Гетерогенность клеток эндотелия
Автор: Живень М.К., Захарова Ирина Сергеевна, Шевченко А.И., Покушалов Е.А., Закиян С.М.
Журнал: Патология кровообращения и кардиохирургия @journal-meshalkin
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 4-2 т.19, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Эндотелиальные клетки, образующие у позвоночных внутренний слой сосудов, обладают важными функциями, необходимыми для нормальной жизнедеятельности организма. В обзоре суммированы сведения о формировании эндотелиальных клеток в онтогенезе, их артериальной, венозной и лимфатической дифференцировке, и также дальнейшей специализации в зависимости от клеточного микроокружения конкретного органа или ткани. Понимание различий в морфологии, ультраструктуре, экспрессии генов и функциях различных субпопуляций эндотелиальных клеток имеет большое значение в регенеративной медицине для протезирования сосудов, лечения различных эндотелиальных дисфункций, реваскуляризации и регенерации ишемизированных органов.
Эндотелиальные клетки, васкулогенез, дифференцировка, дифференциальная экспрессия генов
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142140862
IDR: 142140862
Текст научной статьи Гетерогенность клеток эндотелия
Формирование и специализация эндотелия в онтогенезе
В эмбриональном развитии позвоночных предшественники клеток сосудов появляются в задней части первичной эмбриональной полоски, как клетки мезодермы, несущие рецептор васкулярного эндотелиального ростового фактора 2 (VEGFR2) ( рисунок ) [1, 2]. Из первичной полоски VEGFR2-позитивные клетки мезодермы мигрируют во внезародышевые органы (желточный мешок и аллантоис), а также внутрь эмбриона, где способны давать гемопоэтические и ангиогенные клетки.
В желточном мешке скопления VEGFR2-позитивных предшественников (гемангиобластов) дифференцируются так, что по периферии кластеров образуются эндотелиальные клетки, а в центре – клетки крови, в результате формируются кровяные островки, которые затем сливаются, чтобы создать первичные капиллярные сплетения [1, 2]. Внутри эмбриона ангиобластные клетки мигрируют различными путями, формируя непосредственно трубку эндокарда, а также парные спинные аорты и кардинальные вены. Интересно отметить, что на данной стадии зародышевый и внезародышевый эндотелий отличается дифференциальной экспрессией генов Ephrin-B2 и EphB4, характерных для эндоте-лиоцитов артерий и вен соответственно [3, 4]. Таким образом, артериальная и венозная дифференцировка эндотелиальных клеток по крайней мере частично определяется генетически на ранней стадии развития до формирования кровообращения.
Часть клеток венозного эндотелия в развивающемся эмбрионе специализируется в клетки лимфатических сосудов [5]. Лимфатический эндотелий впервые появляется среди клеток, выстилающих передние кардинальные вены, а затем в более каудально расположенных эмбриональных венах. Специализированные клетки лимфатического эндотелия мигрируют из вен,
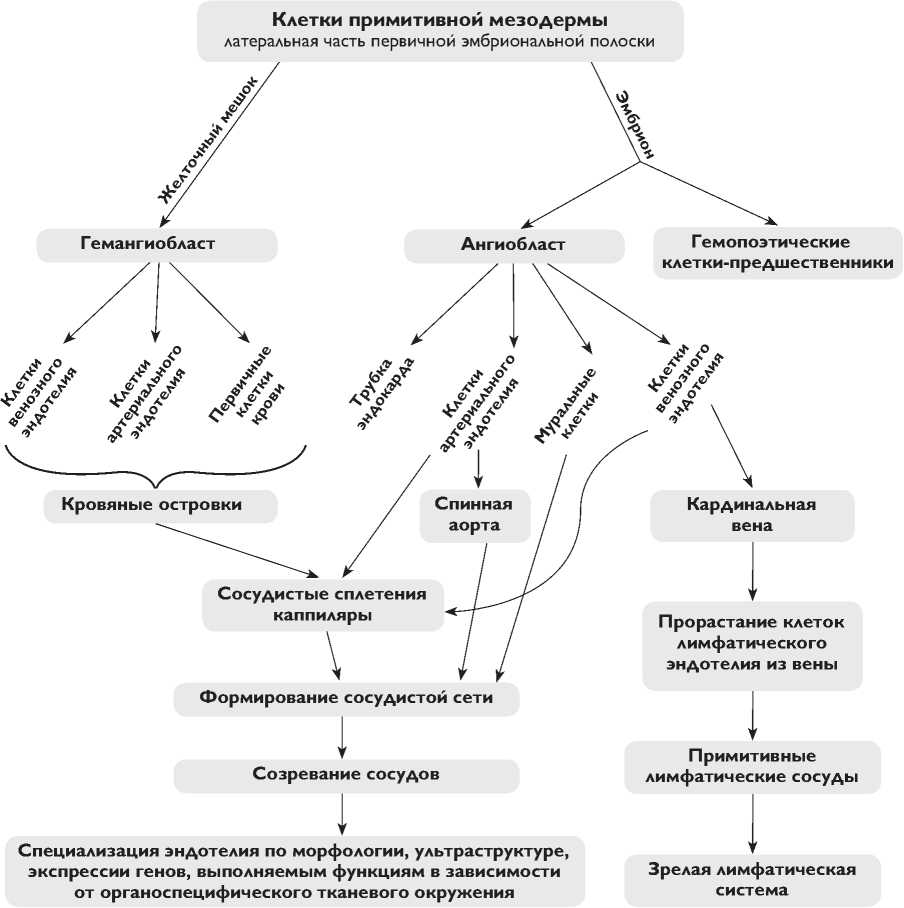
Формирование и специализация эндотелия в эмбриогенезе
образуя примитивные лимфатические мешки, из которых они распространяются далее, чтобы дать начало всей лимфатической сети [6, 7].
