Ergonomics as the scientific bases of design
Автор: Imash A. Hajiyev
Журнал: Science, Education and Innovations in the Context of Modern Problems @imcra
Статья в выпуске: 4 vol.5, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In the presented scientific material have investigated two important factors in design ergonomic and aesthetic. With the purpose of maximum ensure there have broadly used from utilitarian and functional requests in creation and or-ganization of human – thing – machine – environment systems. In this case, ergonomics being the scientific bases of design there specially investigated the historical perfection and discussed its role in design in the modern period. In the scientific article is also explained the types of thinking to be based on composed intuition acts and the first be-ginning thoughts and idea of all creative works. At the result presented the conception of ergonomic thinking putting forward which substantiated by the author. There have giving attention to that showed type of thinking in the processes of creative works design it is necessary to be in special development level on designers. In the preparation of manufactured products has given attention to the succession of complex ergonomic requests.
Design, ergonomics, proportion, function, science, cognition
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/16010232
IDR: 16010232 | DOI: 10.56334/sei/5.4.21
Текст научной статьи Ergonomics as the scientific bases of design
Every creative work first of all, is formalizing in thought and then practically realizing as its products. In this case, the cost of result on creative work is characterized with the level of thought. The creative work and activity are based on different type of thought depending on its own characters. Some forms and types of thought and its maintenance are broadly explained in different scientific literatures (Bayramov A and Alizadeh A 2006; Maharramov M 1999; Maklakov А 2002). The types of thought as the process of mind assume special importance in any of creative work. Depending on maintenance and area of creative work in many times are mutual, connectional and integrative form. In this case, there is no doubt, the creative work, including, artistic-aesthetic creative work belong to the most difficult intellectual and reasonable processes.
The American psychologist Rudolf Arnstein in works “Art and visual perception” (1954), “Visual thinking” (1969) put forward his own visual thought conception (Salamzadeh A 2006, 80).
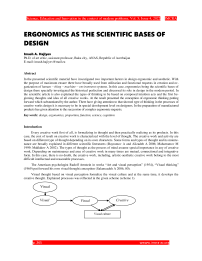
Visual thought based on visual perception formalize the visual culture and at the same time, it develops the creative thought. Explained processes was reflected in the given scheme (scheme 1).
Scheme 1. Formalization processes of visual culture.
Theme
Thought conception we put forward (if it’s possible to say like this) with its many considerable characters assume importance and as a private type could be added to general classification. Before talking about, we think visual thought and staying on tasks about visual culture problems it is necessary to analyze them through subjective view prism. Because, instead of broadening the differences of themes on modern investigation areas in the science of art critic the theoretical and philosophic-aesthetic problems of fine arts in this scientific area will be always in the centre of attraction and will be always urgent.
As we noted above, the type of thought directly realizes the intellect and practical human activity on different areas. Beside type of arranging dominant urgency of thought depending on activity, including, direction and areas of creative activity there is no doubt that sometimes many other types act in integrative form. Of course, for gaining rich creative work it is necessary to have broader thought. Beside with formalization during the processes of richness of thought, the creative work having continuously dexterity and intellectual activity also conditions with the past knowledge and practical experience and all of these the human could be gained with personnel development of many years.
The signs of visual thought based on specific objective laws differing from the samples in the system of communicative and constructive visual information for social activity shows itself more in the samples’ system of artistic skills and in this case, visual comprehensibility of objects quickly realize in analyses and synthesis operations.
There should be noted that visual perception formalizing visual thought characterizes with activity of subject observations on objects. Not depending on its social creation, the subject being in contact with artistic skills’ samples should make effort for learning not only the artistic view of the work also the artistic expression of philosophic meaning and essences. Because, each art work beside with the artistic and aesthetic quality also is the conveyer of philosophic essences in some levels of idea and maintenance. Naturally, the richness of the world outlook assumes special importance in these perception processes.
