Формирование экономического механизма стабилизации деятельности предприятия
Автор: Запорожцева Л.А., Марышева Ю.В., Ткачева Ю.В.
Журнал: Вестник Воронежского государственного университета инженерных технологий @vestnik-vsuet
Рубрика: Экономика и управление
Статья в выпуске: 1 (75), 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В статье проведено исследование закономерностей экономического развития предприятия. Исследована очередность смены стадий жизненного цикла. Установлено, что не всегда стадия зрелости сменяется стадией спада и в дельнейшем - стадией кризиса. Жизненным процессам «старения» предприятия можно успешно противостоять. Доказано, что со стадией зрелости у предприятия связан «кризис стабильности», выход из которого – попадание в стадию спада, роста или сохранение стабильности. Обосновано, что в практике функционирования коммерческих организаций существуют такие зоны пребывания на кривой жизненного цикла, когда необходимо включать механизм стабилизации: при обнаружении «кризиса стабильности», когда предприятие переходит из стадии зрелости в стадию спада и при диагностировании попадания на стадию спада. В этой связи, разработан экономический механизм стабилизации деятельности коммерческой организации как системы мер, направленных на поддержание достигнутого финансового равновесия предприятия в длительном периоде, который включает в себя следующие блоки: информационное обеспечение оценки финансового состояния; оценку уровня платежной, деловой и капитальной устойчивости предприятия; определение стадии жизненного цикла коммерческой организации; характеристика применяемой стратегии функционирования предприятия; необходимость использования инструментария для корректировки стратегии с целью стабилизации деятельности коммерческой организации и оценку результатов. При этом важно ориентироваться на поддержание достижимых темпов роста путем применения специальных управленческих решений, наряду с осуществлением мониторинга жизненного цикла и контроллинга финансового состояния предприятия. Внедрение экономического стабилизационного механизма в деятельность предприятия, совместно с уже существующим организационно-экономическим механизмом, позволит скорректировать элементы базового (организационно-экономического) механизма и обеспечит экономическую стабильность коммерческой организации.
Экономический механизм, стабилизация деятельности, предприятие, жизненный цикл
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140229971
IDR: 140229971 | DOI: 10.20914/2310-1202-2018-1-267-272
Текст научной статьи Формирование экономического механизма стабилизации деятельности предприятия
The current economic conditions of enterprises in Russia determine the necessity to implement not so much the reformation of enterprises as the stabilization of business processes, taking into account the real issues and opportunities of enterprises.
Introduction of stabilizing measures in a commercial organization makes financial managers to have a clear understanding of the moment when they must indeed use it. It is possible to achieve the most preferred stage of the enterprise’s life cycle by using of certain tools on the basis For citation
of a certain idea of the stable functioning of the enterprise and guided by the level of development at a particular time.
The research allowed to define the problems associated with the need to constantly identify "pain" points, in which stable mechanisms should be used. However, there is no practical-oriented economic mechanism of the stabilization of enterprise’s activity.
Theoretical bases and regularities of enterprises’ functioning have been described in numerous publications, domestic and foreign economic schools. Special contribution to the knowledge of this issue has made by such representatives of economic research, as I.A. Blank [1], Z.A. Krush, Y.V. Tkacheva [2], Z.V. Mezonis [3]. A. Chandler [4], S.G. Hanks [5], etc.
The interest of Russian and foreign researchers and practitioners in the essence of financial condition, methods of assessment and mechanism of ensuring financial stability as a basis for the enterprise’s stable functioning is justified by the need for enterprises of the real sector of the economy. The scientific works of V.V. Kovalev [6], A.D. Sheremet [7], etc. must be highlighted here.
The question of the necessity of economic stabilization of enterprise’s activity has attracted attention of scientific researches such as O.V. Golovkina [8], V.I. Zubkova, V.O. Umerova [9], J.A. Saprykina [10], etc.
The evaluation methods of life cycle stages of a commercial organization proposed by I. Adizes [11], L. Greiner [12], A.P. Gradov, B.I. Kuzin [13], L.A. Zaporozhtseva [14], N.V. Egunova [15], etc. catch the scientific interest too.