После первоначального формирования примитивной зародышевой и внезародышевой сосудистой сети (вас-кулогенеза) кровеносная система переходит к процессу ангиогенеза, в результате которого она расширяется и специализируется. Ангиогенез включает прорастание клеток эндотелия, разветвление и инвагинацию сущес- твующих сосудов [1, 2, 8]. В это время клетки стенки сосудов (муральные), к которым относятся перициты и гладкомышечные клетки, активно дифференцируются, профилируют под действием фактора TGF-β и привлекаются для формирования стенок сосудов с помощью тромбоцитарного ростового фактора (PDGF), секретируемого эндотелием. Под воздействием различий в скорости кровотока, давления крови, концентрации кислорода и pH происходит дальнейшая спе- циализация артериального и венозного эндотелия и формирование зрелых капилляров, артерий и вен с характерными для них толщиной сосудистой стенки и соотношением коллагеновых и эластиновых волокон.
Прорастая в разные органы и ткани организма, эндотелиальные клетки сосудов попадают под действие различного органоспецифического клеточного окружения, которое вызывает появление различий между эндотелиальными клетками в морфологии, ультраструктуре, экспрессии генов и выполняемых функциях [8]. Определенная специализация эндотелия может устанавливаться также между близлежащими клетками в пределах одного сосуда.
Сигнальные молекулы и транскрипционные факторы, регулирующие эндотелиальную дифференцировку in vivo
Ключевую роль в эмбриогенезе хордовых для появления клеток мезодермы, несущих рецептор VEGFR2 и преддетерминированных в гемангиогенном направлении, играют основной фактор роста фибробластов (bFGF) и морфогенетический белок кости 4 (BMP4) [9–12]. У человека в специализации мезодермы также участвует морфоген IHH, действие которого предшествует BMP4 и bFGF [13].
Миграция, пролиферация и жизнеспособность VEGFR2-позитивных клеток мезодермы во многом контролируются эндотелиальным ростовым фактором VEGF-A. У мыши секреция VEGF-A клетками висцеральной части внезародышевой энтодермы детектируется с седьмого с половиной дня эмбрионального развития в местах, куда мигрируют VEGFR2-позитив-ные гемангиогенные предшественники для формирования кровяных островков желточного мешка [14]. В собственно эмбрионе ростовой фактор VEGF-A на седьмой с половиной день развития представлен повсеместно, однако его повышенная концентрация наблюдается в районе нервной пластинки в том месте, где произойдет закладка спинных аорт [15]. У гетерозиготных мутантов по VEGF-A полностью подавлен васкулогенез, и они погибают в раннем эмбриональном развитии [16, 17]. На ранних этапах васкулогене-за VEGF-A регулирует главным образом жизнеспособность и распространение VEGFR2-позитивных клеток мезодермы, но он не обязателен для их дальнейшей дифференцировки.
Интегрины – другой значительный компонент, участвующий в развитии эндотелия и сосудистой системы. Экспрессия двух субъединиц интегринов αv и α5 важна на ранних этапах эмбриогенеза: их утрата вызывает множественные дефекты специализации мезодермы и гибель эмбрионов мыши на седьмой с половиной день развития [18]. Интегрины существенны для миграции и выживания эндотелиальных клеток и их предшественников во время васкуло- и ангиогенеза [19]. Различают два пути ангиогенеза: bFGF-индуцируемый ангиогенез, зависящий от интегрина αvβ3, и VEGF-индуцируемый ангиогенез, использующий рецептор αvβ5. Каждый из них может быть заблокирован независимо от другого с помощью антител к αvβ3 или αvβ5 соответственно [20]. Предполагают, что эти два интегриновых рецептора отличаются по предпочтениям к лигандам, в качестве которых выступают различные компоненты внеклеточного матрикса, и могут преимущественно использоваться при формировании сосудистой системы разных органов. Интегрин αvβ3 может связываться с металлопротеиназой MMP-2, что позволяет ангиогенным эндотелиальным клеткам разрушать и модифицировать внеклеточный матрикс и обеспечивает их способность к миграции [21]. Лигандами αvβ3 могут выступать витронектин, фибронектин, тромбоспондин, гидролизованный коллаген, фактор фон Виллебранда и остеопорин. Среди компонентов внеклеточного матрикса критичным для васку-логенеза является фибронектин. В эмбрионах мыши, не имеющих фибронектина, обнаруживают дефекты специализации мезодермы и последующего васкуло-генеза, что приводит к их гибели на девятый день развития [22].
Дифференциальная экспрессия генов во время специализации мезодермы и дифференцировки васкулярных предшественников во многом реализуется благодаря транскрипционным факторам. Большое значение на ранних стадиях развития гемопоэтичеcких и ангиогенных клеток в эмбриогенезе хордовых имеет транскрипционный фактор ETV2 (ER71, ETSRP71) [23– 25]. Экспрессия ETV2 детектируется в кровяных островках желточного мешка и самых ранних сосудах в зародыше, однако исчезает на более поздних стадиях [23, 24]. Эмбрионы мышей, в которых не экспрессируется ETV2, не образуют предшественников эндотелиальных клеток и погибают из-за отсутствия первичных сосудов зародыша и кровяных островков желточного мешка [23, 24]. Установлено, что ETV2 является мощным активатором нескольких ранних эндотелиальных генов, в том числе Vegfr2, Tal1, Mef2c, Рecam1, Tie2, VE-cadherin , при этом ETV2 напрямую связывается с их промоторами или энхансерами [23, 24].
