Features of Regulation and Implementation of Interaction between the Population and Authorities in the System of Strategic Territorial Development in the Region (On the Example of the Murmansk Oblast)
Автор: Badylevich R.V., Kondratovich D.L.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Northern and arctic societies
Статья в выпуске: 60, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The study examines the issues of organizing the interaction of the population with regional and municipal authorities in the strategic planning system. The research investigates the methodological foundations for implementing tools to engage citizens in the development and implementation of strategic documents, presents their classification, and describes the specifics of regulatory control in Russian practice. As part of the practical study, an analysis of the regulation and implementation of public interaction with local and regional authorities in the system of territorial development of the Murmansk Oblast was carried out, an assessment of the implementation of formal and informal methods of public participation in the system of solving issues of local importance and the formation and implementation of strategic planning documents was given. It has been concluded that, despite the positive assessment of the experience of interaction between the population and government authorities in the system of strategic territorial development at the regional level, there is considerable potential for improving the effectiveness of such tools at the municipal level. At present, it seems appropriate to optimize public discussions, public debates, and surveys by strengthening the regulation of the requirements for their conduct and regulating the procedure for recording their results, implementing collective participation of the population in the processes of developing and implementing strategic planning documents at the municipal level, involving citizens in strategic planning processes not only at the stage of developing and approving documents, but also at the stages of setting goals, as well as monitoring and controlling their implementation.
Strategic planning, strategic development documents, regional level, municipal level, population, local government, Murmansk Oblast
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148331897
IDR: 148331897 | УДК: 332.024(470.21)(045) | DOI: 10.37482/issn2221-2698.2025.60.193
Текст научной статьи Features of Regulation and Implementation of Interaction between the Population and Authorities in the System of Strategic Territorial Development in the Region (On the Example of the Murmansk Oblast)
DOI:
The issues of organizing interaction between the population and government bodies in key areas of regional development are currently among the top priorities for several reasons.
Firstly, this is due to the general principles of local government in the Russian Federation. Thus, according to the Federal Law of 06.10.2003 N 131-FZ “On the General Principles of Local Self-Government Organization in the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 131-FZ), public participation in local government takes various forms: local referendums, voting, legislative initiatives, public hearings, citizens’ appeals to various government bodies, municipal elections, citizens’ meetings, citizens’ assemblies, territorial public self-government, etc.
Secondly, the priority use of strategic planning and goal-setting principles for territorial development in Russia, based on the development of long-term documents and programs, in the system of development, adoption, and implementation of which, according to Article 8 of Federal Law No. 172-FZ of June 28, 2014, “On Strategic Planning in the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 172-FZ), the population is assigned an active role.
The main goal of strategic planning in municipalities is to elaborate development targets that balance the interests of all relevant stakeholders: the population, economic entities, and government authorities. In these conditions, ensuring the participation of the entire spectrum of entities in the system of developing a set of strategic documents is a key factor in the effectiveness of the system for solving the main municipal problems and creating a favorable socio-economic environment. Building effective relationships with the population allows government bodies to respond more effectively to emerging challenges, to identify problem areas that require the most urgent attention, to respond to ongoing crises and citizens’ requests [1, p. 76]. When citizens’ interests are taken into account, it is easier to create a favorable urban environment, attractive living and business conditions, and effectively realize the potential of the municipality. In addition, involving the population in the strategic planning process increases citizens’ engagement in public processes and improves the population’s literacy in the organization and implementation of local self-government. The importance of involving the population in strategic planning processes is recognized not only in domestic science and practice [2], but also abroad [3].
Currently, the legislation regulates in sufficient detail the range of documents within the framework of strategic planning at the federal and regional levels, the procedure for their formation and the process of implementation. At the same time, at the municipal level, issues of implementing strategic planning are regulated to a lesser extent. In particular, Federal Law No. 172-FZ includes the following in the list of strategic planning documents: the strategy for the socioeconomic development of the municipality; the action plan for the implementation of the strategy for socio-economic development; the forecast of the socio-economic development of the municipality for a medium or long term; the budget forecast for the municipality for a long term; municipal programs. This list is not exhaustive and is supplemented by other legislative acts. Thus, in recent years, master plans have become an increasingly common document for the spatial devel-
NORTHERN AND ARCTIC SOCIETIES
Roman V. Badylevich, Dmitriy L. Kondratovich. Features of Regulation and Implementation … opment of municipalities, and regulatory framework for their development is being actively formed in the Russian Federation 1.
The sequence and order of developing strategic planning documents at the municipal level are determined by local government bodies in accordance with municipal regulatory legal acts. Despite the fact that the legislation of the Russian Federation establishes the creation of conditions that ensure the involvement of citizens in the strategic planning process as one of the tasks of strategic planning at all levels of management, in practice this area of implementing strategic planning remains poorly regulated.
Taking into account the approaches to regulating and implementing strategic planning processes at the regional and municipal levels, the possibility of fully involving the population in the process of implementing strategic planning can only be seen in the formation of an action plan for the implementation of a socio-economic development strategy and a relatively new tool for Russian practice — a master plan for the development of a municipal entity (Table 1).
Table 1 Possibility of involving the population in strategic planning processes at the municipal and regional levels for the main types of documents 2
|
Document |
Opportunity for public participation |
Participation level |
|
Strategy of socio-economic development of the municipality |
++ |
Informing, consulting |
|
Plan of activities for the implementation of the strategy of socio-economic development |
+++ |
Informing, consulting, participation |
|
Forecast of socio-economic development of the municipality for the medium or long term |
+ |
Informing |
|
Budget forecast of the municipality for the long term |
+ |
Informing |
|
Municipal development programs |
+ |
Informing |
|
Master plans for the development of municipalities |
+++ |
Informing, consulting, participation |
At the same time, the current practice of strategic planning demonstrates predominantly formal participation of the population. In particular, government officials and scientists point to the low level of involvement of the local population in the processes of strategic planning in municipalities 3; formal methods of conducting public hearings in the process of reviewing and approving city development strategies, during the organization of which many aspects remain unregulated; weak information support for the organization of events in the system of public partici-
NORTHERN AND ARCTIC SOCIETIES
Roman V. Badylevich, Dmitriy L. Kondratovich. Features of Regulation and Implementation … pation in the strategic planning process [4, p. 38], an “opaque” system for monitoring the implementation of proposals and comments received from the population [5, p. 146], etc.