The scientific researches of domestic and foreign scientists determine the specifics of the enterprise’s functioning at different stages of the life cycle, as well as methods for financial condition assessment of the enterprise. However, the question of the importance of the formation of the economic mechanism of stabilization of the enterprise’s activity in order to ensure at least a minimal level of development wasn’t raised yet.
During the research of theoretical bases of regularities of functioning of economic entities, the assessment of modern representations of essence of economic stabilization of activity of the commercial organization. It is offered to understand the stabilization of enterprise’s activity as system of internal and external measures for overcoming of unstable financial condition of the enterprise for the purpose of prevention of crisis and ensuring its further development.
On the basis of researching in the field of cycle theory at different levels of the economy it was found that the stages of the life cycle of the organizations begin at "birth" and end at "death" in accord of different approaches. It is mean that the enterprise is doomed to die after birth.
The need for stabilization of enterprise’s activity, in our opinion, arises after passing the point of maturity. At this moment the company, achieving stability, goes to recession and doesn’t know where to move on (figure Figure1. Regularities of cyclic development of the enterprise) .
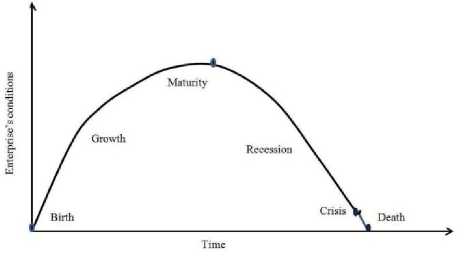
Figure1. Regularities of cyclic development of the enterprise
Such point of view is justified by the need for monitoring of the changes not only in the financial condition, but also in the stages of the enterprise’s life cycle in order to neutralize the threats of the transition to the stage of recession and liquidation of crisis phenomena.
Discussion
We offer to use different assessment methods to determine the stage of life cycle of the Agrarian producers' co-operative “Liskinsky”(tables 1, 2) .
Table 1.
Determination of the stage of the life cycle of the financial condition of the Agrarian producers' co-operative “Liskinsky” of I.A. Pavlova
|
The stage |
Liquidity |
Ability |
Creditability |
Turnover |
Profitability |
|
Birth |
growth |
improvement |
growth |
unstable changes |
unstable changes |
|
Growth |
stability |
stability |
stability |
growth |
growth |
|
Maturity |
stability |
stability |
stability |
stability |
stability |
|
Recession |
reduction |
degradation |
reduction |
reduction |
reduction |
Table 2.
The calculation of indicators to determine the stage of the life cycle of the financial condition of the Agrarian producers' co-operative “Liskinsky”by the I.A. Pavlova’s methods
|
Indicators |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
|
Current liquidity, coefficient |
2.90 |
5.49 |
7.27 |
|
Ability, coefficient |
4.56 |
2.25 |
1.77 |
|
Autonomy, coefficient |
0.74 |
0.84 |
0.88 |
|
Own working assets to assets, coefficient |
0.65 |
0.82 |
0.86 |
|
Assets’ turnover, coefficient |
0.60 |
0.69 |
0.68 |
|
The duration of the turnover, days |
598 |
523 |
533 |
|
Assets’ profitability, coefficient |
0.10 |
0.20 |
0.17 |
|
Recoupment of realized produce, coefficient |
1.15 |
1.37 |
1.31 |
Based on the calculations in tables 1, 2 it is established that liquidity, ability and creditability, profitability and turnover indicators have stable positive dynamics in 2016 as compared with 2015.
Consequently, the company is located at the stage of maturity of financial stability. At the same time, it is impossible to determine for sure where the company should aim: at the stage of growth or at the stage of recession. The indicator of economic value added (EVA)was used to eliminate the identified shortcoming(table 3).
Table 3.
The calculation of economic value added (EVA) of the Agrarian producers' co-operative “Liskinsky”
|
Indicators |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
|
Net operating profit after tax, thousand rubles |
41911 |
112067 |
106242 |
|
Invested capital at the beginning of the period, thousand rubles |
413276 |
515013 |
587446 |
|
The average cost of capital, % |
2.17 |
2.44 |
1.34 |
|
Economic value added (EVA), thousand rubles |
32935 |
97484 |
98369 |
Table4.
