Инактивация ренин-ангиотензин-альдостероновой системы. Какой класс препаратов предпочесть?
Автор: Столов С.В.
Журнал: Евразийский кардиологический журнал @eurasian-cardiology-journal
Рубрика: Особое мнение
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Представлен сравнительный анализ эффективности двух классов лекарственных препаратов - ингибиторов ангиотензинпревращающего фермента (ИАПФ) и блокаторов рецептора 1 типа ангиотензина II (БРА II) в профилактике сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний. Показано преимущество ИАПФ перед БРА II в снижении общей и кардиоваскулярной смертности, инфарктов миокарда, мозговых инсультов, хронической сердечной недостаточности, хронической болезни почек. Причины различного влияния ингибиторов ренин-ангиотензинальдостероновой системы на течение кардиоваскулярной патологии объясняются механизмами терапевтического воздействия ИАПФ и БРА II. Антигипертензивное действие БРА II обеспечивается селективной блокадой АТ1-¬рецепторов к ангиотензину II (АТ II). В результате блокады в крови накапливается дополнительное количество АТ II, который связываясь с АТ2- рецепторами, способствует появлению ряда негативных явлений. Стимуляция АТ2-рецепторов (возможно также АТ3-, АТ4-рецепторов) неутилизированным АТ II приводит к апоптозу структурных элементов артериальной стенки, её фиброзу, склерозированию и гипертрофии, торможению коронарного ремоделирования с нарушением неоваскуляризации миокарда, а также усилению проатерогенных и воспалительных процессов в эндотелии, возможно и сердечной ткани. Стимуляция АТ2-рецепторов также способствует лейкоцитзависимому высвобождению матриксной металлопротеиназы I, которая приводит к деструкции белков внеклеточного матрикса, тем самым дестабилизируя атеросклеротическую бляшку, приводя к ее разрыву, что является возможной причиной увеличения риска инфаркта миокарда при лечении сартанами. Каскад этих негативных влияний может быть основным механизмом дестабилизации ИБС при назначении БРА II. В отличие от сартанов лечебный потенциал ИАПФ реализуется через блокаду синтеза АТ II, не влияя на работу рецепторного аппарата, поэтому вышеуказанных неблагоприятных эффектов, связанных с накоплением АТ II, не происходит. Важной физиологической особенностью ИАПФ является их способность повышать уровень брадикинина, который оказывает положительное влияние на стенку сосудов, снижает их жесткость путем увеличения синтеза простагландинов, демонстрирует антиоксидантный и антиапоптотический эффекты, приводит к снижению постнагрузки и стимуляции ангиогенеза. Именно эти механизмы лежат в основе более выраженного кардиопротективного действия ИАПФ в отличие от БРА II.
Ингибиторы ангиотензинпревращающего фермента, блокаторы рецепторов ангиотензина ii, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143173309
IDR: 143173309 | DOI: 10.38109/2225-1685-2020-4-64-78
Текст научной статьи Инактивация ренин-ангиотензин-альдостероновой системы. Какой класс препаратов предпочесть?
Author contributions. The author meets the ICMJE criteria for authorship. Conflict of Interest. Assistance in the publication of the article was provided by Servier, but it did not affect the authors’ own opinion.
И SV1OOLOV@GMAIL.COM; SERGEY.STOLOV@SZGMU.RU
For quotation: Sergey V. Stolov. Inactivation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Which class of antihypertensive medicine products to prefer? Eurasian heart journal. 2020;(4):64-78 (In Russ.)].
Received: 16.09.2020 | Revision Received: 01.11.2020 | Accepted: 02.11.2020
Активность ренин-ангиотензин-альдостероновой системы (РААС) является важным звеном патофизиологии большинства заболеваний органов и систем организма, в первую очередь – сердечно-сосудистых. Кроме того, РААС влияет на течение хронической болезни почек, эндокринных заболеваний, онкопатологии. Эффективная блокады РААС влияет на прогноз как у больных кардиоваскулярного и почечного риска, так и при сахарном диабете, аутоиммунных заболеваниях и др [14,58].
К блокаторам РААС относятся ингибиторы ангиотензинпревра-щающего фермента (ИАПФ), блокаторы рецептора 1 типа ангиотензина II (БРА II или «сартаны») и прямой ингибитор ренина (алискирен). Практическому врачу необходимо выбрать класс препаратов, который бы оптимально понижал избыточную активность РААС и способствовал эффективному контролю патофизиологии указанных выше заболеваний.
В настоящее время есть достаточно данных, позволяющих утверждать, что именно ингибиторы АПФ являются препаратами выбора для лечения и профилактики сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний и хронической болезни почек. В течение последних 10 лет большинство международных рекомендаций указывают на приоритет ИАПФ перед БРА II при лечении пациентов с ишеми- ческой болезнью сердца (ИБС), цереброваскулярной болезнью (ЦВБ), хронической болезнью почек (ХБП). Сартаны рекомендуют принимать лишь в случае непереносимости ИАПФ из-за кашля. Такое утверждение обосновано значительной базой мета-анализов, представленной вашему вниманию в данном обзоре [12,44,53].
Наличие у ИАПФ побочных эффектов (кашля, реже отека Квинке) привело к созданию относительно нового класса ингибиторов РААС – блокаторов рецептора первого типа АТ II, которые, как полагали, будут не менее эффективны в лечении кардиоваскулярной патологии и помогут избежать негативных эффектов ИАПФ. Поначалу БРА II рекомендовали только для лечения артериальной гипертензии, однако в дальнейшем стали появляться дополнительные показания к их назначению, включающие хроническую сердечную недостаточность, перенесенный инфаркт миокарда, нарушения ритма сердца, ишемическую болезнь головного мозга, микроальбуминурию [4,5]. Многочисленные рандомизированные клинические исследования (РКИ) указывали на высокую эффективность класса сартанов при указанных заболеваниях, подчас опережающие по прогнозу ИАПФ, особенно при ишемической болезни головного мозга, патологии почек, сахарном диабете и
Таблица 1. Риск сердечно-сосудистых исходов в зависимости от проводимой терапии [9]
Table 1. Risk of cardiovascular outcomes depending on the therapy [9]
Начало дискуссии о недостаточной эффективности БРА II в профилактике осложнений у больных ИБС было положено в 2004 году, когда стали известны данные E.J. Lewis о способности ирбе-сартана увеличивать риск сердечно-сосудистых событий на 24% у больных сахарным диабетом 2 типа [37]. В публикации Berl T. et al. (2003) ирбесартан также не снижал комбинированную конечную точку, включающую сердечную смерть и инфаркт миокарда, по сравнению с плацебо у гипертензивных пациентов с сахарным диабетом [9].
Вслед за статьями E.J. Lewis и T. Berl были опубликованы результаты исследования «SCOPE», показавшего увеличение риска развития развития фатального и нефатального инфаркта миокарда у лиц пожилого возраста на фоне приёма кандесартана на 10% [67].
Широкое обсуждение проблем применения БРА II у лиц с сердечно-сосудистой патологией развернулось после публикации систематических обзоров S. Verma (2004) и M.Н. Strauss (2005), в которых авторы обсуждают связь между увеличением частоты возникновения инфаркта миокарда (ИМ) и приёмом сартанов по сравнению с назначением других препаратов. Один из разделов, посвящённый анализу РКИ VALUE, начинался с фразы: «Эти ле- карственные средства (сартаны) могут повысить риск развития ИМ и пациент должен быть об этом предупрежден». В исследовании VALUE, в частности, не было доказано преимущество валсар-тана в отношении предотвращении ИМ по сравнению с блокатором рецепторов кальциевых каналов амлодипином [57].
В систематическом обзоре S. Hall и M. Strauss были представлены результаты применения БРА II в крупных (не менее 1000 участников в каждом) рандомизированных исследованиях: ELITE II, IDNT, CHARM-Alt, SCOPE, LIFE, VALUE, VALIANT [53]. Авторами было показано, что у пациентов, получавших препараты из группы БРАII, риск развития ИМ был выше по сравнению с теми больными, которыми получали другие кардиотропные препаратов. Несмотря на то, что в большинстве случаев (за исключением исследования CHARM-Alt) статистической достоверности для этого феномена получено не было, тенденция к увеличению частоты ИМ у пациентов, получавших препараты из группы БРАII, весьма очевидно прослеживалась (рис. 1).
