Динамика мнений о мерах профилактики и лечения инфекций, передающихся половым путем, на фоне пандемии коронавируса
Автор: Тимошилов В.И., Полякова К.В., Бреусов А.В., Писклаков С.В.
Журнал: Саратовский научно-медицинский журнал @ssmj
Рубрика: Общественное здоровье и здравоохранение
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.18, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Цель: анализ изменения мнений лиц молодого возраста о мерах профилактики и лечения инфекций, передающихся половым путем (ИППП), на фоне пандемии коронавируса по сравнению с допандемийным периодом. Материал и методы. Программа исследования основана на сопоставлении данных социологического опроса 400 респондентов 16-21 года в 2021 г. и анализа 838 анкет участников аналогичного исследования 2017 г того же возраста. Метод исследования - социологический (анкетирование). Использована авторская анкета, состоящая из 46 вопросов, объединенных в пять блоков: самооценка актуальности проблемы ИППП, вероятность риска заражения, готовность к прохождению профилактических скрининговых обследований, предпочитаемые направления обращения за помощью при возникновении симптомов ИППП, согласие на обследование и лечение совместно с половым партнером. По полу распределение было следующим: в 2017 г. женщин - 51% (л=427), мужчин - 49% (л=411); в 2021 г. - 52% (п=208) и 48% (л=192). В обработке и представлении данных использованы экстенсивные показатели, сравниваемые с оценкой значимости различий по f-критерию Стьюдента. Результаты. В 2021 г. отмечен рост заинтересованности молодежи в прохождении скрининговых обследований (79,5 против 63% в 2017 г., р=0,006) и обращении за медицинской помощью (93,5 против 89,5%, р=0,007), однако возросло число случаев сокрытия состояния здоровья от партнера (с 8,3 до 32,2%, р=0,003). Заключение. Проведенное исследование выявило изменение мнений респондентов в отношении ИППП в период пандемии, заключающееся в возрастании понимания необходимости регулярных обследований, обращения за медицинской помощью при появлении симптомов заболевания, но при этом отмечено снижение чувства ответственности за здоровье своего партнера.
Инфекции, передающиеся половым путем, лица молодого возраста, пандемия коронавирусной инфекции
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149141132
IDR: 149141132 | УДК: 614.2
Текст научной статьи Динамика мнений о мерах профилактики и лечения инфекций, передающихся половым путем, на фоне пандемии коронавируса
-
1Введение. Профилактика ИППП строится преимущественно как работа с молодежью. Это связано с тем, что лица в возрасте до 35 лет преобладают в возрастной структуре вновь выявляемых случаев заболеваний данной категории, и для этой возрастной группы актуальны большинство управляемых факторов риска распространения сексуально-трансмиссивных инфекций [1–3]. Большая работа по изучению литературных данных и экспертная оценка факторов риска и их свойств показали, что ключевое влияние на стиль половой жизни, определяющий эпидемиологические процессы ИППП, оказывают модифицируемые факторы общественного мнения и социального самочувствия [4–6].
На фоне пандемии коронавирусной инфекции в 2020–2021 гг. произошли существенные изменения в государственной политике, общественной жизни и социальном самочувствии населения, которые рядом авторов уже охарактеризованы как беспрецедентные [7]. Ограничения на проведение массовых мероприятий и перевод учебных заведений на дистанционный режим работы существенно снизили потенциал традиционного медико-санитарного просвещения молодежи в организованных коллективах [8]. На фоне неизбежного акцента на коронавирусной тематике в работе официальных средств массовой информации возросла роль неформального интернет-сообщества в формировании общественного мнения по вопросам здоровья в целом [9]. Между тем разными авторами приводятся противоположные выводы о том, какие изменения произошли в отношении населения к проблемам общественного здоровья и предпосылках их формирования. В числе позитивных перемен отмечаются повышение восприятия заболеваний как общественной, а не личной проблемы [10], возрастающее внимание к своему здоровью и его ценности [11], увеличение интереса к медицинской информации, уважения и доверия к врачам [12], сплочение определенной части населения вокруг государственных структур и активизация волонтерской деятельности в сфере охраны здоровья [13, 14]. Развитие таких установок всегда рассматривалось в качестве цели профилактики всех заболеваний.