Предполагают, что регуляция транскрипции, приводящая к дифференцировке ангиогенных клеток в эндотелиальном направлении, осуществляется транскрипционными факторами семейств ETS и FOX посредством их взаимодействия с композитными ДНК-связывающими сайтами [26]. Эволюционно консервативные FOX: ETS мотивы в геноме человека строго ассоциированы с промоторами и энхансерами многих известных генов, функционирующих в эндотелии, включая Tal1, Tie2, VegfR2, VE-cadherin. Мотивы FOX:ETS устойчиво связываются с транскрипционными факторами FOXC2 и ETV2, ни один из которых не является строго специфичным для эндотелильных клеток. Совместная эктопическая экспрессия Foxc2 и Etv2 в аваскулярных областях эмбрионов Xenopus levis приводит к облигатному запуску генов, характерных эндотелию, и формированию сосудов, тогда как ни один из этих факторов по отдельности не способен вызвать такой же эффект [26].
Основным этапом в развитии эндотелия является его специализация на артериальный, венозный и лимфатический, которую контролирует многоступенчатая система сигнальных путей и транскрипционных факторов. Кроме того, существуют сигнальные молекулы, являющиеся дополнительными регуляторами в этих процессах.
Для начала артериальной дифференцировки важна секреция морфогена SHH, который индуцирует экспрессию ростового фактора VEGF-A в прилегающих сомитах [27]. Связывание VEGF-A с рецептором VEGFR2 и его корецептором нейрофилином NRP-1 [28] индуцирует в эндотелиальных клетках экспрессию компонентов сигнального каскада Notch [27], среди которых трансмембранный рецепторный белок NOTCH1, его лиганд DLL4, ядерный репрессор HEY2, а также транскрипционные факторы FOXC1 и FOXС2, которые непосредственно регулируют экспрессию Dll4 и Hey2 [29]. Активация сигнального пути Notch способствует экспрессии Ephrin-B2 и подавляет EphB4 [30], что вызывает и поддерживает артериальную специализацию эндотелия. Кровеносные сосуды мышей с дефицитом Foxc1 или Foxc2 имеют только венозный эндотелий [31]. Утрата SHH, VEGF-A или ингибирование каскада Notch приводит к остановке дифференцировки эндотелия в артериальном направлении, в то время как экзогенная активация или гиперэкспрессия этих факторов вызывает эктопическую экспрессию маркеров артериального эндотелия. Исследования дифференцировки эмбриональных стволовых клеток мышей показывают, что артериальный эндотелий формируется при высокой концентрации
VEGF-A, тогда как его низкая и средняя концентрация вызывает венозную специализацию клеток [32, 33]. Ингибирование сигнального каскада Notch приводит к развитию венозного эндотелия вместо артериального [32]. Активность сигнального пути WNT индуцирует экспрессию Dll4 и усиливает сигнальный каскад Notch, способствуя артериальной специализации эндотелиальных клеток [34, 35].
Ключевую роль в венозной дифференцировке эндотелия играет ядерный рецептор COUP-TFII, который ингибирует экспрессию генов и сигнальных каскадов, необходимых для образования артериального эндотелия, включая NRP1 и Notch, и снимает репрессию с венозных маркеров EphB4 , нейрофилина Nrp-2 и рецептора Vegfr3 [36]. Одним из индукторов рецептора COUP-TFII может быть ретиноевая кислота [37].
Существует ряд генов, которые активируются в клетках артериального и венозного эндотелия под действием биомеханических факторов, таких как гемодинамические силы. Например, ламинарный поток крови активирует в эндотелиальных клетках экспрессию транскрипционных факторов KLF2 и NRF2, а также ферментов циклооксигеназы 2 и эндотелиальной синтазы оксида азота eNOS, которые совместно обеспечивают выполнение эндотелием своих функций [38–40].
Способность субпопуляции венозных эндотелиальных клеток преобразовываться в лимфатический эндотелий связывают с началом экспрессии генов транскрипционных факторов SOX18 и PROX1 [41– 43]. SOX18 необходим для запуска дифференцировки лимфатического эндотелия и незначителен для поддержания его свойств, несмотря на высокий уровень экспрессии. Ключевым фактором, ответственным за формирование и поддержание характерных свойств лимфатического эндотелия, является PROX1. Для регуляции экспрессии генов лимфатического эндотелия PROX1 взаимодействует с COUP-TFII. В негативной регуляции экспрессии Prox1 участвуют микроРНК miR-181a и miR-31, препятствуя лимфатической специализации [44, 45]. Для предшественников и клеток лимфатического эндотелия характерно наличие рецептора VEGFR3. В эмбриогенезе этот рецептор выявляется также в венозном эндотелии, однако в постнатальном развитии его распространение ограничивается преимущественно клетками лимфатического эндотелия [43]. Благодаря этому рецептору лимфатический эндотелий способен мигрировать в направлении мезенхимальных клеток, секретирующих ростовой фактор VEGF-C, и формировать сеть лимфатических сосудов [42, 43, 46]. У человека мутации гена VEGFR3 являются причиной наследственной лимфедемы первого типа [47]. В эмбриональном развитии мыши клетки мезенхимы и предшественники кардиомиоцитов экспрессируют ген Ccbe1, белок которого совместно с VEGFR-С индуцирует миграцию предшественников лимфатического эндотелия и лимфогенез [48, 49]. Белок CCBE1 также отвечает за обособление островков лимфатических предшественников у Danio rerio [50]. В миграции и адгезии лимфатического эндотелия, а также формировании лимфатических сосудов задействован трансмембранный гликопротеин подопланин (PDPN), нокаут которого у мышей вызывает перинатальную гибель из-за недоразвитости лимфатических сосудов и сниженного дренажа тканей [51, 52]. Для лимфатического эндотелия эмбриона характерен лимфатический гиалуроновый рецептор 1 (LYVE1), который постнатально выявляется только в клетках лимфатических капилляров. Функции LYVE1 неясны, поскольку дефицитные по Live1 мыши имеют нормальную лимфатическую систему [53]. Кроме того, для развития функциональной лимфатической системы необходим интегрин α9β1, который активируется транскрипционным фактором PROX1 и принимает участие в лимфогенезе [54, 55].
