories of Yakutia with its finished infrastructure and rather large cargo turn-over. It is recommended to begin implementation of plans in construction of transport corridors in the northern zone of the Russian Federation from it, as being the most devel- oped metallurgical and transport complex for exploitation and transportation of diamondiferous de-
posits, especially in Western Yakutia.
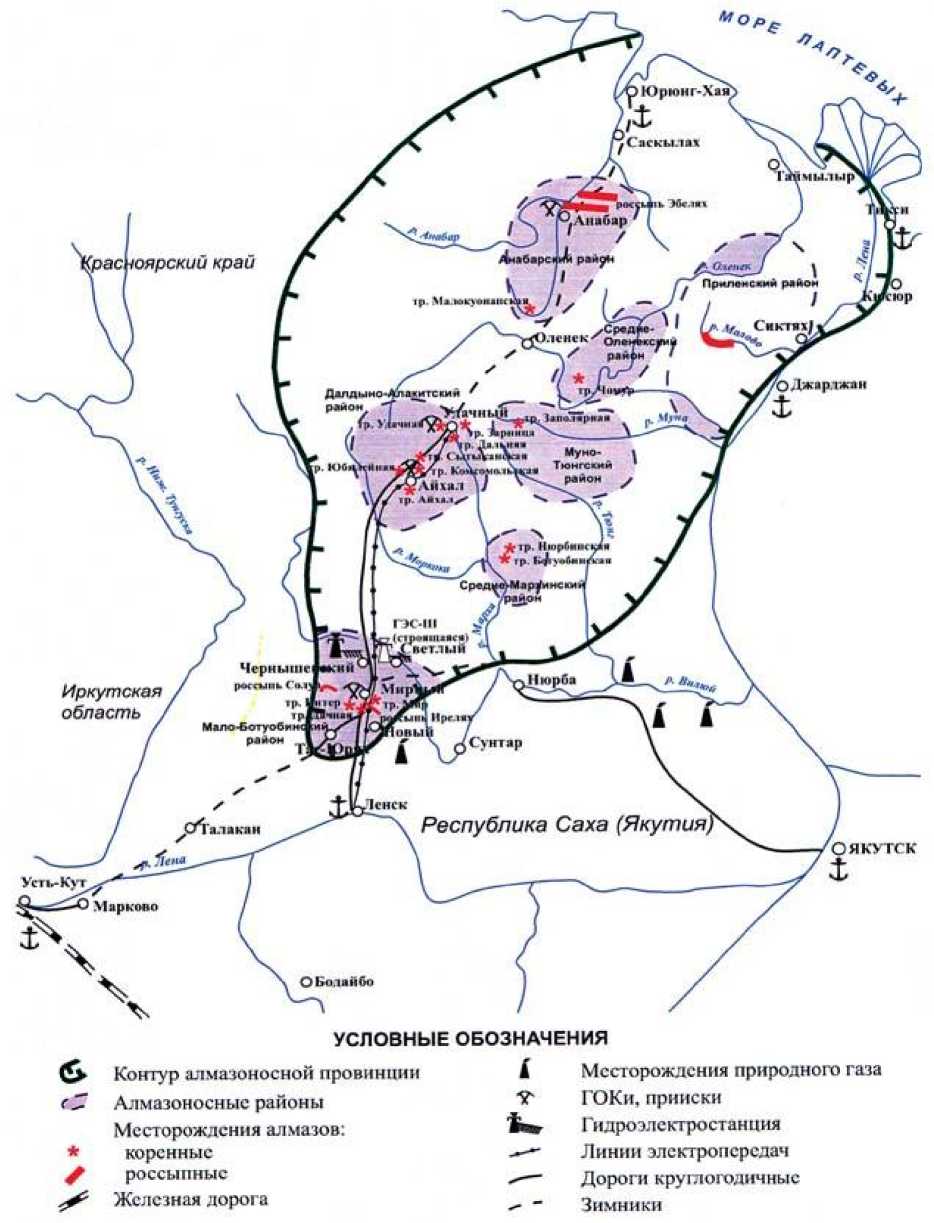
Pic. 1. Map of Western Yakutia deposits
Also a good variant is considered to be use of Yurung-Hai settlement, which nowadays has smaller cargo turn-over, but more comfortable location in comparison with Tiksi. As well as there is no necessity to build the bridge over the Lena river. Creation of modern transport networks corresponds with the needs of economic development.
