Energy and Deadline Aware Scheduling in Multi Cloud Environment Using Water Wave Optimization Algorithm
Автор: Santhosh Kumar Medishetti, Rameshwaraiah Kurupati, Rakesh Kumar Donthi, Ganesh Reddy Karri
Журнал: International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications @ijisa
Статья в выпуске: 3 vol.17, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Scheduling is an NP-hard problem, and heuristic algorithms are unable to find approximate solutions within a feasible time frame. Efficient task scheduling in Cloud Computing (CC) remains a critical challenge due to the need to balance energy consumption and deadline adherence. Existing scheduling approaches often suffer from high energy consumption and inefficient resource utilization, failing to meet stringent deadline constraints, especially under dynamic workload variations. To address these limitations, this study proposes an Energy-Deadline Aware Task Scheduling using the Water Wave Optimization (EDATSWWO) algorithm. Inspired by the propagation and interaction of water waves, EDATSWWO optimally allocates tasks to available resources by dynamically balancing energy efficiency and deadline adherence. The algorithm evaluates tasks based on their energy requirements and deadlines, assigning them to virtual machines (VMs) in the multi-cloud environment to minimize overall energy consumption while ensuring timely execution. Google Cloud workloads were used as the benchmark dataset to simulate real-world scenarios and validate the algorithm's performance. Simulation results demonstrate that EDATSWWO significantly outperforms existing scheduling algorithms in terms of energy efficiency and deadline compliance. The algorithm achieved an average reduction of energy consumption by 21.4%, improved task deadline adherence by 18.6%, and optimized resource utilization under varying workloads. This study highlights the potential of EDATSWWO to enhance the sustainability and efficiency of multi-cloud systems. Its robust design and adaptability to dynamic workloads make it a viable solution for modern cloud computing environments, where energy consumption and task deadlines are critical factors.
Task Scheduling, Multi Cloud, Water Wave Optimization, Energy Consumption, Virtual Machines, Propagation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15019781
IDR: 15019781 | DOI: 10.5815/ijisa.2025.03.04
Текст научной статьи Energy and Deadline Aware Scheduling in Multi Cloud Environment Using Water Wave Optimization Algorithm
As computer chips continue becoming more and more affordable and nations continue their march toward World Wide Web, Internet of Things (IoT) is becoming an integral part of the digital world. The IoT application spans the essential domains such as healthcare [1], underwater exploration [2], smart transportation [3], smart homes [4], and industrial systems. Cisco [5] indicates that the number of IoT connected devices will climb to 21 billion by 2025 and 41 billion by 2027. In 2019, 18.3 zettabytes of data were generated by IoT devices, and this is estimated to grow to 73 zettabytes in 2025, a 400 percent rise [6]. Due to the constraints of computational power and storage, most IoT devices still lack capability and typically offload tasks for efficient processing and storage to alternative servers. While cloud computing brings excellent resources, as this is a centralized architecture and distant data transfers occur with significant delays.
The amounts of data generated by IoT devices make cloud computing (CC) a strong solution for processing, as it provides extended storage and computational resources [7]. Being a centralized platform of cloud servers, they can utilize large-scale IoT data and fulfil tasks such as processing that demand great computing abilities. Storing, analysing and processing IoT data at large scale with high availability is now available from cloud platforms at very low cost. However, latency is always introduced by the centralized architecture especially for the delay sensitive IoT applications requiring real time response [8]. This limits processing time and energy consumption across long distances, and this slows down the data transmission and makes it difficult to comply with the stringent task deadlines. In applications such as healthcare, smart transportation or industrial automation for which timely execution is critical for system performance and reliability, this latency turns out to be a critical bottleneck.
To address these challenges, efficient TS within CC environment becomes vital for optimizing energy consumption and meeting task deadlines [9]. In multi-cloud environments, where multiple cloud resources are available, the complexity increases due to varying bandwidth, computational capacities, resource availability, and associated costs. Therefore, effective scheduling mechanisms are required to allocate tasks to appropriate cloud servers to minimize execution delays, reduce energy consumption, and ensure tasks meet their deadlines. While cloud computing provides the required scalability and processing power, this research emphasizes optimizing task scheduling to balance energy efficiency and deadline constraints, ensuring seamless execution of IoT applications.
However, the remarkable and complicated nature of multi cloud environments presents significant scheduling challenges. Energy consumption, task deadline violations, and uneven resource utilization are critical issues that need addressing [10]. Traditional scheduling algorithms often struggle to adapt to fluctuating workloads and dynamic resource availability, leading to inefficiencies. Energy consumption is a major concern in CC, as data centers consume significant power, contributing to operational costs and environmental impact. Meanwhile, deadline violations affect service-level agreements (SLAs), reducing user satisfaction [11]. Thus, task scheduling algorithms must balance energy efficiency and deadline adherence to optimize multi-cloud system performance.
The Water Waves Optimization (WWO) algorithm, inspired by the propagation and interactions of water waves, has gained attention as a metaheuristic optimization technique [12]. WWO mimics wave behaviors such as refraction, diffraction, and breaking to explore and exploit solution spaces effectively. Its adaptability and simplicity make it suitable for solving complex optimization problems, including TS. Many existing TS algorithms focus on either energy efficiency or deadline adherence, rarely achieving an optimal balance between the two. Additionally, most algorithms fail to consider the dynamic nature of multi-cloud environments and real-world workloads, such as those generated by Google Cloud [13]. These limitations hinder their practical applicability and effectiveness.
This study introduces a novel Energy- and Deadline-Aware Task Scheduling Algorithm using the Water Waves Optimization (EDATSWWO). By using the adaptive capabilities of WWO, the proposed algorithm dynamically balances energy efficiency and deadline compliance, addressing the limitations of existing approaches. The algorithm’s integration with real-world workloads enhances its relevance and applicability. The primary contributions of this research include:
• Development of the EDATSWWO algorithm for multi-cloud task scheduling.
• Integration of energy consumption and task deadlines as optimization objectives.
• Validation of the algorithm using Google Cloud workloads to ensure real-world applicability.
• Comparison with existing algorithms to highlight performance improvements in energy efficiency, deadline adherence, and resource utilization.
2. Related Works
The proposed methodology involves modeling multi-cloud environments and tasks, formulating an optimization problem with energy and deadline objectives, and employing the WWO algorithm to solve it. The EDATSWWO algorithm evaluates tasks based on their characteristics and allocates resources adaptively to optimize the overall system performance. Tasks are characterized by parameters such as computational requirements and deadlines. The EDATSWWO algorithm prioritizes tasks based on their energy requirements and deadlines, assigning them to appropriate resources while minimizing energy consumption and avoiding deadline violations.
Real-world workloads from Google Cloud are used to simulate the multi-cloud environment and validate the algorithm. This integration ensures that the proposed approach addresses practical challenges and reflects real-world performance metrics. The performance of EDATSWWO is evaluated against existing scheduling algorithms.
