Expression of TDM resistance-linked ABC1 and ABC2 transporters in virulent and avirulent Cochliobolus sativus pathotypes
Автор: Jawhar M., Al-shehadah E.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Spot blotch (SB), caused by the fungus Cochliobolus sativus , is most efficiently controlled by using fungicides such as triadimefon (TDM) a triazole group member. This pathogen has the ability to develop resistance against TDM due to its high genetic variability, short lifecycle and plentiful inoculum yield. However, no experimental evidences of the direct contribution of ABC transporters in TDM resistance are available so far. Therefore, changes in ABC1 and ABC2 genes in avirulent Pt1 and virulent Pt4 C. sativus pathotypes were monitored at early time points of TDM treatments using quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR). Our results revealed that ABC1 and ABC2 expressions increased in both virulent and avirulent pathotypes at 24 hours post TDM treatments in comparison with non-treated controls. The most outstanding differences in ABC1 and ABC2 expressions were 3.2 and 1.2-fold, in avirulent Pt1 and 4.2 and 1.5-fold respectively, for virulent Pt4, respectively, after 48 hours of 0.125 µg mL-1TDM treatment. According to results, it is likely that ABC1 and ABC2 genes might play a role in signaling actions during C. sativus exposure to triazole fungicides.
Cochliobolus sativus, abc1, abc2, triazole, qrt-pcr
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143183432
IDR: 143183432
Текст научной статьи Expression of TDM resistance-linked ABC1 and ABC2 transporters in virulent and avirulent Cochliobolus sativus pathotypes
Cochliobolus sativus (Ito & Kurib.) Drechsl. ex Dast. [anamorph: Bipolaris sorokiniana (Sacc. in Sorok.) Shoem.], the causal agent of SB, is an important fungal pathogen that causes substantial yield losses of barley ( Hordeum vulgare ) globally (Al-Sadi, 2021). Using barley resistant genotypes is considered to be the most practical process of managing SB. However, this genotype resistance is not stable due to genotypes specific physiological races of C. sativus, known to spread over growing seasons, have developed on genotypes once supposed to be highly SB resistant (Kumar et al., 2002). Therefore, in the deficiency of varietal resistance, the most active SB management practice is to make multiple protective fungicide applications during the growing season (Leng et al., 2016).
Different fungicides groups have been used on barley worldwide. Triazole group (e.g. triadimefon; TDM) has been demonstrated to be very effective for controlling SB disease (Somani et al., 2019). However, C. sativus poses a high risk to develop resistance against fungicides like TDM, due to its high genetic variability, short lifecycle and abundant inoculum production (Neupane et al., 2010; Gupta et al., 2018). Therefore, understanding C. sativus resistance mechanisms to TDM fungicide, can help to start new strategies for sustainable fungicide management during the growing season.
Fungal pathogens can rapidly develop molecular mechanisms of resistance to triazoles as a result of selective pressure by the continued use of regular or sub-regular dosages of fungicide (Deising et al., 2008; Gupta et al., 2018). Several molecular works have reported that in phytopathogenic fungi, the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter proteins are involved in resistance mechanisms against cytotoxic compounds or fungicides for successful disease development (Kim et al., 2013). They resist to toxic substances, either sequestering the toxic hydrophobic compounds into specialized designated organelles, or by directing them for secretion (Rees et al., 2009). ABC proteins play important roles in antifungal resistance in many species of filamentous fungi (including phytopathogens, Gibberella pulicaris and Penicillium marneffei) against fungicides (Fleissner et al., 2002; Panapruksachat et al., 2016).
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) has been proved to be a valuable and effective technique for measuring changes in ABC expressions due to its high sensitivity (Calcagno and Ambudkar 2010). Understanding the evolution of fungicide resistance in C. sativus population is essential to improve the processing SB disease management program, and for developing management strategies for fungicide resistance. Therefore, the current work aimed to evaluate the changes in ABC1 and ABC2 expressions in two major Syrian C. sativus avirulent (Pt1) and virulent (Pt4) pathotypes at early time series of TDM treatment using qRT-PCR.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
-
C. sativus pathotypes
The two Syrian C. sativus pathotypes Pt1 (avirulent) and Pt4 (Virulent) were used in this study (Arabi and Jawhar 2003). They were grown in Petri dishes containing potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium (DIFCO, Detroit, MI. USA) at 22 °C for10 days in the dark.