В то же время в других работах акцентировано внимание на развитии прямо противоположных течений, обозначенных в виде факторов риска, снижающих эффективность профилактической работы. Отмечается, что внимание людей к своему здоровью проявляется в основном в отношении симптомов коронавируса [15]. Под влиянием масштабных ограничительных мер и их последствий для экономики и социальной сферы нарастают проявления недовольства официальными государственными институтами, включая систему здравоохранения, а многообразие источников «альтернативной» информации в социальных сетях активизирует медицинское диссидентство [9, 16, 17].
Сосуществование противоположных изменений общественного мнения отмечено не только в России, но и за рубежом, в том числе по итогам исследований прошлых, менее масштабных эпидемий и иных социальных потрясений [16, 18, 19].
Литературные данные позволяют сделать вывод о существенной трансформации восприятия медико-социальных проблем в общественном сознании,
которое неизбежно коснулось знаний и установок о профилактике ИППП. В ранее проведенном исследовании профилактика ИППП оценивалась нами как работа, направленная на формирование объективного представления о глобальном риске инфицирования для всех живущих половой жизнью, установок на прохождение скрининговых обследований, своевременное обращение за врачебной помощью и мотивацию к диагностике и лечению полового партнера [3, 6].
Цель — анализ изменения мнений лиц молодого возраста о мерах профилактики и лечения инфекций, передающихся половым путем, на фоне пандемии коронавируса по сравнению с допандемийным периодом.
Материал и методы . Программа исследования основана на сопоставлении данных социологического опроса 400 респондентов 16–21 года в 2021 г. и выборки из 838 анкет участников аналогичного исследования 2017 г. Изученная выборочная совокупность в 2021 г. сформирована методом случайной выборки 100 респондентов из числа школьников старших классов естественно-научного профиля, 100 обучающихся в школах в классах гуманитарного и физико-математического профиля, 100 студентов медицинских и биологических специальностей высших учебных заведений и 100 студентов вузов иного профиля обучения. Данные за 2017 г. получены путем выбора 838 анкет респондентов 16–21 года из базы проведенного нами же в 2017 г. аналогичного исследования. В данной выборке также соблюден принцип равного представительства возрастных, гендерных, социальных и профессиональных групп. Средний возраст опрошенных лиц составил 18±0,83 года. По полу распределение было следующим: в 2017 г. женщин 51% ( n =427), мужчин — 49% ( n =411); в 2021 г. — 52% ( n =208) и 48% ( n =192) соответственно, что исходя из данных таблицы В. И. Паниотто можно считать репрезентативной выборкой. В работе использовались следующие методы: библиографический, аналитический, математико-статистический, социологический (анкетирование). Анкетирование проводилось по разработанной авторской анкете, состоящей из 46 закрытых вопросов, объединенных в пять основных блоков: самооценка актуальности проблемы ИППП и риска заражения, готовности к прохождению скрининговых обследований с профилактической целью, направлений предполагаемых обращений за помощью в случае возникновения симптомов ИППП и намерения мотивировать партнера к совместному обследованию и лечению.
Сбор, систематизация и обработка исходной информации осуществлялись в приложении Microsoft Excel 2016. Статистический анализ проводился с использованием программы PASW (Predictive Analytics SoftWare) Statistics 22. В обработке и представлении данных использованы экстенсивные показатели, сравниваемые с оценкой значимости различий по t -критерию Стьюдента, поскольку по каждой из изучаемых позиций рассматривалось альтернативное распределение качественного признака и производилась оценка достоверности разности экстенсивных показателей их распространенности. Рассчитанные значения t -критерия Стьюдента оценивались путем сравнения с табличными значениями, при этом различия показателей считались статистически достоверными при уровне значимости p <0,05. Доверительный интервал для средних величин высчитывался с уровнем достоверности не менее 0,95.
