Индуцибельная NO-синтаза как фармакологическая мишень противовоспалительной терапии: надежда не потеряна?
Автор: М.М. Галагудза, Ю.П. Бельский, Н.В. Бельская
Журнал: Сибирский журнал клинической и экспериментальной медицины @cardiotomsk
Рубрика: Обзоры и лекции
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.38, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Обзор посвящен текущему пониманию роли оксида азота (NO) и индуцибельной NO-синтазы в физиологических условиях и при некоторых патологических состояниях. Рассмотрены механизмы индукции экспрессии гена индуцибельной NO-синтазы и посттранскрипционной регуляции активности индуцибельной NO-синтазы, приведены сведения об эндогенных ингибиторах индуцибельной NO-синтазы. Проведен анализ статуса клинических исследований, направленных на изучение клинической эффективности ингибиторов NO-синтаз.
Оксид азота, ингибитор индуцибельной синтазы оксида азота, доклинические исследования, клинические испытания
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149141576
IDR: 149141576 | УДК: 616-002-085.276:577.152.6 | DOI: 10.29001/2073-8552-2023-38-1-13-20
Текст статьи Индуцибельная NO-синтаза как фармакологическая мишень противовоспалительной терапии: надежда не потеряна?
Оксид азота (NO) образуется из аминокислоты L-аргинина ферментами NO-синтазами. Время полураспада NO составляет всего около 5 с, что ограничивает роль данного соединения локальной регуляцией кровотока и других функций. NO-синтазы распределены в разных соотношениях в различных органах. Так, имеются три изоформы NO-синтазы, участвующие в синтезе NO: две конститутивные NO-синтазы, всегда присутствующие в клетках (нейрональная и эндотелиальная), и индуцибельная NO-синтаза (iNOS или NOS2), активность которой определяется действием на клетку стимулирующих факторов.
В настоящем обзоре рассматривается функциональное значение iNOS, принципы регуляции экспрессии и активности данного фермента, а также роль образующегося в результате активации iNOS оксида азота в патологических процессах.
Индукция экспрессии гена iNOS iNOS представляет собой небольшой белок с молекулярной массой 131 кДа, состоящий из 1153 аминокислот, которые собраны в два основных домена: С-концевую редуктазу, содержащую субдомен, связывающий флавинмононуклеотид (FMN), и N-концевую оксигеназу. Белок iNOS имеет гомодимерную четвертичную структуру с цинковыми мостиками [1]. Две другие изоформы – нейрональная (nNOS или NOS1) и эндотелиальная (eNOS или NOS3) – регулируются связыванием кальция и кальмодулина, тогда как iNOS регулируется транскрипционно и не зависит от кальция и кальмодулина.
iNOS экспрессируется только в активированных клетках и индуцируется микробными продуктами (липополисахаридом) и воспалительными цитокинами, такими как интерлейкин-1β (IL-1β), фактор некроза опухоли α (TNF-α), интерферон (IFN-γ) [2]. Кроме того, гипоксия также может стимулировать экспрессию гена iNOS [3]. Выработка NO индуцибельной NO-синтазой начинается через несколько часов после индукции и может продолжаться до 5 дней [2]. Количество вырабатываемого NO конститутивными NOS невелико – от пико- до наномоль, в то время как iNOS способна вырабатывать на несколько порядков больше – более микромоль [2].
Способностью экспрессировать iNOS и производить NO обладают не только клетки врожденного и адаптивного иммунитета (моноциты, нейтрофилы, тучные клетки, макрофаги, Т-лимфоциты), но и эндотелиальные и гладкомышечные клетки [4], гепатоциты, хондроциты, глиальные клетки, астроциты, нейроны, кардиомиоциты [1]. Показано, что такой способностью могут обладать и опухолевые клетки, используя NO как защиту от противоопухолевых механизмов [4, 5].
Основным внутриклеточным путем передачи сигналов вышеуказанных стимуляторов экспрессии гена iNOS является активация транскрипционного фактора NF-κB; активный фактор перемещается в ядро клетки, связывается с промоторным регионом гена iNOS и индуцирует экспрессию гена iNOS [6]. IFN-γ активирует путь JAK / STAT-1α: IFN-γ вызывает димеризацию рецептора IFN-γ и активацию Янус киназ (JAK, в частности JAK2), которые затем фосфорилируют STAT-1α, который затем димеризуется и транслоцируется к ядру, где способствует синтезу регуляторного фактора интерферона 1 (IRF-1). Затем IRF-1 связывается с промотором гена iNOS и индуцирует экспрессию iNOS [1, 7].
Посттранскрипционная регуляция активности iNOS
Посттранскрипционная регуляция экспрессии гена iNOS преимущественно происходит с помощью механизмов, которые влияют на стабильность мРНК iNOS и регуляцию каталитической активности [8].
Ферментом, конкурирующим с iNOS за субстрат (L-аргинин), является аргиназа, которая в цикле мочевины превращает аргинин в орнитин и мочевину. Исследования показали, что ингибирование аргиназы приводит к увеличению синтеза NO в макрофагах кролика и крысы, в воспаленных легких мыши [1], а избыточная экспрессия аргиназы, например, в кератиноцитах человека, вовлечена в механизм заболевания псориазом, воспалительным заболеванием кожи [1]. В условиях развития Th1- и Th2-зависимого иммунного ответа у мышей при повышении экспрессии iNOS и продукции NO наблюдалось снижение экспрессии аргиназы и продукции мочевины [9].
