Exploring the influence of mechanical and physical characteristics on transdermal patches: a study on polymeric films composed of hyaluronic acid and zinc oxide nanoparticles
Автор: Dada K.S., Uspenskaya M.V., Elangwe C.N., Nosova A.O., Olekhnovich R.O.
Журнал: Вестник Воронежского государственного университета инженерных технологий @vestnik-vsuet
Рубрика: Химическая технология
Статья в выпуске: 3 (101) т.86, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This study examines the physicomechanical and special properties of polymer films composed of hyaluronic acid (HA) and zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles that can be used as transdermal patches. Transdermal patches are a popular method of medical and cosmetic procedures in various disciplines, not limited to cosmetology, gynecology, oncology, etc. They have advantages such as convenience and simplicity, the possibility of uniform drug delivery, and a wide range of possible applications. These advantages make transdermal patches an important tool for various areas of medicine. However, most biopolymers used as a polymer matrix do not meet the required physicomechanical properties when creating polymer films for medical purposes. That is why hyaluronic acid with ZnO nanoparticles as a filler was chosen as a polymer base. The work examines the effect of nanoparticle concentration on the physicomechanical and special properties of hyaluronic acid-based polymer films. It has been shown that using 5 wt.% ZnO nanoparticles results in the production of a polymer film based on hyaluronic acid, with optimal mechanical parameters for the balance between the relative elongation and strength of the resulting materials and compliance with the skin texture, which is of critical importance for increasing the long-term effectiveness of the use of the obtained polymer films as a base for creating transdermal patches
Young modulus, composite materials, polymer matrix, hyaluronic acid, zinc oxide nanoparticles
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140308197
IDR: 140308197 | УДК: 640 | DOI: 10.20914/2310-1202-2024-3-282-288
Текст научной статьи Exploring the influence of mechanical and physical characteristics on transdermal patches: a study on polymeric films composed of hyaluronic acid and zinc oxide nanoparticles
The use of transdermal patches is one of the most popular medical and cosmetic materials in the modern world, which are used in cosmetology, gynecology, rheumatology, neurology, oncology, etc. [1]. The structure and composition of the polymer matrix has a significant impact on the therapeutic effect of the patch for introducing an active pharmacological agent into the blood through diffusion through the skin.
Currently, the most common are matrix transdermal therapeutic systems, which, compared to membrane systems, are simpler to manufacture and use. In them, under the outer protective material, there is a polymer material with the drug evenly distributed in it (matrix). At the same time, this same material also acts as an adhesive [2].
Many materials can be used as the basis of polymer patches: silicon, stainless steel and polymer and composite matrix [3].
Since transdermal transport systems can provide a continuous, controlled supply of a drug agent into the blood over a long period (day, week)
and allow the concentration to be maintained at a minimum level for the required pharmacological effect, the physical and mechanical characteristics of the material are important parameters when designing such a system.
Drug release kinetics is a determining factor in dosing frequency and irritation control and is essentially a complete functional model created based on the optimal characteristics of the composite materials used [4]. It is important to note that in this case, peak concentrations of the active substance do not occur in the blood, which occurs with oral or injection administration. This reduces the risk of overdose, as well as toxic and negative side effects. The drug is released through diffusion from the surface of the material, through its erosion due to degradation of the polymer matrix, and finally released through the swollen polymer matrix [5]. A thorough understanding of these properties is the basis of manufacturing processes. Moreover, for polymer films to produce drug delivery patches, special attention is paid to high strength, elasticity, surface morphology, color or transparency, and biological characteristics. When obtaining a polymer
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License matrix for patches, low molecular weight polymers are most often used, such as hyaluronic acid, chitosan, alginate, agarose, starch, silk fibroin, collagen, gelatin, and many others [6]. Transdermal patches can be used when no other method of administration is possible, or their classical method of application is less effective. In the production of patches containing microneedles, which can be obtained from either inorganic scaffold coated with polymer compounds or obtained from hydrogels or polymer composites that have a delicate balance of strength to withstand insertion forces and stability to maintain their shape (Figure 1).