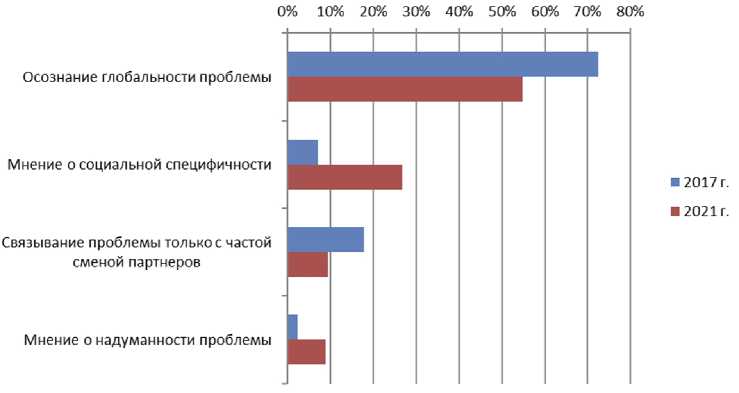
Рис. 1. Изменения в самооценке лицами молодого возраста актуальности проблемы инфекций, передающихся половым путем, %
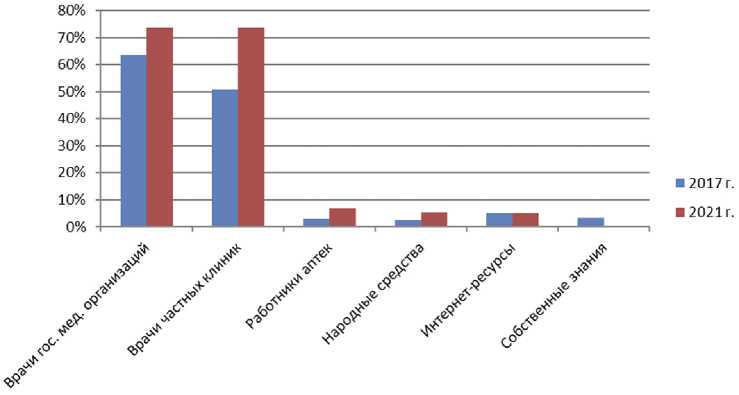
Рис. 2. Предпочтительные направления обращений респондентов за медицинской помощью при возникновении инфекций, передающихся половым путем, %
Результаты. В качестве объективной самооценки эпидемиологической ситуации с ИППП и риска заражения расценивалось осознание подверженности риску инфицирования всех живущих половой жизнью. Такую позицию в опросе 2021 г. указали 54,8% анкетированных. По сравнению с 72,4% в 2017 г., доля молодых людей, имеющих такую объективную позицию, значительно сократилась ( p =0,005). Вместе с тем в 2021 г. достоверно возросла доля лиц, придерживающихся двух видов заблуждений: мнения о социальной специфичности этих заболеваний — подверженности им только неблагополучных социальных слоев общества (26,8% в 2021 г. против 7,2% в 2017 г., p =0,003) и явно диссидентского течения с высказыванием мнения о надуманности проблемы заболеваний, передающихся половым путем (в 2021 г. доля таких респондентов составила 9 против 2,5% в 2017 г. ( p =0,008). При этом в 2021 г. значительно сократился удельный вес опрошенных лиц, связывающих риск половой инфекции исключительно с частой сменой партнеров (9,5% в 2021 г. против 17,8% в 2017 г., p =0,008) (рис. 1).
В 2021 г. значительно возросла готовность молодежи к прохождению скрининговых обследований на половые инфекции с профилактической целью. Доля респондентов, которые высказали на согласие проходить диагностику с профилактической целью, составила 79,5 против 63% в 2017 г. ( p =0,006).
