Инсулин, головной мозг, болезнь Альцгеймера: новые данные
Автор: Булгакова Светлана Викторовна, Романчук Петр Иванович, Тренева Екатерина Вячеславовна
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Медицинские науки
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.6, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Последние четыре десятилетия ознаменовались рядом научных открытий. Так стало известно, что инсулин, рецепторы к нему найдены в структурах головного мозга. Кроме того, стала известна роль этого гормона в активации нейрональных стволовых клеток, росте, развитии нейрональной сети, синаптической передаче, когнитивных функций и так далее. Дисфункция передачи сигналов и метаболизма инсулина способствует развитию ряда дегенеративных заболеваний головного мозга. Все больше данных говорит о связи сахарного диабета 2 типа и болезни Альцгеймера, имеющих много общих патофизиологических характеристик. Данный обзор литература посвящен анализу клинических и экспериментальных данных, связывающих инсулин, инсулинорезистентность с дегенеративными процессами в головном мозге, оценке фармакологических стратегий, направленных на коррекцию сигнальных путей инсулина в ЦНС и когнитивных функций. Искусственный интеллект, нейросети «мозг-микробиота» позволяют управлять взаимодействием генетических и эпигенетических программ старения и здорового долголетия. Новая управляемая здоровая биомикробиота и персонализированное функциональное и сбалансированное питание «мозга и микробиоты» - это долговременная медицинская программа пациента, которая позволяет комбинированному применению питательной эпигенетики и фармэпигенетики, а главное проведению профилактики полипрагмазии.
Инсулин, рецепторы инсулина, болезнь альцгеймера, инсулиноподобный пептид 1, нейродегенеративные заболевания
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14116201
IDR: 14116201 | УДК: 616.83/.85:616.89 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/52/10
Текст обзорной статьи Инсулин, головной мозг, болезнь Альцгеймера: новые данные
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
УДК 616.83/.85:616.89
Нейроось «микробиота–кишечник–мозг» представляет собой динамическую матрицу тканей и органов, включая желудочно–кишечную микробиоту, иммунные клетки, ткани кишечника, железы, вегетативную нервную систему и головной мозг, которые взаимодействуют сложным разнонаправленным образом через ряд анатомически и физиологически различных систем. Долгосрочные возмущения этой гомеостатической среды могут способствовать прогрессированию ряда нарушений путем изменения физиологических процессов, включая активацию гипоталамо–гипофизарно–надпочечниковой оси, нейромедиаторных систем, иммунной функции и воспалительной реакции [1].
Современные инструменты и методики эпигенетической, диетической и биомикробиотической защиты здорового старения — это междисциплинарные, межвузовские и межведомственные направления, которые фокусируются на изучении нервной системы и влияния мозга на поведение и мыслительную способность людей [1–2].
Новая эпигенетика Homo sapiens управляет взаимодействием эпигенетических механизмов старения и долголетия с биологией, биофизикой, физиологией и факторами окружающей среды в регуляции транскрипции. Старение — это структурно–функциональная перестройка (перепрограммирование) и постепенное снижение физиологических функций организма, которые приводят к возрастной потере профессиональной пригодности, болезням, и к смерти. Понимание причин здорового старения составляет одно из самых проблемных междисциплинарных направлений [2].
Генетический и эпигенетический вклад в старение и долголетие человека огромен. В то время как факторы окружающей среды и образа жизни важны в более молодом возрасте, вклад генетики проявляется более доминантно в достижении долголетия и здоровой старости. Эпигеномные изменения во время старения глубоко влияют на клеточную функцию и стрессоустойчивость. Дисрегуляция транскрипционных и хроматиновых сетей, вероятно, является важнейшим компонентом старения. В ближайшем будущем искусственный интеллект и крупномасштабная биоинформационная система анализа сможет выявить вовлеченность многочисленных сетей взаимодействия [2].
Раньше считалось, что мозг является нечувствительным к инсулину и неподверженным его влиянию органом, т. к. гормон не может проходить через гематоэнцефалический барьер (ГЭБ) [3]. Также отрицалась и вероятность локального синтеза инсулина в каком-либо отделе головного мозга. Однако в 1967 г. Р. Марголис и Н. Альтшулер доказали, что уровень инсулина повышается в цереброспинальной жидкости собак при его внутривенном введении. В связи с чем появилась версия о том, что гормон все же может пересекать ГЭБ через высоко специализированную транспортную систему [3–6].
Спустя 10 лет Я. Хавранкова и коллеги обнаружили сам инсулин и его рецепторы в разных отделах головного мозга крысы [6–7].
В настоящее время известно, что инсулинтранспортная система в различных областях мозга существенно различается, что приводит к дифференциации проницаемости инсулина для различных популяций нейронов, вследствие чего гипоталамус, продолговатый мозг, варолиев мост имеют более высокую концентрацию инсулина, а затылочная доля и таламус — сравнительно низкую [3, 8]. Инсулинтранспортная система существенно меняется в условиях голодания, переедания, при ожирении и старении, у пациентов с СД 2-го типа и болезнью Альцгеймера (БА). Кроме того, существует и вторая версия появления инсулина в головном мозге — синтез гормона непосредственно в головном мозге. Эти представления базируются на обнаружении мРНК для инсулина в гипоталамусе, гиппокампе и культурах нейронов [6, 9].
Тем не менее, в настоящее время широко признано, что инсулин играет важную роль в жизнеспособности нейронов и функционировании головного мозга. Фактически, действие инсулина необходимо для синаптической пластичности нейронов и способствует обучению и памяти [10] . Также было показано, что инсулин способствует образованию нейронной сети, активации нейрональных стволовых клеток, росту, репарации и нейропротекции нейронов, регуляции энергетического обмена, защите клеток от окислительного стресса [11] .
Следовательно, изменения в метаболизме и передаче сигналов инсулина в центральной нервной системе (ЦНС) могут способствовать развитию ряда заболеваний головного мозга.
За последние 20 лет многие исследования показали связь между нейродегенеративными расстройствами, такими как БА и нарушением передачи сигналов инсулина в ЦНС [12– 13], предполагая, что снижение действия инсулина и инсулинорезистентность могут играть важную роль в патогенезе этих заболеваний.
Инсулин и инсулиновая сигнальная система в головном мозге
Инсулин и инсулиноподобный фактор роста (IGF)-1 регулируют ряд биологических процессов посредством связывания и активации двух близкородственных рецепторов тирозинкиназы, рецептора инсулина (IR) и рецептора IGF-1 (IGF-1R) [14]. Несколько исследований показали, что IR и IGF-1R, а также их общие нижестоящие пути в большом количестве находятся в головном мозге, и, что более важно, эти пути функционируют как регуляторы нейрогенеза, функций мозга и энергетического баланса и системного гомеостаза [12]. Наибольшая концентрация IR находится в гипоталамусе, гиппокампе, в обонятельной луковице, мозжечке, миндалине и коре головного мозга [15], что свидетельствует о многофункциональности инсулина [12].
