Information Culture Formation as the Most Promising Direction of Individual`s General Culture
Автор: Rasim M. Alguliyev, Rasmiyya Sh. Mahmudova
Журнал: International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science (IJMECS) @ijmecs
Статья в выпуске: 3 vol.7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The essence, structure, formation and conditions of culture have been investigated in the article. The types of culture have been studied in accordance with the development stages of civilization and different spheres. Various approaches on information culture as a part of common culture of a human have been analyzed. The formation issues of personal information culture have been reviewed according to the requirements of information society as a new development stage of a society. The features of human behavior in the virtual environment have been examined. The influence of education, profession and activity peculiarities on the formation of personal information culture has been investigated.
Information culture, information society, information literacy, media literacy
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15014742
IDR: 15014742
Текст научной статьи Information Culture Formation as the Most Promising Direction of Individual`s General Culture
Published Online March 2015 in MECS DOI: 10.5815/ijmecs.2015.03.08
Nowadays fundamental changes occurring in the information sphere, the processes taking place in the direction of formation of the new society and economy based on knowledge caused changes in human resources requirements. Especially, application of information communication technologies (ICT) in all spheres, increasing number of electronic services rendered to the citizens create a demand for mastering new professions and constantly improving general knowledge and skills. Global information society being in the process of formation is characterized by giving people opportunity for realization of their potential, ensuring everyone with accessibility for information and knowledge. On the other hand people encounter a number of difficulties under the condition of information abundance. Selection and application of the most important information from very large volumes of information cause some difficulty. Limitation of human ability for mastering and processing of information prevents them to benefit from the opportunities properly. Nevertheless, the information is also used to manipulate consciousness of people, to create chaos, to damage the national and spiritual values. All above mentioned factors cause great anxiety and make essential the preparations of people for futher life activities, formation of new knowledge and skills to efficient behaviour within the information society. The essence and structure of the traditional culture also change and enrich with new components along with the forms of the traditional culture which is necessary for a person. Information culture is becoming an important attribute of life, as well as professional activity of a person.
-
II. Condition For Culture Origin, Its Essence And Structure
It is difficult to come across a person who does not use the term “culture” in his lexicon today. Various definitions about the explanations of this word are found in the dictionaries and scientific literature.
“Culture” is too complicated concept.It is used in various meanings and contexts: for example,the culture of the period (ancient, medieval, and so on),the culture of the countries and nations (Azerbaijani culture,French culture, etc.),the culture being related to certain activity field, as well as,is used as a morality field of people in the narrow meaning.
First of all, the “culture” concept appeared in the latin language. Scholars and poets of ancient Rome are used this word to describe the work related to soil cultivation. But later this term was related to people, especially if a man selected with his delicate manner, awareness he was considered “cultural”. Formerly aristocrats were called cultural in order to distinguish them from common people.At present time, the word “culture”is related to theater, good literature example, good education.
In 1952, the American anthropologists,Kroeber and Kluckhohn,already critically reviewed concepts and definitions of culture, and compiled a list of 164 different definitions [1]. At present the researchers note that there are much more definition of this word. Some authors explain culture as a collection of spiritual and material values which is created by a man, and is a part of his life,but some authors consider culture a collection of information which is not passed genetically in the field of human behavior and morals. Some authors think that culture – is a development level which is reflected in human and society in organization forms and types of human life activity, and spiritual-moral values created by them.Culture is characterized as creative achievements (for example, Western culture, Islamic culture,modern culture and so on) limited by time,place or other common features [2-5].
Culture is a highly complex, multilevel system. However, it was possible to structure the culture. Structurization of culture based on the classification on carriers, forms, different types and styles of culture. For example, the whole mankind is divided into the world (global) and national (local) culture according to the carriers. World culture unites the achievements of national cultures of various nations settled in our planet.National culture is a culture synthesis of different social groups and strata living in a certain community. The originality and uniqueness of national culture appears both in spiritual (language, literature, music, manuscript, religion),and in material spheres (features of economic structure, economy management, labor and production traditions) of life and activity[6].
Besides,in accordance with the specific values,culture of social associations (noble, city, village, professional, young), family and individual are also distinguished.
