Effect of the time factor on the hydraulic activity of mechanically activated saponin-containing powder
Автор: Morozova M.V., Frolova M.A.
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: Manufacturing technology for building materials and products
Статья в выпуске: 3 Vol.17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. The article examines the problem of the development of transport infrastructure in the Solovetsky archipelago and proposes a solution to reduce the cost of manufacturing reinforced concrete slabs for the road surface. It is proposed to use saponite-containing waste (SCW) of the mining and processing plant JSC Severalmaz as a mineral additive in concrete. Studies have shown that mechanically activated saponite-containing powder (MSP) improves concrete performance and reduces binder consumption. The use of MSP makes it possible to solve the problem of waste disposal and reduce environmental damage. The purpose of the work is to assess the effect of the time factor on the hydraulic activity of the mechanically activated saponitecontaining powder, since the activity of the additive may change during long-term storage. It is known that the degree of activity of mineral components is usually estimated by the amount of Ca2+ ions absorbed from a saturated lime solution. A number of direct analytical methods are available to monitor the change in Ca(OH)2 content over time during the course of the hydraulic reaction. This technique, based on the measurement of the potential of the ion-selective electrode, is fully suitable for monitoring the hydraulic activity of the MSP. Methods and Materials. Saponite-containing waste was used as the main material for the studies, which was isolated, dried and dispersed. A mechanically activated saponite-containing powder was thus obtained. Control of the degree of grinding of the obtained finely divided MSP samples was carried out according to the specific surface area (Ssp, m2/kg). To perform potentiometric analysis, an electrode system consisting of a measuring electrode with a calcium ion detection function (pCa) and a reference electrode was used. In preparation for the experiment, the calcium selective electrode of the Elite-041 model was kept for three days in a calcium chloride solution with a concentration of 0.01 mol/L. The electrode was then washed with distilled water and calibrated to solutions with concentrations (CCa) of 10–1, 10–2, 10–3, 10–4 and 10–5 mol/L, for which pCa = 1÷5. To study the sorption capacity, a lime solution with a concentration of 0.015 mol/l was prepared, as well as a suspension from samples of fine mineral saponite-containing powder. A solution of lime with a volume of 0.2 ml was successively added to the resulting suspension by a doser, while measuring the electromotive force (potential) of the system with continuous stirring. Based on the obtained potential values (mV), the concentration of calcium ions (Сfact Ca) in the bulk phase of the suspension was calculated using a predetermined calibration relationship. Further, using the algorithm for calculating the activity parameters of powders, according to potentiometry data, the maximum amount of absorbed calcium hydroxide (ΔССaO) was determined as the difference between the Сteor Ca and Сfact Ca, and the hydraulic activity coefficient . Results and Discussion. The resulting mechanically activated saponite-containing powder had a specific surface area of 196 m2/kg (10 min), 644 m2/kg (30 min), 1209 m2/kg (60 min), 1428 m2/kg (90 min) at different milling times. The preliminary calibration dependence of the potential of the electrode pair on the pCa value is characterized by the linear equation: E = –23,23pCa+520,35. It was found that when adding a lime solution to the suspension, an increase in EMF is observed due to the sorption of calcium ions by a mechanically activated saponite-containing powder. After reaching the threshold volume of the Ca(OH)2 solution, the potential stabilizes. With a further increase in the concentration of calcium ions, when their interaction with the MSP particles ceases, the E value increases again. Further, dependencies were obtained for all batches of the experiment, the difference of which lies only in the quantitative characteristics of the functional parameters. Initial value of electrode pair potential characterizes background concentration of calcium ions determined by their residual content in water and/or MSP. The obtained functional relationships of the Сfact Ca = f(Сteor Ca) for the test samples made it possible to determine the threshold values of the concentration of calcium ions in the solution, the excess of which creates their excess in the reaction medium. The built functional dependence of the G∞ = f(Ssp), showed that the G∞ reaches its maximum value already at a specific surface area of more than 600 m2/kg (30 minutes of grinding). Since the grinding of 10 minutes has little effect on the specific surface area of the saponite powder, which affects the value of the hydraulic activity coefficient of the MSP, the dependence of G∞ = f(Ssp) for grinding more than 10 minutes was considered.