Инсулин — это пептидный гормон, состоящий из двух цепей и 51 аминокислотного остатка, не может пассивно проходить через гематоэнцефалический барьер (ГЭБ), но, тем не менее, он обнаружен в спинномозговой жидкости (СМЖ). Происхождение «мозгового» инсулина является спорным. Одна из гипотез заключается в том, что плазменный инсулин способен проникать через ГЭБ через насыщаемый транспортный процесс, возможно, через 1R-сосудистого эндотелия. Подтверждением этой гипотезы является доказательство того, что уровни инсулина в СМЖ ниже (примерно на 25%) циркулирующих в крови, и его концентрации увеличиваются после еды или при периферической инфузии инсулина [16]. Другой возможностью является доказательство того, что существуют области мозга, такие как гипоталамус, в которых отсутствует эффективный барьер, обеспечивающий доступ инсулина к ЦНС [17]. Третья гипотеза предполагает, что инсулин синтезируется в областях мозга, но это предположение требует дальнейших исследований [12, 18].
После достижения ЦНС инсулин связывается с IR, который принадлежит к семейству рецепторов тирозинкиназы. Интересно, что IR-субъединицы, обнаруженные в головном мозге, имеют структуру, отличную от периферических, и основным отличием является более низкая молекулярная масса IR-субъединиц мозга, вероятно, из-за различного гликозилирования [19]. Более того, мозг экспрессирует преимущественно изоформу A (- exon 11) IR, которая имеет более высокое сродство к IGF-2, в отличие от периферических тканей, которые преимущественно экспрессируют изоформу B (+ exon 11) [20–21] ,
Предполагается, что инсулин обладает нейропротекторными свойствами и оказывает нейротрофическое действие на нейроны ЦНС [22]. Более того, это может положительно влиять на когнитивные функции, включая эмоции, внимание, исполнительное функционирование, обучение и память [23].
После связывания инсулина с IR происходит аутофосфорилирование рецептора, и активированный IR фосфорилирует каскад белков субстрата IR (Рисунок) [14].
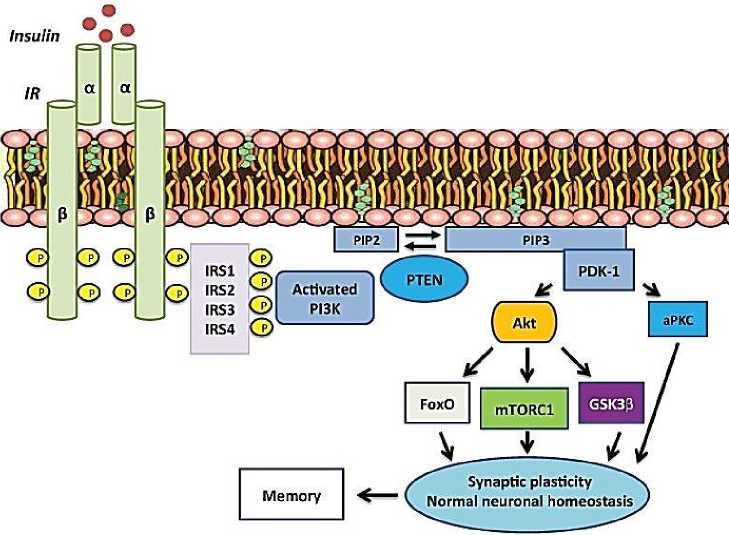
Рисунок. Инсулиновый сигнальный путь [6].
Среди IR-субстратов (IRS) мРНК IRS-2 в головном мозге является наиболее распространенной по сравнению с IRS-1; IRS-4, которые, в основном, экспрессируются в эмбриональном развитии, также в мозге взрослых мышей, особенно в гипоталамусе [12, 24]. На уровне всего тела IRS-1, по-видимому, является критическим для роста, а мыши с IRS-1-нулем приводят к увеличению соотношения мозг–тело [25]. С другой стороны, разрушение гена IRS-2 снижает пролиферацию нейронов во время развития на 50%, и, как следствие, у мышей с нулевым IRS-2 наблюдается пониженное отношение поверхности головного мозга к поверхности тела [26]. Кроме того, во время старения нейрофибриллярные клубки, содержащие фосфорилированный тау, накапливались в гиппокампе у мышей, нокаутированных по IRS-2, предполагая, что передача сигналов IRS-2 является нейрозащитной [26]. Несмотря на это, IRS-2-нулевые мыши являются долгоживущими [27], что согласуется с ролью центральной передачи сигналов инсулин/IGF в контроле продолжительности жизни у млекопитающих. IRS-4 может синергетически взаимодействовать с IRS-2 в гипоталамусе для контроля потребления пищи, расхода энергии и метаболизма глюкозы [28].
После связывания инсулина с рецептором инсулина (IR) происходит аутофосфорилирование, которое необходимо для его активации. Затем активированный рецептор инсулина фосфорилирует белки IRS. IRS активируют PI3K, который катализирует добавление фосфатной группы к мембранному липиду PIP2, тем самым превращая его в PIP3. PTEN может преобразовать PIP3 обратно в PIP2. Связанный с мембраной PIP3 рекрутирует и активирует PDK-1, который фосфорилирует и активирует Akt и атипичные PKC. Akt опосредует большинство метаболических эффектов инсулина и синаптической пластичности мозга, нейронального гомеостаза и памяти (рисунок 1) [6].
Сокращения: IRS (субстрат рецептора инсулина), PI3K (фосфатидилинозитол-3-киназа), PIP2 (фосфатидилинозитол-4,5-бисфосфат), PIP3 (фосфатидилинозитол-3,4,5-трифосфат), PTEN (гомолог фосфатазы и тензина).
Специфическая инактивация IR в головном мозге (то есть нейрон-специфических IR-нокаутов — NIRKO-мышей) показала, что недостаток IR в мозге определяет измененные метаболические фенотипы, включая ожирение, инсулинорезистентность, играет важную роль в регуляции энергетического метаболизма [12, 29]. Более того, инсулинорезистентность в головном мозге существует как явление, независимое от периферической инсулинорезистентности и углеводного обмена [30–31]. Это означает, что сниженная чувствительность к инсулину в головном мозге имеет иные последствия, чем в периферических тканях. Недавно опубликованные данные показали, что периферическая толерантность к инсулину и глюкозе была сопоставимой у пожилых мышей дикого типа и мышей APP / PS1 (модель БА), в то время как уровни серинового фосфорилированного IRS-1 были повышены в мозге мышей APP/PS1 [32]. Это дает некоторую поддержку предположению о том, что центральная инсулинорезистентность может существовать самостоятельно отдельно от периферической и связана с дегенеративными процессами при БА.
Одним из основных нижестоящих путей белков IRS является каскад PI3K / Akt. Это, в свою очередь, нацелено на множественные нисходящие пути, включая mTORC1, гликогенсинтазкиназу 3β (GSK-3β) и семейство транскрипционных факторов FoxO (Figure 1) [33]. Было показано, что многие из этих путей играют ключевую роль в нормальной работе головного мозга.
СД2 и нейродегенеративные процессы: роль нарушений в инсулиновой сигнальной системе головного мозга, инсулинорезистентности и гиперинсулинемии
СД2 представляет собой хроническое заболевание, связанное с возрастом, с растущей распространенностью. В настоящее время во всем мире более четырехсот миллионов человек страдают сахарным диабетом, и ожидается, что это число резко возрастет в течение следующих тридцати лет [34]. СД2, характеризующийся инсулинорезистентностью и хроническим воспалением, вызывает ускоренное старение [35] и приводит к преждевременной заболеваемости и смертности. Влияние СД2 на головной мозг в настоящее время хорошо известно: заболевание является основным фактором риска снижения когнитивных функций и деменции. Фактически, СД2 увеличивает долгосрочный риск развития деменции почти в 2 раза, и каждый десятый случай деменции среди населения мира может быть связан с последствиями СД2 [13]. Взаимная связь в распространенности этих хронических заболеваний обусловлена тем, что диабет и деменция имеют несколько общих особенностей, приводящих к повреждению головного мозга, наиболее важными из которых являются нарушение чувствительности к инсулину, накопление бета-амилоида (Aβ), гиперфосфорилирование тау, повреждение сосудов и воспаление.
