High-Performance Concretes for Machine Building with Nano- and Micro-Scale Raw Materials
Автор: Vitaly A. Beregovoy, Evgeny V. Snadin, Alexander S. Inozemtsev, Anton S. Pilipenko
Журнал: Nanotechnologies in Construction: A Scientific Internet-Journal @nanobuild-en
Рубрика: Construction materials science
Статья в выпуске: 3 Vol.15, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. The unique combination of rheotechnological properties and mechanical performance opens up prospects for the application of self-compacting and high-strength concretes in the manufacturing of base elements for machines and industrial equipment. The processes of adsorption of modern plasticizers on various mineral and polymeric modifiers of concrete mixtures were investigated. The compatibility of nano- and micro-scale mineral additives in composite cementitious binders was determined using calorimetry with an improved semi-adiabatic setup. Materials and methods. The cementitious binders used were CEM 52.5N Portland cement (Asia Cement LLC, Russia) and Nanodur (Germany, Dyckerhoff GmbH); hyperplasticizers included Melflux 1641F, 2651F, 5581F (Germany), PCE TR-6088 (China), Sika ViscoCrete 240 HE Plus and 226-P (Russia); superabsorbent polymer; nano- and micro-scale mineral additives included microsilica MK-85, metacaolin VMK-45, microcalcite MM-315, marshalite Silverbond 15 EW, and ground silica-containing rocks. Selective dissolution, differential thermal analysis, laser granulometry, and semi-adiabatic calorimetry were employed. Results and discussion. The quality of ultrafine mineral additives determines their ability to chemically bind portlandite through pozzolanic activity. Among the investigated additives, microsilica and gaize demonstrated the highest pozzolanic activity. Thermal activation was effective for components consisting of crystalline silica (marshalite, ground quartz sand), resulting in a 25% increase in performance. There was no selective adsorption of hyper plasticizer molecules by superabsorbent modifiers based on sodium polyacrylate compositions. Metakaolin and tremolite exhibited high adsorption to hyper plasticizers among the mineral additives. The rapid evaluation of the influence of formulation factors on the setting of cementitious composites was tested on an improved version of the semi-adiabatic calorimeter. Conclusions. The presence of micro-scale mineral additives based on microsilica in composite cementitious binders enables the development of high-performance concretes adapted for machine building. The study of pozzolanic activity, adsorption capacity, and cumulative heat release curves has indicated the feasibility of replacing microsilica with metacaolin and the potential for its partial blending with finely ground natural gaize. Analysis of the thermal effects accompanying the hydration processes of the "cement-additive-water" system with calorimeters allows us to provide more efficient research on the compatibility of additives in high-performance concrete compositions.
High-performance concretes, machine building, nano- and micrometer-scale additives, compatibility, calorimetry. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS: The research was conducted with the financial support of the Moscow State University of Civil
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142238285
IDR: 142238285 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2023-15-3-200-210
Текст научной статьи High-Performance Concretes for Machine Building with Nano- and Micro-Scale Raw Materials
Original article
Despite all the positive qualities, modern structural materials based on metal alloys are characterized by high energy consumption during production and pro- cessing. In this regard, the search for alternatives with comparable structural quality, technologies of which do not involve hot processes (melting, casting, welding, etc.), is among the relevant tasks of current materials science. The unique combination of rheotechnological proper-
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE ties of mixtures and mechanical parameters of hardened concrete determines the high potential of self-compacting and high-strength types of high-performance concretes (HPC) as a basis for cold casting of massive parts for machines and industrial equipment. The success of the proposed approach depends on solving a complex of tasks related to the adaptation of existing formulations to the features of casting technology and the operating parameters of structural elements.
The main differences in the formulations of HPC compositions are related to the type and quantity of modifying additives, as well as the specifics of preparatory operations and processes of raw material mixture homogenization. A common feature of HPC is the widespread use of high-dispersion (nano- and micrometer-scale) mineral components in the compositions. The structureforming function of such additives varies depending on the scale level [1]:
– Micrometer-scale additives are introduced together with selected chemical plasticizers to increase the physical volume of the rheologically active (watercement-mineral) matrix.
– Nanoscale additives directly participate in the formation of the mineral-phase composition of the solidifying conglomerate, interacting with the hydrolysis lime Ca(OH)2 released during the hydration of the alite component of clinker. As a result, the microstructure of the cement stone is compacted and strengthened by replacing the mineral phase of portlandite with stronger neoformations such as calcium silicate hydrates (tobermorite, xonotlit, truscottite, etc.).
The specificity of participation in structure-forming processes leads to differences in the mineral type of the used high- and ultrafine-dispersed additives. The former, which enhance the rheological properties of the concrete mixture, are represented by powdered stone made from quartzite, limestone, dolomite [2], blast furnace slag, siliceous rocks, etc. Nanoscale components with increased pozzolanic activity are usually nanosilicas of technological origin (condensed, chemically precipitated, pyrogenic) obtained by reducing high-purity quartz with coal in electric arc furnaces during the production of silicon and ferrosilicon.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The cementitious binders used were CEM 0 52.5N Portland cement (Asia Cement LLC, Russia) and Nanodur (Germany, Dyckerhoff GmbH); hyperplasticizers (HP) included Melflux 1641F, 2651F, 5581F (Germany), PCE TR-6088 (China), Sika ViscoCrete 240 HE Plus and 226-P (Russia); superabsorbent polymer; nano- and micro-scale mineral additives included microsilica MK-85, metacaolin VMK-45, microcalcite MM-315, marshalite Silverbond 15 EW, and ground silica-containing rocks. Selective dissolution, differential thermal analysis, laser granulometry, and semi-adiabatic calorimetry were employed.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Compositions based on Nanodur Compound [3, 4] have proven themselves effective in the production of structures and basic components of processing equipment made from cement casting. Despite a high specific binder consumption (610 kg/m3), their application allows for the production of structural fiber-reinforced concretes with compressive strength ranging from 170 to 190 MPa.