As a rule, in small municipalities, the group of people who submit proposals and comments is small, and the weak development of the factual basis and the low level of competence of the population in matters of municipal management lead to the fact that the overwhelming majority of citizens’ initiatives are either not considered or rejected by the authorities. Collective forms of public organization of the population, which would allow for the formation of competently presented and legislatively substantiated initiatives, are currently practically absent at the municipal level. Thus, the institute of strategic planning, which is intended to be the main mechanism for the development of municipalities based on the formation of a consolidated vision of strategic goals, taking into account a wide range of opinions of various entities living and conducting economic activities in the municipality, is currently not in sufficient demand. The presence of methodological gaps in regulation and problems in the practical implementation of the institute of population participation in strategic planning processes determined the choice of the research goal and objectives.
The aim of the study is to determine possible directions for improving the effectiveness of tools for public interaction with local and regional authorities based on a study of the application of tools for involving the population in issues of implementing strategic territorial development in a specific region.
In order to achieve the goal, the following tasks will be addressed in this paper:
-
• to form a systematized list of tools for public interaction with local and regional authorities in the territorial development system based on a study of the regulatory framework;
-
• to analyze and identify problems in the regulation and implementation of tools for public interaction with local and regional authorities in the Murmansk Oblast;
-
• to present possible directions for improving the effectiveness of tools of interaction between the population and local and regional authorities in the territorial development system of the Murmansk Oblast.
The information base of the study consisted of data published by regional and municipal authorities of the Murmansk Oblast, including the Ministry of Information Policy of the Murmansk Oblast; statistical data of official and unofficial accounts in social networks; information collected by the authors while participating in various events organized by city administrations for the population.
The scientific novelty of the study is based on the use of new methods in assessing the effectiveness of interaction between the population and authorities in the territorial development system, based on the authors’ approach to the classification of interaction tools, as well as the use of modern analytical tools, including Internet resources.
The practical significance of the research is based on the possibility of using the results and recommendations presented by the authors in the system of implementation of regional and local governance in the Murmansk Oblast, adjusting the regulatory framework for interaction between the population and government bodies (city charters, municipal regulations on conducting population surveys, public discussions and public hearings), expanding the functionality of the information tools used by government bodies.
Methodological foundations for classification, regulation and implementation of tools for interaction between the population and local authorities in the territorial development system
The range of different forms of public participation in the strategic planning processes of municipal entities is quite broad. Researchers use various principles and criteria for their classification and grouping.
S.A. Revyakin provides a classification based on the degree of influence that citizens have on the decisions made [6]. Within the framework of this classification, the author identifies the following formats: “imitation (absence) of participation”, in which the population is essentially assigned the role of consumers of decisions of government bodies; “symbolic participation”, in which citizens are informed about the processes of strategic planning and are passive participants in consultations (in contrast to the previous format, in this case the process of strategic planning is more transparent); “real participation”, in which citizens actively take part in the processes of strategic planning. In the latter case, S.A. Revyakin identifies proactive analysis of interest groups, brainstorming and various group discussions, surveys, creation of temporary or permanent structures (working groups), and methods of public support in the form of grants, consultations and training as the most effective forms of citizens’ participation.
A.Yu. Volkhonskiy, V.V. Fedorchenko and N.N. Yakimchuk propose a classification of public participation based on normative regulation and consolidation [7]. Within the framework of the classification, the authors distinguish forms provided for by federal legislation on local selfgovernment (local referendums, public hearings, meetings at the place of residence, territorial public self-government, citizen surveys, public discussion during the preparation and approval of strategic planning documents, etc.); forms recommended for use within the framework of programs implemented in accordance with the federal project “Formation of a Comfortable Urban Environment”; and forms provided for by regional legislation and municipal legal acts (for example, public councils, participatory budgeting). In addition, the authors propose four levels of public participation in the strategic planning process (information, consultation, participation, partnership), for each of which they provide a wide range of forms.
The approach presented in the work of I.A. Sekushina is quite interesting; according to it, the mechanisms of public participation in state and municipal governance are conditionally divided into formal, i.e. legally regulated (elections; referendums; citizens’ assemblies; initiative projects; citizen surveys; the institution of elders of rural settlements; public hearings and discussions; conferences and meetings of citizens; territorial public self-government; citizens’ appeals to gov- ernment bodies, etc.) and informal, i.e. not legally enshrined, but playing a significant role in management processes for the development of territories (activities of volunteer and charitable organizations; creation of initiative groups; discussion of issues related to the development of settlements on official websites and social networks, etc.) [8].
The literature widely covers issues of electronic interaction between authorities and the population at the local and regional levels, based on official websites and accounts of administrations, increasingly popular crowdsourcing platforms [9], as well as smart technologies [10]. At the same time, the implementation of such experience in practice is given attention both in the domestic scientific field [11] and abroad [12].
Based on the generalization of the views of various researchers on the issues of classifying the forms of population participation in the local government system, the authors formed a system of tools for interaction between the population and local authorities, used in the processes of strategic territorial development (Table 2).
Table 2 System of tools for interaction between the population and local authorities, used in the processes of strategic territorial development 4
|
Information tools |
Consulting |
Participation and partnership |
|
|
Formal (regulated) |
Posting on the administration website. |
Methods for taking into account public opinion on issues of strategic planning (public hearings, public discussions, citizen surveys). |
Instruments for uniting citizens with possibility of presenting initiative projects (territorial public selfgovernment, meetings, conferences of citizens (meetings of delegates), initiative groups); creation of mechanisms for projects cofinancing (initiative budgeting, grant funds, closed and open mutual investment funds); citizens’ appeals to local government bodies |
|
Informal (initiative) |
Placement of information in print media, social networks, popular Internet resources, stands and other types of outdoor advertising. |
Interviews, including in-depth ones; focus groups, brainstorming sessions and various group discussions; online surveys, online discussions and online questionnaires; exhibitions of projects within the framework of strategic planning documents. |
Conducting sessions in the form of participatory design; expert sessions; author supervision of the implementation of the concept during the preparation of the document; creation of temporary or permanent structures (working groups); competitions of projects and initiatives. |
Formal (regulated) tools for involving the population in the process of municipal strategic planning are regulated by federal, regional and local normative documents, primarily by Federal Law No. 131-FZ (territorial public self-government, meetings, conferences of citizens (meetings of
NORTHERN AND ARCTIC SOCIETIES
Roman V. Badylevich, Dmitriy L. Kondratovich. Features of Regulation and Implementation … delegates), creation of initiative groups, public hearings, public discussions, surveys and appeals of citizens). Informal tools are applied at the initiative of regional and municipal authorities. Most often, the normative regulation of such tools is limited to mention in local regulations or is absent.
