Industrial policy as a mechanism of regional development
Автор: Mazilov Yevgeniy Aleksandrovich
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Young researchers
Статья в выпуске: 1 (25) т.6, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article reveals the essence of industrial policy and determines its role in ensuring the region’s sustainable development. Furthermore, it substantiates the importance of industrial policy in the rationalization of the region’s economy structure and enhancement of its performance. The article also proposes an algorithm for the development of active regional industrial policy.
Region, strategic planning, industrial policy
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223428
IDR: 147223428 | УДК: 338.23:338.45(470.12)
Текст научной статьи Industrial policy as a mechanism of regional development
Industry is the most important part of national economy. Its share in the Vologda Oblast accounted for 44.2% of GRP in 2010 [10]. The industrial complex, among all the branches, is capable of creating the greatest volume of products with the highest value added.
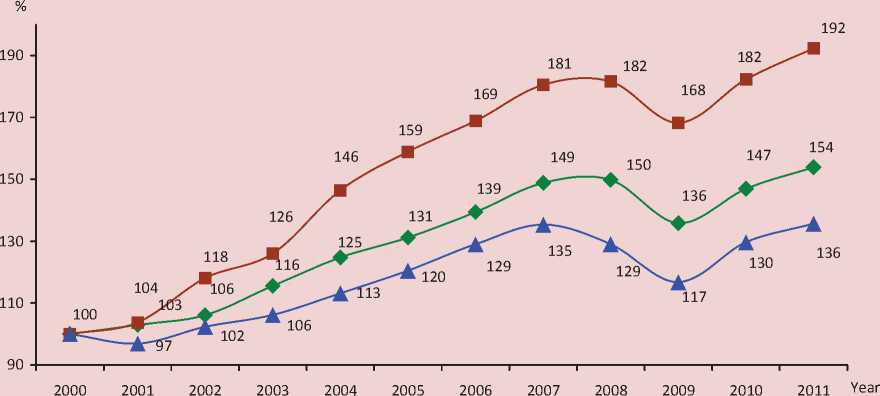
Meanwhile, the industry has been experiencing the most acute consequences of market reforms of the domestic economy. Over the last eleven years the volume of industrial production in the Vologda Oblast increased by only 36%, while in Russia as a whole it grew 1.5-fold, and in the North-Western Federal District – almost twice (fig. 1) . The characteristic features of the region’s industrial complex included the slowdown of positive changes in its structure, the stagnation in the level of economic efficiency and exposure to external and internal negative trends.
The industrial complex structure in 2000 – 2011 was still based on metallurgy (tab. 1). The 2009 – 2011 period witnessed some reduction of its share caused by the decrease in production volumes, as well as in demand and prices for metal products in the world markets.
The share of industries and, first of all, mechanical engineering, producing high-tech products, accounts for only 3%. The share of such an important industrial branch, as woodworking industry decreased 2-fold in 2011 as compared to 2000, and as for light industry, its share accounted for less than 1% in 2011.
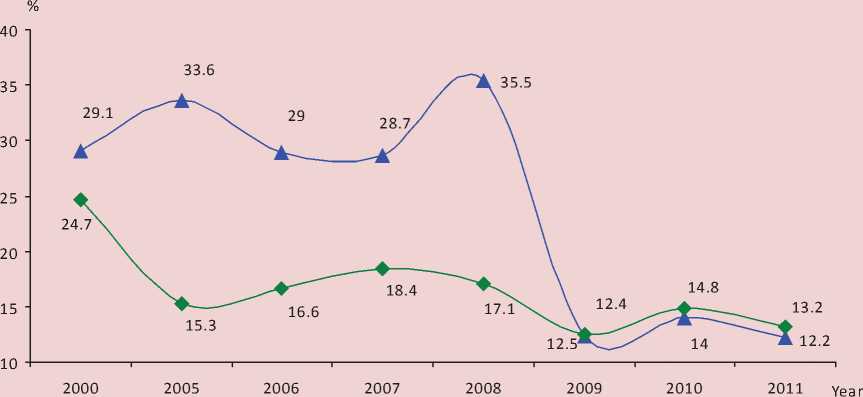
Unsustainable industrial development is confirmed by other indicators as well. Thus, the output profitability for the oblast in 2009 proved to be lower than the national average (fig. 2) . It remained low even in 2011, when the economy was recovering after the financial crisis.