Saponite-containing powder, mechanical grinding, specific surface area, hydraulic activity, calcium oxide, calcium hydroxide concentration, electrode pair potential
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142244830
IDR: 142244830 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2025-17-3-244-253
Текст научной статьи Effect of the time factor on the hydraulic activity of mechanically activated saponin-containing powder
Original article
Морозова М.В., Фролова М.А. Влияние временного фактора на гидравлическую активность механоактивированного сапо-нитсодержащего порошка. Нанотехнологии в строительстве. 2025; 17(3):244–253. – EDN: AFTMHY.
It is of particular importance to create a favorable urban environment on the Solovetsky Archipelago by developing the transport infrastructure of the settlements. Comprehensive renewal of the village’s road network includes both the creation of new facilities and the repair of existing routes with unpaved and transitional surfaces (Fig. 1). The latter are presented in the form of natural stone and reinforced concrete slabs, with a total length of 2.5 km. The construction of such a roadway is one of the faster ways to create a strong and structurally stable coating [1–5].
However, the manufacture of reinforced concrete slabs and related building materials, with their subsequent delivery to the archipelago, is a very material-intensive and laborious task, which makes this process economically inexpedient.
It is known that the cost of producing concrete composites is associated with the use of binders, fillers/fillers and various chemical additives that control the properties of the final product. Therefore, reducing the cost of these components is one lever that can compensate for labor costs and obtain a total economic effect. In addition, an important modern component in the production of building materials is the use of resource-saving technologies,
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS


Fig. 1. The condition of the road surface in the village of Solovetsky
including the effective use of production waste with different chemical compositions and structures, which can reduce costs [6–10].
In the construction industry, steady interest continues to be shown in concrete products and structures, since its manufacture from raw materials (cement, sand, additives) requires minimal energy consumption. In addition, the production of concrete mix has wide opportunities for the utilization of secondary material resources (production waste) [11–12]. Thus, earlier studies have shown the effectiveness of using finely ground dispersed mineral additives in binding compositions of the hydration type of hardening. A classic example of such raw materials is fly ash, finely ground slags and microsilica [13–14]. However, for each region of Russia, local production waste can be used as such an additive, for example, alumina-containing aluminum slags of Donbass [15], technogenic raw materials of energy and metallurgical enterprises [16], finely ground filler based on metacaolin in Chelyabinsk [17] or Tomsk slag waste. For the Arkhangelsk region, this is saponite-containing waste (SСW) of the Severalmaz mining and processing plant, which is stored in a large volume (up to 4 million tons annually) in settling ponds. Large-scale saponitiza-tion of diamond-bearing ore [18] makes it difficult to use process water in the recycling water supply system of the factory [19–20] and forces to constantly increase the area allocated for waste rock dumps.
Previous studies [21] have shown the effectiveness of the use of SСW in the form of mechanically activated saponite-containing powder (MSP) as a mineral additive in concrete, which improves the performance of the composite and reduces the consumption of the most expensive component – binder. Mechanical dispersion to a specific surface area comparable to that of cement is used to activate this component [22]. In this case, the saponite raw material is transformed into a highly active mineral powder, which exhibits: water-sorption properties that regulate the water-cement ratio of the mixture; pozzolanic activity with the formation of hydrosilicates of the tobermorite group [21]. The latter are formed in the pore space of the composite, when it hardens, and provide a strong concrete structure, improving its performance.
Thus, the use of waste from the Arkhangelsk diamond mining industry as a raw material base for the production of highly active mineral saponite-containing powder makes it possible to comprehensively solve the problem of increasing the efficiency and quality of construction production, as well as reduce the environmental damage caused to the region’s environment.