БА является хроническим нейродегенеративным заболеванием, которое обычно начинается медленно и ухудшается со временем. Это является причиной 60–70% случаев деменции [36]. Наиболее распространенным ранним симптомом является трудность запоминания недавних событий (кратковременная потеря памяти). По мере развития болезни симптомы могут включать проблемы с речью, дезориентацию, перепады настроения, потерю мотивации, неспособность к самообслуживанию и поведенческие проблемы [37]. Это прогрессирующее нейродегенеративное заболевание характеризуется накоплением в мозге внеклеточных нейритных бляшек и фибрилл (в основном состоящих из агрегированных амилоидных β-Aβ-пептидов), внутриклеточных нейрофибриллярных клубков (накопление гиперфосфорилированных белков tau-NFTs), микроглиальной инфильтрации, атрофия головного мозга и широко распространенная потеря синаптической и нейрональной передачи. Выраженное нейровоспаление также постоянно наблюдается при БА [38]. Данные исследований показали, что гиперактивность провоспалительных маркеров в головном мозге предшествует развитию бляшек и нейрофибриллярных клубков при БА [39].
Обнаружено ряд патофизиологических связей между БА и нарушениями обмена веществ, такими как СД2, ожирение и метаболический синдром [40–42]. В отличие от небольшого количества случаев БА (~ 3%), обусловленных наследственными генетическими причинами, патогенез и этиология спорадической БА с поздним началом являются многофакторными, включающими генетические факторы и факторы образа жизни [43]. Признание СД2 в качестве основного фактора риска развития деменции, особенно БА, побудило исследователей к поиску основных механизмов, связывающих эти два возрастных хронических заболевания. Известно, что метаболические нарушения, характерные для СД2 (например, гипергликемия, гиперинсулинемия, гиперхолестеринемия), связаны с атрофией головного мозга и патологическими признаками БА [14, 44]. Является ли резистентность к инсулину причиной или следствием БА, пока неясно.
Более того, ряд исследователей подтверждают версию о том, что нарушение регуляции инсулиновой сигнальной системы может быть ключевым фактором, способствующим раннему развитию БА. Так, некоторые ученые показали, что экспрессия и активация белков IR, IGF-1R и IRS-1 снижена в мозге пациентов с БА по сравнению с контрольной группой [45]. Более того, некоторые авторы продемонстрировали, что неокортикальные уровни инсулина и связывание с IR снижаются в мозге больных БА [46]. Наконец, более низкая концентрация инсулина в СМЖ, несмотря на более высокую концентрацию инсулина в плазме [47], предполагает снижение действия инсулина в ЦНС.
Амилоидные бляшки, обнаруженные в мозге пациентов с БА, в основном состоят из Аβ, пептида, происходящего из более крупной молекулы, известной как белок-предшественник амилоида (АРР). Дисбаланс между продукцией, клиренсом и агрегацией пептидов вызывает накопление Aβ, и этот избыток может быть инициирующим фактором для развития БА [48].
Ряд исследователей предположили связь между дефектами энергетического метаболизма и функциональными изменениями, связанными с развитием БА [49]. Ингибирование энергетического обмена может изменить процесс APP и вызвать продукцию амилоидогенных продуктов [50]. Связь между инсулином и метаболизмом Aβ в последнее время привлекает все большее внимание ученых [51].
Известно, что малые олигомеры Aβ способствуют синаптотоксичности и последующим изменениям, которые приводят к нейродегенеративным процессам при БА [52–53]. Как часть этих нейродегенеративных процессов, олигомеры Aβ, по-видимому, оказывают негативное влияние на передачу сигналов инсулина, ингибируя аутофосфорилирование рецептора [54], и заметно снижают уровни IR и их активность на клеточной поверхности дендритов нейронов гиппокампа [55]. IR играют ключевую роль в важных неврологических процессах, включая обучение и память, а также фосфорилирование тау. Таким образом, индуцированная олигомерами Aβ потеря мембранных IR может представлять собой важный ранний механизм, лежащий в основе нарушения памяти и других патологических нарушений при БА.
Также было обнаружено, что олигомеры Aβ определяют аберрантную активацию ингибирования TNFα / JNK и IRS-1 как в моделях in vitro, так и in vivo [30, 56]. Кроме того, олигомеры Aβ также оказывают влияние на передачу сигналов ниже IRS-1 и PI3K, где они могут активировать сериновое фосфорилирование Akt и стимулировать воспалительные процессы [57]. С другой стороны, известно, что резистентность к инсулину ускоряет выработку Aβ, способствуя его накоплению. Когда резистентность к инсулину индуцируется у трансгенных мышей с БА или у мышей с диабетом, страдающих ожирением, путем их кормления пищей с высоким содержанием жира, мыши демонстрируют повышенные уровни Aβ в мозге и рост уровней ключевых ферментов, которые генерируют Aβ (например, γ-секретазу) [58]. Наконец, инсулин и Aβ являются субстратами инсулин-разлагающего фермента, и было высказано предположение, что гиперинсулинемия ингибирует деградацию Aβ путем конкурентной блокировки инсулин-разлагающего фермента [59].
Нарушение в инсулиновой сигнальной системе головного мозга и гиперфосфорилирования тау
Дефицит передачи сигналов инсулина также может усугублять нейродегенерацию за счет увеличения фосфорилирования тау-белка, являющимся нейрональным микротрубочковым белком, обнаруженным в аксонах. Он играет важную роль в сборке и стабильности микротрубочек, а также в транспорте везикул в нейронах. При БА гиперфосфорилирование тау белка является важным патологическим признаком, и способствуют дисфункции и дегенерации нейронов [60]. Было показано, что инсулин и IGF-1 регулируют фосфорилирование тау путем ингибирования GSK-3β в нейронах культуры клеток [61]. GSK-3β представляет собой ключевую киназу, которая фосфорилирует тау белок. Недостатки или нарушения в передаче сигналов инсулина в головном мозге приводят к снижению активности Akt, что ведет к увеличению активности GSK-3β. Это явление вызывает гиперфосфорилирование тау и, следовательно, образование тау-фибрилл [62]. Более того, периферическая гиперинсулинемия способствует фосфорилированию тау in vivo [63] . Было продемонстрировано, что при делеции гена IGF-1 и IRS-2 фосфорилирование тау резко увеличивается у мышей, нокаутированных по IGF-1 и IRS-2 [26, 64]. Действительно, генетическая делеция IGF-1 специфически увеличивает фосфорилирование тау в двух локусах-мишенях GSK-3β [57]. Эти результаты предполагают, что нормальная передача сигналов инсулина и IGF-1 предотвращает гиперфосфорилирование тау в мозге. Учитывая, что СД2 характеризуется инсулинорезистентностью, гиперинсулинемией и нарушением передачи сигналов инсулина, неудивительно, что повышенная активность GSK-3β при СД2 может привести к увеличению продукции Аβ [65] и повышенному фосфорилированию тау [66].