Стимулы, приводящие к повышению экспрессии iNOS, также вызывают увеличение экспрессии транспортеров катионных аминокислот CAT 1, CAT2 и CAT3, которые транспортируют аргинин через клеточную мембрану [1]. Дефицит этих транспортеров, напротив, снижает активность iNOS, что показано при делеции гена CAT2 в астроцитах [1]. Кроме того, при индукции iNOS в макрофагах, гладкомышечных клетках сосудов, микроглии и нейронах наблюдается и повышение экспрессии аргининосукци-натсинтетазы, которая преобразует L-цитруллин (побочный продукт при синтезе NO) обратно в L-аргинин [1].
Активность iNOS в значительной степени зависит от кофактора тетрагидробиоптерина (H4B), обеспечивающего димеризацию iNOS, без чего фермент не активен. Это показали исследования на клеточных линиях: чем больше клетки продуцировали H4B, тем выше была активность iNOS, а добавление в культуру клеток с низким уровнем H4B предшественника H4B (сепиаптерин) значительно увеличивало и активность iNOS [1].
Негативным регулятором iNOS является ее продукт – NO. На макрофагах мыши показано, что внесение в культуру скавенджера NO (гемоглобин) влечет за собой увеличение активности iNOS, а добавление доноров NO приводит к значительному снижению активности iNOS, которая не восстанавливается при удалении доноров NO, что указывает на необратимость действия [1]. Наиболее вероятным механизмом такой деактивации может быть S-нитрозирование кластера тетратиолата цинка, ведущее к необратимой диссоциации димера молекулы iNOS с последующей утратой активности [1].
Функции NO/iNOS
Существует 2 пути реализации физиологической функции NO: зависимый и не зависимый от циклического гуанозинмонофосфата (цГМФ) [4]. NO взаимодействует с активным центром растворимой гуанилатциклазы (sGC) с образованием цГМФ, который затем активирует протеинкиназу G (PKG) с последующим фосфорилированием субстратов [4]. Этот механизм является основным для конститутивных форм NOS, в то время как для iNOS основным механизмом реализации функции служит цГМФ-независимый, для которого характерно образование ряда радикалов и продуктов их взаимодействия с эндогенными белками. При взаимодействии NO с молекулой кислорода (в аэробных условиях) образуется реакционноспособный промежуточный продукт (RNOS), а при его взаимодействии с супероксидным радикалом O2
промежуточный продукт преобразуется в пероксинитрит (ONOO-), который является мощным окислительным и нитрозирующим агентом. В биологических жидкостях основным продуктом окисления является азотистый ангидрид (N2O3), который нестабилен и быстро распадается до тиолов или аминов. Все эти продукты способны модифицировать азотистые основания в ДНК и индуцировать одноцепочечные разрывы в ДНК [2]. Основная функция появившихся продуктов – уничтожение патогенных микроорганизмов.
Итог действия продуктов радикального механизма на клетки зависит от концентрации: при более низкой концентрации NO его действие оказывается, как правило, антиапоптотическим, но при более высокой концентрации он действует как проапоптотическая молекула [2].
Роль NO/iNOS в патологических состояниях
Избыточная и неоправданно долгая выработка повышенного количества NO является ключевым механизмом воспаления, что хорошо показано в научной литературе, например, при воспалительных заболеваниях суставов и дегенеративных заболеваниях опорно-двигательного аппарата [10]; инфекционно-воспалительных заболеваниях, в том числе вызванных вирусами [11] или паразитами – лейшманиозе [12]; при сахарном диабете [7], нейро-дегенеративных заболеваниях [1], сепсисе, кардиальной дисфункции [13], нарушениях метаболизма глюкозы и липидов при метаболическом синдроме [7]. Мы остановимся кратко на онкологических и сердечно-сосудистых заболеваниях.
Опухолевый рост. Роль NO при опухолевом росте достаточно хорошо изучена. В низких концентрациях NO может способствовать пролиферации опухолевых клеток и оказывать антиапоптотическое действие, в то время как высокие концентрации, напротив, могут вызывать остановку клеточного цикла и апоптоз [14, 15], поскольку он вызывает повреждение ДНК и препятствует ее репарации. В других исследованиях показано, что NO может вызывать активацию онкогенов, посттрансляционную модификацию белков, индукцию мутации генов с накоплением мутантного р53, а также способствует ангиогенезу, эпителиально-мезенхимальному переходу (EMT) и метастазированию [2, 14]. Исследования показали, что низкие концентрации NO активируют сигнальный путь цГМФ, который опосредует как краткосрочное действие NO (от 5 мин. до 1 ч), так и длительное действие [14]. По мере увеличения концентрации NO может активироваться сигнальный путь PI3-киназы-Akt, который способствует миграции эндотелиальных клеток и ангиогенезу [16]. При повышении концентрации NO (> 1 мкМ) происходит стабилизация фактора, связанного с гипоксией (HIF-1альфа), который способствует подавлению пролиферации и замедлению заживления ран [17]. Показано, что в клетках рака молочной железы (клетках MCF7) сигнальные белки реагируют на различные количества NO: внеклеточно-сигнальная киназа (ERK) фосфорилируется на уровне 10–30 нМ, а Akt – при 30–60 нМ; если концентрация NO достигает 100 нМ, стабилизируется HIF-1; при повышении концентрации до 400 нМ происходит фосфорилирование р53 [14].
Экспрессия iNOS меняется по мере развития онкологической патологии: она снижается по мере увеличения стадии и становится низкой или не детектабельной в метастазах в легких и печени [18].