At the same time, the culture is divided into certain types.This type of classification is based on the consideration of human activity. The division of culture into material and spiritual parts began to emerge hereon. However,it is necessary to take into consideration that, such division is relative, because in fact they are connected with each other. These are included to the material production culture, life culture, topos culture, to say exactly, the culture of place of residence (apartment, house, village, city) attitude culture to own body, physical culture.
Spiritual culture unites moral, artistic, legal, pedagogical, religious, intellectual cultures and exists in two forms: in the form of moral qualities and in the form of moral values, scientific works, work of art, legal norms, moral and so on.
There are also such types of culture that they cannot be related to material or spiritual culture. Economic, environmental, aesthetic and etc. cultures can be indicated as an example of them.
Culture is also a collection of a certain spiritual norms. Slight punishment is inflicted a punishment for violation of some norms – running down, reproach, preconceived look, stern sanction such as fine, depriving of any right, arresting violation of other norms. From this point of view, all the rules can be classified depending on the seriousness of observing them [7].
Disobeying the norms exists in every society or social groups [8]. The violation of behavioral norms is peculiar to any environment, such as the violation of the etiquette of diplomatic conversation or the ritual of registering the marriage creating unease, bring people to bay. But it does not cause a stern punishment. There are also such cases that more effective sanctions are applied. For example, the use of any material in the examination can result in depreciation, the loss of library literature can result in paying a fine. In some societies, a slight decline from the traditions is strictly punished [9].In the societies where violation of softly penalted cultural norms is observed more frequently.
-
III. The Types Of Culture By The Development
Stages Of The Civilization And Various Spheres
Person constantly interacts as an alive creature with the nature surrounding him and the community he belongs to.Culture plays an important role in the regulation of interrelations with those around. People’s awareness of surrounding processes in the society, active participation in social life,the attitude toward the natural world,as well as, providing material and spiritual needs, along with a number of factors also depend on the cultural level.
The concept “culture” is also used to characterize of certain historical periods,the concrete communities, material and moral development level of people and nations, as well as, specific areas of life and activity.
The types of culture were emerged in accordance with each of them when new areas of activity were created and civilization was developed. In the initial periods of the formation of society,the structure of human culture was simple because of the limited human activity.Previously,a person tried to adopt the environment surrounded him in accordance with his needs, interests and skills being a part of the environment [10]. The ancient human was trying to assimilate these cultures because his work was hunting and fishing.The culture of that period was called cultural assimilastion by culturologists.
Then the people were occupied with cattle-breeding and tillage and thereby, the culture a manufacturingn was founded. People began to produce food products by using land and cattle. This culture emerging in connection with the activity of tillage and cattle-breeding was also called agriculture or agrarian culture. It is considered that, in the society the agrarian culture was dominated up to VIII century,until the industrial revolution took place[11].
The transition took place from the agrarian society to the industrial society as a result of industrial revolu-tion,now the machines began to be used, manual labor was replaced by mechanical labor. Thus, the industrial culture began to form. Agrarian production became a part of the industrial culture by using new technique,technologies. However, after a certain period of time,the opportunities of the industrial culture also finished. Since the end of XX century, the world began to talk about “post-industrial society”, “technotron society”, “information society”.
Information society is rapidly established all over the world and is considered contemporary development stage of civilization.Unlike industrial society,in this society information and knowledge is considered the main production and consumption, but not a material product.Also the production of information products becomes the driving force of society development.The majority of people begins to engage in information activity.Fundamental changes occur in the structure and content of the culture in such a situation. Regardless of the activity field, the necessity of participation in the various information processes requires a new culture form of a person, so it is called the information culture.
Today human life and activity are many-branched. In other words, modern-day person is engaged in a lot of work along with work activity, listens to music, watches a movie, or is in contact with nature in his/her spare time. Some people prefer to watch sport games, others spend their free time on the Internet. At the same time, the people express attitude towards the political processes happened in the country they lived, they try to keep the laws and traditions of religion they belong to. All people want to learn choosing suitable clothes themselves, taking care of their bodies, leading healthy life.
