Effectiveness of isotonic exercise in reduction of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients in dialysis unit
Автор: Srinubabu K., Parimala L., Thenmozhi P.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 23, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Background: Kidney is a vital organ and the main function is to remove waste products and excess water from the blood. Different kidney pathogenesis challenges the function of human body and puts human life danger. Two such important pathogenesis is acute and chronic renal failure. The incidence of acute renal failure has been estimated to be 209 patients per million populations per year and 37% of patients treated in intensive care units. Muscle cramps also can occur when patients are below dry weight. The severe muscle cramping experienced near the end of the hemodialysis treatment and persisting for a time after hemodialysis often is due to dehydration. Treatment for cramping varies from unit to unit. When patients are having cramping and have low blood pressure, the staff may give normal saline. Aim of the study: The main aim of the study to assess effectiveness of isotonic exercise on muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients. Methods: Quantitative research design was adopted for the study with 60 samples which met the inclusion criteria were selected by convenience sampling technique. Demographic variables data were collected by using a multiple-choice questionnaire followed by Pretest was conducted by using muscle cramp assessment tool for both experimental group and control group. Isotonic exercise was given 10 to 15 minutes at one session for experimental group Post test was conducted by using muscle cramps assessment tool and for both experimental group and control group. Result: Out of 60 samples, The calculated student Independent ‘t’ test value of t = 2.500 was found to be statistically highly significant at p function show_abstract() { $('#abstract1').hide(); $('#abstract2').show(); $('#abstract_expand').hide(); }
Renal failure, dialysis, muscle gramps, isotonic exercise, hemodialysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148326562
IDR: 148326562 | DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.23.117122
Текст научной статьи Effectiveness of isotonic exercise in reduction of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients in dialysis unit
Kandukuri Srinubabu, Parimala L, Thenmozhi P. Effectiveness of Isotonic Exercise in Reduction of Muscle Cramps among Hemodialysis Patients in Dialysis Unit. Cardiometry; Issue 23; August 2022; p. 117-122; DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.23.117122; Available from:
Chronic kidney disease, also known as chronic renal failure, is an irreversible and progressive loss of functioning renal tissue that occurs when the remaining kidney mass can no longer maintain the body’s internal environment.1 Renal failure is the result of end stage renal disease when the remaining kidney mass can no longer maintain the body’s internal environment. Chronic renal disease can take years to develop. Severe kidney illness necessitates some sort of renal replacement therapy, which could be hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or a kidney transplant2.
Hemodialysis is a treatment for patients with endstage renal failure that involves the use of an artificial kidney machine to replace the damaged kidney’s excretory function. Dialysis is the act of removing waste and excess water from the blood. It is an artificial replacement for kidney function, especially in cases of chronic renal disease.3 Dialysis cannot replace lost kidney function fully, but it can help regulate its activities to some extent by using diffusion and ultrafiltration over months or years. Serum creatinine levels, which are decretive products of muscle protein, can be used to diagnosis chronic renal failure.4
Muscle cramps are a typical hemodialysis consequence. The discomfort causes the treatment to be temporarily stopped. Interfering with muscle and even preventing cramps has become a key job of the health personnel in charge of the patients.5The patient’s life events and complications due to hemodialysis are under the care and protection of health professionals. With proper care during the treatment period and appropriate nursing management with hemodialysis, patients’ lives and assurance can improve.6
A quasi-experimental investigation was carried out at the PSG dialysis unit in Coimbatore. The purpose of this study was to see if intradialytic stretching exercises affected muscle cramping during hemodialysis. A total of sixty samples were chosen, with 30 in each of the intervention and comparison groups. A standardized cramp questionnaire chart and a visual analogue scale were used to determine the pre-test score of muscle cramps. The intervention group was given intradialytic stretching exercises, and the posttest assessment was done on the 4th, 7th, and 10th day of sitting. The pre and post interventions on muscle cramping showed significant statistically significant benefits. After 6 days of therapy, comparing the Intradialytic stretching exercises to the stretching exercises, the amount of muscle cramping is reduced.7
A clinical investigation involving 60 dialysis patients with muscle spasms was done. The participants were split into experimental and control groups at random. Muscle cramping and pain severity were measured before and after the workout programme was implemented. Before starting hemodialysis, the isotonic exercise programme includes ten 10-minute sessions on a stationary bicycle. The goal of the study was to see how an isotonic exercise regimen affected the pain severity of leg muscle cramps in dialysis patients. The severity and frequency of muscle cramps after exercise were shown to be significantly reduced. The mean pain severity in the experimental and control groups differed before and after the intervention, respectively. Exercise significantly reduced the severity and frequency of leg muscular cramps, according to the findings.8
In 2014, at the Shahrekord and Borujen hospitals, I conducted a study to see how isotonic exercise affected the frequency of muscle cramps. A clinical investigation involving 60 hemodialysis patients was conducted. The findings demonstrated that isotonic continuous cycling exercise has a significant impact on reducing the number of muscle cramps in hemodialysis patients. As a result, it is advised that dialysis units provide facilities for continuous walking and cycling in order to speed up the treatment of patients9.
