How a cardiometer and a polygraph help improve the quality of self-awareness by increasing personal self-efficacy
Автор: Likhacheva E.V., Ognev A.S.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 31, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article shows how exactly it is possible, using a selection of specially prepared visual stimuli, to launch such a mental dialogue by the respondent with his/her internal subpersonalities, denoting complex ideas about his/her desirable and undesirable qualities, which allows him/her to obtain authentic information about his/her Self-concept instrumentally. It is also shown that, according to the data obtained, the process of a person’s awareness of his/her personal characteristics is facilitated by the correlation of his/her ideas about himself/herself in the form of a certain metaphorically described during multimodal game modeling of the Self-concept in the form of answers to questions about what this “my Self” is, with that, which in its complex form he/she classifies as such a complex formation as “not-I”.
Cardiometry, oculometry, projective psychodiagnostics, psychomemantics, psychocorrection, personal vitality
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148328849
IDR: 148328849 | DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2024.31.1924
Текст научной статьи How a cardiometer and a polygraph help improve the quality of self-awareness by increasing personal self-efficacy
Imprint
Elvira V. Likhacheva, Aleksandr S. Ognev. How a cardiometer and a polygraph help improve the quality of self-awareness by increasing personal self-efficacy. Cardiometry; Issue 31; May 2024; p. 19-24; DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2024.31.1924; Available from:
INTRODUCTION AND STATEMENT OF THE RESEARCH PROBLEM
Human consciousness is one of the most important qualities, which allows him/her to be a capable subject. Its presence underlies the ability of each of us to adequately assess what is happening, to set goals and achieve them. And therefore, it is no coincidence that the ability and readiness to realize various situations is among the most essential competencies of such modern occupations as civil aviation pilots, navigators involved in river and sea transportation, rescuers, train operators, power plant operators, supervisors of various transport systems, etc.
The highest forms of development of consciousness include what each of us considers knowledge about ourselves that is amenable to our self-report, i.e. self-awareness. Such knowledge, amenable to formulation and clear understanding in the form of multimodal images (not necessarily only visual), helps us understand the motives for our actions, evaluate our own conditions, volitionally maintain attention on our chosen goals, determine our priorities, and clarify for ourselves the meaning of what is happening.
The process of becoming aware of something always involves an internal dialogue through which a person reconciles what he/she has to deal with, what he/she would like to receive in the future and have in the present. Disagreement with what we see, feel, record and what we expected to see, feel and record necessarily gives rise to an internal protest, a feeling of indignation and other types of frustration at the moment such a discrepancy is discovered. As we have shown more than once in a number of our research papers, recording of this kind of reactions can be a means of detecting momentary events, when something important is realized, an indicator of what spectrum of assessments they belong to and how acceptable the subject of focus is at this moment [2- 5, 10-28].
A person’s awareness of his/her personal characteristics occurs by correlating his/her ideas about him-self/herself in the form of a certain Self-concept in the form of answers to questions about what this “my Self” is with what in a complex form everyone designates for himself/herself as “not-I”. [9]. Therefore, it can be assumed that the forced launch of such an internal dialogue can be successfully used to obtain authentic information about what this kind of Self-concept is like through instrumental recording of the corresponding psycho-physiological reactions to specially selected stimuli.
The validity of this hypothesis, the testing of which this article is devoted to, is supported by our previously conducted oculometric, galvanic skin and cardiometric measurements of the reactions of test subjects to specially selected stimuli in the form of visual-verbal semantic differentials [1-8, 10-28]. Such measurements have shown that a discrepancy between what a person considers true for himself/herself and what he/she considers inacceptable causes a sharp change in the balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system. Subsequent discussion with the respondent about his/her reactions to such stimuli and repeated measurements of such reactions carried out in pilot studies made it possible to clarify and expand the hypothesis as follows: it is possible to assemble stimuli in the form of visual-verbal differentials and such forms of game modeling organized with their help that does not only allow one to identify the components of the subject’s self-awareness, but also to carry out their constructive transformation through awareness of the boundaries of effective use of the previously unconscious personal experience embedded in them.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
To test this hypothesis, compositions created by the test subjects in various options of multimodal game modeling were used as visual stimuli. Such options were constructing compositions from toy miniatures in a sand container, composing from a set of metaphorical associative phrases, sculpting figurines from kinetic sand, drawing on light tables covered with a thin layer of sand symbolic images of what the respondent is not happy with in himself/herself, and what he/ she values in himself/herself and would like to develop in the future. Examples of this kind of compositions are presented in the Figures below herein.