As a result, we became familiar with a sphere of interest, different field according to material and spiritual necessities,the products created by the people who represent these fields, in addition to our activity field.They are presented to us by means of cinema,theater,artists, sculptors,politicians, education and legal system, literary-artistic and religious work and so on.
Thus, the types of culture is formed under each sphere:under art and creativity sphere – music and theater culture, under production and management sphere – labor,production and management cultures, under biosphere – ecological culture, under infosphere – information culture and so on. The types of culture form the general culture of people under separate spheres.A person can be in normal interrelations with the environment due to the culture he belongs to.
-
IV. Information Culture As An Integral Part Of Human Culture
One of the most important elements of general culture of human is the information culture that began to gain a great importance and became more urgent connected with the creation and development of information culture.Information culture is an essential skill of 21st century [12]. İnformation technologies (computer and Internet) create wide opportunities for the way to information and knowledge.At the same time, accesibility to very large information makes data acquisition and processing difficult. On the other hand,a person has faced a number of problems in the result of informatization processes taking place in society: information inequality,manipulation,of public consciousness and psychological impact, cybercriminality, internet dependence and increasing of cyber diseases,information warfare [13,14].
Researchers consider that the history of information culture takes its beginning from the generation of humanity. Indeed, paying observing the past we can see that along with the development of the means of transmission of the human experience and other information, information culture has also developed and expanded, complicated its structure elements [15].
The most powerful means for processing and transmission of information has been achieved with the emergence of computer and the Internet in the history of mankind [16]. These processes occurring in the society have led to fundamental changes in the relations between a man and all strata of society (people, state, etc.), and in order to adapt to this environment, thinking and behavior of person should be change and have special knowledge and skills to use information effectively. It can be achieved by forming information culture on people. And what is information culture? Which knowledge and skills is determined by and how it should be formed?
Numerous different definitions are formed in the scientific articles devoted to the problems of information culture. It is connected with information culture becoming an object of research of various scientific fields.
First of all, information culture concept that began to be used by librarians was often identified with bibliographic culture. Thus, for explaining the essence of the culture, information culture in works written by bibliographer, the knowledge and skills that are necessary within the relations between library-reader are highlighted.
Later,technocratic approach began to prevail knowing the essence of information culture related to intensive development of computer technology. Information culture is viewed within this approachas information working and getting purposefully,the abilities using computers and other modern technical means and methods for processing and transmission of information.
At present, associated with the formation of the information society, information culture is characterized as a new social technology directed to the formation of a person which has the ability to operate effectively and live in the modern information environment, and he/she is viewed as the development of the personality, as the means of the practical realization of the rights and freedoms [17].It is considered that,information culture is a process of formation of the type of professional personality through the adaptation of values, principles and norms that are characteristic for information society.
The approaches to the essence of information culture are divided into two groups:cultural approach and information approach.Within the cultural approach, information culture is explained as information quality of personality, as well as the component of people, social groups and societies of moral culture. In the framework of information approach,information culture is considered to be a totality of skills and abilities on a search,selection,storage,transmission and analysis,in other words, skills and abilities included in the activity arising out from information requirements of a person.
Today,human ability of treating information in a high level and using it properly creates a great advantage among others. Using information is not only passive assimilation of information, but also achieving of information from various sources,comparing, selecting those more appropriate to requirements and creating new information products by using it. When a person is interracting with Infosphere surrounding him, on the one hand, he acts as an information costumer,on the other hand in the role of a number of information processes simultaneously.These processes can be divided into five groups [18]:1)information gathering and perception; 2) information memorization; 3) information processing; 4) information protection and security;5) information presentation.
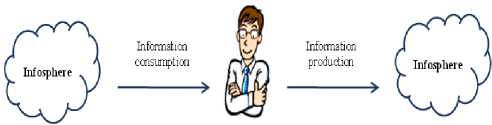
Fig.1. Interractionof a person and Infosphere
At present,information environment surrounding a person is full of a large amount of information materials, contents,information resources, they are different from each other according to the completeness, reliability,the degree of being valuable.As well as information is stored in traditional and electronic libraries,archives, museums, web portals, databases and other sources in various forms (text,images,statistical data,etc.) and in different formats (print,electronic).And of course information presented by these sources is not at the desired quality at all.