Currently, the choice of raw materials for obtaining the most effective modifying additives is based on the results of studies of hydration processes that occur in the “additive-cement binder” system during its hardening and contribute to the formation and development of crystalline neoplasms [23–25]. In this regard, the mechanism of action of MSP has been studied [21]. It has been found that its beneficial effect on the properties of cement compositions largely depends on the amount of activity of the additive and its specific surface area. However, these parameters may change in the case of long-term storage of the MSP and, thereby, limit the shelf life of the product and the range of its transportation.
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
Therefore, the purpose of this work is to evaluate the effect of the time factor on the hydraulic activity of the mechanically activated saponite-containing powder.
It is known that the degree of activity of mineral components is usually estimated by the amount of Ca2+ ions absorbed from a saturated lime solution. A number of direct analytical methods are available to monitor the change in Ca(OH)2 content over time during the course of the hydraulic reaction. Thus, papers [26–27] show the applicability of a potentiometric analysis method using an ion-selective electrode with a pCa function to assess the hydraulic activity of fine materials. This technique, based on the measurement of the potential of the ion-selective electrode, is fully suitable for monitoring the hydraulic activity of the MSP and is very effective in terms of rapidity and labor intensity.
METHODS AND MATERIALS
Saponite-containing waste of the Lomonosov Mining and Processing Plant of Severalmaz JSC, which was isolated, dried and dispersed, was used as the main material for the research. Thus, mechanically activated saponite-containing powder (MSP) was obtained, and the technological redistribution of the rock included the following stages:
-
I – recovery of SCW from circulating water suspension by electrolyte coagulation;
-
II – dilution of thickened sediment to residual humidity of not more than 10% using a drying oven at a temperature of 105 °С;
III – dry grinding of the material to the required degree of dispersion on a planetary ball mill Retsch PM100. The optimal mode parameters of dispersion were selected experimentally: the rotation speed of the mill rotor was 420 min–1, the number of grinding bodies was 20 pcs. (tungsten carbide balls); grinding time 10, 30, 60 and 90 minutes.
Control of the degree of grinding of the obtained finely dispersed SMP samples was carried out by the specific surface area (Ssp, m2/kg) using an automatic multifunctional PSKh-10M device, using the Kozeny-Karman gas permeability method.
To perform potentiometric analysis, an electrode system consisting of a measuring electrode with a calcium ion detection function (pCa) and a reference electrode was used. This system was connected to the ionomer model Expert-001-3.0.1. The electrodes were placed in a 100 ml glass cylindrical container. A magnetic stirrer was used to ensure uniform distribution of the components of the reaction mixture in the volume analyzed. All experiments were conducted under controlled temperature conditions which were maintained at 20 °С with a deviation ± 2 °С. In preparation for the experiment, the calcium selective electrode of the Elite-041 model was kept for three days in a calcium chloride solution with a concentration of 0.01 mol/L. The electrode was then washed with distilled water and calibrated using standard solutions of calcium chloride. Calibration was performed on solutions with concentrations (CCa) of 10–1, 10–2, 10–3, 10–4 and 10–5 mol/L, for which pCa = 1÷5.
To study the sorption capacity, a lime solution with a concentration of 0.015 mol/l was prepared at a temperature of 20 °C, as well as a suspension from samples of highly dispersed mineral saponite-containing powder (0.5 g in 80 ml distilled water). A 0.2 ml lime solution was successively injected into the resulting suspension (almost immediately after preparation) with a dispenser, while measuring the electromotive force (potential) of the system with continuous stirring. Based on the obtained potential values (mV), the concentration of calcium ions was calculated (СfactCa) in the bulk phase of the suspension using a preset calibration dependence.
Similar experiments were carried out after holding the MSP (in a dry state in a polyethylene container) for 7, 14 and 30 days. Further, using an algorithm for calculating the activity parameters of powders based on the potentiometry data presented in [26, 27], the maximum amount of absorbed calcium hydroxide (∆ССaO) was determined as the difference between the values СteorCa and С factCa the coefficient of hydraulic activity (G^ = ln3VAC^).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The mechanically activated saponite-containing powder isolated using the above-described technology with different grinding durations (10 ÷ 90 min) was characterized by the specific surface area: Ssp10 = 196 m2/kg; Ssp30 = 644 m2/kg; Ssp60 = 1209 m2/kg; Sspp90 = 1428 m2/kg p(the superscript symbol corresponds to the grinding duration).