Analysis of regulation and implementation of tools for public interaction with local and regional authorities in the territorial development system of the Murmansk Oblast
This study analyses the involvement of citizens in the process of elaborating strategic municipal and regional development documents in the Murmansk Oblast.
The Murmansk Oblast was chosen as the object of the study for several reasons. On the one hand, this region is a fairly typical Arctic region, the development of which is one of the priorities of modern state policy in the Russian Federation 5. The structure of the economy of this region is dominated by the extractive industry, the population is relatively small (656.5 thousand people) and is distributed mainly among small towns, where the population traditionally takes a more active part in local self-government issues [13; 14]. On the other hand, in recent years, the Murmansk Oblast has paid considerable attention to issues of public involvement in the decisionmaking process by government authorities, both at the level of individual municipalities and the region as a whole. In particular, in May 2019, the regional authorities of the Murmansk Oblast stated that they would pay increased attention to issues of interaction between the population and government bodies on key development issues; Governor Andrey Chibis announced at an extended meeting of the Murmansk Oblast Duma a reset of relations between the authorities and society in the region and the weak organization of dialogue between the population and local authorities 6. The result of this reset was the implementation of a whole range of initiatives, on the basis of which a strategic plan for the development of the Kola Arctic until 2030 “To Live — in the North!” was created and approved in September 2024, formed on the basis of processing over 75 thousand proposals from more than 25 thousand northerners 7.
In recent years, a large number of various projects have been implemented in the Murmansk Oblast aimed at activating the population and forming initiatives that can be included in various strategic documents. However, a full-fledged legislatively enshrined procedure for public participation in the strategic planning system at the regional level has not yet been formed.
The principle of population participation in the public administration system in the Murmansk Oblast is enshrined in the fundamental regional documents. Thus, according to paragraph 2 of Article 12 of the Charter of the Murmansk Oblast, the regional government bodies ensure the implementation of citizens’ rights to participate in the management of state affairs both directly and through their representatives. However, the main regulatory document governing strategic planning at the regional and municipal levels in the Murmansk Oblast (Law of the Murmansk Oblast dated December 19, 2014 N 1817-01-ZMO “On Strategic Planning in the Murmansk Oblast”) does not mention the population as a participant in strategic planning. According to Article 3 of this law, the participants in the strategic planning process in the region are the Murmansk Oblast Duma, the Governor of the Murmansk Oblast, the Government of the Murmansk Oblast, the Chamber of Control and Accounts and executive authorities; and at the municipal level — local government bodies of municipalities, as well as, in some cases, municipal organizations.
In some municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast, issues of public participation in the local government system are in the overwhelming majority of cases enshrined in charters. At the same time, the texts of the relevant chapters of city charters, as well as other adopted regulatory acts, almost verbatim repeat federal legislation.
Table 3 provides an overview of the implementation of formal methods of public participation in the system of resolving issues of local importance and the formation and implementation of strategic planning documents in municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast in terms of the main instruments.
Table 3 Overview of the implementation of formal methods of public participation in the system of resolving issues of local importance and the formation and implementation of strategic planning documents in the Murmansk Oblast 8
|
Level of public participation |
Tool for population engaging |
Features of regulation |
Features of application |
|
Informing |
Posting on the administration website |
At present, the obligation to publish strategic documents for the development of a municipality is due to the need to organize a public discussion of a set of strategic documents |
The entire list of current municipal strategic documents is presented on the websites of the regional municipal administrations |
|
Consulting |
Public hearings |
The obligation to hold public hearings on various areas of strategic planning is enshrined in Federal Law 131 and the charters of municipalities. The procedure is determined by individual regulatory assets |
Public hearings are organized in all municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast, but in most cases they are of a formal nature |
|
Public discussions |
The obligation to conduct public discussions on various areas of strategic planning is enshrined in the urban development code and in the charters of municipalities |
In most cases, they are organized in absentia. Like public hearings, they are often formal in nature |
|
|
Citizen surveys |
According to the charters of municipalities, surveys can be conducted on the initiative of the heads of municipalities, councils of deputies or the population. The results are |
In most cities, these surveys are conducted irregularly and not systematically, the results of the surveys are often not published |
|
advisory in nature |
|||
|
Participation and partnership |
Territorial public self government |
The issues of creating territorial public administration are regulated by Federal Law 131, in the charters of municipalities, and in the Law of the Murmansk Oblast dated 08.11.2019 N 2425-01-ZMO “On state support for territorial public self-government in the Murmansk Oblast” |
TPSs have been created in municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast since 2019, however, the positive practice of using them to involve the population in strategic planning processes has been implemented only in the city of Kirovsk |
|
Meetings and conferences of citizens (meetings of delegates) |
The procedure for holding meetings and conferences of citizens is described in the charters of municipal entities |
In practice, meetings and conferences of citizens to involve the population in municipal strategic planning processes are not held in the region. |
|
|
Initiative groups |
The formation of initiative groups and the procedure for submission of projects for implementation within the framework of strategic documents is regulated by the charters of municipalities and municipal decisions on the approval of provisions on the implementation of initiative projects |
The institution of creating initiative groups has been actively used in recent years to create and implement initiative projects within the framework of regional and municipal strategic development documents |
|
|
Initiative budgeting |
It is implemented by the regional Ministry of Urban Development within the framework of the state program of the Murmansk Oblast “Formation of a modern urban environment of the Murmansk Oblast” since 2020 and is regulated by the Order of the Ministry of Urban Development of the Murmansk Oblast dated 05.02.2020 No. 9 “On certain provisions for conducting a competitive selection of municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast for the provision of subsidies from the regional budget to local budgets to support local initiatives” |
This tool is used in municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast to implement projects for the improvement of city territories. Despite the presence of certain organizational and regulatory problems, the intensity of application of this tool in the region is quite high |
|
|
Grant funds |
The holding of grant competitions is regulated by the regulatory assets of various executive authorities at the regional level (ministries of the Murmansk Oblast) |
This tool for involving the population in the system of regional and municipal strategic planning is currently not used |
|
|
Closed and open mutual investment funds |
Involves the creation of funds to attract financing for economically attractive projects aimed at developing territories; regulated by legislation |
This tool is currently not used in the system of regional and municipal strategic planning |
|
on the formation and functioning of mutual funds |
|||
|
Citizens’ appeals to local governments |
Regulated by the charters of municipalities and approved procedures for handling requests from various municipal authorities |
This tool is used to receive complaints from the population and organize work with them. It is not used as a tool for involving the population in the process of strategic planning in municipalities. |
The practice of implementing formal (regulated) tools for involving the population in the system of local self-government in municipal entities of the Murmansk Oblast shows that there is a group of tools among them that are not currently used in the strategic planning system (meetings and conferences of citizens, financing events within the framework of strategic development of municipalities with the involvement of public funds on the basis of creation of grant and share funds, citizens’ appeals to local government bodies); tools, the effectiveness of which can be assessed as low (public hearings, public discussions, citizen surveys, territorial public selfgovernment), and tools that are actively and effectively used in the municipal strategic planning system (posting information on the administration’s website, creating initiative groups, initiative budgeting).
