Innovative technologies for the treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervix
Автор: Kattakhodjaeva M.Kh., Karshieva E.E., Amonova Z.D.
Журнал: Cardiometry @cardiometry
Рубрика: Original research
Статья в выпуске: 25, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The problem of pathological conditions of the cervix attracts great attention of doctors of many specialties, which is due to the ambiguity of the prognosis of this pathology. The detection of gynecological pathology, including cervical pathology, depends on the use of screening diagnostic methods, improvement of preventive and therapeutic measures carried out in an outpatient setting. In modern medical practice diseases of the cervix uteri occupy a leading position due to the high the frequency of their occurrence, frequent transformation into precancerous conditions, which in turn can be the cause of cervical cancer. Today, both in world practice and in Uzbekistan in the structure of oncological diseases of the genital organs in women cervical cancer is the second most common disease, causing high mortality of patients.
Innovative technologies, treatment of cervical neoplasia
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148326338
IDR: 148326338 | DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.25.7074
Текст научной статьи Innovative technologies for the treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervix
M.Kh. Kattakhodjaeva, E.E.Karshieva, Z.D.Amonova. Innovative technologies for the treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervix. Cardiometry; Special issue No. 25; December 2022; p. 70-74; DOI: 10.18137/cardiometry.2022.25.7074; Available from:
The problem of pathological conditions of the cervix attracts great attention of doctors of many specialties, which is due to the ambiguity of the prognosis of this pathology. The detection of gynecological pathology, including cervical pathology, depends on the use of screening diagnostic methods, improvement of preventive and therapeutic measures carried out in an outpatient setting. In modern medical practice diseases of the cervix uteri occupy a leading position due to the high the frequency of their occurrence, frequent transformation into precancerous conditions, which in turn can be the cause of cervical cancer. Today, both in world practice and in Uzbekistan in the structure of oncological diseases of the genital organs in women cervical cancer is the second most common disease, causing high mortality of patients. WHO identifies as countering cancer mortality such main directions as prevention, screening and early diagnosis of precancerous diseases and early stages. Conditions of the cervix that exist for a long time against the background inflammatory processes, belong to the risk group for the occurrence precancer [1, 2]. According to research data, the incidence of pathological processes on the cervix is about 15% in the structure gynecological diseases, and cervical cancer ranks second among oncogynecological pathology in women [3, 6]. In recent years, significant progress has been made and opportunities in terms of diagnosis and treatment of cervical pathology as the basics of prevention of malignant lesions of a given localization. It should be noted that, in general, the tactics of patient management has become more forgiving. The applied methods of treatment of pathology of the cervix with using coagulation methods (chemical, cryo- and laser destruction, as well as diathermocoagulation and dia-thermoexcision of the cervix) are associated with relatively long-term medical rehabilitation sick. The works of a number of authors have confirmed that, along with convincing the effectiveness of the above methods of treatment takes place a long (up to 12 weeks) the process of regeneration of the epithelium, which causes the possibility of infection, pathological proliferation and metaplasia epithelium and connective tissue [4,5]. Particularly time-consuming process regeneration is noted after diathermocoagulation, excision, cryo- and laser destruction of extensive benign foci of pathology epithelium against the background of ectropion and cicatricial changes in the cervix. Such observations have a high percentage of subepithelial endometriosis (8 to 40%), syndrome “Coagulated neck of womb”, bleeding, exacerbation of chronic inflammatory processes (up to 30%), the formation of cervical stenosis channel, isth-mic-cervical insufficiency [4, 2, 6]. Relevance problems prompts the search for better treatments background processes of the cervix, allowing to accelerate epithe-lization cervix and avoid complications after treatment. It must be remembered that the ablation technique can be applied only if the transformation zone is completely visualized during colposcopy, there is no malignant invasive process and atypia of the glandular epithelium of the canal and there is no discrepancy in the data of cytological and histological studies [4, 7]. Generally accepted indications for the use of this technique are:
– Diseases of the cervix in the form of superficial lesions (ectopia, persistent chronic cervicitis, endometrioid heterotopias, hyperkeratosis, mild CIN);
– stopping bleeding after biopsy, removal of neoplasms and conization.
An important factor is the adequate treatment of this pathology. When taking a biopsy, excision or conization of the cervix, autopsy retention cysts, surgical treatment of ectropion, removal various neoplasms of the cervix, vagina or vulva, very important are the safety of electro surgical technology, regulation the depth of tissue burn injury and cosmetological effects. hus, the issues of correct choosing a method of coagulation or ablation of the affected areas of the cervix, especially in women with ongoing fertility.