In the studies conducted, each respondent was presented with photographs of compositions of the type described that he had created. Reactions to such stimuli were recorded using computer-assisted cardiometers Cardiocode, polygraphs Barrier-14 and KRIS, as well as eye trackers GP-3. Based on the results of the cardiometric measurements using Baevsky’s method, a stress index was calculated, which allows to assess the level of balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the respondent’s autonomic nervous system. Based on measurements using polygraphs of electrodermal activity, the area under the chronological development curve of the respondent’s
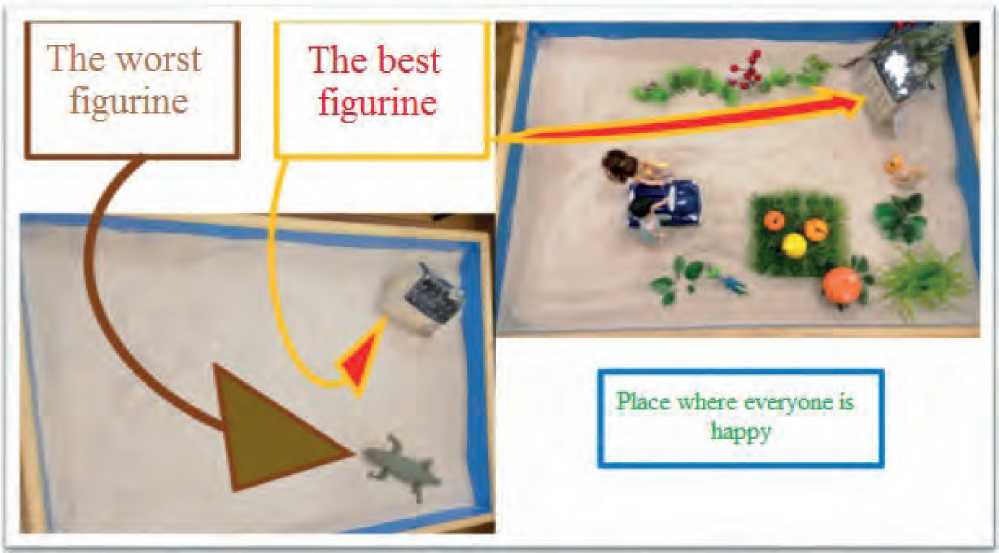

Figure 1. An example of a metaphorical representation of respondents using sand psychotherapy of what they are not happy with in themselves and what characteristics they value. It is also shown how, in metaphorical form, it displays a model of a harmonious combination of all these qualities and the path that can lead to such a balance and an increase in one’s own self-efficacy.

Figure 2. An example of a symbolic display of respondents using metaphorical associative phrases of what does not suit him/her in himself/herself, and how he/she compensates for it in himself/herself.

Figure 3. An example of a metaphorical display by a respondent on the sand-covered surface of a light table of what he/she is not satisfied with in himself/herself, and what the ideal to which he/she strives is.
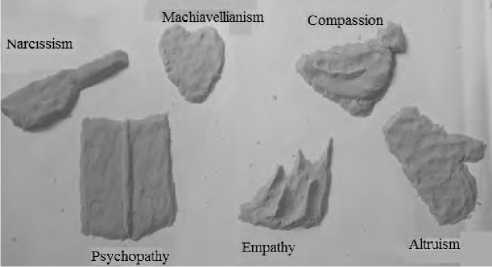
Figure 4. An example of the respondent’s expressing with kinetic sand what he/she is trying to eliminate in himself/herself and what qualities he/she is trying to compensate for these shortcomings.
galvanic skin response was calculated. Using eye trackers, areas of enhanced attention of respondents were determined as a percentage of the total time of demonstration of each stimulus.