Fungicide
The commercial fungicide triadimefon (TDM) [1-(4-chlorophenoxy)-3,3- dimethyl-1-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl) butan-2-one] (25% w/v Bayleton, Bayer, India Ltd, Mumbai) against SB was used in this work. It is a systemic triazole fungicide, that is 1-hydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl) butan-2-one in which the hydroxyl hydrogen is replaced by a 4-chlorophenyl group.
RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis
RNA was extracted from mycelium of each C. sativus pathotypes Pt1 and Pt4 at 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours post TDM treatments using Nucleotrap mRNA mini kit (Macherey-Nagel, MN, Germany). At the same time points, mycelia from non-treated Petri dishes were used as a control. First strand complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized using the Quanti Tect Reverse Transcription Kit (Qiagen) per the manufacturer ’s instructions.
Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR)
The expressions of ABC1 and ABC2 were assayed using SYBR Green Master kit (Roche). Sequence of RT-PCR primers is given in Table 1. The threshold cycle (Ct) value was automatically determined for each reaction by the real time PCR system with default parameters. The final Ct values represented the mean of three replicates and the coefficient of variance was calculated to evaluate the variation of Ct values.
Data analysis
Average Ct values were calculated from the triplicate experiment conducted for each gene, with the ΔCT value determined by subtracting the average Ct value of genes from the Ct value of the EF1α gene. Finally, the equation 2-ΔΔCT was used to estimate relative expression levels, and the fold change in putative target gene expression levels was determined as described by Livak and Schmittgen (2001), with EF1α as a reference gene. Standard deviation was calculated from the replicated experimental data.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this investigation, changes in ABC1 and ABC2 expressions in two C. sativus pathotypes avirulent (Pt1) and virulent (Pt2) pathotypes were monitored at early time series following TDM treatment using qRT-PCR. Data showed that their expressions were significantly upregulated in both pathotypes at 24 hpi, TDM treatment (Figs. 1, 2, 3 and 4), suggesting that robust resistance responses are early initiated. However, the expressed patterns were recorded as cooperative functions which occur after 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours treated by TDM. For instance, ABC1 and ABC2 expressions were 3.2 and 1.2-fold respectively, in avirulent Pt1 and 4.2 and 1.5-fold, for virulent Pt4, respectively, after 48 hours of 0.125 µg mL-1TDM treatment. (Fig. 2).
It has been reported that ABC transporters use ATP energy to transfer substrates as diverse as carboxylates, lipids, pheromones, and xenobiotics (fungicides, antifungal compounds) across cell membranes (Baral 2017). The ABC proteins may serve as importers or exporters, while some members are not involved in transport processes. These different mechanisms might propose that the studied genes might play roles in signaling events during C. sativus exposure to a triazole fungicide during several growing seasons. These findings are supported by the results of Somani et al. (2019) who reported that a strong selection pressure during several years and frequent applications of triazoles for spot blotch control lead to emergence of resistant C. sativus populations.
Our results are in agreement with Fleissner et al. (2002) Who found that in the Fusarium species Gibberella pulicaris (anamorph: Fusarium sambuinum ) ABC1 was reported to be a virulence factor that contributed to the tolerance of the phytoalexin rishitin, a defence secondary metabolite, in potato tubers. In addition, the F. culmorum ABC1 , was reported to be an important virulence factor that protects this plant pathogen against barley phytoalexins and the triazole antifungal (Skov et al. 2004 . In addition, it has been found that the transporter gene ABC2 involved in fungicide susceptibility in rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea (Lee et al., 2005 .
Table 1. Properties and nucleotide sequences of primers used in this study
|
Gene |
Gene description |
Sequence |
|
EF1α |
Elongation factor-1 Alapha |
GGCTGATTGTGCTGTGCTTA TGGTGGCATCCATCTTGTTA GCCTGGCAGGTGGAAGACAAATAC |
|
ABC1 |
ATP_ bining cassette transporter |
ATGGCCAAAATCACAAGGGGTTAGC |
|
ABC2 |
ATP_ bining cassette transporter |
TGTGTGGGCAACTGCATCG GTTGGTTTCCATTTCAGATGACATCCG |
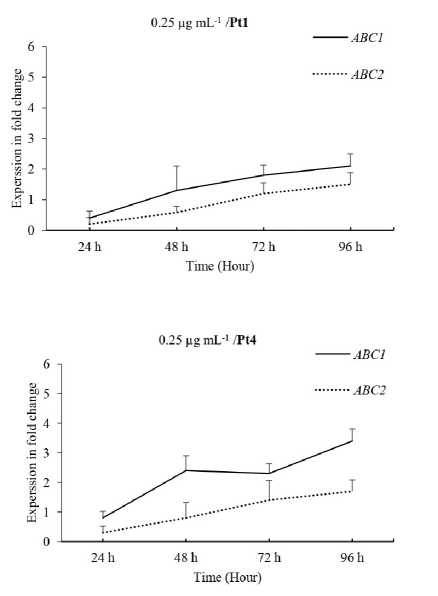
Figure 1. Relative expression profiles of ABC1 and ABC2 genes in the avirulent pt1 and virulent Pt4 C. sativus pathotypes following TDM treatment 0.25 µg mL -1. Error bars are representative of the standard error (Mean ± SD, n 3). Data are normalized to Elongation factor 1α ( EF-1α ) gene expression level (to the calibrator, Control 0 h, taken as 1.00).