Considering the global creative work the design – creative processes realizing on its separate areas naturally in integrative form bases on various types of thinking. In this case, in design and creative activity beside with artistic thought it is very important to develop other types of thinking – technical, logical, visual and etc (Hajiyev I, 2006, 145-148).
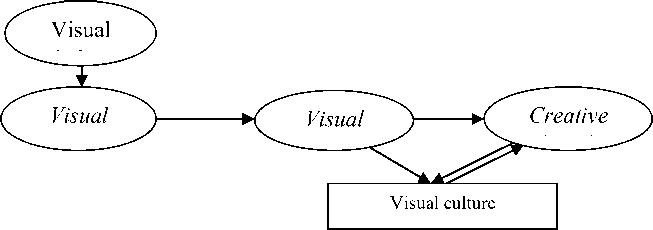
As it noted, design almost have become to global creative areas and at present, its different types separately solution human problems coming from general legislative development of society and civilization. If we take into account the differences of design areas on classification then the complexity of this creative work will approve itself again. In that case, maintenance and essences of creative work of design, basically is on two parallel lines or factors and develop by realizing on the same direction. Formerly, in similar schemes we gave in different scientific works were shown that the formalization and function in design condition with two factors. But in the present scheme we tried to represent the general essence of design maintenance in laconic form (scheme 2).
As we noted above, two important factors are the main leading – mother line of this activities in design. The first of them is ergonomics that determines and solves the most optimal ways of utilitarian – functional requests in objects and things. In the showed source the point of functionalism was explained as below: “Functionalism – being the general tradition of the world design, occurred as the minimum in décor of outward forms but contrary, as more suitableness in things’ peculiarities, maximum degree of taking into account of human factors, ergonomics and utilization during 1950-1970 years” (Lavrentev А 2006, 296).
Scheme 2. The content and laconically expression of design activities.
Beside with this, if do not consider the exceptions, the aesthetic solution of form agreeing with ergonomics in function cannot be in the exterior of utilitarian and functional requests. Thus, as we noted, as an important condition in design two parallel factors arrange the fundament, the main general leading line of this creative work. Consideration of the second factor in design -projecting comes to superiority of artistry, technical drafts, sketches and richness of artistic elements. As we see from the analyses, on design activity idea and content as the production of thought first of all, visually reflects on drafts and projecting. From this point of view the designer being busy with practical activity have to know draft and including, the artistic projecting very well.
The second condition in design activity – for consideration of aesthetic factor the designer univocally has to be broad-minded person and artistic thoughts and artistic knowledge. Beside them, this creative work is also the technical and aesthetic activity, so at the same time it is very important that the designer must have broad technical thought. This type in the classification on the types of thoughts explains with its difference of creation of opportunities on getting high results during the solution of problems and technical operations. This thought develops by engineers, builders, in a word, with the specialists that are busy with these activities. Connecting with the development of technical civilization, at present time, in private life, work, in generally, in material environment, during the successful utilization of installation and equipment on appointment in the processes of dynamic social activities, including for applying of technical means in training, also formalization of technical thought for realization of social and technical requirements that put forward in management in the modern period all of them are very important not only for designers, also for each specialists and human.
From this point of view as we noted above rich technical thought assumes particular importance for designers. However, we approach to the problem in general context and deeper is it enough for design being syncretic creative activity area? Of course, not! The problem is that there is necessary to have another type of thought (even in the level of high development) for designers. This thought is not at present classification in the scientific literature but we can give the name of “ergonomic thought” to that as in the direction of solution of ergonomic problems’ and acting in design creative work. We have come to this conclusion through visual observations and practical experiences of some ten years. (To say the truth, in my childhood I intuitively felt this problem on my souvenirs’ and things that I made with handicraft method and with great interest and effort – I.H. )
The famous psychologist and physiologist V.M.Bekhterev in 1921, at the initiative conference of the I Union Russian on scientific formation of labour and production, at his speech about main problems of physiology, psychology and hygiene, connected with multifold, compound of human labour activity showed that we cannot look to the regulation of work processes separately inside of scientific frame. V.N.Myasishev, the student of Bekhterev, in his time being famous as the leading psychologist in Russia showed that the scientific formation of labour activity can be based on only the synthesis of progresses of various sciences on learning of human. At the same conference, he also put forward a conception about the special scientific area – ergology and then V.M.Bekhterev supported it too (Butusov V 1967, 94).