A total of 36 respondents aged 19 to 34 years participated in the study. With each participant individually, in the intervals between all measurements and tasks performed, a detailed discussion about everything that was happening was carried out in the form of in-depth interviews according to the rules and principles that are set out in more detail in the mentioned publications [10-12, 17, 18, 24, 26-28].
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
A comparative analysis of the results of the final reactions of respondents to the presented stimuli showed that the predominant tendency for that group of the experiment participants was to balance the effectiveness of the parasympathetic and sympathetic systems as each of them moved from a metaphorical depiction of his/her shortcomings to a metaphorical reflection of what qualities he/she would like possess and what he/she would like to develop in himself/herself. This tendency has been also traceable in the experiment participants’ descriptions of their subjective reactions to each of the metaphorical constructions.
In order to provide comparisons of such descriptions on a single basis, they were all built according to a standard scheme, which included a description of their bodily sensations, emotions, thoughts that involuntarily came to mind and behavioral impulses that arose when fixing attention on the created composition. Such descriptions were clearly combined with the cardiometric data recorded by the devices and the recorded galvanic skin responses.
Thus, elevated values of the Baevsky stress index, as a rule, correlated with large values of the area under the line of the graph of changes in the magnitude of the galvanic skin response and with a significant drop in the resistance of the skin surfaces of the test subject measured within the same period of time. In that case, dynamic plots predominated in the respondents’ verbal narratives of what the composition they created symbolized. Often in those cases it was said either about an active resistance to some kind of an aggression, or about the desire to escape, or about intense attempts to search for some kind of protection. In describing their subjective state at such moments, the respondents emphasized the presence of unpleasant physical sensations that reminded them of something associated with excessive stress: increased heart rate, unpleasant spasms in the solar plexus area, etc. Most often in that case, the test subjects had thoughts that they would like to quickly finish working with their composition that reminded them of some unpleasant events from their own life experience. In behavioral terms, the test subjects emphasized the desire to finish it all quickly, to do something that would help avoid or exclude situations of this sort in the future.
Moderate values of the Baevsky stress index, as a rule, correlated with average or reduced values of the area under the line of the graph of changes in the magnitude of the galvanic skin response and with a noticeable increase in the resistance of the skin surfaces of the test subject measured during the same period of time. In those cases, the respondents’ verbal narratives of what the composition they created symbolized was dominated by calm stories, descriptions of something peaceful. Often in those cases they talked about either peaceful pastime or situations with low dynamics of changes that did not threaten the respondent. In describing their subjective state at such moments, the respondents reported on their neutral or even slightly pleasant physical sensations. The majority of test subjects in that case did not describe any alarming phys- 22 | Cardiometry | Issue 31. May 2024
iological sensations. Most often in that case, the test subjects experienced a state of involuntary daydreaming, which was usually characteristic of them at the moment of rest after a well-completed difficult task, or during periods when there was no need to rush anywhere and there was nothing to worry about. In behavioral terms, the subjects described a certain relaxation, which was more consistent with the desire to simply sit quietly or the desire to take a leisurely walk at a place that was pleasant for them.
When working with three respondents, instead of decreasing the current value, when measuring the galvanic skin response to the presentation of a metaphorical reflection of positive qualities, an increase in current and a drop in skin resistance were recorded in them. During the post-test conversations, it turned out that two of those respondents continued to mentally fix in their minds what for them was a symbolic reflection of their own negative qualities. The third subject from that group imagined how many new things would give him/her if he/she achieved what he/ she wanted, and at the same time he/she noted that all that made him very excited. Obviously, each of those results also actually confirmed the hypothesis, although the test subjects followed instructions other than given to them by the experimenters.
