Endocarditis. Diagnostics and therapy based on the theory of cardiometry
Автор: Mikhail Y. Rudenko, Vladimir A. Zernov, Olga K. Voronova
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Статья в выпуске: 19, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148320544
IDR: 148320544 | DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2021.19.610
Текст статьи Endocarditis. Diagnostics and therapy based on the theory of cardiometry
Imprint
Mikhail Y. Rudenko*, Vladimir A. Zernov, Olga K. Voronova. Endocarditis. Diagnostics and therapy based on the theory of cardiometry. Cardiometry; Issue 19; August 2021; p. 6-10; DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2021.19.610; Available from:
The importance of diagnostics based on the theory of cardiometry implies identification of the root cause of pathology or the abnormal primary processes that affect the shape of cardiac signals. As a rule, the root cause entails a whole chain of changes. The logic of the analysis, based on the laws of cardiometry, allows you to establish all the members in this chain. This approach opens up the possibility for a very effective therapy that eliminates not only the root cause of the pathology, but also any changes that may result from its impact.
As practical experience has shown, diagnostics should begin with the identification of signs of endocarditis. The cause of its occurrence is a change in the composition of blood, which affects the function of contraction of the interventricular septum. It is very important to have the normal pathogen-free blood composition, because its quality makes impact on hemodynamics. The presence of such blood is the basis for normal well-being of a human individual and removes many difficult issues in the treatment of other pathologies.
The term “endocarditis” defines the degree of change in the morphology of the muscles of the interventricular septum near the atrioventricular valve. As a rule, this appears in the right ventricle: various pathogens of bacterial, viral, fungal and parasitic nature, having an organ-widespread polysystemic character, enter it to a greater extent through blood. Latent 6 | Cardiometry | Issue 19. August 2021
infectious and toxic processes affect the structure of the muscles adjacent to the valve. First of all, this is manifested in changes in the water exchange and the ionic balance between the extracellular and intracellular fluid.
Cause of endocarditis
Note that the heart is designed in such a way that when the valves are closed during its contraction, corresponding to the QRSL interval, certain conditions of increased pressure in the ventricles are provided. If there are elements in blood, which are not related to its normal composition, they will be concentrated in the area between the atrioventricular valve and the interventricular septum. This zone is passive that allows foreign blood elements to reside and settle therein. Their deposits begin to affect the quality of the muscles in this area that indicates the initial stage of endocarditis. The development of the process can reach the level of alteration of the structure of the muscle cells, turning them into a spongy-type state. Given that the pressure in the left ventricle is greater than in the right, blood will be able to leak from the left ventricle to the right. A disorder in water exchange in the muscle cells within this zone will be recorded during the orthostatic test in the form of a change in the amplitude of the P-Q phase (see Figure 1 herein). As a rule, endocarditis is associated with subjective symptoms, manifested with short-term dizziness, which can last only for a few seconds, periodic increase in blood pressure, and various allergies.
Criteria for the diagnostics of signs of endocarditis
The criteria for assessing the signs of endocarditis cover changes in the amplitude of the P-Q phase in orthostatic test (see Figure 2 herein).
Figure 3 shows the normal form of the P-Q phase, indicating the normal composition of blood and the absence of signs of endocarditis. Figures 4 and 5 show the other two typical cases of signs of endocarditis.
With a more developed form of endocarditis, subjective symptoms begin to manifest to a greater extent in the form of short-term dizziness. This occurs when arterial blood penetrates from the left ventricle to the right one through the interventricular septum. Let us consider a typical case presented in Figure 6 herein.