Among the most effective tools for involving the population in the process of municipal strategic planning, it is necessary to note the tools for informing the population. Thus the entire complex of municipal and regional strategic documents for the development of the Murmansk Oblast is currently available on the websites of city and regional administrations. In addition, municipal authorities publish presentations on the socio-economic development strategies of cities, information on the measures being implemented and their financing on their websites. In particular, the Murmansk Oblast is in “group A” of the budget data transparency ranking for 2023 — a region with a very high level of budget data openness, occupying one of the leading positions in the Northwestern Federal District 9, 10.
Other tools that are actively and effectively used in the system of involving the population in the strategic planning process include the creation of initiative groups for the formation of projects and initiative budgeting. Participatory budgeting projects have been implemented by the regional Ministry of Urban Development as part of the state program “Formation of a modern urban environment of the Murmansk Oblast” since 2020. Municipalities are provided with subsidies from the regional budget for projects to improve residential, courtyard, public areas and places of mass recreation, cultural, educational and sports facilities, organization of children’s playgrounds, solid
NORTHERN AND ARCTIC SOCIETIES
Roman V. Badylevich, Dmitriy L. Kondratovich. Features of Regulation and Implementation … municipal waste collection points, dog walking areas, and repairs of interior property in apartment buildings 11.
In total, more than 230 projects were implemented within the framework of this instrument from 2020 to 2023 (Table 4). In the competition of projects implemented in 2024, 210 applications were submitted from initiative groups from all municipalities of the region, and more than 51 thousand votes were received. The total funding for projects within the framework of this instrument in 2024 amounted to 200 million rubles 12.
Table 4
Indicators of the implementation of initiative group projects and participatory budgeting in the Murmansk Oblast 13
|
Indicator |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2023 |
2024 |
|
Number of municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast participating in the program |
33 |
28 |
29 |
31 |
n/d |
|
Total number of completed projects |
61 |
56 |
54 |
62 |
100 |
Projects proposed by citizens or public organizations are posted for discussion on the websites of municipalities, in social networks and on the portal “Nash Sever” (“Our North”).
Among the tools, the potential of which has not been fully realized in terms of involving the population in the strategic planning process, it is worth highlighting public hearings and discussions, surveys and the creation of territorial public self-government bodies.
Public hearings are a mandatory element of the procedure for developing and adopting strategic planning documents. The need to hold them is enshrined in Article 13 of Federal Law No. 172-FZ and in the charters of municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast. Public hearings are currently held in all municipalities of the region on a regular basis. However, the procedure for holding them is not sufficiently detailed, and the formal attitude of municipal administrations towards them does not allow this tool for involving the population in the strategic planning process to be assessed as effective. In particular, weak information support for public hearings and their frequently inconvenient timing lead to low attendance of such events. At the same time, in order to create a loyal atmosphere at such events and avoid raising controversial issues, some of the attendees are citizens who are close to the administration staff. This situation is possible due to the current lack of regulatory requirements for the number and structure of visitors of public hearings. The proposals made at these events are rarely reflected in municipal strategic documents due to the low level of their development by the population and the lack of sufficient knowledge among citi- zens on the implementation of local self-government. In addition, decisions made during public hearings are currently only advisory in nature for administrations, which, combined with an opaque system for further implementation of public initiatives, leads to a situation where proposals are almost never reflected in adopted municipal strategic documents. It is also not uncommon for public hearings to turn into a platform for unconstructive disputes and arguments with citizens who are negatively disposed towards the administration.
Another tool, the potential of which is not sufficiently realized in the system of involving the population in strategic planning processes in the Murmansk Oblast, is territorial public selfgovernment (TPSG). In the Russian Federation, favorable conditions for the creation and operation of TPSGs were created in 2003 with the adoption of Federal Law No. 131-FZ. Since then, TPSGs have received direct federal regulation and guarantees for their activities. The regulatory framework for the activities of TPSGs has been actively formed in the regions; their total number in 2020 was 34,874 TPSGs in 84 constituent entities of the Russian Federation 14. In the Murmansk Oblast, the impetus for the creation of TPSGs was the adoption of the Law of the Murmansk Oblast dated 08.11.2019 No. 2425-01-ZMO “On State Support for Territorial Public Self-Government in the Murmansk Oblast”. Since 2019, municipal authorities of the region have had a regulatory framework to intensify efforts to create TPSGs on the territory of cities and settlements. However, the creation of TPSGs did not become widespread practice in the cities of the Murmansk Oblast, with the exception of the city of Kirovsk and its subordinate territory, where the municipal authorities accepted the idea of involving the population in issues of improvement and territorial development and fully implemented it on the basis of a public-private partnership with the city-forming enterprise JSC Apatit. By mid-2024, 10 TPSGs were registered in the city of Kirovsk and its subordinate territory, more than 35 events were held on their basis (clean-up days, forums, trainings, thematic sessions, etc.), and about 2.4 thousand people were involved in these events with a total population of about 26.5 thousand people. The city has established the “Kirovsk TPSG Association”, an NPO designed to support and coordinate the activities of TPSGs. Kirovsk’s TPSGs are actively involved in the processes of strategic planning and territorial development of the city. In particular, TPSG activists took part in the discussion of the program “Formation of a Comfortable Urban Environment” (Kirovsk ranked first in the Murmansk Oblast in terms of the number of voters per 1,000 residents); a number of projects were proposed for municipal programs of the city of Kirovsk; a Resource Center for TPSG activists and volunteers was created, which actively participates in the discussion of the main directions of strategic development of the city; the website “Your Kirovsk” was developed, providing address links between users and specific multi-apartment buildings, and between multi-apartment buildings and TPSGs; an interactive platform “Helping together” is being formed on the basis of the website, aimed at implementing requests from resi-
NORTHERN AND ARCTIC SOCIETIES
Roman V. Badylevich, Dmitriy L. Kondratovich. Features of Regulation and Implementation … dents and forming volunteer groups; meetings with the head of the municipal district administration were held, at which proposals for the development of the city were submitted 15. At the same time, despite the positive experience of implementing the work of TPSGs in Kirovsk, this practice has not been replicated in other municipalities of the region, and the creation of TPSGs in other cities remains isolated.