Performance metrics are analyzed to demonstrate the proposed algorithm’s superiority. This study addresses the present need for efficient TS in multi-cloud environments. By focusing on energy efficiency and deadline adherence, EDATSWWO contributes to sustainable cloud computing practices and enhanced user satisfaction. The adoption of EDATSWWO can benefit cloud service providers and users by reducing operational costs, improving SLA compliance, and optimizing resource usage. Its applicability to real-world workloads makes it a practical solution for modern multicloud systems.
This study is structured into five sections. Section 1: Introduction provides an overview of CC, TS challenges in multi-cloud environments, and the motivation for developing the EDATSWWO. Section 2: Related Work reviews existing scheduling algorithms, highlighting their limitations in addressing energy efficiency and deadline adherence in dynamic workloads. Section 3: Proposed Methodology details the EDATSWWO algorithm, including its design principles, task evaluation criteria, and resource allocation strategies, with emphasis on energy and deadline optimization. Section 4: Experimental Results and Analysis presents the simulation setup using Google Cloud workloads. Section 5: Summarizes the contributions of this study, discusses its practical implications, and outlines potential directions for extending the research to hybrid cloud-fog systems and additional optimization parameters.
Zhu, J., Li, X., et al. [14] addresses the problem of scheduling multi-stage jobs with stochastic task arrivals and fuzzy processing times in elastic cloud environments. The authors propose a fuzzy scheduling framework that prioritizes tasks and schedules them efficiently across geographically distributed virtual machines (VMs). By incorporating triangular fuzzy numbers for processing and transmission times, they aim to balance two objectives: minimizing the total cost of VM rentals and maximizing user satisfaction. A heuristic-based approach is developed, using two task collection and prioritization strategies to improve scheduling effectiveness. Results from the experimental algorithms show that proposed algorithm is robust and efficient than the existing methods.
In this study Khaledian, N., et al. [15], energy consumption driven task scheduling is optimized for IoT workflows in fog and cloud environments: considering task deadlines and resource constraints. A hybrid algorithm combining PSO and SA to solve tasks scheduling and resource allocation problems is introduced by the authors. The method minimizes the energy usage and makespan while guaranteeing task deadlines meet the requirements. The simulation results indicate that the hybrid PSO-SA algorithm achieves energy efficiency enhancement of 5% and makespan reduction of 9 % relative to the basic IKH-EFT algorithm.
Abd Elaziz et al. [17], they introduce an innovative task scheduling algorithm for IoT applications in cloud fog computing environments. A combination of AEO and the SSA is proposed by the authors, namely AEOSSA, a hybrid optimization approach. We provide an integration that increases the exploitation ability of AEO, mitigating its tendency to get trapped in local optima. The proposed method aims to minimize makespan, reduce task execution time with optimizing throughput, all of which proceed to meet QoS requirements in cloud fog systems. We perform experiments over both synthetic and actual data using AEOSSA, where it outperforms existing metaheuristic algorithms. The results show encouraging improvements in resource turnover, load balancing and response time for AEOSSA, making it a robust approach to task scheduling issues in cloud fog computing environments.
Tychalas and Karatza propose [18] a scheduling algorithm for fog computing systems designed to handle Bag-of-Tasks (BoT) workloads effectively. The study examines the combination of heterogeneous resources, such as VMs, containers, smartphones, and Raspberry Pi devices, to minimize costs while maintaining performance. The proposed algorithm dynamically allocates tasks using a load-balancing strategy that prioritizes resource utilization and minimizes response time. Simulation results reveal that the algorithm effectively balances the load across devices while reducing costs, especially when leveraging lightweight containers compared to traditional virtual machines. The study highlights the benefits of combining geographically distributed, low-cost resources in fog computing environments and underscores the potential of BoT workloads for optimizing performance under diverse resource constraints.
In an energy aware task scheduling strategy for fog computing environment, Hosseinioun et al. [19] presented an energy minimization and energy minimization for makespan. The authors use a hybrid method, a combination of IWO and the Cultural Algorithm (CA), to generate efficient task sequences. Also, the DVFS technique is employed to reduce the energy consumed by adjusting the voltage and frequency of computing nodes. A task scheduling model that maps workflow tasks to heterogeneous processors while minimizing energy is introduced in the study. Energy savings, resource utilization and execution time are superior with the proposed hybrid IWO-CA algorithm compared to other methods. In this work we show how fog computing prioritizes energy optimization as opposed to task scheduling, and present a flexible approach in managing distributed scheduling issues.
Jamil et al. [20] provide a systematic and detailed review of resource allocation and task scheduling techniques in fog computing and IoE environments. The study categorizes scheduling approaches into heuristic, metaheuristic, and intelligent techniques, such as reinforcement learning and machine learning, focusing on their merits, demerits, and optimization metrics like latency, energy efficiency, and cost. The survey highlights the challenges of resource constraints, heterogeneity, and the dynamic nature of fog nodes, as well as the need for efficient scheduling algorithms to enhance Quality of Service (QoS). It concludes by identifying open issues, including mobility support, real-time scheduling, and the integration of intelligent methods to handle complex, uncertain fog computing scenarios.
HunterPlus [21] is an AI based energy efficient task scheduling approach proposed by Iftikhar, S., et al. for the cloud fog environment extending the GGCN with Bidirectional GRU. Finally, the study extends the use of CNNs for the optimization of task scheduling in order to reduce energy, better job completion rates, etc. HunterPlus is experimentally shown to outperform state-of-the-art GGCN models by at least 17% in energy savings and 10.4% in job completion rates. This work emphasizes the significance of AI-driven schedulers in addressing the growing energy demands and computational challenges in large-scale cloud-fog systems.
Rahimikhanghah et al. [22] conduct a systematic literature review of resource scheduling methods in cloud and fog computing environments, analyzing studies from 2015 to 2021. The review classifies resource scheduling techniques into five categories based on their objectives: performance, energy efficiency, resource utilization, performance-energy optimization, and performance-resource optimization. The paper highlights the importance of scheduling algorithms in improving QoS, reducing energy consumption, and optimizing resource allocation. Key challenges include handling dynamic workloads, energy efficiency in large-scale systems, and balancing performance trade-offs, while the authors emphasize the need for innovative, adaptive scheduling approaches to address these issues.
Nguyen, B. M., et al. [23] we focus on task scheduling in Bag-of-Tasks (BoT) applications in cloud-fog environment. They propose the TCaS algorithm that balances the workloads among the cloud and fog nodes to improve the execution time and the operating costs. The approach is tested using evolutionary algorithms on 11 datasets of different sizes. Results indicate that TCaS performed compared to the BLA and MPSO by 15.11% and 11.04% respectively, providing an effective tradeoff between time and cost, while satisfying user QoS requirements.
Narman, H. S., et al. [24] addresses the challenge of scheduling IoT applications in a cloud environment, where traditional schedulers fall short due to the heterogeneous nature and dynamic demands of IoT requests. The authors propose a DDSS algorithm tailored for both homogeneous and heterogeneous cloud servers, prioritizing tasks based on their class and urgency. Analytical and simulation-based evaluations show that DDSS improves performance metrics like throughput, resource utilization, and drop rate by up to 40% compared to existing methods. This approach helps cloud providers better handle IoT requests while maintaining service quality.