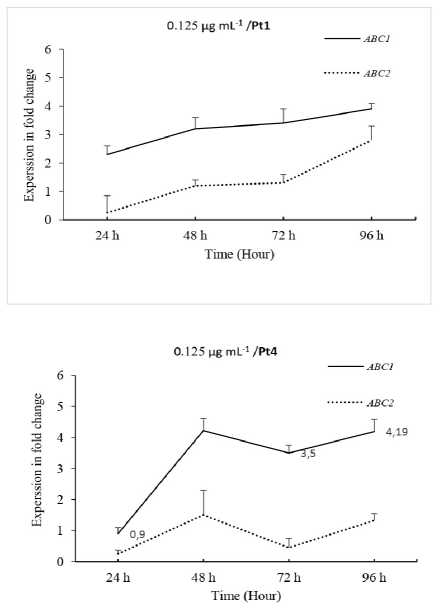
Figure 2. Relative expression profiles of ABC1 and ABC2 genes in the avirulent pt1 and virulent Pt4 C. sativus pathotypes following TDM treatment 0.125 µg mL-1. Error bars are representative of the standard error (Mean ± SD, n 3). Data are normalized to Elongation factor 1α ( EF-1α ) gene expression level (to the calibrator, Control 0 h, taken as 1.00).
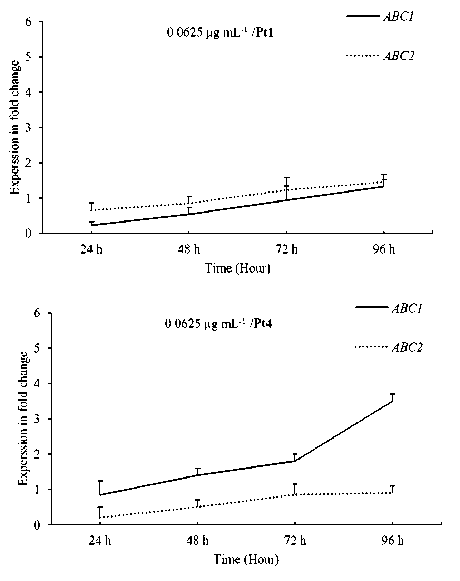
Figure 3. Relative expression profiles of ABC1 and ABC2 genes in the avirulent pt1 and virulent Pt4 C. sativus pathotypes following TDM treatment 0.0625 µg mL-1. Error bars are representative of the standard error (Mean ± SD, n 3). Data are normalized to Elongation factor 1α ( EF-1α ) gene expression level (to the calibrator, Control 0 h, taken as 1.00).
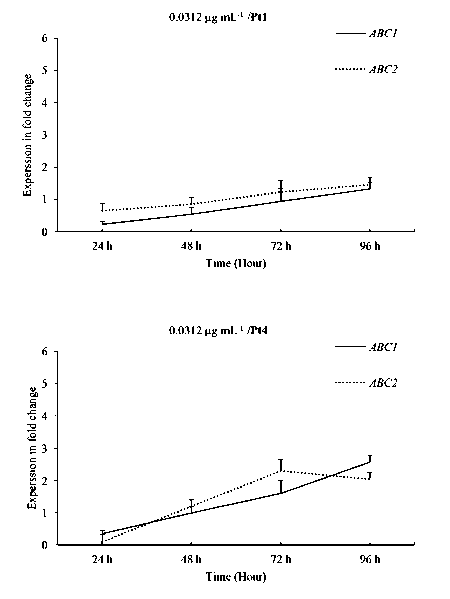
Figure 4. Relative expression profiles of ABC1 and ABC2 genes in the avirulent pt1 and virulent Pt4 C. sativus pathotypes following TDM treatment 0.0312 µg mL-1. Error bars are representative of the standard error (Mean ± SD, n 3). Data are normalized to Elongation factor 1α ( EF-1α ) gene expression level (to the calibrator, Control 0 h, taken as 1.00).