sitting position
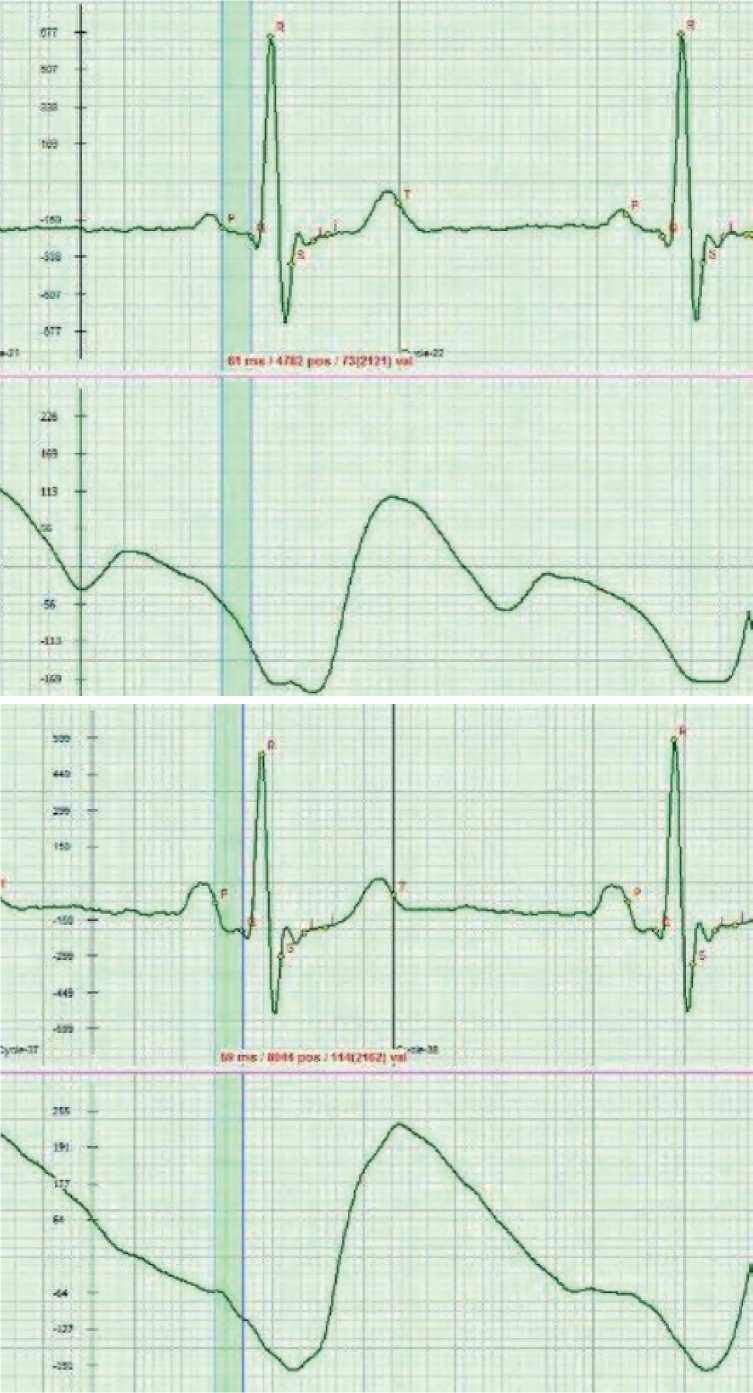
Figure 1. Change in the amplitude of the P-Q phase on the ECG curve relative to the isoline during orthostatic test indicates deposits in the heart ventricles under the atrioventricular valve in the area of the interventricular septum, namely deposits of infectious, bacterial, microbial or other elements, which are abnormal for the blood composition and which affect the quality of muscle performance, changing the water exchange between the extracellular and intracellular fluid.
sitting
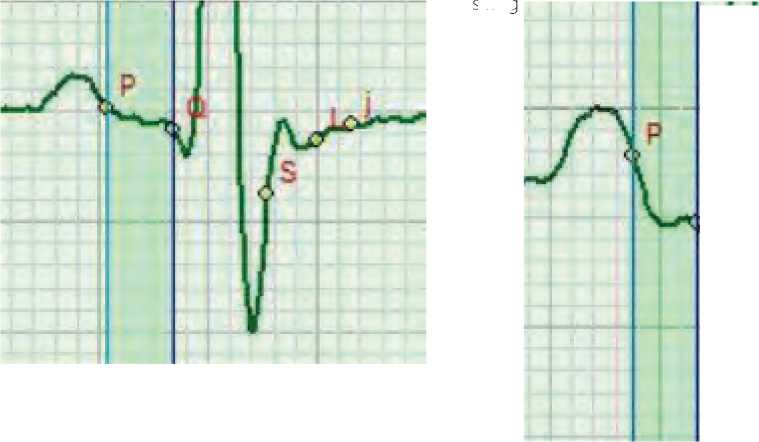
Figure 2. Enlarged view of the change in the amplitude of the P-Q phase relative to the isoline in the orthostatic test. A change in the amplitude is a characteristic sign of the presence of endocarditis
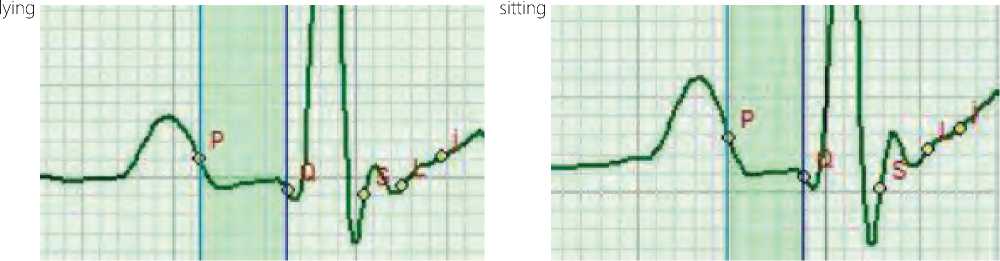
Figure 3. Exhibiting no changes in the amplitude, the P-Q phase relative to the isoline in the orthostatic test corresponds to the norm and indicates the normal state of the blood composition and the absence of signs of endocarditis
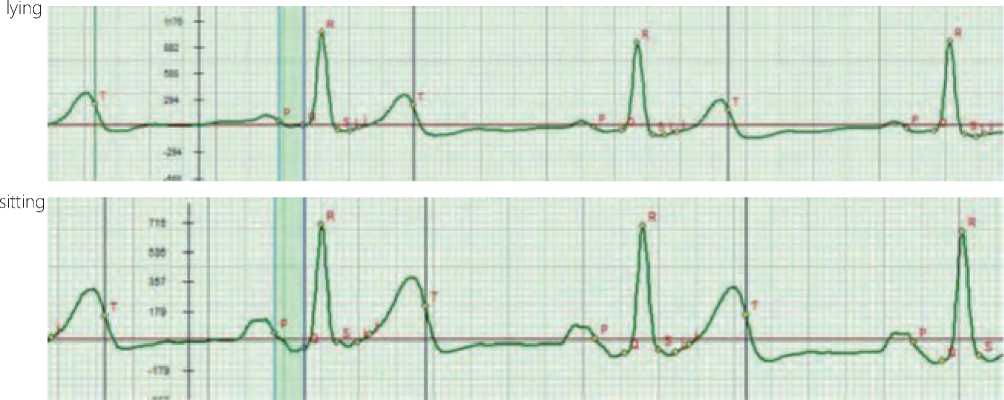
Figure 4. Change in the amplitude of the P-Q phase in the orthostatic test with signs of endocarditis affecting the function of contraction of the interventricular septum
lying
sitting
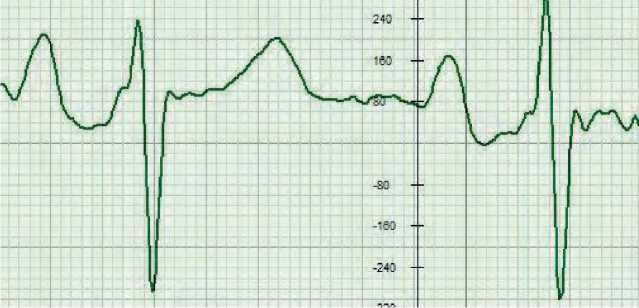
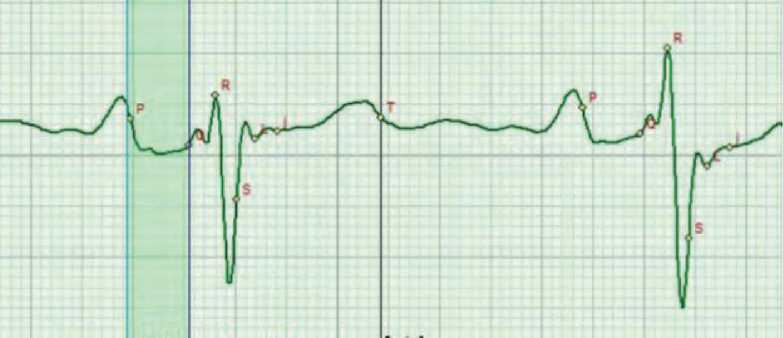
Figure 5. Change in the amplitude of the P-Q phase in the orthostatic test with signs of endocarditis affecting the function of the
interventricular septum contraction and displaying the general health state as “uncomfortable state”
lying sitting
Figure 6. Change in the amplitude of the P-Q phase in the orthostatic test with signs of endocarditis affecting the function of in-
terventricular septum contraction with subjective symptoms of periodic short-term dizziness