Effective use of information obtained from academic, public, statistic and such other sources depends on analyzing their information needs, search and evaluating the quality of information. High information culture is required to achieve professional development, to build a good career in the information society considered the key strategic product of information and knowledge. A person with a high information culture is the one who gets, selects, evaluates the necessary information regardless of its form of assignment (text, audio, video), technology, type of source, can prepare new information product and present in a required form having compared and analyzed the information gathered from various sources. He knows at least one or two leading languages of the world and benefits from the information of those languages. At the same time, the ability of having a good memory, using the information at the time it needs by keeping it in the memory in a systematic way, creating new information by processing information, ensuring the security of the information resources are also the indicators of information culture.
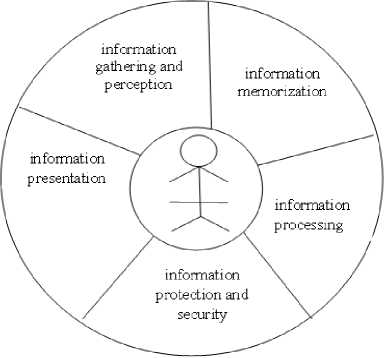
Fig.2. The structure of information culture of a person
Information culture also requires to know legal and ethical norms and to observe it. Laws prohibit using of pirate program produces, promote religious extremism, harmful habits in the Internet. Ethical norms should be observed while communication via e-mail and other electronic services, otherwise it may cause concerns of others. At the same time, it is required to respect the copyright while using information resources. The user should know that any information output (article, book, software, etc.) is a result of mental work of people, and it is considered as their intellectual property and this property is protected by law.
-
V. The Information Culture Of Real And Virtual Worlds
The appearance of the Internet has led to the emergence of a new virtual world for human activity.That is people spend their certain portion of time in this world: communicate, have good time, improve their knowledge, express their views, receive information and so on. The Internet assumed a large portion of activities and relation of real life [19].
At the present time, there are a lot of virtual communication tools on the Internet.These are social network,blogs,chats,forms and others.People often forget the communication norms while in a virtual space.They consider that, it is a virtual world,there cannot be observe ethical rules spelling and writing,communication rules that accepted by all. Non-ethical comments are placed in the social network blogs more freely. The laws,moral and ethical values of the real world still have not been carried out to the Internet.This space has its own laws.
The Internet allows people to hide the real intention,negative characteristics.In real life we can evaluate people of the wear, facial expressions, voice, gesture, timbre, colloquial style. Because of we do not accept any of the above listed indications,we cannot often find a common language with these people in the real life.There is none of these in the virtual world. Because of the absence of non-verbal means of online communication, it is easier to have a contact there.Until then people do not get any negative information about the man that considered their friend.
Behavior style of people in the virtual world arises from the opportunity of anonymity created by the Internet [20]. According to Marx [21], anonymity refers to a state where a person is not identifiable. This feature caused to the emergence of trolling that is directly related to the virtual culture.The word “troll” is a person who focused attention on him/her and divert from the main theme by placing information of provocation character in the network (form, blog, etc).Even in the begining of XXI century,web-trollers began to creat the network to share their experiences about more efficient methods of conflict initiating.
The anonymity in the virtual space gives a person more freedom to express himself. [22]. The people that do not manifest their negativeness in fear of environment reproach, punishment measures, unacceptable by society in the real world, become more active in the Internet. The Internet reveal their so-called “true face”. It may be that, “I” in the Internet is more realistic than “I” introduced in the real world. The mental and ethical norms, legal norms,mental values force them to wear a mask. Also there are punishment measures for insults, swear, words said to humiliate people in the real life. While in the virtual world impunity predominates.
Researchers consider that negative behavior and unethical lexicology was not often observed in the Internet. But now we are faced with these facts at every step. This can be explained by the fact that, at that time only educational, cultural people knew that what the Internet is, but at the present time, people of different categories of society, including criminals,fraudsters,those withlow cultural level wander freely in the virtual space. They bring their behavioral norms with them.
The culture formed in the specific virtual environment created by the Internet is also called cyberculture. There are different explanations of “cyberculture” concept which consists of the combination of the words “cyber” and “culture”. The most widespread definition is as follows: Cyberculture is a culture form that emerged in the result of the use of computer networks with the aim of communication, entertainment and business.