Corneocytes * dead cells
Boundary of lipophilic molecules
♦ Micro Needles patch
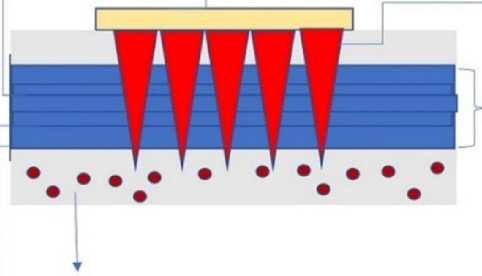
Dissolvable micro needles lOpmThickne ss in nonhydrated state
Systemic circulation channels
Lipid Bilayers ^
Figure 1. The process of painless microneedle insertion of the systemic circulation
The development of transdermal patches involves careful selection of a polymer matrix and modifier, each of which has unique properties such as elasticity, strength, and biocompatibility.
Among the wide variety of metal nanoparticles, zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles have such important properties as strong chemical and physical stability, high catalytic activity, and effective antimicrobial properties against polyantibiotic-resistant pathogenic microbial flora. These properties allow them to be used in biological testing, biological labeling and the development of drug delivery systems [7–9].
Zinc oxide nanoparticles, a unique class of substances, are not only small in size, comparable to the diameter of viruses, but also have a large surface area to volume ratio compared to larger particles or substances. Hyaluronic acid (HA), naturally produced in the human body, is biocompatible, biodegradable, and not only moisturizes, but also attracts and retains moisture in the epidermis and dermis. That is why HA was chosen as a polymer matrix and zinc oxide nanoparticles as a filler.
Materials and methods
During the work, polymer composite films based on HA and PEG and zinc oxide nanoparticles were obtained. During the experiment, the range of acid concentration used varied within 0.5-3 wt.% and zinc oxide, 0.1-0.3 wt.%. The synthesis of the polymer film was carried out in a Petri dish with preliminary dispersion of ZnO nanoparticles on a magnetic stirrer (Figure 2a) for 3 hours at a constant rotation speed of 100 rpm and a temperature of 50 oC and an ultrasonic stirrer (Figure 2b). for 60 minutes, temperature 45 °C. The films were poured into a plastic Petri dish to reduce the adhesion of the surface of the Petri dish to the polymer matrix. The drying time of the resulting films was 4 days at room temperature. Some of the films obtained are shown in Figure 2c and 2d.
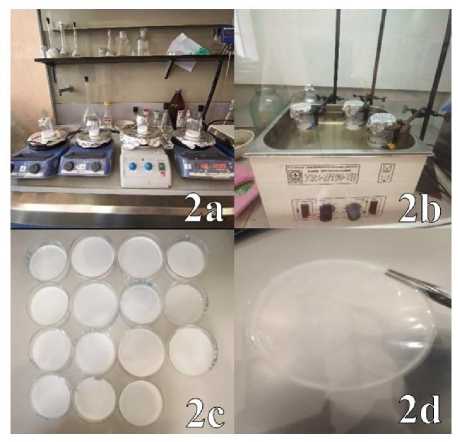

Figure 2. The process of formation of the transdermal patch: the magnetic stirrer (2a), the dispersion of the ZnO using ultrasound bath (2b), formed films (2c, 2d)
The FTIR analysis was carried out using a Tensor 37 IR spectrometer (Bruker) on a MIRacle Pike attenuated total internal reflection (ATR) attachment with a diamond-coated ZnSe crystal. A sample of each polymer film was placed on the FTIR instrument, and the machine was set at baseline with blank sample. The instrument passed infrared lights through the samples and the spectrum was recorded based on the absorption of different wavelengths from 4000 to 400cm-1.
The morphology of the polymer films was studied using an STM6 optical microscope (Olympus) in polarized transmission mode at various magnifications using an objective from 5x to 100x.
Characterization on physical and mechanical properties were studied as follows. Tensile testing of samples of the resulting composite polymer material was carried out according to the requirements on an Instron 5943 testing machine. The test method complies with the requirements of GOST 14236-81 (ST SEV 1490-79) «Polymer films. Tensile test method», GOST 11262-2017 (ISO 527-2:2012) «Plastics. Tensile test method» and ASTM D882-18 «Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic Sheeting». The Test specimens were prepared in compliance with the requirements of GOST 12423-2013 (ISO 291:2008) «Plastics. Conditions for conditioning and testing (samples)».