Use of new technologies on transport in conditions of the Arctic
It is important to understand clearly that for full use of recourse potential of northern territories a complex implementation of new technologies in different branches is necessary. Specifics of works on the territory of high north predetermine the necessity of non-routine decisions’ adoption in the sphere of natural resources mining. But speaking about the process of transporting of mined rocks the approach was always traditional. Important issues were and are always high mobility of technique, rather cheap exploitation, possibility of fast release for use and dependable service in conditions of low temperatures. These arrangements determine wide use of automobile and probably for further extension special type of railway transport. It is worth noticing that the main problem of pit-run technique in conditions of kimberlite pits of Yakutia considers to be the fact, that during transporting of minerals there are absolutely different conditions of transport facilities exploitation (head fall of roads in southern pits up to 10%, works on weak soils in northern deposits in conditions of arctic zone with transportation distance from 10 to 150 km with gradient up to 2—3%). After performing number of economic calculations it was founded that the greatest economic effect could be achieved by the use of multilink trains in automobile or railway order [1]. Works on search and development of specialized pit transport vehicles for conditions of the North together with URAN Institute of Mining Affairs are carried out by National academy of sciences in Belorussia, JSC «Belorussian automobile factory», Russian group of diamond-mining companies «ALROSA» and others.
At the initial stage during the period of prospection, when there are no constructed roads, it is possible to use air-cushion transport. Nowadays commercial prototypes ready for batch production are constructed: «Corsar» (3 passenger seats, capacity — 300 kg), ASVP «SK-20» (10 passenger seats, capacity — 1000 kg). Efficiency of usage of suggested ASVP is 1 times cheaper than the helicopter technics. Project of air-cushion cargo platforms construction with capacity 30 (GSPVP-30 with 6 seats for passengers) and 60 tones (GSPVP-60 — 12 passenger seats). Amphibian off roaders «SK-10» are produced by ZAO «Transecology» together with LLC «Stroykomposit».
On subsoils with low carrying power (bog, virgin snow, lack of road, rough wooded country) snow and swamp-going vehicles found its use. Constructions of both Russian and foreign wheeled and tracked running gears of famous enterprises which create swamp-going vehicles, such as: JSC
Арктика и Север. 2014. № 17 «Zavolzhsky factory of caterpillar tractors» (ZFCT), JSC Engineering company «Vityaz» (Ishimbay), Sweden company Hägglunds Vehicles, LLC «Altaytransmash-service», Ekaterinburg factory of specialized vehicles EFCM «Continent». Their production is available during carrying out of construction, installation and enablement works, and also as a supporting technics for providing of enterprises’ functioning. Different variants of vehicles’ performance are possible: for conveyance of persons; flatbed truck; search-and-rescue; fire trier module; driller; adjustable platform-elevator; craneboom equipment; medical module; location of technical aid; transporter for carriage of long-blade indivisible loads; platform for digger, cisterns and location of other technological equipment of various profiles [1].
Problem of poorly marketable removed kimberlite pits, situated in the northern part of Western Yakutia is that it is not of economic benefit to construct dressing plants near deposits, and the best way in such conditions is considered to be organization of delivery of crude ore over the distance 10-200 km to the place of its processing. In this regard creation of technological transport arteries from automobile and railway roads is suggested, which would penetrate the whole territory of Yakutia diamantiferous province and at the same moment could become the basis of Yakutia transportation corridor. It could let to connect for the West Yakutia region all diamantiferous and other enterprises, and for Russia through Tiksi to connect land part with Northern sea route; through Ust-Kut with western part of Russia; through Yakutsk with eastern part of Russia up to the Pacific Ocean. By that it is important to take into account that nowadays construction of Federal route Ust-Kut—Mirny is conducted and construction of railway Tommot—Yakutsk, and then Yakutsk—Magadan is being finishing.