The potential for involving the population in strategic planning processes based on surveys remains insufficiently exploited at the municipal level. The possibility of conducting surveys to identify the opinions of the population for the purpose of taking them into account in decisionmaking by local self-government bodies is directly stipulated in the charters of the region’s municipalities. At the same time, such surveys can be organized at the initiative of municipal legislative and executive authorities and city residents. As practice shows, in the municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast, surveys are mainly conducted on the basis of official websites and social media accounts of local government bodies. Most often, the subject of the survey is the feasibility of implementing a particular initiative project, as well as the selection of the most attractive projects for citizens for the improvement of municipal territories. In practice, surveys rarely raise issues that are truly acute for municipalities, such as healthcare, education, the housing and utilities system, the effectiveness of municipal programs and strategies, and the performance of various local authorities and municipal institutions. The procedure for conducting surveys, in which local governments most often act as the customer and the direct executor of surveys, does not promote openness. The effectiveness of this tool for identifying public opinion is also reduced by weak information support for conducting surveys, the lack of full-fledged analytical work with the results, and the number of survey participants, which is not always sufficient for making informed decisions. The advisory nature of the survey results, which is enshrined in legislation and allows local administrations to ignore unfavorable results, does not contribute to increasing the significance of this tool. In addition, it should be noted that in the Murmansk Oblast, the results of surveys, questionnaires, and the use of other tools for studying public opinion conducted by specialized scientific and educational institutions, in particular, the institutes of the Kola Science Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences, currently remain in low demand.
Along with formal tools for involving the population in the strategic planning process, a system of informal (initiative) tools is widely used in the Murmansk Oblast (Table 5).
Table 5
Overview of the implementation of informal (proactive) methods of population participation in the system of resolving issues of local importance and the formation and implementation of strategic planning documents in the Murmansk Oblast 16
|
Level of public participation |
Tool for population engaging |
Features of regulation |
Features of application |
|
Informing |
Placement of information in print media, social networks, popular Internet resources, stands and other types of outdoor advertising |
The use of this tool in the region is currently not regulated |
Widely and actively used. Information is provided through groups in social networks of city administrations, local newspapers and TV channels, billboards on city streets |
|
Consulting |
Interviews, including in-depth ones; online discussions |
The use of this tool in the region is currently not regulated |
Used in limited format |
|
Involving the population in focus groups and various group discussions on issues of developing strategic documents |
The use of this tool in the municipalities is currently not regulated |
This tool is actively used in the strategic planning system at the regional level, in particular for the creation of the strategic plan “To Live — in the North!” |
|
|
Conducting an exhibition of projects within the framework of strategic planning documents |
The use of this tool in the region is currently not regulated |
This tool is not used in the system of regional and municipal strategic planning |
|
|
Participation and partnership |
Conducting sessions in the format of participatory design, expert sessions |
Regulated by normative acts on the preparation of strategic documents for territorial development, in particular by the RF Government Resolution of June 29, 2023 No. 1076 “On approval of the Rules for the preparation and approval of a single document of territorial planning and urban zoning of a settlement, municipal district, urban district, amendments to it and the composition of materials to justify a single document of territorial planning and urban zoning of a settlement, municipal district, urban district” |
It is actively used in creating master plans and comprehensive plans for long-term socio-economic development of Arctic supporting point |
|
Conducting competitions of projects and initiatives |
The use of this tool in the region is currently not regulated |
Projects are proposed using such tools as the creation of initiative |
|
groups and participatory budgeting |
|||
|
Authorial supervision of the implementation of the concept during the document preparation |
The use of this tool in the region is currently not regulated |
This tool is not used in the system of regional and municipal strategic planning |
|
|
Creation of temporary or permanent structures (working groups) |
Regulated by separate decrees of the administrations of municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast |
This tool is rarely used in the system of regional and municipal strategic planning |
Today, among informal (initiative) tools for involving the public in strategic planning processes, the following are actively used: informing the population through various online and offline mechanisms, supporting and promoting competitions for initiative projects based on the unified Internet portal “Our North” and holding expert sessions.
The function of informing the population on strategic planning issues is implemented, along with the use of official websites of municipal and regional administrations, through interviews with representatives of authorities in regional media, placement of information materials on billboards in cities of the Murmansk Oblast, and use of official groups on social networks. The latter tool is currently used most actively by regional and local authorities. Since December 1, 2022, government agencies are required to maintain official accounts on VKontakte and Odnoklassniki. At present, accounts on these social networks have been created by the administrations of all municipalities in the region and are actively used to inform the public (Table 6).