CONCLUSION
The results of the present study revealed significant increases in ABC1 and ABC2 expressions found in the virulent and avirulent C. sativus pathotypes at early time points following TDM application as compared with the non-treated ones, which is of value to give us an indicator about their roles in signaling events during exposure to a triazole fungicide. Furthermore, the expression of the genes was higher in the virulent pathotype Pt4 as compared to the avirulent pathotype Pt1, this might suggest their roles in the C. sativus pathogenicity that need further experiments.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors present their special thanks to the Director General of AECS and the Head of Biotechnology Department for their help throughout the period of this research. They would also like to thank Dr. A. Al-Daoude for critical reading of the manuscript.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Expression of TDM resistance-linked ABC1 and ABC2 transporters in virulent and avirulent Cochliobolus sativus pathotypes
- Al-Sadi AM. (2021). Bipolaris sorokiniana-induced black point, common root rot and spot blotch diseases of wheat: A review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 11: 584899.
- Arabi MIE, Jawhar M. (2003). Pathotypes of Cochliobolus sativus (spot blotch) on barley in Syria, J. Plant Pathol., 85: 193-196. Baral, B. (2017). Evolutionary trajectories of entomopathogenic fungi ABC transporters. Advances in genetics, 98: 117-154.
- Calcagno AM, Ambudkar SV. (2010). Analysis of expression of drug resistance-linked ABC transporters in cancer cells by quantitative RT-PCR. Methods Mol Biol., 637: 121-32.
- Deising HB, Reimann S, Pascholati SF. (2008). Mechanisms and significance of fungicide resistance, Braz. J. Microbiol., 39: 286-295.
- Fleissner A, Sopalla C, Weltring KM. (2002). An ATP-phytoalexins and virulence on potato tubers. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact., 15: 102-108.
- Gupta PK, Vasistha NK, Aggarwal R, Joshi AK. (2018). Biology of B. sorokiniana (syn. Cochliobolus sativus) in genomics era, J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol., 27: 123-138.
- Kim Y, Park SY, Kim D, Choi J, Lee YH, Lee JH, Choi W, (2013). Genome-scale analysis of ABC transporter genes and characterization of the ABCC type transporter genes in Magnaporthe oryzae, Genomics, 101: 354-361
- Kumar J, Schäfer P, Hückelhoven R, et al. (2002). Bipolaris sorokiniana, a cereal pathogen of global concern: cytological and molecular approaches towards better controldouble dagger. Mol. Plant Pathol., 3: 185-195.
- Lee YJ, Yamamoto K, Hamamoto H, Nakaune R, Hibi T. (2005). A Novel ABC transporter gene ABC2 involved in multidrug susceptibility but not pathogenicity in rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol., 81: 13-23.
- Leng Y, Wang R, Ali S, Zhao M, Zhong S. (2016). Sources and genetics of spot blotch resistance to a new pathotype of Cochliobolus sativus in the USDA small grains collection, Plant Dis., 100: 1988-1993.
- Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method, Methods, 25: 402-408.
- Neupane AC, Sharma RC, Duveiller E, Shrestha, SM. 2010. Sources of Cochliobolus sativus inoculum causing spot blotch under warm wheat growing conditions in South Asia, Cereal Res. Comm., 38: 541-549.
- Panapruksachat S, Iwatani S, Oura T, Vanittanakom N, Chindamporn A, Niimi K, et al. 2016. Identification and functional characterization of Penicillium marneffei pleiotropic drug resistance transporters ABC1 and ABC2. Med. Mycol., 54: 478-491.
- Rees DC, Johnson E, Lewinson O. (2009). ABC transporters the power to change. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 10: 218-227.
- Somani D, Adhav R, Prashant R, Kadoo NY. (2019). Transcriptomics analysis of propiconazole-treated Cochliobolus sativus reveals new putative azole targets in the plant pathogen, Funct. Integr.
- Genomics, 9: 453-465. Skov J, Lemmens M, Giese H. (2004). Role of a Fusarium culmorum ABC transporter (FcABCl) during infection of wheat and barley. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol., 64: 245-254.