It is recommended on automobile roads to introduce special multielement road-trains of long length and correspondingly of high capacity, developed by NAS of Belorussia. Currently it is one of the most promising directions of development of cargo, including pit and auto technics. Developers and operating organizations notice its high efficiency during transportation of cargoes in conditions of the RF Arctic zone. In work «Explanation of ways of transport vehicles development for exploitation of Russian northern territories» [1] description of this mean of transport is given and following main advantages of all-wheel drive multielement road-trains are pointed, which were developed by NAS of Belorussia together with URAN Institute of Mining Affairs in comparison with single vehicles with the same capacity:
-
a) road-train has productivity 1,5-2 times higher, and production costs of carriage during its appliance reduces over 20-35%;
-
b) increase of capacity of road-train and its productivity in comparison with single vehicles is not connected with overloading;
-
c) road-train is cheaper;
-
d) for last of trail cars and semitrailers less inputs are demanded for construction of support of repair-sponsor base and storage areas in inter-time;
-
e) motor drown park demands less inputs for repair and service support of smaller depreciation;
-
f) higher productivity of road-trains determine smaller park;
-
g) road-trains effective range;
-
h) technological motor roads with low intensity or lack of road public traffic;
-
i) motor roads with satisfactory condition of roadway;
-
j) by considerable distance of carriage (20—200 km);
-
k) by wide annual output of carriage.
Most significantly is that during work on weak soils transport axis pressure on ground is important. Within this framework use of road-trains is more preferable than of hard dumpers with the same capacity. Because during exploitation of developed road-train turning is not demanded, it means that shuttle principle is provided, its length is not considered to be a serious problem. It is worth noticing that in Arctic conditions transport vehicles are used in different conditions: auto run in pit under definite gradient changes for aclinal after running from it. In different parts different engine out-of-work is needed.
More fully-featured exploitation of northern territories is possible second-stage during construction and exploitation of railways. But use of «light» railways is more preferable. It is determined by the fact that during exploitation of usual railway in Arctic conditions it is not always possible to provide cargo turn-over, which could use it effectively, and reloading from one mean of transport to another is problematic. In suggested variant of «light» railway it is thought to use container type of carriage. «Lightweight» type supposes construction of railway based on automobile, which is built according to distance of transportation and volume of carriage. Its implementation is possible according to distance of transportation in one or two direction variant with all technological structures but in easier way. Construction of different structures and transport vehicles for normal railway could be defer to a later time when needed or it could not be needed during exploitation on temporary shares to definite deposits, where road-trains could be used.
Availability of railways to certain pits is necessary only during the period of its exploitation. And then, because of small ore reserves and lack of other deposits in this direction ways could be dismantled and moved to another places, thus to any other objects. Cost of tracks construction for special «lightweight» railway will be significantly lower because of reduces of materials consumption and level of effort (rails, cross-ties, hight of roadbed, etc.). The suggested form let to use main advantages of earlier used light narrow-gage railroads (rate of construction, effectiveness) and to liquidate its main disadvantage — necessity of reloading when run-off from one narrow gage line to normal with width 1520 mm.
«Lightweight» railway involves use of lightweight rolling equipment (wagons and locomotives). Speaking about use of wagons the solution could be use of classic and lightweight highsided wagons, which are used on a daily basis in public and non-public tracks by various enterprises. As a lightweight locomotive traction could be used locomotive TGM4BL (mechanical-hydraulic drive locomotive with 610 kilowatt) with weight 68 tones or superlight TEM31M (electric motor drive locomotive with 420 kilowatt) with weight just 46 tones. The above overviewed locomotives are proposed for switching and export operations and are mostly used by industrial enterprises. For moving of trains through «arteries» it is viable to use electric propulsion locomotive TEM31M, which efficiency factor in comparison with allhydraulic drive at the speed of 10 km/h is significantly higher. For moving of trains over short distances (formation of trains, export works near pits) more proper is TGM4BL.
Use of container principle of transport arteries could let to provide its exploitation on all the transport vehicles — automobile, railway, air, river and sea. Containers are of different capacity, which could allow the customer to choose the most proper variant for him. In our variant it is 20-25 tones. To the main advantages of container carriage we identify:
-
I. Flexibility of containers. Standard sizes of containers let to transport the carriage independent from bulks, sizes and weight by practically each means of transport — railway, marine or air.
-
II. Safety of cargo. Container is a kind of safe, which guarantees safety of inlying cargo. Inherent vise during such carriage is minimal.
-
III. Speed and convenience. Cargo carriage in containers — is a fast and comfortable way to transport cargo over long distances.
-
IV. Cost effectiveness. At the cost of the fact that containers could be loaded with great amount of cargo, filling the whole container, expenses for carriage are saved significantly. In this turn reduction of transport and logistic expenses will increase profitability of cargo, and it could lead to profit markup.