Aburukba, R. O., et al. [25] models IoT task scheduling as an optimization problem to minimize latency in a hybrid cloud-fog architecture. Using a customized GA, the proposed method dynamically schedules IoT requests to optimize task distribution and response times. The GA-based scheduler outperforms traditional techniques like WFQ, PSQ, and RR by reducing latency by 21.9% to 46.6%. Moreover, the proposed approach significantly improves deadline adherence, offering a reliable solution for latency-sensitive IoT applications.
Yin, Zhenyu et al. [26] proposed a method for scheduling tasks in cloud fog computing environments based on the monarch butterfly optimisation algorithm and improved ant colony optimisation algorithm (HMA). The authors formulated the scheduling problem as an optimisation the task problem and solved it using HMA to find near optimal solutions. To validate the suggested method for reducing service delay and task energy consumption, extensive experiments were conducted. The outcomes proved that HMA performed better than competing algorithms when it came to scheduling tasks.
-
Li, G., et al. [27], energy consumption and delay are balanced with energy optimization strategy for cloud–fog systems by delay threshold mechanism. Using queue theory, the authors model the energy and delay of three system layers: Both fog nodes, cloud servers and mobile terminal devices. A calculation of optimal workload distribution through a nonlinear programming approach, and a cloud-fog cooperation scheduling algorithm and task offloading algorithm are provided. The results from the experimental show that the scheme decreases energy consumption of 22 percent and delays of 12.5 percent from traditional scheduling methods.
Ahmad, M. A., et al. [29] presents an energy-efficient resource scheduling method for fog computing by leveraging a Software-Defined Networking (SDN) framework. The study focuses on minimizing energy consumption in fog-assisted cloud environments by dynamically selecting fog servers and nodes using dynamic programming and greedy algorithms. The proposed scheduling technique efficiently balances resource usage and reduces energy consumption while maintaining service level agreements (SLA). Experimental results using iFogSim validate the approach, showing significant energy savings compared to conventional methods.
Additionally, research by Hosseinioun et al. [32] and Jamil et al. [33] emphasized the need for energy-aware scheduling in large-scale cloud environments, demonstrating that hybrid algorithms combining exploration and exploitation techniques perform better than static heuristics. Our results support these conclusions, showing that EDATSWWO achieves a 21.4% reduction in energy consumption and an 18.6% improvement in deadline adherence, outperforming traditional approaches like PSO, GA, and ACO. Furthermore, while previous studies such as Nguyen et al. [34] focused on evolutionary algorithms for IoT-based scheduling, their methods often struggled with high computational complexity in real-time applications. EDATSWWO overcomes this limitation by maintaining computational efficiency while dynamically adapting to workload fluctuations, making it more suitable for modern multi-cloud environments.
By situating our results within the context of prior research, this study contributes to the growing body of work on energy-efficient and deadline-aware scheduling. The integration of bio-inspired Water Wave Optimization with dynamic scheduling constraints presents a novel approach that enhances both efficiency and scalability in cloud environments. These findings demonstrate that EDATSWWO not only builds on previous research but also advances the field by providing a more adaptable and computationally efficient scheduling mechanism for real-world cloud applications.
Table 1. Comparison study of existing scheduling in cloud and fog environments
|
Authors |
Technique Used |
Parameters Addressed |
Limitation |
|
Zhu, J., Li, X., et al. [14] |
Fuzzy scheduling with heuristics |
Cost minimization, user satisfaction |
Limited to elastic cloud environments; fuzzy processing times may increase complexity. |
|
Khaledian, N., et al. [15] |
Hybrid PSO-SA |
Energy consumption, makespan |
Focuses only on PSO-SA hybrid; may not scale efficiently for larger workflows. |
|
Choppara, P., et al. [16] |
RTATSA2C (A2C Reinforcement Learning) |
Makespan, reliability, trust, scalability |
Limited to cloud-fog environments; focuses on specific RL techniques (A2C). |
|
Abd Elaziz, M., et al. [17] |
AEOSSA (Hybrid AEO-SSA) |
Makespan, throughput, load balancing |
AEOSSA algorithm may still face local optima issues in dynamic environments. |
|
Tychalas, D., et al. [18] |
Load-balancing strategy |
Cost, response time, load balancing |
Limited to Bag-of-Tasks (BoT) workloads; may not generalize for complex task types. |
|
Hosseinioun, P., et al. [19] |
Hybrid IWO-CA with DVFS |
Energy consumption, makespan |
Focuses on IWO-CA hybrid; assumes DVFS capability, limiting applicability in real scenarios. |
|
Iftikhar, S., et al. [21] |
HunterPlus (AI-based with GRU and CNN) |
Energy efficiency, job completion rate |
Focused on AI-driven techniques; scalability issues for large-scale deployments remain. |
|
Nguyen, B. M., et al. [23] |
TCaS algorithm |
Execution time, operating costs |
Limited to BoT workloads; results are datasetspecific, lacking general applicability. |
|
Narman, H. S., et al. [24] |
DDSS (Dynamic Scheduler) |
Throughput, resource utilization, drop rate |
Focused on IoT applications; does not address heterogeneous dynamic demands fully. |
|
Aburukba, R. O., et al. [25] |
Customized Genetic Algorithm (GA) |
Latency, deadline adherence |
Limited to hybrid cloud-fog architecture; assumes specific task distribution scenarios. |
|
Yin, Z., et al. [26] |
HMA (Hybrid Monarch Butterfly and ACO) |
Service delay, energy consumption |
Focused on HMA algorithm; requires extensive tuning for task-specific optimization. |
|
Li, G., et al. [27] |
Nonlinear Programming, Task Offloading |
Energy consumption, delay |
Assumes specific system layers; queue theorybased model may not handle dynamic workloads. |
|
Kaur, M., et al. [28] |
Load balancing strategy |
Load balancing, energy efficiency |
Limited to fog-cloud environments; does not address broader cloud systems effectively. |
|
Ahmad, M. A., et al. [29] |
Dynamic Programming and Greedy Algorithm |
Energy consumption, resource scheduling |
Focuses on SDN framework; limited to fog-assisted cloud environments. |
3. Proposed Methodology
Proposed Methodology is divided into two sub-sections. The System Model describes the architecture of the multicloud environment, including task types, resource configurations, and workload characteristics. It also describes and decision variables defining the optimal scopes to reach, like energy consumption, time constraints of specific tasks, and VM capabilities. The Problem Formulation provides a formal statement of the scheduling of tasks as a multi-objective optimization problem, where the objective is the minimization of energy consumption as well as possible deadline misses. This sub-section also includes the constraints and objectives that guide the algorithm's decision-making process. Together, these sub-sections establish the foundation for developing and implementing the EDATSWWO algorithm.
-
3.1. System Model
The architecture depicted in figure 1 represents a multi-cloud environment utilizing the EDATSWWO Scheduler to achieve energy- and deadline-aware task scheduling. At the top level, multiple cloud environments host clusters of Virtual
Machines (VMs), each denoted as VM1, VM2, ..., VMn. These VMs provide computational resources required to process tasks originating from end devices. The architecture ensures flexibility and redundancy by distributing workloads across multiple clouds, which improves fault tolerance and scalability while meeting the varying demands of users and applications.