The technical and economic indicators of modern materials used in the production of structures, including basic components of machinery and equipment, are presented in Table 1.
Table 1
Industrial materials indicators
|
Material |
Compressive strength (Rc), MPa |
Tensile strength (Rr), MPa |
Elastic modulus (Est), GPa |
Density (ρ), t/m3 |
Cost, thousand rubles per ton |
|
Cast iron |
550 |
170 |
115 |
7…7.8 |
30 |
|
Steel |
500 |
500 |
210 |
7.7…8.2 |
50.5 |
|
Aluminum alloys |
200 |
200 |
70 |
2.6…2.9 |
140 |
|
Natural granite |
230 |
10 |
49 |
2.34…2.78 |
10 |
|
Polymeric composite “ Syntegran ” |
120 |
27 |
27 |
2.4 |
150 |
|
Nanodur compound “ Nanodur 5941 ” |
135–150 |
15 |
46.5 |
2.45 |
н/д |
|
High-performance concretes (HPC) |
130 |
10 |
50 |
2.4…2.5 |
10 |
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
From the tabulated data, it can be observed that the properties of construction materials based on Nanodur cement compound reflect the modern level of development in the field of concrete technology. The composition of Nanodur was determined using selective dissolution and differential thermal analysis (DTA) methods. The results of DTA analysis are presented in Figure 1. The absence of endothermic effects in the temperature range of 800 to 1000 °C on the DTA curve, coupled with mass loss data and chemical analysis, allowed the conclusion that Nanodur does not contain carbonate components.
The measured values of specific surface area (Ss) ranged from 540 to 542 m2/kg, significantly higher than the average values for ordinary Portland cement. The particle size distribution of Nanodur was analyzed using a Shimadzu SALD-3101 laser diffraction analyzer. The obtained histogram shows the distribution of particle sizes, and the cumulative particle size distribution curve is shown in Figure 2. The analysis revealed that the particle size distribution is limited to the range of 0.3 to 154 µm. The histogram displays three peaks in the particle size distribution: the first peak at 0.41 µm, the second peak at 1.3 µm, and the third peak at 39.0 µm. Thus, in addition to the predominance of micrometer-sized particles, a significant fraction of submicrometer particles was identified, which contributes to the formation of a denser rheological and chemically active dispersed structure during the solidification of the compound. The presence of a ho-
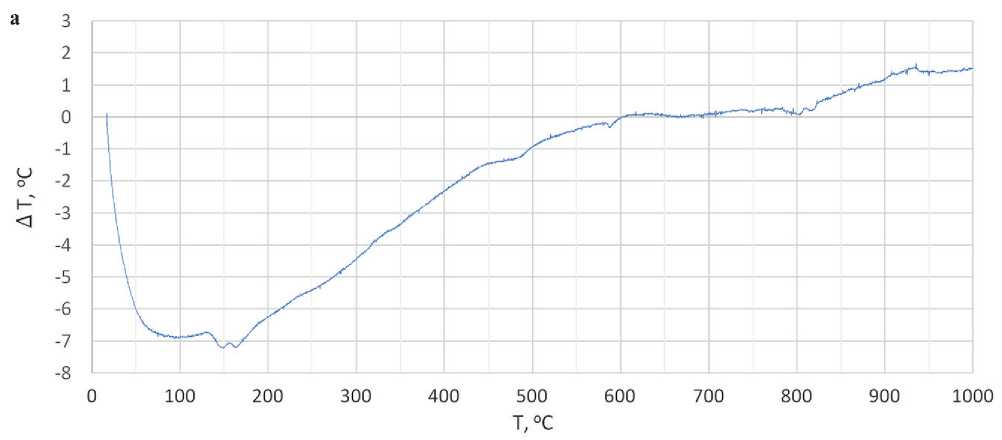
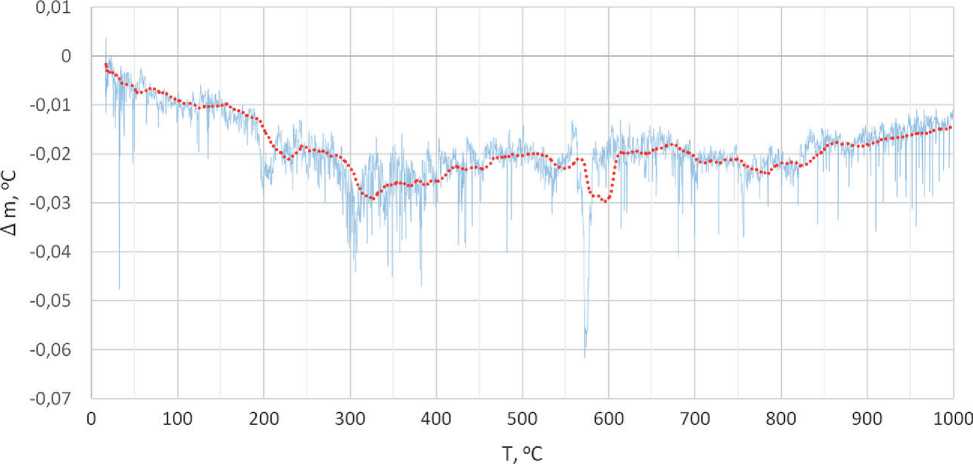
Fig. 1. Results of thermal analysis of Nanodur binder: a – differential thermogram; b – thermogravimetric curve
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE mogeneous fraction with particles in the range of 0.35 to 0.50 µm indicates the presence of technogenic microsilica in the composition.