In 1959, was published the first scientific work dedicated to the problems of connections between human and scientific calculating machines (SCM); in 1969, was carried out the first scientific conference dedicated to the problems of “human and machine”. In 1970, was created the ergonomic search centre in England and USA. All the lectures and international conferences carried out at the sphere of ergonomics proved that this sphere has more broad directed scope. Ergonomist B.Shekkel divided the historical development way of ergonomics to the followed stages in the XX centuries:
In 1950th years – military ergonomics;
In 1960th years – industrial ergonomics;
In 1970th years- manufactured products and service ergonomics;
1980th years – computer ergonomics;
1990th years – informational (the new informational technologies), free time and cosmos ergonomics (Runge V and Manoshevich Yu 2008, 23).
In modern period, in the one of the last literatures have given broader explanation about the scientific bases of design, the feature as the base, purpose, duties and requirements of ergonomics (Runge V 2006, 26-46). The ergonomics based on synthesis of different sciences, at the creative processes on design becoming to the main composition part of creative thought and create necessary dominant other type of thought that all of these as we noted above could be characterized as the ergonomic thought. As we noted at the beginning, everything first of all happens in the consciousness and thinking and after these practically realizes. This thought being different from the technical thought is based on special mental agility, inborn mentality perfection, talent, mental sense, observation and analyses of mechanical processes, intuitive understanding and broadly discussion. In fact, the same thought manage all activity areas in this or that level. Ergonomic thought in the creative processes directs to the ergonomic solution of object. In this processes happens quick intellectual and cognitive operations, searching the most optimal ergonomic solution ways of problem and organizes the most ergonomics. The observations show that in indemnification of ergonomic requirement on things, manufactured products, objects, different transport facilities and etc. installations and equipment are relativity in many times. Thus, in the most perfection things we can meet even partly the ergonomic problems. For example, at the present, the “Gillette” (made in Russia) being known as the most quality shaving machine at the republic differs for its simplicity, neatness, form, materials’ quality and it sells more expensive than other prototypes of foreign countries and we also use from that machine. (For learning material ingredients, durability, sustainability to corrosion we visually carried out experiment on it – I.H. ). The problem is that on the same machine that sells on the world markets has less two ergonomic problems and one of them reconstructed and solved (of course, for ourselves) with the handicraft method by us but there is still another problem. Because, only with technological processes could be solved that problem. As an offer was dedicated to send the project on solution that problem to the producing establishment. However, it is necessary to say that both the soviet and post-soviet period the products made in Russia was always differed for its simplicity and ergonomics.
In generally, in the soviet period, in the allied countries was seriously take into account of simplicity and ergonomics of various type of consumer goods and it is natural, here the experience of Russia showed itself. At the modern period various form of consumer goods belonging to the production of different countries has put to forward plan. Apparently, it connected with the demand of the method of “stylize” becoming to the broadly spreading experience of modern period.
In one of illustrative literatures on design has given some samples from different things about the creative work of classic European designers. For example, Peter Berens (1869-1940) - one of the founders of design activity in Ger- many made a tea-kettle (1908), which was in very beautiful design and was more ergonomic (Clark P and Friman Dj 2003, 56).