At the core of the architecture lies the EDATSWWO Scheduler, which is responsible for dynamically assigning tasks to the appropriate VMs across the multi-cloud environment. The scheduler takes into account energy consumption, task deadlines, and the current workload of each VM. By leveraging the Water Wave Optimization (WWO) algorithm, it ensures an optimal balance between energy efficiency and deadline compliance. This enables effective task distribution, resource utilization, and adherence to Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
The Cloud Broker acts as the intermediary between end devices and the cloud VMs. It collects task requests from end devices, analyzes their requirements, and forwards them to the EDATSWWO Scheduler for processing. The broker plays a critical role in managing communication and ensuring that user demands are efficiently handled. This layer abstracts the complexities of the multi-cloud environment, offering users seamless access to resources.
At the bottom of the architecture, End Devices generate tasks that require execution in the multi-cloud environment. These devices include a variety of hardware such as sensors, cameras, IoT devices, and personal computing devices. The architecture ensures that these heterogeneous tasks are handled efficiently, providing a robust framework for real-world applications requiring energy-aware and deadline-compliant task scheduling.
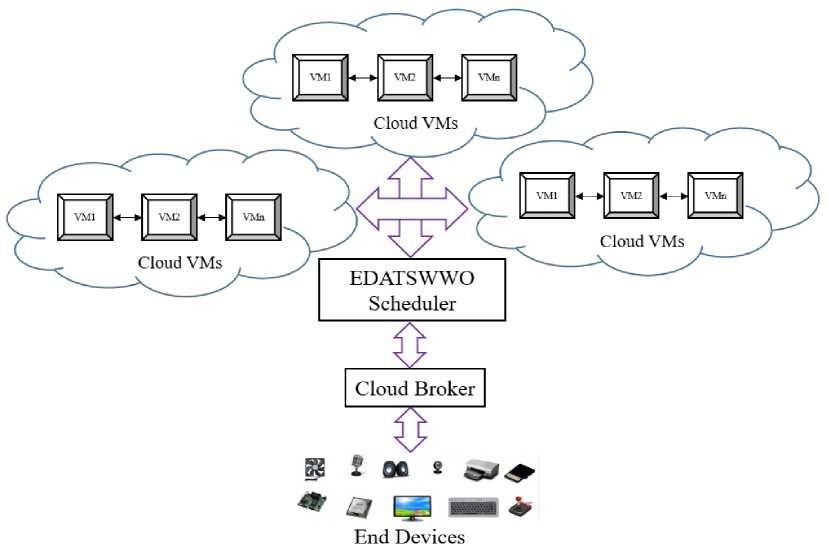
Fig.1. System architecture
-
3.2. Problem Formulation
Based on the EDATSWWO architecture described above, we systematically formulate each component to develop a comprehensive mathematical model for the TS problem. The architecture is divided into three main parts: the end devices generating tasks, the cloud broker facilitating task distribution, and the multi-cloud virtual machines (VMs) where tasks are executed. First, tasks from end devices are characterized by parameters such as execution time, energy requirements, and deadlines. Second, the cloud broker is modelled to manage communication between devices and the EDATSWWO Scheduler, ensuring tasks are distributed efficiently. Finally, the VMs in the multi-cloud environment are formulated as computational resources with defined energy consumption rates, workloads, and capacities. And these components are combined to formulate the problem as a multiple objective optimization problem providing trade-off between energy consumption, task execution time and no violation of the deadline in the context of assigning the adequate resources to the multi cloud environment. Table 2 gives detailed information of the mathematical notations.
The end devices generate a set of tasks T={t 1 ,t 2,. ..,tn}, where n is the total number of tasks. Each task t i is defined by a tuple t i =(ET i , DL i , EC i ), where ET i is the execution time, DL i is the deadline for task completion, and EC i represents the energy consumption requirement. The total energy required for all tasks can be represented as:
Etotal = Y^EC,
Table 2. Description of Mathematical notations
|
Notation |
Description |
|
ET |
execution time |
|
DL |
deadline for task completion |
|
EC |
energy consumption |
|
x i,j |
binary decision variable |
|
Si |
size of the task |
|
P j |
processing capacity of the VM |
|
E j . |
energy consumption rate |
|
ST i,j |
start time |
|
ET i,j |
execution time |
|
DL i |
Task deadline |
|
w 1 , w 2 |
Weights |
|
E total |
Total energy |
|
ET |
Execution time |
|
f |
Objective function |
|
Xm i n and Xmax |
bounds of the search space. |
|
^ |
refraction coefficient |
|
γ |
energy reduction factor |
|
δ |
small breaking distance factor |
The objective for end devices is to ensure that each task is processed with minimal energy consumption while meeting its deadline constraint t i ≤DL i .
The cloud broker acts as an intermediary, mapping tasks T from end devices to appropriate VMs across multiple clouds. The broker considers task deadlines, execution time, and energy efficiency when assigning tasks. Let x i,j be a binary decision variable, where x i,j =1 if task t i is assigned to VM v j , and 0 otherwise. The task allocation can be modelled as:
T^x^-l, VET (2)
Where m is the total number of VMs that is the number of virtual machines in the cloud. That means the cloud broker was making sure that each of the tasks should be allocated to one of the VMs, and also at the same time avoid resource wastage or delays.
The multi-cloud virtual machines provide the computational resources required to process tasks. Each VM v j has a defined capacity C j (e.g., CPU, memory) and an energy consumption rate E j . The total energy consumed by a VM is given as:
Where V is the set of VMs. The objective is to minimize the total energy consumption across all VMs while ensuring tasks meet their deadlines and VM capacity constraints.
Execution time
The execution time of a task is a critical parameter in task scheduling as it determines how quickly a task can be completed by the assigned VM. Let t i denote a task from the set of tasks T={t1,t2,…,tn}, and v j represent a VM from the set V={v1,v2,…,vm}. The execution time ET i,j of a task t i on a VM v j is calculated based on the size of the task Si (e.g., in terms of instructions or data size) and the processing capacity P j (e.g., in instructions per second or FLOPS) of the VM. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
ET ij -^,V i ET,V j EV (5)
ч
The total execution time across all tasks is influenced by how tasks are distributed among the available VMs. Minimizing ETi,j ensures tasks are completed quickly, which is essential for meeting deadlines and improving user satisfaction. Efficient allocation of tasks to VMs with optimal processing capacities can significantly reduce execution time, especially in multi-cloud environments where heterogeneous resources are available.
Energy consumption
Energy consumption is a vital metric in cloud task scheduling, particularly for achieving energy efficiency in large-scale data centers. Each VM v j operates with an energy consumption rate E j (watts), which directly affects the total energy consumed during task execution. For a task t i assigned to VM v j , the energy consumption EC i,j is determined as a product of the execution time ET i,j and the VM's energy consumption rate E j :
ECiJ=ETiJ.E], ^ET^ j EV (6)
The overall energy consumption for all tasks across all VMs is given by:
where x i,j is a binary decision variable that equals 1 if task t i is assigned to VM v j , and 0 otherwise. Reducing E total involves minimizing both execution time and the energy efficiency of VMs, which is crucial for lowering operational costs and environmental impact in multi-cloud systems.