Источником NO могут быть сами опухолевые клетки. Так, например, в нормальных тканях кишечника экспрессия iNOS крайне низкая или отсутствует, в то время как почти 60% клеток аденомы толстой кишки человека экспрессируют ее в больших количествах [18]. При этом опухолевые клетки могут вырабатывать NO и стимулировать его продукцию, хотя сами обладают резистентностью к цитотоксическому действию NO [5].
Сложная ситуация с NO складывается в опухолевом окружении, насыщенном противоопухлолевыми цитотоксическими Т-лимфоцитами, макрофагами и миелоидными супрессорными клетками. Первые два типа клеток, казалось бы, экспрессируя высокий уровень iNOS, должны уничтожать опухолевые клетки, однако этого часто не происходит по ряду причин. Одна из причин может заключаться в способности NO индуцировать появление популяции регуляторных клеток CD4+CD25+Foxp3- (Tregs), которые подавляют функции эффекторных CD24+CD25-Т-клеток [19], что подтверждается наблюдениями о наличии корреляции между частотой встречаемости в опухолевом микроокружении Treg и иммуносупрессией противоопухолевого ответа [20]. Некоторые авторы считают, что длительная антигенная стимуляция Т-клеток при опухолевом росте приводит к снижению интенсивности дифференцировки специфических к антигенам опухоли Т-лимфоцитов и истощению их пула [21], к повышенной экспрессии рецепторов, ингибирующих иммунные функции, например, PD-1, и снижению продукции цитокинов, способствующих противоопухолевому ответу, таких как IL-2, TNF-α и IFN [22]. Следует также обратить внимание на миелоидные супрессорные клетки, которые экспрессируют L-аргиназу 1, и таким образом в опухолевой ткани происходит истощение субстрата (аргинина), снижение экспрессии TCR и нарушение пролиферации Т-клеток [23]. Другими авторами отмечается, что механизм подавления противоопухолевых CD8 Т-клеток миелоидными супрессорными клетками может происходить через выработку ими NO, который подавляет пролиферацию Т-кле-ток и вызывает их апоптоз [24]. Не исключено, что вырабатываемый миелоидными супрессорами NO реагирует с кислородом и превращается в пероксинитрит, который нитрозилирует TCR и MHC. В свою очередь нарушается связывание TCR-MHC I/антиген, что приводит к развитию у опухолевых клеток резистентности к апоптозу, опосредованному цитотоксическими Т-клетками [24].
В последние годы к вопросу о регуляции NO/iNOS стали обращаться в контексте способности NO вызывать или усиливать резистентность к лечению онкологических заболеваний химиопрепаратами на основе платины, ионизирующей лучевой и неионизирующей фотодинамической терапией. Клетки опухоли, выжившие после указанной терапии, часто приобретают более агрессивный фенотип, ускоряется и усиливается их пролиферация и миграция. Имеются экспериментальные данные, показывающие, что введение в комплекс лечения ингибиторов NO/iNOS может приводить к более успешному результату [25].
По мнению ряда исследователей, уровень экспрессии iNOS и циклооксигеназы 2 (СОХ-2) или только определение iNOS (с помощью полимеразной цепной реакции (ПЦР) в реальном времени или иммуноблот-анализа) являются надежным показателем выживаемости при раке, причем пациенты с самыми высокими уровнями имеют наименьшие шансы [26, 27]. Важное значение iNOS и СОХ-2 в развитии опухолей показывают и эксперимен- тальные данные: при перевивном опухолевом росте молочной железы на iNOS-негативных мышах введение ингибитора СОХ-2 приводило не только к регрессии у 20–25% мышей, но и делало их резистентными к повторной перевивке опухолевых клеток, что показывает развитие полноценного противоопухолевого ответа при снятии функций iNOS и СОХ-2 [28].
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания. Наибольшее очевидна роль NO/iNOS в той стадии патогенеза сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, которая связана с воспалением. На мышиной модели, связанной с дефицитом аполипопротеина Е, показано, что снижение образования атеросклеротических поражений, вызванных диетой, связано с низким уровнем экспрессии iNOS [29]. В остром периоде инфаркта миокарда ингибирование iNOS и восстановление активности eNOS небивололом уменьшали размер инфаркта миокарда за счет предотвращения нитрозативного повреждения [30]. На модели атеросклероза, вызванного у кроликов холестериновой диетой с развитием гиперхолестеринемии, введение ингибитора iNOS (агматин) приводило к уменьшению выраженности атеросклеротических изменений [31]. У мышей с нокаутом iNOS введение бактериального липополисахарида вызывало эндотелиальную дисфункцию (при оценке аорты и брыжеечных артерий), которая зависела от индукции iNOS [32]. Использование доноров NO при ишемическом прекондиционировании на мышиной модели оказывало на кардиопротекторное действие [33]. Сверхэкспрессия iNOS в кардиомиоцитах мыши вызывала брадиаритмию, кардиомиопатию и внезапную сердечную смерть [34]. Следует отметить, что единого мнения о роли NO/iNOS в патогенезе сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, исключая этап с преобладанием воспаления, пока не сложилось [35].
Имеются экспериментальные данные о влиянии ингибиторов iNOS на различные модели артериальной гипертензии у животных, которые показывают, что ингибирование iNOS оказывает антигипертензивное действие, уменьшает окислительный и нитрозативный стресс и улучшает функцию сосудов [36].
