Evaluation of agonistic tennis in Greece: tennis players' beliefs and position
Автор: Koronas V.
Журнал: Человек. Спорт. Медицина @hsm-susu
Рубрика: Спортивная тренировка
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.20, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Aim. Tennis popularity in Greece has been gaining ground in the last decade. The study examines the views of Greek tennis players about the sport. Materials and methods. The survey was conducted during the Hellenic Juniors' Tennis Tournament that took place in Athens, March 2019. Data were collected from a sample of 45 teenagers, participating at the Tournament. Survey participants completed a self-completion questionnaire. Data were analyzed with SPSS. Questions regarded the demographics and the teenagers' beliefs about the level of tennis in Greece, their preferences regarding tennis coaches, whether there are opportunities for tennis athletes to be promoted in Greece, the preferred characteristics of trainings and their view about organization of tennis in Greece. Results. The level of tennis in Greece is considered moderate to high. The quality of coaching is considered to be medium to high and coaches are expected to display many qualities and give at least once a month their feedback to the athletes. Tennis is an expensive sport that needs to be advertised by the media. The introduction of tennis in schools would augment the popularity of tennis in Greece. Conclusion. In order to have a broader view of tennis in Greece, it is important to take into consideration the beliefs of young tennis players, as well as the beliefs of tennis coaches and tennis agents.
Tennis, greece, beliefs, level, evaluation, tennis players
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147233606
IDR: 147233606 | УДК: 796.342(495) | DOI: 10.14529/hsm200314
Текст научной статьи Evaluation of agonistic tennis in Greece: tennis players' beliefs and position
During the last twenty years, tennis in Greece is gaining more and more popularity and Greece is one of the European countries with the fastest increase of in tennis players. According to the figures published in the 2018 European Tennis Report and the numbers shared by the Hellenic Tennis Federation, in the last ten years, the number of tennis players in Greece has increased by 20%. In the last decade, the number of licensed players and coaches has doubled. As far as participation in international events is concerned, Greece presence has raised by 50%, especially in the professional category [23].
Participation in the wheeled-tennis category has been rising during the last years in Europe. However, the wheeled-tennis category is still quite unknown in Greece. Technological innovations have been applied in the construction of the gear of the wheelchair sports and this has increased the popularity of these sports [7]. Even though the demand of tennis has increased in the last years, Greece did not spend funds for the construction of extra tennis facilities [23].
Tennis coaching is a permanently actual field of study and several methods have been created to assist coaches in assessing tennis players and preventing strenuous training that could damage their physical condition [10, 24]. Coaches cannot communicate with the player during the game, and this raises the difficulty for both the player and the coach [18]. Coaches must prepare the player physically and mentally for the game, consider what motivates each player and organize the preparation according to the needs of the individual. For this reason, tennis players and coaches build a different “bond” in time [1, 5].
As a matter of fact tennis attracts wealthier people due to its cost, since equipment and coaching costs are rather high and can be afforded only by those who have higher incomes [23].
According to literature, tennis is a sport that offers a wide range of benefits for both adults and children [9]. Tennis reduces the risk of metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, high blood lipids, cardiovascular diseases, sudden death and death after a cardiovascular event [15]. Playing tennis is not only advantageous for maintaining a good physical condition, but it can also improve the individual on the psychosocial level [16, 19]. Children who play tennis have better school results, are better able to cope with anxiety, are less likely to develop disruptive activity at school and in the future, and are less vulnerable to substance abuse [18, 27].
Tennis is not just an individual sport; it can be played as a group activity. Tennis clubs and tennis federations have improved tennis programs and school projects with the goal of fostering the “team player” mentality of tennis and have an important role to play in raising the popularity of tennis in the media and hosting more tennis events [20, 23].
Evaluation is an important step in the development process in order to monitor progress and assess the impact of change [25, 26]. Since Greece is one of the five countries with the fastestgrowing popularity of tennis, evaluation is im- perative. The aim of this study is to assess the beliefs and position of young tennis players on the quality of Greek agonistic tennis, the opportunities for promoting tennis.