При проведении многофакторного анализа на достаточно большом по объёму материале (55 тыс. больных принимали БРА II и 150 тыс. – ингибиторы АПФ), авторы M.H. Strauss и A.S.Hall показали отсутствие кардиопротективного эффекта в подгруппе пациентов, принимавших сартаны. Было отмечено, что в отличие от пациентов, рандомизированных в группу ингибиторов АПФ, у больных, получавших сартаны, наблюдается повышение частоты развития ИМ на 8% (р=0,03). Кроме того, была зафиксирована тенденция к увеличению сердечно-сосудистой и общей смертности (рис. 2). При этом в группе ингибиторов АПФ прослеживалось достоверное снижение этих же показателей.
Негативное влияние препаратов из группы сартаны на риск развития ИМ M.H. Strauss и A.S. Hall обосновали более слабым вли-
|
Исследование |
БРА II, n/N (MI) |
Контроль, n/N (MI) |
ОР |
Вес % |
ОР (95% ДИ) |
|
|
(95% |
ДИ) |
|||||
|
ELITE |
3/352 |
4/370 |
--Q— |
0,25 |
0,79 (0,17-3,54) |
|
|
DETAIL |
9/120 |
6/130 |
— |
0,34 |
1,68 (0,58-4,86) |
|
|
ELITE II |
31/1578 |
28/1574 |
— |
-□— |
1,78 |
1,11 (0,66-1,85) |
|
IDNT |
39/579 |
66/1136 |
— |
-□— |
2,69 |
1,17 (0,78-1,76) |
|
CHARM-Alt |
75/1013 |
48/1015 |
2,87 |
1,61 (1,11-2,34) |
||
|
SCOPE |
70/2477 |
63/2460 |
— |
-□— |
3,97 |
1,11 (0,78-1,56) |
|
RENAAL |
50/751 |
68/762 |
—□-- |
4,08 |
0,73 (0,50-1,06) |
|
|
LIFE |
188/4605 |
188/4588 |
□— |
11,66 |
1,05 (0,86-1,29) |
|
|
VALUE |
369/7649 |
313/7596 |
19,34 |
1,18 (1,01-1,38) |
||
|
OPTIMAAL |
384/2744 |
379/2733 |
—г |
21,13 |
1,01 (0,87-1,18) |
|
|
VALIANT |
587/4909 |
559/4909 |
31,84 |
1,06 (0,93-1,20) |
||
|
ВСЕГО |
26 777 |
27 273 |
о |
1,08 |
(1,01-1,16) |
|
|
Всего (95% ДИ) |
||||||
|
Всего событий: 1826 (БРА), 1722 (контроль) |
||||||
|
Тест на неоднородность. Chi2=11,7 |
||||||
|
df=10 (p=0,32), I2=14,6% |
||||||
|
Тест на общий эффект: Z=2,18 (p=0,03) |
||||||
|
0,5 |
0,7 1,0 |
1,5 2,0 |
||||
|
БРА лучше |
Контроль лучше |
|||||
Рисунок 1 Результаты метаанализа M.H. Strauss и A.S. Hall, включавшего 11 клинических исследований, свидетельствуют о том, что БРА II увеличивают риск инфаркта миокарда [53]
Picture 1. Results of metaanalysis of M.H. Strauss and A.S. Hall which included 11 clinical trials prove the fact that ARB can increase the risk of myocardial infarction [53]
янием данных препаратов на системное артериальное давление. Утверждение базировалось на данных крупного мета-анализа, который включал 21 РКИ (137 356 пациентов): в 16 из них изучались ингибиторы АПФ (AASK, ABCD-H, ABCD-N, ALLHAT, ANBP2, CAPPP, DIAB-HYCAR, EUROPA, HOPE, JMIC-B, PART-2, PEACE, PROGRESS, SCAT, STOP-2, UKPDS-HDS), а в 5 – БРА II (IDNT, LIFE, RENAAL, SCOPE, VALUE). В данном мета-анализе было установлено статистически достоверное увеличение риска развития ИМ на 15% (p=0,001). Данный феномен авторы связывали с более выраженным снижением артериального давления в группе ИАПФ. В то же время между указанными двумя группами не отмечалось различий по влиянию на риск развития новых случаев сердечной недостаточности и инсульта [55].
Однако значение снижения артериального давления как одного из ключевых факторов, влияющих на течение ИБС, не нашло подтверждения в крупном РКИ «LIFE», в котором не было доказано достоверное уменьшение риска ИМ на фоне лозартана по сравнению с атенололом, несмотря на более выраженное (на 1,7 мм рт. ст.) снижение систолического артериального давления [16].
По следам приведенных выше мета-анализов в медицинской литературе проблема повышения сердечно-сосудистого риска вследствие приёма сартанов получила название «БРА II-парадокс».
Вскоре после выхода публикаций об отсутствии позитивного влиянии препаратов из группы сартанов на течение ИБС в печати стали появляться обзоры и мета-анализы, в которых S. Verma и M. Strauss обвинялись в недобросовестной обработке клинического материала и искажении данных статистического анализа. Например, в мета-анализе M. McDonald и соавт., посвящённом формированию первичного или повторного ИМ, в 11 РКИ изучалась эффективность сартанов по сравнению с плацебо (21 062 пациента), а в 9 – эффективность сартанов против ИАПФ
Ингибиторы АПФ и БРА II оказывают различное влияние на вероятность развития инфаркта миокарда и смертность
Ингибиторы АПФ vs препараты сравнения (39 исследований; n=150 943)
БРА II vs препараты сравнения (11 исследований; n=55 050)
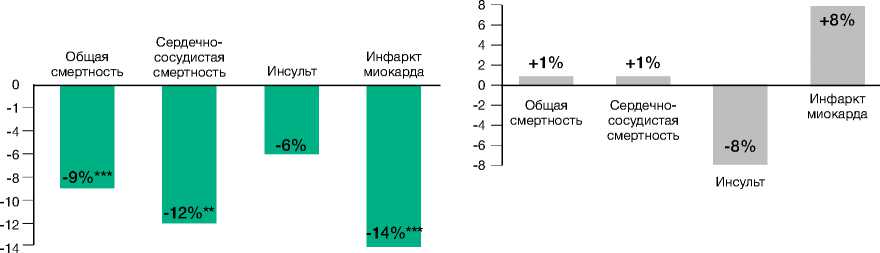
*р=0,0005; ***р<0,00001
*р=0,03
Adapted from: Strauss МН. Hall AS. Circulation. 2006;114:838-854.
Рисунок 2. Ингибиторы АПФ и БРА II по-разному влияют на сердечно-сосудистые осложнения [53]
Picture 2. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin receptor blockers have different effect on cardio-vascular complications [53]
Сердечно- Инсульт Госпитализация Новые случаи
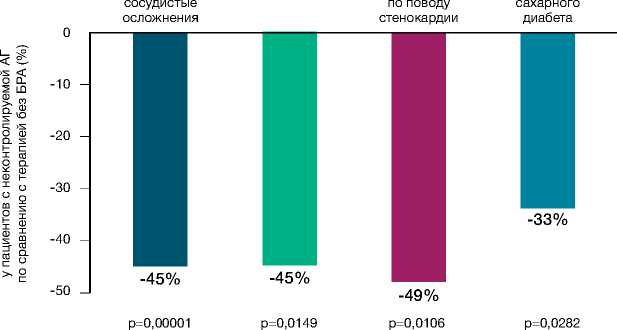
Рисунок 3. Результаты исследования Kyoto Heart Study [49]
Picture 3. Results of Kyoto Heart Study [49]
68 ЕВРАЗИЙСКИЙ КАРДИОЛОГИЧЕСКИЙ ЖУРНАЛ, 4, 2020
(10 625 пациентов). Авторы доказали, что назначение БРА II не было ассоциировано со снижением риска развития ИМ. Отношение рисков (ОР) против плацебо составило 0,94, а против ингибиторов АПФ (ОР = 1,01). В заключении был сделан вывод: «…как пациенты, так и врачи могут быть спокойны в отношении назначения сартанов в целях профилактики любого сердечнососудистого осложнения, включая ИМ, независимо от наличия у больного какой-либо сердечно-сосудистой патологии...» [39].
R. Tsuyuki представил обзор эффективности назначения сар-танов по сравнению с любой другой лекарственной терапией. Данный обзор включал 25 РКИ, в которых приняли участие 68 711 пациентов. В ходе анализа большого числа конечных точек не было выявлено негативного влияния сартанов на риски развития ИМ (ОР =1,03). В заключении обзора автор отметил безопасность назначения БРАII при любом сердечно-сосудистом заболевании: «… сартаны являются альтернативой ингибиторам АПФ в профилактике сердечно-сосудистой смертности и ИМ» [66].