On picture 2 you can see the suggested network of «lightweight» railways, which connects the biggest populated localities of Western Yakutia: Yakutsk—Mirny—Ust—Kut—Udachniy—Tiksi (or Yurung-Haiya) and first of all Mirny—Udachniy. When anthropogenic terrain variation hydrological regime of grounds is troubled and bog formation of contiguous to receiving pits terri-
tories takes place. Except bog formation we can notice mechanic move of sole clay fraction, which
appeared on the spot of soil by water and air flows.
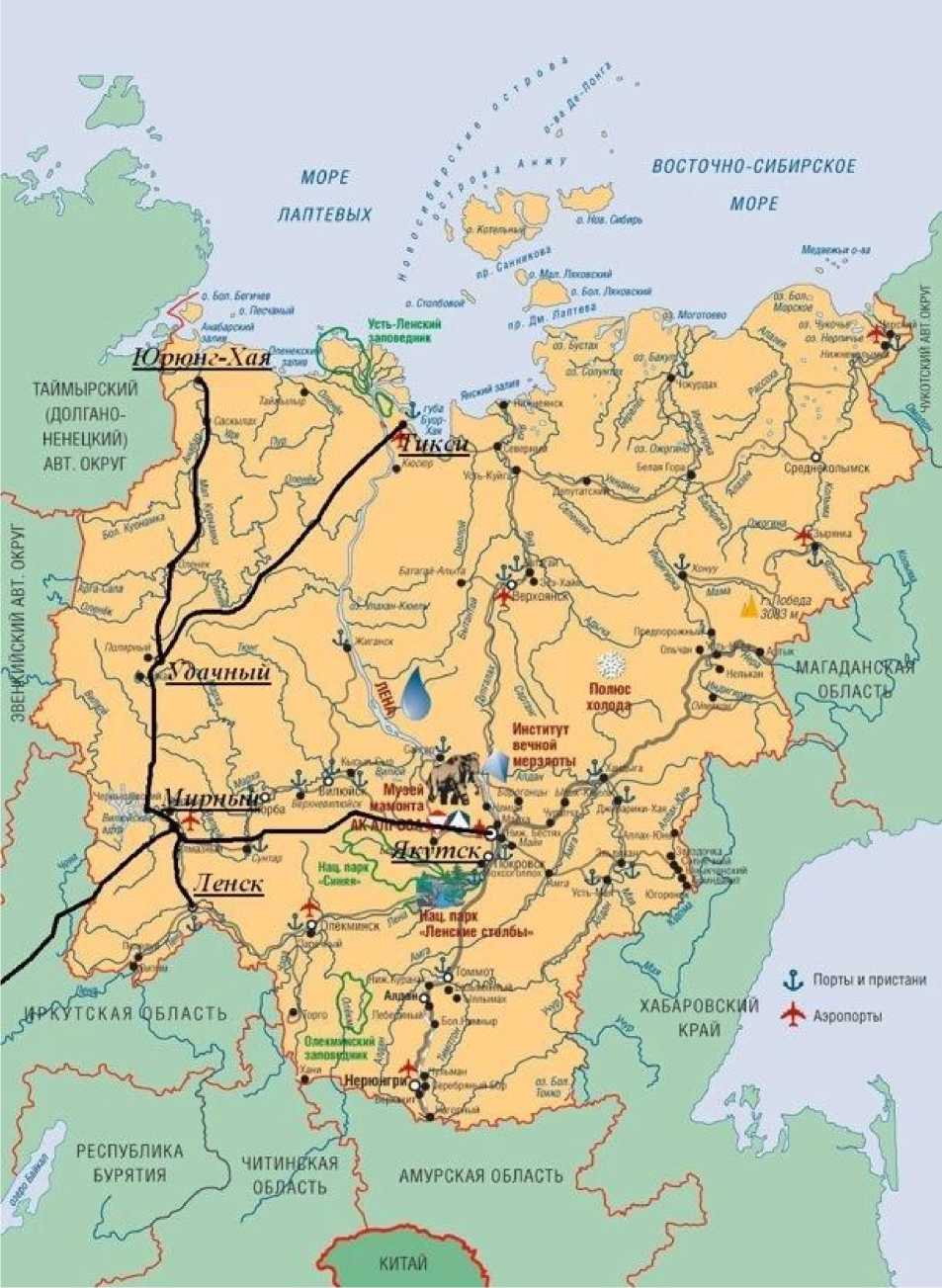
Pic. 2. Suggested network of «lightweight» railways
Comprising wide range of macro- and micro-elements, high concentrations of toxicant salts and substrates of refuses negatively influence the state of natural soil and vegetation cover of boarding with refuses territories, forming wide bands of «dead forest», which edges refuse piles (Pic. 3) [4].