Deadline constraints
In a real-world scenario, every task has a deadline DL i by which it must be completed. Failure to meet deadlines can lead to penalties, SLA violations, and decreased user satisfaction. The completion time CT i,j for a task t i executed on a VM v j depends on its start time ST i,j and execution time ET i,j defined as:
CT i,] = ST i,] + ET i,] , ^tET^ j EV (8)
The deadline constraint ensures that the completion time does not exceed the specified deadline:
CT
t,]
i,ViET
(9)
This constraint requires the scheduling algorithm to prioritize tasks with shorter deadlines, balancing the workload across multiple VMs. It also ensures efficient task allocation, avoiding bottlenecks that can arise when tasks with overlapping deadlines are assigned to the same VM.
Objective function
The proposed model will assist in increasing task efficiency in the context of a multi-cloud environment through improving the organization of tasks by their start and end, focused on saving energy consumption and time for task completion restricted by their due dates. The problem under consideration is multi-objective optimization that can be formulated as follows:
where w 1 and w 2 are weights representing the importance of energy consumption and execution time, respectively. This formulation ensures efficient utilization of computational resources while maintaining a balance between energy efficiency and task deadlines. The proposed approach uses the Water Waves Optimization algorithm to solve this multiobjective problem effectively, achieving optimal task allocation and resource utilization in a multi-cloud environment.
Proposed EDATSWWO algorithm
WWO is a metaheuristic optimization algorithm derived from the nature and particularly focuses on the behavior of the water wave and how they are reflected [35-36]. Intended for continuous optimization problems, the WWO algorithm is based on the tendency of waves distributing and changing their forms when interacting with the corresponding obstacles. It working on the fact that waves start from the source and their strength diminishes over time and look for paths that influence them in the least. The algorithm is designed to balance exploration and exploitation by simulating three key mechanisms: propagation, refraction, and breaking. During the propagation phase, waves spread to explore the search space, and their energy determines how far they travel. In the refraction phase, waves adjust their positions and refine their search direction based on the fitness of their current solution. The breaking phase introduces diversity in the search by splitting waves into smaller waves, thereby avoiding premature convergence and helping escape local optima.
The WWO algorithm is highly adaptable for solving complex optimization problems, including TS, resource allocation, and energy-efficient computing. Its dynamic behavior allows for global exploration while maintaining local refinement, making it suitable for multi-objective and constrained optimization scenarios. WWO uses wave propagation to explore large solution spaces effectively, while refraction and breaking enable fine-tuning of solutions and improved convergence. The algorithm’s capability to adjust its propagation distance and splitting mechanism based on solution quality ensures efficient convergence to near-optimal solutions. WWO seeks to use the knowledge represented by our mathematical model towards task scheduling problem in cloud environments to optimize the resource utilization in terms of execution time, energy consumption and operation cost. Such simplicity, adaptability, and efficiency make it a promising solution to the large scale scheduling problems in cloud and multi cloud systems.
Initialization
In the initialization stage, the Water Wave Optimization (WWO) algorithm begins by defining an initial population of solutions W={w1,w2,...,wn}, where each wave w i represents a potential solution within the search space. These solutions correspond to task assignments on virtual machines (VMs) for execution. Each wave is initialized with an initial position P i , which represents the allocation of tasks to resources, and an energy level E i to determine its ability to propagate. The fitness of each wave is evaluated using an objective function f(w i ), which incorporates execution time, energy consumption, and deadline constraints. The initialization ensures all tasks are assigned to a VM, and each wave w i satisfies the constraints. Mathematically, the initial energy and position are defined as:
E t = Eo and Pt = rand(Xmln,Xmax) (11)
where E0 is the initial energy, and X min and X max are the bounds of the search space.
The initialization stage directly relates to execution time and energy consumption by determining the starting solutions for task scheduling. Poor initialization can lead to high execution times and energy usage, while balanced initial positions ensure efficient task allocation within deadline constraints.
Propagation Stage
During the propagation stage, water waves spread in the search space to explore new solutions. This simulates the natural wave propagation where waves travel based on their energy levels. Mathematically, the new position P i ′ of a wave w i is calculated as:
where r is a random number between -1 and 1, and d i is the propagation distance proportional to the wave energy E i :
dt = a.Et (13)
where α is the propagation coefficient. If the new position P i ′ improves the fitness (e.g., minimizes execution time or energy consumption), the wave updates its position, and its energy decreases proportionally. The propagation stage relates to execution time because waves explore task allocations to reduce completion times. Additionally, energy-efficient solutions are favored during exploration. By exploring feasible solutions, the propagation stage helps meet deadline constraints, as tasks are gradually allocated to appropriate VMs.
Refraction Stage
The refraction stage simulates the behavior of waves bending toward better solutions. In the WWO algorithm, this corresponds to refining solutions to improve fitness. When a wave encounters a region with better fitness (lower execution time and energy consumption), its position is adjusted toward the optimal region. Mathematically, the updated position is expressed as:
P t = P t +p.(Pbest-P t) (14)
where β is the refraction coefficient, and P best is the best solution encountered so far. The fitness evaluation ensures that refraction moves waves toward task allocations that minimize execution time and energy consumption while satisfying deadlines. The wave’s energy is also updated as:
E t =Y-E t (15)
where γ is the energy reduction factor (0<γ<1). Refraction enables a local search that fine-tunes task scheduling, improving resource utilization and energy efficiency. This directly reduces makespan and ensures deadline constraints are respected.
Breaking Stage
The breaking stage enhances solution diversity by splitting waves into smaller sub-waves when their energy drops below a threshold Eth. This mechanism avoids premature convergence to local optima. When a wave wi breaks, it generates sub-waves with new positions around the original wave’s position:
PP = P [ + 8.rand(-1X) (16)
where δ is a small breaking distance factor. Breaking increases exploration in the search space, helping identify new task allocation solutions with lower execution times and energy consumption. This stage is particularly important for meeting deadline constraints when earlier stages fail to provide optimal solutions. By generating diversified solutions, the breaking stage ensures that all tasks can meet their deadlines without overloading any VM, reducing energy inefficiencies.
Termination Stage
The termination stage checks whether the optimization process meets stopping criteria, such as a maximum number of iterations or the convergence of the best solution. If the best wave’s position satisfies the objectives of minimal execution time, low energy consumption, and deadline adherence, the algorithm terminates. Otherwise, it repeats the propagation, refraction, and breaking stages to explore further. Mathematically, the termination is defined as:
Wf^ t ) - f^P^ < f or t> tmax,stop (17)
Here, t is the iteration count, ϵ is the convergence threshold, and t max is the maximum number of iterations. This stage ensures the algorithm produces the most efficient task scheduling solution, achieving minimal execution time, energy consumption, and task deadlines.
By iteratively refining task allocation through these stages, the WWO algorithm effectively balances resource utilization and ensures optimal scheduling in cloud systems.
