Evaluation of the effectiveness of mineral additives in cement systems in the development of “core – shell” photocatalytic compositions
Автор: Artemy S. Balykov, Tatyana A. Nizina, Vladimir M. Kyashkin, Sergey V. Volodin
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: The results of the specialists’ and scientists’ researches
Статья в выпуске: 5 Vol.14, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. Creation of highly efficient photocatalysts for construction composites, which are characterized by increased activity and an extended spectral range of action, is a very important area of research. It is known that “core (substrate) – shell (photocatalyst)” compositions, where mineral raw materials of various genesis can act as carriers, are one of the most effective types of photocatalytic additives for cement systems. It is worth noting that for integrated assessment of the substrate efficiency, we need to obtain information on the composition and properties of raw materials used among which its chemical activity and structure-forming role in cement systems are of paramount importance. The purposes of this study are (1) to establish the influence pattern of four types of mineral additives (silica fume, metakaolin, expanding sulfoaluminate modifier and microcalcite) on the structure formation processes of plasticized cement systems and (2) to identify the most effective modifiers for further use as mineral substrates in the photocatalytic compositions. Methods and materials. Specific surface area and granulometric composition of mineral modifiers were determined by the Kozeny-Karman and laser diffraction methods. The phase composition of mineral additives and modified cement systems were studied using X-ray diffraction phase analysis. Results and discussion. Features of mineralogical and granulometric compositions of mineral additives were revealed. It was determined that the use of individual and complex mineral additives based on silica fume, metakaolin and ESAM made it possible to directionally influence on content of the main phases of cement stone such as ettringite, portlandite, calcium hydrosilicates of different basicity. Conclusions. The increased chemical activity of these modifiers in cement systems, due to presence of reactive minerals in the structure, along with features of the granulometric composition (high dispersity and narrow particle size distribution), indicated the potential prospects for their use as mineral substrate in “core – shell” photocatalytic compositions.
Cement system, photocatalytic composite nanomodifier, substrate, mineral raw materials, phase composition, activity, granulometry, structure parameter, efficiency
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142235387
IDR: 142235387 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2022-14-5-405-418
Текст научной статьи Evaluation of the effectiveness of mineral additives in cement systems in the development of “core – shell” photocatalytic compositions
Original article
The development and application of photocatalytically active construction materials is one of the promising directions for improving environmental safety and ensuring sustainable development of settlements and territories that contribute to reducing concentrations of pollutants in the atmospheric air (volatile organic substances, ammonia, nitrogen and sulfur oxides, etc.) due to their decomposition to low-toxic or non-toxic products (oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, sulfates, nitrates and nitrites) as a result of redox reactions occurring in the structure of the material when irradiated with light [1–8]. Achieving the self-cleaning mechanism of the outer layers of composites with photocatalysts through more efficient flushing of pollutants with water due to surface hydrophilization is another positive aspect of the use of such materials, which makes it possible to maintain the original purity and color of building products and structures for a long time under the influence of adverse environmental factors [6, 9–11].
Anatase form of titanium dioxide is currently the most widely studied and successfully used photocatalyst [4, 5, 7, 8, 9–15] due to its chemical stability, non-toxicity, and the special band structure, which determines its high
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES photocatalytic activity. However, photocatalysis using titanium dioxide also has a number of disadvantages.
As a rule, the efficiency of the photocatalytic action of TiO2 increases by varying the sizes of titanium dioxide crystallites, in particular, by decreasing them down to a few nanometers [16]. At the same time, the production of TiO2 powder with such particle sizes involves the use of special techniques and technologies for the preparation of nanoscale samples, which leads to an increase in the cost of the photocatalyst.
The narrow spectral range of action, characterized by insensitivity to the main visible region of the solar spectrum, is another significant disadvantage of titanium dioxide. In particular, the band gap of rutile and anatase is 3.0 and 3.2 eV, respectively, which is higher than that of other known semiconductors (for example, GaAs, CdSe, Fe2O3, CDs, GaP, WO3, SiC with band gap of 1.4–3.0 eV [11]).
Thus, increasing the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide is an urgent task of modern photocatalysis. The preparation of photocatalytically active compositions by deposition of TiO2 nanoparticles on particulate carriers (“core – shell” systems) is a promising direction. The photocatalytic activity of such systems grows due to an increase in the TiO2 active surface and its more uniform distribution in the material volume [11].
When developing photocatalytic composite modifiers, special attention is paid to the selection and evaluation of the raw materials efficiency, in particular, particulate carriers (substrates) of photocatalytic agents. At the same time, the following basic requirements for mineral raw materials as a photocatalyst substrate for cement systems are indicated in [17–21], such as increased values of the material amorphization degree and SiO2 content (at least 70 and 50%, respectively), homogeneous granulometric composition with a tendency to monodisperse particle size distribution, highly developed chemically active surface (the presence of micro- and nanopores, the predominant content of Brönsted acid centers), etc.
It is worth noting that natural and technogenic pozzo-lanic materials of silica and aluminosilicate compositions, in particular, diatomite, silica fume, metakaolin, mordenite, zeolite, etc. [11, 17], are among the most effective substrates in the synthesis of “core – shell” photocata-lytic nanomodifiers for cement systems. The prospect of using this kind of raw material as a carrier lies in its wide applicability in building composites, as well as increased values of porosity and amorphous phase content, which contribute to the formation of an active acid-base surface, which has a high chemical affinity with cement hydration products and provides improved adhesion of the photo-catalytic material to cement matrix [18, 22–27].
It is known that the action mechanism of the above mineral modifiers is associated with their high pozzolanic activity, which consists in the ability of amorphous silica and aluminosilicate to react with calcium hydroxide of the hardening cement system to form high-strength calcium hydrosilicates and calcium hydroaluminosilicates of low basicity. The formation of these compounds is accompanied by acceleration of hydration processes, increase in the amount of chemically bound water, decrease in the content of low-strength portlandite crystals, and increase in the specific surface area and strength of cement stone [28–32].