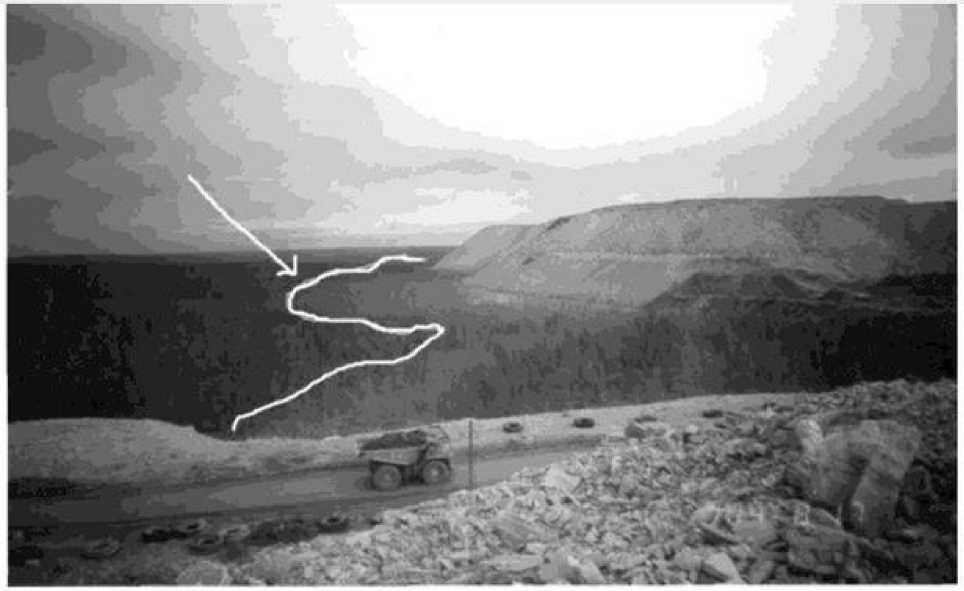

Pic. 3. «Dead forest», formed near Western refuse of Udachninsk mining and concentration complex (line shows border of «dead forest»)
As a result of pits’ composition of rocks researches it was founded that materials, which were recovered in between during development of diamondiferous deposits of Western Yakutia, based in refuses and with volume over hundreds of millions m 3 , are suitable for use during construction of roads. For kimberlite formations wide variant composition is characteristic, which eventually strongly influences during both projecting and exploitation of the object [5] (pic. 4). There is no strong border between different layers in refuse, but the common structure of kimberlite allows to use it for creation of foundation bed of roads and other objects, as it doesn’t contradict to construction standards and regulations 2.05.07-91 «Industrial vehicles» and industry building code 84-89 «Research, designing and construction of automobile roads in regions of perpetually frozen soil». This method not only positively influences from the economic point of view, but also leads to reduction of negative influence of works on environment. In future this method could fully exclude creation of refuses. By that, material, removed from the pit will be carried by specialized road-trains of Belorussian
RAS directly to the constructed part of the road. But hereby, machine builders must additionally develop and implement complexes for dismantling of refuses, crushing of oversize, as well as special transport and car loading facilities.