Инсулин также может регулировать экспрессию тау, и снижение передачи сигналов инсулина может привести к нарушению экспрессии гена тау [57], что приводит к снижению уровня нормального растворимого тау, в то время как гиперфосфорилированный тау накапливается, усугубляя коллапс нейронального цитоскелета, ретракцию нейритов и нарушения в образовании синапсов. Более того, было продемонстрировано, что ассоциированное с БА снижение экспрессии мРНК tau коррелирует с нарушением передачи сигналов инсулина и IGF-1, наблюдаемым в тех же самых образцах БА [67], демонстрируя сильную связь между этими двумя механизмами.
Инсулинорезистентность, васкулопатия головного мозга и нейровоспаление
Нейродегенеративные расстройства и СД2 характеризуются как сосудистым поражением, снижением мозгового кровотока, так и аберрантным воспалительным ответом [68].
Было доказано, что у пациентов с БА наблюдается снижение регионарного мозгового кровотока, что может привести к снижению снабжения мозга кислородом, глюкозой и питательными веществами [68–69]. Это явление связано с нарушением пути трансдукции инсулина. Инсулиновая сигнальная система участвует в регуляции вазодилатации и вазоконстрикции [70]. Активация IR опосредует вазодилатацию через путь PI3K / Akt. Он стимулирует эндотелиальную синтазу оксида азота (eNOS), что приводит к выработке оксида азота (NO) и сосудистой релаксации [70]. В инсулинорезистентном состоянии наблюдается специфическое нарушение вазодилататорного пути PI3K, что приводит к снижению продукции NO и, следовательно, к вазоконстрикции. В результате происходит снижение поступления питательных веществ в головной мозг, увеличение окислительного стресса и продукции активных форм кислорода (АФК) и, следовательно, активация реакции воспаления. Выброс провоспалительных цитокинов и рекрутирование макрофагов провоцируют атеросклероз, что в конечном итоге приводит к макрососудистым осложнениям [68].
Хорошо известно, что процессы хронического воспаления составляют основную часть патогенеза СД2, а также нейродегенеративных заболеваний. Ряд исследователей доказали, что индуцированное хроническое воспаление является важной ранней стадией патогенеза БА [71–72].
Было показано, что гиперинсулинемия способствует развитию процессов воспаления в ЦНС [73]. Установлено, что повышение уровня периферического инсулина приводит к увеличению в головном мозге уровней провоспалительных цитокинов, таких как интерлейкин-1 (IL-1), интерлейкин-6 (IL-6) и фактор некроза опухоли-α (TNF-α), повышенных при БА и локализованных в амилоидных бляшках и связанных с ними глиальных клетках [74].
При периферической инсулинорезистентности выработка воспалительных цитокинов и активация передачи сигналов о воспалительном стрессе могут привести к сериновому фосфорилированию IRS-1 с помощью киназ, ингибитора каппа-B-киназы (IKK), c-Jun N-терминальной киназы (JNK) и ERK2, которая, в свою очередь, нарушает IR-опосредованную передачу сигналов, блокируя внутриклеточное действие инсулина [75]. Предполагается, что подобный механизм встречается в головном мозге, где олигомеры Aβ могут активировать микроглию, что приводит к секреции провоспалительных цитокинов, которые связываются с их соответствующими рецепторами, активируя одну или несколько серинкиназ IRS-1 и, в свою очередь, фосфорилируя IRS [56]. Повышенные уровни сосудистых провоспалительных цитокинов, наблюдаемые как при СД2, так и при БА, также могут влиять на передачу сигналов инсулина в головном мозге. При повреждении ткани сосудов головного мозга цитокины могут пересекать ГЭБ и активировать фосфорилирование IRS-1 [76–77].
Сосудистое воспаление также может быть опосредовано активацией и увеличением количества рецепторов конечных продуктов гликирования (RAGE). RAGE экспрессируется в нейрональных клетках, астроцитах микроглии и в эндотелиальных клетках головного мозга, и уровни его повышаются как при БА, так и при СД 2. Повышенные уровни RAGE были предложены в качестве возможного механизма сосудистой дисфункции как при СД2, так и при БА [78], а взаимодействие между нарушенным церебральным метаболизмом глюкозы, окислительным стрессом и накоплением конечных продуктов гликирования играет важную роль в порочном цикле, который способствует прогрессированию БА [79]. RAGE представляет собой путь опосредованного рецептором транспорта Aβ через ГЭБ от периферии к мозгу [80], индуцируя цереброваскулярную дисфункцию, приводящую к нервно-сосудистому стрессу, выработке TNF-α и IL-6, способствуя синаптотоксичности и нейродегенерации [78].
Лекарственная коррекция нейродегенеративных изменений головного мозга с учетом патогенеза
Поскольку СД2 имеет несколько общих патогенетических характеристик с нейродегенеративными расстройствами, как обсуждалось ранее, было высказано предположение, что некоторые препараты, используемые при терапии СД2, могут иметь потенциальную пользу при лечении БА:короткая характеристика препаратов представлена ниже:
Метформин
Восстанавливает митохондрии, ослабляет эффекты AGE путем активации AMPK в нейронах [81–82].
Активирует передачу сигналов инсулина и уменьшает фосфорилирование тау в клеточных линиях нейронов [83].
Индуцирует протеинфосфатазу 2А и снижает фосфорилирование тау в нейронах трансгенной мыши Тау [84].
Ослабляет когнитивные нарушения у мышей с ожирением, устойчивых к лептину [85].
Увеличивает выработку бета-белка амилоида в клеточных моделях человека ( отрицательный эффект ) [86].
Уменьшает риск снижения когнитивных функций у больных диабетом [87].
Улучшает когнитивные функции у пациентов с депрессией [88–89].
Увеличивает риск когнитивных нарушений в исследованиях, проведенных на пациентах с БА ( отрицательный эффект ) [90].
Препараты сульфонилмочевины
Глимепирид защищает нейроны от индуцированной бета-амилоидом дегенерации синапсов in vitro [91].
Гликлазид оказывает антиоксидантное действие на мозг, у крыс с диабетом [92] Глибенкламид уменьшает депрессию и беспокойство у крыс с БА [93]
В сочетании с метформином, снижают риск развития деменции у пациентов с диабетом [94].
Глитазоны
Нейропротективные эффекты при БА, связанные с ингибированием воспаления и отложения Aβ [95].
Пиоглитазон препятствует снижению глиальной активации у мышей с БА [96]
Пиоглитазон усиливает передачу сигналов Akt и гиперфосфорилирование тау у мышей с БА [97].
В сочетании с лептином пиоглитазон снижает уровень амилоида в мозге у мышей с БА [98].
Пиоглитазон улучшает когнитивные функции и регионарный мозговой кровоток у пациентов с СД 2 [99].
Пиоглитазон может обеспечить улучшение когнитивных функций на ранних стадиях и при легких и умеренных проявлениях БА у людей [100].
Агонисты глюкагоноподобного пептида 1
Уменьшают окислительный стресс и апоптоз клеток головного мозга; улучшает синаптическую пластичность у мышей с БА [101].
Влияют на клеточные механизмы нейрональной защиты и митохондриальной функции [102].
Снижение фосфорилирования тау, предотвращение синаптической потери, уменьшение отложения Aβ у мышей с БА [103–104].
Предотвращают снижение метаболизма глюкозы в головном мозге у пациентов с БА [105].
Ингибиторы ДПП-4
Снижение фосфорилирования тау, амилоидной нагрузки и когнитивных нарушений с улучшением памяти [106–107].