В мета-анализ M. Law и J. Morris (2009 г.) были включены исследования с участием больных с артериальной гипертензией и сопутствующей ИБС. Результаты показали, что назначение сарта-нов оказывает не менее эффективное влияние на профилактику сердечно-сосудистых осложнений по сравнению с другими классами гипотензивных средств, включая ИАПФ [36]. Убедительные данные о наличии у сартанов кардиопротективных свойств по сравнению с другими классами препаратов были показаны в РКИ Kyoto Heart Study, проводившееся в японской популяции. Использование валсартана у больных с сердечно-сосудистой патологией привело к существенному снижению кардиоваскулярных осложнений (рис. 3).
Результаты исследований Jikei Heart Study и Kyoto Heart Study показали, что сартаны в целом не способствуют увели- чению частоты развития ИМ. Снижение риска ИМ на фоне применения валсартана составило почти 35% [49]. В этой связи известный эксперт в области кардиологии F.H. Messerli отметил, что «…внушительные результаты исследования Kyoto приводят к пониманию того, что сартаны сегодня достигли как класс своего совершеннолетия и должны теперь рассматриваться как предпочтительные или базисные в терапии гипертонии» [41]. Вместе с тем, F.H. Messerli не счёл нужным акцентировать внимание на позитивном эффекте только одного из представителей БРА II – валсартана, причём, полученного в японской популяции. Позднее у экспертов появились сомнения относительно преимуществ валсартана, выявленных в этом РКИ. При проведении Kyoto Heart Study были установлены существенные нарушения, заставившие усомниться в объективности полученных результатов (так называемый «Diovan scandal») [50].
В развернувшейся полемике вокруг «БРА II-парадокса» заслуживает внимания «веский аргумент» в защиту сартанов следующего содержания: «При проведении плацебо-контролируемого исследования CHARM-Alternative (2028 больных) в подгруппе кандесартана действительно наблюдалось увеличение количества ИМ на 36%!, но при этом происходило высокодостоверное снижение риска развития сердечно-сосудистой смерти и необходимости госпитализаций по поводу ХСН на 23% (р<0,0004)» [19].
Всё вышеуказанное позволило экспертам прийти к заключению о том, что сартаны в равной степени с ингибиторами АПФ способствуют улучшению прогноза для больных ИБС и/или артериальной гипертензией. При этом подчёркивалось, что «БРА II-парадокса» не существует и «…обсуждение данного вопроса имеет в основном академический интерес и не касается практической деятельности врача».
С
ELITE-I 1997
Lang 1997
STRETCH 1999
ELITE-II 2000
REPLACE 2001
HEAVEN 2002
ARCH-J 2003
CHARM-Alt 2003
CHARM-Pres 2003
CHARM-Added 2003
Mitrovic 2003
LIFE 2002
OPTIMAAL 2002
SCOPE 2003
VALIANT 2006
DETAIL 2005
VALUE 2004
Jikei 2007
ONTARGET 2008
ОШ
n
10 696
13 244
13 462
14 670
19 607
29 425
29 675
44 920
48 001
65 119
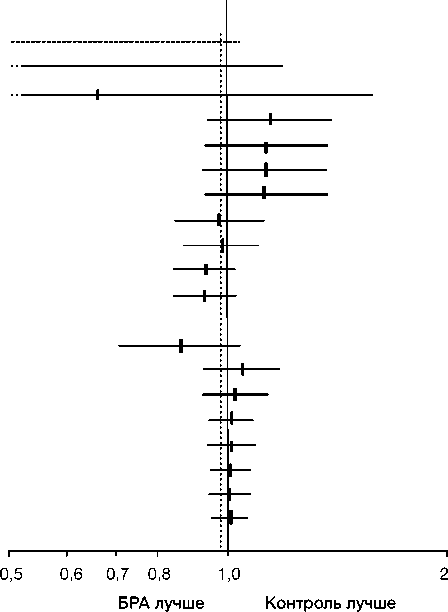
Рисунок 4 Кумулятивные форест-графики (двусторонние 95% ДИ) зависимости между инфарктом миокарда, смертью от сердечно-сосудистых причин и проводимой терапии
Picture 4. Cumulative forest-plots (95% CI) of the correlation between myocardial infarction, cardiovascular death and respective therapy
Однако сторонники «БРА II-парадокса» оспаривали данные Kyoto Heart Study/Jikei Heart Study, ссылаясь на другие РКИ– CASE-J и HIJ-CREATE, которые были проведены ранее на таких же выборках в японской популяции [42]. В них не были установлены преимущества применения БРА II кандесартана по снижению риска осложнений сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний ни в сравнении с блокатором рецептором кальциевых каналов, ни со стандартной терапией. Приняв во внимание данные 4-х РКИ (Kyoto Heart Study, Jikei Heart Study, CASE-J и HIJ-CREATE), «противники» БРА II сделали вывод о том, что групповой эффективности сартанов при лечении больных ИБС не существует [52]. Известно, что в группа БРА II включает различные лекарственные препараты, которые имеют различную эффективность в профилактике сердечно-сосудистой заболеваемости и смертности. В японской популяции кардиопротективный эффект был показан в отношении валсартана, но не кандесартана. Однако в исследовании VALUE с участием пациентов европеоидной расы кардио-протективный потенциал валсартана был выражен существенно меньше. В этом наиболее крупном РКИ (более 15000 пациентов) проводилось сравнение валсартана с другим антигипертензивным препаратом из группы блокаторов рецептора кальциевых каналов (амлодипином) у пациентов с артериальной гипертензией и высоким риском кардиоваскулярных осложнений. Через 5 лет наблюдений различий по первичной точке (эффективности предупреждения сердечно-сосудистой заболеваемости и смертности) получено не было [33]. Аналогичные результаты были получены в РКИ «GISSI-AF», в котором валсартан назначался уже в максимальной суточной лечебной дозе (320 мг) [30].
В публикации Al Khalaf и соавт. вновь обсуждается вопрос «БРА II-пародокса». Авторами был опубликован мета-анализ, в котором изучались сердечно-сосудистые исходы у пациентов из группы высокого риска развития ИБС, но без хронической сердечной недостаточности (ХСН), которые получали сартаны. После объединения баз данных, в которую вошли более 89 тысяч больных, доказательств того, что БРА II имеют сходное с ингибитора- ми АПФ кардиопротективное действие, авторами обнаружено не было (рис. 4); отношение шансов возникновения инфаркта миокарда на фоне лечения сартанами составляло 1,09 по сравнению с группой контроля (р=0,05). Справедливости ради, необходимо отметить, что при сравнении других исходов ИБС, в частности смерти от сердечно-сосудистых причин, статистически достоверной разницы в группах ингибиторов АПФ и сартанов не было отмечено (рис. 4). По мнению авторов данного обзора, полученные результаты свидетельствуют об отсутствии преимуществ назначения БРА II перед назначением ингибиторов АПФ у больных ИБС и АГ без ХСН. Полученные Al Khalaf и соавт. данные подтверждали наличие «БРА II-парадокса». Авторами был сделан выводе лишь о преимуществе БРА II перед ингибиторами АПФ в отношении риска развития инсульта, да и то, с оговоркой о неоднородности имеющихся исследований. В заключении обзора были предложены следующие рекомендации для клинических врачей: «… принимая во внимание тот факт, что ингибиторы АПФ снижают риск развития как инфаркта миокарда, так и инсульта, следует соблюдать осторожность при их замене на БРА II у больных без ХСН или при непереносимости ингибиторов АПФ» [34].
Дальнейшее изучение эффективности БРА II у больных с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями в исследованиях TRANSCEND и PRoFESS также не выявило их протективного действия среди пациентов с ИБС и церебро-васкулярной болезнью (ЦВБ). Сравнительное РКИ TRANSCEND включало 5926 пациентов с высоким риском развития сердечно-сосудистых осложнений и не переносящих ИАПФ в связи с развитием нежелательных реакций на фоне приема препаратов из этой группы. Участники исследования были рандомизированы в группы телмисартана в суточной дозе 80 мг (n=2954) и плацебо (n=2972). Результаты этих РКИ показали, что длительная (более 3 лет) терапия БРА II телмисартаном не способствовала предупреждению прогрессирования ХСН, не способствовала профилактике осложнений СД 2 типа, но увеличивала частоту формирования хронической почечной недостаточности (на 59%!) в отличие от β -адреноблокатора или диуретика [54].