The Victorian Institute of Sport Assessment-Gluteal conducted a randomized controlled trial. To alleviate the symptoms of greater trochanteric pain syndrome During the trial period, both programmes included daily, progressive home exercise for 12 weeks and 8 individual physiotherapy sessions. The trial was completed by twenty-three people. After 12 weeks, the isotonic exercise group had a 55 percent success rate while the isometric exercise group had a 58 percent success rate. Exercise programmes that are isometric and isotonic appear to be useful in lowering Greater trochanteric pain syndrome and should be considered in the loading management of people with pain.10Dis-comfort is the most common consequence among hemodialysis patients, so it’s been recommended that isotonic and isometric exercise can help hemodialysis patients in various health care settings reduce pain.11
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 60 samples who met the inclusion criteria were selected by using convenient sample. After selecting the sample, the investigator introduced him and explained the purpose of the study to the patients. Informed consent was obtained after assuring confidence. Each patient was assessed on the bed side. The patient was placed in a comfortable position. The demographic variables and clinical variables were collected by using structured interview questionnaire. Pretest was conducted by using muscle cramp assessment tool for both experimental group and control group. Isotonic exercise was given 10 to 15 minutes at one session for experimental group Post test was conducted by using muscle cramps assessment tool and for both experimental group and control group. The data were tabulated and analyzed by descriptive and inferential statistics. The pilot study was found to be feasible.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 1 shows that the majority of hemodialysis patients in the experimental group were between the ages of 51 and 60, were male, 17(56.7 percent) were illiterate, 26(86.7 percent) were unemployed, 16 (53.3 percent) had an economic status of 5,000 to 10,000, 16 (53.3 percent) belonged to a nuclear family, and 17 (56.7 percent) had previously experienced cramps.
Table 1 also shows that most hemodialysis patients in the control group were between the ages of 51 and
Table 1
Frequency and percentage distribution of demographic variables of hemodialysis patients in the experimental and control group. N = 60(30+30)
|
Demographic Variables |
Experimental Group |
Control Group |
||
|
No |
% |
No |
% |
|
|
Age in years |
||||
|
21–30 |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
31 – 40 |
9 |
30.0 |
5 |
16.7 |
|
41 – 50 |
10 |
33.3 |
7 |
23.3 |
|
51 – 60 |
11 |
36.7 |
18 |
60.0 |
|
Gender |
||||
|
Male |
21 |
70.0 |
19 |
63.3 |
|
Female |
9 |
30.0 |
11 |
36.7 |
|
Education status |
||||
|
Literacy |
13 |
43.3 |
11 |
36.7 |
|
Illiteracy |
17 |
56.7 |
19 |
63.3 |
|
Occupational status |
||||
|
Employed |
4 |
13.3 |
5 |
16.7 |
|
Unemployed |
26 |
86.7 |
25 |
83.3 |
|
Economic status |
||||
|
5,000 – 10,000 |
16 |
53.3 |
8 |
26.6 |
|
11,000 – 20,000 |
5 |
16.7 |
11 |
36.7 |
|
21,000 – 40,000 |
4 |
13.3 |
2 |
6.7 |
|
Dependent |
5 |
16.7 |
9 |
30.0 |
|
Type of family |
||||
|
Joint family |
14 |
46.7 |
17 |
56.7 |
|
Nuclear family |
16 |
53.3 |
13 |
43.3 |
|
Previous experience of cramps |
||||
|
Yes |
17 |
56.7 |
14 |
46.7 |
|
No |
13 |
43.3 |
16 |
53.3 |
-
60, were male, 19(63.3 percent) were illiterate, 25(83.3 percent) were unemployed, 11(36.7 percent) had an economic status of 11,000 – 20,000, 17(56.7 percent) belonged to a joint family, and 16(53.3 percent) had no previous experience with cramps.