In order to find alternatives to expensive microsilica, fine-dispersed additives were tested: metacaolin, marshalite, gaize, diatomite, tripolite, waste glass cullet, and gas silicate, as well as ground quartz sand and granite screenings.
The quality of ultrafine mineral additives largely depends on their ability to chemically bind portlandite by exhibiting their pozzolanic properties [5, 6]. The pozzo- lanic activity coefficient (K) was determined by dissolving the tested suspension in a 10% NaOH solution. The results of the experiments are shown in Fig. 3.
Based on the value of K , the investigated additives form the following group series: microsilica, gaize (max) → diatomite, tripolite (med) → marshalite, glass, gas silicate, quartz sand, granite screenings (min).
Thermal activation is an effective method for increasing the activity of mineral additives [7]. The thermal activation of natural fillers was carried out using two thermal treatment modes (TM): № 1 – heating for 20 minutes to
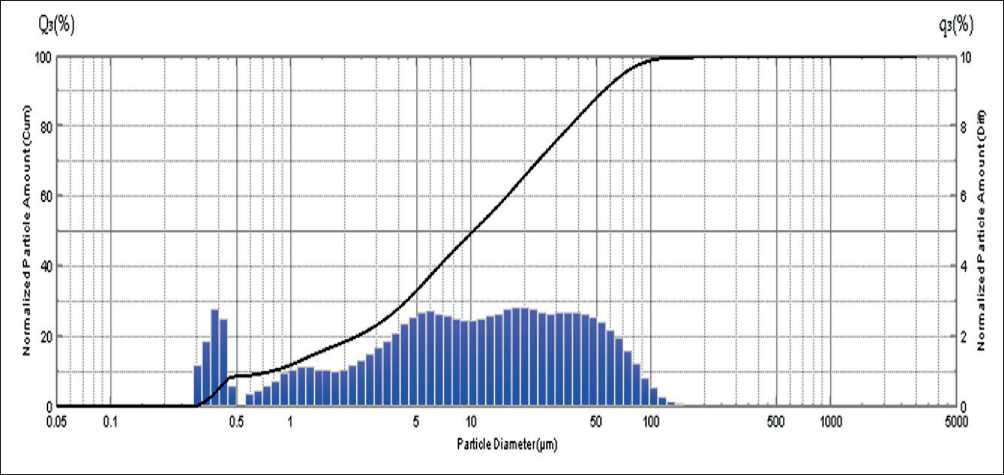
Fig. 2. Results of granulometric analysis
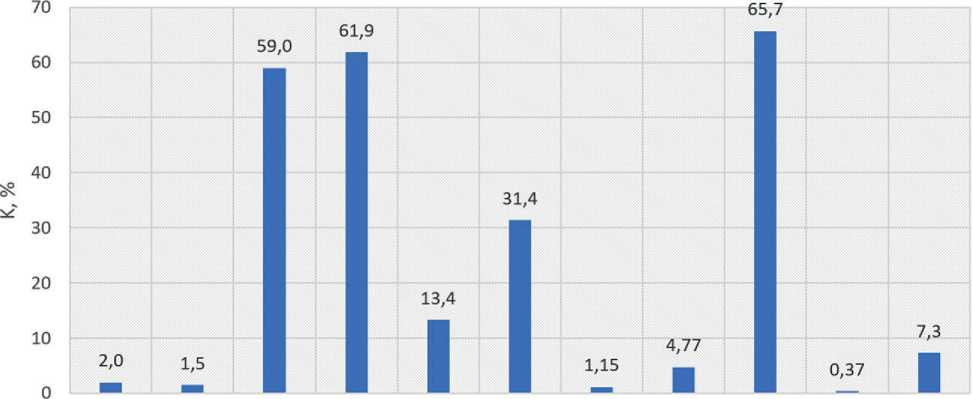
marshalite quartz sand gaize (gr) gaize (yel) tripolite diatomite granite scr. glass ser. MK-85 gas silicate VMK-45
Fig. 3. Results of determining the pozzolanic activity
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE t = 620оC; isothermal holding – 30 minutes; cooling – 120 minutes; № 2 – heating for 20 minutes to t = 620оC; isothermal holding – 30 minutes and rapid cooling with an air flow. The results of the experiments are presented in Fig. 4.