Materials and Methods
Sample
The study was conducted in March 2019, during the Hellenic Juniors' Tennis Tournament in Athens. 45 teenager tennis players (28 males and 17 females) participated in the survey.
Table 1 Questionnaire
|
QUESTIONS |
||||||
|
• |
Age |
|||||
|
Male |
Female |
|||||
|
• |
Gender of participants |
|||||
|
Coach |
Athlete |
Factors |
Parents |
|||
|
• |
Capacity |
|||||
|
Very high |
High |
Average |
Low |
Very low |
||
|
1 |
Professional players level evaluation |
|||||
|
2 |
Evaluation of sports facilities |
|||||
|
3 |
Coach knowledge evaluation |
|||||
|
4 |
Estimation of the economic cost of tennis training |
|||||
|
5 |
Evaluation of media promotion of tennis |
|||||
|
6 |
Evaluation the ranking in relation to other sports |
|||||
|
7 |
Improvement of tennis by introducing in school’s curriculum |
|||||
|
8 |
Evaluation of athlete promotion opportunities |
|||||
|
9 |
Rating of federated tournaments |
|||||
|
10 |
Teaching theoretical knowledge |
|||||
|
11 |
The media promotion potential |
|||||
|
Teacher |
Player |
Certificate |
Experienced |
All the above |
||
|
12 |
Preferred coach's traits |
|||||
|
Per day |
Per week |
Per month |
Every 6 month |
Never |
||
|
13 |
Trainees' evaluation frequency preference |
|||||
|
One |
Two |
Three to five |
Seven ` |
More than seven |
||
|
14 |
Training hours per week |
|||||
|
Federation |
Coaches |
Facilities |
||||
|
15 |
Requirement for improvement |
|||||
|
Championship |
Sport |
Entertainment |
Body health |
|||
|
16 |
Purpopse of teaching |
|||||
|
One |
Two |
Three |
Four |
Five to eight |
||
|
17 |
Ideal number of participants |
|||||
|
Psychology |
Diet |
Pedagogical |
Management |
All the above |
||
|
18 |
Coaches' educational background |
Method
A random sample of teenager tennis players, participating at the Hellenic Juniors' Tennis Tournament, was selected and a 21 self-completion close-ended items questionnaire was completed by the survey participants. The questionnaire consisted of questions on the demographic data, such as gender, age and qualification, while 18 items of the questionnaire examined their beliefs about the quality of tennis facilities, the quality of coaching and the preferred coaches' characteristics, the comparison of tennis to other sports, the frequency of tennis tournaments in Greece organized by the Hellenic Federation, the components of the ideal tennis training (number of participants, frequency, evaluation frequency), the cost of tennis, the level of promotion of tennis in Greece and the opportunity for athletes' promotion. The validity of the questionnaire was evaluated by a panel of experts who examined all the items of the tool [2]. The answer variants to the questionnaire items were of the closed answer type, Likert scale, in 5 steps (Table 1).