В плане направленности возможных обращений за помощью в случае возникновения признаков половой инфекции наибольшая доля участников обоих исследований (2017 и 2021 гг.) отдавала предпочтение официальной медицине: в 2017 г. доля лиц, готовых обращаться за врачебной помощью, составляла 89,5%; в 2021 г. она достоверно увеличилась до 93,5% ( p =0,007). Наиболее значительный рост доверия произошел в отношении специалистов частной системы здравоохранения: с 50,7% в 2017 г. до 73,8% в 2021 г. ( p =0,004); удельный вес заинтересованных в обращении в государственную дерматовенерологическую службу также вырос с 63,5 до 73,8% ( p =0,009) (рис. 2). В результате уровни доверия к специалистам государственной и частной систем здравоохранения сравнялись, и к тому же возросла доля молодых людей, для которых либо выбор
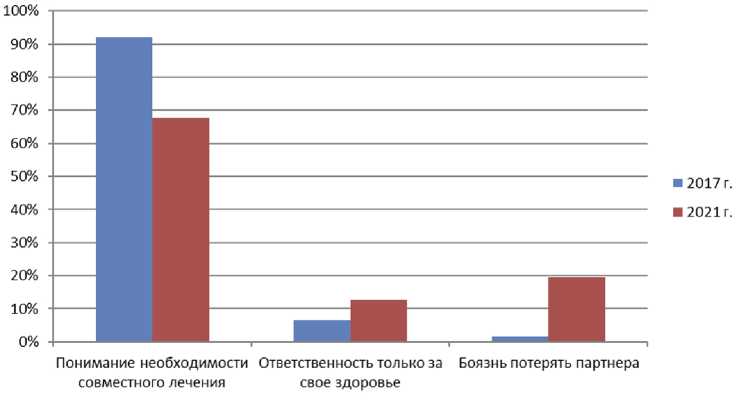
Рис. 3. Распространенность среди лиц молодого возраста установки на обследование и лечение вместе с партнером, %
медицинской организации не принципиален, либо они настроены получать консультации и проходить лечебные мероприятия в нескольких учреждениях: в 2017 г. о намерении обращаться как в государственные, так и в частные медицинские организации выразили желание 24,7% участников исследования, а в 2021 г. их доля возросла до 54% ( p =0,002).
Вместе с ростом доверия к врачам возрос уровень доверия и к фармацевтическим работникам: с 3% в 2017 г. до 6,8% в 2021 г., но доля таких респондентов все равно остается небольшой на общем фоне.
Распространенность установок на самолечение, как без обращения к врачам, так и в сочетании с врачебными консультациями, возросла незначительно: с 11% в 2017 г. до 15% в 2021 г. ( p =0,068). Статистически значимо возрос интерес к использованию народных средств (с 2,4 до 5,3%, p =0,048), напротив, на собственные знания, в том числе получаемые в ходе профессионального обучения, молодые люди стали полагаться реже (всего 0,5 против 3,3% в 2017 г., p =0,009).
ИППП требуют лечения обоих партнеров, и в 2017 г. делиться проблемой и обращаться за помощью совместно были готовы 91,9% респондентов. В 2021 г. распространенность этой крайне важной установки снизилась до 67,8% ( p =0,024). При этом возросла распространенность эгоистической установки — восприятия здоровья как личного дела каждого — с 6,6% в 2017 г. до 12,8% в 2021 г. ( p =0,009), но в еще большей степени увеличилась доля лиц, которые боятся разрушения отношений в паре из-за заболевания (с 1,7% в 2017 г. до 19,5% в 2021 г., p =0,004) (рис. 3).
Обсуждение. Преобладание в средствах массовой информации тематики о COVID-19, сокращение возможностей для проведения профилактической работы в коллективах, выраженная переориентация всей санитарно-просветительной работы на обеспечение прививочной кампании — меры и явления в период пандемии вынужденные, так как ее масштабы и уже имеющиеся последствия беспрецедентны. В результате этого сегодня мы видим неблагоприятные последствия такой переориентации, проявляющиеся в снижении информированности молодых людей о различных аспектах проблемы ИППП, сокращении доли лиц, объективно оценивающих возмож- ность риска инфицирования при половых контактах, что может быть связано с уверенностью молодых людей в надежности имеющегося арсенала средств контрацепции и регулярном их использовании. Сокращение числа тех, кто видит в сексуально-трансмиссивных заболеваниях глобальную проблему, сопровождается большей, чем ранее, распространенностью убеждений о подверженности этим болезням неблагополучных слоев общества, причем вне связи с числом половых партнеров как таковым. Параллельно растет и доля тех, кто придерживается убеждений о преувеличенности проблемы ИППП — такая позиция стала наблюдаться почти у 10% интервьюированных, тогда как в допандемийный период этот показатель не превышал 3%.