Similar confirmations, but through a different type of deviation from the given instructions, were two cases of a significant increase in both the stress index of various components of the autonomic nervous system and the magnitude of the galvanic skin reaction that was reported throughout the experiment. It turned out that both of those respondents were trying to check whether they were able to “deceive the polygraph.” During the post-test conversation, one of those subjects reported that from measurement to measurement, his feeling of internal discomfort was constantly increasing, since he was dissatisfied with the instrument readings. Another subject from that pair reported that during the experiment his feeling of guilt became more pronounced, since he realized that he was deceiving not the device, but the experimenters who invited him to take part in the research. Consequently, both of the above cases also did not disprove the original hypothesis. The validity of this statement was confirmed by repeated experiments with the test subjects in question, where they faithfully followed the experimenters’ instructions. In those repeated experiments, when working with both subjects, the same patterns were recorded as it was the case with the entire main group.
Finally, without exception, all the participants in the experiments noted in one form or another that for them it was a kind of discovery to realize that he/ she had to clearly imagine for himself/herself what kind of personal qualities he/she wants to cultivate. Many participants in the experiments also consider as a significant circumstance that they actually feel the importance of taking responsibility for what their personality is at the moment, and for what it will become in the future. And, as we know, it is precisely this attitude towards the experience at our disposal that constitutes the essence of that is commonly referred to as “self-efficacy”.
CONCLUSIONS
As a result of the conducted research, it was possible to confirm the validity of the hypothesis according to which it is possible, using a selection of specially prepared visual stimuli, to launch such a mental dialogue by the respondent with his/her internal subpersonalities, denoting complex ideas about his/her desirable and undesirable qualities, which allows instrumentally to obtain authentic information about his/her Self-concepts. According to the data obtained, the process of a person’s awareness of his/her personal characteristics is facilitated by the correlation of his/ her ideas about himself/herself in the form of a certain metaphorically described during multimodal game modeling of the Self-concept in the form of answers to questions about what this “My Self” is with the fact that in a complex form, he/she classifies it as such a complex formation as “not-I”.
The data also showed that the discrepancy between what a person considers true for himself/herself and what he/she considers inacceptable causes a sharp change in the balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic components of the autonomic nervous system. In addition, it was experimentally shown that the subsequent discussion with the respondent about his/her reactions to such stimuli and repeated measurements of such reactions carried out in pilot studies make it possible not only to identify the components of the subject’s self-awareness, but also to carry out their constructive transformation due to awareness of the boundaries of effective use of the personal experience embedded in them. It turned out that such awareness is facilitated by the subject’s understanding of what personal new formations are in his/her own personality and taking responsibility for their implementation.
The article was prepared based on the results of research carried out according to a state assignment by the Financial University within the framework of budget funding.
Список литературы How a cardiometer and a polygraph help improve the quality of self-awareness by increasing personal self-efficacy
- Azarov AA, et al. PREDICTOR MINING: application of data mining methods in social computing tasks. Proceedings of SPIIRAS. 2013;3(26):136-61. EDN:QIXKLB [in Russian]
- Brodovskaya EV, et al. Internet communications of Russian political parties in the current electoral cycle: results of oculometric analysis of network content. Political Science. 2021;3:112-41. EDN:GTYLYP [in Russian]
- Dombrovskaya AYu. Measuring the image of the future of the Russian Federation in the minds of Russian youth: cognitive science and cybermetry in applied political research. Humanities. Bulletin of the Financial University. 2023;13(3):128-34. EDN GOTQLV. [in Russian]
- Ognev AS, Likhacheva EV. The practice of introducing positive-oriented subjectogenesis into the system of higher education. Psychology. Journal of the Higher School of Economics. 2014;11(2):51-67. EDN: TWHXML [in Russian]
- Rosenova MI, et al. Methods for assessing the effectiveness of Sandplay therapy for adults. Modern foreign psychology. 2022;11(4):61-72. EDN:IACGGP [in Russian]
- Rosenova MI, et al. Modern anti-stress technologies in extreme and helping professions. Modern foreign psychology. 2023;12(3):19-30. EDN: QRQMSY [in Russian]
- Rosenova MI, et al. Stress and fear in extreme situations. Modern foreign psychology. 2020;9(1):94-102. EDN: YAXMRI [in Russian]
- Rosenova MI, et al. Fear as a mental health crisis in the context of global risks and changes. Modern foreign psychology. 2021;10(1):17-26. EDN: JMSWTE [in Russian]
- Stolin VV. Personal self-awareness. Moscow: Moscow State University Publishing House, 1983. 285 p.
