Дизайн индивидуальных вертлужных компонентов: влияние типа дефекта на вид конструкции
Автор: Коваленко А.Н., Тихилов Р.М., Шубняков И.И., Джавадов А.А., Билык С.С., Мидаев А.И., Маслов Л.Б., Жмайло М.А.
Журнал: Российский журнал биомеханики @journal-biomech
Статья в выпуске: 2 (92) т.25, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Варианты лечения массивных дефектов области вертлужной впадины очень разнообразны и остаются вызовом для хирурга. Хотя индивидуальные конструкции не показывают результатов, превосходящих другие методы реконструкции, вариабельность дизайна предлагает широкие возможности надежной первичной фиксации. В Национальном медицинском исследовательском центре травматологии и ортопедии имени Р.Р. Вредена за период с 2015 по 2019 год выполнено 115 ревизий вертлужного компонента с использованием индивидуальных конструкций с целью определить и классифицировать основные типы индивидуальных конструкций, применяемых в реконструкции обширных дефектов вертлужной впадины. Несмотря на то, что большинство дефектов относилось к категориям дефектов 3 A , 3 B степени по Paprosky , нарушения целостности тазового кольца, тип индивидуальной конструкции определялись в большей степени геометрией дефекта. При дефектах, сопровождающихся отсутствием опоры медиальной стенки, конструкция имела антипротрузионные свойства и мостовидный вариант фиксации. В наиболее тяжелых случаях при отсутствии опорности и связи с осевым скелетом вертлужный компонент имел фланец для фиксации к оставшейся части крыла подвздошной кости и ножку, фиксирующуюся в задних отделах тела подвздошной кости. Основные типы дизайна индивидуальных конструкций были представлены аугментами, трехфланцевыми конструкциями и фланцевыми конструкциями с ножкой. Наряду с реконструкцией области дефекта это расширяло возможности первичной фиксации винтами и позволяло оптимизировать положение и ориентацию вертлужного компонента уже на этапе планирования. Индивидуальное проектирование вертлужных компонентов позволяет сочетать варианты фиксации разных типов конструкций.
Ревизионное эндопротезирование тазобедренного сустава, костные дефекты вертлужной впадины, индивидуальные имплантаты
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146282200
IDR: 146282200 | УДК: 617-089.844 | DOI: 10.15593/RZhBiomeh/2021.2.04
Текст научной статьи Дизайн индивидуальных вертлужных компонентов: влияние типа дефекта на вид конструкции
Существует множество вариантов реконструкции вертлужной области при ревизионном эндопротезировании тазобедренного сустава [23, 27, 31]. Однако вопрос оптимального дизайна ревизионных вертлужных конструкций остается недостаточно освещенным в литературе. При установке имплантатов для восстановления функции и опороспособности нижней конечности, а также реализации свойств поверхностей с остеоинтегративным покрытием требуется стабильная фиксация. Это достигается методом тугой посадки ( press-fit ) либо фиксацией винтами [5, 9, 10]. При этом в ревизионной хирургии метод тугой посадки часто недостижим или ненадежен из-за наличия дефектов и дефицита костной ткани. Расширенная фиксация винтами представлена, как правило, в типовых антипротрузионных конструкциях, которые в свою очередь в основном лишены остеокондуктивных покрытий [7, 24, 30]. К тому же, несмотря на наличие размерного ряда антипротрузионных компонентов, не через все отверстия можно гарантированно обеспечить фиксацию винтами к кости в связи с большим разнообразием размеров и формы дефектов [18, 37].
Ввиду разнообразия дефектов вертлужной области при ревизионном эндопротезировании тазобедренного сустава целью нашего исследования было классифицировать основные типы индивидуальных конструкций, применяемых в реконструкции обширных дефектов вертлужной впадины, и определить, существует ли зависимость типа конструкции от типа дефекта.
Материалы и методы
В клинике Национального медицинского исследовательского центра травматологии и ортопедии имени Р.Р. Вредена за период с 2015 по 2019 год выполнено 115 ревизий вертлужного компонента с использованием индивидуальных конструкций, 101 случай из которых имели 36 дефектов 3 A степени, 47 дефектов – 3 B степени по Paprosky и 18 дефектов сочетались с нарушением целостности тазового кольца. Для каждого пациента был изготовлен персонифицированный имплантат для реконструкции области вертлужной впадины в соответствии с особенностями геометрии дефекта. Индивидуальные конструкции были представлены полусферическими компонентами (чашками) – 4, аугментами – 24, двудольными чашками – 2, трехфланцевыми конструкциями – 62 и полусферами с ножкой и подвздошным фланцем – 9 (рис. 1). Двудольные чашки и аугменты были объединены в одну группу по реконструкции вертлужной области – аугментации недостающей области вертлужной впадины. Проектирование производилось научными сотрудниками Национального медицинского исследовательского центра травматологии и ортопедии при активном участии хирургов, выполнявших операции. Принципы проектирования базировались на опорности оставшейся кости.
Описание методов статистического анализа
Материалы исследования были подвергнуты статистической обработке с использованием методов непараметрического анализа. Накопление, корректировка, систематизация исходной информации и визуализация полученных результатов осуществлялись в электронных таблицах Microsoft Office Excel 2016. Статистический анализ проводился с использованием программы Past 3.16.