There are other promising types of particulate carriers of photocatalytic agents for cement systems:
-
• expanding additives of the sulfoaluminate type [33, 34], which make it possible to control the deformations of cement systems by stimulating the formation of crystalline hydrates with increased volume (ettringite, etc.);
-
• carbonate rocks (limestone, chalk, marble, dolomite), characterized by high content of calcite [35, 36, 37], which can act as the crystallization center for new phases of various compositions (calcium hydrosilicates, AFm hydrate phases, etc.), which makes it possible regulate the kinetics of structure formation of cement composites.
Thus, domestic and foreign experience in the development and application of photocatalytic composite modifiers for cement systems shows that the main parameters of the synthesized material largely depend on the choice of the photocatalyst carrier. At the same time, for integrated assessment of the substrate efficiency, you need to have information on the composition and properties of raw materials used among which its chemical activity and structure-forming role in cement systems are of paramount importance.
The purpose of this study was to establish the influence regularities of four types of mineral additives (silica, aluminosilicate, sulfoaluminate and carbonate) on the structure formation processes of plasticized cement systems and to identify the most effective modifiers for later use as mineral substrate in the photocatalytic compositions of “core (particulate carrier) – shell (photocatalyst)” types.
The following tasks were solved during the research:
-
1) the phase (mineralogical) and granulometric composition of mineral additives was studied;
-
2) the effects of type and content of mineral additives on the hydration degree of plasticized Portland cement and phase composition of cement stone at the age of 28 days were researched;
-
3) the effective modifiers and their complexes, allowing you to directionally manage the structure parameters of cement composites, were installed.
METHODS AND MATERIALS
Materials
The following main components were used to prepare the cement systems:
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
-
• Portland cement CEM I 42.5R (PC) produced by Mordovcement PJSC;
-
• Melflux 1641 F polycarboxylate superplasticizer (PS) produced by BASF Construction Solutions;
-
• four types of mineral additives (MA):
-
1) condensed uncompacted silica fume SF-85 (CUSF) produced by Kuznetskie Ferrosplavy JSC is silica MA;
-
2) MKZhL-2 highly active metakaolin (HAMK) produced by Plast-Rifey LLC is aluminosilicate MA;
-
3) expanding sulfoaluminate modifier (ESAM) produced by Parade-Rus LLC is sulfoaluminate MA;
-
4) KM100 microcalcite (MCCT) produced by Polypark LLC is carbonate MA.
The efficiency of the above modifiers was evaluated in cement systems with water-binder ratio W/(PC+MA) = 0.24 and the total dosage of mineral additives of 20% by weight of the binder. Composition without mineral additives with plasticizer content of 1% by weight of Portland cement was adopted as control composition.
Two groups of factors varied according to the experimental study plan:
-
• dosage of superplasticizer and carbonate filler (Table 1): x 1 (PS); x 2 (MCCT);
-
• type and content of active mineral additives (AMA) (Table 2): ν 1 (CUSF); ν 2 (HAMK); ν 3 (ESAM).
Table 1
Numerical values of variation levels for the first group of studied factors
|
Factors Variation levels |
Type of component, % by weight of binder (PC+MA) |
|
|
x 1 (PS) |
x 2 (MCCT) |
|
|
–1 |
0.5 |
0 |
|
0 |
1.0 |
5 |
|
+1 |
1.5 |
10 |
The following conditions were met during the planning of experimental study:
xi = –1, 0, +1; i = 1, 2;
0 ≤ νi ≤ 1; ∑ νi = 1; i = 1, 2, 3. (1)
Methods
The specific surface area and granulometric composition of mineral modifiers were determined by the methods of Kozeni-Karman and laser diffraction using the PSKh-12 dispersion analysis device and the Shimadzu Sald-3101 particle size analyzer.
The phase composition of mineral additives and modified cement systems was studied using X-ray diffraction (XRD) phase analysis on the Empyrean diffractometer by PANalytical (Netherlands) with a vertical goniometer in the radiation of a copper anode with a nickel filter. Shooting was done in the geometry according to Bragg-Brentano (θ–2θ scanning) using a spectral doublet Cu Kα1,2 with weighted average wavelength λ = 1.5406 Å.
The main controlled parameters of the cement stone structure were:
-
• the hydration degree of Portland cement (α), which was estimated by reducing the intensity of the C3S main reflex (d=1.76–1.77 Å) in the hydrated sample of cement stone at the time under study relative to the sample of the original binder (cement + mineral additives) before hydration;
-
• the relative content of ettringite (Ca6Al2(SO4)3(OH)12• 26H2O), which was estimated by the intensity ratio of the main reflex at d = 9.81–9.83 Å for cement stone samples of modified and control compositions;
-
• the relative content of portlandite (Ca(OH)2), which was estimated by the intensity ratio of the main reflex at d = 4.94–4.96 Å for cement stone samples of modified and control compositions;
-
• the relative amounts of low-basic (C–S–H(I)) and high-basic (C–S–H(II)) calcium hydrosilicates,
Table 2
Numerical values of variation levels for the second group of studied factors
|
Factors Variation levels |
Type of active mineral additive (AMA), % by weight of binder (PC+MA) |
||
|
ν 1 (CUSF) |
ν 2 (HAMK) |
ν 3 (ESAM) |
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0.333 |
3.33/5/6.67* |
3.33/5/6.67* |
3.33/5/6.67* |
|
0.5 |
5/7.5/10* |
5/7.5/10* |
5/7.5/10* |
|
1.0 |
10/15/20* |
10/15/20* |
10/15/20* |
Note. *The amount of active mineral additive at the content of the carbonate filler (MCCT), respectively, equal to 10/5/0% by weight of the binder (PC+MA).
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES which were estimated by comparing the intensities of the main reflexes of α-CS (d = 3.23–3.25 Å) and β-CS (d = 2.97–2.99 Å) for C–S–H(I) and β-C2S (d = 2.79–2.80 Å) for C–S–H(II) in the samples of cement stone of modified and control compositions calcined at 980–1000oC.
According to the analysis results of diffraction patterns, the crystallinity degree (α c ) of mineral modifiers containing amorphous halo (silica fume and metakaolin) was calculated using the formula:
\-=,,Л 'l^v, (2)
where I c is the integrated intensity (total area) of all crystalline peaks;
Ia is the integral intensity (area) of amorphous halo.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Phase (mineralogical) composition of the studied mineral additives
Figure 1 presents the diffraction patterns of the studied mineral additive powders. The results of qualitative XRD phase analysis to determine the main phases for modifier samples are given in Table 3.