Ингибиторы iNOS
Нами был проведен поиск публикаций в базе PubMed по ключевым словам «Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor» и «Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors» с и без дополнительного фильтра «Clinical Trial», графическое отражение результатов поиска представлено на рисунке 1.
Results by year
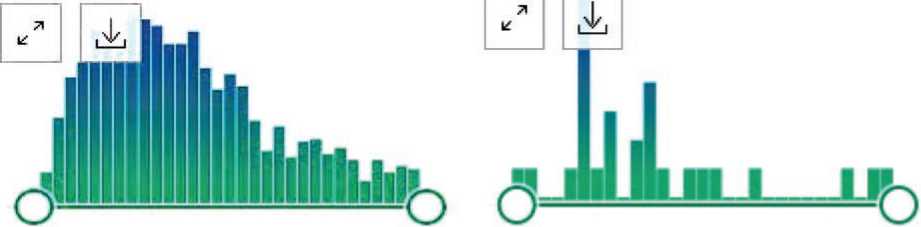
1991 2023 1994 2023
A B
Рис. 1. Количество публикаций за период с 1991 по январь 2023 гг., посвященных ингибиторам NOS, по данным сайта PubMed [37]:
А – общее число публикаций, B – количество публикаций с данными клинических испытаний
Fig. 1. The number of publications from 1991 to January 2023 on nitric oxide synthase inhibitors, according to the PubMed website [37]:
A – total number of publications, B – number of publications with data from clinical trials
Отражением большого интереса к ингибиторам NOS как перспективным кандидатам в лекарственное средство является и число патентуемых соединений. Так, за 3 года (с 2011 по 2014 гг.) фармацевтическими компаниями и исследовательскими центрами было запатентовано более 100 новых малых молекул – ингибиторов NOS [38]. Среди фармацевтических компаний, ведущих разработки ингибиторов NO-синтазы: Altana Pharma (два класса препаратов – на основе oxazolo[4,5-B]pyridines и имидазола); Aventis Pharmaceuticals (производные кумарина); Nycomed (производные имидазопиридина); Schering (N-гетероциклические производные); Berlex; Pharmacia; Pfizer (S-[2[(1-iminoethyl)amino]ethyl]-2-methyl-L-cysteine maleate hydrochloride); AstraZeneca (производные 3-arylthio-3-thiazolyl- и phenylarylamine).
Среди научных центров можно выделить: Северо-Западный университет (Эванстон, США) с разработкой хиральных соединений на основе пирролидина. Национальный университет Сеула, Корея (Seoul National University
Industry Foundation), в котором разрабатываются производные Theopederin. Обнадеживающие результаты на биологических моделях сепсиса, воспаления легких, артритов и аутоиммунного диабета получены при изучении таких соединений, как 1400W, GW274150 и GW273629, AR-C102222, ONO1714, ряда производных L-аргинина, L-NIL и SC-51 и ингибитора димеризации BBS-1.
Большое количество публикаций посвящено описанию ингибиторных свойств растительных компонентов в отношении iNOS [39]. Фарнезилфенолы (грифолиноны А и В, грифолин и неогрифолин), извлеченные из несъедобного гриба Albatrellus caeruleoporus, производные лигнана (эудесмин, манголин, янгабин, эпиманголин В) из Magnolia fargesii, фенантреноиды (юнкутол, юнку-зол, дегидроункузол), выделенные из корневищ Juncus acutus L., 5-О-метилгирсутанонол, выделенный из листьев Alnus japonica Steud., бензокамфорин Н, выделенный из съедобного гриба Taiwanofungus camphoratus, ресвератрол из виноградных косточек, сесквитерпеноиды, выделенные из Artemisia austroyunnanensis, и многие другие вещества в исследованиях in vitro показали значительную ингибиторную активность в отношении iNOS.
Ингибиторы синтетического происхождения некоторые авторы разделяют по месту связывания с молекулой iNOS на 4 типа [2]:
-
1 – ингибиторы, связывающиеся с сайтом связывания аргинина;
-
2 – ингибиторы, имитирующие кофактор тетрагидробиоптерин;
-
3 – соединения, непосредственно взаимодействующие с гемом молекулы iNOS;
-
4 – соединения, взаимодействующие с кофакторами кальмодулин или флавин.
Наиболее многочисленная группа – ингибиторы, связывающиеся с сайтом аргинина, ее разделяют на аналоги L-аргинина и не аналоги L-аргинина, последние состоят из двух групп веществ – амидиновые и гетероциклические соединения [39]. Остановимся на некоторых из них.
Аналоги L-аргинина . L-NMMA (NG-монометил-L-арги-нин) образуется в организме в процессе деградации метилированных по аргинину белков, не селективный ингибитор (подавляет продукцию NO всеми тремя изоформами фермента). Из ряда других ингибиторов это соединение наиболее часто используется в экспериментах, поскольку оно хорошо растворимо в водной среде и растворы стабильны. В форме гидрохлорида имеет наименование «546С88». При введении здоровым добровольцам (3 мг/кг, внутривенно и 0,03–1,0 мг/кг/мин в течение 3 мин внутривенно) снижал частоту сердечных сокращений, ударный объем и, следовательно, сердечный выброс, повышал сосудистое сопротивление и кровяное давление, а также сопротивление легочных сосудов, но не повышал давление в легочной артерии [39].
L-Nω,Nω-диметиларгинин (часто в литературе его называют асимметрично диметилированным аргинином – ADMA) также является продуктом деградации метилированных по аргинину белков и неселективным ингибитором iNOS [39].