- Brodovskaya EV, et al. Cardiometric assessment of the subjective significance of personal strategic goals as components of the image of the desired future. Cardiometry. 2022;24:159-64. EDN: YFZKIS [in Russian]
- Brodovskaya EV, et al. Cardiometric assessment of visual stimuli to identify likely reactions to destructive network content. Cardiometry. 2023;29:47-53. EDN: SNSUKW
- Brodovskaya EV, et al. Reverse techniques as a means of increasing the validity of the cardio-oculometric diagnostics. Cardiometry. 2021;18:33-7. EDN: DJTXKL
- Brodovskaya EV, et al. The use of cardiometric and electrodermal activity indicators for the attestation of visual online content. Cardiometry. 2023;26:122-6. EDN: VGXIPQ
- Likhacheva EV, Ognev AS, Kazakov KA. Hardiness and purpose in life of modern Russian students. Middle East Journal of Scientific Research. 2013;14(60)795-8.
- Ognev AS. Cardio-oculometric (cardio-oculographic) detection of functional states in a human individual. Cardiometry. 2019;14:105. EDN: KJSPIZ
- Ognev AS. New possibilities of combining multimodal game modeling and cardiometric detection in instrumental cognitive science. Cardiometry. 2023;28:13-8. EDN: TBNXMP
- Ognev AS. The use of visual stimuli in combination with measured cardiometric and galvanic skin reactions to identify the hierarchy of moral and ethical regulators in individual’s social behavior. Cardiometry. 2024;30:55-61. EDN TPBJZS.
- Ognev AS, Likhacheva EV. Implementation of Positive Subjectivity Genesis in Higher Education System. Psychology. Journal of the Higher School of Economics. 2014;11(2):51-67. EDN: TWHXML
- Ognev AS, et al. Cardiometric detection of effects and patterns of emotional responses by a human individual to verbal, audial and visual stimuli. Cardiometry. 2019;14:79-86. EDN: OUWRLY
- Ognev AS, et al. Cardiometric taxonomy of stress-indicators potential in diverse domestic situations. Cardiometry. 2019;14:101-104. EDN: LNQTOU
- Ognev AS, et al. Use of cardiometry and oculography in concealed information detection. Cardiometry. \2019;14:87-95. EDN: VUAFMP
- Ognev AS, et al. Validity of cardiometric performance data: an integral part of complex assessment of training session effectiveness. Cardiometry. 2019;14:96-100. EDN: YWMEUX
- Zernov VA, et al. Cardiometric fingerprints of various human ego states. Cardiometry. 2019;15:38-42. EDN: FGZNDX
- Zernov VA, et al. Cardio-oculometric indicator of psychophysiological readiness of students to examinations. Cardiometry. 2020;16:28-34. EDN: USIYPP
- Zernov VA, et al. Cardiometric confirmations of psychotherapeutic effectiveness of psychological sand modeling. Cardiometry. 2021;19:38-42. EDN: BFXJSF
- Zernov VA, et al. Cardiometric evidence data on human self-control of emotional states in the context of the use of metaphoric associative cards. Cardiometry. 2020;16:55-61. EDN: KDHMIH
- Zernov VA, et al. Cardiometric support of visual kinetic modeling. Cardiometry. 2022;23:41-5. EDN: EOLVJT
- Zernov VA, et al. The use of Cardiometry in development self-control skills by means of game sand modeling. Cardiometry. 2022;22:95-9. EDN: QNGXRQ