Table 6
Activity of municipal administrations of the Murmansk Oblast in maintaining accounts on the VKontakte social network 17
Municipality cd Q. О CD Q. C О ГО Q. О С Z3 О ГО CD "го С > 2 CD СП (Л ъ Е ZD 2 С CD CD to Q. CD _Q tn ъ to _Q E 2 (Л О Q. ъ to _Q E c "ro c 3 cz >. з ГО О ? b ~ CD ro 73 Q. CD CD H £ ГО £ CD E 2 £ S § > z " c о 8 CD ro Q Municipal districts Kandalaksha municipal district 39 935 https:// andarayon / 3 075 0.08 5 144 5.2 22.12.2021 Kolskiy municipal district 33 510 https:// kolr51 8 568 0.26 19 880 7.8 05.09.2017 Lovozerskiy municipal district 8 695 https:// ovozeroadm / 1 380 0.16 3 435 1.6 10.10.2018 Terskiy municipal district 4 619 https:// erskyrayon 2 524 0.55 10 699 4.0 02.06.2017
17 As of 28.08.2024. Source: compiled by the authors.
Municipal okrugs the city of Apatity with subordinate territory 48 763 https:// patity__city / 8 712 0.18 10 812 4.2 28.07.2017 the city of Kirovsk with subordinate territory 26 253 https:// voy_kirovsk 12 868 0.49 18 754 7.1 08.06.2017 Kovdorskiy municipal okrug 16 762 https:// monokovdor 7 693 0.46 18 470 6.8 09.03.2017 the city of Monchegorsk with subordinate territory 41 729 https:// v_murman / 15 320 0.37 21 123 5.7 06.06.2014 the city of Olenegorsk with subordinate territory 27 974 https:// lenegorsk_adm / 6 530 0.23 11 419 4.1 25.01.2017 Pechengskiy municipal okrug 30 591 https:// echengamr_ru / 6 325 0.21 18 051 5.8 03.02.2016 the city of Poly-arnye Zori with subordinate territory 15 726 https:// olyarniezori / 10 377 0.66 13 126 2.0 14.01.2007 Urban okrugs CATU Aleksandrovsk 32 232 https:// to_alexandrovsk / 15 070 0.47 38 934 9.8 14.10.2013 CATU Vidyaevo village 4 346 https:// atovid / 2 640 0.61 5 649 2.4 08.02.2018 CATU Zaozersk city 7 760 https:// aozadm / 5 064 0.65 15 921 7.4 24.09.2018 Murmansk 267 422 https:// tymurmanskru / 18 423 0.07 8 025 3.3 02.02.2018 CATU Ostrovnoy city 1 432 https:// ato_ostrov / 697 0.49 2 932 1.5 04.04.2019 CATU Severomorsk city 50 949 https:// tyseveromorsk / 9 061 0.18 14 032 6.3 17.07.2018 MURMANSK OB LAST 65 6438 https:// murman_sever / 47 266 0.07 32 052 10.5 26.04.2016
In most municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast, official accounts of municipal administrations in the VKontakte network were created before the adoption of a regulatory act on their mandatory maintenance. Currently, approximately every 5th resident of the region is subscribed to the official accounts of government bodies, and the average number of posts in official groups is about 5 per day. Government agencies of the Murmansk Oblast maintain more than 800 official accounts in social networks, and their total audience is about 750 thousand users 18.
Among the positive aspects of using accounts in social networks, it is worth highlighting their active use as tools for informing the population on strategic planning issues, presence of structured system for responding to constructive suggestions and complaints, and availability of general coordination with regional authorities.
The disadvantages include significant differences in the activity of municipal administrations of the Murmansk Oblast in managing and attracting subscribers to official accounts (for example, at present, the number of subscribers per capita in the Kandalaksha district and in some closed administrative-territorial units differs by more than 8 times). A comparison of the number of subscribers to official accounts and unofficial city communities on VKontakte indicates that there is significant potential for increasing interest in the official accounts of municipal administrations (Fig. 1).
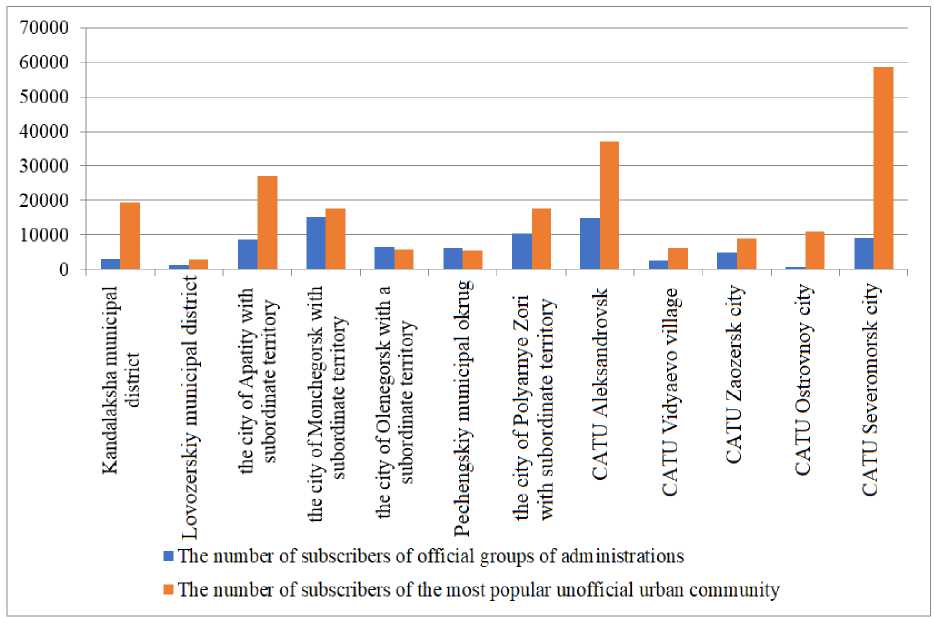
Fig. 1. Comparison of the number of subscribers to official accounts and unofficial city communities on the VKontakte network in the cities of the Murmansk Oblast 19 .
In addition, it should be noted that some technical capabilities provided by social networks are not used effectively enough. In particular, the potential for conducting population surveys on the development and formation of strategic planning documents and assessing the effectiveness of the implementation of measures is not fully realized.
Another proactive and innovative project that is actively used by regional authorities both to support the use of regulated tools for involving the population in strategic planning processes and as an independent tool is the project to create a special Internet portal called “Nash Sever” (“Our North”) . This project is currently one of the most successful regional projects to involve the population in the development of regional and municipal strategic documents and the collection of initiatives.
This portal provides the public with the opportunity to identify problems, ask questions to the authorities, propose their own projects, and participate in surveys and votes.
The main section of the portal, “Active Resident”, offers several formats of public participation in the municipal governance system:
-
1. Residents’ appeals. This implies that citizens raise specific issues and receive responses from the authorities (it is possible to specify the category of the issue and the status of the appeal).
-
2. Surveys and voting. This provides residents of the Murmansk Oblast with the opportunity to express their opinion when choosing the most relevant and important projects in the region’s municipalities.