Нефизиологические аминокислоты на основе ацетамидиновых производных лизина и гомолизина, содержащих сульфидную, сульфоксидную или сульфонную часть, были синтезированы и введены в качестве ингибиторов NOS в 90-х гг. XX в. Среди них производное сульфона (2R)-2-амино-3-{[2-(этанимидоиламино) этил] сульфонил}пропановая кислота (в литературе упоминается как GW273629) и сульфидное производное (2S)-2-амино-4-{[2-(этанимидоиламино)этил]тио}бутановой кислоты (в литературе – GW274150) показало селективное действие в отношении рекомбинантной человеческой iNOS [39].
Не аналоги L-аргинина. Наиболее ранний и самый известный селективный ингибитор iNOS – аминогуанидин. В исследованиях на животных аминогуанидин проявлял высокую эффективность: подавлял развитие энцефаломиелита мышей [1], снижал гиперпродукцию NO в экспериментальных инфекционных моделях [40], оказывал антиэкссудативный эффект при воспалении мочевого пузыря у кошек [41], проявлял анальгезирующий эффект [42], предотвращал или снижал морфиновую зависимость [43], предотвращал образование гликозилированных продуктов и нарушение соединительной ткани артериальной стенки у крыс с диабетом [44], значительно снижал эм- бриональную смерть при аллогенной беременности мышей [45], увеличивал срок выживаемости трансплантата [46], предупреждал индуцированные гипергликемией атеросклеротические изменения при экспериментальной диабетической нефропатии [47], предупреждал различные осложнения диабета [48].
Доклинические исследования аминогуанидина позволили рассматривать его как перспективное средство для предотвращения осложнений диабета, таких как ретино-и нефропатия. В разработке лекарственного средства на основе аминогуанидина «Пимагедин», начавшейся в 1989 г., участвовало 2 компании – Marion Merrell Dow и Alteon. Лекарство предполагалось использовать для замедления прогрессирования нефропатии у людей с инсулинозависимым диабетом в клинических исследованиях в США (плановое начало в 1990 г.) и в странах Европы (начало в 1994 г.). Однако в середине 1995 г. компанию Marion Merrell Dow купила компания Hoechst Marion Roussel, которая решила выйти из проекта, что не предполагалось в ходе предварительных соглашений до продажи. Из-за нехватки финансов Alteon остановила все клинические испытания.
Это вызвало скандал в научном сообществе стран Европы, поскольку была уже проведена большая работа по привлечению пациентов. Исследователи – участники многоцентрового исследования обратились с открытым письмом к общественности, опубликованным в журнале «The Lancet» [49], редакция которого поддержала мнение исследователей о недопустимости прерывания начавшегося клинического испытания по причинам, отличным от научных, о чем изложено в редакционной статье с названием «Странное правило остановки от Hoechst Marion Roussel» [50]. Препарат аминогуанидина этим скандалом был опорочен и не увидел дальнейшего развития, хотя, возможно, причины кроются не только в этом.
Пяти- и шестичленные гетероциклические соединения . Обладают селективностью по отношению к iNOS, в экспериментах in vitro подавляют продукцию NO, однако дальше небольшого числа результатов на моделях патологий пока их разработка не прошла [39].
Клинические испытания ингибиторов iNOS
L-NMMA. Клинические испытания (фаза I/II) по использованию L-NMMA для преодоления резистентного к химиотерапии трижды негативного рака молочной железы [51]. L-NMMA (ингибитор всех трех изоформ NOS) применялся в сочетании с таксаном для лечения 35 пациентов с химиопротективным, местнораспространенным раком молочной железы (LABC) или метастатическим раком молочной железы (TNBC). Общая частота положительного ответа на химиотерапию составила 45,8% (11 из 24): 81,8% (9 из 11) для пациентов с LABC и 15,4% (2 из 13) для пациентов с метастатическим TNBC. Среди пациентов с LABC у трех пациентов был патологический полный ответ на операцию (27,3%). Токсичность ≥ 3-й степени была отмечена у 21% пациентов; однако никаких побочных эффектов, связанных с L-NMMA, выявлено не было. У пациентов, ответивших на химиотерапию, наблюдали увеличение количества CD15-позитивных нейтрофилов периферической крови и снижение в биоптатах, полученных после терапии, экспрессии аргиназы (маркера проопухолевого статуса нейтрофилов). Аналогичные обнадеживающие результаты в преодолении резистентности к химиотерапии трижды негативного рака молочной железы при использовании ингибиторов NOS опубликованы и другими коллективами [52].
Результаты клинических испытаний L-NMMA в лечении септического шока (в дозах 5 мг/кг в час и выше) и кардиогенного шока (в дозе 1 мг/кг в час), сопровождающего инфаркт миокарда, приведены в обзоре [53]. Ингибитор NOS повышал смертность от септического шока, что авторы связывали с вызываемыми им неблагоприятными гемодинамическими изменениями (снижение сердечного выброса, повышение сопротивления легочных сосудов и снижение доставки кислорода тканям). У пациентов с кардиогенным шоком L-NMMA не оказывал никакого положительного действия, что предположительно связано со слишком малой дозой.
Применение 4 различных ингибиторов NOS, среди которых был один ингибитор nNOS и неселективный ингибитор L-NMMA, у 705 пациентов для лечения острой и хронической мигрени в четырех плацебо-контролируе-мых исследованиях и в одном открытом клиническом исследовании выявило эффективность только у L-NMMA. У селективных ингибиторов GW273629, GW274150 и агониста рецептора 5-HT1B/1D (NXN-188) были не эффективны [54].