Cyberspace,the changes that occur in this space is currently research object of many scientific fields. The researchers note that cyberculture displays itself in computer games. Computer games have become an integarl part of life of children, youth, and adults. Information content is often delocalized, fragmen-tized,asynchronized, therefore there is no importance of closeness to traditional place and time and the identity of information is remained undecided [23]. Such features lead to the expansion of cosmopolitan way of thinking among the users and gamers.
According to American culturalogist Jenkins, problems and other obstacles to the inequality in the internet connection, censorship, lack of transparency of networks, processes of information socialization of societies directly related to the formation of the modern cyberculture [25].
-
VI. Common And Professional Information Culture
Information requirement and feature of information activity change depending on age, educational level, profession in accordance with it affects their content of the information culture. For example, the information culture of pupils,students, post-graduate students, differ from each other according to their education level. The structure of the student information culture includes:to keep in mind educational information, to be able to find additional information from information sources (library, the Internet),to carry out simple operations related to information processing,to convey brief essence of received information,to be able to prepare simple presentations. The demand of information culture of postgraduate-student is different because he is engaged in the scientific research. He should know the features of information environment: should be able to differ scientific information from other information, should be informed about scientific publications, scientific libraries, to get, to analyze information on centers, scholars and their works that engaged in research of the scientific problem, should know that what the scientific reference indices mean, and be able to search scientific bases.At the same time he should be able to prepare an article,to compile a list of literature, to present the results obtained in the conference and seminars,the skills as to answer the questions based on scientific evidence and facts. At the same time, he should know the scientific ethical issue, his legal and moral-ethical aspects.
Information culture can be divided into general (elementary) and special (professional) information. General information culture can be attributed to general knowledge and skills required to everybody for treating with information, professional information culture can be attributed information culture of specialists. The global information space, the process of information society formation being a development stage of civilization changes the demands of specialist. Unlike previous time,nowadays, specialist is demanded to follow innovations related to his specialization and activity field,to get new knowledge and skills. Because now information and knowledge in any field change rapidly,being replaced with new ones,it means that the knowledge gained from the period of specialist studying soon loses its urgency [26].Therefore,the specialist should be ready to increase his knowledge constantly and independently,regardless of which field he works in. It is only possible in the case of formation of specialist’s information culture.
Along with the skills of using ICT, the specialist should know the regularity of information resources related to his field,the opportunities of various information searching systems,he should be able to work with different information resources, to know the methods of information processing, and have lots of such knowledge and skills.That is why in addition to being information consumer, every specialist is an active participant of the information processes related to the activity of worked organization.When it is necessary he is an information producer as well as expert, reviewer, consultant.
At present, forming information culture of specialist is considered an urgent problem all over the world. It means using skills in his professional activity from the opportunities of new information space. The need of reading theoretical and methodological literature,skills of obtaining, evaluating, selecting required information are the components of information culture of new technologies are not perceived by everyone. The reason is that the information culture of workers as well as those who engaged in the management is at a poor level. To solve this problem, it would be more reasonable to teach general components of information culture in the secondary educational institutions, in accordance with the subject of “information culture” in the specialized secondary schools. Hereby the process of information culture formation of people can be implemented in two phases: general knowledge and skills that is a necessary form dealing with information activity and certain knowledge and skills for the features of information environment by each occupation.
It is known that the quality of specialist training depends directly on the activity of teachers. Therefore, at the time of forming the information society, the formation of information culture of the teacher that preparing people to the society may be the first stage of solution of this problem. At the same time, there is also a need for preparing teacher of “information culture” in the educational institutions engaged in training of pedagogical personnel. These issues are in the spotlight of international organizations and scientific community. In 2011, the training program has been published for teaching information and media literacy to the teachers on the initiative of UNESCO.
It should be noted that concept of information culture is not used in the international community, but the concept of information literacy. The concept of “information literacy” was first introduced in the United States by Paul Zurkowski in the early 1970’s [27]. In the proposal, Zurkowski described information literate individuals as those who are “trained in the application of information resources to their work” and campaigned for a national program to teach the necessary skills, which would eventually yield an information literate generation a decade later [28].At present,the standards of information literacy have been worked out and are applied for those of studying in many countries [29,30].Information literacy enables learners to engage critically with content and extend their investigations, become more self-directed,and assume greater control over their own learning [31].