Analysis of the experimental study results indicated the prospects for the use of CUSF, HAMK, ESAM and MCCT mineral additives in cement materials due to the presence in their structure of reactive phases of silica, aluminosilicate and sulfate composition, in particular, amorphous silica (for CUSF); amorphous phase of metakaolinite and dehydroxylation products of the illite group minerals (for HAMK); anhydrite and thermal destruction products of micas and hydromicas (for ESAM).
It was established that the crystallinity degree of silica fume and metakaolin samples was 11.8 and 25.0%, respectively. The high level of material structure amorphization with predominance of active silica and alumina forms caused increased physico-chemical efficiency of silica fume and metakaolin in cement systems.
Granulometric composition of the studied mineral additives
According to the study results (Fig. 2 and Table 4), the specific surface area values of 20.0, 1.65, 1.00 and 0.25 m2/g, as well as the particle size ranges of 0.2–13.7, 0.2–23.7, 0.2–11.0 and 0.3–137.8 µm, were established for samples of silica fume, metakaolin, ESAM and microcalcite, respectively. The indicator d 50%, which characterized the average volumetric diameter of powder particles, increased in the range of CUSF → ESAM → HAMK → MCCT; 0.7, 2.5, 3.7 and 13.3 microns, respectively.
Thus, analysis of the experimental data showed that silica fume, metakaolin and sulfoaluminate modifier were characterized by increased dispersity and narrowed particle size range, which indicated high homogeneity of their granulometric composition. The noted features of the granulometric composition of CUSF, HAMK and
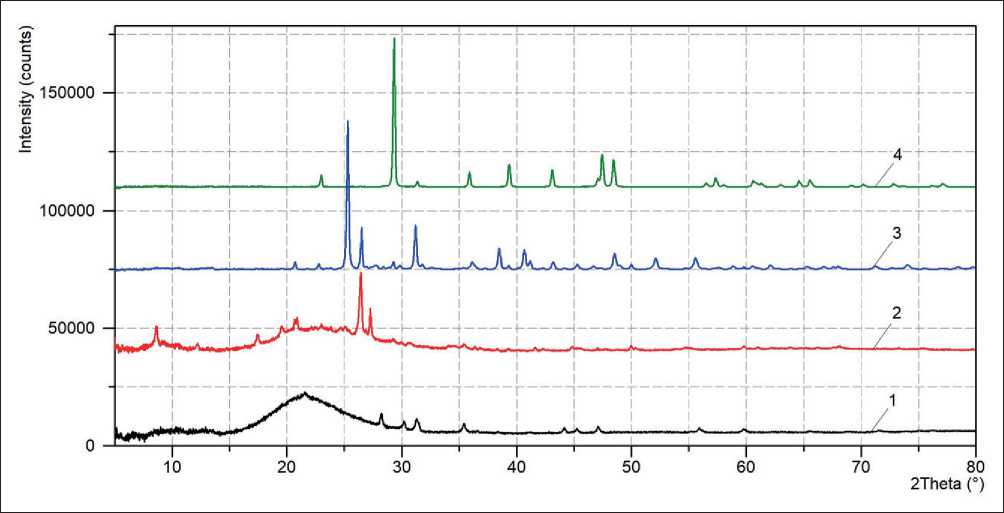
Figure 1. Diffraction patterns of the studied mineral additive powders: silica fume (1); metakaolin (2); ESAM (3); microcalcite (4)
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
Table 3
Main phases of the mineralogical composition of the studied mineral additives
|
Type of mineral additive |
Phase name |
Reflection position of the main phases on the diffraction pattern (2θ, o) |
|
silica fume (CUSF) |
amorphous phase (amorphous silica (SiO2)) |
15–30 (halo) |
|
quartz (SiO2) modifications of different crystallographic systems (syngonies): triclinic, cubic and tetragonal |
28.2; 30.2; 31.4; 35.4 |
|
|
metakaolin (HAMK) |
amorphous phase (metakaolinite) |
15–32 (halo) |
|
kaolinite group (Al2(Si2O5)(OH)4) |
12.2; 20.1; 22.1; 23.3; 25.1; 25.4; 38.3 |
|
|
quartz (SiO2) modifications |
8.6; 17.4; 20.8; 26.4; 50.0 |
|
|
feldspars |
21.0; 24.0; 26.4; 27.2; 27.3; 41.7 |
|
|
illite group (micas and hydromicas) |
8.7; 19.6; 25.4; 26.5; 34.8; 35.1 |
|
|
expanding sulfoaluminate modifier (ESAM) |
anhydrite (CaSO4) |
22.8; 25.3; 31.2; 31.9; 36.2; 38.5; 40.7; 41.2; 43.2; 45.4; 46.7; 48.5; 52.1; 55.6 |
|
quartz (SiO2) modifications |
20.7; 21.8; 26.5; 39.4; 50.0 |
|
|
gehlenite (Ca2Al2SiO7) |
23.8; 28.9; 31.2; 52.1 |
|
|
illite group (micas and hydromicas) |
25.3; 26.5; 27.8; 29.9 |
|
|
feldspars |
26.5; 27.8; 29.3 |
|
|
microcalcite (MCCT) |
calcite (CaCO3) |
23.0; 29.4; 31.4; 36.0; 39.4; 43.1; 47.1; 47.5; 48.5; 56.5; 57.4; 58.1 |
ESAM could be considered as indicators of their potential efficiency as a photocatalyst carrier in the assumption that when synthesizing “core – shell” compositions using monodisperse substrates, their surface coverage with photocatalytic component was more uniform.
Influence of mineral additives on the structure formation processes of cement systems
Using XRD phase analysis of the cement stone at the age of 28 days it was found that the hydration degree of Portland cement in compositions with mineral additives differed from the indicator of the control composition in both greater and lesser directions, in particular, changes varied from –17 to +8%. At the same time, the average value of the indicator in the considered modified cement systems was 71%, which was close to the indicator of the control composition (74%). It was worth noting that the lark of clear patterns of change in the hydration degree of Portland cement when varying the content of plasticizer and mineral additives of different chemical nature in the formulation could be due to the complexity and multicomponent nature of the considered cement system compositions, in which the modifiers showed complex and non-additive effect on the studied indicator.