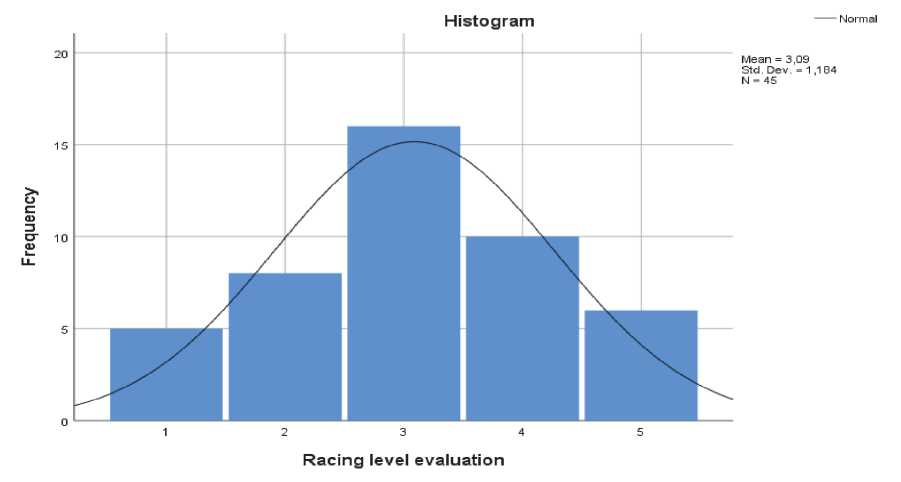
Fig. 1. Professional players' level evaluation
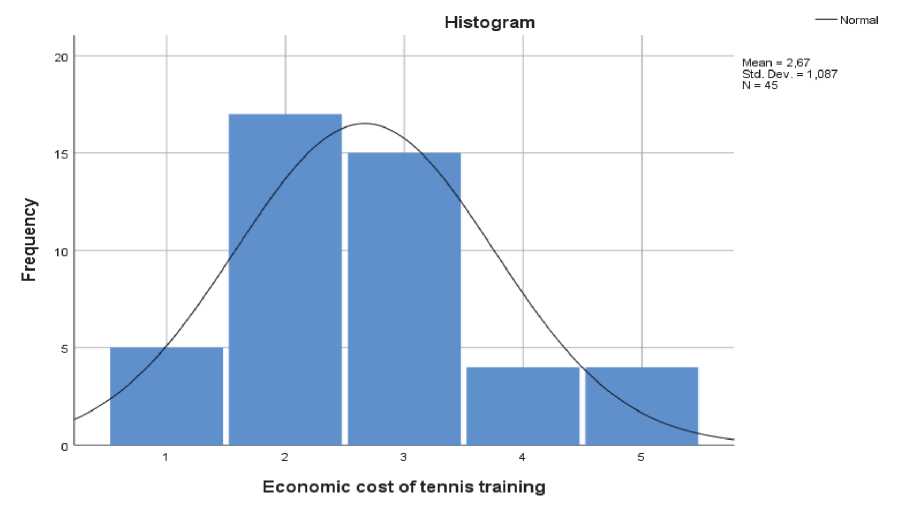
Fig. 2. Economic cost of tennis training
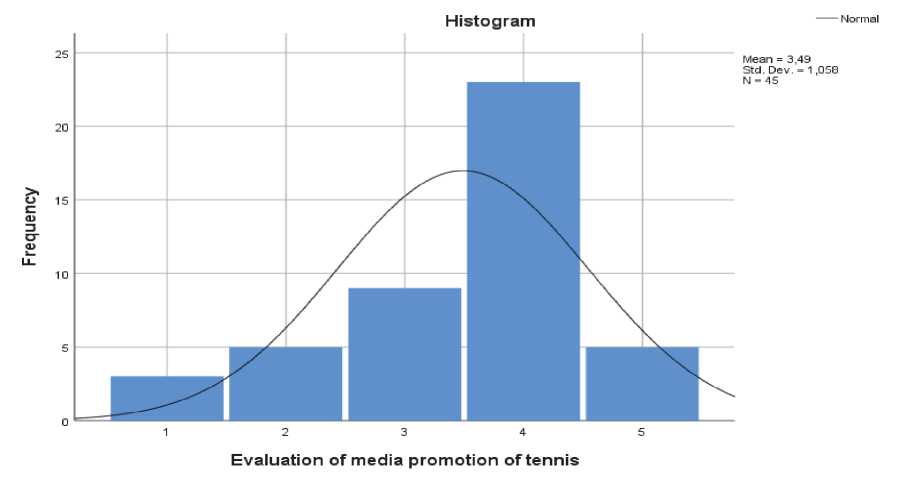
Fig. 3. Evaluation of media promotion of tennis
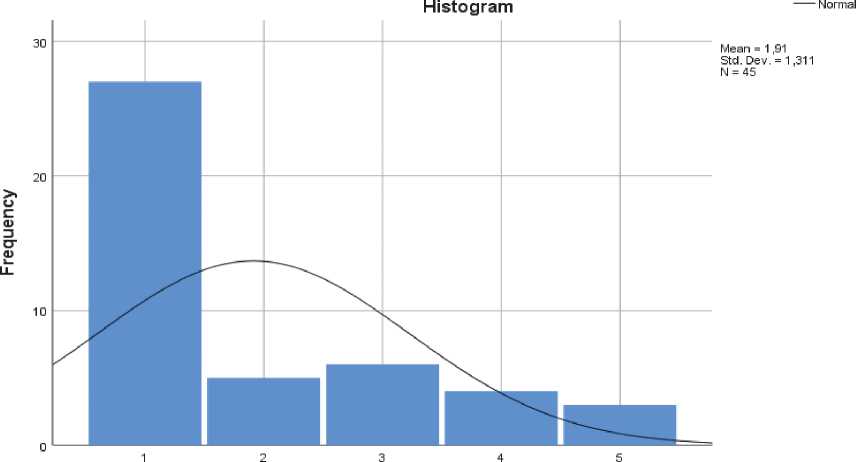
Introducing tennis in schools curriculum
Fig. 4. Introducing tennis in schools' curriculum
Statistical Analysis
For statistical analysis, computer software (Statistical Package for Social Sciences, Version 25.0 for Windows, IBM: 734f175c920b6217d39, Corp. 2019, Aristotelian University of Thessaloniki, Department of Physical Education and Sports) was used. After checking out the variables for normal distribution profile (by using the Shapiro–Wilk test) (Figs. 1–4), cross tabulation of data analysis was performed according to the Pearson Chi-Square test [8, 13]. Significance was accepted at p < 0.05.
Results. Although two third of the participants believed that agonistic tennis in Greece is average of below average level, the very same sample considered sport facilities and coaches’ knowledge above average level. The answers given to those three questions prompted us to examine the probable statistical relation between those apparently unmatched results. Thus, actual research explored relation between the variable of “Professional players level evaluation” and three other variables:
-
a) The economic cost of training tennis in Greece,
-
b) The promotion of this sport by Greek media,
-
c) Introducing tennis at the standard school curriculum.
Records of the frequency of responders to the couple of questions “Professional players’ level evaluation” and “Economic cost of tennis training in Greece” and their relationship is shown in the following cross-tabulation Table 2.