Figure 2 shows the calibration dependence of the potential (EMF) of the used electrode pair on the pCa value. A mathematical expression is characterized by a straight line and can be represented by the following equation: E = –23,23pCa+520,35.
The value of the angular coefficient of the presented expression corresponds to the theoretical value of the steepness of the calibration characteristic of the electrode, which indicates the correctness of the obtained data.
Figure 3 shows the experimental dependence of the potential value of the electrode pair ( E ) on the volume of lime solution introduced into the reaction medium. It was found that the addition of lime solution to the suspension is accompanied by an increase in EMF, which is associated with the process of sorption of calcium ions by a mechanically activated saponite-containing powder. At the same time, it was recorded that with the addition of a certain threshold volume (Vmv, ml) of Ca(OH)2 solution, the electrode potential practically stabilizes. A further increase in the concentration of calcium ions in the analyzed solution (at which the interaction of the analyzed
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
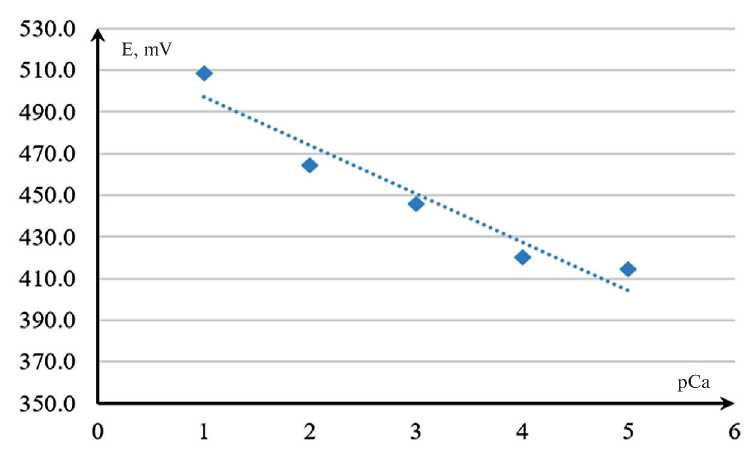
Fig. 2. Calibration dependence of the view E = f(pCa)
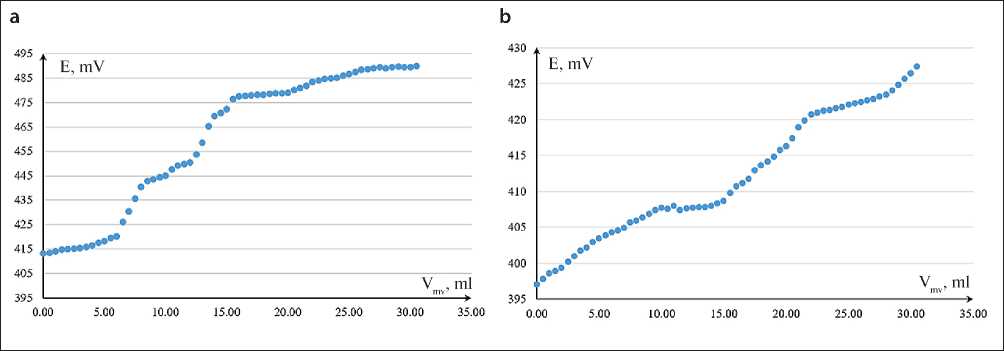
Fig. 3. Potential of the electrode pair upon adding Ca(OH)2 solution to the MSP suspension: a – grinding time 10 min; b – grinding time 60 min.
ions with the MSP particles ceases) leads to a repeated increase in the value of E .