Систематизируя эти данные, можно сделать вывод, что среди молодых людей сегодня распространена недооценка проблемы, исключение для себя риска заражения, а это — индикатор неблагополучия, который отмечается как неблагоприятный фактор для всех социально обусловленных заболеваний. Такая тенденция — прямое указание на снижение эффективности профилактической работы с данной категорией лиц в последние два года.
Повышение заинтересованности молодых людей в прохождении профилактических обследований, рост готовности к обращению за врачебной помощью при возникновении симптомов половой инфекции — тенденции позитивные, и они соответствуют таким социальным трендам 2020–2021 гг., как консолидация общества вокруг государственных структур и институтов здравоохранения, повышение внимания к вопросам личного и общественного здоровья [11, 12]. В то же время другими авторами на фоне пандемии и достаточно жестких ограничительных мер отмечен рост протестных общественно-политических настроений, распространения конспирологических теорий, в которых органам власти и государственному здравоохранению отводится отрицательная роль [15–17]. Вместе с активизацией антипрививочного движения эти процессы заставляют говорить о возникновении вместе с пандемией нового явления — ковид-диссидентства, во многом аналогичного ранее описанному СПИД-диссидентству, но при этом вызывающего более масштабные деструктивные явления в плане недоверия к официальной информации и государственной политике. Систематизируя полу- ченные данные, мы можем отметить аналогичную проблему и с ИППП. Так, более чем вдвое возросло число желающих обращаться за консультациями и помощью к специалистам нескольких медицинских организаций в рамках одного клинического случая (с 24,7 до 54%). Это может указывать на то, что государственной дерматовенерологической службе доверяют не во всех вопросах, дополнительно обращаясь в частные клиники. В меньшей степени, но все же статистически значимо (с 11 до 15% респондентов) возрос и интерес к самолечению. Одновременно с этим критически — в 3 раза — возросло и число тех, кто открыто не доверяет официальной позиции государства и медицинского сообщества, заявляя о надуманности, преувеличенности проблемы ИППП, исключительно коммерческой основе профилактических мер — такая позиция стала отмечаться почти у 10% молодых людей. Таким образом, полученные результаты доказывают, что поляризация общества на фоне коронавирусной «инфодемии» переносится и на тему охраны репродуктивного здоровья.
Что касается влияния ограничительных мер на межличностные отношения, то здесь нами получены доказательства только в пользу негативного сценария: почти в 4 раза увеличилось число настроенных на сокрытие проблемы от партнера (с 8,3 до 32,2%) — за счет и тех, кто просто не считает необходимым делиться медицинскими проблемами, и тех, кто испытывает страх разрыва отношений из-за угрозы или свершившегося факта заражения.
Заключение. Проведенное исследование показало, что пандемия коронавируса и общегосударственные меры борьбы с ней, оказав влияние на общественное мнение и социальное самочувствие населения, привели к поляризации позиций молодых людей в отношении половых инфекций и их профилактики. При этом в плане установок на безопасность половой жизни большее значение приобрели негативные тенденции: недооценка угрозы заражения, мнение о намеренном преувеличении проблемы со стороны государства и врачей, нежелание мотивировать партнера к совместному обследованию и лечению при возникновении проблем. В противоположность снижению превентивных установок возросло понимание необходимости регулярных обследований, обращения за врачебной помощью при появлении симптомов заболевания, но практическое воплощение этих компонентов касается в основном действий при подозреваемом или свершившемся заражении, что способно повлиять как на рост выявляемости заболеваний, так и приверженности больных к лечению, но на их профилактику — в меньшей степени. В связи с этим дальнейшее течение эпидемических процессов ИППП становится труднопредсказуемым, а подходы к профилактической работе требуют существенного пересмотра — большего внимания к развитию у молодых людей понимания глобальности угрозы половых инфекций и чувства ответственности за здоровье партнера и семьи.
Список литературы Динамика мнений о мерах профилактики и лечения инфекций, передающихся половым путем, на фоне пандемии коронавируса
- Kuvaeva IO, Strelnikova AM. Features of coping with a specific difficult situation: the COVID-19 pandemic. Izvestia. Ural Federal University Journal. Series 1: Problems of education, science and culture 2021; 27 (2): 84-91. Russian (Куваева И. О., Стрельникова А. М. Особенности совладания со специфической трудной ситуацией: пандемия COVID-19. Известия Уральского федерального университета. Сер. 1: Проблемы образования, науки и культуры 2021; 27 (2): 84-91).