The purpose of this study was to study the comparative efficacy and safety of argon plasma coagulation and other methods of destruction of pathological foci of the cervix with benign background and precan-cerous processes.
Materials and methods
The object of the study was 67 women reproductive age with various pathologies of the cervix. V the main group included 37 patients, in whose treatment was used radio wave biopsy and argon ablation. In the treatment of 30 women traditional diathermoelectro-coagulation was used using apparatus K57.
Radio wave biopsy and argon plasma coagulation procedures were carried out with the apparatus “Fo-tek EA-141” in the first phase menstrual cycle - 5-9 days. Ablation was performed under the condition complete colposcopic visualization of the transformation zone and absence of discrepancy between the data of the conducted surveys. For for this, an argon plasma flow was used in the “Spray” mode and power of 36–38 W (soft, smooth argon plasma ablation). A radio wave passing through the patient’s body from an active electrode with a small size to a receiving plate of a relatively large size causes heating of the tissues at the point of contact of the active electrode. The use of a cutting working electrode (knife type) of appropriately selected radio wave power allows simultaneous cutting and coagulation of tissues. The active electrode is blown with Argon gas. With the passage of a high-frequency current, the gas is ionized and an argon plasma torch appears between the electrode and the tissue, which causes tissue coagulation. The method is non-contact, the depth of coagulation is -3 mm, in connection with which the subsequent scar tissue is tender and does not lead to subsequent deformations of the cervix. Tissues with large vessels are clamped with bipolar clamps. The effect of “brewing” of tissues is achieved by a combination of mechanical and thermal effects. Another of the positive properties of argon plasma coagulation of tissues is the absence of smoke, which will facilitate the work of the surgeon. At the same time, collagenate is formed in the tissues, which, like a “filling”, closes the lumen of the vessels. A so-called “thermo-suture” is formed, which subsequently gradually resolves.
Anesthesia was not routinely performed .
Results
The study of the features of the reproductive history was carried out according to a single method: the gynecological pathology suffered by women in the anamnesis was studied, as well as gynecological diseases registered at the outpatient appointment at the time of the examination. The age of the examined women with various pathologies of the cervix ranged from 20 to 45 years. The mean age at the time of the examination was 29.8±5.13 years. When analyzing outpatient records, it was revealed that in 78.3% the duration of observation of the patient in the consultative polyclinic ranged from 1 to 3 years, in 13.0% - from four to six years, in 3.7% - 7-9 years and only 5% - for 10 years or more. The number of visits per year in 87% was one or two. The frequency of cervical disease depended on the early onset of sexual activity and a large number of sexual partners. When analyzing the onset of sexual activity, it can be seen that at present, the early onset of sexual contacts prevails: in the group under 20 years old, the onset of sexual intercourse occurred in 47.9% of cases, in the group of 20-29 years old - 75%. At the same time, diseases of the cervix were encountered in the anamnesis in almost half of the women - 48.2%.
Most of the women who applied were employees (49.6%), and 12.6% were students. Noteworthy is the high percentage of officially unemployed women -37.7%. From the anamnesis it was found that more than half of the women - 56.5% - suffered from inflammatory diseases of the genitals. The second most common disease was the pathology of the cervix (in particular, complicated ectopia or erosion and ectropion of the cervix and other diseases - 29.3%). Polyps of various localization were in the anamnesis in 3.3% of the total number of patients examined, and
1.7% of them were cervical polyps. It was revealed that among all diseases and conditions of the cervix, 43.6% accounted for ectopia with its various causes. In different age groups, ectopia and pathology of the cervix occurred with approximately the same frequency.
In the structure of viral infection, HPV types 16 and 18 accounted for 37.9% and 33.3%, respectively, other oncogenic HPV types - 28.8%. Herpetic infection was in 28.8% of the examined. Koilocytosis in smears was found in 88.1% of the study participants.