It should be noted that similar dependencies were obtained for all series of the experiment, the difference between which lies only in the quantitative characteristics of the functional parameters. In this case, the value of the potential of the electrode pair at the start of the experiment (before adding the calcium hydroxide solution) characterizes the background concentration of calcium ions, which is determined by their residual content in the H2O and (or) MSP used.
Figure 4 shows, as an example, the functional dependencies СfactCa = f(СteorCa) for the studied MSP, calculated based on potentiometric measurement data. Similar data were obtained for the other two powder fractions.
The obtained results (Fig. 4) allow us to determine the threshold values of calcium ion concentration in the solution, an increase of which leads to their excess in the reaction medium.
The ratio of the set concentration (СteorCa) to the determined concentration of calcium ions in the suspension (СfactCa) in the region of threshold values of these parameters characterizes the degree of activity of the tested MSP sample in relation to Ca2+. The obtained results and the calculated values of the hydraulic activity coefficient are presented in Table 1.
The functional dependence G∞ = f(Ssp) shown in Figure 5 shows that G∞ reaches its maximum value already at a specific surface area of more than 600 m2/kg (30 min of milling).
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
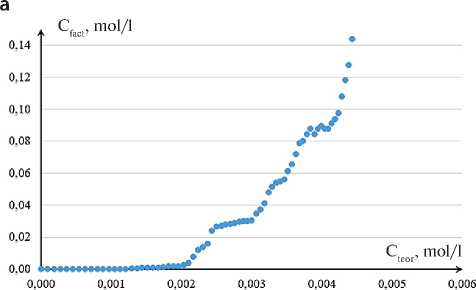
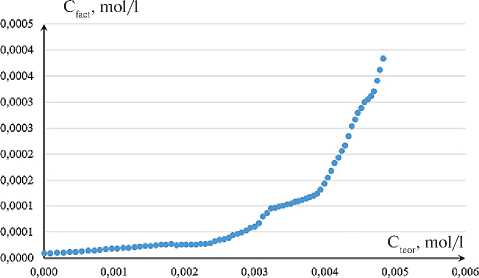
Fig. 4. Concentration dependences СfactCa = f(СteorCa) for MSP with different grinding times: a – 10 minutes; b – 60 minutes.
Table 1. Characteristics of the activity of mechanically activated saponite-containing powders
|
Sample |
Grinding time, min |
Ssp, m2/kg |
СteorCa / СfactCa |
∆ССaO, mg/g |
G ∞ |
|
MSP10 |
10 |
196 |
0.52 |
0.39 |
0.010 |
|
MSP 30 |
30 |
644 |
223.40 |
169.09 |
0.783 |
|
MSP 60 |
60 |
1209 |
256.50 |
194.14 |
0.803 |
|
MSP 90 |
90 |
1428 |
274.42 |
207.70 |
0.813 |
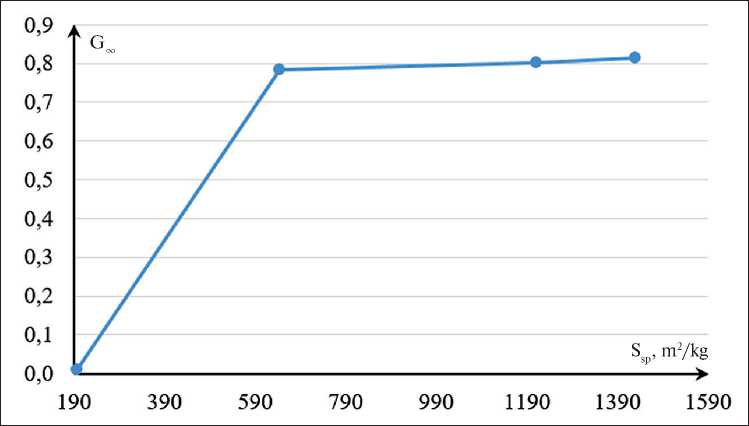
Fig. 5. Functional dependence G∞ = f(Ssp) for MSP obtained with different grinding durations
Taking into account the fact that a grinding duration of 10 min has practically no effect on the specific surface area of saponite powder, which is reflected in the value of the hydraulic activity coefficient of the MSP, we separately considered the dependence G∞ = f(Ssp) for a grinding duration of the raw material of more than 10 min (Fig. 6).