Determination of the stage of the life cycle of the financial condition of the Agrarian producers' co-operative “Liskinsky” of I.A. Pavlova, L.A. Zaporozhtseva
|
The stage |
Liquidity |
Ability |
Creditability |
Turnover |
Profitability |
Change in the value of the enterprise |
|
Birth |
growth |
improvement |
growth |
unstable changes |
unstable changes |
unstable changes |
|
Growth |
stability |
stability |
stability |
growth |
growth |
growth |
|
Maturity |
stability |
stability |
stability |
stability |
stability |
low growth |
|
Recession |
reduction |
degradation |
reduction |
reduction |
reduction |
destruction |
The EVA indicator lets us to conclude that the Agrarian producers' co-operative “Liskinsky” strengthened its financial position in 2016 and transferred from the maturity stage to the growth stage (tables 3, Table4.) . Agrarian producers' co-operative “Liskinsky”, being at the stage of maturity, survived the "crisis of stability" and moved into a new growth. These changes are illustrated in figure 2.
Thus, the Agrarian producers' co-operative “Liskinsky” needs to consolidate the transfer to the growth stage by using the special management decisions, along with the implementation of lifecycle monitoring and controlling the financial condition of the enterprise.
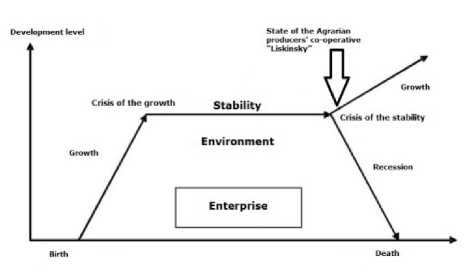
Figure 2. The model of the enterprise’s lifecycle, the determination of the state of the Agrarian producers' cooperative “Liskinsky”
It is clear that the stage of maturity is not always replaced by the stage of recession and the stage of crisis later on. Life processes of "ageing" of the enterprise can be successfully resisted.
The practical application of this approach is based on the development and implementing of the economic mechanism of stabilization of the enterprise’s activity as a system of measures aimed at maintaining the achieved financial equality of the enterprise in the long term.
The project of economic mechanism of stabilization of the enterprise’s activity proposed by the authors is presented in figure 3.
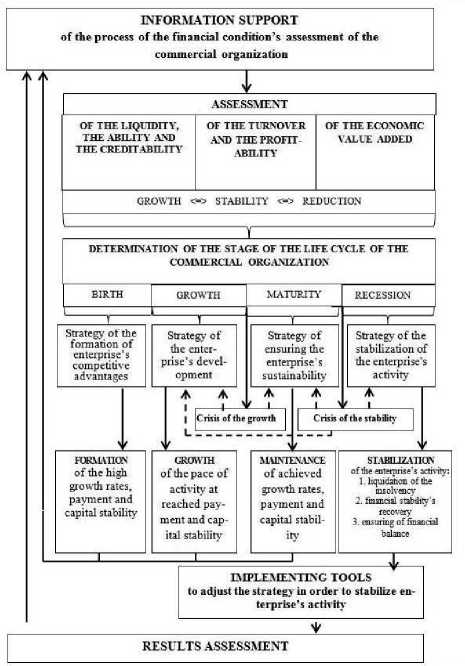
Figure 3. The economic mechanism of the stabilization of the enterprise’s activity
The economic mechanism of the stabilization of the enterprise’s activity includes the following blocks:
-
1. information support of financial condition’s assessment;
-
2. assessment of the level of payment, business and capital stability of the enterprise;
-
3. determination of the stage of the life cycle of a commercial organization;
-
4. characteristic of the strategies of functioning of the enterprise;
-
5. implementing tools to adjust the strategy in order to stabilize enterprise’s activity;
-
6. results assessment.
At the Birth stage the enterprise should use the strategy of formation of enterprise’s competitive advantages which exact the formation of high growth rates, payment and capital stability.
At the Growth stage we offer to use the strategy of the enterprise’s development based on the growth of the pace of business activity (turnover and profitability) at the reached payment and capital stability.
The Maturity stage is characterized by the using of the strategy of ensuring the enterprise’s sustainability based on maintenance of achieved growth rates, payment and capital stability.
The authors emphasize that the enterprise's passing through these three stages (Birth, Growth and Maturity) should base on the realization of the internal potential of the enterprise’s development within the economic regularity.