Warts 23%
Poliposis 22%
Hiperplasia 15%
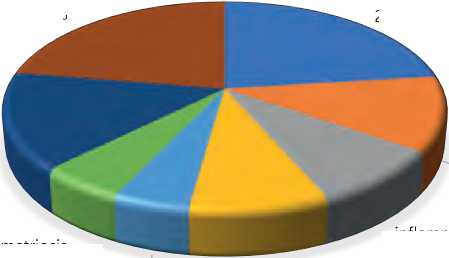
inflammation of the uterus 12% multifollicular ovaries 9%
Endometriosis 5% uterine fibroids 5%
Figure 1. Associated gynecological diseases
inflammation of the ovarium 9%
Vaginal dysbiosis was diagnosed in 59.6% of patients, more often in the severe stage of dysplasia than in the mild one (76.5% and 50.0%, respectively). Concomitant gynecological diseases occurred in 61.5% of the study participants: genital warts of the vagina and vulva (38.5%), inflammatory diseases of the uterus (19.3%) and uterine appendages (14.7%), multi-follicular ovaries (14.7%), uterine fibroids (8.2%), endometriosis (9.1%), endometrial hyperplastic processes (25.0%), cervical canal polyps (37.5%), diffuse mastopathy (56.2%). The diagnosis of mastopathy was made on the basis of the clinical picture and ultrasound data. Infertility was in 12 (11.0%) women, including primary in 8 (7.3%). Menstrual disorders were detected in 59.4% of the examined, including: dysmenorrhea - in 53.0% of them, abnormal uterine bleeding - in 18.8%. Before applying the methods of argon plasma tissue coagulation and other methods of destruction of pathological foci in for this pathology of the cervix, all 67 patients were selected after conducting a comprehensive examination: cytological, general clinical examination, extended colposcopy, diagnostics by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), bacteriological and bacterioscopic examination of discharge from the cervical canal and vagina, excluding infectious and inflammatory processes. At colposcopic studies revealed the following diseases: ectopia of columnar epithelium - in 21 patients (37%), benign transformation 72 | Cardiometry | Issue 25. December 2022
zone - in 12 women (21%), a combination of the listed processes were diagnosed in 17 cases (30%), subepi-thelial endometriosis - in 7 (12%) women.
In world practice, various methods of treating dysplasia are used, but none of them has 100% efficiency [7, 11]. Most modern treatment regimens are based on the destruction of the affected epithelium using elec-trosurgical excision, laser or cryodestruction. More than half of the patients experience relapses of the disease, which are difficult to treat, and the possibilities for repeated surgical intervention are limited [3, 9].
Often, with insufficient examination of patients (without studying the biocenosis of the vagina and the hormonal background on which dysplasia occurred), as well as inadequate sanitation of the partner, the patient is re-infected, and even with good treatment results, relapses of the disease occur [9, 11].
In our study, we applied in the practice of treating cervical dysplasia a new method of treatment using innovative technologies - a device for wide-band argon plasma energy. The results of treatment were compared with the results of traditional therapy for cervical dysplasia using diathermocoagulation. The listed pathological processes of the cervix with the same frequency were distributed in both groups of patients. The examined patients were divided into 2 groups. Group I consisted of 37 women who coagulation of pathological foci was performed using argon plasma coagulation of tissues using the device “FOTEK-ЕА 141” in the scattering mode at a power of 36-38 Wt, gas consumption -7 liters per minute. Coagulation was carried out with an argon plasma torch in a circular motion from the periphery to the center with partial grip of healthy tissue, until the formation of a light yellow area of the treated epithelium. Before carrying out the procedure for the purpose of local anesthesia, the cervix was treated with lidocaine spray.
II group covered 30 women who underwent elec-trodiathermocoagulation of cervix. The groups were matched for the age of the patients, anamnestic data and the results of a comprehensive study. The intervention was carried out on an outpatient basis. If necessary sanitation of the vagina, anti-inflammatory therapy was prescribed. Usually in during the operation, the patient noted slight discomfort in the lower abdomen or a “tingling sensation” that did not require application of medicines. The duration of the operation was 10-15 minutes. There were no complications during and after the procedure. At the end of the in- tervention, the patients were discharged home with recommendations to refrain from sexual intercourse until the control examination after 1.5 months, limit physical activity, exclude bathing and, if necessary, use panty liners. The clinical efficacy of therapy was assessed by the positive dynamics of clinical symptoms, colposcopic and cytological picture. As a result of the poll after the execution procedure, it was found that in the 1st group of women pain in the form of moderate tingling or burning sensation was noted by 30% of patients. Complaints in duration were within 2-5 minutes, later the feeling of discomfort was not manifested. In women of the II group, pain sensations of varying severity were present in 15 (79%) patients that involved the use of injecting the cervix 2% - 1 ml lidocaine or ultracaine or treatment of the cervix with a drug lidocaine spray and various pain relief medications after procedures. Painful sensations were noted for 2-4 hours. In the postoperative period, the wound exudate was presented by scanty serous or smearing secretions that lasted 6-11 days. When the scab is rejected from the wound surface the cervix on the 7-10th day in all cases did not require excretion therapeutic measures. In group II, where diathermodestruction was used pathological foci, abundant watery discharge were observed in all 100% of patients within 20 days, then the intensity gradually decreased, completely disappeared after 28-30 days. When conducting control colposcopy 28-30 days after the treatment it was noted that in group I, after argon plasma coagulation of tissues complete epithelialization of the cervical tissue occurred in 90% of patients, the average period of complete epithelialization was 35 days (25-45 days earlier, than in the comparison group. In the group of patients after diathermodestruction cervix with colposcopy after 35 days complete epithelialization was found only in 38.8% of women, and the average period of full epithelialization was 3 months. Cicatricial changes were present in 22% of cases. Re-intervention after diathermodestruction 4 women had to perform the method of argon plasma coagulation. Control examination and extended colposcopy were performed after 1.5–2 months after surgery and, if necessary, further in dynamics.