The consumption of fixed capital is still extremely high. The volume of investments in the fixed capital of enterprises in 2005 – 2011 reduced almost twice. The share of those employed in the industry in the total number of economically active population is decreasing
Figure 1. Dynamics of industrial production in the Russian Federation, the North-Western Federal District and the Vologda Oblast in 2000 – 2011, % [10]
|
— ♦ — Russia |
■ NWFD |
|
|
Vologda Oblast |
Table 1. Structure of industrial complex in the Vologda Oblast in 2000 – 2011, %
|
Branch of industry |
2000 |
2005 |
2007 |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
Absolute deviation of 2011 from 2000 |
|
Metallurgical |
68 |
72.0 |
69.8 |
59.9 |
63.2 |
62.5 |
-5.5 |
|
Chemical |
9 |
9.3 |
10.0 |
15.5 |
19.3 |
19.7 |
10.7 |
|
Food processing |
5 |
6.4 |
6.0 |
9.5 |
7.0 |
7.1 |
2.1 |
|
Mechanical engineering |
3 |
4.3 |
5.7 |
5.5 |
2.9 |
3 |
0 |
|
Woodworking |
6 |
4 |
4.2 |
4.6 |
2.9 |
3 |
-3 |
|
Light |
1 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
-0.8 |
|
Other |
8 |
1.6 |
3.7 |
4.5 |
4.5 |
4.6 |
-3.4 |
Source: Official website of the Federal State Statistics Service. Available at: enterprise because of the labour outflow to the services sector (tab. 2). The level of innovation activity of the oblast industrial enterprises is less than 10%. This figure contradicts the main international trends: for instance, in 2009 the share of organizations engaged in innovation activity in the total number of organizations reached 79.9% in Germany, 52.2% – in Finland, 50.2% – in France [11].
The situation in the region urges government authorities to take active measures concerning industry and its transition to innovation development.
The experience of economic reforms in developed and developing foreign countries highlights the importance of industrial policy development and implementation, as it is the main institutional and economic basis of successful comprehensive transformations.
Academic literature contains many interpretations of the concept “industrial policy”. The analysis enables us to identify its main features, defined by the authors [1, 5, 6, 9, 13, 14, 15]. Firstly, industrial policy is implemented by state and local government authorities. Secondly, the creation of new hi-tech industries
-
Figure 2. Output profitability at industrial enterprises of the Russian Federation, the Vologda Oblast in 2000 – 2011, % [10, 17]
—*— Vologda Oblast — ♦ — Russia
Table 2. Main performance indicators of industrial enterprises of the Russian Federation and the Vologda Oblast in 2000 – 2011, %
Indicator 2000 2005 2009 2010 2011 Absolute deviation of 2011 from 2000, p.p. 2005, p.p. Russia Consumption of fixed capital 50.4 47.1 45.7 46.1 46.7 -3.7 -0.4 Share of persons employed in the industry in the total number of economically active population 22.6 21.7 19.9 19.7 19.7 -2.9 -2 Level of innovation activity 8.8 9.7 9.3 9.5 9.6 0.8 -0.1 Vologda Oblast Consumption of fixed capital 45.5 50.1 36.6 40.6 43.2 -2.3 -6.9 Share of persons employed in the industry in the total number of economically active population 26.7 21.7 19.7 19.4 18.1 -8.6 -3.6 Level of innovation activity 11.0 8.4 7.6 7.4 9.3 -1.7 0.9 Source: Official website of the Federal State Statistics Service. Available at: account/#
should become the main guideline in the development of a competent industrial policy in modern conditions. Thirdly, it should influence all the aspects of industrial complex, providing its harmonious and efficient development.
In this respect, we believe that the essence of industrial policy is described most comprehensively by Academician A.I. Tatarkin.
He considers that industrial policy is a system of relations between state authorities and municipal authorities, economic entities, scientific and public organizations concerning the formation of a structurally balanced, competitive industry with its intellectual core represented by the latest technological mode [12].
This definition allows highlighting the major objective of industrial policy that consists in ensuring the country’s sustainable economic development, enhancement of domestic producers’ competitiveness and, as a consequence, citizens’ welfare.
Enterprises, corporations and production complexes are the objects of industrial policy, and state authorities are its subjects.
Using the tool under consideration, regional authorities carry out the management of individual industries and enterprises for enhancing their commercial and budgetary efficiency and social responsibility.
Development and implementation of regional industrial policy includes a whole range of legal, economic and organizational measures promoting the formation of a competitive industrial complex, ensuring its efficient performance and dealing with the region’s social problems [12].
The main mechanisms of realization of industrial policy are the restructuring of declining industries, development of knowledge-intensive industries and creation of compensation mechanisms, aimed at reducing the negative impact of proposed solutions. The constituent parts of regional industrial policy are as follows: the creation of conditions for improving investment climate; establishment of a favorable tax regime; provision of benefits on loan rates to enterprises, simplification of a crediting system as a whole; increase of investments in R&D; other measures aimed at introducing innovations and achieving scientific and technological progress [3].
The principles of industrial policy are usually contained in various official documents. The most important document is the concept of industrial policy, since it is an ideological and value landmark that forms the basis of strategic, tactical, and operational activities aimed at the development of the region’s industry.
However, due to the absence of documents, regulating industrial policy at the federal level, the concepts of industrial policy, already adopted in 40 Russian regions, coordinate with each other rather poorly and they do not have common principles and a clear purpose. Besides, these documents do not contain the mechanisms of federal industrial policy implementation. Therefore, in our opinion, the time is right to work out a balanced federal industrial policy, which will form the basis for the concepts of industrial development of Russia’s subjects.
The so-called “strategic” approach is applied most frequently in the elaboration of regional industrial policy. It is based on a specific algorithm of creation and realization of the policy project. Here we consider it possible to use the following algorithm (fig. 3) with regard to the peculiarities of development and organization of the region’s industrial complex.
The Vologda Oblast industrial policy concept for the period of 2003 – 2010, elaborated in the framework of this approach, turned out to be inefficient in the conditions of the financial and economic crisis of 2008. The new concept of industrial policy is still under development. In the meantime, a number of measures aimed at the development of industry are being implemented in the region.
The Directorate for Industry and Science under the Department of Economy of the Vologda Oblast Government carries out organizational and legislative support of industrial policy. This structural division is focused on the regulation of investment activity and provision of government support to innovation activities in the industry.
The Vologda Oblast has developed and is now implementing the programmes on providing support to individual industries in the short and medium term. In particular, a number of investment projects are being carried out in the primary sectors of industry, advanced
-
Figure 3. Development and implementation algorithm of the region’s industrial policy concept
Formulation of problem and justification of the necessity to work out the concept of industrial policy
|
Section 1. Analysis of data base |
|||||
|
Stage 1 Collection of theoretical data |
Z^> |
Stage 2 Analysis of the experience of development and implementation of adopted concepts |
Stage 3 Analysis of federal and regional legislation |
||
Result
Determination of main principles, mechanisms, tools of implementation of industrial policy
|
Section 2. Analysis of initial conditions |
|||||
|
Stage 1 Collection and analysis of statistical data on industry |
Stage 2 Identification of problems and trends in industry development |
Stage 3 Forecasting the development of the region’s industry |
|||
Result
SWOT analysis of the region’s industry
Section 3. Definition of the main provisions of the concept
|
Stage 1 Determination of strategic targets |
Stage 2 Determination of target landmarks |
Stage 3 Determination of development priorities |
||
|
Result Concept of industrial policy |
||||
|
Section 4. Implementation of selected provisions of the concept |
||||
|
Stage 1 Beginning of the concept implementation |
Stage 2 Supervision over the concept implementation |
Stage 3 Adjustment of the concept’s provisions |
||
Result
Provision of sustainable development of the region’s industry wood processing, house-building, production of transport and electronic equipment, food production. Industrial parks Sheksna and Sokol have been established and are now developing, the project of Industrial Park Vologda – East is currently under development.
Besides, a Guarantee Fund has been established with the main goal of providing securities for bank loans to small and mediumsized businesses. And although the amount of guarantees can’t exceed 70% of the sum set in the credit agreement, establishment of such a structure allows organizations that lack resources to provide loan guarantees to receive funds necessary for their development. However, it can be noted that the provision of guarantees by the Fund is a very complicated and time-consuming process, which requires collecting a large set of documents. The fact, no doubt, reduces the attractiveness of this tool of state support.
Such organizations as the Union of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs of the Vologda Oblast(UIEVO) and the Vologda Chamber of Commerce and Industry (VCCI) have been already functioning for a long time.
UIEVO is mainly aimed at establishing efficient cooperation with power and administration bodies on the issues of the region’s industrial development. At the same time, the Union should participate in the implementation of active regional policy by considering the oblast legislation and developing recommendations on its improvement. The Union should also promote the establishment of competitive environment in mechanical engineering and other industries. Today almost 100 enterprises are included in the registry of the regional employers’ association.