Гетерогенность эндотелиальных клеток внутри и между органами
Изначально отличающиеся по морфологии и экспрессии генов, артериальные, венозные и лимфатические эндотелиальные клетки в дальнейшем становятся более гетерогенными и формируют множество субпопуляций под воздействием тканеспецифического окружения разных органов и из-за необходимости выполнять особые органоспецифические функции.
Так, эндотелиальные клетки сосудов мозга образуют гематоэнцефалический барьер, контролирующий трансэндотелиальный транспорт веществ и миграцию клеток [56]. Эндотелиальные клетки сосудов мозга тесно прилегают друг к другу, формируя так называемые плотные межклеточные контакты, предотвращающие миграцию клеток и пассивный транспорт веществ из крови в ткань и наоборот. Для образования плотных контактов эндотелиальные клетки, формирующие гематоэнцефалический барьер, нарабатывают большое количество трансмембранных белков, таких как окклю-дин и клаудины, которые герметизируют пространства между латеральными отделами клеточных стенок [57].
Для обеспечения необходимого транспорта через гематоэнцефалический барьер эндотелиальные клетки сосудов мозга имеют специфические мембранные транспортеры, переносящие к тканям мозга глюкозу, аминокислоты и ряд других веществ [56]. Эндотелиальные клетки гематоэнцефалического барьера, осуществляющие активный транспорт, имеют повышенную потребность в энергии, поэтому количество митохондрий в них в 5–10 раз больше, чем в эндотелии периферических сосудов.
Клетки эндокарда – самые крупные клетки эндотелия [58, 59], имеющие множество микроворсинок. По сравнению с эндотелием капилляров миокарда клетки эндокарда имеют мало везикул, демонстрируют повышенную экспрессию фактора фон Виллебранда и еNOS и формируют преимущественно щелевые контакты, образованные с помощью коннексинов (Cx43, Cx40, Cx37). В клетках эндокарда eNOS концентрируется в аппарате Гольджи, тогда как в эндотелиальных клетках миокарда он диффузно распределен по цитоплазме. Как эндокард, так и эндотелий миокарда выделяют аутокринные и паракринные факторы, которые, воздействуя на кардиомиоциты, регулируют метаболизм сердца, его рост, ритм и сократимость. В норме эндотелиальные клетки сердца продуцируют NO, эндотелин, простациклин (PGI 2), простагландины и превращают неактивный ангиотензин I (Ang I) в активный ангиотензин II (Ang II). Эндокард и эндотелий внутримиокарди-альных сосудов отличаются местом в иерархии регуляции деятельности сердца и вкладом в нее, а также приемом и передачей сигналов.
Мембраны эндотелиальных клеток капилляров эндокринных желез, поджелудочной железы, кишечника, почечных клубочков и синусоид печени содержат небольшие, плотно кластеризующиеся поры диаметром 60–100 нм, которые увеличивают проницаемость сосуда и облегчают обмен между кровью и окружающими тканями. В некоторых случаях поры снабжены диафрагмами, которые подразделяют их на несколько мелких отверстий. Основным компонентом диафрагм, необходимым и достаточным для их формирования, является мембранный гликопротеид второго типа PV-1 [60, 61]. Тканеспецифическим ангиогенным регулятором, ответственным за образование пор в эндотелиальных клетках, является особая форма ростового фактора VEGF (EG-VEGF), секретируемого железистым эпителием [62].
Эндотелиальные клетки сосудов печени видоизменяются на протяжении сосудистого русла. Эндотелий воротной вены печени имеет веретенообразную морфологию и содержит микроворсинки на поверхности клеток. В месте перехода воротной вены в синусоидальные капилляры в цитоплазме эндотелия содержатся актиновые волокна, а в мембранах – снабженные диафрагмами поры [63]. В синусоидальных капиллярах эндотелий формирует прерывистый монослой и также имеет поры, диаметр которых составляет 100 нм [64]. Синусоидальный эндотелий обладает уникальными функциями. Высокая активность эндоцитоза в клетках синусоидального эндотелия делает их высокопропускной системой, способной очищать кровь от содержащихся в ней коллоидов и токсических макромолекул. В этих клетках выявлено три основных рецептора эн-доцитоза: рецептор монозы, фагоцитарный рецептор и рецептор IIb2. Клетки синусоидального эндотелия экспрессируют характерный для эндотелия поверхностный антиген PECAM1, участвующий в формировании клеточных контактов, однако в данном типе клеток он локализуется в цитоплазме, а не на мембране. Другой отличительной чертой эндотелия синусоидальных капилляров является наличие поверхностного антигена CD45, классического маркера гемопоэтических клеток. Клетки эндотелия синусоидальных капилляров играют важную роль в регенерации печени [64]. При повреждениях печени они способны привлекать стволовые клетки, обеспечивать их дифференцировку в гепатоциты с помощью экспрессии фактора HGF, а также участвовать в восстановлении сосудистой системы регенерирующегося органа.