Роноптерин. Оценка действия ингибитора NOS ро-ноптерина (аналога тетрагидробиоптерина, VAS203, 10 мг/кг массы тела) на функции почки в двойном слепом рандомизированном плацебо-контролируемом перекрестном исследовании I фазы выявила снижение почечной перфузии и функции клубочков в пределах фи- зиологического диапазона, главным образом, из-за сужения сосудов в прегломерулярном участке [55].
GW274150. С 2005 по 2014 гг. компания GlaxoSmithKline провела ряд клинических исследований (фазы II) нового селективного ингибитора iNOS по 2 показаниям – мигрень и ревматоидный артрит. Эти исследования не продемонстрировали высокую эффективность GW274150 в сравнении с другими препаратами [1].
Cindunistat (SD-6010) . Компания Phizer провела клинические испытания селективного ингибитора iNOS cindunistat (код SD-6010) при симптоматическом остеоартрите колена. По результатам 2-летнего испытания фазы II было показано, что новый препарат хорошо переносится пациентами, при его приеме отмечено улучшение в течение 48 нед. состояния больных стадии 2, но не отмечено влияния на больных стадии 3 [2].
Заключение
Из тех сотен соединений – ингибиторов NOS, которые были запатентованы до 2015 г., только 4 перешли в клинические испытания, несмотря на доказанную в доклинических исследованиях высокую эффективность в подавлении экспрессии iNOS и положительном влиянии на патологические процессы. При этом из этих четырех только два (GW274150 и Cindunistat) являются селективными ингибиторами iNOS. Однако при этом продолжают появляться публикации, подтверждающие тот факт, что iNOS представляет собой вполне перспективную фармакологическую мишень.
Список литературы Индуцибельная NO-синтаза как фармакологическая мишень противовоспалительной терапии: надежда не потеряна?
- Cinelli M.A., Do H.T., Miley G.P., Silverman R.B. Inducible nitric oxide synthase: regulation, structure, and inhibition. Med. Res. Rev. 2020;40(1):158–189. DOI: 10.1002/med.21599.
- Ahmad N., Ansari M.Y., Haqqi T.M. Role of iNOS in osteoarthritis: Pathological and therapeutic aspects. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020;235:6366–6376. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29607.
- Ferreiro C.R., Chagas A.C.P., Carvalho M.H.C., Dantas A.P., Jatene M.B., Bento De Souza L.C. et al. Infl uence of hypoxia on nitric oxide synthase activity and gene expression in children with congenital heart disease: a novel pathophysiological adaptive mechanism. Circulation. 2001;103(18):2272–2276. DOI: 10.1161/01.cir.103.18.2272.
- Navasardyan I., Bonavida B. Regulation of T cells in cancer by nitric oxide. Cells. 2021;10:2655. DOI: 10.3390/cells10102655.
- Бельский Ю.П., Бельская Н.В., Данилец М.Г., Трофимова Е.С., Патрушев В.К., Агафонов В.И. Клетки опухоли Эрлиха стимулируют продукцию интерферона-γ Т-клетками и не чувствительны к аутокринному оксиду азота. Вопросы онкологии. 2004;50(6):689–692. [Bel’skiĭ Iu.P., Bel’skaia N.V., Danilets M.G., Trofi mova E.S., Patrushev V.K., Agafonov V.I. Ehrlich tumor cells stimulate T-cell production of interferon-gamma and are resistant to autocrine nitric oxide. Vopr. Oncol. 2004;50(6):689–692. (In Russ.)].
- Pautz A., Art J., Hahn S., Nowag S., Voss C., Kleinert H. Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Nitric Oxide. 2010;23(2):75–93. DOI: 10.1016/j.niox.2010.04.007.
- Anavia S., Tirosha O. iNOS as a metabolic enzyme under stress conditions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020;146:16–35. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.10.411.
- Lirk P., Hoff mann G., Rieder J. Inducible nitric oxide synthase-time for reappraisal. Curr. Drug Targets Infl amm. Allergy. 2002;l(1):89–108. DOI: 10.2174/1568010023344913.
- Данилец М.Г., Бельский Ю.П., Бельская Н.В., Трофимова Е.С., Учасова Е.Г., Агафонов В.И. Экспрессия аргиназы перитонеальными макрофагами и продукция ими оксида азота при Th1- и Th2-зависимом иммунном ответе. Бюлл. эксперим. биол. и медицины. 2007;S1:97–100. [Danilets M.G., Bel’skiĭ Iu.P., Bel’skaia N.V., Trofi mova E.S., Patrushev V.K., Agafonov V.I. Arginase expression by peritoneal macrophages and their production of nitric oxide in Th1- and Th2-dependent immune responses. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007;S1:97–100. (In Russ.)].
- Nagy G., Koncz A., Telarico T., Fernandez D., Ersek B., Buzás E. et al. Central role of nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010;12(3):210. DOI: 10.1186/ar3045.
- Burggraaf S., Bingham J., Payne J., Kimpton W.G., Lowenthal J.W., Bean A.G. Increased inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in organs is associated with a higher severity of H5N1 infl uenza virus infection. PLoS One. 2011;6(1):e14561. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014561.
- Almeida-Souza F., Souza C., Taniwaki N., Silva J., Oliveira R., Abreu-Silva A.L. et al. Morinda citrifolia Linn. fruit (Noni) juice induces an increase in NO production and death of Leishmania amazonensis amastigotes in peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c. Nitric Oxide 2016;58:51–58. DOI: 10.1016/j.niox.2016.06.004.
- Sharma J.N., Al-Omran A., Parvathy S.S. Role of nitric oxide in infl amatory diseases. Infl ammopharmacology. 2007;15(6):252–259. DOI: 10.1007/s10787-007-0013-x.
- Thomas D.D., Ridnour L.A., Isenberg J.S., Flores-Santana W., Switzer C.H., Donzelli S. et al. The chemical biology of nitric oxide: Implications in cellular signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008;45(1):18–31. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.03.020.
- Szabo C. Gasotransmitters in cancer: From pathophysiology to experimental therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016;15(3):185–203. DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2015.1.
- Kawasaki K., Smith R.S.Jr., Hsieh C.M., Sun J., Chao J., Liao J.K. Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase Akt pathway mediates nitric oxide-induced endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003;23:5726–5737. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.16.5726-5737.2003.
- Olson N., van der Vliet A. Interactions between nitric oxide and hypoxia-inducible factor signaling pathways in infl ammatory disease. Nitric Oxide. 2011;25(2):125–137. DOI: 10.1016/j.niox.2010.12.010.
- Ambs S., Merriam W.G., Bennett W.P., Felley-Bosco E., Ogunfusika M.O., Oser S.M. et al. Frequent nitric oxide synthase-2 expression in human colon adenomas: Implication for tumor angiogenesis and colon cancer progression. Cancer Res. 1998;58(2):334–341.
- Lee S.W., Choi H., Eun S.Y., Fukuyama S., Croft M. Nitric oxide modulates TGF-beta-directive signals to suppress Foxp3+ regulatory T cell differentiation and potentiate Th1 development. J. Immunol.2011;186(12):6972–6980. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100485.
- Cinier J., Hubert M., Besson L., Di Roio A., Rodriguez C., Lombardi V. et al. Recruitment and expansion of Tregs cells in the tumor environment-how to target them? Cancers. 2021;13(8):1850. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13081850.
- Schietinger A., Greenberg P.D. Tolerance and exhaustion: Defining mechanisms of T cell dysfunction. Trends Immunol. 2013;35(2):51–60. DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2013.10.001.
- Jiang W., He Y., He W., Wu G., Zhou X., Sheng Q. et al. Exhausted CD8+Tcells in the tumor immune microenvironment: new pathways to therapy. Front. Immunol. 2021;11:622509. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.622509. 11.
- Rodriguez P.C., Quiceno D.G., Zabaleta J., Ortiz B., Zea A.H., Piazuelo M.B. et al. Arginase I production in the tumor microenvironment by mature myeloid cells inhibits T-cell receptor expression and antigen-specific T-cell responses. Canc. Res. 2004;64(16):5839–5849. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0465.
- Parker K.H., Beury D.W., Ostrand-Rosenberg S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: critical cells driving immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Cancer. Res. 2015;128:95–139. DOI: 10.1016/bs.acr.2015.04.002.
- Girotti A.W., Fahey J.F., Korytowski W. Role of nitric oxide in hyper-aggressiveness of tumor cells that survive various anti-cancer therapies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022;179:103805. DOI: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103805.
- Khan F.H., Dervan E., Bhattacharyya D.D., McAuliffe J.D., Miranda K.M., Glynn S.A. The role of nitric oxide in cancer: master regulator of NoT? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21(24):9393. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249393.
- Vannini F., Kashfi K., Nath N. The dual role of iNOS in cancer. Redox Biol. 2015;6:334–343. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.009.
- Somasundaram V., Ridnour L.A., Cheng R.Y., Walke A.J., Kedei N., Bhattacharyya D.D. et al. Systemic NOS2 depletion and COX inhibition limits TNBC disease progression and alters lymphoid cell spatial orientation and density. Redox Biol. 2022;58:102529. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102529.
- Miyoshi T., Li Y., Shih D.M., Wang X., Laubach V.E., Matsumoto A.H. et al. Deficiency of inducible NO synthase reduces advanced but not early atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Life. Sci. 2006;79(6):525–531. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.01.043.
- Mercanoglu G., Safran N., Ahishali B.B., Uzun H., Yalcin A., Mercanoglu F. Nitric oxide mediated effects of nebivolol in myocardial infarction: the source of nitric oxide. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015;19(24):4872–4889.
- El-Awady M.S., Suddek G.M. Agmatine ameliorates atherosclerosis progression and endothelial dysfunction in high cholesterol-fed rabbits. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014;66(6):835–843. DOI: 10.1111/jphp.12204.
- Chauhan S.D., Seggara G., Vo P.A., Macallister R.J., Hobbs A.J., Ahluwalia A. Protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial dysfunction in resistance and conduit vasculature of iNOS knockout mice. FASEB. J. 2003;17(6):773–775. DOI: 10.1096/fj.02-0668fje.
- Guo Y., Jones W.K., Xuan Y.T., Tang X.L., Bao W., Wu W.J. et al. The late phase of ischemic preconditioning is abrogated by targeted disruption of the inducible NO synthase gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999;96(20):11507–11512. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.20.11507.
- Mungrue I.N., Gros R., You X., Pirani A., Azad A., Csont T. et al. Cardiomyocyte overexpression of iNOS in mice results in peroxynutrite generation, heart block, and sudden death. J. Clin. Invest. 2002;109(6):735–743. DOI: 10.1172/JCI13265.