Extrapolation of the obtained dependence (Fig. 6) to the specific surface area of the MSP equal to 300 m2/kg
(this value of this characteristic is possessed by the mineral saponite-containing powder obtained industrially under the conditions of the technological process of obtaining mineral saponite-containing powder using an activator (two-stage grinding on a hammer crusher MPS 300L and a ball mill – the grinding complex “Activator S1000” [28]) yields the value of G∞ = 0,772. This value of the hydraulic activity coefficient is expectedly close to
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
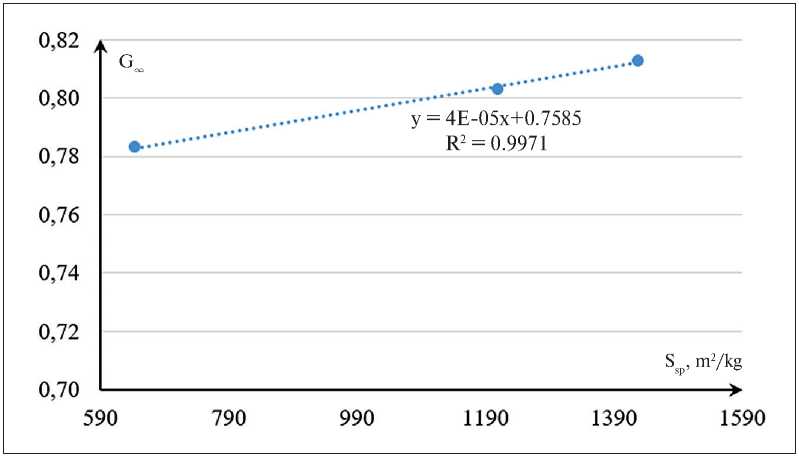
Fig. 6. Functional dependence G∞ = f(Ssp) for MSP obtained with a grinding duration of more than 10 min.
Table 2. Characteristics of MSP activity with increasing storage time
To clarify the influence of the time factor on the value of the hydraulic activity coefficient of the MSP, the powder obtained after 60 minutes of grinding (Ssp = 1209 m2/kg) was used, assuming that a high value of the specific surface of the powder will more actively contribute to the change in its reactivity during long-term storage. The determination of the experimental characteristics (potential of the electrode pair) and processing of the obtained data were carried out according to the above-described method after 7, 14 and 30 days of aging the mineral powder. The results obtained are given in Table 2.
The presented results (Table 2) show that during the storage of mechanically activated saponite-containing powder under natural conditions, a spontaneous decrease in the value of its specific surface occurs due to the conglomeration of primarily clay fraction particles. However, this process is accompanied by a decrease in the powder Ssp after 7 and 30 days by 1.5% and 25% (respectively). At the same time, the hydraulic activity of the MSP during these time intervals decreases only by 2.6% and 4.1% (respectively).
The obtained data, in our opinion, confirm the fact of maintaining a long-term (30-day) period of sufficiently high hydraulic activity of mechanically activated saponitecontaining powders in a wide range of variation of their specific surface area (300÷1200 m2/kg).
CONCLUSION
-
1. It is shown that the potentiometric method for determining the sorption capacity with respect to calcium oxide can be used as an express method for quantitatively determining the hydraulic activity coefficient of mechanically activated saponite-containing powder and assessing the effect of the time factor on this indicator.
-
2. It is established that the hydraulic activity of mechanically activated powders is functionally related to their specific surface area (in the range of specific surface area values of 300÷1200 m2/kg), and the nature of this relationship is described by a linear equation with a high value of the approximation reliability coefficient (0.99).
-
3. Mechanically activated saponite-containing powders retain their hydraulic activity when stored under natural conditions for 30 days. The decrease in the hydraulic activity of the MSP over this time interval is 4.1%.
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY FOR BUILDING MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS


