Effects of varying concentrations of ethanol leaf extract of Paullinia pinnata on histopathology of Clarias gariepinus juveniles
Автор: Ibrahim F.O., Idowu A.A., Taiwo I.O., Adekola M.B., Towolawi A.T., Adesanya O.E.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The study investigated of varied levels’ effects of Paullina pinnata ethanol leaf extract on Clarias gariepinus juveniles in a 2-phase (range-finding and main) experiment. Two hundred and fifty Clarias gariepinus juveniles were acclimatised for two weeks at the Fish Hatchery complex of the Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, where they were weighed with a mean weight of 9.00 ± 1.00 g, distributed into 12 plastic tanks of 35 L capacity, and arranged in a completely randomised system with a stocking density of 9 fish per tank. For the first phase (i.e., range-finding) experiment, 99 C. gariepinus juveniles were stocked into the plastic tanks (35 liters) filled to 10 litres of the volume, dosed with 5 mL syringe drops of 500, 1000, and 1500 mg L-1 extracts in triplicate, where no behavioural changes and mortality were observed. For the main experiment, 108 C. gariepinus juveniles were stocked and dosed with increased 5 mL syringe drops of 0, 3000, 5000, and 7000 mg L-1 extracts in triplicated. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) analysed the data, and the Duncan Multiple Range Test separated the means. The histological results of the main experiment revealed severe lesions on the gills of the varied-extract exposed fish. The extract had a significantly negative effect on the exposed fish and posed a threat, which eventually led to death at a higher concentration. The study concluded and recommended that the range-finding concentrations of the extract should always be administered by the fish farmers while exploring the ethanol leaf extract of Paullinia pinnata to lessen the threat to life below water.
Fish lesions, fish toxicity, range-finding test, sdg 14, severe lesions
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143183444
IDR: 143183444
Текст научной статьи Effects of varying concentrations of ethanol leaf extract of Paullinia pinnata on histopathology of Clarias gariepinus juveniles
Nigeria is the third largest fish consumer in Africa, with about 3.2 million metric tons consumed annually (FAO , 2018). Forty per cent of the average Nigerian's animal protein intake comes from fish. In addition to providing animals with protein, fish is useful for therapeutic purposes since it refills the body's supply of vitamins A and D, calcium, phosphorus, lysine, sulfur, and amino acids. Catfish, tilapia, clupeids, croaker, and other fish species are among those found in Nigerian reservoirs, which make up 90 % of the country's fisheries.
Plant extracts are becoming increasingly popular in aquaculture due to their natural biocides, extensive therapeutic history and potential for healing (Reveter et al., 2017); their preventive and therapeutic qualities have been shown in copious research (Talpur et al., 2013). Plants are known to contain complex chemical compounds that influence a range of biological activities and have the potential to either prevent or treat disease. Bioactive substances in plants include flavonoids, alkaloids, tannins, saponins, and terpenoids. Also, they are confirmed as an antinutrient known to promote growth and stimulate reproduction in finfish and shellfish species ( otb et al., 2018).
Paullinia pinnata is a tropical plant belonging to the family Sapindaceae. It is popularly known as Bread or cheese plant. It is a woody or sub-woody plant commonly found in tropical Africa and savannah. The leaves and the root of the plant have been reported to be the major part of the plant used for medicinal purposes such as the treatment of wounds and fever, and as insect repellant. The plant has also been reported to be used in the treatment of gonorrhoea, wounds and microbial infections. It is also known that the antioxidant activity of the phenolic compounds contained in the roots and plant leaves is the basis of its efficiency in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (Ouattara et al., 2019).
Clarias gariepinus belongs to the Family Clariidae; it is among the widely cultured fish species in many tropical and subtropical regions of the World. It grows well under various cultured systems. It is highly favoured because of its hardy nature, rich taste, and good food.
The study of the histopathological parameters such as the gill, liver and kidney health are important biomarkers to determine the health status of animals, including fish. Therefore, the study aimed to determine the histopathological effect of Clarias gariepinus exposed to varying concentrations of ethanolic Paullinia pinnata leaf extract.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experimental site
The study was carried out at the Aquaculture and Fisheries Management Hatchery unit of the Federal University of Abeokuta, FUNAAB, Ogun state, Nigeria.
Collection and identification of plant materials
Matured P. pinnata leaves were obtained and taken to the Herbarium for identification and authentication at the Department of Forest Resource Management, Federal University of Agriculture Abeokuta.
Acclimatisation of experimental fish
Two hundred and fifty (250) catfish juveniles with an average weight of 9.00 g and mean length of 9.00 ± 1.20 cm were collected from a fish farm in Abeokuta, Ogun state, Nigeria. They were transported in oxygenated 25-litre plastic bags, half filled with water, and then taken to the laboratory. Acclimatisation was done two weeks before the experiment. During this period, they were fed 2 mm extruded feed. The water in the culture system was regularly changed with the feeding of the test fish stopped 48 hours to the commencement of the experiment.
Preparation of Paullinia pinnata leaf extract
Fresh leaves of Paullinia pinnata were washed in clean water and air-dried at room temperature for fourteen days, after which the air-dried sample was milled using an electric blender to increase the surface area of the leaves. 250 g of fine powdered Paullinia pinnata leaf was weighed using a sensitive balance and soaked in a 70 % ethanol solvent system (70 % ethanol: 30 % distilled water). The mixture sttod for 72 hours as stirring was done at intervals, then filtered into a bowl using a muslin cloth, after which it was concentrated in the rotary evaporator at 40 oC to obtain the P. pinnata ethanol extract, which was lastly stored in an air-tight container and preserved in the refrigerator at 4 °C.
Phytochemical screening
The milled leaf sample was subjected to several phytochemical tests using Standard procedures reported by (Egwaikhide et al., 2009) to carry out the test for the presence of various phytochemicals found in the P. pinnata leaves extract.
Sub-acute renewal bioassay test
The bioassay test was carried out to determine the toxicity after a long exposure period of Clarias gariepinus juveniles to Paullinia pinnata leaf extract. Twelve (4 Treatments and 3 replicates, including the control) 35-litre circular plastic tanks were used for this experiment. They were arranged according to their treatments and replicates: T1R1, T1R2, T1R3. The plastic tanks were covered with netting materials to prevent them from jumping out of the cultured system. A 5 mL of the prepared extract (3000, 5000, and 7000 mg L-1) was injected into the experimental tank containing 9 fish samples in 10 litres of water. Control animals were kept under the same conditions without any treatment. The experimental fish were fed every 24 hours, and their water was changed every 48 hours throughout the 23 days of the experiment. Behavioural response and water quality parameters were observed every 24 hours during the experiment. Dead fish were also taken out of the system immediately to avoid pollution.
Histopathological Test
The Soar Research and Diagnostic Laboratory conducted the histopathological analysis by removing the gill and liver of the fish exposed to P. pinnata ethanolic leaf extract after 96 h using haematoxylin and Eosin techniques as described by Survarna (2013) Statistical Analysis
Mean values were analysed for significant differences (p < 0.05) using the analysis of variance (ANOVA). The difference between means was partitioned using the Duncan Multiple Range Test, and the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS), version 17, was used for all the analysis.
RESULTS
Phytochemical screening
The outcome of the qualitative and quantitative phytochemical analysis indicated that the ethanol leaf extract of P. pinnata contains the tested phytochemicals (saponins, tannins, terpenoids, alkaloids, cardiac glycosides, flavonoids, and phytosterols) as listed in Table 1.
Water analysis recorded
The result showed there was no significant (p < 0.05) difference in the temperature recorded across the treatments (Table 2). There was a slight reduction in DO when compared to control. The highest value of DO was recorded in the control (3.39 ± 0.60). However, the values in pH and TDS increased with increasing concentrations of P. pinnata across the treatment. The highest pH value was observed in treatment 3 (8.14 ± 0.77), while the lowest pH value was recorded in the control (7.62 ± 0.53).
Histopathological changes in the gills
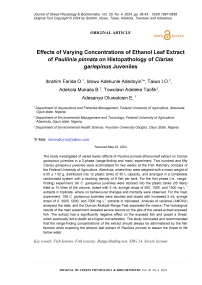
Goblet cell hyperplasia was observed in treatment 1 (Figure 1 B), and diffuse hyperplasia of secondary lamellae was observed in treatment 2 (Figure 1 C) when exposed to Paullinia pinnata leaf extract. However, there was no observable lesion in the control (Figure 1 A).
Histopathological changes in the liver
The liver cells showed several alterations with increasing concentrations of P. pinnata leaf extract. Changes in the liver cells showed moderate diffuse hepatocellular atrophy in treatment 1 (Figure 2 B), mild congestion of venules and sinusoids in treatment 2 (Figure 2 C), centrilobular hepatocellular atrophy in treatment 3 (Figure 2 D), while there was no alteration observed in the control.
Histopathological changes in the kidney
The results indicated that the lower concentrations had no effects on the kidney; however, the increased extract concentration of treatment 2 (Figure 3 B) and treatment 3 (Figure 3 C), respectively, caused the kidney to suffer from patchy glomerular atrophy and random tubular epithelial necrosis.
Table 1. Quantitative and qualitative phytochemical profile of P. pinnata leaf extract
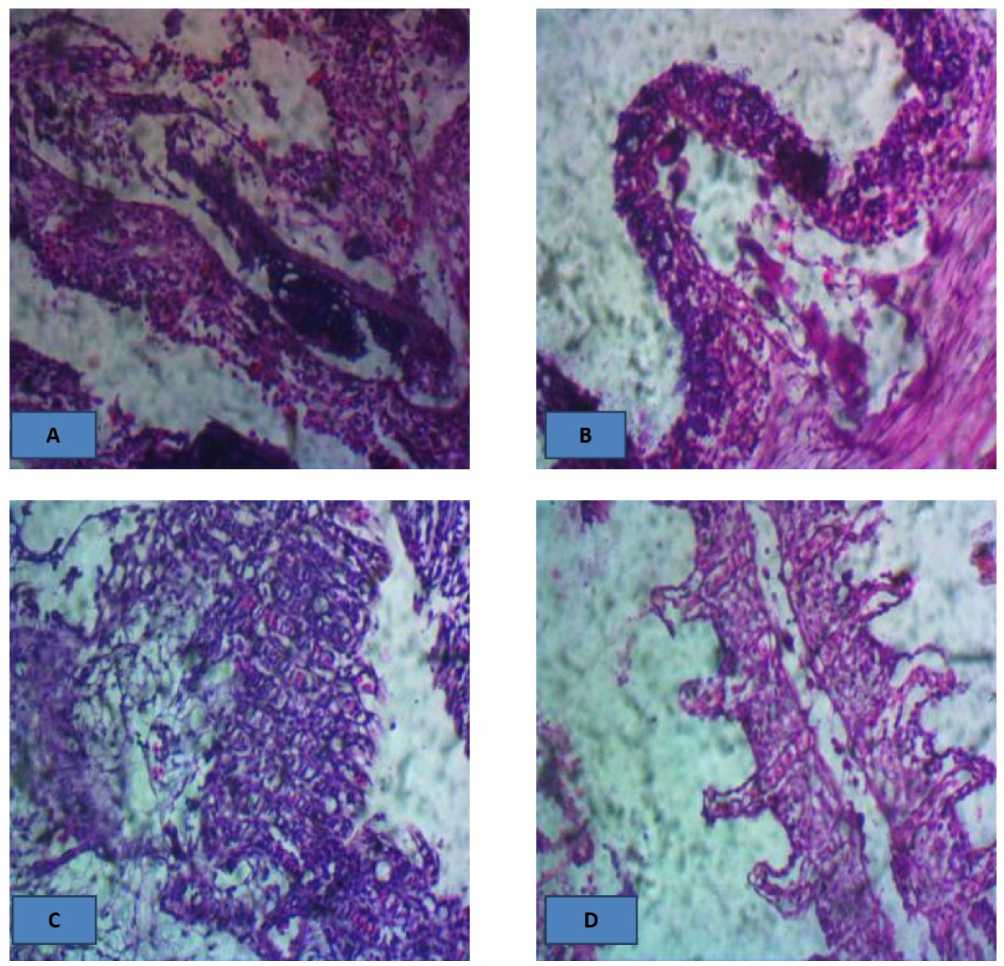
Figure 1. A (control): There is no observable lesion HE x100, 400;
B (3000 mg/ 25 cL): There is goblet cell hyperplasia. HE x400;
C (5000 mg/ 25 cL): There is diffuse hyperplasia of secondary lamellae. HE x400;
D (7000 mg/ 25 cL): There is atrophy of and necrosis of secondary lamellae. HE x400
Table 2. Experimental water (i.e., the cultured system) physicochemical parameters
|
Water parameters |
Concentration (0 mg) |
Concentration (3000 mg/ 25 cL) |
Concentration (5000 mg/ 25 cL) |
Concentration (7000 mg/ 25 cL) |
|
Temp (° C ) |
26.94 ± 1.29a |
26.45 ± 0.85a |
26.6 ± 3.03a |
26.79 ± 2.91a |
|
pH |
7.62 ± 0.53a |
7.84 ± 0.62b |
7.89 ± 0.36b |
8.14 ± 0.77c |
|
DO (mg/l) |
3.39 ± 0.60a |
3.37 ± 0.51a |
3.31 ± 0.55a |
3.37 ± 0.60a |
|
EC |
0.36 ± 0.82c |
0.33 ± 0.06ab |
0.35 ± 0.65bc |
0.33 ± 0.55ab |
|
TDS (g/l) |
0.33 ± 0.80a |
0.34 ± 0.57a |
0.34 ± 0.76a |
0.36 ± 0.55b |
NOTE: Means of the same superscript across each row were not significantly different (p < 0.05)
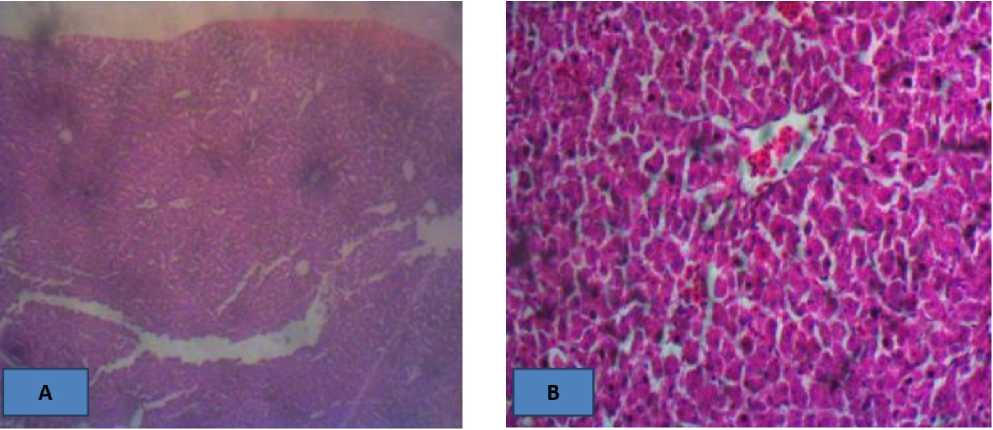
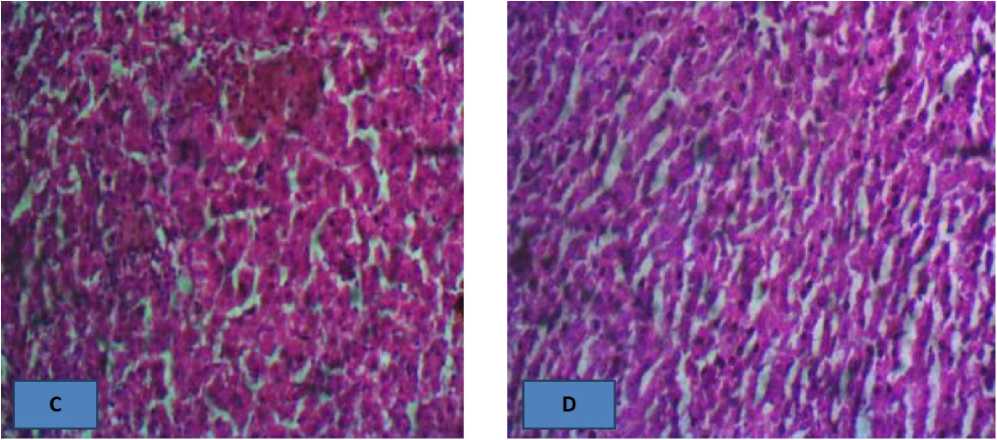
Figure 2. A (0.0ml): There is no observable lesion HE x100, 400
B (3000 mg/ 25 cL): There is moderate diffuse hepatocellular atrophy. HE x400
C (5000 mg/ 25 cL): There is mild congestion of venules and sinusoids. HE x400
D (7000 mg/ 25 cL): There is centrilobular hepatocellular atrophy. HE x400
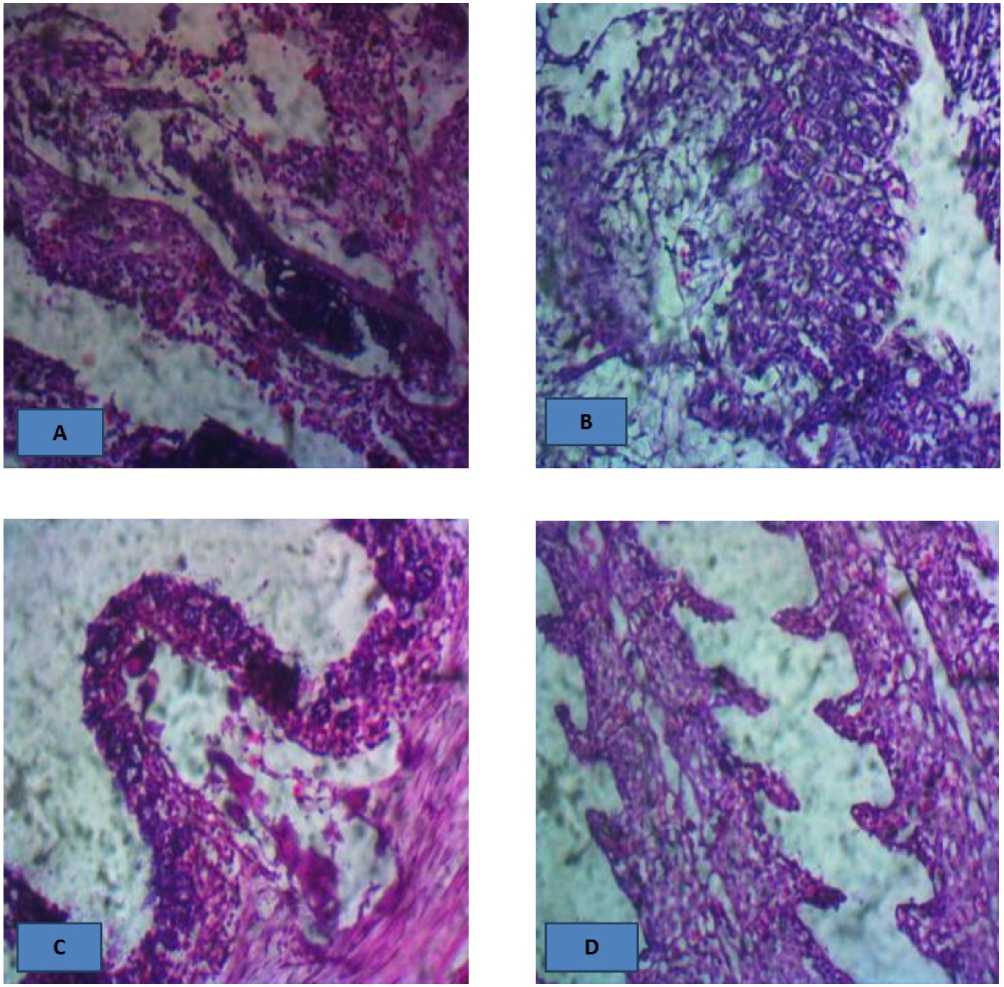
Figure 3. A (control): there is no observable lesion HE x100, 400
B (0.0ml): there is no observable lesion HE x400
C (5000 mg/ 25 cL): There is patchy glomerular atrophy. HE x400
D (7000 mg/ 25 cL): There is random tubular epithelial necrosis. HE x400
DISCUSSION
Aquatic species' ability to develop and function effectively depends on the water quality (Abalaka et al., 2015). changes in the physico-chemical qualities of water can affect the physiological and metabolic processes of aquatic animal species. The potential for contamination by P.pinnata leaf extract might be the reason for variations in the test media's temperature, conductivity, and dissolved oxygen content, as the presence of pollutants can impact these characteristics of water. The result of the water analysis showed no obvious deviation from regulatory standards. Despite being within the permissible range, the dissolved oxygen decreased as the Paullinia pinnata ethanol leaf extract increased; this is in line with the study of Idowu et al. (2019). The results of phytochemical screening show that P. pinnata contains saponins, alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, glycosides and steroids. The low concentration of steroids (9.10 %) as compared to others may be due to climate change, time of collection, soil type, and solvent used during the extraction process. The biological function of flavonoids includes protection against allergies, inflammation, free radicals, platelet aggregation, microbes, ulcers, hepatotoxins, viruses and tumours (Okwu, 2004).
The behavioural responses observed in the current studies aligned with the reports of Orji et al. (2014), who observed similar behaviours upon exposing the test fish to acute concentrations of Psychotria microphylla . The restlessness of the fish observed in this study could be attributed to the release of stress hormones to initiate a series of physiological changes as the hormone control system began to compensate (Erondu, 1991). The agitated behaviours could be an attempt of the test fish to escape the toxic aquatic environment as observed by Ayotunde et al. (2011), who exposed C. gariepinus to the Carica papaya seed powder aqueous extract.
In the present study, gill epithelial of the control treatments were similar to that of other teleost when not exposed to plant extracts, with no observed tissue alteration or distortion. However C. gariepinus showed several gill histopathological alterations upon exposure to the ethanol leaf extract varied concentrations. These include goblet cell hyperplasia, diffuse hyperplasia of secondary lamellae, and necrosis of secondary lamellae. Ayoola et al. (2018) had earlier reported filament cell proliferation, lamellar fusion, lamellar cell hyperplasia and epithelial lifting in C. gariepinus juveniles exposed to glyphosate. The severity of the lesion observed in gill tissues in this study increases with an increase in extract concentration. The functional implication of these distortions could advance into of respiration activities of the interlamellar space (water channel) obstructions; this has a direct effect on gaseous exchange across the gill lamellar epithelium (Reddy, 2013). The changes in the gills were adaptations by the fish to cope with the challenge of the toxicant (Camargo, 2007). The liver, in its role as the primary organ for the detoxification of xenobiotics, is a target of a wide variety of pollutants and other toxic by- products. These tend to accumulate in high concentrations within it, and the fish consequently suffers harmful effects, including death as a result of excessive work done by the organ in detoxifying the toxicant. In this study, the liver of the exposed fish showed diffuse hepatocellular atrophy, congestion of venules and sinusoids, and centrilobular hepatocellular atrophy. Pathological alterations in the liver also serve as useful markers of exposure to environmental stress.