Карьер
■190
--210 м
310 м
Литологическии разрез
Породы
-100
Гапогеи но- карбонат пая толща
-500
-630 м
Битуминозные доломиты
-700
Галотенно-карбонатовые отложения
Нефтеносные отложения
-900
Доломиты с прослоями аргиллитов
-1500
Аргиллиты с прослоями доломитов
-1700 l
Граниты крупнозернистые
Переслаивание солей с гинс-ангидритами
Доломиты, известняки, гипс-аигидриты
Долео иты
Мергели, доломиты, глинистые известняки ________________
Апевритистые мергели, известковистые алевролиты. глинистые доломиты Чередование доломитов и ангидритов
410 м*
1 1
Доломиты трещиноватые нефтвнасыщенныв Аргиллиты, доломиты
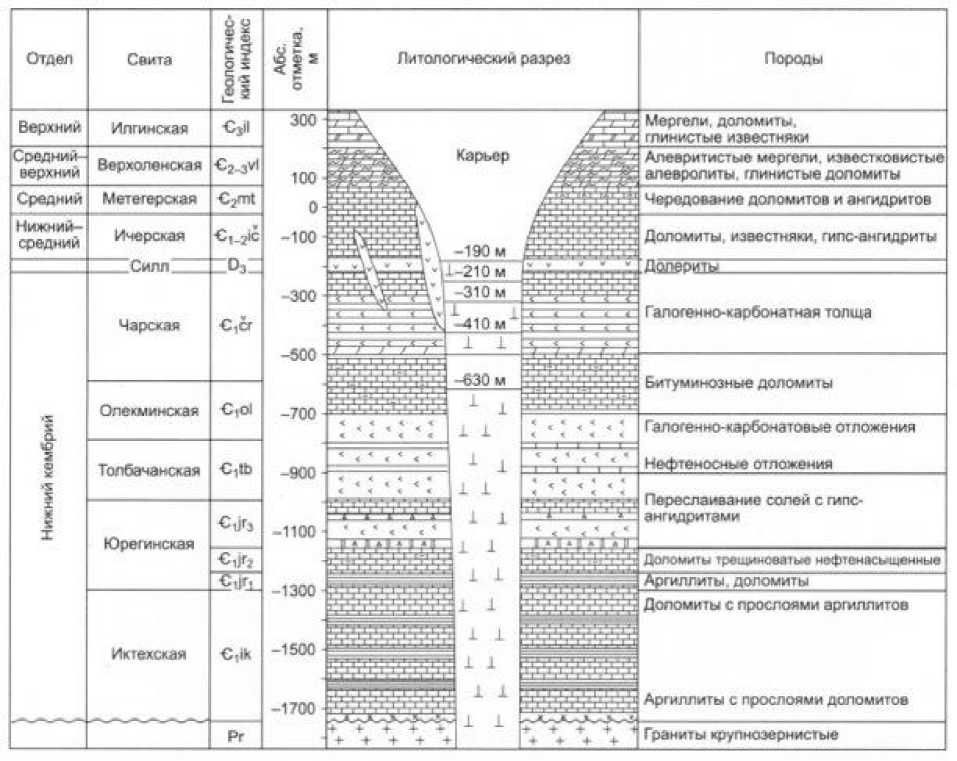
Pic. 4. Schematic geological sheet of Mir deposit
Author suggests creation of transport networks on the base of already existed settlements
|
Отдел |
Свита |
и II |
|
Верхний |
Илгинсхая |
€,11 |
|
Средний— верхний |
Верхоленская |
€г-з*1 |
|
Средний |
Мететерская |
С/nt |
|
Нижний-средний |
Ичерская |
Ci-zic |
|
Силл |
D3 |
|
|
X к S ■X к I |
Чарская |
€,« |
|
Олекминская |
€,ol |
|
|
Толбача некая |
€i№ |
|
|
Юрегинская |
€ijr, |
|
|
€,jr2 |
||
|
€ijrj_ |
||
|
Иктехская |
||
-1300
in the Northern territories, which would provide markup of the region’s raw materials source and additional workplaces. Potential partners of this program could be following establishments: Russian group of diamond-mining companies «ALROSA», JSC «Russian railroads», JSC «Corporation of Middle Urals development», JSC Corporation «Ural Industrial — Ural Polar», JSC «Belorussian automobile factory», URAN Institute of Mining Affairs, Federal Government Budgetary Science RAS Institute of Comprehensive Exploitation of Mineral Resources, National Belorussian Academy of Sciences, Ural State University of Lines of Communications, JSC «Zavolzhsky Crawler Vehicle Plant», JSC Engineering company «Vityaz» (Ishimbay), LLC «Altaytransmash-Service», Ekaterinburg factory of specialized machines «Continent» and others.
Rigth with the first transport network in Tiksi, which will connect in future marine, railway, automobile, river and air means of transport, which possesses nowadays the most favorable conditions, including fact, that there will be created and implemented special road-trains, «lightweight» railway, methods of construction of automobile beds from materials, winning in between during works on diamondiferous deposits, practise will be attained and mining-industrial equipment, which could let to continue research and use of Russian Federation Arctic territories. During further work it is necessary to make economic assessment of suggested projects and determine volume of needed investments and payback period.
Conclusion
In such a way, the idea of multielement transport use on weak soils of remoted kimberlite deposits correlates with necessity in the RF of transport corridors creation which will allow to connect the Northern sea route with continent transport network up to main Trans-Siberian railway and is based on a number of factors speaking about the Sakha Republic (Yakutia).