Thermal treatment has the maximum effect on materials consisting of crystalline silica (marshalling, ground quartz sand). This is due to the development of structural defects resulting from thermal stress and the phase (α → β) transition of quartz, which increases the surface energy of the particles. It is logical that this effect is enhanced after thermal treatment involving rapid cooling of the material grains (TM-2). Rocks formed by amorphous silica showed low susceptibility to thermal activation.
Influence of mineral and superabsorbent additives on the surface activity of polycarboxylate-based hyperplasticizers in cement systems (Melflux, Sika, PCE TR) was evaluated by measuring the surface tension of aqueous solutions (σ, J/m2) (Fig. 5).
According to the obtained data, Melflux additives (1641f, 2651f, 5581f) demonstrate a nearly linear decrease in surface tension with increasing concentration up to 1...1,5%, followed by reaching a plateau. Sika hyperplasticizers (226-p, 240), as well as PCE TR-6088, show a more moderate reduction in the surface tension coefficient at an optimal concentration of 0,5%.
An innovative method for reducing shrinkage and internal water loss in hardening concrete involves the use of superabsorbent polymers (SAP) that effectively accumulate excess process water during the initial stages of monolithic construction manufacturing [8–10]. To investigate the interaction of hyperplasticizer solutions and SAP, a model system was used consisting of a 1% solution of HP Melflux 5581F and water-saturated sodium polyacrylate granules. The ratio between the components corresponds to their dosages used in SCC compositions (HP:SAP = 1:1) [11]. The change in σ of distilled water and the hyperplasticizer solution after the addition of water-saturated SAP was investigated. The experimental results are shown in Figure 6.
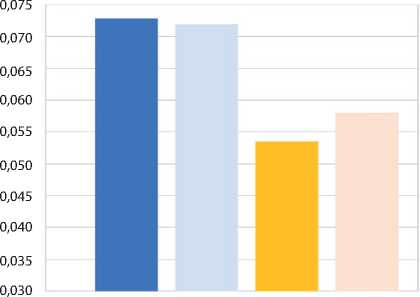
From the graph, it can be seen that the introduction of SAP does not affect the σ value of the aqueous solution. The mechanism of increasing the surface tension of the hyperplasticizer solution when SAP is added may be attributed to both a decrease in the concentration of the HP-solution due to the replacement of a portion of the solution with water previously absorbed by SAP and the sorption of the hyperplasticizer by the sodium polyacrylate granules. A verification experiment to determine the mechanism of interaction between the considered components involved adding dry SAP to hyperplasticizer solutions (0,5% and 1%).