Сравнение номинальных данных проводилось при помощи критерия χ2 Пирсона, позволяющего оценить значимость различий между фактическим количеством видов конструкций или качественных характеристик типа дефекта, попадающих в каждую категорию, и теоретическим количеством, которое можно ожидать в изучаемых группах при справедливости нулевой гипотезы.

а б в

г д
Рис. 1. Варианты применяемых индивидуальных конструкций: а – полусферический компонент; б – аугмент; в – двудольная чашка; г – трехфланцевый компонент; д – фланцевый компонент с внутрикостной ножкой
Результаты
Несмотря на то, что большинство дефектов относились к категориям 3 A , 3 B дефектов по классификации Paprosky и нарушению целостности тазового кольца, вид индивидуальной конструкции определялся в значительной степени геометрией дефекта. Например, при сохранении медиальной опоры использовались конструкции с целью аугментации недостающей передней, задней или верхней стенок вертлужной впадины. При дефектах, сопровождающихся отсутствием опоры медиальной стенки, конструкция имела антипротрузионные свойства и мостовидный вариант фиксации. В наиболее тяжелых случаях при отсутствии опорности и связи с осевым скелетом нижней половины полутаза вертлужный компонент имел фланец для фиксации к оставшейся части крыла подвздошной кости и ножку с покрытием для остеоинтеграции, устанавливаемую внутрикостно в задние отделы тела подвздошной кости (таблица).
Тем не менее определенная нелинейная закономерность между типом имплантата и видом дефекта существовала. Статистически значимая зависимость подтвердилась значением критерия χ2 Пирсона, величина которого составила
56,2 (критическое значение χ2 16,812, р < 0,01). При более стабильных дефектах преобладали варианты аугментации дефекта, в то время как при нарастающем дефиците опорности вертлужной области вектор смещался в сторону имплантатов, не требующих реконструкции костного ложа вокруг полусферического компонента (рис. 2).

■ Трехфланцевая конструкция
3 B по Paprosky
■ Фланцевый вертлужный компонент с ножкой
3 A по Paprosky
Нарушение целостности тазового кольца
Виды конструкции
|
Тип дефекта вертлужной впадины |
Полусферический компонент |
Аугментация (аугмент, двудольная чашка) |
Трехфланцевая конструкция |
Фланцевый вертлужный компонент с ножкой |
Всего |
|
3 A по Paprosky |
4 |
22 |
9 |
1 |
36 |
|
3 B по Paprosky |
0 |
4 |
40 |
3 |
47 |
|
Нарушение целостности тазового кольца |
0 |
0 |
13 |
5 |
18 |
|
Всего |
6 |
26 |
62 |
9 |
101 |
Рис. 2. Изменение структуры типов индивидуальных имплантатов с прогрессированием обширности костного дефекта вертлужной впадины
%
Ограниченный
Неограниченный
■ Полусфера ■ Аугмент ■ Трехфланцевая ■
Фланцевый вертлужный компонент с ножкой
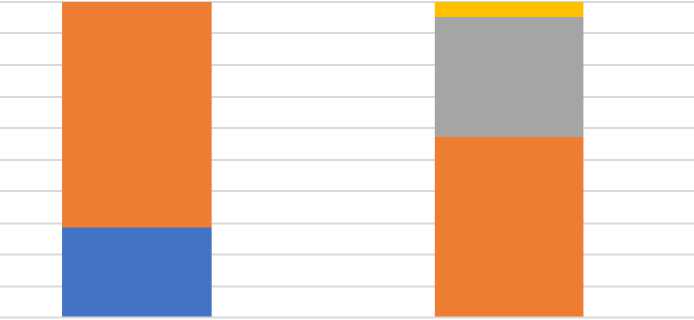
Рис. 3. Структура видов индивидуальных имплантатов при дефектах вертлужной впадины 3A типа по классификации W. Paprosky с учетом параметра ограниченности дефекта
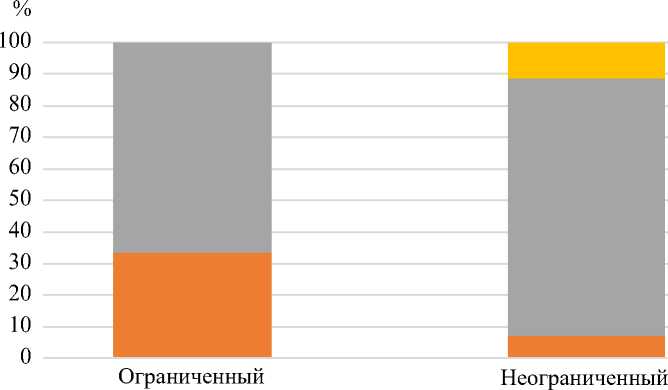
Структура видов имплантатов внутри типов дефектов 3 A и 3 B по классификации W. Paprosky оказалась неоднородной. Для оценки однородности использовался критерий ограниченности дефекта их классификации Garbuz , который предполагает пластику опорных структур в случае неограниченных дефектов. Согласно полученным нами данным, распределение видов имплантатов имело статистически значимое различие в зависимости от того, являлся ли дефект ограниченным или неограниченным для 3 A типа дефектов по классификации W. Paprosky (χ2 = 13,05; р < 0,01) (рис. 3). Для дефектов 3 B параметр ограниченности не выявил статистически значимой разницы в структуре видов имплантатов по параметру ограниченности дефекта (χ2 = 6,32; р = 0,1) (рис. 4).