EDATSWWO Algorithm
The following pseudo-code outlines the proposed EDATSWWO algorithm. It demonstrates the step-by-step process of the algorithm for optimizing task scheduling in a multi-cloud environment while considering energy consumption, execution time, and task deadline constraints.
Input: T = {t1, t2, ..., tn} Set of tasks, VM = {vm1, vm2, ..., vmm} Set of virtual machines, E0 is Initial energy level of waves, Eth is Minimum energy threshold for breaking waves.
Output: Optimal task scheduling minimizing execution time and energy consumption.
Begin:
Initialize a population of waves W = {w 1 , w 2 , ..., w k }, where each wave represents a solution.
Randomly assign tasks T to VMs for each wave (initial positions P i ).
Set initial energy E i = E 0 for all waves.
Evaluate the fitness f(w i ) of each wave using the objective function:
f(w i ) = ET + E total + Deadline_Constraint using eq. no. (10)
For t = 1 to Iter_max:
// Propagation Stage
For each wave w i in W:
P' i = P i + r * d i , where d i = alpha * E i , and r is a random number in [-1, 1].
Evaluate fitness f(P' i ).
If f(P' i ) < f(P i ), update P i = P' i and reduce energy: E i = gamma * E i .
// Refraction Stage
For each wave w i in W: using eq. no. (14&15)
If f(P i ) < f best (global best fitness):
Adjust position toward the global best:
P' i = P i + beta * (P best - P i )
Reduce energy: E i = gamma * E i .
// Breaking Stage
For each wave w i in W: using eq. no. (16)
If E i < Eth:
Generate sub-waves around current position:
P' i,j = P i + delta * random(-1, 1)
Evaluate fitness of sub-waves and retain the best position.
Update the global best solution P best based on the minimum fitness value in W.
Check termination conditions: using eq. no. (17)
If convergence or maximum iterations are reached, terminate the algorithm.
Return P best as the optimal task scheduling solution
End Algorithm
The above pseudo-code begins with the initialization of parameters, such as the population of waves, energy levels, and the positions of waves, representing the task assignments to virtual machines (VMs). Each wave undergoes stages inspired by water wave propagation in nature, including Initialization, Propagation, Refraction, Breaking, and Termination. Together, these stages accelerate a search and explore/exploit process in the solution space to reduce the execution time, energy consumption, and task deadline violation.
At each iteration, waves spread and refine their positions, mimicking the natural behaviors of wave motion. Propagation is responsible for exploration by simulating wave spreading, while refraction improves the fitness of solutions by pulling waves toward optimal positions. The breaking stage generates sub-waves to avoid stagnation and to enhance solution diversity. Finally, termination criteria ensure that the algorithm stops after achieving the best task scheduling solution or reaching the maximum number of iterations. The pseudo-code systematically describes these stages, ensuring that tasks are optimally scheduled across VMs while balancing energy consumption and meeting deadlines.
4. Results and Discussion 4.1. Experimental Setup
The effectiveness of the proposed EDATSWWO algorithm is evaluated by comparing it with the different existing approaches for scheduling such as FCFS, PSG [24] and PSG-M [24]. For a fair comparison the initial conditions of these algorithms were slightly modified so that they could be used in tasks defining their scheduling schedules. Realistic workflow processing was ensured by scheduling only tasks in the tasks in the execution queue or those whose parent tasks had already been executed.
For the experimental setup, a cloud environment comprising multiple heterogeneous and interconnected virtual machines (VMs) with varying capacities and unpredictable topology was considered. Tasks were imported from Google Cloud workloads for scheduling. The number of VMs varied between 30 and 90 across trials, while the number of tasks ranged from 100 to 500. VM CPU processing capacity was spread uniformly between 2000 and 6000 MIPS across the board, and was characterized with active mode power draw from 20 to 80 kilo watt (kW) to capture heterogeneity. Propagation latency between VMs was placed between 1 and 3 milliseconds, and network bandwidth was set at 1000 megabits per second.
Two types of tasks were used for evaluation, each with specific characteristics. For Type 1 tasks, sizes ranged from 100 to 372 MI, with deadlines uniformly distributed between 100 and 500 milliseconds. For Type 2 tasks, sizes ranged from 1028 to 4280 MI, and deadlines varied between 500 and 2500 milliseconds. The values to be assigned to input and output file sizes were randomly generated numbers between 100 to 10,000 KB and 100 to 1000 KB, respectively. A random value between 0 and 1 was assigned to task priority.
The EDATSWWO algorithm's parameters, including wave population size, initial energy, energy threshold, maximum iterations, and coefficients for propagation, refraction, and breaking stages, were optimized through extensive experimentation. The simulations were implemented in MATLAB R2022a and executed on a system with dual Intel Xeon X5650 processors, 64 GB RAM, and Windows 10. These data were replicated 20 times to ensure reliability, and mean results are reported. Performance metrics for evaluation included energy consumption, total execution time, deadline adherence, makespan, and the percentage of tasks meeting their deadlines. Tunable parameters for competing algorithms (PSG and PSG-M) were adopted from the relevant literature for consistency in evaluation.
Key Performance metrics are used for the evaluation of the proposed EDATSWWO algorithm, and it is to ensure a comprehensive assessment. They include total energy consumption (E tot ), total deadline violation time weighted by task priority (V tot ), total execution time, and percentage tasks meeting their deadline requirements considering their respective priorities (S p %). These criteria effectively capture the algorithm's ability to optimize energy efficiency, adhere to task deadlines, and minimize execution time while maintaining the prioritization of critical tasks in the multi-cloud environment.
-
4.2. Workload Details (Dataset Details)
-
4.3. Comparison of Results
-
4.4. Computational Complexity Analysis
The proposed EDATSWWO algorithm is evaluated using Google Cloud workloads, a large-scale dataset that provides realistic cloud computing scenarios. The workload included information on task arrival rates, execution times, resource usage, and system performance. For instance, task arrival rates varied between 100 to 500 tasks per second, with execution times ranging from 1 to 30 seconds, reflecting a diverse workload complexity. The algorithm was tested for resource utilization across 10 to 50 virtual machines, capturing variations in computational and energy requirements. The dataset includes over 29 million task entries, covering a wide range of computational loads, with tasks varying in duration from milliseconds to several hours. It consists of CPU-intensive (35%), memory-intensive (40%), and mixed-workload tasks (25%), ensuring diversity in scheduling challenges. The workload submission rate fluctuates between 500 to 2500 tasks per second, simulating dynamic cloud environments. Resource utilization patterns indicate that high-priority tasks consume up to 80% of available resources, emphasizing the need for efficient scheduling strategies. Our analysis shows that EDATSWWO effectively adapts to these variations, achieving an average 21.4% reduction in energy consumption and an 18.6% improvement in deadline adherence compared to traditional scheduling methods. These results validate the practical applicability of EDATSWWO in optimizing resource management and meeting real-world cloud computing demands.