-
3. Initiatives. This allows citizens to propose initiatives which, if supported by the public, can be included in various strategic documents.
-
4. Rewards. This allows active citizens to receive points for proposing and supporting initiatives, submitting applications for competitions held on the portal, attracting new users to the portal; points can be exchanged for souvenirs dedicated to the Murmansk Oblast.
The portal, created in 2019 on the initiative of the Governor of the Murmansk Oblast, continues to be actively developed. Thus, in 2022, modules were launched to provide information on the implementation of national projects and the plan “To live — in the North!” For each object or event, users can see a detailed report, including a list of completed works and the amount of funding.
The popularity of the project is evidenced by data provided by representatives of the Murmansk Oblast authorities, as well as objective figures from various services that generate website traffic statistics. As of February 1, 2023, according to data provided by the Minister of Digital Development of the Murmansk Oblast Aleksandr Nikipelov, residents sent more than 40 thousand messages to “Nash Sever”, 76 votes were held on various topics, and the number of registered users exceeded 80 thousand people 20. In 2024, the portal collected proposals for the updated strategic plan for the development of the region “To Live — in the North!” The total number of proposals received from the population exceeded 72 thousand 21. According to statistics from the online service Similarweb , the total number of visits to the portal “Nash Sever” over a three-month period (from May to July 2024) was 132 thousand times, with 81.7 thousand visits in July 2024, when the portal was collecting initiatives for the program “In the North — Your Project” 22. The website traffic statistics are comparable to the traffic of the main administrative Internet resources of the Murmansk Oblast (in 2024, the Murmansk Oblast government website had 441 thousand visits).
In recent years, large municipalities in the Murmansk Oblast have been increasingly using strategic sessions as a tool to engage the population in the preparation of strategic development documents. In particular, this tool was used in 2023–2024 when elaborating master plans for cities in the region that are included in the list of Arctic supporting points.
Currently, the formation and development of supporting cities is a priority approach in the strategic development system of the Far East and the Russian Arctic. The initiative to apply this approach belongs to the President of the Russian Federation. Following a meeting on the development of closed administrative-territorial units and settlements of the Arctic Zone of the Russian Federation, held on July 20, 2023, the Head of state instructed to determine the list of Arctic supporting settlements. The list of municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast included in the specified list is presented in Table 7.
Table 7
Municipalities of the Murmansk Oblast included in the list of Arctic supporting cities
|
Supporting city/ agglomeration |
Composition |
|
1. Murmansk agglomeration |
municipal formation urban district: hero city of Murmansk; urban district: closed administrative-territorial unit city of Severomorsk, municipal formation Kolskiy municipal district |
|
2. Kirov-Apatity agglomeration |
municipal formation municipal okrug city of Kirovsk with the subordinate territory of Murmansk Oblast, municipal formation municipal okrug city of Apatity with the subordinate territory of Murmansk Oblast |
|
3. Monchegorsk agglomeration |
municipal okrug city of Monchegorsk with the subordinate territory of the Murmansk Oblast |
|
4. Polyarnye Zori |
municipal okrug Polyarnye Zori |
According to official information, master plans should become general plans for territorial development, created on the basis of public opinion and serving as a basis for the development of other strategic documents, in particular comprehensive plans for long-term socio-economic development. In practice, the positive initiative to involve a wide range of experts and the population in the development of these documents has encountered a number of difficulties, caused by the minimal timeframes for the formation of plans and weak regulation of the process of involving the population in the development of master plans. Thus, less than eight months (from November 2023 to July 2024) were allocated for the development and approval of master plans for the development of cities and agglomerations included in the initial approved list, and in less than three months (by 1 October 2024), comprehensive plans for long-term socio-economic development for the period up to 2035 were to be developed on the basis of the approved master plans. The limited timeframe for the development and approval of strategic documents for the development of Arctic supporting cities is also confirmed by a comparison with the timeframe for the development of similar documents for cities in the Far East — more than a year and a half.
Due to the limited time available for drafting strategic documents and the strict requirements for their content set by the Ministry for the Development of the Far East and the Arctic, the elaboration of master plans for the development of Arctic supporting cities and agglomerations
Roman V. Badylevich, Dmitriy L. Kondratovich. Features of Regulation and Implementation … was entrusted to organizations in the capital. Despite all the efforts of the master plan developers, it was not always possible to fully take into account regional specifics, as well as the entire range of problems facing Arctic municipalities. This problem was to be solved by holding a broad public discussion of the master plans under development, involving regional scientific and educational organizations, the business community and the local population. However, it was quite difficult to realize the full potential of optimizing master plans on the basis of public discussion for several reasons.
Firstly, many public meetings were held without the necessary preparation, with participants receiving invitations to the event without being provided in advance with the agenda for the discussions and the main issues on which proposals and comments could be made. The brainstorming method used in such strategic sessions in target groups turned out to be ineffective due to time constraints, poor preliminary preparation, and lack of sufficient information and factual base. It was a difficult task to determine possible solutions to acute problems in key areas of development of Arctic municipalities on the basis of short-term discussions in target groups composed of representatives of various regional organizations and institutions and to present them to the developers of master plans in a limited time.
Secondly, there was no regulatory mechanism for amending strategic documents for the development of supporting municipalities based on public discussions and public opinion. During the preparation of master plans, the implementing organizations, together with government bodies, carried out significant work in the field of receiving feedback from the population on the most acute problems of the cities selected as Arctic supporting points, conducted sociological research based on Internet surveys 23, and discussions in social networks. However, in most cases, the results of the work carried out with the population remained undisclosed, the results of the surveys were not published, and the degree to which the population’s opinion on certain aspects of the master plans being formed was not clear. The absence of a legally established mechanism for the development and approval of master plans leads to the fact that today the entire range of functions in determining the structure of master plans, as well as their specific content, is concentrated in the organizations-developers, while the results of public discussions are of a recommendatory and advisory nature.
Directions for improving the efficiency of the tools for public interaction with local and regional authorities in the territorial development system of the Murmansk Oblast
Currently, when involving the population in the strategic planning process in the Murmansk Oblast, considerable attention is paid to the mechanism for informing the population about existing strategic initiatives and building an effective system for including projects proposed by citizens and initiative groups in the system of strategic documents. At the same time, the population practically does not perform the functions of monitoring the timely implementation of the activities of
Roman V. Badylevich, Dmitriy L. Kondratovich. Features of Regulation and Implementation … strategic documents and achieving the established target guidelines. In addition, while actively participating in filling strategic documents with specific activities and projects, citizens are limited in their ability to participate in the development of key strategic documents at the level of goalsetting and establishing the main targets and objectives, while the prerogative of developing these documents remains entirely with the authorities.