Thus, for solution ergonomic problems (for the most optimal ergonomic solution of this problem) there is necessary to have broad ergonomic thought and it must become the main intellectual and cognitive activity factors for designer. Even in the history of scientific and technical development of the earth there also were many persons that had such thoughts. One of them was great Leonardo da Vinci famous member of the Renaissance. Yes, exactly he had extraordinary scientific and ergonomic thought. On his fascinating invents belonging to his technical activity it is not difficult to see his thoughts’ light, production and results (Khudojestvennaya gallereya. Da Vinchiyu 2004; Uolleys R 1997).
The term of “Ergonomics” (in Greek ergon- work + namos - law) was adopted in England in 1949 and at the same period a group of English scientists created ergonomic research society. The members of that society discovered the solution problems of rational arrangement of labour (Kvasov А. 1989, 131).
If we considered not only the work, as we analysed above, also multisided activity areas, then there is no doubt that this term conveys special broad importance and could be used for multisided work directions.
It is necessary to note that in Eastern thought and comparatively the superiority of the type of this thought feels in mental outlook. Beside this, both on designers and on other specialists, including on simple persons it is necessary permanently develop this type of thought. And these could be based on the results of both intellectual and practical activity.
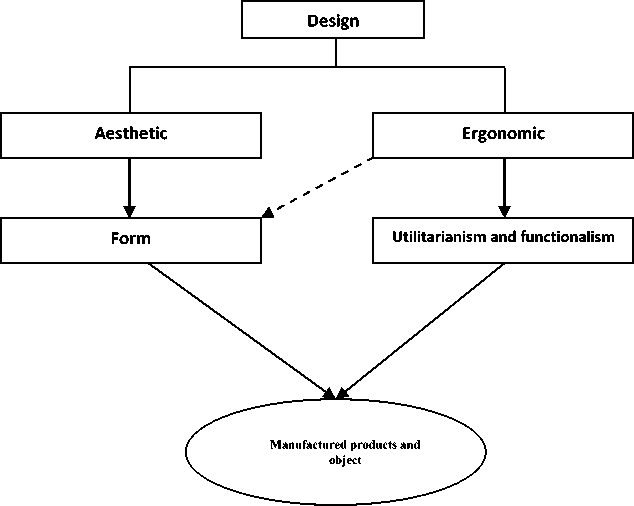
The most perfect forms’ structure was created by the nature. The form in a beautiful woman’s figure view point of functionality has an ergonomic indicators and how much to show those “indicators” essentially, (of course, till the general harmonic degree) then there will increase the maintenance of form beauty too. Ordinary the ergonomic solution of sustainability of grass, ears or branch of growing along the vertically lines is regulated by the nature (Kvorachkin T.N. 2019).
From famous architectures I.Joltoviskiy, D.Hembidge, E.Messel looked to the golden area as legislative of organic growth that proved itself in the size of forms in different parts of spirited nature (Kvasov А 1989, 70) (figure 1, a ).
Geometrical regularities being in the form structures of creatures in animated nature in our periods was extensively analysed by C.Elam the designer and trainer at the Institute of Art and Design of Florida (USA). He wrote a book about investigation of the same problem and met with very big interest in all over the world (Elam C 2013).
For example, in binding the book the comparison of width and length is near to 0.618 figures. On Parthenon monument, the fascinating sample of ancient Greek architecture that was built in the B.C. V also has the same proportionality (Vilenkin N, Jokhov V, Chesnekov A and Shvarchbud S 2000, 140-141). We can say for the forms to be based on nature samples, in fact, this ratio is the most ergonomic measure neutralizing any of extraneous pressure, organizing the sustainability and durability along the vertical lines. In the preparation of things is used from this ratio’s principles (figure 1, b ).