The graphs in Figure 7 show that the introduction of dry SAP does not result in a change in the σ of the solutions, indicating that the concentration of the hyperplasticizer remains constant. This suggests the absence of a selective adsorption process of hyperplasticizer molecules, with the solution being absorbed by the SAP granules without separation.
The adsorption capacity towards hyperplasticizer molecules was determined by changes in the surface tension of the filtrate in relation to mineral additives with different pozzolanic properties (Fig. 8 and 9).
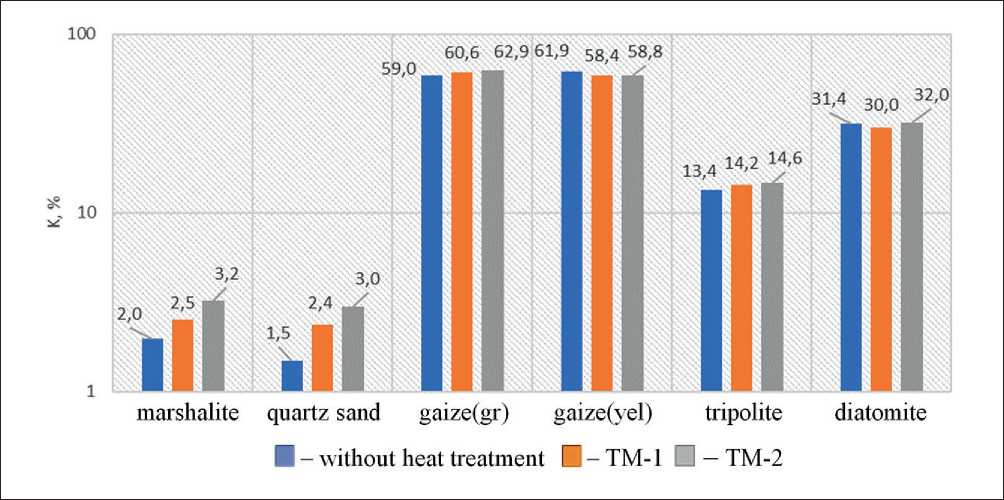
Fig. 4. Influence of thermal treatment on pozzolanic activity
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
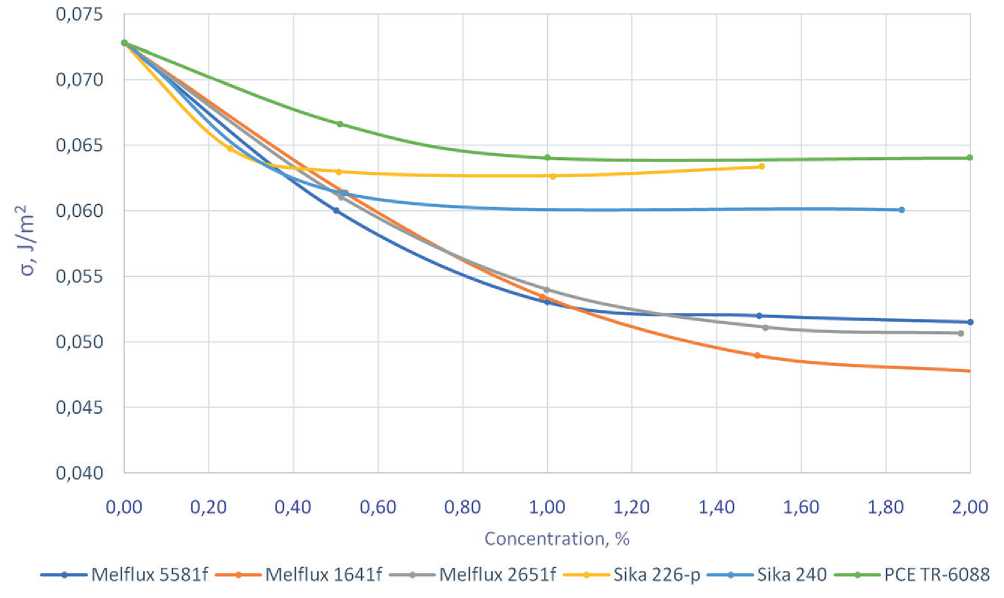
Fig. 5. Influence of hyperplasticizers on surface tension
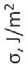
■ Water
Water passed through SAP
■ HP (1%)
HP (1%) after aging with water-saturated SAP (1:1)
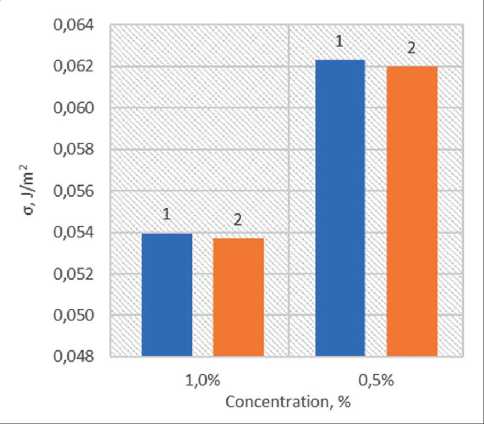
Fig. 7. Influence of SAP additive on the surface tension of hyperplasticizer solutions: 1 – without additive;
2 – with additive
Fig. 6. Influence of SAP and hyperplasticizer additives on the surface tension of solutions
The obtained data indicate that the introduction of all investigated additives leads to an increase in the surface tension coefficient of the solution. The highest adsorption effect is observed for metakaolin and trass additives.
An effective method for the rapid assessment of the influence of formulation and technological factors on the hardening of cement composites is calorimetry [12–14]. Analysis of the resulting thermal effects accompanying the hydration processes of the “cement-additive-water” system allows for determining the compatibility of the additive in the early stages of designing HPC. Considering the positive experience of using heat-flow calorimeters,
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
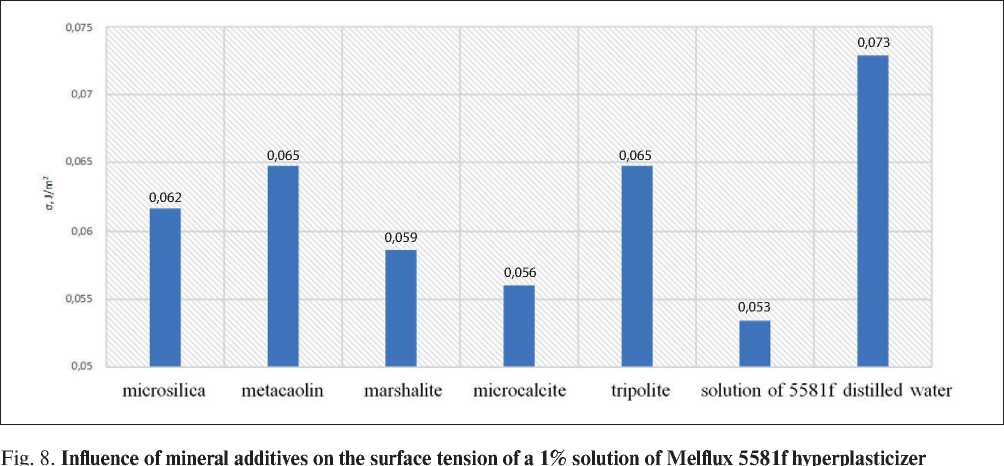
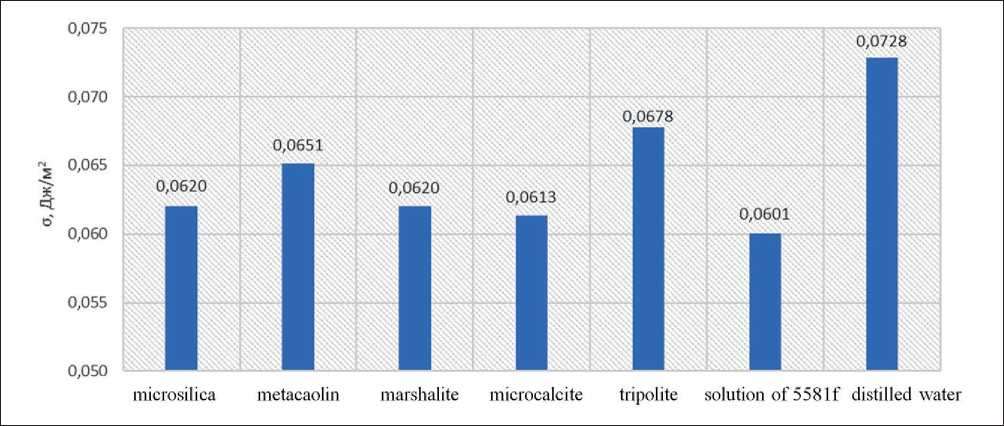
Fig. 9. Influence of mineral additives on the surface tension of a 0.5% solution of Melflux 5581f hyperplasticizer
improved prototypes of such devices were developed for the upcoming research [15].