Улучшение уровня инкретина, уменьшение отложения Aβ, фосфорилирования тау, активации GSK-3β и АФК [108].
Улучшение контроля глюкозы и предотвращение ухудшения когнитивных функций у пожилых пациентов с СД2 [109].
Инсулин
Ослабляет когнитивные нарушения и улучшает память у взрослых с БА [110–111].
In vitro подавляет апоптоз; in vivo регулирует фосфорилирование тау, метаболизм и клиренс Aβ [112].
Улучшает память, настроение, церебральный метаболизм глюкозы; сохраняет объем мозга у пациентов с БА [113].
Метформин
Метформин — бигуанид, снижает опосредованную инсулином выработку глюкозы в печени, повышает чувствительность к инсулину и представляет собой терапию первой линии при СД2. Он быстро пересекает ГЭБ, распределяется по областям головного мозга [114] и, благодаря активации пути AMPK, по-видимому, оказывает нейропротективное действие на нервные стволовые клетки человека, восстанавливая функции митохондрий и ослабляет эффекты конечных продуктов гликирования [81–82].
Данные о влиянии метформина на нейродегенеративные нарушения противоречивы. В исследованиях in vitro сообщалось о способности метформина снижать фосфорилирование тау в клеточных линиях нейронов [83–84]. Исследования in vivo показали, что у мышей с ожирением, устойчивых к лептину, метформин ослаблял когнитивные нарушения и БА-подобную патологию [85]. Напротив, исследование культуры клеток показало, что метформин увеличивает выработку Aβ [86].
Наблюдательные исследования у лиц с СД2, принимающих метформин, показывают снижение проявлений легкой когнитивной недостаточности (MCI) [87] и деменции [94, 115] по сравнению с плацебо. Длительное лечение метформином, по-видимому, уменьшает риск снижения когнитивных функций у пациентов с диабетом [85] и снижает депрессивные и улучшает когнитивные функции, изменяя метаболизм глюкозы, у пациентов с депрессией [88]. Пилотное клиническое исследование пациентов с MCI в течение 12 месяцев показало, что метформин улучшал когнитивные функции у людей без диабета по сравнению с плацебо [116].
Клиническое исследование, в котором изучалось влияние различных методов лечения СД2 на когнитивные функции, показало, что пациенты с диабетом, которые использовали только метформин, обладали лучшими когнитивными функциями в области словесного обучения, рабочей памяти и исполнительной функции по сравнению с участниками других форм лечения диабета [89].
С другой стороны, повышенный риск когнитивных нарушений и развития БА был продемонстрирован с использованием метформина в исследовании, проведенном на пациентах с БА [90]. Это явление было частично обусловлено дефицитом витамина В12, вызванным метформином. Тем не менее, результаты анализа когнитивных функций, проведенный через 8–10 лет после терапии метформином в рамках исследования результатов программы профилактики диабета (DPPOS) [117], не показали какого-либо негативного влияния от длительного применения метформина.
Планируемые в настоящее время рандомизированные клинические исследования позволят оценить, может ли метформин предотвратить снижение когнитивных функций или улучшить когнитивные функции у людей [118].
Препараты сульфонилмочевины
Препараты сульфонилмочевины — это сахароснижающие препараты, которые стимулируют высвобождение инсулина, блокируя чувствительные к АТФ калиевые каналы бета-клеток поджелудочной железы. In vitro глимепирид защищает нейроны от бета-амилоид-индуцированной дегенерации синапсов [91]. У крыс с диабетом, индуцированным стрептозотоцином, гликлазид оказывал антиоксидантное действие на головной мозг [85]. Кроме того, глибенкламид снижает депрессию и тревожность у крыс с БА [93].
Клиническое проспективное исследование, проведенное в течение 8 лет на пациентах с СД2, показало, что комбинация препаратов сульфонилмочевины и метформина снижала риск развития деменции [94], однако, другое исследование «случай–контроль» показало, что длительное использование препаратов сульфонилмочевины не влияет на риск развития деменции [119].
Для подтверждения потенциальной терапевтической роли этого класса лекарств необходимы дальнейшие исследования.
Тиазолидиндионы (глитазоны)
Тиазолидиндионы (TZD) (пиоглитазон и росиглитазон) являются мощным и селективным стимулятором ядерных гамма-рецепторов, активируемых пролифератором пероксисом (гамма-PPAR), которые улучшают чувствительность к инсулину в мышечной, жировой и печеночной тканях; снижают системную инсулинорезистентность. TZD могут играть роль в улучшении функции нейронов и формировании памяти. Эти препараты показали нейропротекторные эффекты при БА, связанные с ингибированием экспрессии воспалительных генов и изменением образования и отложения Aβ [95].
Пиоглитазон способен проникать в головной мозг, подавляет глиальную активацию и уменьшает клинические проявления БА [96] .
У мышей с БА пиоглитазон, вводимый в течение 4 месяцев, усиливает передачу сигналов Akt, улучшает пространственное обучение и снижает гиперфосфорилирование тау [95] . Кроме того, применение в комбинации с лептином уменьшает дефицит памяти и уровень амилоида в головном мозге [98].
Пилотное исследование пациентов с СД2, получавших пиоглитазон в течение 6 месяцев, показало улучшение когнитивных функций и регионарного мозгового кровотока в теменной доле [99]. Однако 18-месячное исследование пациентов с БА без диабета, направлененое на оценку безопасности пиоглитазона, показало отсутствие влияния на когнитивные функции [120].
Мета-анализ влияния PPAR-гамма-агонистов у пациентов с БА показал, что только пиоглитазон может обеспечить клиническое улучшение на ранних стадиях БА от легкой до умеренной степени [100, 122].
Фаза 3 клинического испытания эффективности пиоглитазона у пациентов с легкими когнитивными нарушениями с использованием алгоритма для оценки генетических биомаркеров для доклинической диагностики, таких как статус APOE и генотипы продолжается. (Идентификатор клинического испытания NCT01931566) . Данные будут доступны в 2020 году.
Агонисты рецепторов глюкагоноподобного пептида-1 (GLP-1)
Другой класс сахароснижающих препаратов — агонисты рецептора GLP-1. GLP-1 представляет собой инкретиновый пептид, секретируемый кишечником, который усиливает глюкозозависимую секрецию инсулина и ингибирует секрецию глюкагона. GLP-1 также обладает трофическими свойствами, такими как стимуляция неогенеза, роста и дифференцировки β-клеток, ингибирование апоптоза β-клеток и повышение выживаемости клеток [122–123].
GLP-1 и большинство аналогов пересекают ГЭБ и рецептор GLP-1 экспрессируется во многих отделах головного мозга, таких, как лобная доля, гипоталамус, таламус, гиппокамп, мозжечок и черная субстанция [124]. GLP-1 играет нейропротекторную роль: в мозге мышей с БА, по-видимому, за счет снижения апоптоза, защиты нейронов от окислительного стресса и синапсов от вредного воздействия пониженной синаптической пластичности в гиппокампе, вызванной Aβ [101]. Нативный GLP-1 имеет короткий период полураспада, поскольку он легко разлагается дипептидилпептидазой-4 (DPP-4). Было разработано несколько более стабильных чем нативный аналогов GLP-1. Среди них эксенатид, лираглутид и ликсисенатид, которые проходят через ГЭБ и, независимо от их влияния на контроль глюкозы, влияют на клеточные пути нейрональной защиты, митохондриальной функции, апоптоза и окислительного стресса [102]. Из-за их нейропротекторных эффектов аналоги GLP-1 были изучены, как потенциальное препараты для лечения БА и других нейродегенеративных расстройств. В исследованиях на мышиной модели БА аналоги GLP-1 снижали гиперфосфорилирование тау нейронов, предотвращали синаптическую потерю, улучшали моторную функцию, улучшали синаптическую пластичность, ослабляли дефицит памяти и обучения и уменьшали количество Aβ в головном мозге [103–104].