Along with the concept of information literacy,the concepts as “media literacy”, “media education” are widesread associated with the mass media means,especially increasing the role and expanding influence of mas media means or “new media”.
As Manovich [32] states: “Today we are in the middle of a new media revolution - the shift of all culture to computer-mediated forms of production, distribution, and communication.” Media literacy – is knowledge, skills and abilities for perceiving formats (newspapers and magazines, radio and television, CD, DVD, mobile phones, PDF text format, JPEG format for photographs and graphic images) used for creation, memorization, tranmission and presentation of all communication means and data, information and knowledge.
In general as the result of the rapid development of ICT, the emergence of new types of information, many of such concepts are used: computer literacy, visual literacy,multimedia literacy, network literacy, electronic literacy and so on. In fact, these concepts are used to express the skills needed for the people for consumption and production of different types of information (text,video,audio,etc.)circulated in the information environment.
At present, a number of measures are undertaken by UNESCO and IFLA in the direction of integration of concepts of “information literacy” and “media literacy” [33].
In 2010, a conference was held with the participation of international experts for the first time in connection with the problems of preparing information and media literacy in Thailand. All of these concepts might be covered with the concepts of information culture used in Russia and the post –Soviet space.
In our opinion, the concept of “information culture” is much broader than media literacy and etc.,as other literacy concepts mentioned above.Knowledge, skills and abilities regulating the relations between a person and all type of information can be attributed to information culture including media information. From this point of view, information culture covers all these consepts.
-
VII. Conclusion
Formation of information culture of all citizens, in particular, the future specialists is a demand of our age. At present being lower of information training of people in comparison with the rapid technological development hinders them to use of emerging opportunities.Technical training (skills of using computer and the Internet) and psychological training should be added to the information training. For example, using as a means of influence and psychological weapon,information warfare,information terrorism,and other factors require people to be psychological prepared.
In this regard a number of issues related to information training of citizen are awaiting their solutions:
-
1) Ensuring of teaching the subject of information culture of all levels of the education system;
-
2) Preparation of education programs according to the
age level of those studying at schools providing general education;
-
3) Preparation of programs and standards according to the profile for forming information culture of those studying at higher education institutions;
-
4) Opening speciality of information culture and create a certain chair in the pedagogical universities;
-
5) Traning information culture within the courses of improvement of professional skills to specialists.
It is possible to adopt using the programs and other materials prepared by UNESCO, as well as, standards, programs and textbooks applied in different countries.
Список литературы Information Culture Formation as the Most Promising Direction of Individual`s General Culture
- A.L.Kroeber & C.Kluckhohn (1952).Culture:a critical review of concepts and definitions, Cambridge:The MIT Press.
- S.A.Sackmann (1992).Culture and sub-cultures:an analysis of organizational knowledge. Administrative Science Quarterly 37(1),140-161.
- G.Hofstede (1998).dentifying organizational subcultures:an empirical approach Journal of Management Studies, 35(1),1-12.
- D.W.DeLong & L.Fahey (2000).Diagnosing cultural barriers to knowledge management, Academy of Management Executive, 14(4), 113-127.
- S. Burchell, C. Clubb, A. G. Hopwood, J. Hughes, & J. Nahapiet, (1980). The roles of accounting in organizations and society.
- A.M.Pettigrew.On studying organizational cultures, Administrative Science Quarterly, 1979, 24(4), 570-581.Retrieved from http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images /0015/001570/157020E.pdf
- G.Hofstede.Culture's consequences:international differences in work-related values. Sage Publications,Beverly Hills, CA,1980, 335-355.
- A.I.Kravchenko. Kulturologiya: uchebnoye posobie dlya vuzov. M.: Akademicheskiy proekt (in Russian), 2001.
- S.D.Hunt & S. Vitell. A general theory of marketing ethics. Journal of Macromarketing, 1986, 8, 5-16
- R.Rugimbana & S.Nwankwo. Cross-cultural marketing. London: Thomson Learning, 2003.