Эндотелиальные клетки и их предшественники также могут быть задействованы в регенерации легких, почки, поджелудочной железы и сердца [65–67]. Предполагают, что эндотелиальные клетки способны вырабатывать ангиокринные факторы, которые обеспечивают регенерацию поврежденного органа, способствуя активации, привлечению и дифференцировке региональных стволовых клеток. Вероятно, ангиокринные факторы функционируют не только при регенерации, но и играют важную морфогенетическую роль в развитии, поскольку нарушение в закладке кровеносных сосудов приводит к дефектному развитию органов [68].
Высокопроизводительные методы анализа транс-криптома показывают, что эндотелиальные клетки разных органов различаются экспрессией нескольких сотен генов [69]. Наблюдаемые различия затрагивают гены, экспрессия которых характерна эндотелиальным клеткам. Однако в большинстве случаев это тканеспецифические гены, кодирующие отличительные росто- вые факторы, молекулы адгезии и факторы, регулирующие обмен веществ, экспрессия которых никогда не рассматривалась как свойство клеток эндотелия.
Эндотелиальные клетки, получаемые путем дифференцировки плюрипотентных стволовых клеток мыши и человека, являются гетерогенными и не имеют тканеспецифических особенностей [70]. Вопрос об универсальности их применения для регенеративных целей остается дискуссионным. Эндотелиальные клетки мыши, полученные из эмбриональных стволовых клеток, при трансплантации животным с частично удаленной печенью участвуют в регенерации и приобретают маркеры, характерные для эндотелия синусоидальных сосудов [69]. В то же время гетерогенная популяция эндотелиальных клеток, дифференцированных из индуцированных стволовых клеток человека, демонстрирует более низкий ангиогенный потенциал по сравнению с эндотелиальными клетками, дифференцированными из индуцированных стволовых клеток в специфическом артериальном направлении [70]. В экспериментах по восстановлению ишемизированных конечностей иммунодефицитных мышей более низкие показатели реваскуляризации обнаруживаются в случае трансплантации эндотелиальных клеток пупочной вены по сравнению с трансплантацией гетерогенной эндотелиальной популяции дифференцированных производных плюрипотентных клеток [71]. Таким образом, при исследовании регенеративного потенциала эндотелиальных клеток необходимо учитывать их гетерогенность и тканеспецифичность. Достаточно ли для проявления наилучшего регенеративного потенциала специализации эндотелия в ответ на сигналы клеточного микроокружения или же эффективнее использовать преддетермини-рованные эндотелиальные популяции, продемонстрируют в дальнейших исследованиях.
Заключение
Формирование специализированных типов эндотелиальных клеток – сложный и многоэтапный процесс, в основе которого лежат биомеханические факторы и взаимодействие сигнальных каскадов. Знание механизмов формирования различных популяций эндотелиальных клеток позволит получать из стволовых клеток специализированные типы эндотелия, которые можно использовать для исследования сосудистых патологий и их лечения, создания эффективных тканеинженерных протезов сосудов, а также реваскуляризации и регенерации ишемизированных органов.
Работа поддержана грантом РФФИ № 14-04-00082 и бюджетным проектом Института цитологии и генетики СО РАН VI.60.1.2.
Список литературы Гетерогенность клеток эндотелия
- Flamme I., Frölich T., Risau W. Molecular mechanisms of vasculogenesis and embryonic angiogenesis//J. Cell. Physiol. 1997. Vol. 173. № 2. P. 206-10.
- Patan S. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis//Cancer Treat. Res. 2004. Vol. 117. P. 3-32.
- Adams R.H., Wilkinson G.A., Weiss C., Diella F., Gale N.W., Deutsch U., Risau W., Klein R. Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis//Genes Dev. 1999. Vol. 13. № 3. P. 295-306.
- Wang H.U., Chen Z.F., Anderson D.J. Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4//Cell. 1998. Vol. 93. № 5. P. 741-53.
- Oliver G., Alitalo K. The lymphatic vasculature: recent progress and paradigms//Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005. Vol. 21. P. 457-83.
- Oliver G., Srinivasan R.S. Lymphatic vasculature development: current concepts//Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008. Vol. 1131. P. 75-81.
- Vondenhoff M.F., van de Pavert S.A., Dillard M.E., Greuter M., Goverse G., Oliver G., Mebius R.E. Lymph sacs are not required for the initiation of lymph node formation//Development. 2009. Vol. 136. № 1. P. 29-34.
- Aird W.C. Endothelial cell heterogeneity//Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012. Vol. 2. № 1. P. a006429.
- Marom K., Levy V., Pillemer G., Fainsod A. Temporal analysis of the early BMP functions identifies distinct anti-organizer and mesoderm patterning phases//Dev. Biol. 2005. Vol. 282. № 2. P. 442-54.
- Winnier G., Blessing M., Labosky P.A., Hogan B.L. Bone morphogenetic protein-4 is required for mesoderm formation and patterning in the mouse//Genes Dev. 1995. Vol. 9. № 17. P. 2105-16.
- Yamaguchi T.P., Harpal K., Henkemeyer M., Rossant J. fgfr-1 is required for embryonic growth and mesodermal patterning during mouse gastrulation//Genes Dev. 1994. Vol. 8. № 24. P. 3032-44.
- Huber T. L., Zhou Y., Mead P.E., Zon L.I. Cooperative effects of growth factors involved in the induction of hematopoietic mesoderm//Blood. 1998. Vol. 92. № 11. P. 4128-37.
- Kelly M.A., Hirschi K.K. Signaling hierarchy regulating human endothelial cell development//Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009. Vol. 29. № 5. P. 718-24.
- Breier G., Clauss M., Risau W. Coordinate expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (flt-1) and its ligand suggests a paracrine regulation of murine vascular development//Dev. Dyn. 1995. Vol. 204. № 3. P. 228-39.
