Environmental governance as a mechanism for promoting digital citizenship and developing the skills of individuals and communities
Автор: Mohamed Kaki, Naziha Chaouche, Fatima Fendil
Журнал: Science, Education and Innovations in the Context of Modern Problems @imcra
Статья в выпуске: 1 vol.8, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The world today is witnessing a rapid increase in the use of technology, creating new challenges that require strengthening awareness of the importance of its responsible use. Despite the significant benefits technology offers, its misuse poses a threat to societies and the environment, making it essential to instill the concept of digital citizenship, especially among youth. Digital citizenship is viewed as a behavior based on conscious and responsible use of technology, while adhering to ethical values, respecting the rights of others, and preserving the environment. The research shows that digital citizenship is not limited to technical skills but also includes awareness of the legal and ethical responsibilities that accompany digital use, making it a key tool for achieving sustainable development. It also highlights that building the capacities of individuals and communities through environmental governance and global citizenship contributes to achieving a real balance between technological advancement and environmental preservation. Conscious use of technology enhances human well-being and protects natural resources for future generations, fostering more inclusive and sustainable societies.
Digital citizenship, sustainable development, responsible use of technology, environmental governance, global citizenship
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/16010387
IDR: 16010387 | DOI: 10.56334/sei/8.1.81
Текст научной статьи Environmental governance as a mechanism for promoting digital citizenship and developing the skills of individuals and communities
Citation. Kaki M, Naziha Ch., Fatima F. (2025). Environmental governance as a mechanism for promoting digital citizenship and developing the skills of individuals and communities. Science, Education and Innovations in the Context of Modern Problems, 8(1), 1252-1265. doi: 10.56352/sei/8.1.81.
Our world is witnessing a steady increase in the use of technology, which calls for an urgent need to raise awareness about the importance of its responsible use. Although technology offers tremendous benefits, its misuse presents a serious challenge that threatens our societies on one hand, and urges us to think about harnessing it to serve the environment and the ecosystems we live in on the other.
In this context, the importance of "digital citizenship" emerges as a fundamental concept that must be firmly established in our societies, particularly among the youth. Digital citizenship does not simply mean using technology; it means using it consciously and responsibly, while adhering to ethics and values, respecting the rights of others, and protecting the living beings around us.
This research aims to highlight the importance of digital citizenship in sustainable development and in serving nature, and to present an integrated approach to promoting it. The goal is to build a generation capable of engaging with technology positively and responsibly, utilizing it to preserve the environment, and contributing to the creation of a safe and thriving digital society.Accordingly, we can pose the following question: How do environmental governance and global citizenship contribute to building the capacities and skills of individuals and communities and putting them at the service of environmental sustainability?
1-The Nature of Digital Citizenship
Digital citizenship is a set of standards, rules, and principles that regulate the responsible and effective use of technology. These standards include:
-
• Digital Access: Ensuring that all individuals have fair and equal access to technology and digital information.
-
• Digital Participation: Using technology to engage in social, political, and cultural activities online.
-
• Digital Security: Protecting personal information and data from cyber threats and fraud.
-
• Digital Ethics: Adhering to ethical standards and values when using technology, such as respecting intellectual property rights and avoiding the spread of misinformation.
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA
-
• Digital Health: Maintaining physical and mental well-being while using technology, and avoiding digital addiction and other negative effects.(El-Mallah, 2017)
-
1 -1. Global Citizenship:
Global citizenship is a central concept that reflects an individual's awareness of their responsibility toward the world and the international community as a whole, not just toward their own country or local community. A global citizen is characterized by the ability to understand complex global issues such as human rights, climate change, social justice, and international conflicts, and to engage with these issues in a positive and responsible manner that promotes the values of solidarity and coexistence. Global citizenship encourages individuals to think with a holistic mindset that transcends geographical and cultural boundaries, contributing to the creation of a fairer and more equitable world.
Building on this awareness, global citizenship plays an active role in empowering individuals, helping them use technology with confidence and efficiency to achieve their personal and professional goals. A global citizen possesses the digital and cognitive skills that enable them to interact with modern tools competently and intelligently, opening wide horizons in fields such as education, employment, and entrepreneurship, and strengthening their role as an active participant in the global digital economy.The role of global citizenship is not limited to empowering individuals; it also extends to building better societies based on mutual respect, protection of rights, and preservation of freedoms. Global citizens believe in the importance of collective action and dialogue among different cultures, leading to the creation of digital environments characterized by safety and prosperity. In this way, societies become more inclusive and diverse, capable of addressing shared challenges with a spirit of cooperation and solidarity.