Statistical evaluation of the cross-tabulation Table 2 data by the Chi-square test revealed that there was no significant relation between those two parameters (p > 0.05), namely the variables are independent.
Records of the frequency of responders to the couple of questions “Professional players’ level evaluation” and “Evaluation of media promotion of tennis” and their relationship is shown in the following cross-tabulation Table 3.
Statistical evaluation of the cross-tabulation Table 3 data by the Chi-square test revealed that there was no significant relation between those two parameters (p > 0.05), namely the variables are independent.
Records of the frequency of responders to the couple of questions “Professional players’ level evaluation” and “Introducing tennis in schools curriculum” and their relationship is shown in the following cross-tabulation Table 4.
Statistical evaluation of the cross-tabulation Table 4 data by the Chi-square test revealed that there was no significant relation between those two parameters (p > 0.05), namely the variables are independent.
Although none of the three parameters exhibited statistically significant correlation with the lack of agonistic tennis in Greece, the economic cost of tennis training seemed to be closer than the other two parameters to it (Tables 2–4). Those conclusions may drive a new research in the future.
Results were analyzed in categories regarding the athletes' beliefs about the quality of tennis in Greece, the potential of promotion of tennis and athletes in Greece, the quality of organization of tennis in Greece, the quality of tennis trainers in Greece and the ideal characteristics of trainings.