Table 1
Cardiometric diagnosis of signs of endocarditis
|
Detected physiological, functional, metabolic and other changes |
ECG signs |
Possible consequences |
Recommendations |
|
Signs of endocarditis. The effect of changes in blood composition on the function of reducing the IVS |
Change in the amplitude of the P-Q phase in the orthostatic test |
Rapid fatigue, possible blood pressure surges and sudden short dizziness |
1. Tinctures «Yuglon», «9-ka STOPrazit», «Nuxen-II» (black walnut), two therapy courses. 2. Wave resonance therapy with the «EZH-2»device |
As a rule, the early stage of endocarditis is accompanied by the corresponding symptoms noted above. Examples of the manifestation of signs of endocarditis are shown in Figures 4-6 herein.
Therapy
-
1. If there are marked criteria available, it makes no sense to accurately identify the nature of foreign blood elements. It is important to normalize the blood composition. A highly effective natural remedy is a tincture of black walnut with the addition of natural components of herbs. The most effective tinctures for blood normalization are the following products:
-
2. It is necessary to maintain the alkaline prevalence in the organism balance. It is important to pay attention to nutrition, first of all, by reducing protein food.
-
3. The wave resonance therapy with the “EZH-2” device to induce genome expression should be recommended. This is a fundamental factor in the proper performance of the human organism: its stimulation provides for normalization and restoration of improper functions in the affected human body.
“9-ka STOPrazit”, “Yuglon” and “Nuxen II”. You can also use the phytotherapy agent of vegetable origin, biologically active health-improving additive “Troy-chatka Ehvalar”.