Moreover, global citizenship directly contributes to promoting sustainable development by directing the use of technology toward serving comprehensive development goals. A global citizen recognizes the importance of linking technological advancement to addressing key issues such as quality education, gender equality, and climate action. Through this awareness, technology is transformed into an effective tool for driving positive and sustainable changes, ensuring human well-being and protecting the planet for future generations.
-
1 -2. Characteristics of a Global Citizen : A global citizen is distinguished by several essential characteristics that reflect their awareness and sense of responsibility toward the entire world. The first of these characteristics is awareness of global issues, as a global citizen possesses a deep understanding of the major challenges facing humanity, such as poverty, climate change, human rights violations, and armed conflicts. This awareness enables them to engage with international issues critically and responsibly, and encourages them to adopt positions that seek fair and sustainable solutions.
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA
In addition, a global citizen is characterized by respect for cultural diversity, recognizing the importance of cultural diversity as a source of human richness rather than a cause for conflict or discrimination. They value and respect religious, racial, and linguistic differences, and believe in the necessity of peaceful coexistence, thus contributing to the building of more tolerant and inclusive societies in an era of accelerating globalization.
A global citizen also demonstrates a strong commitment to defending human rights, viewing the protection of human dignity as a fundamental duty, regardless of race, religion, gender, or social affiliation. They work to oppose all forms of injustice and discrimination and support initiatives and policies that safeguard individual rights and promote social justice both locally and globally.
Finally, a global citizen is marked by active participation in both their local community and the broader world, engaging in civic and political activities aimed at improving public life. Whether through volunteering, raising awareness, supporting environmental causes, or participating in international campaigns, a global citizen believes that change begins with organized and responsible collective action.
-
1 -3 The Importance of Global Citizenship:
2. A Comparison between Digital Citizenship and Traditional Citizenship Tamer Al-Mallah (2017, p. 122) noted that the difference between digital citizenship and traditional citizenship appears through several aspects, providing greater clarification of the significant distinctions between them, which are evident in the definitions of each. These differences are summarized as follows:
Global citizenship is one of the fundamental pillars for building a safer and more just future for all the peoples of the world. It actively contributes to promoting peace and cooperation among nations and peoples by encouraging dialogue, the exchange of experiences, and joint efforts to address global challenges such as poverty, armed conflicts, and climate change. Thanks to the values of global citizenship, international cooperation becomes a necessary choice for achieving security and stability.Global citizenship also seeks to achieve social justice by defending human rights and promoting equality among all individuals, regardless of their cultural or social backgrounds. It upholds the principles of fairness and human dignity and calls for the removal of barriers that prevent individuals from enjoying their fundamental rights and freedoms, thus creating more balanced and equitable societies.
Moreover, global citizenship contributes to building a better world by supporting sustainable development across its economic, social, and environmental dimensions. It instills in individuals a sense of responsibility toward future generations and encourages them to adopt practices that respect the environment and ensure the fair and sustainable use of natural resources, securing humanity’s long-term prosperity.