Нейропротективные эффекты лираглутида, по-видимому, опосредованы через сигнальный путь PI3K-Akt [125], тогда как эффекты ликсисенатида были отнесены к индуцированным сигнальным путям Akt и MEK [126].
Пилотное клиническое исследование показало, что 6-месячное лечение пациентов с БА лираглутидом предотвращает снижение метаболизма глюкозы в мозге, что уменьшает риск прогрессирования заболевания [105]. Другие исследования, оценивающие эффективность у пациентов с БА аналогов GLP-1, продолжаются.
Разумеется, аналоги GLP-1 имеют то преимущество, что не влияют на уровень сахара в крови у людей, не страдающих диабетом, и поэтому могут представлять потенциальное безопасное лечение БА или других нейродегенеративных состояний также у пациентов без СД2.
Ингибиторы дипептидилпептидазы-4 (DPP-4)
DPP-4 являются сахароснижающими препаратами, которые, ингибируют DPP-4 — протеолитический фермент, ответственный за деградацию GLP-1, продлевают период его полужизни в плазме, стабилизируя его уровень и вызывая функциональное усиление его сахароснижающего эффекта. Ингибиторы DPP-4 показали нейропротективные эффекты, которые могут быть частично опосредованы эффектами GLP-1 в мозге.
На моделях животных с БА лечение ингибиторами DPP-4 (саксаглиптин, вилдаглиптин, ситаглиптин) снижает фосфорилирование тау, амилоидную нагрузку и маркеры воспаления, также устраняет когнитивный дефицит с улучшением памяти [106–107].
В нейрональных клетках человека линаглиптин снижает отложение Aβ, гиперфосфорилирование тау, предотвращает активацию GSK3β и ослабляет внутриклеточную продукцию ROS, стимулируя передачу сигнала 5’АМФ-активируемой протеинкиназы (AMPK) -Sirt1 [108]. Все эти эффекты способствуют улучшению когнитивных функций.
У пожилых пациентов, страдающих СД2 и умеренными когнитивными нарушениями, лечение ингибитором DPP-4 улучшает контроль глюкозы и предотвращает ухудшение когнитивных функций [109]. Также в проспективном клиническом исследовании, оценивающем 6-месячное лечение ситаглиптином у пожилых пациентов с СД2, сообщалось об улучшении когнитивной функции [127].
Инсулин
Инсулин оказывает несколько воздействий на мозг в отношении познания, обучения, памяти и синаптической пластичности, возможно, вовлекая сложный путь инсулиновой сигнальной системы головного мозга / IR. Введение инсулина замедляет снижение когнитивных функций [110, 128–129] и улучшает память у взрослых с БА [111]. Однако системное введение инсулина характеризуется низким проникновением в головной мозг и повышенным риском гипогликемии. По этим причинам в нескольких клинических исследованиях было проведено изучение интраназального введения инсулина. После интраназального введения инсулин, минуя ГЭБ, достигает биологически значимых концентраций в мозге [111]. In vitro инсулин ингибирует апоптоз нейронов посредством активации протеинкиназы B и in vivo регулирует фосфорилирование тау, метаболизм белка-предшественника Aβ и клиренс Aβ [112].
Интраназальное введение инсулина улучшает память и настроение у здоровых взрослых, а также у пациентов с умеренными когнитивными нарушениями и поздним началом БА, у которых улучшается церебральный метаболизм глюкозы и сохраняется объем областей мозга [113]. Терапевтическое воздействие инсулина на ЦНС зависит от его дозы и модулируется генотипом APOE, сильным генетическим предиктором развития БА [111].
Выводы
В настоящее время признано, что инсулин может оказывать важное влияние на работу головного мозга.
Изменения метаболизма и передачи сигналов инсулина могут способствовать развитию нейродегенеративных заболеваний, таких как БА.
Ряд исследований in vivo и in vitro подтверждают тесную связь между СД2 и нейродегенеративными процессами в головном мозге и предполагают потенциальную терапевтическую роль некоторых сахароснижающих препаратов в профилактике и лечении БА. Однако не полная изученность этих вопросов диктует необходимость дальнейших исследований.
Список литературы Инсулин, головной мозг, болезнь Альцгеймера: новые данные
- Романчук П. И. Возраст и микробиота: эпигенетическая и диетическая защита, эндотелиальная и сосудистая реабилитация, новая управляемая здоровая биомикробиота // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №2. С. 67-110. DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/51/07
- Романчук П. И., Волобуев А. Н. Современные инструменты и методики эпигенетической защиты здорового старения и долголетия Homo sapiens // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №1. С. 43-70. DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/50/06
- Сухов И. Б. Нарушения гормональной регуляции аденилатциклазной системы в мозге крыс с сахарным диабетом и их коррекция с помощью интраназально вводимых инсулина и серотонина: автореф. дис.. канд. биол. наук. Санкт-Петербург, 2016.
- Булгакова С. В., Романчук П. И., Волобуев А. Н. Нейросети: нейроэндокринология и болезнь Альцгеймера // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2019. Т. 5. №6. С. 112-128. DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/43/16
- Булгакова С. В., Романчук П. И., Волобуев А. Н. Клинико-биофизические принципы лечения сосудистой деменции и болезни Альцгеймера // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2019. Т. 5. №5. С. 57-72. DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/42/08
- Tumminia A. et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease: role of insulin signalling and therapeutic implications // International journal of molecular sciences. 2018. V. 19. №11. P. 3306.
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19113306
- Волобуев А. Н., Романчук П. И., Булгакова С. В. Нейросеть "мозг-микробиота": регуляция "висцерального" мозга и накопление когнитивной памяти // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2019. Т. 5. №2. С. 33-52.
- DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/39/05
- Волобуев А. Н., Пятин В. Ф., Романчук Н. П., Булгакова С. В. Давыдкин И. Л. Когнитивная дисфункция при перевозбуждении структур головного мозга // ВРАЧ. 2018. T. 29. №9. С. 17-20.
- DOI: 10.29296/25877305-2018-09-04
- Волобуев А. Н., Романчук П. И., Романчук Н. П., Давыдкин И. Л., Булгакова С. В. Нарушение памяти при болезни Альцгеймера // ВРАЧ. 2019. T.30. №6. С. 10-13.
- DOI: 10.29296/25877305-2019-06-02
- Chiu S. L., Chen C. M., Cline H. T. Insulin receptor signaling regulates synapse number, dendritic plasticity, and circuit function in vivo // Neuron. 2008. V. 58. №5. P. 708-719.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.014
- Apostolatos A. et al. Insulin promotes neuronal survival via the alternatively spliced protein kinase CδII isoform // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2012. V. 287. №12. P. 9299-9310.
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.313080
- Kleinridders A. et al. Insulin action in brain regulates systemic metabolism and brain function // Diabetes. 2014. V. 63. №7. P. 2232-2243.
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-0568
- Biessels G. J. et al. Dementia and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes and prediabetic stages: towards targeted interventions // The lancet Diabetes & endocrinology. 2014. V. 2. №3. P. 246-255.