- Hiratsuka S., Kataoka Y., Nakao K., Nakamura K., Morikawa S., Tanaka S., Katsuki M., Maru Y., Shibuya M. Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) is involved in guidance of VEGF receptor-positive cells to the anterior portion of early embryos//Mol. Cell. Biol., 2005. Vol. 25. № 1. P. 355-63.
- Ferrara N., Carver-Moore K., Chen H., Dowd M., Lu L., O'Shea K.S., Powell-Braxton L., Hillan K.J., Moore M.W. Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene//Nature. 1996. Vol. 380. № 6573. P. 439-42.
- Carmeliet P., Ferreira V., Breier G., Pollefeyt S., Kieckens L., Gertsenstein M., Fahrig M., Vandenhoeck A., Harpal K., Eberhardt C., Declercq C., Pawling J., Moons L., Collen D., Risau W., Nagy A. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele//Nature. 1996. Vol. 380. № 6573. P. 435-9.
- Yang J.T., Bader B.L., Kreidberg J.A., Ullman-Culleré M., Trevithick J.E., Hynes R.O. Overlapping and independent functions of fibronectin receptor integrins in early mesodermal development//Dev. Biol. 1999. Vol. 215. № 2. P. 264-77.
- Rupp P.A., Little C.D. Integrins in Vascular Development//Circ. Res. 2001. Vol. 89. № 7. P. 566-572.
- Friedlander M., Brooks P.C., Shaffer R.W., Kincaid C.M., Varner J.A., Cheresh D.A. Definition of two angiogenic pathways by distinct alpha v integrins//Science. 1995. Vol. 270. № 5241. P. 1500-2.
- Brooks P.C., Strömblad S., Sanders L.C., von Schalscha T.L., Aimes R.T., Stetler-Stevenson W.G., Quigley J.P., Cheresh D.A. Localization of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-2 to the surface of invasive Cells by interaction with integrin alpha v beta 3//Cell. 1996. Vol. 85. № 5. P. 683-93.
- George E.L., Georges-Labouesse E.N., Patel-King R.S., Rayburn H., Hynes R.O. Defects in mesoderm, neural tube and vascular Development in mouse embryos lacking fibronectin//Development. 1993. Vol. 119. № 4. P. 1079-91.
- Ferdous A., Caprioli A., Iacovino M., Martin C.M., Morris J., Richardson J.A., Latif S., Hammer R.E., Harvey R.P., Olson E.N., Kyba M., Garry D.J. Nkx2-5 transactivates the Ets-related protein 71 gene and specifies an endothelial/endocardial fate in the developing embryo//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009. Vol. 106. № 3. P. 814-9.
- Lee D., Park C., Lee H., Lugus J.J., Kim S.H., Arentson E., Chung Y.S., Gomez G., Kyba M., Lin S., Janknecht R., Lim D.-S., Choi K. ER71 acts downstream of BMP, Notch, and Wnt signaling in blood and vessel progenitor specification. Cell Stem Cell. 2008. Vol. 2. № 5. P. 497-507.
- Sumanas S., Gomez G., Zhao Y., Park C., Choi K., Lin S. Interplay among Etsrp/ER71, Scl, and Alk8 signaling controls endothelial and myeloid cell formation//Blood. 2008. Vol. 111. № 9. P. 4500-10.
- De Val S., Chi N.C., Meadows S.M., Minovitsky S., Anderson J.P., Harris I.S., Ehlers M.L., Agarwal P., Visel A., Xu S.-M., Pennacchio L.A., Dubchak I., Krieg P.A., Stainier D.Y.R., Black B.L. Combinatorial regulation of endothelial gene expression by ets and forkhead transcription factors//Cell. 2008. Vol. 135. № 6. P. 1053-64.
- Lawson N.D., Vogel A.M., Weinstein B.M. Sonic hedgehog and vascular endothelial growth factor act upstream of the Notch pathway during arterial endothelial differentiation//Dev. Cell. 2002. Vol. 3. № 1. P. 127-36.
- Gu C., Rodriguez E.R., Reimert D.V., Shu T., Fritzsch B., Richards L.J., Kolodkin A.L., Ginty D.D. Neuropilin-1 conveys semaphorin and VEGF signaling during neural and cardiovascular development//Dev. Cell. 2003. Vol. 5. № 1. P. 45-57.
- Hayashi H., Kume T. Foxc transcription factors directly regulate Dll4 and Hey2 expression by interacting with the VEGF-Notch signaling pathways in endothelial cells//PLoS One. 2008. Vol. 3. № 6. P. e2401.
- Lawson N.D., Scheer N., Pham V.N., Kim C.-H., Chitnis A.B., Campos-Ortega J.A., Weinstein B.M. Notch signaling is required for arterial-venous differentiation during embryonic vascular Development//Development. 2001. Vol. 128. № 19. P. 3675-3683.
- Seo S., Fujita H., Nakano A., Kang M., Duarte A., Kume T. The forkhead transcription factors, Foxc1 and Foxc2, are required for arterial specification and lymphatic sprouting during vascular development//Dev. Biol. 2006. Vol. 294. № 2. P. 458-70.
- Lanner F., Sohl M., Farnebo F. Functional arterial and venous fate is determined by graded VEGF signaling and notch status during embryonic stem cell differentiation//Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007. Vol. 27. № 3. P. 487-93.
- Zhang G., Zhou J., Fan Q., Zheng Z., Zhang F., Liu X., Hu S. Arterial-venous endothelial cell fate is related to vascular endothelial growth factor and Notch status during human bone mesenchymal stem cell differentiation//FEBS Lett. 2008. Vol. 582. № 19. P. 2957-64.