- Kahneman D. Thinking, fast and slow. N. Y.: Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2011; 499 p.
- Kahneman D, Slovic P, Tversky A, eds. Judgment under uncertainty: heuristics and biases. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001; 555 p.
- The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM). PubMed. URL: https://pubmed. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=Infectio ns&sort=pubdate&size=50&show_snippets=off (10 Apr 2022).
- Tony AA, Ahmed SBA, Tony EAE, et al. Predictors of neurological presentations of COVID-19 infected patients in South Egypt, Aswan Governorate: A single center study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2021; (17): 3471-82.
- Aragao MFVV, Leal MC, Andrade PHP, et al. Clinical and radiological profiles of COVID-19 patients with neurological symptomatology: A comparative study. Viruses 2021; 13 (5): 845.
- Au SCL. Comments on stroke as a neurological complication of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of incidence, outcomes and predictors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2021; 30 (10): 105863.
- Flores-Silva FD, García-Grimshaw M, Valdés-Ferrer SI, et al. Neurologic manifestations in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Mexico City. PLoS One 2021; 16 (4): e0247433.
- Siow I, Lee KS, Zhang JJY, et al. Encephalitis as a neurological complication of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of incidence, outcomes, and predictors. Eur J Neurol 2021; 28 (10): 3491-502.
- Zare Dehnavi A, Salehi M, Arab Ahmadi M, et al. Clinical, laboratory and imaging characteristics of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with neurologic involvement: A cross-sectional study. Arch Acad Emerg Med 2022; 10 (1): e10.
- Amanat M, Rezaei N, Roozbeh M, et al. Neurological manifestations as the predictors of severity and mortality in hospitalized individuals with COVID-19: A multicenter prospective clinical study. BMC Neurol 2021; (21): 116.
- Aragón-Benedí C, Oliver-Forniés P, Galluccio F, et al. Is the heart rate variability monitoring using the analgesia nociception index a predictor of illness severity and mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19? A pilot study. PLoS One 2021; 16 (3): e0249128.
- Chachkhiani D, Soliman MY, Barua D, et al. Neurological complications in a predominantly African American sample of COVID-19 predict worse outcomes during hospitalization. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2020; (197): 106173.
- Eskandar EN, Altschul DJ, de la Garza Ramos R, et al. Neurologic syndromes predict higher in-hospital mortality in COVID-19. Neurology 2021; 96 (11): e1527-38.
- García-Azorín D, Trigo J, Martínez-Pías E, et al. Neurological symptoms in COVID-19 patients in the emergency department. Brain Behav 2021; 11 (4): e02058.
- Liotta EM, Batra A, Clark JR, et al. Frequent neurologic manifestations and encephalopathy-associated morbidity in COVID-19 patients. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2020; 7 (11): 222130.
- Martinot M, Eyriey M, Gravier S, et al. Predictors of mortality, ICU hospitalization, and extrapulmonary complications in COVID-19 patients. Infect Dis Now 2021; 51 (6): 518-25.
- Pan Y, Yu Z, Yuan Y, et al. Alteration of autonomic nervous system is associated with severity and outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Front Physiol 2021; (12): 630038.
- Zifko U, Schmiedlechner T, Saelens J, et al. COVID-19: involvement of the nervous system. Identifying neurological predictors defining the course of the disease. J Neurol Sci 2021; (425): 117438.
- Chaumont H, Meppiel E, Roze E, et al. Long-term outcomes after NeuroCOVID: A 6-month follow-up study on 60 patients. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2022; 178 (1-2): 137-43.
- Gordon I, Horesh D, Milstein N, et al. Pre-pandemic autonomic nervous system activity predicts mood regulation expectancies during COVID-19 in Israel. Psychophysiology 2021; 58 (11): e13910.
- Jopling E, Rnic K, Tracy A, LeMoult J. Impact of loneliness on diurnal cortisol in youth. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021; (132): 105345.