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) measurement was carried out using a Libra 209 F1 thermogravi-metric analyzer (Netzsch). The change in mass for the sample was measured using TGA, the sample was cut into smaller pieces and placed on TGA instruments, the sample was heated up in a controlled atmosphere (nitrogen) and the mass differentiation was recorded as the temperature increased.
Results and discussions
FTIR analysis. FTIR analysis was done on the characterization peak of the resulting spectrum which corresponds to the functional group of HA and ZnO. Figure 3 shows FTIR spectra of HA-ZnO composites obtained using solution method. No obvious difference was observed from the FTIR spectra of HA-ZnO filled with different concentration of ZnO, i.e., the structure of HA-ZnO composites was not affected by the filling with nanoparticles. A strong absorption band was observed at 3435.24 cm-1, indicating OH and NH stretching vibrations; the band at 2919.30 cm-1 indicates CH symmetrical and CH2 asymmetrical stretching; the band at 1256.81 cm-1 can be attributed to v(C-O) (of COOH). The absorption bands at ~1155.32 cm-1, 1084.82 cm-1, 1040.67 cm-1, and 944.61 cm-1 are typical for carbohydrates, and the bands at 1632.53 cm-1, 1553.51 cm-1, and 1320.33 cm-1 can be assigned to amide I, II, and III. The band at 1416.39 cm-1 is assigned to symmetric C-O stretching vibrations [10–20].
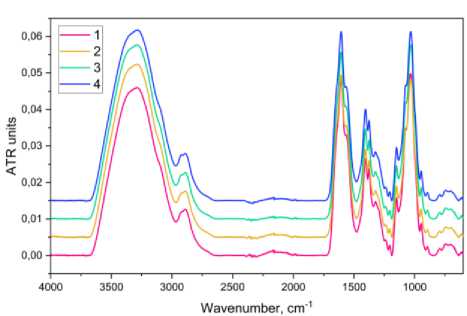
Figure 3. ATR-FTIR spectra of HA film filled with ZnO: 1 – HA; 2 – HA+2% of ZnO; 3 – HA+5% of ZnO; 4 – HA+7% of ZnO.
Optical microscopy. Figure 4 shows micrographs of the resulting polymer films based on HA and zinc oxide nanoparticles. As can be seen from Figure 4, the surfaces of polymer films are rough, and an increase in the proportion of zinc nanoparticles by more than 5 % leads to their aggregation. The effect of clustering of zinc oxide nanoparticles can affect the mechanical properties of the polymer membrane, thereby affecting its strength and flexibility, as shown below.
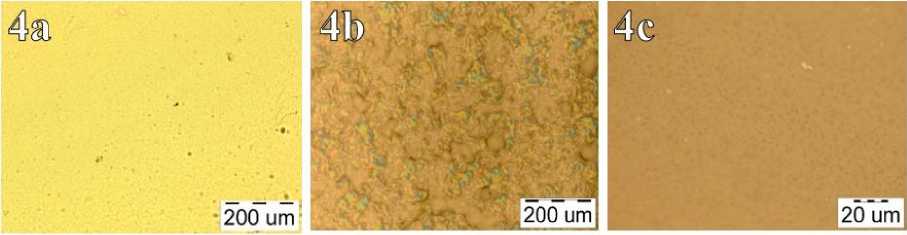
Figure 4. The surface morphology of the HA (0.2%) films: (4a) 7% of ZnO, (4b) 5 % of ZnO and (4c) 0 % of ZnO
Characterization on physical and mechanical properties. The various samples of thin film were cut into stripes of equal length and breadth of 5cm by 1 cm respectively and the thickness was measured using a digital micrometer.
Each film was cut into 5 to 6 pieces of stripes and measured separately. The measured thickness was taken within the 3mm range from the middle to both end for each stripes in a film and the average thickness was recorded, see Table 1 and Table 2.
As can be seen from Table 2, all the obtained polymer films based on HA and ZnO nanoparticles have a low relative elongation value, which is in the range of 2 - 7% with an increase in the concentration of nanoparticles from 1% to 10 wt.%. It is natural that the addition of zinc oxide to the polymer matrix leads to a decrease in the relative elongation compared to an unfilled polymer film. At the same time, the tensile strength of polymer films based on HA and zinc oxide naturally increases by 1.5 - 3.5 times with the addition of nanoparticles compared to an unfilled polymer film. It should be noted that the increase is extreme: first, the strength value increases and reaches a maximum value of 26.76 MPa at 5 wt.% zinc oxide. A further increase in the proportion of inorganic substances in the composition of the polymer matrix leads to a deterioration in the strength characteristics of the obtained polymer films, which is associated with the aggregation of nanoparticles, and consequently, a decrease in the tensile strength of the films.