- Yamamizu K., Matsunaga T., Uosaki H., Fukushima H., Katayama S., Hiraoka-Kanie M., Mitani K., Yamashita J.K. Convergence of Notch and beta-catenin signaling induces arterial fate in vascular progenitors//J. Cell Biol. 2010. Vol. 189. № 2. P. 325-38.
- Corada M., Nyqvist D., Orsenigo F., Caprini A., Giampietro C., Taketo M.M., Iruela-Arispe M.L., Adams R.H., Dejana E. The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway modulates vascular remodeling and specification by upregulating Dll4/Notch signaling//Dev. Cell. 2010. Vol. 18. № 6. P. 938-49.
- You L.-R., Lin F.-J., Lee C.T., DeMayo F.J., Tsai M.-J., Tsai S.Y. Suppression of Notch signalling by the COUP-TFII transcription factor regulates vein identity//Nature. 2005. Vol. 435. № 7038. P. 98-104.
- Kruse S.W., Suino-Powell K., Zhou X.E., Kretschman J.E., Reynolds R., Vonrhein C., Xu Y., Wang L., Tsai S.Y., Tsai M.-J., Xu H.E. “dentification of COUP-TFII orphan nuclear receptor as a retinoic acid-activated receptor//PLoS Biol. 2008. Vol. 6. № 9. P. e227.
- Dekker R.J., van Soest S., Fontijn R.D., Salamanca S., de Groot P.G., VanBavel E., Pannekoek H., Horrevoets A.J.G. Prolonged fluid shear stress induces a distinct set of endothelial cell genes, most specifically lung Krüppel-like factor (KLF2)//Blood. 2002. Vol. 100. № 5. P. 1689-98.
- Kim M., Kim S., Lim J.H., Lee C., Choi H.C., Woo C.-H. Laminar flow activation of ERK5 protein in vascular endothelium leads to atheroprotective effect via NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activation//J. Biol. Chem. 2012. Vol. 287. № 48. P. 40722-31.
- Topper J.N., Cai J., Falb D., Gimbrone M.A. Identification of vascular endothelial genes differentially responsive to fluid mechanical stimuli: cyclooxygenase-2, manganese superoxide dismutase, and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase are selectively up-regulated by steady laminar shear stress//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996. Vol. 93. № 19. P. 10417-22.
- François M., Caprini A., Hosking B., Orsenigo F., Wilhelm D., Browne C., Paavonen K., Karnezis T., Shayan R., Downes M., Davidson T., Tutt D., Cheah K.S.E., Stacker S.A., Muscat G.E.O., Achen M.G., Dejana E., Koopman P. Sox18 induces development of the lymphatic vasculature in mice//Nature. 2008. Vol. 456. № 7222. P. 643-7.
- Kiefer F., Adams R.H. Lymphatic endothelial differentiation: start out with Sox-carry on with Prox//Genome Biol. 2008. Vol. 9. № 12. P. 243.
- Kume T. Specification of arterial, venous, and lymphatic endothelial cells during embryonic development//Histol. Histopathol. 2010. Vol. 25. № 5. P. 637-46.
- Kazenwadel J., Michael M.Z., Harvey N.L. Prox1 expression is negatively regulated by miR-181 in endothelial cells//Blood. 2010. Vol. 116. № 13. P. 2395-401.
- Pedrioli D.M.L., Karpanen T., Dabouras V., Jurisic G., van de Hoek G., Shin J.W., Marino D., Kälin R.E., Leidel S., Cinelli P., Schulte-Merker S., Brändli A.W., Detmar M. miR-31 functions as a negative regulator of lymphatic vascular lineage-specific differentiation in vitro and vascular development in vivo//Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010. Vol. 30. № 14. P. 3620-34.
- Karkkainen M.J., Haiko P., Sainio K., Partanen J., Taipale J., Petrova T.V., Jeltsch M., Jackson D.G., Talikka M., Rauvala H., Betsholtz C., Alitalo K. Vascular endothelial growth factor C is required for sprouting of the first lymphatic vessels from embryonic veins//Nat. Immunol. 2004. Vol. 5. № 1. P. 74-80.
- Irrthum A., Karkkainen M.J., Devriendt K., Alitalo K., Vikkula M. Congenital hereditary lymphedema caused by a mutation that inactivates VEGFR3 tyrosine kinase//Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000. Vol. 67. № 2. P. 295-301.
- Facucho-Oliveira J., Bento M., Belo J.-A. Ccbe1 expression marks the cardiac and lymphatic progenitor lineages during early stages of mouse development//Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011. Vol. 55. № 10-12. P. 1007-14.
- Bos F.L., Caunt M., Peterson-Maduro J., Planas-Paz L., Kowalski J., Karpanen T., van Impel A., Tong R., Ernst J.A., Korving J., van Es J.H., Lammert E., Duckers H.J., Schulte-Merker S. CCBE1 is essential for mammalian lymphatic vascular development and enhances the lymphangiogenic effect of vascular endothelial growth factor-C in vivo//Circ. Res. 2011. Vol. 109. № 5. P. 486-91.
- Hogan B.M., Bos F.L., Bussmann J., Witte M., Chi N.C., Duckers H.J., Schulte-Merker S. Ccbe1 is required for embryonic lymphangiogenesis and venous sprouting//Nat. Genet. 2009. Vol. 41. № 4. P. 396-8.
- Matsui K., Breitender-Geleff S., Soleiman A., Kowalski H., Kerjaschki D., Podoplanin, a novel 43-kDa membrane protein, controls the shape of podocytes//Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999. Vol. 14. Suppl. 1. P. 9-11.