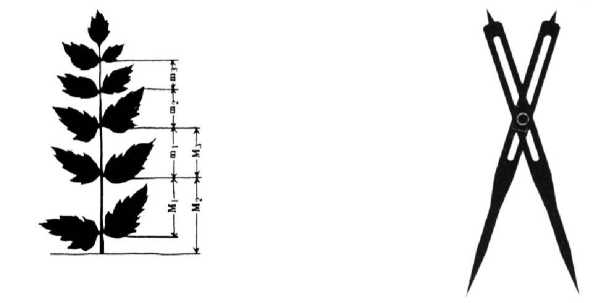
a) b)
The golden ration in nature. A pair of compasses fastened on the base of golden ratio.
Figure 1 a, b.
The most famous man figure that imagined by “magical” Leonardo da Vinci in the system of proportionality could be considered ideal, but ergonomic viewpoint of anatomic-physiology structure and proportionality of form’s system and for functionality. One of the most interesting side is that when we analyze the imagination there discovers the principles of golden ratios on various parts of figure. On the investigated figure we have determined exactly three of them, but approximately four of them. Formerly, on our published scientific work (Hajiyev I 2008, 219-227)we have showed them (parts) separately with conventionally equality signs (=; ≈) (figure 2, 219-227). In the figure to be based on proportionality and symmetric legislatives, the “ideal” figure organize the aesthetic appearance of form, including, the ergonomics and equilibrium for dynamic function.
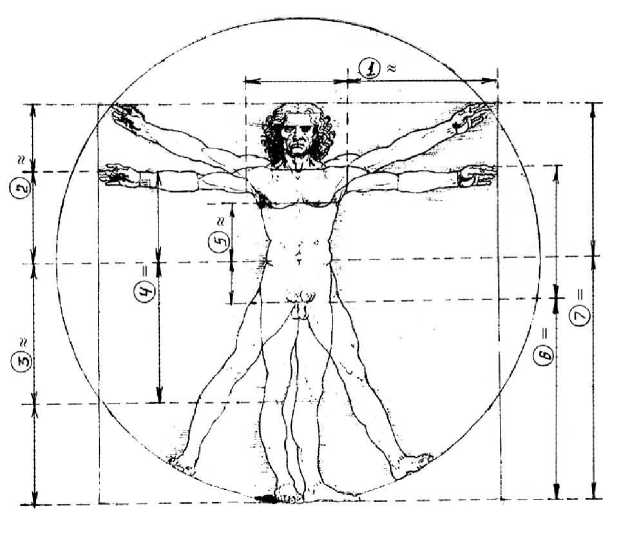
Figure 2. The golden ratio in man figure imagined in the system of proportionality by Leonardo da Vinci.
In woman’s anatomy it is familiar to specialists that ergonomic solution of functional essences is not only in salient visual form, being different from the man’s skeleton, it is in the center, in the bottom pelvis of front region in skeleton.
It means, to be available in all creations and creatures that is in dynamic development and for functionality view point of acting there discovers ergonomic indicators in a definite level. The human being the highest creature of creation in a relative form have such indicators (for age, sex and for anthropological characters).
In this meaning, it approaches to organization of human-thing-machine-environment systems with its ratios’ criteri-ons in all situations and as the first duty there put forward of ergonomics of these systems (Fazil, S. A., & Hasan, A. F. 2022).
If things, object or environment is not ergonomic it will soon make tired influencing to humans’ physiology and psychology and even it will perilous for health. As it noted, ergonomic thing, in fact, personify beauties and aesthetic indicators on it, create harmony in the system of human-thing-machine-environment and attains practical and aesthetical maintenance. It means, it is not primitive and arbitrary view, it embraces the ergoaesthetic essences of maintenance and forms of goals.
In the represented scheme showed the appearance of ergonomic problem and depending on its specific peculiarities, comprehensibility on the base of different types of thought and formalization and development of ergonomic thought in this context (scheme 3).
As we noted, at present time, there is possible to see enough things, installations, equipment and various transport means that partial have solved their ergonomic problems. Sometimes, in processes of projecting of object or manufactured products there could be created other “artificial” ergonomic problems during whole solution of one problem or with the purpose of gaining the highest aesthetic essences of form.