- Trigo J, Garcla-Azorln D, Planchuelo-Gomez Â, et al. Factors associated with the presence of headache in hospitalized COVID-19 patients and impact on prognosis: A retrospective cohort study. J Headache Pain 2020; 21 (1): 94.
- Almeria M, Cejudo JC, Sotoca J, et al. Cognitive profile following COVID-19 infection: Clinical predictors leading to neuropsychological impairment. Brain Behav Immun Health 2020; (9): 100163.
- Eden A, Simrén J, Price RW, et al. Neurochemical biomarkers to study CNS effects of COVID-19: A narrative review and synthesis. J Neurochem 2021; (159): 61-77.
- Liu JM, Tan BH, Wu S, et al. Evidence of central nervous system infection and neuroinvasive routes, as well as neurological involvement, in the lethality of SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Med Virol 2021; (93): 1304-13.
- Dadkhah M, Talei S, Doostkamel D, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on diagnostic biomarkers in neuropsychiatric and neuroimmunological diseases: A review. Rev Neurosci 2021; 33 (1): 79-92.
- Gupta S, Chandra A, Ray BK, Pandit A. Treatment related fluctuation and response to intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in post COVID-19 Guillain-Barre syndrome. Diabetes Metab Syndr 2021; 15 (5): 102246.
- Nersesjan V, Amiri M, Lebech AM, et al. Central and peripheral nervous system complications of COVID-19: a prospective tertiary center cohort with 3-month follow-up. J Neurol 2021; 268 (9): 3086-104.
- Putilina MV, Grishin DV. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) as a predictor of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration: potential therapy strategies. S. S. Korsakov Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry 2020; (120): 58-64. Russian (nyTMnMHa M. B., Tpw-шин Д. В. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) как предиктор нейрово-спаления и нейродегенерации: потенциальные стратегии терапии. Журнал неврологии и психиатрии им. С. С. Корсакова 2020; (120): 58-64).
- Joshee S, Vatti N, Chang C. Long-Term Effects of COVID-19. Mayo Clin Proc 2022; (97): 579-99.
- Margulis MS. Chronic infectious and parasitic diseases of the nervous system. Moscow; Leningrad: Medgiz, 1933; 388 р. Russian (Маргулис М. С. Хронические инфекционные и паразитарные заболевания нервной системы. М.; Л.: Медгиз, 1933; 388 с.).
- Reverby SM. More than fact and fiction. Cultural memory and the Tuskegee syphilis study. Hastings Cent Rep 2001; (31): 22-8.
- Gonzalez H, Koralnik IJ, Marra CM. Neurosyphilis. Semin Neurol 2019; (39): 448-55.
- Ho EL, Tantalo LC, Jones T, et al. Point-of-care treponemal tests for neurosyphilis diagnosis. Sex Transm Dis 2015; (42): 48-52.
- Kolokolov OV. Damage to the nervous system in patients with syphilis: modern pathomorphosis, diagnosis and prevention: DSc diss. Moscow, 2013; 325 р. Russian (Колоколов О. В. Поражение нервной системы у больных сифилисом: современный патоморфоз, диагностика и профилактика: дис. ... д-ра мед. наук. М., 2013; 325 с.).
- Kolokolov OV, Tikhonova LA, Bakulev AL, et al. Syphilitic cerebral vasculitis: diagnostic possibilities. S. S. Korsakov Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry 2012; 112 (4): 11-17. Russian (Колоколов О. В., Тихонова Л. А., Бакулев А. Л. и др. Сифилитический церебральный васкулит: возможности диагностики. Журнал неврологии и психиатрии им. С. С. Корсакова 2012; 112 (4): 11-17).
- Bobrova LA. Cognitive distortions. Domestic and foreign literature. Series 3: Philosophy 2021; (2): 69-79. Russian (Боброва Л. А. Когнитивные искажения. Отечественная и зарубежная литература. Сер. 3: Философия 2021; (2): 69-79).
- Pokrovsky VI, Pak SG, Briko NI, Danilkin BK. Infectious diseases and epidemiology. 3rd ed. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2016; 1008 p. Russian (Покровский В. И., Пак С. Г., Брико Н. И., Данилкин Б. К. Инфекционные болезни и эпидемиология. 3-е изд. М.: ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2016; 1008 с.).