БРА и ССЗ (ИБС, ЦВБ)
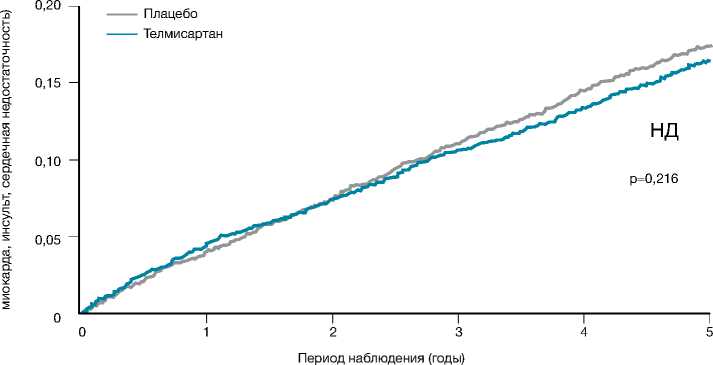
Рисунок 5. Результаты исследования TRANSCEND: отсутствие влияния телмисартана на конечную точку (сердечно-сосудистую смерть, ИМ, инсульт или госпитализацию из-за хронической сердечной недостаточности) у пациентов с непереносимостью ингибиторов АПФ [62]
Picture 5. Results of TRANSCEND study: no effect of telmisartan on the combinatory end-point (cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke and hospitalization due to chronic heart failure) in patients who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors [62]
Таким образом, в исследовании TRANSCEND не было подтверждено наличие у телмисартана способности снижать вероятность развития сердечно-сосудистых осложнений у больных ИБС, но без артериальной гипертензии.
В другом крупном (21000 человек) исследовании (PRoFESS) изучалось влияние этого же БРА II (телмисартана) на частоту развития повторных острых нарушений мозгового кровообращения (ОНМК) в сравнении с группой плацебо [62]. Такие сердечно-сосудистые события, как сердечно-сосудистая смерть, повторное ОНМК, инфаркт миокарда и возникновение/прогрессирование ХСН (комбинированная вторичная конечная точка), возникали у 1 367 (13,5%) в группе телмисартана и у 1 463 (14,4%) в группе пла- цебо (ОР=0,94, р=0,11). Таким образом, в исследовании PRoFESS также была показана неспособность телмисартана контролировать течение как ИБС, так и ЦВБ (рис. 6). Это РКИ было одно из самых представительных, т.к. включало более 2000 пациентов с ЦВБ и продолжалось 3 года. Частота возникновения ОНМК на фоне приёма телмисартана достоверно не отличалась от контрольной группы плацебо.
По результатам исследований РКИ «TRANSCEND» и «PRoFESS» авторы Maung K. и Zhang J. подготовили для FDA презентацию, в которой указали на то, что кардиопротективный эффект у препарата телмисартан не обнаружен. Анализ Трёх- и четырёхкомпонентных конечных точек в этих РКИ, включавший
БРА и ЦВП
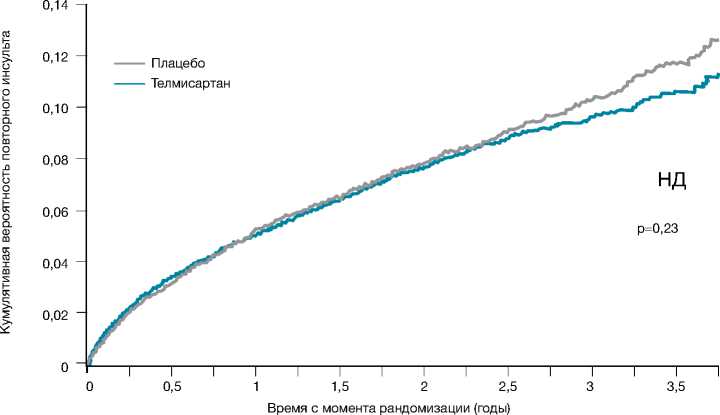
Рисунок 6. Исследование PRoFESS: телмисартан не влияет на риск развития повторного инсульта [64]
Picture 6. PRоFESS study: telmisartan has no effect on the risk of repeated stroke [64]
Телмисартан не превосходит плацебо в отношении первичной (4-компонентной) конечной точки и лишь немного лучше в отношении вторичной (3-компонентной) конечной точки в исследовании TRANSCEND
|
Телмисартан |
Плацебо |
ОР (95% ДИ); р* |
|
|
Рандомизированы, n (%) |
2954 (100) |
2972 (100) |
|
|
Первичная (4-компонентная) конечная точка, n (%) |
465 (15,7) |
504 (17,0) |
0,92 (0,81-1,05); 0,219* |
|
События на 100 пациенто-лет |
3,59 |
3,87 |
|
|
Вторичная (3-компонентная) конечная точка, n (%) |
384 (13,0) |
440 (14,8) |
,z ^, 0,87 (0,76-1,00); 0,048* |
|
— События на 100 пациенто-лет |
— 2,9 |
— 3,33 |
Примечание: первичная конечная точка failed.
*Значение р не корректируется для множественных сравнений.
Рисунок 7. Результаты исследования TRANSCEND [62]
Picture 7. Results of TRANSCEND study [62]
сердечно-сосудистую смертность, ИМ, ОНМК и госпитализацию в связи с прогрессированием сердечной недостаточности, не показал преимуществ телмисартана по сравнению с плацебо (рис. 7 и 8).
В рекомендациях Американской ассоциации по изучению инсульта (ASA, 2010) также указано на отсутствие какого-либо преимущества БРА II у пациентов в постинсультном периоде [31]. В методическом руководстве по профилактике инсультов у больных гипертонической болезнью, рекомендовано применение диуретиков в монотерапии или в комбинации с ингибиторами АПФ, но не с сартанами (Класс I; уровень доказательности A).
Не вселяют оптимизма применение БРА II в отношении прогноза у кардиоваскулярных больных два других более ранних исследования: RENAAL и IDNT [10,37]. В этих РКИ, выполненных при АГ в сочетании с сахарным диабетом 2-го типа и имеющих признаки почечной недостаточности, присоединение к многокомпонентной терапии препаратов лозартан и ирбесартан, позволило замедлить прогрессирование ХБП (первичная конечная точка). В то же время в этих группах пациентов не было получено статистически достоверного снижения сердечно-сосудистых осложнений (вторичные конечные точки).
Европейское общество кардиологов, ссылаясь на два этих мета-анализа, в рекомендациях по ведению больных АГ (2013) также подчеркнуло недостаточный потенциал БРА II по сравнению с ИАПФ в профилактике инфаркта миокарда и общей смертности [18,29, 56].
Основываясь на установленных фактах существенно меньшей органопротекции у БРА II по сравнению с ИАПФ, большинство существующих в настоящее время клинических рекомендаций учитывают данное положение, сопровождая текст рекомендаций обязательной фразой: «применение сартанов возможно лишь в случае непереносимости ИАПФ из-за кашля». Это нашло отражение в гайдлайнах АНА/АСС, ESC по сердечной недостаточности, артериальной гипертензии, острому коронарному синдрому, реваскуляризации миокарда, цереброваскулярной болезни, заболеваниям почек [20-28,37,52,57,68].
Весьма показательны стандарты лечения взрослых в США (2014), в которых нет упоминания о применении сартанов у больных с ИБС/ постинфарктным кардиолсклерозом (ПИКС) и ЦВБ/ транзиторной ишемической атакой (ТИА); показаниями к их на- значению в этих стандартах значатся лишь сердечная недостаточность, сахарный диабет и заболевания почек. Забегая вперед, необходимо отметить, что в рекомендациях 2017 года (США) сар-таны при заболеваниях почек также предлагают назначать лишь в случае непереносимости ИАПФ [22,23,32,70].
Особого внимания заслуживает метанализ Brugts J.J. (2014), в котором проведено сравнение этих классов препаратов у больных артериальной гипертензией. Согласно этому метанализу, потенциал сартанов в отношении риска развития инфаркта миокарда оказался слабее, чем у ИАПФ, в 6,8 раза (NNT для ИАПФ – 80 и 338 – для БРА II), общей смертности – в 5 раз (NNT 67 для ИАПФ и 335 – БРА II), сердечно-сосудистой смертности – в 3,5 раза (NNT 116 для ИАПФ и 409 – БРА II), инсультам – в 3 раза (NNT 131 для ИАПФ и 337– БРА II). Метанализ Бруггса проводился в репрезентативной группе больных-гипертоников; средняя продолжительность наблюдения составила 4,3 года, что, по нашему мнению, позволяет объективизировать выводы о различной эффективности препаратов. Индекс NNT максимально наглядно демонстрирует преимущества ИАПФ перед БРА II [69]. В рекомендациях по лечению АГ (США, 2017) указано на способность ИАПФ снижать риск сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, а назначение сартанов у больных гипертонической болезнью возможно лишь при непереносимости ИАПФ из-за кашля [8].