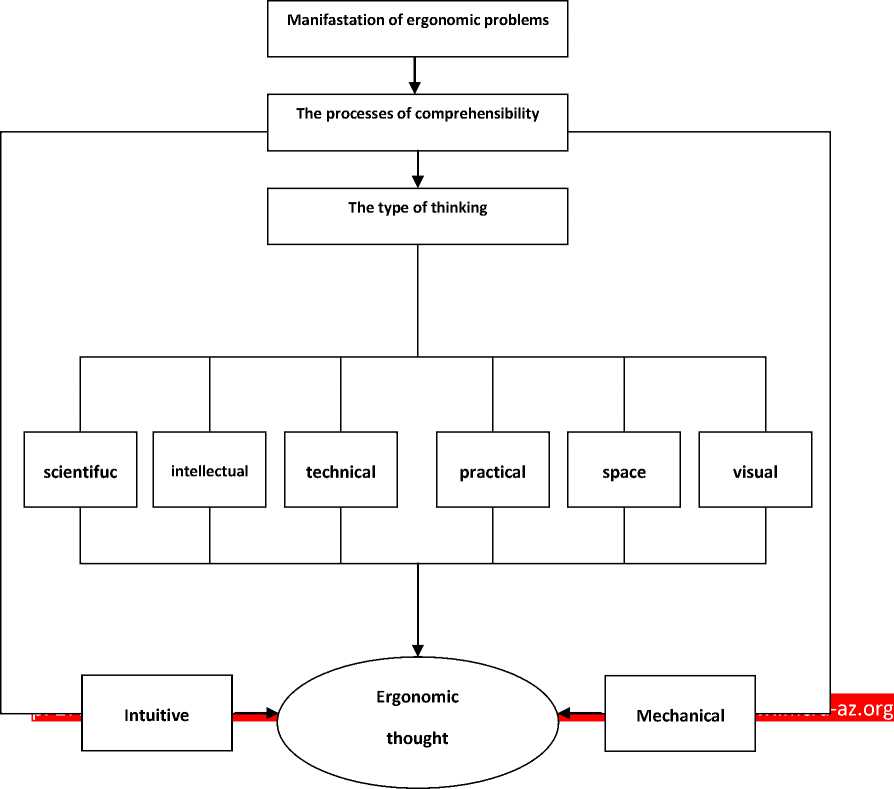
Scheme 3. Formalizing processes of ergonomic thought.
Conclusion
On the base of multifold of ergonomic requests of prepared manufactured products, equipment and installations for human-thing-machine-environment systems taking them into maximum account, view point of utilitarianfunctionality of manufactured products ensure the solution of ergonomic problem more effective and in a high level. In the preparation of manufactured products there is very important to take into account of complex ergonomic request with following succession:
-
- ergonomics of reconstruction-structure5;
-
- ergonomics of separately pieces according to each other and general structure;
-
- ergonomics of materials’ (for utilization and durability);
-
- ergonomics of texture;
-
- ergonomics of colours on appointment;
-
- static and dynamic ergonomics of form;
-
- arrangement of forms and decors with ergonomics;
-
- ergonomics for utilitarian and functionality on appointment;
-
- ergonomics of packing;
-
- ergonomics of composition consisting of shrift – word, including information in the preparation of packing;
In the preparation of manufactured products the consideration and solution of complex ergonomic requests, at the same time, utilization in human-thing-machine-environment systems would be ensured the following existing ergonomic requests for connection:
-
- anthropometric;
-
- psychophysiology;
-
- psychology;
-
- physiology;
-
- hygienic;
-
- social-psychology;
-
- economic
The designer should have broadly ergonomic thought for finding the most optimal and ergonomic solution ways and for complex approaches of all explained problems. They permanently have to enrich, develop their thought in this direction, have to come from visual observations to practical creative work, apply skilfully their gained knowledge in experience in the level of professional specialists.