According to the young tennis players, the quality of agonistic and professional tennis in
Table 2
Professional players level evaluation and Economic cost of tennis training:
Cross tabulation of data analysis according to the Pearson’s Chi-Square Test (n = 45)
|
Economic cost of tennis training in Greece |
Total |
|||||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
||||
|
Professional players level evaluation |
1 |
Count |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
|
Expected Count |
0.6 |
1.9 |
1.7 |
0.4 |
0.4 |
5.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
0.0 |
20.0 |
80.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
100.0 |
||
|
2 |
Count |
0 |
5 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
8 |
|
|
Expected Count |
0.9 |
3.0 |
2.7 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
8.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
0.0 |
62.5 |
12.5 |
12.5 |
12.5 |
100.0 |
||
|
3 |
Count |
3 |
3 |
7 |
2 |
1 |
16 |
|
|
Expected Count |
1.8 |
6.0 |
5.3 |
1.4 |
1.4 |
16.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
18.8 |
18.8 |
43.8 |
12.5 |
6.3 |
100.0 |
||
|
4 |
Count |
1 |
6 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
10 |
|
|
Expected Count |
1.1 |
3.8 |
3.3 |
0.9 |
0.9 |
10.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
10.0 |
60.0 |
20.0 |
0.0 |
10.0 |
100.0 |
||
|
5 |
Count |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
6 |
|
|
Expected Count |
0.7 |
2.3 |
2.0 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
6.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
16.7 |
33.3 |
16.7 |
16.7 |
16.7 |
100.0 |
||
|
Total |
Count |
5 |
17 |
15 |
4 |
4 |
45 |
|
|
Expected Count |
5.0 |
17.0 |
15.0 |
4.0 |
4.0 |
45.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
11.1 |
37.8 |
33.3 |
8.9 |
8.9 |
100.0 |
||
Table 3
Professional players level evaluation and Evaluation of media promotion of tennis, Cross tabulation of data analysis according to the Pearson’s Chi-Square Test (n = 45)
|
Evaluation of media promotion of tennis |
Total |
|||||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
||||
|
Professional players level evaluation |
1 |
Count |
0 |
0 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
5 |
|
Expected Count |
0.3 |
0.6 |
1.0 |
2.6 |
0.6 |
5.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
0.0 |
0.0 |
40.0 |
60.0 |
0.0 |
100.0 |
||
|
2 |
Count |
0 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
8 |
|
|
Expected Count |
0.5 |
0.9 |
1.6 |
4.1 |
0.9 |
8.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
0.0 |
25.0 |
25.0 |
37.5 |
12.5 |
100.0 |
||
|
3 |
Count |
2 |
1 |
1 |
10 |
2 |
16 |
|
|
Expected Count |
1.1 |
1.8 |
3.2 |
8.2 |
1.8 |
16.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
12.5 |
6.3 |
6.3 |
62.5 |
12.5 |
100.0 |
||
|
4 |
Count |
0 |
1 |
4 |
4 |
1 |
10 |
|
|
Expected Count |
0.7 |
1.1 |
2.0 |
5.1 |
1.1 |
10.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
0.0 |
10.0 |
40.0 |
40.0 |
10.0 |
100.0 |
||
|
5 |
Count |
1 |
1 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
6 |
|
|
Expected Count |
0.4 |
0.7 |
1.2 |
3.1 |
0.7 |
6.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
16.7 |
16.7 |
0.0 |
50.0 |
16.7 |
100.0 |
||
|
Total |
Count |
3 |
5 |
9 |
23 |
5 |
45 |
|
|
Expected Count |
3.0 |
5.0 |
9.0 |
23.0 |
5.0 |
45.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
6.7 |
11.1 |
20.0 |
51.1 |
11.1 |
100.0 |
||
Table 4
Professional players level evaluation and Introducing tennis in schools curriculum, Cross tabulation of data analysis according to the Pearson’s Chi-Square Test (n = 45)
|
Introducing tennis in schools curriculum |
Total |
|||||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
||||
|
Professional players level evaluation |
1 |
Count |
3 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
5 |
|
Expected Count |
3.0 |
0.6 |
0.7 |
0.4 |
0.3 |
5.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
60.0 |
20.0 |
0.0 |
20.0 |
0.0 |
100.0 |
||
|
2 |
Count |
4 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
8 |
|
|
Expected Count |
4.8 |
0.9 |
1.1 |
0.7 |
0.5 |
8.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
50.0 |
12.5 |
25.0 |
0.0 |
12.5 |
100.0 |
||
|
3 |
Count |
9 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
16 |
|
|
Expected Count |
9.6 |
1.8 |
2.1 |
1.4 |
1.1 |
16.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
56.3 |
18.8 |
12.5 |
6.3 |
6.3 |
100.0 |
||
|
4 |
Count |
7 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
10 |
|
|