Table 2 shows that the clinical variable duration of hemodialysis (2=6.600, d.f=0.37) had a statistically significant association with posttest level of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients in the experimental group at the p0.05 level, while the other clinical variables had no statistically significant association with posttest level of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients.
In the pretest of the experimental group, 24 (80%) had moderate cramps and 6 (20%) had mild cramps, while in the pretest of the control group, 21 (70%) had moderate cramps and 9 (30%) had mild cramps.
Lekha J and her colleagues (2017) A quasi-experimental investigation was carried out at PSG Hospitals’ dialysis facility in Coimbatore. The purpose of this study was to see if intradialytic stretching exercises affected muscle cramping during hemodialysis. The pre and post therapies on muscle cramping showed significant statistical benefits. After 6 days of therapy, comparing the Intradialytic stretching exercises to the stretching exercises, the amount of muscle cramping is reduced.12
In the pretest, 8(26.67%) experienced significant cramps and 6(20%) had mild cramps, according to the results of the current study. In the post-test following the administration of Isotonic Exercise, 6 (20%)
Table 2
Association of posttest level of muscle ramp among hemodialysis patients with their selected clinical variables in the experimental group. n = 30
|
Clinical Variables |
No Cramp |
Mild |
Moderate |
Severe |
Chi-Square Value |
||||
|
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
||
|
Duration of disease |
χ2=6.863 d.f=6 p= 0.334 N.S |
||||||||
|
Less than or equal to 6 months |
3 |
10.0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
- |
- |
|
|
1 – 2 years |
8 |
26.7 |
4 |
13.3 |
2 |
6.7 |
- |
- |
|
|
3 – 4 years |
4 |
13.3 |
2 |
6.7 |
5 |
16.7 |
- |
- |
|
|
>4 – 5 years |
1 |
3.3 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
3.3 |
- |
- |
|
|
Duration of hemodialysis |
χ2=6.600 d.f=2 p= 0.037 S* |
||||||||
|
2 hours |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
3 hours |
2 |
6.7 |
3 |
10.0 |
0 |
0 |
- |
- |
|
|
4 hours |
14 |
46.7 |
3 |
10.0 |
8 |
26.7 |
- |
- |
|
|
5 hours |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
Clinical Variables |
No Cramp |
Mild |
Moderate |
Severe |
Chi-Square Value |
||||
|
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
No. |
% |
||
|
Amount of fluid removed during dialysis |
χ2=7.083 d.f=4 p= 0.132 N.S |
||||||||
|
500 ml – 1.5 Lit |
4 |
13.3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
- |
- |
|
|
2 – 3 Lit |
5 |
16.7 |
5 |
16.7 |
5 |
16.7 |
|||
|
3.5 – 4 Lit |
7 |
23.3 |
1 |
3.3 |
3 |
10.0 |
- |
- |
|
|
5Lit |
- |
- |
|||||||
|
Serum sodium |
χ2=2.845 d.f=2 p= 0.241 N.S |
||||||||
|
>Normal value |
16 |
53.4 |
6 |
20.0 |
7 |
23.3 |
- |
- |
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
3.3 |
- |
- |
|
|
Serum potassium |
χ2=1.129 d.f=2 p= 0.569 N.S |
||||||||
|
>Normal value |
3 |
10.0 |
2 |
6.7 |
3 |
10.0 |
- |
- |
|
|
|
13 |
43.3 |
4 |
13.3 |
5 |
16.7 |
- |
- |
|
|
Frequency of muscle cramps |
χ2=4.406 d.f=4 p= 0.354 N.S |
||||||||
|
1 – 2 times |
9 |
30.0 |
6 |
20.0 |
5 |
16.7 |
- |
- |
|
|
3 – 4 times |
6 |
20.0 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
10.0 |
- |
- |
|
|
5 – 6 times |
1 |
3.3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
- |
- |
|
|
>6 times |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|||
*p<0.05, S – Significant, N.S – Not Significant
had mild cramps, 16 (53.3%) had no cramps, and 8 (26.67%) had significant cramps.