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA
Table (1): A Comparison between Digital Citizenship and Traditional Citizenship
|
Aspect of Comparison |
Digital Citizenship |
TraditionalCitizenship |
|
Definition |
It is an individual's interaction with others using digital tools and resources, such as various forms of computers and the internet as a medium of communication through multiple technological means. |
It is a lived practice where the citizen fulfills their duties in exchange for receiving rights guaranteed by the constitution and the law, expressing the bond and commitment between the individual and the state, allowing them to integrate into society and actively participate at all humanitarian and community levels, driven by strong belonging, loyalty, and love for their homeland. |
|
Nature of Society |
A virtual digital society where individuals interact using technological means as intermediaries. |
A real interactive society where individuals deal face-to-face without any intermediaries. |
|
Nature of Individuals |
Virtual characters representing real people. |
Real individuals. |
|
Interaction Environment |
Electronic / Digital. |
Natural / Traditional. |
|
Trust |
No complete security in all sources. |
Complete security in all sources. |
|
Focus |
Revolves around the standards, skills, and rules of conduct necessary for interacting with technology. |
Revolves around the sense of belonging, rights, and duties of individuals toward the homeland and the land. |
|
Participation |
Large participation. |
Limited participation. |
|
IntellectualPropertyRights |
Intellectual property rights are largely unprotected. |
Intellectual property rights are protected. |
|
Communication |
Easy remote communication from anywhere in the world. |
Face-to-face communication. |
|
How It Is Learned |
Through curricula and courses; it develops with age. |
Values that grow within the individual socially and through interactions within the community. |
In the present era, we are no longer able to limit the use of technology, whether in the educational or societal spheres, in order to contain its risks and confront them. Therefore, it is
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA necessary to work on employing it optimally across all aspects of educational and non-educational life. Consequently, there must be scientific frameworks established to embed the values and principles of digital citizenship in our lives and the lives of our children, to prevent the problems and disasters generally caused by technology. Every individual must be aware of their rights and responsibilities regarding the technology that currently exists and is used in our daily lives.(El-Dahshan, 2016)
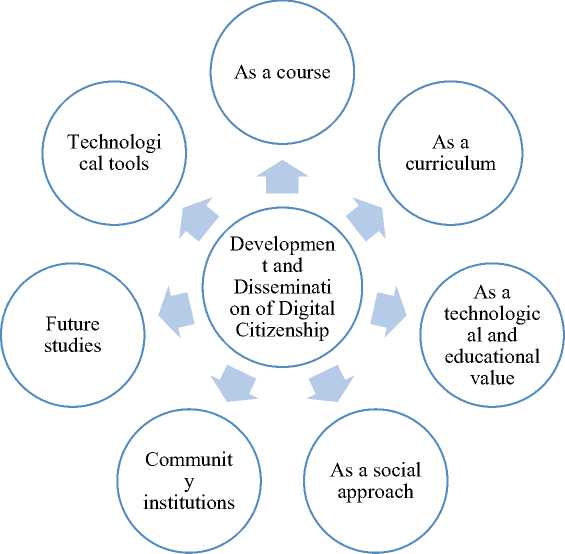
Figure 1. Proposed Concept: "A Plan for the Development and Dissemination of Digital Citizenship Culture" (Tamer Al-Mallah, 2017)
* Clarification of the Previous Plan:
With the increasing reliance on technology and digitization in all aspects of life, the urgent need to instill the concepts of digital citizenship in educational systems has emerged to ensure the responsible and safe use of technology. From this perspective, this proposed framework suggests a set of integrated approaches aimed at embedding the values and skills of digital citizenship among various age groups in the educational community, contributing to the preparation of a generation that is conscious and proficient with the tools of the digital age.
The proposal begins with the first axis, which is the inclusion of digital citizenship as a standalone course dedicated to teaching students the principles of digital citizenship at an appropriate educational stage, taking into account the age characteristics of each group. This course focuses on raising awareness and ethical standards for using technology.

Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA
As for the second axis, it adopts digital citizenship as an integrated curriculum that accompanies the student through various stages of their education, gradually incorporating the concepts and skills of digital citizenship in line with the evolution of their use of technology. This ensures the development of cumulative and sustainable awareness of responsible digital behavior.
In the third axis, the focus is on digital citizenship as a technological approach and an educational value. This is achieved by organizing workshops, seminars, and discussion forums within educational institutions to establish responsible technology practices and raise awareness among students and teachers about the ethics of digital usage.
As for the fourth axis, it involves presenting digital citizenship as an integrated chapter within the computer science subject, with a dedicated study unit for each educational stage, designed according to the students' age needs and their level of interaction with digital tools.
The proposal moves to the fifth axis, which addresses digital citizenship as a social approach. It involves preparing awareness campaigns targeting the entire community, with a focus on the role of parents in monitoring and guiding their children's digital behavior, utilizing youth centers and school councils for this purpose.
As for the sixth axis, it emphasizes the importance of various community institutions— religious, media, social, and cultural—in promoting the culture of digital citizenship through awareness programs and purposeful activities, alongside the vital roles of the family, school, and state.
The seventh axis highlights the importance of future studies, by tracking technological developments and studying how to employ them to spread the culture of digital citizenship, through flipped learning, virtual reality, and social media networks, ensuring the ability to keep pace with modern technological advancements.