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(13)70088-3
- Vigneri R., Goldfine I. D., Frittitta L. Insulin, insulin receptors, and cancer // Journal of endocrinological investigation. 2016. V. 39. №12. P. 1365-1376.
- DOI: 10.1007/s40618-016-0508-7
- Derakhshan F., Toth C. Insulin and the brain // Current diabetes reviews. 2013. V. 9. №2. P. 102-116.
- DOI: 10.2174/157339913805076454
- Woods S. C. et al. Insulin and the blood-brain barrier //Current pharmaceutical design. 2003. V. 9. №10. P. 795.
- DOI: 10.2174/1381612033455323
- Martins J. P. et al. Communication from the periphery to the hypothalamus through the blood-brain barrier: an in vitro platform // International journal of pharmaceutics. 2016. V. 499. №1-2. P. 119-130.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.12.058
- Devaskar S. U. et al. Insulin gene expression and insulin synthesis in mammalian neuronal cells // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994. V. 269. №11. P. 8445-8454.
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12866
- Pomytkin I. et al. Insulin receptor in the brain: Mechanisms of activation and the role in the CNS pathology and treatment // CNS neuroscience & therapeutics. 2018. V. 24. №9. P. 763-774.
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12866
- Belfiore A. et al. Insulin receptor isoforms in physiology and disease: an updated view // Endocrine reviews. 2017. V. 38. №5. P. 379-431.
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2017-00073
- Belfiore A. et al. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease // Endocrine reviews. 2009. V. 30. №6. P. 586-623.
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2008-0047
- Hölscher C. New drug treatments show neuroprotective effects in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases // Neural regeneration research. 2014. V. 9. №21. P. 1870.
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.145342
- Akintola A. A., van Heemst D. Insulin, aging, and the brain: mechanisms and implications // Frontiers in endocrinology. 2015. V. 6. P. 13.
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2015.00013
- Numan S., Russell D. S. Discrete expression of insulin receptor substrate-4 mRNA in adult rat brain // Molecular brain research. 1999. V. 72. №1. P. 97-102.
- DOI: 10.1016/S0169-328X(99)00160-6
- Araki E. et al. Signalling in mice with targeted disruption // Nature. 1994. V. 372. №1. P. 186-90.
- Schubert M. et al. Insulin receptor substrate-2 deficiency impairs brain growth and promotes tau phosphorylation // Journal of Neuroscience. 2003. V. 23. №18. P. 7084-7092.
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-18-07084.2003
- Taguchi A., Wartschow L. M., White M. F. Brain IRS2 signaling coordinates life span and nutrient homeostasis // Science. 2007. V. 317. №5836. P. 369-372.
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1142179
- Sadagurski M. et al. Irs2 and Irs4 synergize in non-LepRb neurons to control energy balance and glucose homeostasis // Molecular metabolism. 2014. V. 3. №1. P. 55-63.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2013.10.004
- Brüning J. C. et al. Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction // Science. 2000. V. 289. №5487. P. 2122-2125.
- DOI: 10.1126/science.289.5487.2122
- Bomfim T. R. et al. An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer's disease-associated Aβ oligomers // The Journal of clinical investigation. 2012. V. 122. №4. P. 1339-1353.
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI57256
- Talbot K. et al. Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline // The Journal of clinical investigation. 2012. V. 122. №4. P. 1316-1338.
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI59903
- Denver P., English A., McClean P. L. Inflammation, insulin signaling and cognitive function in aged APP/PS1 mice // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2018. V. 70. P. 423-434.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.03.032
- Boucher J., Kleinridders A., Kahn C. R. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states // Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology. 2014. V. 6. №1. P. a009191.
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009191
- Cho N. H. et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045 // Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2018. V. 138. P. 271-281.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.023
- Pugazhenthi S., Qin L., Reddy P. H. Common neurodegenerative pathways in obesity, diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease // Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease. 2017. V. 1863. №5. P. 1037-1045.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.04.017
- Reitz C., Mayeux R. Alzheimer disease: epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers // Biochemical pharmacology. 2014. V. 88. №4. P. 640-651.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.024
- Anor C. J. et al. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer disease, vascular dementia, and mixed dementia // Neurodegenerative Diseases. 2017. V. 17. №4-5. P. 127-134.
- DOI: 10.1159/000455127
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G. The amyloid cascade-inflammatory hypothesis of Alzheimer disease: implications for therapy // Acta neuropathologica. 2013. V. 126. №4. P. 479-497.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-013-1177-7
- Wright A. L. et al. Neuroinflammation and neuronal loss precede Aβ plaque deposition in the hAPP-J20 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease // PloS one. 2013. V. 8. №4.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059586
- Li J. et al. Effects of diabetes mellitus on cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer disease: a systematic review // Canadian journal of diabetes. 2017. V. 41. №1. P. 114-119.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2016.07.003
- Sripetchwandee J., Chattipakorn N., Chattipakorn S. C. Links between obesity-induced brain insulin resistance, brain mitochondrial dysfunction, and dementia // Frontiers in endocrinology. 2018. V. 9. P. 496.
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00496
- Diaz A., Escobedo C., Treviño S., Chávez R., Lopez-Lopez G., Moran C.,.. Muñoz-Arenas G. Metabolic syndrome exacerbates the recognition memory impairment and oxidative-inflammatory response in rats with an intrahippocampal injection of amyloid beta // Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity. 2018. P. 1-42.
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1358057
- Treviño S. et al. A high calorie diet causes memory loss, metabolic syndrome and oxidative stress into hippocampus and temporal cortex of rats // Synapse. 2015. V. 69. №9. P. 421-433.
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.21832
- Pierce A. L., Bullain S. S., Kawas C. H. Late-onset Alzheimer disease // Neurologic clinics. 2017. V. 35. №2. P. 283-293.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncl.2017.01.006
- Yin F. et al. Energy metabolism and inflammation in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease // Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2016. V. 100. P. 108-122.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.04.200
- Denver P., McClean P. L. Distinguishing normal brain aging from the development of Alzheimer's disease: inflammation, insulin signaling and cognition // Neural regeneration research. 2018. V. 13. №10. P. 1719.
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.238608
- Frölich L. et al. Brain insulin and insulin receptors in aging and sporadic Alzheimer's disease // Journal of neural transmission. 1998. V. 105. №4-5. P. 423-438.
- DOI: 10.1007/s007020050068
- Ratzmann K. P., Hampel R. Glucose and insulin concentration patterns in cerebrospinal fluid following intravenous glucose injection in humans // Endokrinologie. 1980. V. 76. №2. P. 185-188. PMID:
- ISBN: 7004864
- Querfurth H. W., LaFerla F. M. Mechanisms of disease // N Engl J Med. 2010. V. 362. №4. P. 329-344.
- Suzanne M. Insulin resistance and neurodegeneration: progress towards the development of new therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease // Drugs. 2017. V. 77. №1. P. 47-65.
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-016-0674-0
- Gabuzda D. et al. Inhibition of energy metabolism alters the processing of amyloid precursor protein and induces a potentially amyloidogenic derivative // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994. V. 269. №18. P. 13623-13628.
- Gasparini L. et al. Stimulation of β-amyloid precursor protein trafficking by insulin reduces intraneuronal β-amyloid and requires mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling // Journal of Neuroscience. 2001. V. 21. №8. P. 2561-2570.