In 2012, the Union of Constructors and Designers of the Vologda Oblast was established on the initiative and with the assistance of UIEVO. Organizational activities have been carried out for establishing the sectoral association of employers in the fuel and energy complex. Consultations are going on concerning the transformation of such organizations as the association “MachineBuilding Enterprises of Vologda Oblast” and the non-commercial partnership “Housing and Communal Services of the Vologda Oblast” into sectoral associations of employers. The Agreement on the regulation of social and employment relations for 2013 was signed between the Vologda Oblast Federation of Trade Unions, UIEVO and the Vologda Oblast Government in the framework of the extended session of the oblast tripartite commission.
But in practice, the activities of UIEVO are only of a formal, consultative nature, the majority of the Union’s decisions haven’t been reflected in the oblast legislation.
The Vologda Chamber of Commerce and Industry provides on a commercial basis assistance in drawing up the documents for registration of trademarks and intellectual property, participates in the certification of goods, carries out training seminars on the issues of taxation and business, as well as marketing research. The chamber organizes the annual contest “Silver Mercury” with the nomination of titles “best enterprise in the sphere of industrial production», “best enterprise in the sphere of construction”, “best enterprise in the sphere of consumer goods production”.
However, it should be noted that the tools used by the authorities to support the industrial complex are not always interrelated and sufficient. It is consistency and comprehensiveness that are necessary to make industrial policy a more efficient mechanism of regional development.
In our viewpoint, the development and implementation of active regional industrial policy should become one of the priority directions ensuring the region’s transition to innovation development.
Список литературы Industrial policy as a mechanism of regional development
- On the national industrial policy of the Russian Federation: the draft Federal law. Available at: http://docs.kodeks.ru/document/902135400.
- Vyacheslavov A.M. Problems of formation of the innovative climate in the region. Modern research of social problems. 2012. No. 1 (09). Available at: http://sisp.nkras.ru/issues/2012/1/Vyacheslavov.pdf.
- Gulin K.A. On the issue of socio-economic modernization of Russian regions. Economic and social changes: facts, trends, forecast. 2012. No. 4. P. 35-49.
- Investment processes in the Vologda Oblast: statistical collection. Vologdastat. Vologda, 2011.
- Carson R.B. What economists know: an economic policy primer for the 1990’s and beyond. Moscow, 1993.
- Kuznetsov B.V. Does Russia need industrial policy? Industrial policy in Russia: to be or not to be? Moscow: TEIS, 2002.
- Mazilov Ye.A. Innovation activity as the tool of development of the region’s industrial complex. New economy -new society: materials of the 6th inter-academic scientific and practical conference, Vologda, 29 April 2011. Vologda: ISEDT RAS, 2011. P. 76-80.
- Mazilov Ye.A. Industrial policy as a basis for modernization of the region’s economy. Strategy and tactics of implementation of socio-economic reforms: regional aspect. Materials of the international scientific and practical conference. Vologda, 6 -8 October 2011. Vologda: ISEDT RAS, 2011. Vol. 2. P. 414-422.
- On industrial policy in the Russian Federation. Industrial policy in the Russian Federation. 2007. No. 5. P. 3.
- Official website of the Federal State Statistics Service. Available at: http://www.gks.ru/wps/wcm/connect/rosstat/rosstatsite/main/account/#.
- Official website of Eurostat. Available at: http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/science_technology_innovation/data/main_tables.
- Tatarkin A.I., Romanova O.A., Chenenova R.I., Filatova M.G. Regional industrial policy: theoretical foundations, the practice of formation and the mechanism of implementation. Yekaterinburg: Ural RAS Department, 2000. P. 67.
- Romanova O.A., Chenenova R.I. The industrial policy as the factor of maintenance of economic security of the regions. Ekonomika regiona. 2008. No. 3.
- Smirnov Ye. Innovation vector of the industrial policy of the European Union. International Economics. 2007. No. 2. P. 58.
- Tatarkin A.I., Romanova O.A. The industrial policy and the mechanism of its realization: the system approach. Ekonomika regiona. 2007. No. 3 (11). P. 19-31.
- Terebova S.V., Mazilov Ye.A. Structure of the region’s industry: state and problems of target-oriented change. Modern research of social problems. 2012. No. 3 (11). Available at: http://sisp.nkras.ru/e-ru/issues/2012/3/mazilov.pdf.
- Financial condition of organizations of the Vologda Oblast in 2009 -2011: statistical collection. Vologdastat. Vologda, 2012. P. 137.
- Rodrick D. Trade and industrial policy reform in developing countries: a review of recent theory and evidence. NBER working paper No. 4417 August, 1993. Available at: http://www.nber.org/papers/w4417.pdf