Фланцевый вертлужный ■ Полусфера ■ Аугмент ■ Трехфланцевая ру компонент с ножкой
Рис. 4. Структура видов индивидуальных имплантатов при дефектах вертлужной впадины 3 B типа по классификации W. Paprosky с учетом параметра ограниченности дефекта
Особенности дизайна аугментов и двудольных конструкций
Несмотря на то, что принцип аугментации подразумевает достройку недостающей стенки костного ложа, варианты аугментов были достаточно разнообразными. От стандартных серийных аугментов они отличались в первую очередь заданными направлениями отверстий для проведения винтов в костную ткань. Индивидуальные аугменты могли иметь интерфейсную поверхность как под обработку фрезой, так и под копию контактной поверхности кости. Количество отверстий проектировалось с целью выполнения максимально надежной фиксации, зависело от размеров аугмента, количества прилежащей кости и варьировалось от 5 до 10.
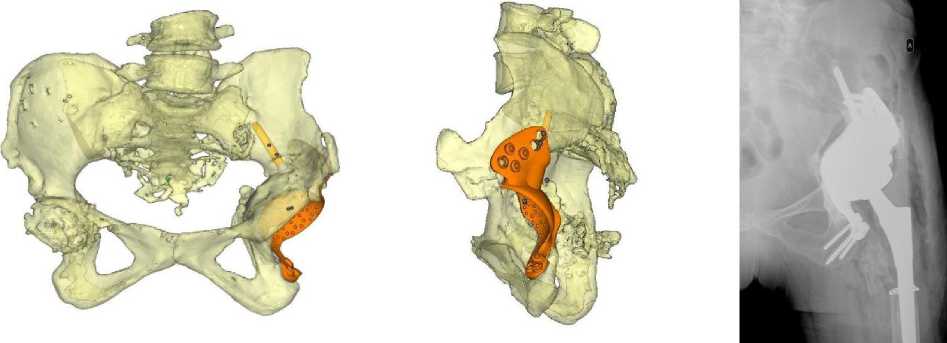
Фиксация винтами через все отверстия не являлась обязательной. Надежной считалась фиксация в трех и более разнонаправленных зонах. При недостаточной области фиксации через аугмент зона фиксации могла быть расширена добавлением фланцев к аугменту. В одном случае потребовалась дополнительная фиксация аугмента в теле подвздошной кости внутрикостной ножкой (рис. 5). Двудольные конструкции представляли собой монолитный имплантат из полусферической части для пары трения и аугмента, который также мог иметь поверхность для установки под обработку фрезой или без (см. рис. 1, г ). В отношении двудольных конструкций следует отметить, что они являются переходной формой между аугментированием и трехфланцевыми конструкциями, поскольку сочетают принципы первых и вторых видов имплантатов.
a б в
Рис. 5. Аугмент с внутрикостной ножкой: a – спроектированный аугмент в области дефекта левой вертлужной впадины, вид спереди; б – спроектированный аугмент в области дефекта левой вертлужной впадины, вид сбоку; в – послеоперационная рентгенограмма пациента с установленным имплантатом
Подвздошный участок, проектируемый в виде части полусферы и, по сути, выполняющий роль аугмента, можно расценивать в качестве подвздошного фланца. Однако, с другой стороны, построение его в виде части полусферы не имеет целесообразности при дефекте или нарушении опорности медиальной стенки. Хотя этот вопрос остается дискутабельным, на наш взгляд, в этом исследовании строгой категоризацией двудольных вертлужных компонентов можно пренебречь, поскольку их было установлено всего два.
Особенности дизайна трехфланцевых конструкций
При неопорности медиальной стенки, которая часто сочеталась с дефектами передней или задней колонн, имплантат обладал свойствами антипротрузионных конструкций и опирался фланцами на участки здоровой кости. В отличие от наиболее
а
б в
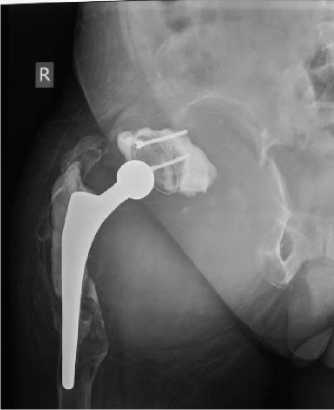
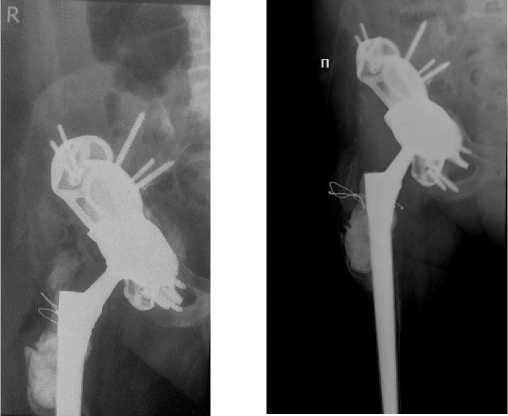
Рис. 6. Рентгенограммы пациентки 71 года: a – до операции – обширное разрушение крыши и крыла подвздошной кости, дефекты передней и задней колонн, нарушение целостности тазового кольца; б – имплантирована индивидуальная трехфланцевая конструкция с фиксацией 9 винтами; в – через 2 года после ревизии конструкция стабильна, пациентка довольна результатом, передвигается с помощью трости
распространенных антипротрузионных кейджей Бурх–Шнайдера, фиксация которых предполагает наличие двух фланцев – седалищного и подвздошного и опорной задней колонны, индивидуальные фланцевые конструкции имели три фланца, к вышеуказанным добавлялся лонный фланец. Подвздошный фланец фиксировался 5–7 винтами, седалищный 2–3 винтами, для фиксации лонного фланца устанавливалось 0–2 винта. Еще одной отличительной особенностью было наличие на фланцах индивидуальных конструкций пористого покрытия для обеспечения остеоинтеграции. Трехфланцевые конструкции применялись и при отсутствии одной из колонн, и при нарушении целостности тазового кольца (рис. 6). Вместе с тем конструкция должна была быть стабильной в краниальном направлении и иметь элементы, которые бы препятствовали ее миграции вверх. Важным было сочетать достаточные размеры фланцев для фиксации и одновременно необоснованно не проектировать конструкцию слишком громоздкой. Последнее затрудняло установку, требовало дополнительного рассечения тканей и скелетирования кости.