It was found that the average duration of healing of the cervix after procedures were 42 ± 2.5 days. Delayed epithelialization (50-60 days) noted in 3 cases, and in all these situations the procedure argon plasma coagulation of the neck was carried out after sanitation vagina due to bacterial vaginosis and / or STIs -mycoplasma, ureaplasma and human papillomavirus infections; after examination, such patients were prescribed dexpanthenol vaginally (in candles) and Actovegin (in pills) orally in standard course dosages.
Conclusions
Our observations have shown that in recent years the incidence of pathological conditions of the cervix has been increasing, and also, from year to year, the number of precancerous diseases is increasing - from 2019 to 2021. Their incidence rate has increased by 1.5 times. Moreover, in the age aspect, the incidence of the latter is recorded mainly in the age period of 37-45 years, which requires special vigilance during this period of life. In accordance with the results obtained, a number of conclusions can be drawn about the expediency of using the method of argon plasma coagulation in treatment of pathology of the cervix. The advantages of this method are:
– the possibility simultaneous and quick removal of pathological tissues from a large lesion focus;
– minimal discomfort during the operation, which allows you to refuse anesthesia in most cases;
– absence of physical contact of the working part of the tool with tissues of the patient negates the possibility of infection and formation of carbon deposits on the electrode, provides the ability to control depth and area of coagulation;
– the bloodlessness of the intervention and the absence of smoke ensures the doctor good visualization and the ability to produce fast and accurate manipulations;
– the sterilizing effect of radio waves allows you to use it when treatment of persistent chronic cervicitis; - preservation of the shape of the cervix and the absence of rough scarring allow to apply this method to nulliparous and planning repeated pregnancy to women;
– short time of postoperative wound healing.
Список литературы Innovative technologies for the treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervix
- Bushes, V. N. Pathology of the cervix/V. N. Kustarov, V. A. Linde. SPb.: Publishing house "Hippo-crates", 2002. 141 p.
- Belokrinitskaya, I. et al. Prevention of cervical cancer: a glimpse into future: materials of the International Scientific and Practical Conference, April 2-4, 2008, Moscow, Russia.
- Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the cervix, vagina and external genital organs broadband radio wave surgery and Argon plasma ablation / S. I. Rogovskaya, V. N. Prilepskaya, T. N. Bebneva et al. ] Manual for doctors. Moscow, 2008. 44 p.
- Diseases of the cervix, vagina and vulva / ed. V. N. Prilepskaya. M.: "MEDpressinform", 2003. 430 p.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of diseases of the cervix argon plasma coagulation in nulliparous women / T.E. Prilepskaya V. N. Ectopia and erosion of the cervix / Prilepskaya V. N., Rudakova E. B..
- Glukhov, T. V. Kuzina [et al.] Cervical pathology and genital infections - from theory to practice: proceedings of the Conference, Moscow, 2007.
- Keppler D., Lin A. Cervical cancer: methods and protocols. NY, Springer Science, 2015.
- Luttmer R., Lise M., De Strooper A., Steenbergen R.D., Berkhof J. Management of high risk HPV-positive women for detection of cervical (pre)cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016 Jul 26 11.
- Oboskalova T. A. Optimization of methods of treatment of cervical pathology uterus (experience of using argon plasma ablation) / T.A. Obskalova, E.NS. 10. Shumacher A. Laser therapy of the uterine cervix / A. Shumacher. Zentralbl. Gynakol. 1994. Vol. 116, no. 2. P. 17-22.
- Ulrikh E.A., Verbitskaya E.A., Urmancheeva A.F.,Novik V.I., Mikaya N.A., Kutusheva G.F., Berlev I.V. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in combination with pregnancy: diagnosis, management, outcomes. Problems of Oncology. 2014. No. 3. V. 60. p. 263-266.