Expected Count |
6.0 |
1.1 |
1.3 |
0.9 |
0.7 |
10.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
70.0 |
0.0 |
20.0 |
10.0 |
0.0 |
100.0 |
||
|
5 |
Count |
4 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
6 |
|
|
Expected Count |
3.6 |
0.7 |
0.8 |
0.5 |
0.4 |
6.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
66.7 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
16.7 |
16.7 |
100.0 |
||
|
Total |
Count |
27 |
5 |
6 |
4 |
3 |
45 |
|
|
Expected Count |
27.0 |
5.0 |
6.0 |
4.0 |
3.0 |
45.0 |
||
|
% within Professional players level evaluation |
60.0 |
11.1 |
13.3 |
8.9 |
6.7 |
100.0 |
||
Greece is in the average (Fig. 1) and as far as popularity is concerned, tennis is believed to be rather popular in Greece, compared to other sports. The survey participants suggest that tennis is an expensive sport (Fig. 2).
Tennis and promotion
The survey participants believe that tennis is not promoted enough by press and electronic media (Fig. 3), while the opportunities for tennis players to be promoted are few. Teenagers tennis players agree that tennis needs to be supported and advertised by the media and the introduction of tennis in schools' curriculum would further increase the visibility of tennis in Greece (Fig. 4) [4].
Even though tennis facilities are evaluated as moderate, survey participants suggest that tennis Federation and coaching are the sectors that need more improvement. As far as the frequency of Tennis Federation tournaments is concerned, participants consider it satisfactory.
Coaching level in Greece is considered high. Coaching is rather demanding and tennis players prefer coaches who are experienced teachers, experienced professional tennis players and are certified teachers. Coaches with educational and psychology knowledge are preferred [22].
Daily trainings are ideal and the preferred number of players per class is two to three, even though some would rather train alone. Tennis players prefer being evaluated at least once a month and some of the participants suggest weekly evaluations. The theory of tennis should be taught during trainings because it is considered very useful and according to the participants, when learning tennis, engaging in sport is the main target.
Conclusions
Tennis and coaching
Tennis coaches have a cardinal role in the career of tennis players and the teenagers participating in the survey suggest that coaches should display a variety of characteristics. Apart from their educational role, coaches are expected to guide athletes in gaining a right attitude towards sport. Coaches may sometimes underestimate the difficulty of trainings and the trainees' fatigue and increase the organize difficult and exhausting training programs [3, 28]. In order to avoid misjudgments and the exposure of tennis players at risks, new tools have been developed that aid coaches in quantifying the efficiency of trainings and the needs of athletes [21]. Finally, literature suggests that coaches have a central role in keeping young tennis players committed to the sport by structuring customized trainings and by reminding athletes that tennis is not a job, but a hobby as well [6, 14].
Introduction of tennis in schools
Tennis players agree that children should be taught tennis at school. The sport would definitely benefit from this visibility and more children would be attracted to tennis. According to a study conducted in the Netherlands, it has been suggested that changes in the teenagers' environment (e.g. educational) have a negative impact on their commitment to the sport. Thus, the introduction of tennis at schools can keep young tennis players focused on the sport [6].
Tennis training
Even if tennis players may have a competitive nature, they agree that one of the most important aims during trainings is that of learning how to stay committed to sport and being disciplined. In this regard, coaches have a major role in teaching tennis players the not only tennis technique and theory, but also supporting them psychologically and giving them nutritional advice. Literature suggests that coaches are an important part of every athlete's life and can teach them how to keep concentrated and focused [5]. In this survey, tennis players agree that coaches should be certified trainers and would rather receive frequent feedback from their coach (at least once a month). This finding is supported by other studies as well. Frequent evaluations help tennis players remain concentrated on the target and improve their performance [17].