Особенности дизайна полусферических компонентов с подвздошным фланцем и внутрикостной ножкой
Концепция полусферического компонента с внутрикостным стержнем заимствована из костной онкологии, когда при объемных резекциях остатки костной ткани не предполагают заклинивания полусферического компонента [8]. Для фиксации в таких случаях применяется внутрикостная ножка, которая заклинивается в теле подвздошной кости или боковой массе крестца и служит опорой для полусферического компонента. Однако срок службы таких компонентов ограничен выживаемостью 5 лет, что, вероятно, связано с отсутствием надежной ротационной стабильности. Индивидуализация компонента позволила увеличить ротационную стабильность, дополнив имплантат подвздошным фланцем. Кроме того, пористое покрытие стержня и фланца расширяет потенциальную область остеоинтеграции. Такой тип дизайна был актуален в основном при посттравматических деформациях тазового кольца,
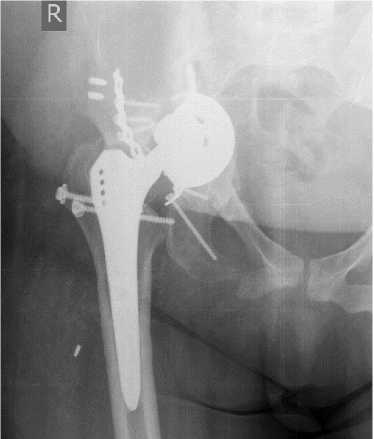
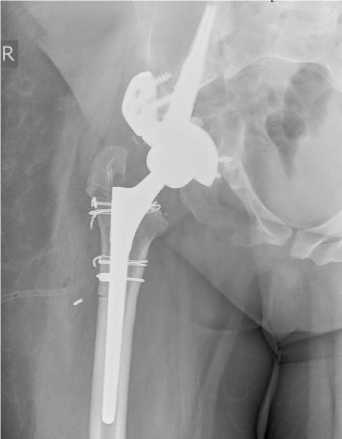
a б
Рис. 7. Рентгенограммы пациентки 35 лет: a – до операции – посттравматическая деформация таза, нарушение целостности тазового кольца, отсутствие контакта седалищной кости с осевым скелетом; б – имплантирована индивидуальная полусферическая конструкция с ножкой и подвздошным фланцем когда достраивание вертлужной области не представлялось возможным, а фрагмент седалищной кости не имел связи с осевым скелетом и, таким образом, не являлся опороспособным (рис. 7).
Обсуждение
Хирургическое лечение костных дефектов в области вертлужной впадины имеет продолжительную историю. Классификация дефектов вертлужной впадины от Wayne Paprosky впервые была опубликована в 1994 г., в этой статье автор уже представлял свой подход и многолетние наработки в области решения этой проблемы [29]. При этом выработанные основные принципы реконструкции вертлужной области практически не менялись с середины 80-х годов [21]. Это восстановление центра ротации, аугментация дефекта, противодействие краниальной и медиальной миграции. Эволюция реконструкции дефектов развивалась в основном в отношении используемых материалов и дизайна конструкций. Изначально для крупных дефектов использовались массивные структурные трансплантаты, однако высокий процент неудачных исходов стимулировал к разработке более надежных методов реконструкции [13, 32]. Примерно в то же время появилась импакционная костная пластика, которая показала хорошие результаты, но лишь в условиях отграниченных дефектов [14, 34].
Параллельно разрабатывались конструкции с расширенной зоной фиксации, выходящей за пределы вертлужной области [11, 15]. С накоплением опыта и большим количеством неудачных результатов пришло понимание того, что для обеспечения долгосрочных результатов конструкции, наряду с надежной первичной фиксацией, должна иметься возможность остеоинтеграции. Результатом стало развитие комбинаций методик и появление на рынке компонентов из пористых материалов, тантала, титана [20, 26, 35]. Но несмотря на в целом удовлетворительные исходы, серийные конструкции не покрывали всех потребностей ревизионного эндопротезирования вертлужной области [12]. С внедрением методов аддитивного производства стало понятно, что данные технологии позволяют производить индивидуальные компоненты, дизайн которых может учитывать все принципы реконструкции вертлужной области, совмещать преимущества ранее использованных конструкций и избегать их недостатков.