The solution to these problems and the improvement of the effectiveness of public involvement in the strategic planning process is seen, first of all, in the in-depth regulatory elaboration of issues related to the implementation of relevant instruments at the level of the Murmansk Oblast and individual municipalities. In particular, it is necessary to include the population as a full participant in the strategic planning process in the main document regulating this sphere in the region — the Law of the Murmansk Oblast No. 1817-01-ZMO “On Strategic Planning in the Murmansk Oblast”. The procedure for public participation in strategic planning processes at the municipal level should be specified in detail. In this regard, attention should be paid not only to the organization of public discussions and debates, but also to the creation of a mechanism for taking into account the results of such events. Initiatives adopted at such meetings should be additionally submitted for discussion to administrative bodies, while the process of adopting or rejecting such initiatives should be transparent to citizens.
The effectiveness of initiatives proposed by the public can be increased by introducing mechanisms for the collective participation of citizens in the processes of developing and adopting municipal strategic documents. Thus, it seems expedient to create permanent public associations (expert groups) on key areas of strategic planning (healthcare, education, housing and communal services, youth policy, etc.) under the administrations of municipal entities, which will involve representatives of the public, specialized institutions, and proactive citizens. The practice of creating public councils under administrations on issues of territorial improvement in the cities of the Murmansk Oblast, which participate in issues of city improvement and the implementation of federal and regional programs in this area, should be considered as a successful experience in the creation of such associations and groups. At the same time, it seems appropriate to involve representatives of such associations not only at the stage of final approval of strategic documents, when it is difficult to make changes and adjustments, but also at the initial stages of their formation, when it is possible to have a real impact on their content. It is also advisable to provide for the participation of representatives of the public not only at the stage of developing and adopting documents, but also at the stage of monitoring their implementation and controlling their effectiveness. The participation of official representatives from associations (public councils) will strengthen the validity of the proposed directions for optimizing municipal strategic documents and will increase the level of public awareness of issues related to the implementation of local selfgovernment.
An alternative to the creation of permanent associations (public councils) could be the implementation of collective participation of the population in strategic planning processes based on the development and expansion of activities of territorial public self-governments in the cities of the Murmansk Oblast. As the experience of the city of Kirovsk shows, in case of interest from local authorities, as well as broad support for TSG initiatives from large and medium-sized businesses, this tool can become an effective mechanism for attracting active citizens to the formation of municipal strategies and programs, as well as control and monitoring of their implementation. Positive experience of using TSGs in strategic planning at the municipal level is currently available in the Arkhangelsk Oblast [15], in the Khabarovsk Krai [16], in the Nizhny Novgorod Oblast [17]. It should be noted that the priority use of this form is more consistent with the specifics of single-industry towns in the Murmansk Oblast, where there are strong links in the system of public-private partnerships between municipal administrations and city-forming enterprises.
It is possible to increase the level of justification for taking into account the opinion of the population on certain aspects of the development and implementation of municipal strategic documents by optimizing the surveys conducted. In particular, it is necessary to clearly regulate not only the procedure for conducting such surveys, but also to specify the features of taking into account the results obtained. In order to increase the objectivity of the data obtained from public surveys on key strategic planning issues, it seems appropriate to entrust their implementation to structures independent of the administration, in particular, analytical agencies, educational institutions, scientific organizations operating in the region. The results of the surveys should be available to all interested parties. At the same time, the range of topics covered in the surveys should be significantly expanded, including questions on the formation of key goals and objectives of the main municipal strategic documents.
Conclusion
Involvement of the population in the elaboration and implementation of the main longterm and medium-term development documents is one of the prerequisites for effective strategic planning at the regional and municipal levels. Only this approach makes it possible to take into account the full range of problems faced by specific municipalities, focus efforts on solving the most pressing issues, and create conditions for increasing the attractiveness of cities for living.
Currently, Russian legislation provides a wide range of tools for involving the population in the strategic planning process, regulating at the federal level the procedure for their management and application at the regional and municipal levels. However, the intensity and effectiveness of using such tools at the local level largely depends on the interest in them on the part of regional and municipal authorities, their desire and ability to make the process of development and implementation of strategic development documents open to the population.
The Murmansk Oblast is a region where regional authorities have paid considerable attention to issues of activating the role of the population in the local self-government system as a whole and increasing the involvement of citizens in strategic planning processes in particular. As a result, a strategic plan “To Live — in the North!” has been created with the involvement of popula- tion and organizations operating in the region, which should become the basis for the development of the Kola Arctic until 2030. In recent years, the region has established an effective system for informing the population about regional strategic initiatives through the media, official and unofficial Internet resources, billboards, the Internet portal “Nash Sever”; a system for collecting and implementing initiative projects proposed by residents of the region’s cities has been built, municipalities are actively involved in competitions and various federal and regional programs aimed at developing urban infrastructure and creating a favorable environment.
However, it should be noted that the region has reserves for increasing the effectiveness of involving the population in strategic planning processes, which are primarily related to the need to resolve problematic issues at the local level. In particular, public hearings and public discussions on the development of municipal strategies and programs are characterized by low efficiency in cities; surveys are conducted in a formal manner, and their results are often not taken into account when adjusting municipal strategic documents; the institution of territorial public self-government does not fully fulfil its goals.
It seems possible to increase the effectiveness of the tools for interaction between the population and local and regional authorities in the territorial development system of the Murmansk Oblast on the basis of the following: abandoning formal approaches to working with the population on the part of local authorities; careful elaboration of regulatory documents ensuring the participation of all categories of entities interested in ensuring the development of municipal formations in the local self-government system; broad support for the participation of the most active part of the population and various forms of public associations of citizens in the strategic planning system.
The implementation of the entire range of measures for optimizing the mechanisms and tools for population participation in the local self-government system, as well as the refusal of municipal authorities from their formal use in favor of real involvement of citizens in the problems of cities and settlements will create the prerequisites for the implementation of a full-fledged partnership between all interested parties in the strategic planning system at the municipal and regional levels in the Murmansk Oblast.