The heat evolution over a period (J/min) was calculated using the following formula:
Q = c mix • m mix •(T 2 –T 1 ) + W • t p , (1)
where cmix – heat capacity of the mixture (J/(kg•оC)), mmix – mass of the mixture (kg), T2 and T1 – temperatures of the mixture at the end and the beginning of the respective period (оC), W – power of heat loss at a certain temperature difference for the corresponding period (W), tp – duration of the period (s).
The specific heat capacity of the mixture was determined according to the additivity rule using the following formula:
Cmix — / ci ' I h ™J ^^mb: (2)
1=1
where n – number of components in the mixture, c i – specific heat capacity of the i -th component (J/(kg•оC)), mi – mass of the i -th component (kg).
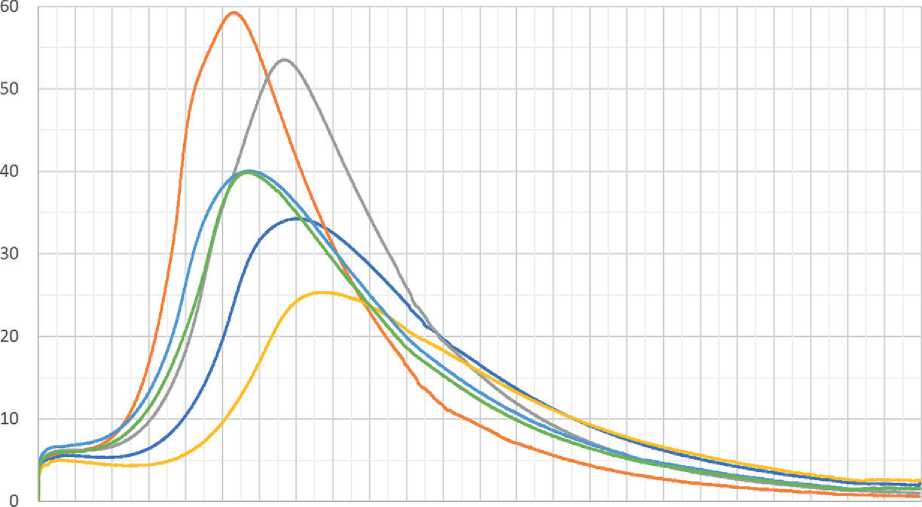
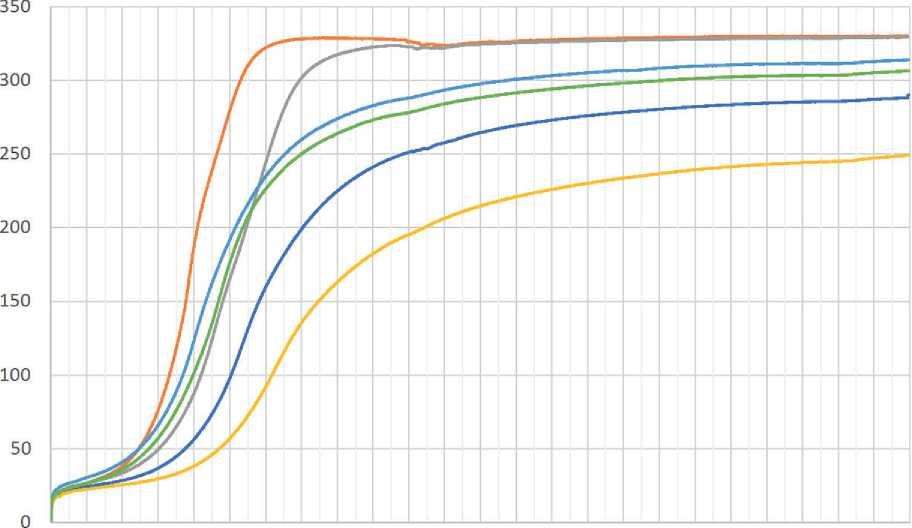
Then, a cumulative heat release curve was constructed to determine the durations of the main periods: preinduction, induction, and post-induction. Examples of thermometric curves constructed from data obtained on the experimental setup are shown in Figure 10.