Все вышесказанное объясняет приоритет назначения ИАПФ перед сартанами у кардиоваскулярных больных в большинстве международных рекомендаций. Это нашло отражение в руководствах по ИБС, ЦВБ, ХСН, реваскуляризации миокарда в течение последних 9 лет, а при хронической болезни почек (ХБП) – с 2017 года. В американских рекомендациях по лечению АГ [8] в разделе, посвященному ХБП, указано, что для замедления прогрессирования почечной недостаточности показаны ИАПФ, а назначение сартанов показано только в случае непереносимости ИАПФ, хотя в рекомендациях по лечению взрослых 2014 года [22], в разделе, посвященному ХБП, ингибиторы АПФ и БРА II указывались как равноценные классы. Европейский гайдлайн по АГ (ESH/ESC, 2018) в разделе по ХБП также указывает на приоритет ИАПФ; только в случае их непереносимости рекомендовано назначать сартаны или недигидропиридиновые антагонисты кальция [25].
Таким образом, большинство крупных РКИ, посвящённых эффективности БРА II у кардиологических больных, установили
Телмисартан не превосходит плацебо в отношении первичной конечной точки в исследовании PRoFESS
|
Телмисартан |
Плацебо |
ОР (95% ДИ); р |
|
|
Рандомизированы, n (%) |
10 146 (100) |
10 186 (100) |
|
|
Первичная конечная точка инсульт, n (%) |
880 (8,7) |
934 (9,2) |
0,95 (0,86-1,04); 0,231 |
|
Вторичная (4-компонентная) конечная точка, n (%) |
1367 (13,5) |
1463 (14,4) |
0,94 (0,87-1,01); 0,107 |
|
Post hoc 3-компонентная конечная точка, n (%) |
1289 (12,7) |
1337 (13,5) |
0,94 (0,87-1,02); 0,126 |
Рисунок 8. Результаты исследования PRoFESS [64]
Picture 8. Results of PRoFESS study [64]
их ограниченную способность предотвращать неблагоприятные сердечно-сосудистые события по сравнению с другими классами препаратов [53,57].
Кроме того, ряд авторов отмечает низкую эффективность контроля частоты новых пароксизмов фибрилляции предсердий (ФП) у больных ИБС на фоне применения сартанов по сравнению с назначением ингибиторов АПФ. Так, например, в РКИ «GISSI-AF» у больных ИБС, артериальной гипертензией, сахарным диабетом или изолированной дилатацией левого предсердия было установлено, что валсартан в максимальной суточной дозе (320 мг!), добавленный к стандартной кардиотропной терапии, не предотвращал развитие пароксизмов ФП на протяжении всего периода наблюдения (1 год). По вторичной конечной точке, включающей госпитализацию по сердечно-сосудистой причине, комбинацию смерти и тромбоэмболических осложнений, также не было установлено различий за исключением более частых тромбоэмболических событий в группе валсартана (10 против 2 в группе контроля; ОР –5,0; р=0,04).
Несмотря на вышеизложенное, практика приоритетного назначения сартанов при сердечно-сосудистых заболеваниях последние годы основательно закрепилась в России. Во внимание не принимаются отечественные рекомендации. Так, например, в рекомендациях по лечению ХСН (2017) указано: «антагонисты рецепторов 1 типа АII (сартаны) в максимально переносимых дозах должны применяться у больных ХСН I-IV ФК c ФВ ЛЖ<40% для снижения риска смерти и госпитализаций по поводу ХСН при непереносимости ИАПФ (класс IIa)».
Рекомендация по приоритету ИАПФ перед сартанами отражена и в национальном руководстве по кардиологии под редакцией Е.В. Шляхто (2019 [7]; в главах по ИБС и ХСН подчеркнуто, что назначение сартанов показано в случае непереносимости ИАПФ из-за кашля. Здесь же, авторы указывают на большую эффективность рамиприла и периндоприла в противовес хиноприлу и трандолаприлу, потенциал которых оказался менее выраженным у больных ИБС. Аналогичные положения изложены и в клинических рекомендациях МЗ РФ (2020) по лечению ИБС: «…при непереносимости иАПФ, по тем же показаниям, в качестве альтернативы назначают АРА», «…предпочтение следует отдавать рамиприлу и периндоприлу» [2].
Таким образом, основные регламентирующие лечебную практику национальные и зарубежные руководства, а также и врачебные ассоциации однозначно отдают предпочтение ингибиторам АПФ при лечении сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний.
Для того, чтобы объяснить причину низкой эффективности влияния сартанов на течение кардиоваскулярной патологии, необходимо остановиться на механизмах терапевтического воздействия БРА II. Известно, что антигипертензивное действие БРА II обеспечивается селективной блокадой АТ1-рецепторов к ангиотензину II (АТ II). В результате этой блокады в крови накапливается дополнительное количество активного АТ II, который связываясь с АТ2-рецепторами (в физиологических условиях этого, как правило, не происходит), способствует появлению ряда негативных явлений. Стимуляция АТ2-рецепторов (возможно также АТ3-, АТ4-рецепторов) неутилизированным АТ II приводит к апоптозу структурных элементов артериальной стенки, её фиброзу, склерозированию и гипертрофии, торможению коронарного ремоделирования с нарушением неоваскуляризации миокарда, а также усилению проатерогенных и воспалительных процессов в эндотелии, возможно и сердечной ткани [70]. Стимуляция АТ2-рецепторов также способствует лейкоцитзависимому высво-
EUROPEAN European Heart Journal
SOCIETY OF
Ингибитор АПФ Смертность от всех причин ОР (95% ДИ)

Ингибиторы ангиотензинпревращающего фермента снижают смертность при артериальной гипертензии: метаанализ
158 998 пациентов
БРА Смертность от всех причин ОР (95% ДИ) (модель случайных эффектов)
|
RENAAL |
1,03 (0,83-1,29) |
|
IDNT |
0,92 (0,69-1,23) |
|
LIFE |
0,88 (0,77-1,01) |
|
SCOPE |
0,96 (0,81-1,14) |
|
VALUE |
1,04 (0,94-1,14) |
|
MOSES |
-■ 1,07 (0,73-1,57) |
|
JIKEI HEART |
1,09 (0,64-1,85) |
|
PRoFESS |
1,03 (0,93-1,14) |
|
TRANSCEND |
1,05 (0,91-1,22) |
|
CASE-J |
0,85 (0,62-1,16) |
|
HIJ-CREATE |
■ 1,18 (0,83-1,67) |
|
KYOTO HEART |
0,76 (0,40-1,30) |
|
NAVIGATOR |
0,90 (0,94-1,04) |
|
-1% |
|
|
Всего |
НД 0,99 (0,94-1,04) |
|
0,50 0,75 |
1 1,33 2,0 |
ОР
БРА лучше Контроль лучше р для неоднородности 0,631, I2 0%
Рисунок 9. Влияние ингибиторов АПФ и БРА II на общую смертность [56]
Picture 9. Different effect of ACE inhibitors and ARB on total mortality [56]
бождению матриксной металлопротеиназы I, которая приводит к деструкции белков внеклеточного матрикса, тем самым дестабилизируя атеросклеротическую бляшку, приводя к ее разрыву, что является возможной причиной увеличения риска инфаркта миокарда при лечении сартанами. Каскад этих негативных влияний в сердечно-сосудистой системе может быть основным механизмом дестабилизации ИБС. В отличие от этого лечебный потенциал ИАПФ реализуется через блокаду синтеза АТ II, не влияя на работу собственно рецепторного аппарата, поэтому вышеуказанных неблагоприятных эффектов, связанных с накоплением АТ II, не происходит. С нашей точки зрения, именно по этой причине сравнительный анализ эффективности лечения сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний показывает преимущество ИАПФ перед БРА II. Весомым агрументом в пользу этого положения служат данные еще одного крупного метанализа (L. C. van Vark и соавт.), наглядно демонстрирующего снижение общей смертности на 10% в подгруппе ингибиторов АПФ и отсутствие таковой при лечении сартанами (рис. 9).