Tennis and organization
According to this survey, tennis federation and coaching are the sectors that need more improvement. National tennis federations have a significant role in advertising the sport and in promoting tennis players in the country. Survey participants agree that the Federation should host more tennis events. Finally, tennis federations can also run public health campaigns in order to promote health through sport [11, 12].
Limitations and subjects for further study
The restricted number of survey participants is a limitation to the study since there are not enough available data to in order to draw significant conclusions about the level of tennis in Greece. Moreover, there could be selection bias when conducting the survey in a tournament context. As far as a method is concerned, a qualitative survey with semi-structured interviews could help make better correlations between the characteristics of the survey participants (sex, age, origin, socioeconomic background) and their opinion.
Finally, more descriptive parameters should have been used in order to evaluate the participants' view about the level of tennis in Greece.
As far as future studies are concerned, it would be interesting to extend the study to adult tennis players in Greece and compare the results of the survey. Another important field of study is that of wheelchair-accessibility of tennis facilities, since the interest in Paralympics tennis is increasing in Europe [23].
The survey gives some interesting suggestions about the trend of tennis in Greece. There are no significant discrepancies between the views of tennis agents, which were analyzed in a previous publication by the same researcher, and that of teenager tennis players regarding tennis in Greece. In both studies, participants suggest that tennis should be promoted in schools and by the media in order to increase the popularity and quality of the sport.
Список литературы Evaluation of agonistic tennis in Greece: tennis players' beliefs and position
- Alexe D.I., Alexe C.I., Tohanean D.I., Tudose A.V. Mijloace utilizate in pregatirea, monitorizarea, profilaxia, refacerea si cercetarea din domeniul sportului [Means Used in Training, Monitoring, Prophylaxis, Recovery and Research in the Field of Sports]. Cluj-Napoca, Risoprint Publ., 2020. 178 p.
- Bolarinwa O. Principles and Methods of Validity and Reliability Testing of Questionnaires Used in Social and Health Science Researches. Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal, 2015, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 195-201. DOI: 10.4103/1117-1936.173959
- Brink M.S., Frencken W.P., Jordet G., Lemmink K.M. Coaches' and Players' Perceptions of Training Dose: Not a Perfect Match. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2014, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 497-502. DOI: 10.1123/ijspp.2013-0009
- Brouwers, J., Sotiriadou P., De Boss-cher V. Sport-Specific Policies and Factors that Influence International Success: The Case of Tennis. Sport Management Review, 2015, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 343-358. DOI: 10.1016/j.smr.2014.10.003
- Crespo M., Reid M.M. Motivation in Tennis. British journal of sports medicine, 2007, vol. 41, no. 11, pp. 769-772. DOI: 10.1136/bjsm. 2007.036285
- Deelen I., Ettema D., Kamphuis C. Time-Use and Environmental Determinants of Dropout from Organized Youth Football and Tennis. BMC public health, 2018, vol. 18, no. 1, 1022 p. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-018-5919-2
- Goosey-Tolfrey V. Supporting the Para-lympic Athlete: Focus on Wheeled Sports. Disability and Rehabilitation, 2010, vol. 32, no. 26, pp. 2237-2243. DOI: 10.3109/09638288.2010. 491577
- Greenwood P.E., Nikulin M.S. A Guide to Chi-Squared Testing. New York, Wiley, 1996. 304 p.