Figures 3–6 show the study results of the effect of CUSF, HAMK, ESAM and MCCT mineral additives on the main controlled indicators of the phase composition of cement systems with the establishment of correlation dependencies.
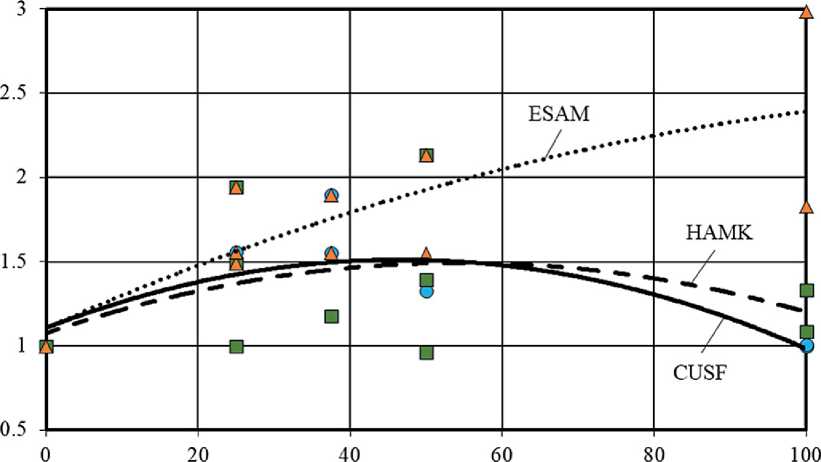
An important phase of the hardening cement system is ettringite (Ca6Al2(SO4)3(OH)12•26H2O), which can potentially contribute to the nanoreinforcing of the cement stone structure. According to Figure 3, the ratio of CUSF, HAMK, ESAM and MCCT additives in the mineral complexes used had a significant effect on the ettringite content in the phase composition of cement stone at the age of 28 days. In particular, the increase in the share of ESAM in the total weight of mineral additives led to a significant increase in the ettringite concentration, reaching maximum values equal to 3.0 rel. units (i.e., 3 times higher than the similar indicator of the control composition without mineral additives) in the cement stone sample with the highest ESAM content (20% by
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
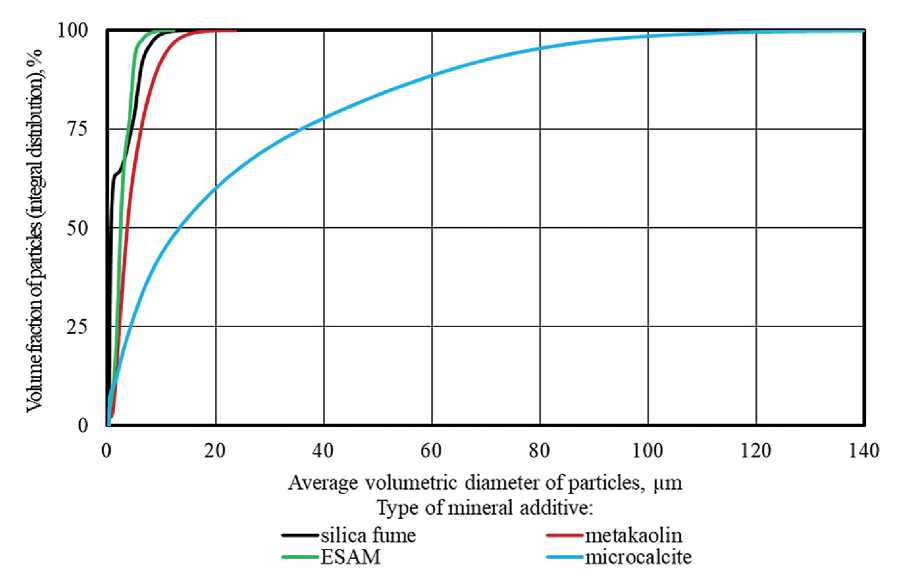
Figure 2. Integral curves of the volumetric distribution of particles of the studied mineral modifier powders
Table 4
Key indicators of the granulometric composition of the studied mineral additive powders
Complete or partial replacement of the expanding sulfoaluminate modifier with silica fume, metakaolin, microcalcite, and their complexes led to a decrease in the ettringite content in the phase composition of cement stone (Figure 3). In the absence of ESAM the highest concentration of Ca6Al2(SO4)3(OH)12•26H2O, equal to 1.4 rel. units (i.e., by 40% higher than the indicator of the control composition), was recorded in composition without microcalcite when the ratio of CUSF/HAMK = 1/1 (10% by the total weight of the binder (PC+MA) each) and the superplasticizer dosage of 1% by weight of the binder.
The patterns of changes in the content of the main hydrated phases (portlandite and calcium hydrosilicates) of cement stone at the age of 28 days depending on the type and concentration of the studied mineral additives were established based on the analysis results of Figures 4, 5 and 6.