Продолжает обсуждаться роль антигипертензивных препаратов в развитии онкопатологии; в конце 90-х под подозрение попали дигидропиродиновые антагонисты кальция (нифедипин), симпатолитики (резерпин); однако, последние годы обсуждается наличие пронкогенного эффекта у ряда сартанов. Этой проблеме в 2010 г. был посвящен субанализ 8 РКИ (LIFE, OPTIMAAL, CHARM, TRANSCEND, PROFESS, VALIANT, ONTARGET, VAL-HEFT), посвященных лечению сердечно-сосудистой патологии препаратами БРА II. Результаты показали противоречивые данные; в заключении «онкологического» субанализа автор (Nissen S.E.) отметил: «Мы должны использовать сартаны, особенно телми-сартан с большой осторожностью. Эти препараты часто назначаются больше, чем нужно, и при этом отсутствуют доказательства их превосходства над ИАПФ» [43]. Возможная причина “проонко-генного” влияния сартанов связывалась с механизмом действия, который в отличие от ИАПФ заключается в блокаде рецептора, но не самого ангиотензина II, избыток которого может оказывать пролиферативный эффект.
К теме проонкогенных эффектов сартанов вернулись 2018 г., когда появились подозрения в отношении препарата валсартан, синтезируемого Китаем, Индией. Фармкомпания Новартис по этому поводу подготовила релиз, в котором было указано на наличие в составе «китайского» валсартана потенциального канцерогена, однако убедительных данных о роли этого химического вещества в канцерогенезе представлено не было. В настоящее время ясно только то, что ставить точку в этом вопросе преждевременно, необходимы дополнительные исследования в этой области для формирования окончательных выводов.
Дополнительные аргументы в пользу ИАПФ были получены у сосудистых больных, инфицированных коронавирусом. Поначалу публикации, посвященные лечению COVID-19, ставили под сомнение целесообразность назначения ингибиторов РААС кардиологическим больным; высказывалось предположение о возможной инвазии вируса в клетку через рецептор к АТ II из-за возрастания плотности рецептора при лечении ингибиторами РААС. Более того, предлагалось ограничивать использование ИАПФ и БРА II у инфицированных коронавирусом [17,35]. Однако по мере накопления клинических данных стало ясно, что блокаторы РААС не только не ухудшают течение COVID-19, но способствуют улучшению прогноза, особенно у лиц пожилого возраста: «рекомендовано продолжить терапию блокаторами РААС у пациентов уже получающих их…, имеются доказательства того, что отказ от этих препаратов увеличивает риск сердечно-сосудистых катастроф (инфаркт, инсульт)» [1,38].
В другом исследовании, посвященном клиническим исходам у больных пневмонией, вызванной COVID-19, было установлено значимое достоверное преимущество ИАПФ перед БРА II. Так, по данным Mehra M.R. et al., среди 8910 больных коронавирусом внутрибольничная летальность при лечении ИАПФ составила 2,1%, в то время как при лечении сартанами – 6,8%. Назначение ИАПФ больным COVID-19 (рис. 11) ассоциировалось со снижением госпитальной смертности на 67% (0.33 (0.20–0.54)), в то время как при лечении сартанами этот показатель имел тенденцию к увеличению (1.23 (0.87–1.74)) [40].
|
Фактор риска |
Есть фактор риска число умерших паци |
Фактора риска нет ентов / общее число (%) |
Отношение шансов (95% ДИ) |
|
Возраст >65 лет |
147/1474 (10,0) |
368/7436 (4,9) |
' —■— |
|
Женский пол |
179/3571 (5,0) |
336/5339 (6,3) |
|
|
Ишемическая |
|||
|
болезнь сердца |
103/1010 (10,2) |
412/7900 (5,2) |
|
|
Хроническая |
|||
|
сердечная |
29/189 (15,3) |
486/8721 (5,6) |
1 ■---- |
|
недостаточность |
|||
|
Аритмия |
35/304 (11,5) |
480/8606 (5,6) |
1 ■— |
|
ХОБЛ |
32/225 (14,2) |
483/8685 (5,6) |
1 ■--- |
|
Курильщики |
46/491 (9,4) |
469/8419 (5,6) |
1 --■-- |
|
в настоящее время |
|||
|
Получают иАПФ |
16/770 (2,1) |
499/8140 (6,1) |
—■— |
|
Получают сартан |
38/556 (6,8) |
477/8354 (5,7) |
1 ■— |
|
Получают статин |
36/860 (4,2) |
479/8050 (6,0) |
--■— 1 |
|
0,1 |
1 1 1,0 10,0 |
Рисунок 10. Независимые прогностические факторы внутрибольничной смертности [40]Picture 10. Independent prognostic factors for community-acquired mortality [40]
74 ЕВРАЗИЙСКИЙ КАРДИОЛОГИЧЕСКИЙ ЖУРНАЛ, 4, 2020
Также представляет интерес данные Caldeira D. и соавт., показавшие очевидное преимущество ИАПФ перед БРА II по способности снижать вероятность развития пневмонии (рис. 11). По результатам проведенного мета-анализа (37 исследований) риск пневмонии при лечении ИАПФ составил 0,66 (0,55-0,80), тогда как при использовании сартанов практически не снижался – 0,95 (0,87-1,04), что демонстрирует принципиальную разницу влияния различных ингибиторов РААС на инфекционную патоло- гию легких. Данный мета-анализ становится особенно важным в период продолжающейся эпидемии коронавирусной инфекции, поскольку позволяет выстраивать оптимальную тактику ведения больных с заболеваниями сердечно-сосудистой системы и высоким риском бронхолегочной инфекции [11].
Один из частых вопросов практических врачей относится к рациональному выбору среди 11 препаратов ИАПФ, представленных на отечественном фармацевтическом рынке. По мнению
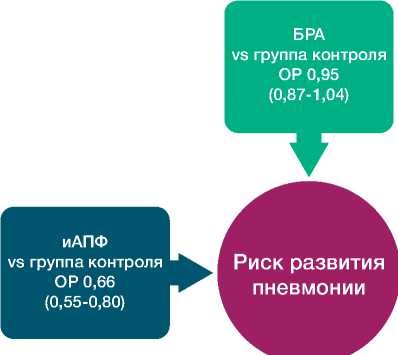
Рисунок 11 Риск развития пневмонии в зависимости от применения ИАПФ или БРА [11]
Picture 11. Risk of pneumonia depending on ACE inhibitors or ARBs [11]
иАПФ vs БРА ОР 0,69 (0,56-0,85)
Выживаемость после ОИМ в зависимости от иАПФ
Кумулятивная выживаемость (%)
Квинаприл n=276
^^^^^^ Фозиноприл n=889
^^^^^м Каптоприл n=421
n=7512
р<0,001 для лонг-рангового
---------------------------1111----------------------------г
0 2 4 6 8 10
и
Месяцы
Pilote Letal. Ann Intern Med 2004;141:102-112.
Рисунок 12. Выживаемость после ИМ в зависимости ИАПФ [46]
Picture 12. Survival after myocardial infarction (MI) depending on ACE inhibitor [46]
ряда экспертов, наилучшим профилем эффективности и безопасности обладают липофильные ИАПФ – рамиприл, периндо-прил. Их способность блокировать АТ II существенно превышает потенциал водорастворимых ИАПФ, таких, как например, каптоприл, эналаприл, лизиноприл, поскольку жировая ткань синтезирует и аккумулирует значимое количество АТ II, становящегося недоступным для водорастворимых ИАПФ. Американские рекомендации по лечению АГ (2017) упоминают о высокой эффективности рамиприла и периндоприла, потенциал которых по снижению риска развития сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний примерно одинаков (22% и 20% соответственно) [8].
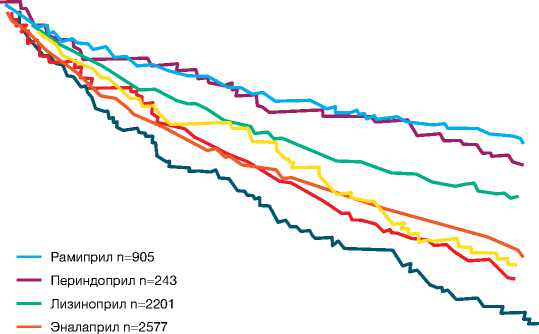
По данным Pilot L. наибольшее влияние на выживаемость в постинфарктном периоде оказывают именно эти два препарата (рис. 12) [46].