-
I. Necessity of development of remote poor-commercial kimberlite and other deposits, which are situated in Western Yakutia up to the Arctic Ocean.
-
II. Necessity of transportation of mined rock from pits, which are situated in the Arctic to working enriching factories.
-
III. Demands in technological roads for pits under definite succession of their construction in Arctic direction, which could possess the base for creation of Yakutia transport corridor, which connects the Northern sea route with main Trans-Siberian railway (there is no the same possible opportunity in the RF).
-
IV. Presence of pit heaps with great volumes of mined rocks, which are situated near enriching factories and which can be used for construction of road bed of automobile and railway tracks.
-
V. Possibility to transport mined rocks from pit heaps with loading of road-trains backwards from enriching factories to pits, in other words to any place where construction of road bed takes place.
-
VI. Development of drilling-and-blasting as well as crushing-and-sorting complexes for pit heaps’ dismantlement and getting from them ballasts of different fraction.
-
VII. Use of multielement road-trains of the Belorussian Republic, which have the opportunity to move wheels within wheels and facility which prevents the possibility of «sto-wage» of road-train.
-
VIII. Presence in the Western Yakutia of metallurgical complex JSC «ALROSA», which is situated nearest in Russia to the Arctic zone, and presence of needful deposits up to the Arctic Ocean, which are available for exploitation on behalf of JSC «ALROSA» and Russia.
-
IX. Possibility to use state and private investments as well as state-private partnership.
-
X. Substantiation, development and possible production of special waggons by JSC «Be-lAz», as well as presence in Arctic conditions and surrounding territories of the RF exploitation of «lightweight» railway with organizing of container carriage.
Nowadays northern regions of our country are considered to be underexplored in comparison with other territories in the RF. Specifics of works demand for changes in traditional ap- proaches in different challenges. And just complex use of world scientists’ achievements as well as positive practice of foreign countries on implementation of new methods and technologies could become perfect allies in problem of the Far North exploitation.
Список литературы Development of transport networks of the Sakha Republic (Yakutia)
- Tarasov P.I. Obosnovaniye putei razvitiya transportnyh sredstv dlya osvoyeniya severnyh territoiy Rossii [Justification of ways of transport vehicles development for exploitation of Russian northern territories]. Problemy kariernogo transport: materially XII Mezhdunarodnoy nauchno-prakticheskoy konferencii 1—4 oktyabrya 2013, IGD UrO RAN [Problems of pits’ transport: materials of the XIIth International science-practical conference, October 1—4th 2014, URAN Institute of Mining]. Ekaterinburg, URAN, 2013 (in Russian).
- Tarasov P.I., Zhuravlev A.G., Cherepanov V.A., Isakov M.V., Balanchuk V.R., Akishev A.V., Babaskin S.L. Problemy magistral’nogo transportirovaniya rusy ot udalennyh kimberlitovyh mestorozhdeniy [Problems of magistral transportation of ore from kimberlite deposits]. Problemy kariernogo transport: materially XII Mezhdunarodnoy nauchno-prakticheskoy konferencii 1—4 oktyabrya 2013 g., IGD UrO RAN [Problems of pits’ transport: materials of the XIIth International science-practical conference, October,1—4th 2014, URAN Institute of Mining]. Ekaterinburg, URAN, 2013 (in Russian).
- Razvitiye Arktiki i pripolyarnyh regionov [Development of Arctic and circumpolar regions]. Morskiya informacionno-upravlyayushchiye sistemy: nauchno-tehnicheskiy zhurnal [Marine information-control systems: science-technical magazine. 2014, no. 2.
- Danilov P.P., Legosayev Y.B., Savvinov T.N. Tehnogenniye landshafty i ih vliyaniye na estesstvenniy pochvenniy pokrov Zapadnoy Yakutii [Technogenic landscapes and their influence on natural soil covering of Western Yakutia]. Vestnik Severo-vostochnogo federal’nogo universiteta named after M.K.Ammosov, 2005, no 3, volume 2.
- Kolganov V.F. Korenniye mestorozhdeniya almazov Zapodnoy Yakutii [Primary deposits of rough diamonds on Western Yakutia]. Spravochnoye posobiye AK «ALROSA»; Institut «Yakitniproalmaz» [Resourse book, JSC «ALROSA», Institute «Yakutniproalmaz»]. Novosibirsk, Akademicheskoye publ., 2011, 215 p.