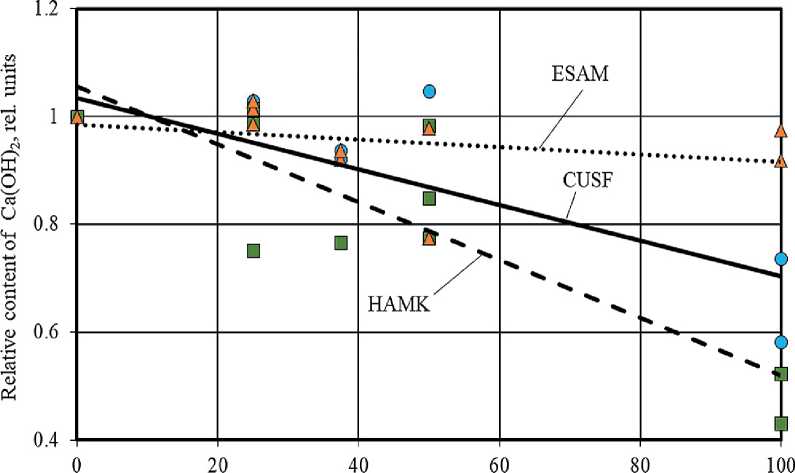
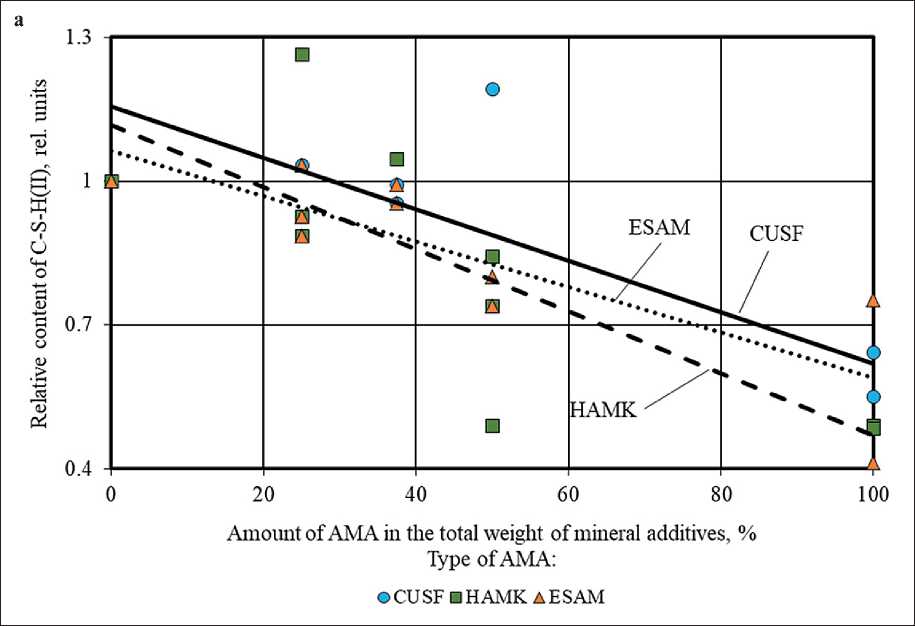
It was found that the use of silica fume, metakaolin and ESAM in the cement system compositions allowed to reduce the content of high-basic calcium hydrosilicates C–S–H(II) and low-strength Ca(OH)2 crystals up to 2.4 and 2.3 times, respectively (Fig. 4 and 5 (a)), as well as to
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
Amount of AMA in the total weight of mineral additives, % Type of AMA:
OCUSF ИНАМК ДЕ8АМ
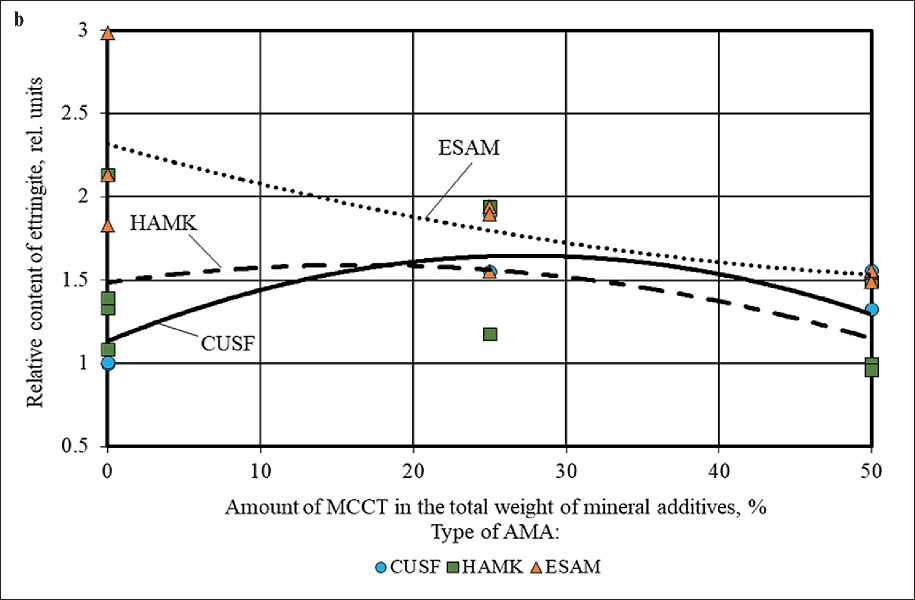
Figure 3. Change in the relative content of ettringite in the phase composition of cement stone at the age of 28 days (relative to the control composition) depending on the amount of AMA (a) and MCCT (b) in the total weight of mineral additives
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
Amount of AMA in the total weight of mineral additives, % Type of AMA:
®CUSF1HAMK AESAM
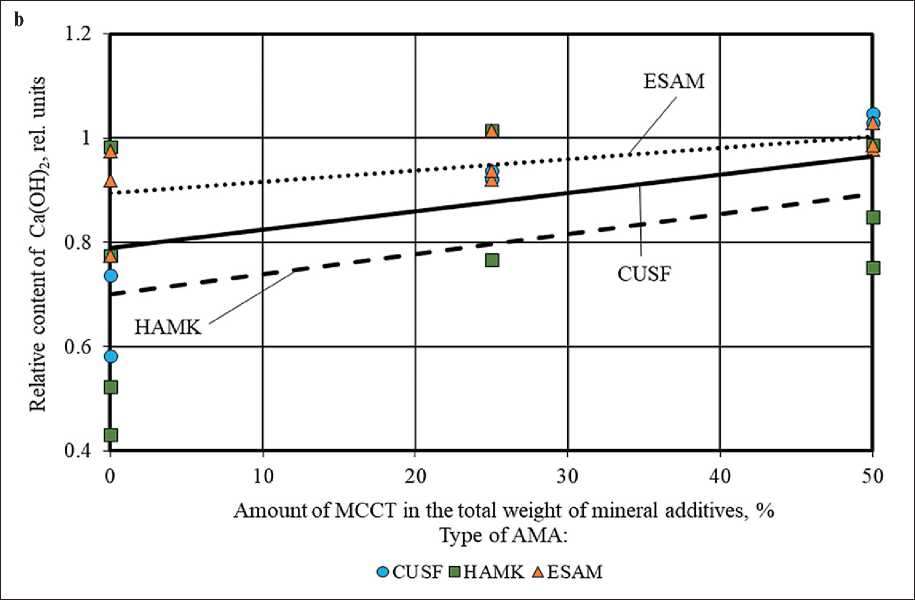
Figure 4. Change in the relative content of Ca(OH)2 in the phase composition of cement stone at the age of 28 days (relative to the control composition) depending on the amount of AMA (a) and MCCT (b) in the total weight of mineral additives