In the post-test of the experimental group, the Isotonic Exercise delivered to hemodialysis patients was found to be helpful in reducing the amount of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients.
Isotonic exercise is an effective strategy to alleviate leg muscle cramp among hemodialysis patients, according to the findings of Mahdi Poornazari1, et al, (2017). More research is needed to fully understand the effectiveness of isotonic exercise workouts on leg muscle cramp in hemodialysis patients in various health care settings. According to the findings of Mahdi Poornazari1, et al, isotonic exercise is an effective method for alleviating leg muscular cramp in hemodialysis patients (2017). To fully grasp the effects of isotonic exercise sessions on leg muscle cramp in hemodialysis patients in diverse health care settings, more research is needed.13
AlirezaDashtidehkordi, et al., Alireza Dashtideh-kordi1, et al., AlirezaDashtide (2018) The clinical experiment was carried out at two hospitals in Isfahan, Iran, to see how exercise affected health-promoting behaviors. The study’s sample consisted of 60 hemodialysis patients in Isfahan who were randomly assigned to one of two groups: control or intervention, using a random allocation procedure. The intervention group 120 | Cardiometry | Issue 23. August 2022
received an 8-week exercise programme using stationary bicycles (Mini-bike), whereas the control group received standard care. The findings of this study revealed that stationary bicycle exercise during hemodialysis can enhance health-promoting behaviors.As a result, this activity should be regarded as part of the therapeutic plan for these hemodialysis patients.14
The current study found that none of the demographic variables had a statistically significant association with posttest level of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients in the experimental group, but the clinical variable duration of hemodialysis (2=6.600, d.f=0.37) had a statistically significant association with posttest level of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients.
Joannes M Hallegraeff and colleagues (2016) The effect of muscle stretching exercise on nocturnal muscle cramps was investigated in a randomized trial. The findings demonstrated that muscular stretching exercises have a significant impact on reducing nocturnal muscle cramps in the elderly. Because chronic renal disease affects 40% of the elderly, it is proposed that muscle stretching be considered as an alternate therapy. It’s simple to do, has a low risk of adverse effects, and relieves pain quickly when a cramp occurs. Stretching exercise is a useful intervention for hemodialysis patients in many health care settings to minimize muscle cramps.15 Percentage distribution of pretest and posttest level of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients in the experimental group is shown in Figure 1.
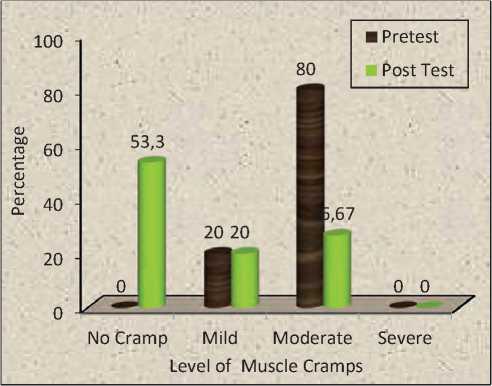
Figure 1. Percentage distribution of pretest and posttest level of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients in the experimental group
CONCLUSION
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Список литературы Effectiveness of isotonic exercise in reduction of muscle cramps among hemodialysis patients in dialysis unit
- SamahSaad Salem (2017). The effect of intra-dialytic stretching exercises on leg muscle cramp among hemodialysis patients.IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science, Volume 6, Issue 2.