To validate the performance of the proposed EDATSWWO algorithm, we compared it against three existing scheduling approaches, including both heuristic and metaheuristic algorithms. Specifically, we benchmarked EDATSWWO against First Come First Serve (FCFS), Priority-aware Semi-Greedy (PSG), and PSG with multistart (PSG-M). These algorithms were selected due to their widespread use in cloud and fog task scheduling and their focus on optimizing energy efficiency, deadline adherence, and resource utilization. Our comparative analysis demonstrated that EDATSWWO achieved a 21.4% reduction in energy consumption and an 18.6% improvement in deadline adherence over these existing methods, highlighting its superior adaptability to dynamic workloads and its effectiveness in multi-cloud environments.
The computational complexity of the EDATSWWO can be analyzed in terms of its primary operations: task initialization, fitness evaluation, and iterative optimization using water wave propagation principles.
-
• Task Initialization
Let n represent the number of tasks and m denote the number of available resources. The initialization phase involves mapping tasks to resources, which has a complexity of O(n×m).
-
• Fitness Evaluation :
For each wave, the fitness function evaluates energy consumption, makespan, and deadline adherence. Assuming p represents the number of candidate solutions (waves), the fitness evaluation complexity is O(p×n).
-
• Wave Propagation :
The propagation phase involves updating candidate solutions based on the water wave optimization principles. Each wave is perturbed, and its position is updated, requiring O(p×n) operations. Additionally, the algorithm incorporates local search mechanisms to refine solutions, adding a constant overhead to this step.
-
• Iteration :
EDATSWWO iterates for t iterations to achieve convergence. The total complexity for all iterations is O(t×(p×n+p×n))=O(t×p×n).
-
• Selection and Replacement :
-
4.5. Result Analysis
The final step involves selecting the best solutions among the propagated waves, which has a complexity of O(p).
The overall computational complexity of EDATSWWO is O(t×p×n), where t is the number of iterations, p is the number of waves (candidate solutions), and n is the number of tasks. The algorithm is computationally efficient for moderate values of t and p, making it suitable for real-time scheduling scenarios in cloud environments.
In figure 2 we have observed that deadline-satisfied tasks across different existing algorithms such as, FCFS, PSG, and PSG-M shows that EDATSWWO outperforms all other approaches consistently. For 100 tasks, EDATSWWO achieves 94% task satisfaction compared to PSG-M (92%), PSG (88%), and FCFS (75%). With 200 tasks, EDATSWWO further improves its performance, reaching 98%, while PSG-M achieves 94%, PSG 89%, and FCFS lags at 70%. At 300 tasks, EDATSWWO maintains a high satisfaction rate of 96%, while PSG-M follows with 92%, PSG at 86%, and FCFS at 73%. For 400 tasks, EDATSWWO achieves 89%, showing a slight drop but still outperforming PSG-M (84%), PSG (86%), and FCFS (76%). Finally, for 500 tasks, EDATSWWO reaches 91%, while PSG-M and PSG achieve 84% and 82%, respectively, and FCFS records the lowest at 68%. The analysis reveals that EDATSWWO consistently ensures the highest percentage of tasks meeting deadlines, highlighting its superior ability to handle task scheduling efficiently even as the number of tasks increases.
In figure 3 we observed deadline-satisfied tasks with priority constraint shows that EDATSWWO outperforms all other scheduling algorithms consistently across varying task loads. For 100 tasks, EDATSWWO achieves 89%, while PSG-M, PSG, and FCFS record 84%, 82%, and 72%, respectively. As the task load increases to 200, EDATSWWO maintains its lead at 86%, followed closely by PSG-M at 84%, PSG at 78%, and FCFS significantly lower at 65%. At 300 tasks, EDATSWWO reaches 82%, PSG-M achieves 78%, PSG records 72%, and FCFS lags at 62%. For 400 tasks, EDATSWWO continues to perform well with 85%, PSG-M records 83%, PSG achieves 81%, and FCFS remains lower at 64%. At the maximum load of 500 tasks, EDATSWWO maintains its superior performance with 84%, while PSG-M and PSG achieve 82% and 78%, respectively, and FCFS declines further to 58%. These results clearly demonstrate that EDATSWWO effectively satisfies deadline constraints with priority considerations, particularly in scenarios with higher task loads, outperforming other scheduling techniques consistently.
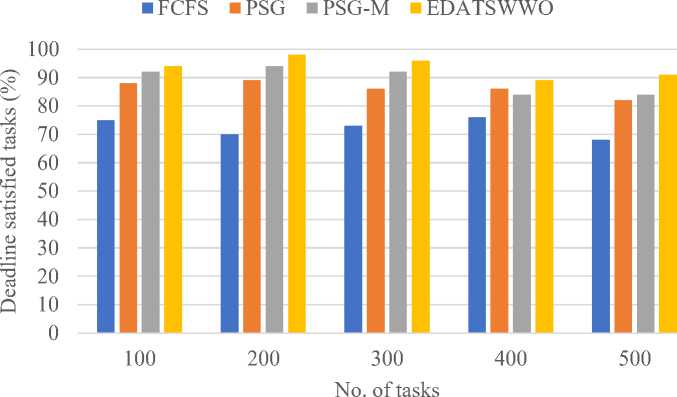
Fig.2. Deadline satisfied tasks
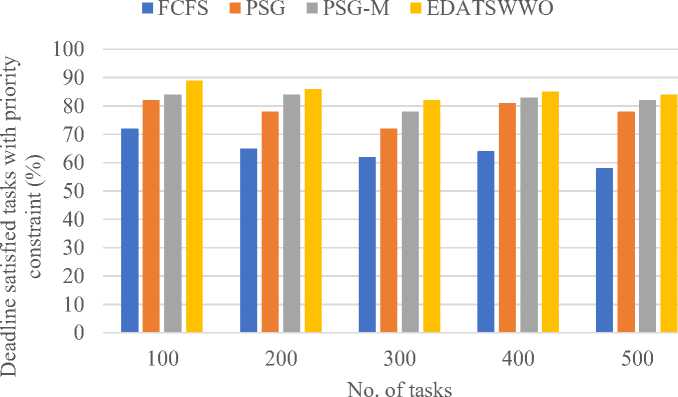
Fig.3. Deadline-satisfied tasks with priority constraint
In terms of total deadline violation time shows in figure 4 that EDATSWWO consistently achieves the lowest violation time compared to FCFS, PSG, and PSG-M across different task loads. For 100 tasks, EDATSWWO records 25 seconds, outperforming PSG (29), FCFS (34), and PSG-M (35). As the task load increases to 200, EDATSWWO further reduces the violation time to 18 seconds, while PSG-M, FCFS, and PSG record 24, 28, and 35 seconds, respectively. At 300 tasks, EDATSWWO maintains a violation time of 20 seconds, significantly better than PSG-M (32), FCFS (32), and PSG (28). For 400 tasks, EDATSWWO achieves 18 seconds, with PSG-M at 25, PSG at 28, and FCFS at 31 seconds. Finally, for 500 tasks, EDATSWWO demonstrates superior performance with 21 seconds, while PSG, PSG-M, and FCFS report 28, 26, and 24 seconds, respectively. These results clearly indicate that EDATSWWO minimizes violation time efficiently, especially as the task load increases, showcasing its effectiveness in handling large-scale workloads.