- F.Braudel, A history of civilizations. London: Penguin Books, 1994.
- V.P.Bolshakov & L.F.Novitskaya. Osobennosti kul'tury v yego istoricheskom razvitii (ot zarojdeniya do epoxy vozrojdenia), Velikiy Novqorod: NovQU im. Yaroslava Mudrogo (in Russian), 2000.
- C.Bruce & P.Candy (Ed.).Information literacy around the world. Wagga, Australia:Centre for Information Studies Charles Sturt University,2000.
- N.Gendina.Coordination of higher educational institutions and professional library associations - the key to training quality rise of libra?rians of XXI century. Management, Marketing and Promotion of Library Services. Based on Statistics, Analyses and Evaluation / edited by Trine Kolderup Flaten; International Federation of Library Associati?ons and Institutions.-Munchen:K.G. Saur,2006, 169-178.
- K.K.Kolin..Kachestvo jizny v informatsionnom obshestve. Chelovek i trud, 2010, 1, 39-43 (in Russian).
- L.H.Savchuk. Informatsionnaya kultura na razlichnix etapach razvitiya chelovecheskogo obshestva. Informatizatsiya obrazovaniya, 2005, 2, 28-34 (in Russian).
- L.Haddon. Personal information culture: the contribution of research on ICTs in everyday life. Paper presented at the 'UNESCO between Two Phases of the World Summit on the Information Society', 2005, St. Petersburg, Russia.
- S.Q.Korkonosenko. Personal communication freedom as a problem and a research project. Journalism and Mass Communication, 2012, 2(1), 317-328.
- R.M. Alguliev & R.Sh. Mahmudova. Structural approach to the formation of information culture of individuals, Proceedings of the International Conference on Informatics Engineering & Information Science (ICIEIS2011), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia, 2011, pp. 29-40.
- B.Danet. Communication and culture on the internet.Retrieved from http://www.europhd.eu/html/_onda02/04/ss8/pdf_files/lectures/Danet_culture_Internet. pdf.
- Jones, G.Steven (Ed.).Virtual culture: identity and communication in cybersociety. London: Sage Publication, 1997.
- G.T.Marx.What's in a name? Some reflections on the sociology of anonymity.The Information Society,1999,15(2),99-112.
- Z. Papacharissi. The presentation of self in virtual life:characteristics of personal home pages.Journalism and Mass Communication, 2002, 79(3), 643-660.
- P.K.Nayar. Virtual Worlds: Culture and Politics in the Age of Cybertechnology. London: Sage Publication, 2004.
- D.Bell.An introduction to cybercultures. London & New York: Routledge, 2005, 276 p.
- H.Jenkins. Confronting the challenges of participatory culture: media education for the 21st century. Cambridge, MIT Press, 2009,145 p.
- Ava Clare Marie O. Robles, "The Use of Educational Web Tools:An Innovative Technique in Teacher Education Courses",IJMECS,vol.5,no.2,pp.3440,2013.DOI:10.5815/ijmecs.2013.02.05.
- S.Webber, & B.Johnston. Conceptions of information literacy: new perspectives and implications, Journal of Information Science, 2000, 26(6), 381-397.
- Ting-ting LIU, Hai-bin SUN. Gender Differences on Information Literacy of Science and Engineering Undergraduates. International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science (IJMECS) vol.4, No.2, March 2012.
- Association of College & Research Libraries.Information literacy competency standards for higher education.Chicago,IL:Association of College & Research Libraries,2008.Retrieved from http://www.ala.org/acrl/standards/informationliteracycompetency.
- SCONUL.The seven pillars of information literacy, 2011. Retrieved from http://www.informationliteracy.org.uk/ information-literacy-definitions/sconul-seven-pillars-of-information-literacy/.
- Delwar Hossain, Cheryl Perrin, Kaye Cumming. Information Literacy and its Application in Nursing Education. International Journal of Modern Education and Computer Science (IJMECS) vol.4, No.10, October 2012.
- L.Manovich. The language of new media. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 2001.
- F.W.Jr.Horton. Understanding information literacy: a primer. Paris: UNESCO, 2008.