Finally, the eighth axis addresses the role of modern technological tools in developing digital citizenship, through the development of electronic applications and interactive educational websites, or by using virtual reality technologies to create learning environments that simulate reality. This contributes to practically reinforcing the values of positive digital behavior.
This procedural proposal aims to build an integrated methodology for developing digital citizenship, relying on formal education, extracurricular activities, and community work, thereby enhancing the educational community's ability to engage with technology consciously and responsibly.
Table1. Proposed Concept: "Plan for Developing Digital Citizenship in the Educational Sphere" (Tamer Al-Mallah, 2017)
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA
|
Learner |
|
|
Teacher |
|
|
School |
Administrative Policy |
|
Surrounding Community |
|
|
Ministry of Education |
|
In our pursuit to enhance the culture of digital citizenship within the educational and community sectors, the proposed plan includes several key axes aimed at spreading and developing digital awareness among individuals through interconnected educational and societal systems.
The school is considered a fundamental environment for fostering digital citizenship, where it should provide well-equipped technological labs that ensure digital equality for all students and
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA support equitable access to technology. By integrating curricula, effective educational outcomes are achieved that positively change students' behaviors. Furthermore, the school should be a key driver for campaigns promoting digital citizenship concepts within the school community, as well as providing training courses for both teachers and students. Parents' councils also play an important role in monitoring children's behaviors at home, organizing periodic seminars and discussion forums to refresh and expand digital knowledge within the school. It is also essential for the school to adopt clear administrative policies that require all parties to adhere to responsible digital practices.
The learner is the central element in this plan, and therefore, an educational environment must be provided to support them by organizing training courses during school breaks to teach basic digital skills and apply the values of digital citizenship. It is also essential to include study programs that focus on building digital awareness among students and equipping them with the knowledge needed to use technology responsibly. Providing suitable technological labs that allow students to learn using modern tools, following ethical guidelines, is a crucial step. Educational supervision should be flexible, with teachers collaborating with parents to monitor student behavior and ensure proper use of technology.
The teacher is considered a key pillar in spreading the culture of digital citizenship within classrooms. It is necessary to provide specialized training courses for teachers to develop their technological skills, in addition to organizing workshops that focus on the practical aspects of using technological tools correctly. Teachers should also be provided with educational resources to support their continuous learning in this field, with policies and conditions in place to ensure their commitment to applying what they learn in the classroom.
Given the differences in educational stages, their needs, and the development levels of students, educational programs should be designed to suit each age group. These programs include appropriate digital skills that help students use technology in a safe and balanced way according to their educational and developmental needs. This is achieved by integrating digital citizenship concepts into the curriculum in a way that takes individual differences and the evolution of technology usage into account.
The task of spreading the culture of digital citizenship is not limited to educational institutions alone; the surrounding community also plays a role, including media outlets, youth centers, and social clubs, which serve as main platforms for raising digital awareness among individuals. The Ministry of Education should also be involved in adopting clear educational policies aimed at promoting digital citizenship, by providing specialized curricula, preparing trained teachers, and setting mechanisms to implement digital citizenship within schools. This also requires holding individuals accountable for failing to implement these policies through appropriate disciplinary
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA actions. Additionally, peer groups are one of the factors influencing individuals' behaviors, so students should be educated on the importance of choosing their friends carefully to achieve a positive impact on their digital practices.
With this integrated approach, the right path towards building a responsible and safe digital society is realized, where individuals possess digital awareness capable of facing the challenges of the digital age and building a sustainable, healthy educational environment.
2-2 Challenges of the Digital Age: The Need for Global Governance
As reliance on technology increases in various aspects of our daily lives, it has become clear that the digital age brings with it new and complex challenges. While technology offers many benefits, it also opens the door to significant issues that threaten societal stability, such as the spread of misinformation, which can lead to confusion among the public and undermine trust between individuals and institutions. Furthermore, cyberbullying has become a distressing issue for many, especially among young people, leading to psychological and social consequences that can be devastating. The digital space has also witnessed a noticeable rise in cybercrimes targeting both individuals and businesses, resulting in the loss of personal and financial data. Additionally, privacy violations have become a serious threat to individuals in the face of weak security systems.