- Groppel J., DiNubile N. Tennis: for the Health of it! The Physician and Sports Medicine, 2009, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 40-50. DOI: 10.3810/psm.2009.06.1708
- Krause L., Farrow D., Reid M. et al. Helping Coaches Apply the Principles of Representative Learning Design: Validation of a Tennis Specific Practice Assessment Tool. Journal of Sports Sciences, 2018, vol. 36, no. 11, pp. 1277-1286. DOI: 10.1080/02640414.2017. 1374684
- Mountjoy M., Junge A. The Role of International Sport Federations in the Protection of the Athlete's Health and Promotion of Sport for Health of the General Population. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 2013, vol. 47, pp. 1023-1027. DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2013-092999
- Mountjoy M., Costa A., Budgett R. et al. Health Promotion Through Sport: International Sport Federations' Priorities, Actions and Opportunities. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 2018, vol. 52, pp. 54-60. DOI: 10.1136/ bjsports-2017-097900
- Plackett R.L. Karl Pearson and the Chi-Squared Test. International Statistical Review, 1983, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 59-72. DOI: 10.2307/ 1402731
- Popescu-Bradiceni I., Plastoi C. Synchronization and the Performance Sports Model Subjected to the Philosophical Interference. The Book of Proceedings - GIDNI-01, 2014, pp.93-100.
- Pluim B.M., Staal J.B., Marks B.L. et al. Health Benefits of Tennis. British journal of sports medicine, 2007, vol. 41, no. 11, pp. 760-768. DOI: 10.1136/bjsm.2006.034967
- Pluim B.M, Groppel J.L., Miley D. et al. Health Benefits of Tennis. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 2018, vol. 52, no. 3, pp. 201-202. DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-098623
- Reid MM., Crespo M., Lay B., Berry J. Skill Acquisition in Tennis: Research and Current Practice. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 2007, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 1-10. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsams.2006.05.011
- Sabo D., Veliz P., Rafalson L. More Than a Sport: Tennis, Education and Health. White Plains, 2013, pp. 1-43.
- Sandovici A., Alexe D.I., Nechifor C. The Role Played by Psychodiagnosis and Psychological Training in Professional Sports. Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Brasov, Series IX - Sciences of Human Kinetics, 2017, vol. 10 (59), no. 2, pp. 75-86.
- Schut P.O., Pierre J. The Economic Impact of a Women's Professional Tennis Tournament: the Example of the GDF-Suez Open of Seine-et-Marne, France. Journal of Policy Research in Tourism, Leisure and Events, 2016, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 71-86. DOI: 10.1080/19407963. 2015.1065266
- Slosar L., Simunic B., Pisot R., Ma-rusic U. Validation of a Tennis Rating Score to Evaluate the Technical Level of Children Tennis Players. Journal of Sports Sciences, 2019, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 100-107. DOI: 10.1080/02640414. 2018.1483184
- Stoszkowski J., Collins D. Sources, Topics and Use of Knowledge by Coaches. Journal of Sports Sciences, 2016, vol. 34, no. 9, pp. 794-802. DOI: 10.1080/02640414.2015.1072279
- Tennis Europe. European Tennis Report. 2018. Available at: https://www.tenniseurope.org/news/124330/2018-European-Tennis-Report-published (accessed 04.01.2020).
- Tohanean D.I. Evaluarea - Precursor al Monitorizarii in Antrenamentul Sportiv [Evaluation - Precursor of Monitoring in Sports Training]. New Educational Evolutions for Sports, Health Therapy and Free Time in European Context, Editura Universitatii Transilvania, Bra§ov, 2009,pp.198-200.
- Tohanean D.I. Selection in Team Sports -Analysis of Specialist Opinions. Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Brasov Series IX: Sciences of Human Kinetics, 2019, vol. 12 (61), no. 2, pp. 77-84. DOI: 10.31926/but.shk.2019. 12.61.2.42
- U.S. Census Bureau. Census. 2010. Available at: https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial-census/decade.2010.html (accessed 04.01.2020).
- Vergauwen L., Madou B., Behets D. Authentic Evaluation of Forehand Groundstrokes in Young Low- to Intermediate-Level Tennis Players. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 2004, vol. 36, no. 12, pp. 2099-2106. DOI: 10.1249/01.mss.0000147583.13209.61
- Veykut A. On the Proprietary Method of Breathing Exercises Applied in Training of Professional Tennis Players. Human. Sport. Medicine, 2017, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 61-66. (in Russ.) DOI: 10.14529/hsm170307