- Mohamed, S. A., Kanona, A. A., & El-Gahsh, N. F. (2020). Effect of Intradialytic Range of Motion Exercises on Dialysis Efficacy and Blood pressure among Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. Menoufia Nursing Journal, 5(2), 39-54.
- Vadakedath, S., &Kandi, V. (2017). Dialysis: A Review of the Mechanisms underlying Complications in the Management of Chronic Renal Failure. Cureus, 9(8), 1603. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.1603
- Murdeshwar, H. N., &Anjum, F. (2021). Hemodialysis. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
- J, Ms.Lekha& Abraham, Elizabeth &Malarvizhi, Dr.G.. (2017). Effectiveness of Intradialytic Stretching Exercises on Prevention and Reduction of Muscle Cramps among Patients undergoing Haemodialysis at PSG Hospitals Coimbatore. IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science. 06. 47-53. 10.9790/1959-0602044753.
- Zelko, A., Skoumalova, I., Kolarcik, P., Rosenberger, J., Rabajdova, M., Marekova, M., Geckova, A. M., van Dijk, J. P., Reijneveld, S. A., & NEPHRO-team (2019). The effects of intradialytic resistance training on muscle strength, psychological well-being, clinical outcomes and circulatory micro-ribonucleic acid profiles in haemodialysis patients: Protocol for a quasi-experimental study. Medicine, 98(19), e15570. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000015570
- Moriyama, Y., Hara, M., Aratani, S. et al. The association between six month intra-dialytic resistance training and muscle strength or physical performance in patients with maintenance hemodialysis: a multicenter retrospective observational study. BMC Nephrol 20, 172 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-019-1375-1
- Salem, Samah& Mohamed, Shaimaa. (2017). Effectiveness of Intra-dialytic Stretching Exercises on Leg Muscle Cramp among Hemodialysis Patients. IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science. 06. 47-53. 10.9790/1959-0602094753.
- Dashtidehkordi, A., Shahgholian, N. &Attari, F. “Exercise during hemodialysis and health promoting behaviors: a clinical trial”. BMC Nephrol 20, 96 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-019-1276-3
- Kingsle Kishore (2016). The effect of intra-dialytic stretching exercises on muscle cramp (pain) among patients undergoing hemodialysis. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Development. Volume 3; Issue 1; January 2016; Page No. 314-319.
- Mahdi Poornzaari (2019).The effect of isotonic exercise on the frequency of muscle cramps. Medical Surgical Nursing Journal, 2(11), 34-67.
- Lekha& Abraham, Elizabeth &Malarvizhi, Dr.G.. (2017). Effectiveness of Intradialytic Stretching Exercises on Prevention and Reduction of Muscle Cramps among Patients undergoing Haemodialysis at PSG Hospitals Coimbatore. IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science. 06. 47-53. 10.9790/1959-0602044753.
- Poornazari, M., Roshanzadeh, M., Mohammadi, S., Tajabadi, A., Dehghani, K., &Parsa, S. (2019). Effect of Isotonic Exercise on the Frequency of Muscle Cramps in Hemodialysis Patients: A Clinical Trial. Medical-Surgical Nursing Journal, 8(1), 85770-85775.
- Dashtidehkordi A, Shahgholian N, Attari F. “Exercise during hemodialysis and health promoting behaviors: a clinical trial”. BMC Nephrol. 2019 Mar 19;20(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1276-3. PMID: 30890122; PMCID: PMC6425622.
- Joannes M. Hallegraeff, Cees P. van der Schans, Renee de Ruiter, Mathieu H.G. de Greef,Stretching before sleep reduces the frequency and severity of nocturnal leg cramps in older adults: a randomised trial, Journal of Physiotherapy,Volume 58, Issue 1,2012,Pages 17-22,