В публикациях об индивидуальных вертлужных конструкциях речь, как правило, идет о трехфланцевых компонентах, другие варианты при ревизионном эндопротезировании практически не описываются [16, 25]. Однако технологии персонализации имплантата предоставляют гораздо более широкий спектр для реконструкции вертлужной области, который сложно описать одним типом дизайна. Индивидуальное проектирование общей формы, опорной области, количества и расположения винтовых отверстий ограничивается только геометрией и размерами дефекта. Разумеется, кроме этого, нужно учитывать хирургическую анатомию конкретного пациента, планируемый доступ и технику операции. В противном случае может оказаться, что непроработанный в этом отношении имплантат окажется сложным в установке или вовсе неустановимым [2, 6].
Сравнение дизайна стандартных и индивидуальных аугментов и двудольных конструкций
Согласно опубликованной литературе, пористые танталовые аугменты показывают хорошие средне- и долгосрочные результаты [3, 22, 28]. Вместе с тем для адаптации секторных аугментов требуется обработка кости фрезой, что уменьшает количество кости в области дефекта. Благодаря высокой степени сцепления с поверхностью обеспечивается надежная первичная стабильность, несмотря на то, что в аугментах минимальной высоты (10 мм) предусмотрено всего два отверстия для фиксации винтами [36]. При увеличении высоты серийного аугмента количество отверстий возрастает, но каналы винтов имеют если не параллельную, то достаточно невариабельную направленность, что не позволяет изменить направления винта при необходимости. Особенно это актуально в ситуациях, когда не все участки доступной кости имеют достаточную толщину и плотность. Индивидуальные аугменты не всегда требуют обработки для посадки, каналы винтов планируются с заданным направлением в кости с достаточной протяженностью и плотностью. В случаях когда количество винтов в кости хорошего качества на этапе планирования оказывалось недостаточным, зона фиксации могла быть расширена добавлением фланцев, контактирующих с костью за границами области дефекта. Для достаточной фиксации не обязательно использовать все винтовые каналы, но, как показала наша практика, минимум 4 винта в индивидуальный аугмент всегда удавалось надежно установить. Индивидуальные двудольные конструкции в отличие от аугментов чаще проектировались под обработку кости фрезой и требовали прецизионного следования операционному плану для корректной установки.
Сравнение дизайна антипротрузионных и трехфланцевых конструкций
Серийные антипротрузионные конструкции представлены кольцами, кейджами, среди которых наиболее известны имплантаты Бурх–Шнайдера, Ганса, и другими аналогами с фирменными названиями. Продолжающиеся разработки дизайна и методов имплантации серийных компонентов указывают на то, что размерный ряд одного типа конструкции не может решить всех задач, которые ставит перед хирургом ревизионное эндопротезирование вертлужного компонента [30]. Толщина конструкций не превышает 3 мм, что, с одной стороны, позволяет моделировать фланец конструкции под костную поверхность конкретного пациента, а с другой стороны, является ограничением в реализации антипротрузионных свойств имплантата. В литературе можно найти термин «усиливающая конструкция ( reinforcement cage )», характеризующий возможности имплантатов данной группы. Другими словами, такие имплантаты в большей степени устанавливаются на ослабленную, источенную, но имеющуюся кость, усиливая и препятствуя ее дальнейшему разрушению. Серийные конструкции предусмотрены для фиксации винтами через поверхности их фланцев, как правило, они не имеют покрытия для остеоинтеграции, поэтому биологическая вторичная фиксации антипротрузионных конструкций невозможна [7]. Установка в варианте фиксации по типу мостовидной, когда область для вертлужного компонента не имеет опоры на кость, а антипротрузионная конструкция крепится к кости только в области фланцев, в условиях циклических нагрузок закономерно приводит к несостоятельности фиксации [24].
Одним из последних эволюционных вариантов установки антипротрузионных конструкций является модульный имплантат кап-кейдж (cup-cage), при котором в дефект заклинивается чашка больших размеров с остеоинтеграционным покрытием, а поверх него монтируется антипротрузионный кейдж с ложем для установки вертлужного компонента [17]. Дизайн индивидуальных трехфланцевых конструкций позволяет реализовать мостовидную фиксацию с заданной толщиной солидной части при значительных костных дефектах, расположить пористое покрытие на всех участках конструкции, контактирующих с костью, моделировать фланцы соответственно костной поверхности тазовой кости конкретного пациента, таким образом, сохраняя преимущества антипротрузионных конструкций и устранив большую часть их недостатков. Если границы области дефекта распространяются значительно выше анатомической вертлужной области, конструкция должна иметь опорную зону или площадку для профилактики краниального смещения [39]. Вместе с тем при проектировании монолитных трехфланцевых конструкций наряду с достаточной площадью фланцев и количеством каналов винтов нужно стремиться к эргономичности и лаконичности конструкции, насколько это возможно, поскольку громоздкую конструкцию сложно устанавливать и корректно позиционировать в области дефекта. Кроме этого, в конструкции нужно избегать областей концентрации напряжений, сопряжения ее элементов должны иметь плавные переходы.