These challenges are not limited to the scope of a single country; rather, they transcend national borders to become global issues that affect everyone. Therefore, addressing them requires continuous international cooperation between countries and international organizations to establish common rules and practices that regulate the digital space and protect individuals' rights. This cooperation must be based on fundamental principles that ensure digital justice for all. Hence, the importance of "global governance of the internet" emerges as an urgent necessity in this age, where the digital space has become an integral part of our daily lives.
Global governance of the internet means establishing a legal and ethical framework that regulates internet use globally, ensuring the respect for human rights, enhancing privacy protection, and providing guarantees for freedom of expression without allowing violations. There must also be international cooperation to combat cybercrimes that threaten the security of information and personal property. In this context, the role of digital citizenship is increasing in supporting this global governance. Digital citizenship not only concerns the safe use of technology, but also extends to individuals' awareness of the responsibilities that come with using the internet.
Through digital citizenship, dialogue and discussions on digital policies can be enhanced, allowing individuals the opportunity to actively participate in shaping the digital future. With digital awareness, a citizen becomes capable of distinguishing between correct and misleading information and contributing to the widespread dissemination of digital safety culture. Thus, digital
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA citizenship can become a key driver in promoting global governance of the internet by encouraging shared human values and working towards establishing governance rules that ensure safety and fairness in the digital space.
3- Governance, Digital Citizenship, and Their Relationship with Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection:
3-1 Digital Citizenship and Sustainable Development.
In the age of the digital revolution, digital citizenship has become one of the essential elements for achieving sustainable development in modern societies. With technology intertwining in all aspects of life—whether social, economic, or environmental—it has become crucial for individuals to gain the ability to interact with this technology in a responsible and ethical manner. Digital citizenship is not merely about using modern technologies; it is a commitment to maintaining the principles of social justice and inclusive development. It involves the ability to harness technology to improve daily life, while also ensuring that its use does not harm human rights or the environment.(Muhareb, 2006).
While sustainable development seeks to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, digital citizenship plays a pivotal role in this by facilitating access to education, technology, and a sustainable economy. Through inclusive digital education, communities can reduce the digital divide between different countries, contributing to the achievement of social justice. This approach aims to empower individuals with the essential digital skills that ensure them a comprehensive and quality education, in line with the fourth goal of the Sustainable Development Goals.
In the economic aspect, sustainable digital economies foster economic growth by encouraging digital entrepreneurship and providing online job opportunities. Modern technologies such as blockchain contribute to enhancing financial transparency and combating corruption, which aligns with Goal 8 of the Sustainable Development Goals, focusing on decent work and economic growth. Additionally, smart and sustainable communities, relying on big data and the Internet of Things, help improve resource management such as energy and water, thereby enhancing the sustainability of cities and communities while reducing carbon emissions.
From an environmental perspective, digital environmental responsibility plays a crucial role in preserving nature. Encouraging green technologies such as energy-efficient cloud computing and reducing electronic waste through recycling and conscious consumption contribute to minimizing the environmental impact of technology. These efforts align with Goal 13 of the Sustainable Development Goals, which focuses on climate action, and therefore, these initiatives support the natural environment and reduce pollution.
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA
On the other hand, digital health is considered one of the important aspects of sustainable development, as applications of artificial intelligence and modern technology can be used in telemedicine, contributing to the improvement of healthcare quality. Additionally, digital citizenship helps combat health misinformation online by educating individuals on how to verify information and rely on trustworthy sources.
Regarding governance and building the capacities of individuals and communities to preserve nature, technology plays a prominent role in providing the necessary tools and resources to achieve this goal. Using digital technologies to offer solutions that contribute to environmental conservation ensures a healthy and safe natural environment for both the current and future generations. Digital governance focuses on establishing a legal and regulatory framework that organizes the use of technology and ensures that everyone benefits from its development in a way that aligns with environmental and social values. Building these capacities requires investment in digital education and skill development that enables individuals to understand digital environmental issues and apply sustainable solutions. Through these efforts, we can ensure a balance between technological progress and the preservation of the Earth for future generations.