General trends of the hardening processes are expressed by thermo-kinetic dependencies of the rate dQ/dτ = f (τ), heat release Q = f (τ), or cement hydration
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
О 2 4 б 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48
Times, h
-----microcalcite -----MK85 -----VMK45 -----marshalite -----gaize (gr) -----tripolite
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48
Times, h
— microcalcite -----MK85 -----VMK45 marshalite -----gaize (gr) -----tripolite
Fig. 10. Thermometric curves: influence of mineral additives on the heat release of cement paste with HP Sika226p
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
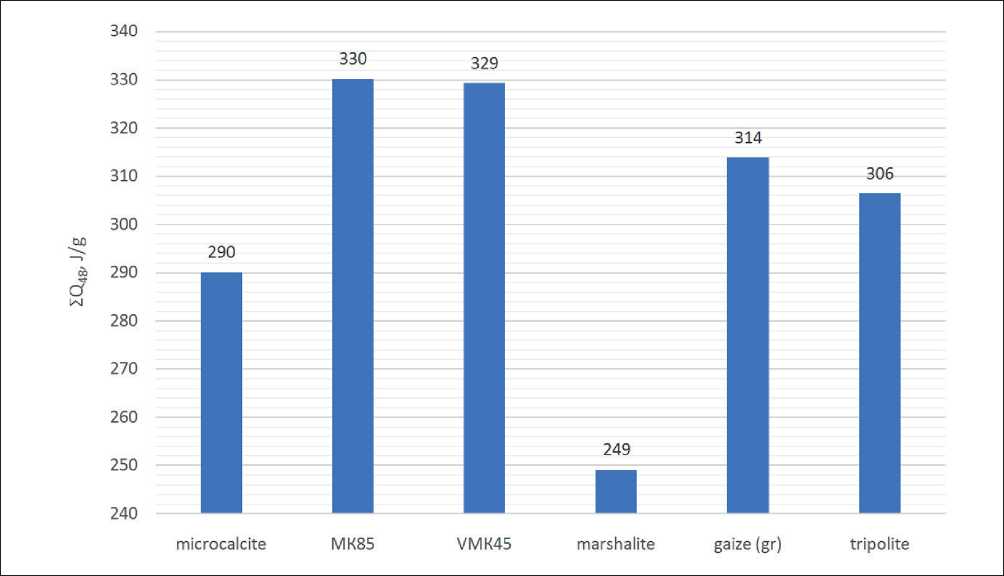
Fig. 11. Total heat release of cement pastes (48 hours)
α = f (τ) [16, 17]. The kinetics of heat release during hardening is in agreement with the process of cement hydration, which is determined by nucleation and subsequent growth of hydrated new formations [18–20]:
α = 1–e– ktn , (3)
where α – degree of hydration of the binder, t – time, k and n – constants dependent on the type of cement and the prevailing reaction mechanism.
The calculated values of heat release for the studied cement systems containing various types of micro- and nano-additives are presented in Figure 11.
The influence of the superabsorbent additive on the heat release kinetics of cement paste with a hyperplasticizer is shown in Figure 12.
From the analysis of the heat release curves, it can be concluded that the plasticizing additive Sika226p prolongs the induction period by 35%. The SAP additive, at a dosage of 0.1% of the cement mass, does not affect the heat release kinetics of the studied compositions.
Thus, the calorimetry method using improved semi-adiabatic calorimeters provides sufficient informativeness and accuracy for assessing the thermal effects accompanying the hardening process of composite cement binders. The analysis of thermal effects accompanying the hydration processes of the “cement-additive-water” system has shown the possibility of replacing microsilica with metacaolin, as well as the prospect of its partial mixing with finely ground natural pozzolan.
CONCLUSIONS
The quality of ultrafine mineral additives determines their ability to chemically bind portlandite through the manifestation of pozzolanic properties. Among the studied range, microsilica and pumice demonstrate high pozzolanic activity. Thermal activation is effective for additives consisting of crystalline silica (marl, ground quartz sand), resulting in a 25% increase in the indicator.
There is no selective adsorption of hyperplasticizer molecules by additives of superabsorbent polymer based on sodium polyacrylate. Among the mineral additives, metakaolin and diatomite exhibit the highest adsorption capacity for hyperplasticizers.
The study of pozzolanic activity, adsorption capacity, and the nature of cumulative heat release curves has shown the possibility of replacing microsilica with meta-caolin, as well as the prospects of partially mixing it with finely ground natural diatomite.
The calorimetry method with semi-adiabatic calorimeters provides sufficient informativeness and accuracy for assessing the effect and nature of the influence of introduced fine-dispersed additives on the process of structure formation in cement stone. With sufficient sensitivity, the semi-adiabatic calorimetry method is rapid, which determines its effectiveness in the initial stages of adapting the component composition of high-performance concretes for construction purposes.