Сравнение дизайна серийных вертлужных конструкций с внутрикостной ножкой и их индивидуальных аналогов
Сообщения о серийных полусферических вертлужных компонентах с внутрикостной ножкой впервые были опубликованы в первой половине прошлого века [38]. Изначально они применялись для первичного эндопротезирования для усиления фиксации вертлужного компонента [33]. С улучшением вариантов фиксации вертлужных компонентов показания для этой конструкции сместились в сторону реконструкции крупных костных дефектов при ревизии, а также при первичном эндопротезировании в онкологической ортопедии, когда после резекций тазовых костей в периацетабулярной области стоял вопрос восстановления функции. Результаты применения таких конструкций в 5-летнем периоде говорят о существенном проценте развития ротационной и аксиальной нестабильности на уровне внутрикостной ножки [19]. Индивидуальное проектирование компонентов с внутрикостной ножкой позволяет усилить фиксацию за счет добавления накостного подвздошного фланца, покрыть пористым слоем все поверхности, контактирующие с костью, а также сохранить модульность конструкции для удобства установки. Говорить о значительно превосходящих предыдущие серии результатах пока рано, однако предварительные данные весьма обнадеживающие [1].
Общие тенденции дизайна индивидуальных вертлужных компонентов и выводы
С нарастанием категории сложности дефекта и снижением степени опороспособности вертлужной области вариант фиксации становится все менее зависимым от ритма и более зависимым от частей тазовой кости, имеющих связь с осевым скелетом. Иерархию большинства конструкций, согласно выявленной закономерности, по мере снижения опорности кости можно представить следующим образом: аугмент – аугмент с расширенной зоной фиксации (фланцами) – аугментированная или двудольная чашка – трехфланцевый компонент – полусферический компонент с подвздошным фланцем и внутрикостной ножкой.
Стоит обратить внимание на классификации, описывающие дефекты вертлужной области. Поскольку их основная задача определить, с чем придется столкнуться хирургу в операционной, то это во многом определяет значимость классификации в отношении дизайна индивидуальной конструкции. С одной стороны, основное преимущество широко распространенной классификации Paprosky в возможности классифицировать тип дефекта по стандартным рентгенограммам. Однако другим важным параметром, который определяет хирургическую тактику, оказалась ограниченность дефекта, впервые описанная в классификации Garbuz и соавторов. Согласно их исследованию, понятие «неограниченный дефект» подразумевает возможность фиксации вертлужного компонента только при выполнении костной пластики структурным трансплантатом, т.е. восстановлении утраченных опорных структур. В соответствии с полученными нами данными этот параметр имеет статистически значимое влияние на выбор вида индивидуального имплантата в пределах одной категории обширных 3A типов дефектов по классификации W. Paprosky. Общеизвестным фактом на сегодня является то, что одна классификация не в силах полностью описать дефект и учесть все его характеристики, требуемые для оптимальной реконструкции вертлужной области [4]. Среди них абсолютные геометрические размеры дефекта, опороспособность и жизнеспособность оставшейся кости, причины, вызвавшие дефект – остеолиз, посттравматические изменения или ятрогения. Всё это приводит к тому, что одна категория дефекта в пределах одной классификации может представлять собой достаточно разнородные состояния, требующие разных хирургических подходов или их комбинаций. Сдерживающим фактором разработки всеобъемлющей классификации является сложность ее внедрения и практического применения. Тем не менее в нашей практике трехмерная визуализация стала стандартом диагностики в случаях обширных дефектов вне зависимости от того, планируется ли реконструкция индивидуальным или стандартным компонентом. Дополнительная информация о дефекте в трехмерном виде, по нашему мнению, однозначно стоит тех усилий, которые приложены для ее получения, а параметр ограниченности дефекта следует учитывать при планировании операции и разработке дизайна индивидуального вертлужного компонента.
Открытым остается вопрос достаточной и оптимальной площади контакта фланцевых конструкций. В условиях отсутствия медиальной стенки, передней и задней колонн вертлужной впадины площадь контакта фланцевых конструкций является определяющей в отношении возможности остеоинтеграции конструкции. В настоящее время оптимальные значения этого параметра сложны даже на уровне определения адекватного метода его оценки, вследствие разных антропометрических характеристик пациентов, размеров дефекта и качества костной ткани, сложностей позиционирования индивидуальных конструкций. На сегодняшний день они остаются эмпирическими и требуют исследования отдаленных результатов.
Одними из наиболее важных определяющих факторов дизайна вертлужного компонента, по нашему мнению, является геометрия и размер дефекта. Тем не менее абсолютные размеры сложно оценивать в связи с тем, что антропометрические данные пациентов различаются. Соответственно, условные дефекты размером 5 см в диаметре у пациента ростом 150 см и у пациента ростом 180 см представляют собой разные клинические ситуации. Кроме того, дизайн индивидуальных вертлужных компонентов при обширных дефектах должен удовлетворять двум основным качествам.
Наряду с адекватной площадью для фиксации и количеством фиксирующих элементов конструкция должна быть достаточно компактной и не создавать трудности при установке. Как показывает практика проектирования и установки индивидуальных вертлужных имплантатов, зачастую эти свойства могут иметь противоположную направленность. Чем больше дефект и, соответственно, размеры индивидуального компонента, тем больше сложностей это может создавать при установке и приводить к ошибкам позиционирования.
Основные типы дизайна индивидуальных конструкций в данном исследовании были представлены аугментами, трехфланцевыми конструкциями и фланцевыми конструкциями с ножкой. Наряду с реконструкцией области дефекта это расширяло возможности первичной фиксации винтами и позволяло оптимизировать положение и ориентацию вертлужного компонента уже на этапе планирования. Индивидуальное проектирование вертлужных компонентов позволяет сочетать варианты фиксации разных типов конструкций.