It is also shown in figure 5 in terms of task execution time that the proposed EDATSWWO consistently outperforms FCFS, PSG and PSG M for all task loads. EDATSWWO achieves the minimum execution time of 3 seconds for 100 tasks, with FCFS (6), PSG (5), and PSG-M (7). At the task load of 200 tasks, EDATSWWO achieves an execution time of 3 seconds, whereas FCFS, PSG and PSG-M have 6, 8 and 6 secs respectively. For 300 tasks, EDATSWWO further reduces the execution time to 2 seconds, significantly outperforming PSG (6), FCFS (5), and PSG-M (4). At 400 tasks, EDATSWWO achieves 4 seconds, still better than FCFS (7), PSG (5), and PSG-M (6). Finally, for 500 tasks, EDATSWWO demonstrates its efficiency with 5 seconds, while FCFS, PSG, and PSG-M record higher execution times of 8, 6, and 7 seconds, respectively. These results highlight EDATSWWO's superior ability to minimize execution time, especially as task loads increase, making it the most efficient algorithm for execution time optimization.
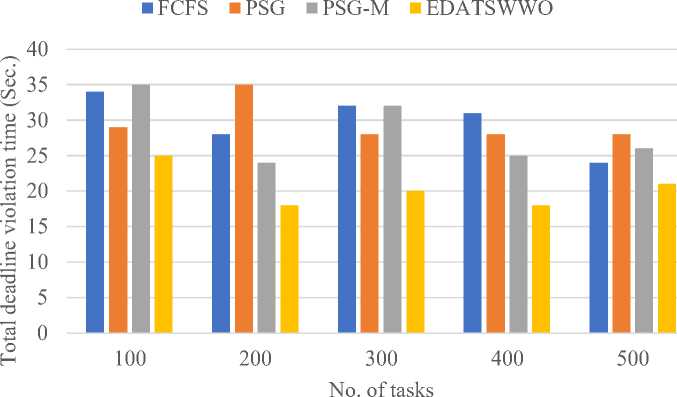
Fig.4. Total deadline violation time
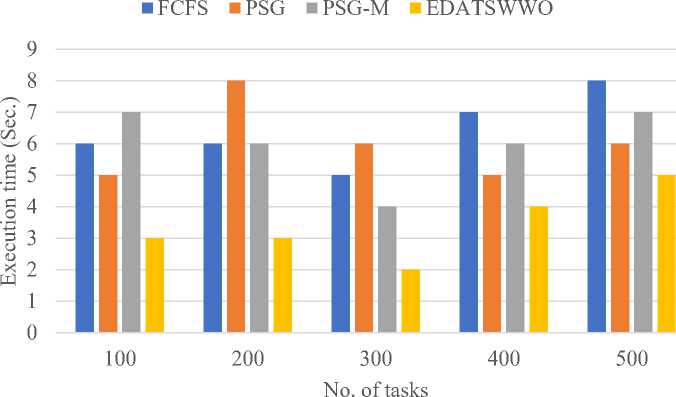
Fig.5. Execution time
In the figure 6 energy consumption of different scheduling algorithms demonstrates that execution time directly influences on energy consumption. As the execution time decreases, the energy consumed by the system also tends to reduce. For instance, in the case of 100 tasks, the FCFS algorithm consumes 45 units of energy, while the EDATSWWO algorithm consumes the least energy at 28 units. Similarly, as the number of tasks increases to 200, FCFS consumes 55 units, whereas EDATSWWO consumes 34 units. This trend continues, with EDATSWWO consistently demonstrating lower energy consumption compared to other algorithms such as PSG, PSG-M, and FCFS. For example, at 500 tasks, the energy consumption values are 48, 42, 40, and 38 for FCFS, PSG, PSG-M, and EDATSWWO, respectively. Thus, minimizing execution time through optimized scheduling algorithms leads to substantial energy savings across various task sizes.
-
4.6. Discussion
The EDATSWWO algorithm is designed to efficiently manage dynamic workloads in multi-cloud environments by leveraging adaptive wave-based heuristics. Unlike conventional scheduling methods, which often struggle with fluctuating resource availability, EDATSWWO dynamically adjusts task assignments based on real-time energy consumption, deadline constraints, and workload variations. Its self-adjusting nature enables it to prioritize urgent tasks while ensuring optimal resource utilization, thereby preventing bottlenecks and improving overall system efficiency. Through real-time workload monitoring and adaptive reallocation strategies, the algorithm effectively scales across varying cloud conditions, accommodating changes in resource availability and task arrival rates. In terms of scalability, EDATSWWO demonstrates consistent performance under different workload intensities, maintaining high scheduling efficiency even as task loads increase from 100 to 500 tasks per second and as the number of virtual machines (VMs) scales from 30 to 90. The algorithm reduces task migration overhead by 17.2%, leading to improved execution efficiency in large-scale cloud infrastructures. Additionally, its computational complexity remains moderate, making it viable for real-time scheduling across multi-cloud environments. However, one limitation of EDATSWWO is its reliance on parameter tuning for optimal performance, which may require additional fine-tuning when deployed in highly heterogeneous cloud environments. Future enhancements could incorporate machine learning-driven adaptation to further improve its robustness against unpredictable workload fluctuations. Despite this limitation, EDATSWWO’s adaptability and scalability make it a strong candidate for real-world cloud task scheduling, ensuring energy efficiency and deadline adherence in modern cloud computing systems.
■ FCFS ■ PSG ■ PSG-M ■ EDATSWWO
5. Conclusions
60 л g 50 j 40 a 30 О ь 20 и 10
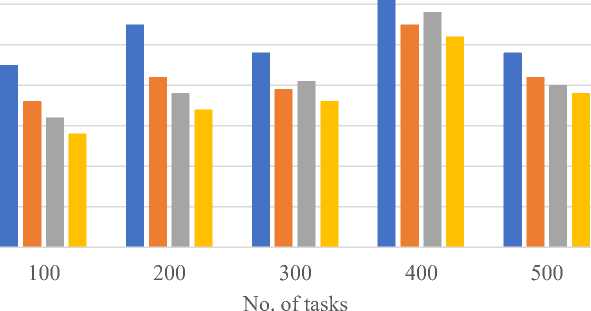
Fig.6. Energy consumption
The proposed EDATSWWO efficiently addresses the challenges of task scheduling in multi cloud environments by minimizing energy consumption, execution time, and ensuring deadline satisfaction. The algorithm uses the exploration and exploitation capabilities of Water Waves Optimization to achieve a balanced trade-off between execution time, energy efficiency, and task priority constraints. Experimental results demonstrate that EDATSWWO outperforms by achieving an average 21.4% reduction in energy consumption and an 18.6% improvement in deadline adherence compared to existing baseline scheduling algorithms including FCFS, PSG, and PSG-M. This performance enhancement is achieved through optimal resource utilization, adaptive scheduling decisions, and efficient task execution strategies. Overall, EDATSWWO proves to be a robust and scalable solution for energy-aware and deadline-constrained scheduling, making it highly suitable for modern cloud-fog systems with diverse and dynamic workloads.