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SCIENCE
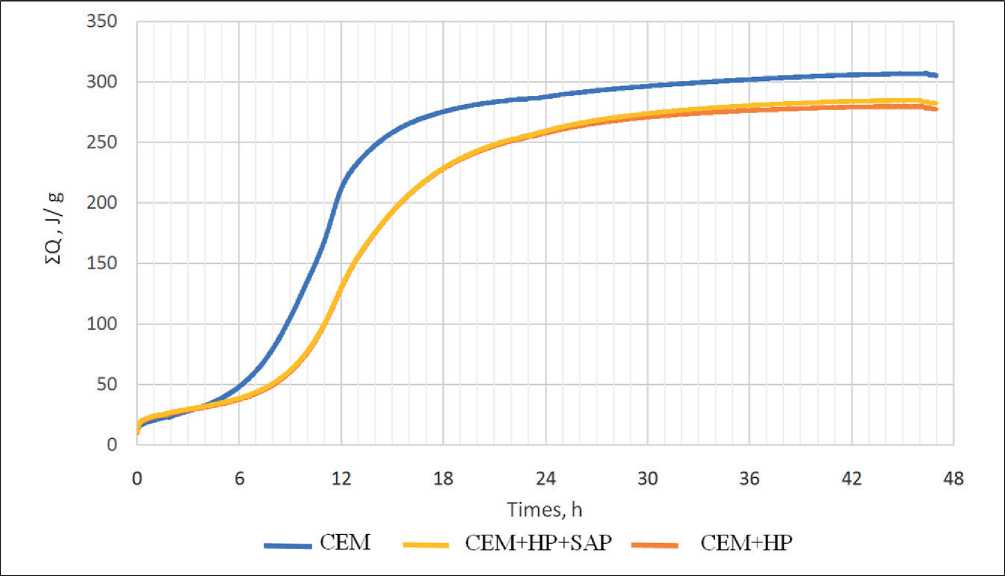
Fig. 12. Kinetics of heat release for experimental compositions
Список литературы High-Performance Concretes for Machine Building with Nano- and Micro-Scale Raw Materials
- Kalashnikov V.I., Abramov D.A., Volodin V.M. Concretes: macro-, nano-, and picoscale raw materials components. Dorogi. 2013; 33: 88-92.
- Inozemtsev A.S., Korolev E.V., Zyong T.K. Rheological peculiarities of cement-mineral systems plasticized with polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Regional Architecture and Construction. 2019; 3: 24-34.
- Application of high-tech concrete based on special binder Nanodur® Compound 5941. Available: https://www.cpi-worldwide.com/ru/journals/artikel/23781 (accessed: 19.03.2023).
- Kalashnikov V.I. Terminology of the new generation concrete science. Construction Materials. 2011; 3: 103-106.
- Fernandez R., Martirena F., Scrivener K.L. The origin of the pozzolanic activity of calcined clay minerals: A comparison between kaolinite, illite and montmorillonite. Cement and Concrete Research. 2011; 41: 113-122.
- Lin R.-S., Wang X.-Y., Yi-Han. Effects of cement types and addition of quartz and limestone on the normal and carbonation curing of cement paste. Construction and Building Materials. 2021; 305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124799
- Balykov A.S., Nizina T.A., Volodin S.V. Optimization of technological parameters for obtaining mineral additives based on calcined clays and carbonate rocks for cement systems. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2022;14: 145-155. https://doi.org/10.15828/2075-8545-2022-14-2-145-155
- Justs J., Wyrzykowski M., Bajareb D., Lura P. Internal curing by superabsorbent polymers in ultra-high performance concrete. Cement and Concrete Research, 2015; 76: 82-90.
- Lura P., Durand F., Jensen O.M. Autogenous strain of cement pastes with superabsorbent polymers. International RILEM Conference on Vol. Changes of Hardening Concrete: Testing and Mitigation, RILEM Publications SARL. 2006; 57-65.
- Popov D.Yu., Lesovik V.S., Meshcherin V.S. Influence of superabsorbent polymers on plastic shrinkage of cement stone. Bulletin of BSTU im. V.G. Shukhov. 2016; 11: 6-11.
- Beregovoy V.A., Lavrov I.Yu., Shurygin I.S. Study of the influence of superabsorbent and mineral additives on the surface tension of hyperplasticizer solutions. Bulletin of PGUAS: Construction, Science and Education. 2022; 2: 3-8.
- Ivanov I.M., Matveev D.V., Orlov A.A.,. Kramar L.Ya. Influence of water-cement ratio and superplasticizers on the processes of heat release, hydration and hardening of cement. Bulletin of SUSU. Series: Construction and architecture. 2017; 2: 42-49.
- Usherov-Marshak A., Zlatkovskyy O., Ciak M. Estimation of Influence of New Generation Admixtures of Early Hydration of Cements. Intern. Conf. on Durability of High-Performance Concrete “Conlife”. Freiburg. 2004; 63-69.
- Barannik N.V, Kotov S.V, Potapova E.S., Malahin S.S. Determination of heat release of concrete during its hardening under isothermal conditions. Bulletin of the Research Center “Construction”. 2022; 2: 44-62.
- Beregovoy V.A., Lavrov I.Yu., Shurygin I.S., Makhmudov M.G. Portable calorimeter for solving formulation problems in the field of practical concrete science. Bulletin of PGUAS: Construction, Science and Education. 2023; 1: 4-8.
- Kostoya Sh., Bishnoi E. Gallucci K.L. Scrivener. Synthesis and hydration of tricalcium silicate. Cement and its Applications. 2010; 5: 18-22.
- Tennis P.D., Jennings H.M. A model for two types of calcium silicate hydrate in the microstructure of Portland cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000. Vol. 30(6):855–863
- Brown P.W., Pommersheim J., Frohnsdorff G. A kinetic model for the hydration of tricalcium silicate. Cem. Concr. Res. 1985; 15(1): 35–41.
- Bezjak A., Jelenic I. On the determination of rate constants for hydration processes in cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1980; 10 (4):553-563.
- Garrault S., Behr T., Nonat A. Formation of the C–S–H layer during early hydration of tricalcium silicate grains with different sizes. J. Phys. Chem. 2006; 110:270–275.