CONCLUSION
The plant extracts’ efficacy and benefits on aquatic life’s health depend on the phytochemicals and the solvent used for extraction. The findings of this study indicated that P. pinnata had toxic effects on the internal organs of C. gariepinus juveniles, which posed a death threat to the fish species upon exposure to higher concentrations than the range-finding test doses.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The Departments of Aquaculture and Fisheries Management, Environmental Management and Toxicology of the Federal University of Agriculture Abeokuta, Ogun State and the Department of Environmental Health Science, Fountain University Osogbo, Osun State are appreciated for establishing the collaborative campaign of the United Nations’ SDG 17 from the inception to the end of the research.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Effects of varying concentrations of ethanol leaf extract of Paullinia pinnata on histopathology of Clarias gariepinus juveniles
- Abalaka, S.E. and Auta J. (2010). Toxicity of Aqueous and Ethanol Extracts of Parkia biglobosa Pods on Clarias gariepinus Juveniles. Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advances, 9(6), 1068-1072.
- Ayoola, S.O. (2008). Toxicity of glyphosate herbicide on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) juvenile. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 3(12), 825-834.
- Ayotunde, E.O., Offem, E.O. Bakeh, A.F. (2011). Toxicity of Carica papaya Linn: Haematological and Piscicidal effect on adult catfish Clarias gariepinus. Journal of Fisheries and Aquaculture Sciences, 6, 291-308.
- Erondu, E.S. (1991). Pond management. Proceedings of the fish seed propagation course conducted by African Regional Aquaculture Centre, Aluu Port Harcourt.- Lagos (Nigeria): NIOMR, p.44-49.
- O.C. (2019). Effect of Euphorbia hirta leaf extracts on histopathology of juvenile Clarias gariepinus. Nigerian Journal of Animal Science, 21(1), 96-109.
- Kotb, A.M. Abd-Elkareem, M. Abou Khalil, N.S. and Sayed, A.E.H. (2018). Protective effect of Nigella sativa on non (phenol-induced nephrotoxicity in Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). The Science of the Total Environment, 619-620, 692-699.
- Okwu, D.E. (2004). Phytochemicals and vitamin content of Indigenous spices of South Eastern Nigeria. Journal of Sustainable Agricultural Environment, 6,30- 34
- Orji, O.U., Ibiam, U.A. and Aja, P.M. (2014). Acute toxicity studies of the lyophilised aqueous extract of Psychotria microphylla leaf on Clarias gariepinus juveniles. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 3(4), 038-044.
- Ouattara, L.H., Kabran, G.R.M., and Konan, K.M. (2019). Biological activities and phytochemicals of Paullinia pinnata Linn. International Journal of Current Research, 11(10), 7728-7733.
- Reddy, P.B., Baghel, B.S. Archana, K. and Shehla I. (2010). Biochemical and haematological studies on the effect of textile Industry effluent in Muscus albinus, In; Proc. ICEM., 10(2), 713-719
- Reveter, M., Tapisrier-Bontemps, N. Sasal, P. Saulnier, D. (2017). Use of medicinal plants in Aquaculture. Diagnosis and Control of Diseases of Fish and Shellfish, 1st Edition p 223. London, United Kingdom: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
- Talpur, A.D. Ikhwanuddin, M. Ambok, A.M. (2013). Nutritional effects of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) on the immune response of Asian sea bass, Lates calcarifer (Bloch) and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi. Aquaculture, 400401, 46-52.