The Maturity stage or the Stability stage isn’t the stage where the mechanisms of stabilization of activity should be used because it is the zone of achieved stability. The enterprise at the Stability stage is going through the crisis of the growth. It is characterized by the reducing of the rate growth of the turnover and the profitability and by the stabilization of the values of monitored indicators. In this case, the company has two ways: to increase profitability and turnover or to adopt an internal process of stabilization and occupy a zone of maturity or stability.
Another type of crisis is connected with the Maturity stage of the enterprise. This is the crisis of the stability. The way out of this crisis is getting into the Recession, Growth stages or maintaining stability.
Thus, the crisis of the stability does not always lead to the Recession stage. The enterprise, maintaining the achieved growth rates and the payment and capital stability, retains its positions at the Maturity stage as long as necessary. In the case of increasing of the turnover, profitability, economic value added with the achieved stability, the commercial organization can move back to the Growth stage.
In practice of enterprises’ functioning are known such zones of staying on a life-cycle curve when it is necessary to use the stabilization mechanism:
-
1. crisis of the stability, when the enterprise moves from Maturity stage to Recession stage;
-
2. diagnosis of hit in a Recession stage.
In this case, the enterprise should adopt a strategy to stabilize the company’s activity, which consists in the implementation of the following measures (depending on the complexity of the situation):
-
1. the removal of the insolvency;
-
2. the restoring of the financial sustainability;
-
3. the ensuring of the long-term financial balance.
Conclusion
The controlling process of the enterprise’s financial condition and monitoring its lifecycle should systematically pass in order to identify the "pain" points and to launch an economic mechanism of stabilization of the enterprise’s activity, including the implementation of tools for correction of the strategy.
Список литературы Формирование экономического механизма стабилизации деятельности предприятия
- Бланк И.А. Финансовая стратегия предприятия. Киев: Эльга, Ника -Центр, 2004. 720 с.
- Круш З.А., Ткачева Ю.В. Инновационный подход к диагностике финансовой несостоятельности сельскохозяйственных предприятий//Экономика сельскохозяйственных и перерабатывающих предприятий. 2010. № 5. С. 61-65.
- Межонис З.В. Управление организационными изменениями: повышение качества принятия управленческих решений с помощью новой теории факторов производства//Известия Волгоградского государственного технического университета. 2013. Т. 16. № 11 (114). С. 56-62.
- Chandler A.D. Strategy and Structure: A Chapter in the History of Industrial Enterprises. Cambridge, Mass, MIT Press, 1962. 210 р.
- Hanks S.H. The Organization Life Cycle: Integrating 8. Content and Process//Journal of Small Business Strategy. 1990. № 1. P. 1-13.
- Ковалев В.В. Финансы предприятий. М.: ТК Велби, Проспект, 2011. 450 с.
- Шеремет A.Д., Негашев Е.В. Методикa финaнсового aнaлизa деятельности коммерческих оргaнизaций. М.: ИНФAМ, 2011.237 с.
- Головкина О.В. Механизм оценки финансово-экономической стабильности функционирования предприятия. Волгоград: ВГУ, 2003. 24 с.
- Зубкова В.И., Умерова Д.О. Механизмы финансовой стабилизации предприятия//Science Time. 2016. № 4(28). С. 316-320.
- Сапрыкина Ю.А. Рациональный процесс принятия решения при стабилизации финансового состояния предприятия//Научные исследования: от теории к практике. 2016. № 1(7). С. 285-287.
- Адизес И.К. Управление жизненным циклом корпорации. СПб.: Питер, 2007. 383 с.
- Грейнер Л.Е. Эволюция и революция в процессе роста организаций//Вестник Санкт-Петербургского университета. Серия Менеджмент. 2002. № 4. С. 76-94.
- Градов А.П., Кузин Б.И. Стратегия и тактика антикризисного управления фирмой. СПб.: Спец. литература, 1996. 510 с.
- Запорожцева Л.А. Жизненный цикл предприятия и его взаимосвязь с уровнем стратегической экономической безопасности//Социально-экономические явления и процессы. 2014. № 12. С. 81-89.
- Егунова Н.В. Развитие организационной структуры предприятий на основе теории жизненных циклов//Вестник Бурятского государственного университета. 2011. № 2. С. 13-17.