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
b
Amount of MCCT in the total weight of mineral additives, % Type of AMA:
О CUSP DHAMK AESAM
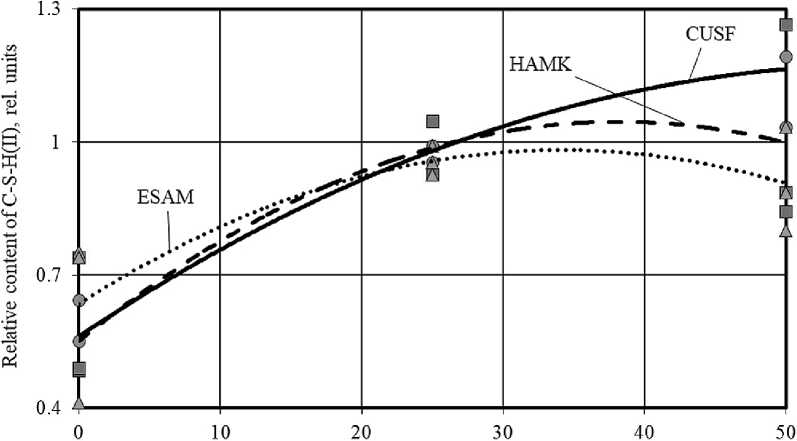
Figure 5. Change in the relative content of high-basic calcium hydrosilicates (C–S–H(II)) in the phase composition of cement stone at the age of 28 days (relative to the control composition) depending on the amount of AMA (a) and MCCT (b) in the total weight of mineral additives
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES
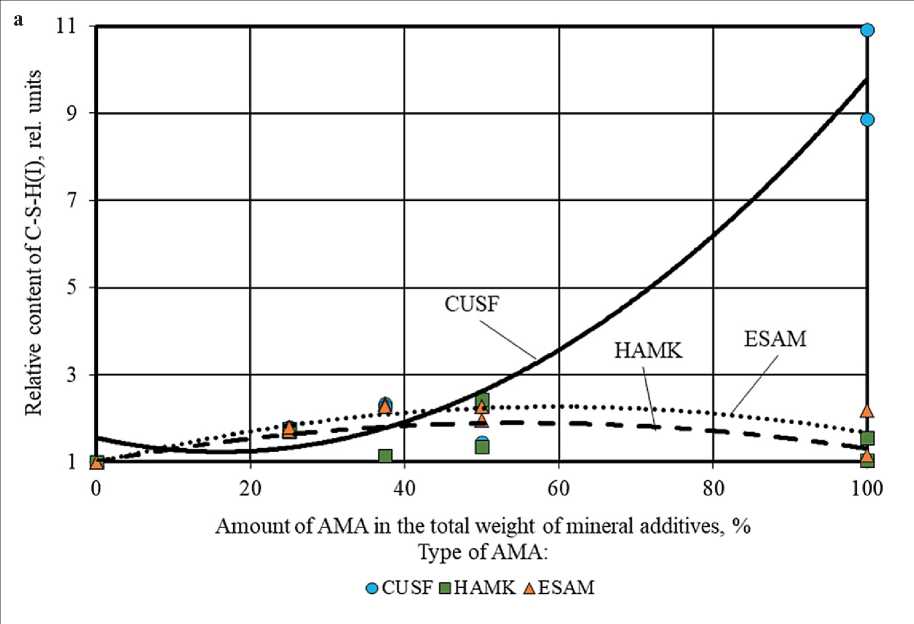
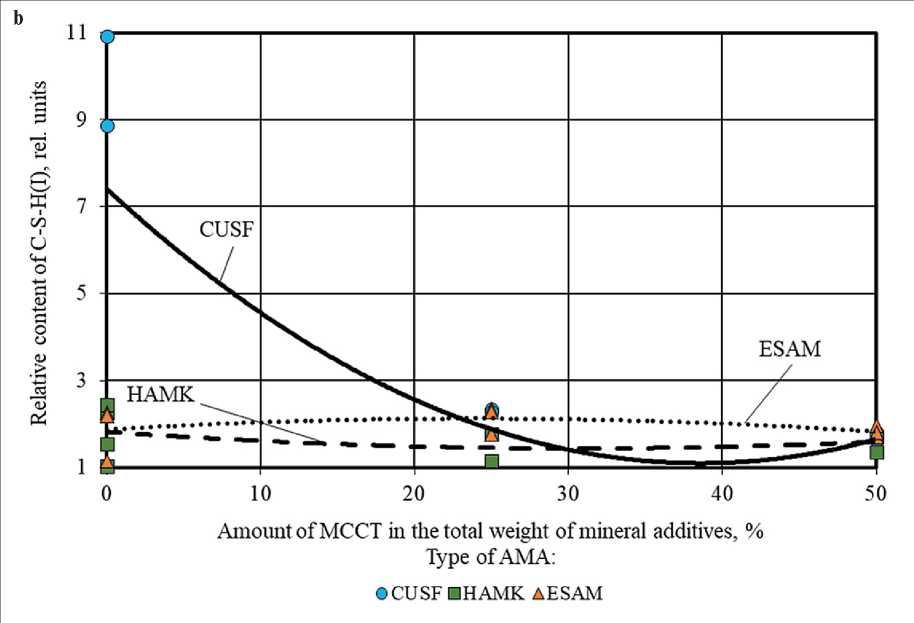
Figure 6. Change in the relative content of low-basic calcium hydrosilicates (C–S–H(I)) in the phase composition of cement stone at the age of 28 days (relative to the control composition) depending on the amount of AMA (a) and MCCT (b) in the total weight of mineral additives
THE RESULTS OF THE SPECIALISTS’ AND SCIENTISTS’ RESEARCHES increase up to 11 times the amount of low-basic calcium hydrosilicates C-S-H(I) (Fig. 6 (a)), characterized by high dispersity and strength.