3-2 Governance and Building the Capacities of Individuals and Communities in Nature Conservation:
In light of increasing environmental challenges such as climate change, loss of biodiversity, and pollution, there is an urgent need to strengthen environmental governance and capacity building as essential tools for enabling individuals and communities to contribute effectively to nature conservation. Environmental sustainability is not only about protecting the environment from damage caused by human activities, but also about promoting sound management of natural resources, ensuring they are used in a way that balances the present and the future. Achieving effective environmental sustainability requires a combination of smart policies and community awareness of the need to act quickly and effectively.
Environmental governance plays a crucial role in regulating the interaction between humans and the environment. This includes the establishment of environmental legislation that governs various human activities such as manufacturing, agriculture, and mining, with the aim of reducing the environmental impact of these activities. Additionally, the enforcement of strict laws to combat pollution and protect nature reserves is central to this governance, as is ensuring the sustainable exploitation of natural resources. However, environmental governance is not limited to legislation alone; it also includes decentralization in environmental management, where local communities are granted the authority to manage their natural resources in a way that suits their environmental needs. Involving citizens, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector in environmental
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA decision-making is a key step toward achieving effective community partnerships that promote sustainable environmental solutions. Furthermore, transparency and accountability contribute to ensuring the fair application of these policies by combating corruption and ensuring the equitable distribution of resources among all parties.
To empower individuals and communities and enhance the preservation of nature, the focus must be on building the capacities of individuals and groups in the environmental field. In this context, environmental awareness becomes crucial in spreading knowledge about the importance of biodiversity and the harms of unsustainable resource consumption. This can be achieved through educational programs in schools and universities that focus on promoting environmental understanding, as well as through media campaigns that encourage people to adopt positive environmental behaviors, such as recycling and water conservation. In addition to awareness, training and qualification are an integral part of building environmental capacities.Through specialized workshops, farmers can learn sustainable farming techniques and how to rationalize the use of chemical pesticides. Local leaders can also be trained on how to manage environmental conflicts and apply the principles of green economy in their communities. Additionally, economic empowerment is required through supporting small projects that rely on natural resources sustainably, such as eco-tourism and sustainable handicrafts. Providing financial incentives to communities that adopt environmentally friendly practices helps encourage these practices among the population.
Despite the efforts made to achieve environmental sustainability, there are many challenges that countries and communities may face in this regard. One of the most prominent challenges is the lack of financial and human resources in some countries, which hinders the implementation of effective environmental policies. Additionally, resistance to change by some groups due to unsustainable traditional practices poses another obstacle. Furthermore, the conflict of interests between short-term economic development and environmental preservation may hinder progress toward sustainability goals. In the face of these challenges, multiple solutions can be adopted. Among the proposed solutions, International cooperation between developed and developing countries enhances the capacity building for environmental sustainability. Environmental standards can also be integrated into industrial and agricultural development policies to ensure that economic growth aligns with resource sustainability. The use of modern technologies such as the Internet of Things and artificial intelligence can be an effective tool in monitoring natural resources and improving their management, helping to preserve these resources for future generations.
Conclusion:
Sci. Educ. Innov. Context Mod. Probl. P-ISSN: 2790-0169 E-ISSN: 2790-0177 Issue 1, Vol. 8, 2025, IMCRA
Digital citizenship and global citizenship are fundamental concepts in our connected world. We must all strive to be responsible digital citizens and active global citizens in order to contribute to building a better world for everyone. Our world is witnessing a rapid digital transformation, where technology has become an integral part of our daily lives. With the increasing reliance on technology, new challenges arise, such as its misuse, which calls for the need to focus on strengthening "digital citizenship."
Digital citizenship is not just a set of technical skills; it is a comprehensive concept that includes awareness of the ethical and legal responsibilities that come with using technology, as well as the ability to handle it in a safe and responsible manner.
This research highlights the concept of digital citizenship, defines its key principles, and provides an integrated vision to strengthen it in our societies, with the aim of empowering individuals to use technology positively and contribute to building a better digital community. Digital citizenship is not merely safe internet usage; it is a cornerstone for achieving sustainable development. By promoting digital awareness and adopting sustainable policies, we can build more inclusive and resilient communities, where technology contributes to human well-being and the protection of the planet. Effective governance and the capacity-building approach are interconnected, as they form two essential pillars to achieve a balance between human development and environmental preservation. By empowering individuals and communities and involving them in decision-making, we can ensure a more sustainable future, where humans live in harmony with the environment without depleting its resources, while giving clear thought to future generations.