Table 2.
Mechanical analysis of obtaining polymer films
|
Composition |
Tensile strength, MPa |
Extension, % |
Young's module, MPa |
|
HA0,2% Only |
7,69 |
4,22 |
145,26 |
|
HA0,2% +ZnO1% |
9,14 |
2,03 |
104,55 |
|
HA0,2% + ZnO 3% |
15,45 |
2,67 |
151,89 |
|
HA0,2% +ZnO5% |
26,76 |
4,87 |
273,10 |
|
HA0,2% + ZnO 7% |
25,50 |
4,49 |
292,66 |
|
HA0,2% +ZnO10% |
23,33 |
3,25 |
375,78 |
Table 1.
The display of obtained film thickness sizes
|
Composite material |
Thickness (mm) |
|
HA0,2% only |
0,012 |
|
HA0,2% +ZnO1% |
0,012 |
|
HA0,2% +ZnO3% |
0,012 |
|
HA0,2% +ZnO5% |
0,012 |
|
HA0,2% +ZnO7% |
0,013 |
|
HA0,2% +ZnO10% |
0,018 |
Thermogravimetric analysis. The detail of the result is the graphical illustration of mass plotted against temperature as shown in Figure 5. The residue left after the decomposition provides insight into the inorganic component such as zinc oxide. Figure 5 shows the TGA and DTG curves of HA powder and HA-based composites with different ZnO loading percentages. The TGA curve for pure HA has 2 stages of weight loss. The first stage of weight loss from 25 to 200 °C corresponds to the evaporation of water and the stage of polysaccharide destruction at 210-320. As can be seen from the DTG curves, the temperature of water evaporation from the original HA powder is lower than for composites filled with zinc oxide, that is, zinc oxide nanoparticles retain moisture in the composite more strongly. In addition, filling HA with zinc oxide leads to a slight loss in the thermal stability of the material, which is evident from the decrease in the temperature at which the polymer matrix begins to degrade (Table 3)
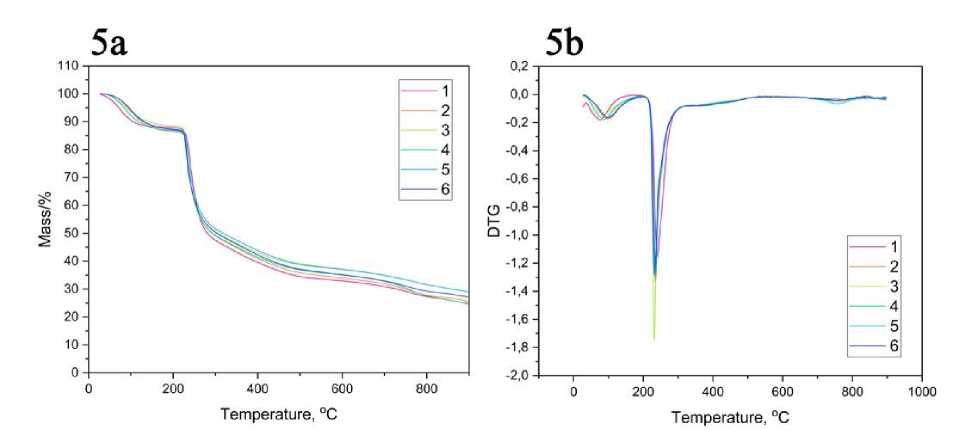
Figure 5. TGA (5a) and DTG (5b) curves of HA powder (1) and HA-ZnO composites with 1% (2), 3% (3), 5% (4), 7% (5), 10% (6) ZnO
|
Sample |
1 st step |
2 nd step |
||
|
% Н 2 О |
T max, °C |
T onset, °C |
T max, °C |
|
|
HA powder |
12 |
75 |
231 |
240 |
|
1% ZnO |
13,5 |
99 |
228 |
235 |
|
3% ZnO |
11,2 |
83 |
227 |
232 |
|
5% ZnO |
13,2 |
87 |
228 |
235 |
|
7% ZnO |
12,6 |
97 |
229 |
236 |
|
10% ZnO |
12,8 |
97 |
227 |
232 |
Kolawole S. Dada et al. Proceedings of VSUET, 2024, vol. 86, no. 3, pp. 282-288
Table 3.