The established change in the balance between the hydrate phases in the structure of cement stone with additives of silica fume, metakaolin and ESAM towards an increase in the volume of more strenght and steady low-basic calcium hydrosilicates C–S–H(I) with a ratio of CaO/SiO2 ≤ 1.5 instead of primary crystallohydrates of portlandite and high-basic calcium hydrosilicates C– S–H(II) with a ratio of CaO/SiO2 > 1.5 was a manifestation of the chemical effect in the mechanism of action of these mineral modifiers. This chemical effect was associated with the pozzolanic activity of CUSF, HAMK, and ESAM mineral additives in cement systems and was due to the presence of active components (reactive phases with amorphized structure or metastable crystal lattice) in their mineralogical composition.
The reverse pattern was observed when introducing microcalcite into cement systems. Increasing the proportion of MCCT in the complex of mineral additives (AMA+MCCT) helped to increase the amount of Ca(OH)2 and high-basic calcium hydrosilicates C–S– H(II) (Figures 4 and 5 (b)). At the same time, the content of low-basic calcium hydrosilicates changed in different ways, in particular, the content of C–S–H(I) significantly decreased in compositions with MCCT and practically did not change in compositions with HAMK and ESAM (Figure 6 (b)). The results obtained confirmed the relative chemical inertia of microcalcite in cement systems.
The highest amount of low-basic calcium hydrosilicates was recorded in the compositions with a maximum content of silica fume (with the CUSF share equal to 100% by the total weight of the mineral complex (CUSF+HAMK+ESAM+MCCT) and amounted to 10.9 and 8.9 rel. units at Melflux superplasticizer dosages of 0.5 and 1.5% by weight of the binder (PC+MA), respectively, i.e., 11 and 9 times higher than the indicator of the control composition without mineral additives. At the same time, threshold level of CUSF concentration was set equal to 50% of the total weight of mineral additives, above which the amount of C–S–H(I) in the phase composition of cement stone sharply increased (up to 7.5 times) (Figure 6 (a)).
Replacing silica fume with metakaolin, ESAM and their complexes led to a decrease in the content of C– S–H(I) in the phase composition of cement stone, while according to Figure 6 (a), the optimal ratio of HAMK/ ESAM to reduce this effect was 50/50 (% by the total weight of the MA complex). In particular, among cement systems without silica fume, composition without microcalcite with equal share of HAMK and ESAM (10% by the total weight of the binder (PC+MA) each) and superplasticizer dosage of 1% by weight of the binder had the highest content of C–S–H(I) equal to 2.3 rel. units. The results showed that the content of low-basic calcium hydrosilicates in the phase composition of cement stone directly depended on the amount of amorphous silica and the specific surface area of the mineral additive introduced into the formulation of cement systems.
CONCLUSIONS
The conducted experimental studies allowed us to obtain the following scientific results:
-
1) the features of phase (mineralogical) and granulometric composition of four types of mineral additives (silica fume, metakaolin, expanding sulfoaluminate modifier and microcalcite) were established;
-
2) the effects of type and content of mineral additives on the hydration degree of plasticized Portland cement and phase composition of cement stone at the age of 28 days were revealed;
-
3) the effective modifiers and their complexes, allowing us to manage the structure parameters of cement composites, were installed.
The use of individual and complex mineral additives based on silica fume, metakaolin and ESAM made it possible to directionally influence on content of the main phases of cement stone such as ettringite, portlandite, calcium hydrosilicates of different basicity.
Thus, the increased chemical activity of CUSF, HAMK and ESAM in cement systems, due to the presence of reactive minerals in the structure, along with features of the granulometric composition (high dispersity and narrow particle size distribution), indicated the potential prospects for their use as a mineral substrate in “core – shell” photocatalytic compositions.
Список литературы Evaluation of the effectiveness of mineral additives in cement systems in the development of “core – shell” photocatalytic compositions
- Gallus M., Akylas V., Barmpas F. et al. Photocatalytic de-pollution in the Leopold II tunnel in Brussels: NOx abatement results. Building and Environment. 2015; 84: 125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2014.10.032
- George C., Beeldens A., Barmpas F., Doussin J.F., Manganelli G., Herrmann H., Kleffmann J., Mellouki A. Impact of photocatalytic remediation of pollutants on urban air quality. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering. 2016; 10(5): 2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-016-0834-1
- Yang L., Hakki A., Wang F., Macphee D.E. Photocatalyst efficiencies in concrete technology: The effect of photocatalyst placement. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2018; 222: 200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.10.013
- Amor F., Baudys M., Racova Z., Scheinherrová L., Ingrisova L., Hajek P. Contribution of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles to the hydration of Portland cement and photocatalytic properties of High Performance Concrete. Case Studies in Construction Materials. 2022; 16: e00965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e00965
- Janczarek M., Klapiszewski Ł., Jędrzejczak P., Klapiszewska I., Ślosarczyk A., Jesionowski T.. Progress of functionalized TiO2-based nanomaterials in the construction industry: A comprehensive review. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2022; 430(3): 132062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132062
- Falikman V.R. Nanocoatings in modern construction. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2021; 13(1): 5–11. https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2021-13-1-5-11
- Tyukavkina V.V., Tsyryatyeva A.V. The structure of the cement stone modified by nanodispersed titanium-bearing additive. Proceedings of the Fersman Scientific Session of the State Institute of the CSC RAS. 2019; 16: 597–601. https://doi.org/10.31241/FNS.2019.16.122
- Lukuttsova N.P., Pykin A.A., Postnikova O.A., Golovin S.N., Borovik E.G. The structure of cement stone with dispersed titanium dioxide in daily age. Bulletin of Belgorod State Technological University named after V.G. Shukhov. 2016; 11: 13–17. https://doi.org/10.12737/22432
- Emeline A.V., Rudakova A.V., Sakai M., Murakami T., Fujishima A. Factors affecting UV-induced superhydrophilic conversion of TiO2 surface. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 2013; 117(23): 12086–12092. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp400421v
- Falikman V.R. About the use of nanotechnologies and nanomaterials in сonstruction. Part 1. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2009; 1(1): 24–34.