- Schacht V., Ramirez M.I., Hong Y.-K., Hirakawa S., Feng D., Harvey N., Williams M., Dvorak A.M., Dvorak H.F., Oliver G., Detmar M. T1alpha/podoplanin deficiency disrupts normal lymphatic vasculature formation and causes lymphedema//EMBO J. 2003. Vol. 22. № 14. P. 3546-56.
- Jackson D.G. Biology of the lymphatic marker LYVE-1 and applications in research into lymphatic trafficking and lymphangiogenesis//APMIS. 2004. Vol. 112. № 7-8. P. 526-38.
- Mishima K., Watabe T., Saito A., Yoshimatsu Y., Imaizumi N., Masui S., Hirashima M., Morisada T., Oike Y., Araie M., Niwa H., Kubo H., Suda T., Miyazono K. Prox1 induces lymphatic endothelial differentiation via integrin alpha9 and other signaling cascades//Mol. Biol. Cell. 2007. Vol. 18. № 4. P. 1421-9.
- Danussi C., Del Bel Belluz L., Pivetta E., Modica T.M.E., Muro A., Wassermann B., Doliana R., Sabatelli P., Colombatti A., Spessotto P. EMILIN1/a9ß1 integrin interaction is crucial in lymphatic valve formation and maintenance//Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013. Vol. 33. № 22. P. 4381-94.
- Zlokovic B.V. The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders//Neuron. 2008. Vol. 57. № 2. P. 178-201.
- Haseloff R.F., Dithmer S., Winkler L., Wolburg H., Blasig I.E. Transmembrane proteins of the tight junctions at the blood-brain barrier: structural and functional aspects//Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015. Vol. 38. P. 16-25.
- Brutsaert D.L. Cardiac endothelial-myocardial signaling: its role in cardiac growth, contractile performance, and rhythmicity//Physiol. Rev. 2003. Vol. 83. № 1. P. 59-115.
- Aird W.C. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds//Circ. Res. 2007. Vol. 100. № 2. P. 174-90.
- Ioannidou S., Deinhardt K., Miotla J., Bradley J., Cheung E., Samuelsson S., Ng Y.-S., Shima D.T. An in vitro assay reveals a role for the diaphragm protein PV-1 in endothelial fenestra morphogenesis//Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006. Vol. 103. № 45. P. 16770-5.
- Stan R.V., Tkachenko E., Niesman I.R. PV1 is a key structural component for the formation of the stomatal and fenestral diaphragms//Mol. Biol. Cell. 2004. Vol. 15. № 8. P. 3615-30.
- LeCouter J., Kowalski J., Foster J., Hass P., Zhang Z., Dillard-Telm L., Frantz G., Rangell L., DeGuzman L., Keller G.A., Peale F., Gurney A., Hillan K.J., Ferrara N. Identification of an angiogenic mitogen selective for endocrine gland endothelium//Nature. 2001. Vol. 412. № 6850. P. 877-84.
- Oda M., Yokomori H., Han J.-Y. Regulatory mechanisms of hepatic microcirculation//Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2003. Vol. 29. № 3-4. P. 167-82.
- DeLeve L.D. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and liver regeneration//J. Clin. Invest. 2013. Vol. 123. № 5. P. 1861-6.
- Ding B.-S., Nolan D.J., Guo P., Babazadeh A.O., Cao Z., Rosenwaks Z., Crystal R.G., Simons M., Sato T.N., Worgall S., Shido K., Rabbany S.Y., Rafii S. Endothelial-derived angiocrine signals induce and sustain regenerative lung alveolarization//Cell. 2011. Vol. 147. № 3. P. 539-53.
- Jia X., Lü H., Li C., Feng G., Yao X., Mao L., Ke T., Che Y., Xu Y., Li Z., Kong D. Human embryonic stem cells-derived endothelial cell therapy facilitates kidney regeneration by stimulating renal resident stem cell proliferation in acute kidney injury//Chinese Sci. Bull. 2013. Vol. 58. № 23. P. 2820-2827.
- Talavera-Adame D., Dafoe D.C. Endothelium-derived essential signals involved in pancreas organogenesis//World J. Exp. Med. 2015. Vol. 5. № 2. P. 40-9.
- Ramasamy S.K., Kusumbe A.P., Adams R.H. Regulation of tissue morphogenesis by endothelial cell-derived signals//Trends Cell Biol. 2015. Vol. 25. № 3. P. 148-57.
- Nolan D.J., Ginsberg M., Israely E., Palikuqi B., Poulos M.G., James D., Ding B.-S., Schachterle W., Liu Y., Rosenwaks Z., Butler J.M., Xiang J., Rafii A., Shido K., Rabbany S.Y., Elemento O., Rafii S. Molecular signatures of tissue-specific microvascular endothelial cell heterogeneity in organ maintenance and regeneration//Dev. Cell. 2013. Vol. 26. № 2. P. 204-19.
- Rufaihah A.J., Huang N.F., Kim J., Herold J., Volz K.S., Park T.S., Lee J.C., Zambidis E.T., Reijo-Pera R., Cooke J.P. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells exhibit functional heterogeneity//Am. J. Transl. Res. 2013. Vol. 5. № 1. P. 21-35.
- Yamahara K., Sone M., Itoh H., Yamashita J.K., Yurugi-Kobayashi T., Homma K., Chao T.-H., Miyashita K., Park K., Oyamada N., Sawada N., Taura D., Fukunaga Y., Tamura N., Nakao K. Augmentation of neovascularization in hindlimb ischemia by combined transplantation of human embryonic stem cells-derived endothelial and mural cells//PLoS One. 2008. Vol. 3. № 2. P. e1666.