Thermal properties of HA-ZnO composites
Conclusion
The behavioral properties patterns of the polymer film made from HA-ZnO with various concentration percentages of ZnO nanoparticles filler dis-play a significant variation in strength at break region, elongation at break, and finally Young's modulus. There is a trend reflected, as the percentage of ZnO increases from 1% to 10%, the strength at break concisely increases too, getting to a peak at 5% of ZnO concentration, thereafter there is an observed slight decrease. This infers to an optimal concentration range for improving the mechanical property of the polymer composite for obtained polymer films as a base for creating transdermal patches.
Maintaining the transdermal patch's comfort as it conforms to the skin's structure over the course of its intended wear period requires balancing these features which are important for future researching.
Список литературы Exploring the influence of mechanical and physical characteristics on transdermal patches: a study on polymeric films composed of hyaluronic acid and zinc oxide nanoparticles
- Pastore M. N., Kalia Y. N., Horstmann M., Roberts M. S. Transdermal patches: history, development and pharmacology. British journal of pharmacology. 2015. vol. 172. no. 9. pp. 2179-2209. DOI: 10.1111/bph.13059
- Wong W. F., Ang K. P., Sethi G., Looi C. Y. Recent Advancement of Medical Patch for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Medicina (B Aires). 2023. vol. 59. no. 4. p. 778. DOI: 10.3390/medicina59040778 EDN: BUAPKY
- Raju N. S., Krishnaswami V., Vijayaraghavalu S., Kandasamy R. Transdermal and bioactive nanocarriers. Nanocosmetics. 2020. pp. 17-33. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-822286-7.00002-4
- Fu Y., Kao W. J. Drug release kinetics and transport mechanisms of non-degradable and degradable polymeric delivery systems. Expert opinion on drug delivery. 2010. vol. 7. no. 4. pp. 429-444. DOI: 10.1517/17425241003602259
- Kamaly N., Yameen B., Wu J., Farokhzad O.C. Degradable Controlled-Release Polymers and Polymeric Nanoparticles: Mechanisms of Controlling Drug Release. Chemical reviews. 2016. vol. 116. no. 4. pp. 2602-2663. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00346 EDN: YWHZID
- Pires, P. C., Mascarenhas-Melo, F., Pedrosa, K., Lopes, D., Lopes, J., Macário-Soares, A.,... Paiva-Santos, A. C. Polymer-based biomaterials for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications: A focus on topical drug administration. European Polymer Journal. 2023. vol. 187. p. 111868. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2023.111868
- Dovnar R. I., Smotryn S. M., Anufrik S. S., Sakalova T. M., Anuchin S. N., Iaskevich N. N. Antibacterial and physico-chemical properties of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Journal of the Grodno State Medical University. 2022. vol. 20. no. 1. pp. 98-107. DOI: 10.25298/2221-8785-2022-20-1-98-107 EDN: SLIUXX
- Nair, S., Sasidharan, A., Divya Rani, V. V., Menon, D., Nair, S., Manzoor, K., Raina, S. Role of size scale of ZnO nanoparticles and microparticles on toxicity toward bacteria and osteoblast cancer cells. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine. 2009. vol. 20. no. S1. pp. 235-241. DOI: 10.1007/s10856-008-3548-5 EDN: ELUPCG
- Wahab, R., Kaushik, N. K., Verma, A. K., Mishra, A., Hwang, I. H., Yang, Y. B.,... Kim, Y. S. Fabrication and growth mechanism of ZnO nanostructures and their cytotoxic effect on human brain tumor U87, cervical cancer HeLa, and normal HEK cells. JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry. 2011. vol. 16. no. 3. pp. 431-442. DOI: 10.1007/s00775-010-0740-0 EDN: BZAKXM
- Gilli R., Kacuráková M., Mathlouthi M., Navarini L., Paoletti S. FTIR studies of sodium hyaluronate and its oligomers in the amorphous solid phase and in aqueous solution. Carbohydrate Research. 1994. vol. 263. no. 2. pp. 315-326. DOI: 10.1016/0008-6215(94)00147-2 EDN: XYWIIL