- Antonenko M.V., Ogurtsova Yu.N., Strokova V.V., Gubareva E.N. Photocatalytic active self-cleaning cementbased materials. Compositions, properties, application. Bulletin of Belgorod State Technological University named after V.G. Shukhov. 2020; 3: 16–25. https://doi.org/10.34031/2071-7318-2020-5-3-16-25
- Li Y.-N., Chen Z.-Y., Bao S.-J., Wang M.-Q., Song C.-L., Pu S., Long D. Ultrafine TiO2 encapsulated in nitrogen-doped porous carbon framework for photocatalytic degradation of ammonia gas. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2018; 331: 383–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.119
- Henderson M.A. A surface science perspective on TiO2 photocatalysis. Surface Science Reports. 2011; 66: 185–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfrep.2011.01.001
- Nakata K., Fujishima A. TiO2 photocatalysis: Design and applications. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews. 2012; 13(3): 169–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2012.06.001
- Timokhin D.K., Geranina Yu.S. Titanium Dioxide as a Photocatalyst in Cement Concrete. Scientific Review. 2015; 8: 46–50.
- Hela R., Bodnarova L. Research of Possibilities of Testing Effectiveness of Photoactive TiO2 in Conrete. Construction materials. 2015; 2: 77–81.
- Falikman V.R., Vainer A.Y. New high performance nanoadditives for photocatalytic concrete: synthesis and study. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2015; 7(1): 18–28. https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2015-7-1-18-28
- Strokova V.V., Gubareva E.N., Ogurtsova Yu.N. Evaluation of the properties of the silica raw materials as a substrate as component of composite photocatalytic material. Bulletin of Belgorod State Technological University named after V.G. Shukhov. 2017; 2: 6–12. https://doi.org/10.12737/23819
- Wang D., Hou P., Stephan D., Huang S., Zhang L., Yang P., Cheng X. SiO2/TiO2 composite powders deposited on cement-based materials: Rhodamine B removal and the bonding mechanism. Construction and Building Materials. 2020; 241: 118124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118124
- Fatimah I., Prakoso N.I., Sahroni I., Miqdam Musawwa M., Sim Y.-L., Kooli F., Muraza O. Physicochemical characteristics and photocatalytic performance of TiO2/SiO2 catalyst synthesized using biogenic silica from bamboo leaves. Heliyon. 2019; 5(11): e02766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02766
- Pal A., Jana T.K., Chatterjee K. Silica supported TiO2 nanostructures for highly efficient photocatalytic application under visible light irradiation. Materials Research Bulletin. 2016; 76: 353-357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.12.040
- Nedunuri S.S.S.A., Sertse S.G., Muhammad S. Microstructural study of Portland cement partially replaced with fly ash, ground granulated blast furnace slag and silica fume as determined by pozzolanic activity. Construction and Building Materials. 2020; 238: 117561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117561
- Chand G., Happy S.K., Ram S. Assessment of the properties of sustainable concrete produced from quaternary blend of portland cement, glass powder, metakaolin and silica fume. Cleaner Engineering and Technology. 2021; 4: 100179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100179
- Taoukil D., El meski Y., Lahlaouti M.L., Djedjig R., El bouardi A. Effect of the use of diatomite as partial replacement of sand on thermal and mechanical properties of mortars. Journal of Building Engineering. 2021; 42: 103038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103038
- Balykov A.S., Nizina T.A., Kyashkin V.M., Volodin S.V. Prescription and technological efficiency of sedimentary rocks of various composition and genesis in cement systems. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2022; 14(1): 53–61. https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2022-14-1-53-61
- Balykov A.S., Nizina T.A., Volodin S.V. Optimization of technological parameters for obtaining mineral additives based on calcined clays and carbonate rocks for cement systems. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2022; 14(2): 145–155. https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2022-14-2-145-155
- Nizina T.A., Balykov А.S. Formation of experimental-statistical models “composition – property” of physical and mechanical properties of modified fiber-reinforced fine-grained concretes. Bulletin of Volgograd State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering. Series: Civil Engineering and Architecture. 2016; 45(64): 54–66.
- Bazhenov Yu.M., Chernyshov E.M., Korotkikh D.N. Designing of modern concrete structures: determining principles and technological platforms. Construction materials. 2014; 3: 6–14.
- Rassokhin A.S., Ponomarev A.N., Figovsky O.L. Silica fumes of different types for high-performance finegrained concrete. Magazine of Civil Engineering. 2018; 78: 151–160. https://doi.org/10.18720/MCE.78.12
- Kocak Y. Effects of metakaolin on the hydration development of Portland–composite cement. Journal of Building Engineering. 2020; 31: 101419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101419
- Chernishov E.M., Artamonova O.V., Slavcheva G.S. Nanomodification of cement-based composites in the technological life cycle. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2020; 12(3): 130–139. https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2020-12-3-130-139
- Balykov A.S., Nizina T.A., Volodin V.V., Kyashkin V.M. Effects of Calcination Temperature and Time on the Physical-Chemical Efficiency of Thermally Activated Clays in Cement Systems. Materials Science Forum. 2021; 1017: 61–70. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.1017.61
- Le Saoût G., Lothenbach B., Hori A., Higuchi T., Winnefeld F. Hydration of Portland cement with additions of calcium sulfoaluminates. Cement and Concrete Research. 2013; 43: 81–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2012.10.011
- Carballosa P., García Calvo J.L., Revuelta D., Sánchez J.J., Gutiérrez J.P. Influence of cement and expansive additive types in the performance of self-stressing and self-compacting concretes for structural elements. Construction and Building Materials. 2015; 93: 223–229 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.05.113
- Lin R.-S., Wang X.-Y., Yi-Han. Effects of cement types and addition of quartz and limestone on the normal and carbonation curing of cement paste. Construction and Building Materials. 2021; 305: 124799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124799
- Celik K., Hay R., Hargis C.W., Moon J. Effect of volcanic ash pozzolan or limestone replacement on hydration of Portland cement. Construction and Building Materials. 2019; 197: 803–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.193
- Nizina T.A., Balykov A.S., Korovkin D.I., Volodin V.V. Modified fine-grained concretes based on highly filled self-compacting mixtures. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2019; 481: 012048. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/481/1/012048