- Lind M., Hayesa A., Caprndab M., Petrovicc D., Rodrigod L., Kruzliake P. et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase: Good or bad? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017;93:370–375. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.036.
- Oliveira-Paula G.H., Lacchini R., Tanus-Santos J.E. Inducible nitric oxide synthase as a possible target in hypertension. Curr. Drug Targets. 2014;15(2):164–174. DOI: 10.2174/13894501113146660227.
- Результаты поиска по запросу: публикации, посвященные ингибиторам NOS за период с 1991 по январь 2023 гг. (по данным сайта PubMed). [Search results on demand: publications on NOS inhibitors from 1991 to January 2023 (accoding to PubMed)]. URL: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=%28%28Nitric+oxide+synthase+inhibitor%5BTitle%5D%29+OR+%28Nitric+oxide+synthase+inhibitors%5BTitle%5D%29%29+AND+%28%28%221900%2F01%2F01%22%5BDate+-+Publication%5D+%3A+%223000%22%5BDate+-+Publication%5D%29%29&sort=&fil er=pubt.review&fil er=pubt.review (02.03.2023).
- Yang Y., Yu T., Lian Y.J., Ma R., Yang S., Cho J.Y. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors: a review of patents from 2011 to the present. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015;25(1):49–68. DOI: 10.1517/13543776.2014.979154.
- Minhas R., Bansal Y., Bansal G. Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitors: A comprehensive update. Med. Res. Rev. 2020;40:823–855. DOI: 10.1002/med.21636.
- Sorrells D.L., Friend C., Koltuksuz U., Courcoulas A., Boyle P., Garrett M. et al. Inhibition of nitric oxide with aminoguanidine reduces bacterial translocation after endotoxin challenge in vivo. Arch. Surg. 1996;131(11):1155–1163. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1996.01430230037007.
- Nilsson B., Delbro D., Hedin L., Conradi N., Thune A., Friman S. et al. Role of nitric oxide in induction of inflammatory fluid secretion by the mucosa of the feline gallbladder. Gastroenterology. 1996;110(2):598–606. DOI: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8566609.
- Lu G., Su R.B., Li J., Qin B.Y. Modulation by alpha-difluoromethyl-orn - thine and aminoguanidine of pain threshold, morphine analgesia and tolerance. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003;478(2–3):139–144. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2003.08.048.
- Abdel-Zahera A.O., Hamdya M.M., Alya S.A., Abdel-Hadyb R.H., Abdel-Rahmanc S. Attenuation of morphinetolerance and dependence by aminoguanidine in mice. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 2006;540(1–3):60–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.03.059.
- Brownlee M., Vlassara H., Kooney A., Ulrich P., Cerami A. Aminoguanidine prevents diabetes-induced arterial wall protein cross-linking. Science. 1986;232(4758):1629–1632. DOI: 10.1126/science.3487117.
- Haddad E.K., Duclos A.J., Baines M.G. Early embryo loss is associated with local production of nitric oxide by decidual mononuclear cells. J. Exp. Med. 1995;182(4):1143–1151. DOI: 10.1084/jem.182.4.1143.
- Worrall N.K., Lazenby W.D., Misko T.P., Lin T.S., Rodi C.P., Manning P.T. et al. Modulation of in vivo alloreactivity by inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase. J. Exp. Med. 1995;181(1):63–70. DOI: 10.1084/jem.181.1.63.
- Kihara M., Schmelzer J.D., Poduslo J.F., Curran G.L., Nickander K.K., Low P.A. Aminoguanidine effects on nerve blood flo , vascular permeability, electrophysiology, and oxygen free radicals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1991;88(14):6107–6111. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6107.
- Onorato J.M., Jenkins A.J., Thorpe S.R., Baynes J.W. Pyridoxamine, an inhibitor of advanced glycation reactions, also inhibits advanced lipoxidation reactions. Mechanism of action of pyridoxamine. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275(28):21177–21184. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M003263200.
- Viberti G., Slama G., Pozza G., Czyzyk A., Bilous R.W., Gries A. et al. Early closure of European Pimagedine trial. Steering Committee. Safety Committee. The Lancet. 1997;350(9072):214–215. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)26029-0.
- A curious stopping rule from Hoechst Marion Roussel (Editorial). The Lancet. 1997;350(9072):155. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)21029-9.
- Chung A.W., Anand K., Anselme A.C., Chan A.A., Gupta N., Venta L.A. et.al. A phase 1/2 clinical trial of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-NMMA and taxane for treating chemoresistant triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021;13(624):eabj5070. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abj5070.
- Dávila-González D., Choi D.S., Rosato R.R., Granados-Principal S.M., Kuhn J.G., Li W.F. et al. Pharmacological inhibition of NOS activates ASK1/JNK pathway augmenting docetaxel-mediated apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018;24(5):1152–1162. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1437.
- Howes L.G., Brillante D.G. Expert opinion on tilarginine in the treatment of shock. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2008;17(10):1573–1580. DOI: 10.1517/13543784.17.10.1573.
- Barbanti P., Egeo G., Aurilia C., Fofi L., Della-Morte D. Drugs targeting nitric oxide synthase for migraine treatment. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2014;23(8):1141–1148. DOI: 10.1517/13543784.2014.918953.
- Ott C., Bosch A., Winzer N., Friedrich S., Schinzel R., Tegtmeier F. et al. Effects of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor ronopterin (VAS203) on renal function in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019;85(5):900–907. DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13870.