Список литературы Дизайн индивидуальных вертлужных компонентов: влияние типа дефекта на вид конструкции
- Коваленко А.Н., Джавадов А.А., Шубняков И.И., Билык С.С., Денисов А.О., Черкасов М.А., Мидаев А.И., Тихилов Р.М. Среднесрочные результаты использования индивидуальных конструкций при ревизионном эндопротезировании тазобедренного сустава // Травматология и ортопедия России. - 2019. - Т. 25, № 3. - С. 37-46.
- Коваленко А.Н., Тихилов Р.М., Билык С.С., Шубняков И.И., Черкасов М.А., Денисов А.О. Позиционирование индивидуальных вертлужных компонентов при ревизиях тазобедренного сустава: действительно ли они подходят как "ключ к замку"? // Вестник травматологии и ортопедии им. Н.Н. Приорова. - 2017. - № 4. - С. 31-37.
- Корыткин А.А., Новикова Я.С., Ковалдов К.А., Королёв С.Б., Зыкин А.А., Герасимов С.А., Герасимов Е.А. Среднесрочные результаты ревизионного эндопротезирования тазобедренного сустава с использованием ацетабулярных аугментов // Травматология и ортопедия России. - 2019. -Т. 25, № 1. - С. 9-18.
- Тихилов Р.М., Шубняков И.И., Денисов А.О. Классификации дефектов вертлужной впадины: дают ли они объективную картину сложности ревизионного эндопротезирования тазобедренного сустава? (критический обзор литературы и собственных наблюдений) // Травматология и ортопедия России. -2019. - Т. 25, № 1. - С. 122-141
- Amirouche F., Solitro G.F., Walia A., Gonzalez M., Bobko A. Segmental acetabular rim defects, bone loss, oversizing, and press fit cup in total hip arthroplasty evaluated with a probabilistic finite element analysis // International Orthopaedics. - 2017. - Vol. 41, no. 8. - P. 1527-1533.
- Baauw M. van Hellemondt G.G., van Hooff M.L., Spruit M. The accuracy of positioning of a custom-made implant within a large acetabular defect at revision arthroplasty of the hip // Bone and Joint Journal. -2015. - Vol. 97-B, no. 6. - P. 780-785.
- Berry D.J. Antiprotrusio cages for acetabular revision // Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. - 2004. - Vol. 420. -P. 106-112. DOI: 10.1097/00003086-200403000-00015
- Bus M.P., Szafranski A., Sellevold S., Goryn T., Jutte P. C., Bramer J. A., Fiocco M., Streitbürger A., Kotrych D., van de Sande M. A., Dijkstra P.D. LUMiC ® endoprosthetic reconstruction after periacetabular tumor resection: short-term results // Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. - 2017. - No. 3. -P. 686-695.
- Chiarlone F., Zanirato A., Cavagnaro L., Alessio-Mazzola M., Felli L., Burastero G. Acetabular custom-made implants for severe acetabular bone defect in revision total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review of the literature // Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery. - 2020. - Vol. 140, no. 3. - P. 415-424.
- Faizan A., Black B.J., Fay B.D., Heffernan C.D., Ries M.D. Comparison of head center position and screw fixation options between a jumbo cup and an offset center of rotation cup in revision total hip arthroplasty: a computer simulation study // The Journal of Arthroplasty. - 2016. - Vol. 31, no. 1. - P. 307-311.
- Fink B., Grossmann A., Sebena P. Exchange of acetabular cups with severe bone defects using antiprotrusion cages // Operative Orthopadie und Traumatologie. - 2010. - Vol. 22, no. 3. - P. 256-267.
- Fröschen F.S., Randau T.M., Hischebeth G.T.R., Gravius N., Gravius S., Walter S.G. Mid-term results after revision total hip arthroplasty with custom-made acetabular implants in patients with Paprosky III acetabular bone loss // Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery. - 2020. - No. 2. - P. 263-273.
- Garbuz D., Morsi E., Gross A.E. Revision of the acetabular component of a total hip arthroplasty with a massive structural allograft: Study with a minimum five-year follow-up // Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. Series A. - 1996. - Vol. 78, no. 5. - P. 693-697.
- Gilbody J. Taylor C., Bartlett G.E., Whitehouse S.L., Hubble M.J., Timperley A.J. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of acetabular impaction grafting without cage reinforcement for revision hip replacement // The Bone & Joint Journal. 2014. - Vol. 96-B, no. 2. - P. 188-194.
- Gill T.J., Sledge J.B., Müller M.E. The Burch-Schneider anti-protrusio cage in revision total hip arthroplasty. Indications, principles and long-term results // Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. Series B. -1998. - Vol. 80, no. 6. - P. 946-953.
- Gladnick B.P., Fehring K.A., Odum S.M., Christie M.J., DeBoer D.K., Fehring T.K. Midterm survivorship after revision total hip arthroplasty with a custom triflange acetabular component // Journal of Arthroplasty. - 2018. - Vol. 33, no. 2. - P. 500-504.
- Hipfl C., Janz V., Löchel J., Perka C., Wassilew G.I. Cup-cage reconstruction for severe acetabular bone loss and pelvic discontinuity: mid-term results of a consecutive series of 35 cases // Bone and Joint Journal. - 2018. - Vol. 100B, no. 11. - P. 1442-1448.
- Holt G.E., Dennis D.A. Use of custom triflanged acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty. -Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2004. - P. 209-214.