Ранее проведенные РКИ подтвердили наличие значимого кардиопротективного потенциала периндоприла (EUROPA, ADVANCE, ASCOT-BPLA, HYVET, PROGRESS) и рамиприла (HOPE, ONTARGET). В рекомендациях РФ (2020) по лечению ИБС эксперты также отмечают наибольшую эффективность у препаратов рамиприл и периндоприл [7]. Менее значимые результаты по улучшению прогноза кардиологических больных были установлены у других представителей этого класса: трандолаприла [(исследование РЕACE), хинаприла [47], эналаприла [59], лизиноприла [63]. Ради справедливости необходимо отметить, что прямых сравнений внутри этого класса препаратов не выполнялось.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Результаты многочисленных клинических исследований указывают на имеющиеся определенные преимущества ингибиторов АПФ перед блокаторами АТ II, которые позволяют более рационально выстраивать тактику ведения кардиологических больных. При выборе собственно ингибитора АПФ из достаточно большого репертуара, представленного на фармрынке России, мы должны учитывать наличие двух важных свойств препарата: продолжительность действия (не менее 24 часов) и липофильность, которая позволяет ИАПФ накапливаться в различных тканях, не ограничиваясь эффектами блокады АТ II лишь в сосудистой стенке. Именно с липофильностью во многом связаны благоприятные эффекты ряда ИАПФ, максимально обеспечивающих сердечно-сосудистую, почечную, метаболическую протекцию, профилактику пролиферации, защиту от апоптоза и др. Этим свойствам в большей мере отвечают периндоприл и рамиприл, поскольку именно у этих препаратов накоплена наибольшая доказательная база. Так, например, препарат периндоприл способствует снижению риска острых сердечно-сосудистых катастроф, эффективен при лечении ХСН, нарушениях ритма сердца, снижает риск развития почечной недостаточности, сахарного диабета, деменции, оказывает позитивное влияние на липидный спектр, уровень лептина и др. В рекомендациях АНА/ АСС по лечению АГ (2017) указано, что риск развития сердечно-сосудистой смерти, инфаркта миокарда и остановки сердца на 20% ниже на фоне периндоприла по сравнению с плацебо [8]. В то время как для других представителей препаратов этого класса – трандолаприла [48], лизиноприла [63], квинаприла [47], эналаприла [59] – доказательная база по профилактике сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний оказалась недостаточной. Важной особенностью периндоприла, которые отличают его от других препаратов этого класса, является его способность максимально повышать уровень брадикинина. Именно брадикинин оказывает положительное влияние на стенку сосудов, снижает их жесткость путем увеличения синтеза простагландинов, демонстрирует антиоксидантный и вазодилатирующий эффекты
-
[15 ]. Монотерапия ингибиторов АПФ, например, препаратом пе-риндоприл (Престариум) может быть рекомендована молодым пациентам с артериальной гипертензией для достижения целевых цифр АД и предотвращения ранних сердечно-сосудистых катастроф.
Периндоприл входит в состав целой группы антигипертензивных препаратов, объединенных в так называемую «семью» – Пре-стариум, Престанс и Трипликсам. В соответствии с российскими и зарубежными рекомендациями, лечение большинства больных АГ необходимо начинать с фиксированных комбинации. Всем пациентам с АГ (кроме пациентов низкого риска с АД <150/90 мм рт. ст., пациентов старше 80 лет, пациентов с синдромом старческой астении) в качестве стартовой терапии рекомендована комбинация антигипертензивных препаратов, предпочтительно фиксированная, для улучшения приверженности к терапии. Одной из стартовых схем первой линии является комбинация ингибитора АПФ и дигидропиридинового блокатора кальциевых каналов. Примером такой фиксированной комбинации может служить препарат Престанс, важной особенностью которого является влияние на вариабельность АД – важного фактора риска развития сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, а также смерти от всех причин [3]. Имеются различные варианты дозы компонентов в препарате Престанс – 5/5, 5/10, 10/5,10/10 мг, соответственно, для периндо-прила и амлодипина. При различной степени АГ для стабильного контроля АД и его вариабельности необходимо выбирать оптимальную дозировку Престанса.
В соответствии с российскими и зарубежными рекомендациями пациентам, не достигшим целевого АД на фоне двойной комбинированной терапии, рекомендуется тройная комбинация блокатора РААС с АК и диуретиком, предпочтительно в форме фиксированной комбинации, например, препарат Трипликсам.
Все препараты “семьи” периндоприла отличает низкая частота побочных действий (кашля, ангионевротического отёка, постуральной гипотензии, электролитных и метаболических расстройств, сексуальной дисфункции и др.), возможность однократного приема и удобство подбора дозировки, что повышает приверженность пациентов к лечению.
Список литературы Инактивация ренин-ангиотензин-альдостероновой системы. Какой класс препаратов предпочесть?
- Временные методические рекомендации МЗ РФ: "Профилактика, диагностика лечение новой коронавирусной инфекции (COVID-19)", версия 6 от 28.04.2020; https://static-1.rosminzdrav.ru/system/attachments/attaches/000/050/116/original/28042020_%D0%9CR_COVID-19_v6.pdf
- Клинические рекомендации по лечению стабильной ишемической болезни сердца МЗ РФ 2020; https://scardio.ru/content/Guidelines/2020/Clinic_rekom_IBS.pdf
- Кочетков А.И. и др. Механизмы формирования вариабельности артериального давления и возможности антигипертензивных препаратов в ее коррекции. Кардиология, 2019; 59 (11):1-56
- Инструкция по медицинскому применению препарата валсартан 2019
- Инструкция по медицинскому применению препарата лозартан 2019
- Мареев и соавт. Клинические рекомендации ОССН-РКО-РНМОТ. Сердечная недостаточность: хроническая (ХСН) и острая декомпесированая (ОДСН) Диагностика, профилактика и лечение. 2018;58(6S):8-158.
- Е.В. Шляхто. Кардиология: нац. руков / под ред. Е.В. Шляхто. - 2-е изд. перераб. и доп. - М.: ГЭОТАР-Медиа. - 2019. - 800 с.
- 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults VOL. 71, NO. 19, 201
- Berl T Cardiovascular Outcomes in the Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Overt Nephropathy Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:542-549.
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, et al. RENAAL Study Investigators. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2001;345:861-9.
- Caldeira D, Alarcao J, Vaz-Carneiro A, Costa J. Risk of pneumonia associated with use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: systematic review and meta-analysis BMJ 2012;345:e4260
- Caldeira D, David C, Sampaio C. Tolerability of angiotensin-receptor blockers in patients with intolerance to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012;12(4):263-277.
- Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes of Renin-Angiotensin System Blockade in Adult Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review with Network Meta-Analyses. Catalá-López F, Macías Saint-Gerons D, González-Bermejo D, Rosano GM, Davis BR, Ridao M, Zaragoza A, Montero-Corominas D, Tobías A, de la Fuente-Honrubia C, TabarésSeisdedos R, Hutton B.PLoS Med. 2016 Mar 8;13(3):e1001971. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001971. eCollection 2016 Mar
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001971.eCollection2016Mar
- Catalá-López F, Macías Saint-Gerons D, González-Bermejo D, Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes of Renin-Angiotensin System Blockade in Adult Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review with Network Meta-Analyses. B.PLoS Med. 2016 Mar 8;13(3):e1001971. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001971. eCollection 2016 Mar
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001971.eCollection2016Mar
- Ceconi C, Francolini G, Bastianon D. Differences in the effect on the ACEinhibitors on the rate of endothelial cell apoptosis: in vitro and in vivo stusies. Cardiovascular Drugs Therapy 2007 Dec; 21(6): 423-9
- Dahlof B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002;359:995-1003
- Diaz JH. Hypothesis: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers may increase the risk of severe COVID-19. J Travel Med 2020;
- DOI: 10.1093/jtm/taaa041
- Hall et al. Dialogues in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2014; 3(19)151-155
- Ducharme A, Swedberg K, Pfeffer MA, et al. Prevention of atrial fibrillation in patients with symptomatic chronic heart failure by candesartan in the Candesartan in Heart failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) program. Am Heart J. 2006;152(1):86-92.
- ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal, ehaa575,
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa575
- 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) European Heart Journal (2013) 34, 2159-2219
- 2014 Evidence-Based Guideline for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults Report From the Panel Members Appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8) JAMA. 2014;311(5):507-520
- 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal, Volume 37, Issue 27, 14 July 2016, Pages 2129-2200,
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128
- 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal, Volume 39, Issue 2, 07 January 2018, Pages 119-177,
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx393
- 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). European Heart Journal, Volume 39, Issue 33, 01 September 2018, Pages 3021-3104,
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy339
- 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for themanagement of arterial hypertension The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). European Heart Journal (2018) 00, 1-98
- 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes: The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal, Volume 41, Issue 3, 14 January 2020, Pages 407-477,
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz425
- 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal (2016) 37, 2129-2200 European Heart Journal (2016) 37, 2129-2200
- Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). European Heart Journal, Volume 35, Issue 37, 1 October 2014, Pages 2541-2619
- GISSI AF investigators group Valsartan for Prevention of Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2009; 360:1606-1617
- Guidelines for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2011;42;227-276; originally published online Oct 21, 2010
- Go A. et al. An Effective Approach to High Blood Pressure Control A Science Advisory From the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hypertension 2014.
- Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, Weber M et al. Outcomes in hypertensive patients at high cardiovascular risk treated with regimes based on valsartan or amlodipine: the VALUE randomized trial. Lancet 2004;363:2022-31.
- Al Khalaf, L. Thalib, S.A.R. Doi. в Cardiovascular Outcomes in High-Risk Patients without Heart Failure Treated with ARBs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 2009; 9 (1): 29-43
- Kuster GM, Pfister O, Burkard T, Zhou Q, Twerenbold R, Haaf P, Widmer AF, Osswald S. SARS-CoV2: should inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system be withdrawn in patients with COVID-19? Eur Heart J 2020;
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa235
- Law MR, Morris JK, Wald NJ. Use of blood pressure lowering drugs in the prevention of cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis of 147 randomised trials in the context of expectations from prospective epidemiological studies. BMJ 2009; 338: b1665,
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.b1665
- Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2001;345:851- 60.
- Mancia G., Rea F., Ludergnani M. et al. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and the Risk of Covid-19. May 1, 2020, at NEJM.org.
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2006923
- McDonald MA, Simpson SH, Ezekowitz JA, et al. Angiotensin receptor blockers and risk of myocardial infarction: systematic review. BMJ 2005;331;873-9.
- Mehra M. R., apan. Desai S.S., Kuy S, R. Cardiovascular Disease, Drug Therapy, and Mortality in Covid-19. May 8, 2020, at NEJM.org.
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007621
- Messerli FH, Bangalore S, Ruschitzka F. Angiotensin receptor blockers: baseline therapy in hypertension? Eur Heart J 2009; 30: 2427-30.
- Mochizuki S, Dahl f B, Shimizu M, et al. Valsartan in a Japanese opulation with hypertension and other cardiovascular disease (Jikei Heart Study): a randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint morbiditymortality study. Lancet 2007;369:1431-9.
- Niessen S.E. Angiotensin receptor blockers and cancer: urgent regulatory review needed, Lancet Oncol 11(7): 605-606.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Type 2 diabetes: the management of type 2 diabetes. NICE clinical guideline 87. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg87/resources/guidance-type-2-diabetes-pdf. Accessed September 15, 2014.
- Papademetriou V, Farsang C, Elmfeldt D, et al. Stroke prevention with the angiotensin II type 1-receptor blocker candesartan in elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension: the Study on Cognition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44(6):1175-80.
- Pilot L. et al. Mortality rates in elderly patients who take different angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors after acute myocardial infarction: a class effect? Ann Intern Med 2004 Jul 20;141(2):102-12 47. Pitt B, O'Neill B, Feldman R, et al. The QUinapril Ischemic Event Trial (QUIET): evaluation of chronic ACE inhibitor therapy in patients with ischemic heart disease and preserved left ventricular function. Am J Cardiol 2001;87:1058 -63
- The PEACE Trial Investigators Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme Inhibition in Stable Coronary Artery DiseaseN Engl J Med 2004; 351:2058-2068
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa042739
- Sawada T, Yamada H, Dahlof B, Matsubara H. KYOTO HEART Study Group. Effects of valsartan on morbidity and mortality in uncontrolled hypertensive patients with high cardiovascular risks: KYOTO HEART Study. Eur Heart J 2009; 30: 2461-9.
- Sawano T, Ozaki A, Saito H, Shimada Y, Tanimoto Payments From Pharmaceutical Companies to Authors Involved in the Valsartan Scandal in Japan. T.JAMA. 2019 May 3;2(5):e193817. : 31099864.
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.3817.PMID
- Sipahi I et al. Angiotensin-receptor blockade and risk of cancer: metaanalysis of randomised controlled trials. The Lancet Oncology. Published Online June
- Strauss MH, Lonn EM, Verma S. Is the jury out? Class specific differences on coronary outcomes with ACE-inhibitors and ARBs: insight from meta-analysis and The Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists'Collaboration. Eur Heart J 2005; 26: 2351-3.
- Strauss MH., Hall AS. Do angiotensin receptor blockers increase the risk of myocardial infarction? Angiotensin Receptor Blockers May Increase Risk of Myocardial Infarction. Unraveling the ARB-MI Paradox. Circulation. 2006; 114: 838-54.
- The Telmisartan Randomised AssessmeNt Study in ACE iNtolerant subjects with cardiovascular Disease (TRANSCEND) Investigators. Effects of the angiotensin-receptor blocker telmisartan on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients intolerant to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008;372:1174-83.
- Turnbull F, Neal B, Algert C, et al. Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists' Collaboration. Effects of different blood pressure-lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events in individuals with and without diabetes mellitus: results of prospectively designed overviews of randomized trials. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(12):1410-9.
- van Vark L.C., M. Bertrand, K. M. Akkerhuis, J. J. Brugts K. Fox et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors reduce mortality in hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors involving 158 998 patients. European Heart Journal Advance Access published April 17, 2012.
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs
- Verma S, Strauss M. Angiotensin receptor blockers and myocardial infarction. BMJ 2004;329:1248-9.
- Wang K, Hu J, Luo T, Wang Y, Yang S, Qing H, Cheng Q, Li Q Effects of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers on All-Cause Mortality and Renal Outcomes in Patients with Diabetes and Albuminuria: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2018;43(3):768-779. Epub 2018 May 22.
- DOI: 10.1159/000489913
- Wing L.M.H., Reid C.M., Ryan P. et al. A comparison of outcomes with angiotensin coverting enzyme inhibitors and diuretics for hypertension in the elderly // N. Engl. J. Med. 2003; 348: 583-592
- Windecker et al. 2014 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: The Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). European Heart Journal, Volume 35, Issue 37, 1 October 2014, Pages 2541-2619
- van Vark L.C. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors reduce mortality in hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors involving 158 998 patients. European Heart Journal (2012) 33, 2088-2097
- Yusuf et al. The Telmisartan Randomised AssessmeNt Study in ACE iNtolerant subjects with cardiovascular Disease (TRANSCEND) Investigators* Effects of the angiotensin-receptor blocker telmisartan on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients intolerant to angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors: a randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2008; 372: 1174-83Lancet 2008; 372: 1174-83
- Yui Y., Sumiyoshi T., Kodama K. et al. Comparison of nifedipine retard with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in Japanese hypertensive patients with coronary artery disease: the Japan Multicenter Investigation for Cardiovascular Diseases-B (JMIC-B) randomized trial // Hypertens. Res. 2004; 27: 181-191
- Yusuf et al. PROFESS study group. Telmisartan to Prevent Recurrent Stroke and Cardiovascular Events. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1225-37.
- Zheng et al. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2017 Sep;14(5):400-406
- Tsuyuki R T, McDonald M A. Angiotensin receptor blockers do not increase risk of myocardial infarction. Circulation 2006114855-860.
- Papademetriou V, Farsang C, Elmfeldt D, et al. Stroke prevention with the angiotensin II type 1-receptor blocker candesartan in elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension: the Study on Cognition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44(6):1175-80.
- Brugts JJ, van Vark L, Akkerhuis M, et al. Impact of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on mortality and major cardiovascular endpoints in hypertension: a number-needed-to-treat analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2014.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.11.179
- Windecker S. et al. 2014 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: The Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). European Heart Journal, Volume 35, Issue 37, 1 October 2014, Pages 2541-2619
- Levy B. et al. How to explain differences between renin angiotensin system modulators. American Journal og Hypertension, 2005; 18(Issue S5): P.134S-141S.