- Issa S.P., Biau D., Leclerc P., Babinet A., Hamadouche M., Anract P. Stemmed acetabular cup as a salvage implant for revision total hip arthroplasty with Paprosky type IIIA and IIIB acetabular bone loss // Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. - 2020. - Vol. 106, no. 3. - P. 589-596.
- Jafari S.M., Bender B., Coyle C., Parvizi J., Sharkey P. F., Hozack, W. J. Do tantalum and titanium cups show similar results in revision hip arthroplasty? - New York: Springer, 2010. - P. 459-465.
- Jasty M., Harris W.H. Total hip reconstruction using frozen femoral head allografts in patients with acetabular bone loss // Orthopedic Clinics of North America. - 1987. - Vol. 18, no. 2. - P. 291-299.
- Lochel J., Janz V., Hipfl C., Perka C., Wassilew G.I. Reconstruction of acetabular defects with porous tantalum shells and augments in revision total hip arthroplasty at ten-year follow-up // Bone and Joint Journal. - 2019. - Vol. 101, no. 3. - P. 311-316.
- Makinen T.J., Common H., Girard J., Huten D., Putman S. Role of cages in revision arthroplasty of the acetabulum // The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. - 2016. - Vol. 98, no. 3. - P. 233-242.
- Marongiu G. Podda D., Mastio M., Capone A. Long-term results of isolated acetabular revisions with reinforcement rings: a 10- to 15-year follow-up // HIP International. - 2019. - Vol. 29, no. 4. - P. 385-392.
- De Martino I., Strigelli V., Cacciola G., Gu. A., Bostrom M.P., Sculco P.K. Survivorship and clinical outcomes of custom triflange acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review // Journal of Arthroplasty. - 2019. - Vol. 34, no. 10. - P. 2511-2518.
- Marx A., Beier A., Richter A., Lohmann C.H., Halder A.M. Major acetabular defects treated with the burch-schneider antiprotrusion cage and impaction bone allograft in a large series: a 5- to 7- year follow-up study // HIP International. - 2016. - Vol. 26, no. 6. - P. 585-590.
- Migaud H., Common H., Girard J., Huten D., Putman S. Acetabular reconstruction using porous metallic material in complex revision total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review // Orthopaedics and Traumatology: Surgery and Research. - 2019. - Vol. 105, no. 1. - P. 53-61.
- O'Neill C.J., Creedon S.B., Brennan S.A., O'Mahony F.J., Lynham R.S., Guerin S., Harty J.A. Acetabular revision using trabecular metal augments for Paprosky type 3 defects // The Journal of Arthroplasty. -2018. - Vol. 33. no. 3. - P. 823-828.
- Paprosky W. G., Perona P. G., Lawrence J. M. Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation // The Journal of Arthroplasty. - 1994. - Vol. 9, no. 1. - P. 33-44.
- Park K.S., Seon J.K., Lee K.B., Kim S.K., Chan C.K., Yoon T.R. Revision total hip arthroplasty using an acetabular reinforcement ring with a hook: a precise follow-up, at average 11.4 years, of a previous report // Journal of Arthroplasty. - 2017. - Vol. 32, no. 2. - P. 503-509.
- Philippe R., Gosselin O., Sedaghatian J., Dezaly C., Roche O., Sirveaux F., Molé D. Acetabular reconstruction using morselized allograft and a reinforcement ring for revision arthroplasty with Paprosky type II and III bone loss: Survival analysis of 95 hips after 5 to 13 years // Orthopaedics and Traumatology: Surgery and Research. - 2012. - Vol. 98, no. 2. - P. 129-137.
- Pierannunzii L., Zagra L. Bone grafts, bone graft extenders, substitutes and enhancers for acetabular reconstruction in revision total hip arthroplasty // EFORT Open Reviews. - 2016. - Vol 1, no. 12. -P. 431-439.
- Ring P.A. Complete replacement arthroplasty of the hip by the ring prosthesis. // The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume. - 1968. - Vol. 50, no. 4. - P. 720-731.
- Schreurs B.W. Keurentjes J.C., Gardeniers J.W., Verdonschot N., Slooff T.J., Veth R.P. Acetabular revision with impacted morsellised cancellous bone grafting and a cemented cup // Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. Series B. - 2004. - Vol. 86, no. 4. - P. 492-497.
- Sporer S.M., Paprosky W.G., Lawrence J. Acetabular revision using a trabecular metal acetabular component for severe acetabular bone loss associated with a pelvic discontinuity // Journal of Arthroplasty. - 2006. - Vol. 21, suppl. 6. - P. 87-90.
- Surgical Technique. Trabecular metal acetabular restrictor and augment acetabular assessment and preparation. 2006 Zimmer, Inc., avaliable at: http://www.rpa.spot.pt/getdoc/10606164-319b-45b2-80d2-32a5d4f218c1/TMT_augments.aspx (20 October 2020).
- Taunton M.J., Fehring, T.K., Edwards P., Bernasek T., Holt G.E., Christie M.J. Pelvic discontinuity treated with custom triflange component: a reliable option. - New York: Springer, 2012. - P. 428-434.
- Testut L., Lataijet A. Lower or pelvic limb osteology //Traité d'anatomie humaine. - Paris: Librairie Doin, 1928. - P. 374-375.
- Woo S.H. Sung M.J., Park K.S., Yoon T.R. Three-dimensional-printing technology in hip and pelvic surgery: current landscape // Hip & Pelvis. - 2020. - Vol. 32, no. 1. - P. 1.