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-08-02561.2001
- Nisbet R. M. et al. Tau aggregation and its interplay with amyloid-β // Acta neuropathologica. 2015. V. 129. №2. P. 207-220.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-014-1371-2
- Zimbone S. et al. Amyloid Beta monomers regulate cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein functions by activating type-1 insulin-like growth factor receptors in neuronal cells // Aging cell. 2018. V. 17. №1. P. e12684.
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12684
- Ling X. et al. Amyloid beta antagonizes insulin promoted secretion of the amyloid beta protein precursor // Journal of Alzheimer's disease. 2002. V. 4. №5. P. 369-374.
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-2002-4504
- Zhao W. Q. et al. Amyloid beta oligomers induce impairment of neuronal insulin receptors // The FASEB Journal. 2008. V. 22. №1. P. 246-260.
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.06-7703com
- Ma Q. L. et al. β-amyloid oligomers induce phosphorylation of tau and inactivation of insulin receptor substrate via c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling: suppression by omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin // Journal of Neuroscience. 2009. V. 29. №28. P. 9078-9089.
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1071-09.2009
- Schubert M. et al. Role for neuronal insulin resistance in neurodegenerative diseases // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2004. V. 101. №9. P. 3100-3105.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0308724101
- Vandal M. et al. Insulin reverses the high-fat diet-induced increase in brain Aβ and improves memory in an animal model of Alzheimer disease // Diabetes. 2014. V. 63. №12. P. 4291-4301.
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-0375
- Farris W. et al. Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid β-protein, and the β-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2003. V. 100. №7. P. 4162-4167.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0230450100
- Ittner L. M. et al. Dendritic function of tau mediates amyloid-β toxicity in Alzheimer's disease mouse models // Cell. 2010. V. 142. №3. P. 387-397.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.036
- Hong M., Lee V. M. Y. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 regulate tau phosphorylation in cultured human neurons // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997. V. 272. №31. P. 19547-19553.
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.272.40.25326
- Bhat R. et al. Structural insights and biological effects of glycogen synthase kinase 3-specific inhibitor AR-A014418 // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2003. V. 278. №46. P. 45937-45945.
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M306268200
- Freude S. et al. Peripheral hyperinsulinemia promotes tau phosphorylation in vivo // Diabetes. 2005. V. 54. №12. P. 3343-3348.
- DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.54.12.3343
- Cheng C. M. et al. Tau is hyperphosphorylated in the insulin-like growth factor-I null brain // Endocrinology. 2005. V. 146. №12. P. 5086-5091.
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2005-0063
- Phiel C. J. et al. GSK-3α regulates production of Alzheimer's disease amyloid-β peptides // Nature. 2003. V. 423. №6938. P. 435-439.
- DOI: 10.1038/nature01640
- Sims-Robinson C. et al. How does diabetes accelerate Alzheimer disease pathology? // Nature Reviews Neurology. 2010. V. 6. №10. P. 551.
- DOI: 10.1038/nrneurol.2010.130
- De la Monte S. M. et al. Neuronal thread protein regulation and interaction with microtubule-associated proteins in SH-Sy5y neuronal cells // Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences CMLS. 2003. V. 60. №12. P. 2679-2691.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-003-3305-3
- Bedse G. et al. Aberrant insulin signaling in Alzheimer's disease: current knowledge // Frontiers in neuroscience. 2015. V. 9. P. 204.
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00204
- Zlokovic B. V. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and other disorders // Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2011. V. 12. №12. P. 723-738.
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn3114
- Kahn A. M. et al. Insulin Acutely Inhibits Cultured Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Contraction by a Nitric Oxide Synthase-Dependent Pathway // Hypertension. 1997. V. 30. №4. P. 928-933.
- DOI: 10.1161/01.HYP.30.4.928
- Bhamra M. S., Ashton N. J. Finding a pathological diagnosis for A lzheimer's disease: Are inflammatory molecules the answer? // Electrophoresis. 2012. V. 33. №24. P. 3598-3607.
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201200161
- Mushtaq G. et al. Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes via chronic inflammatory mechanisms // Saudi journal of biological sciences. 2015. V. 22. №1. P. 4-13.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2014.05.003
- Fishel M. A. et al. Hyperinsulinemia provokes synchronous increases in central inflammation and β-amyloid in normal adults // Archives of neurology. 2005. V. 62. №10. P. 1539-1544.
- DOI: 10.1001/archneur.62.10.noc50112
- Sokolova A. et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 plays a dominant role in the chronic inflammation observed in Alzheimer's disease // Brain pathology. 2009. V. 19. №3. P. 392-398.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00188.x
- Nakamura M., Watanabe N. Ubiquitin-like protein MNSFβ/endophilin II complex regulates Dectin-1-mediated phagocytosis and inflammatory responses in macrophages // Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2010. V. 401. №2. P. 257-261.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.09.045
- Akash M. S. H., Rehman K., Chen S. Role of inflammatory mechanisms in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus // Journal of cellular biochemistry. 2013. V. 114. №3. P. 525-531.
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.24402
- Erickson M. A., Hansen K., Banks W. A. Inflammation-induced dysfunction of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 at the blood-brain barrier: protection by the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2012. V. 26. №7. P. 1085-1094.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.07.003
- Matrone C. et al. Inflammatory risk factors and pathologies promoting Alzheimer's disease progression: is RAGE the key // Histology and histopathology. 2015. V. 30. №2. P. 125-139.
- Münch G. et al. Alzheimer's disease-synergistic effects of glucose deficit, oxidative stress and advanced glycation endproducts // Journal of neural transmission. 1998. V. 105. №4-5. P. 439-461.
- DOI: 10.1007/s007020050069
- Deane R. et al. RAGE mediates amyloid-β peptide transport across the blood-brain barrier and accumulation in brain // Nature medicine. 2003. V. 9. №7. P. 907-913.
- DOI: 10.1038/nm890
- Chiang M. C. et al. Metformin activation of AMPK-dependent pathways is neuroprotective in human neural stem cells against Amyloid-beta-induced mitochondrial dysfunction // Experimental cell research. 2016. V. 347. №2. P. 322-331.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.08.013
- Chung M. M. et al. The neuroprotective role of metformin in advanced glycation end product treated human neural stem cells is AMPK-dependent // Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease. 2015. V. 1852. №5. P. 720-731.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.01.006
- Gupta A., Bisht B., Dey C. S. Peripheral insulin-sensitizer drug metformin ameliorates neuronal insulin resistance and Alzheimer's-like changes // Neuropharmacology. 2011. V. 60. №6. P. 910-920.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.033
- Kickstein E. et al. Biguanide metformin acts on tau phosphorylation via mTOR/protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) signaling // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2010. V. 107. №50. P. 21830-21835.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912793107
- Li J. et al. Metformin attenuates Alzheimer's disease-like neuropathology in obese, leptin-resistant mice // Pharmacology biochemistry and behavior. 2012. V. 101. №4. P. 564-574.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.03.002
- Chen Y. et al. Antidiabetic drug metformin (GlucophageR) increases biogenesis of Alzheimer's amyloid peptides via up-regulating BACE1 transcription // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2009. V. 106. №10. P. 3907-3912.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0807991106
- Ng T. P. et al. Long-term metformin usage and cognitive function among older adults with diabetes // Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2014. V. 41. №1. P. 61-68.
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-131901
- Guo M. et al. Metformin may produce antidepressant effects through improvement of cognitive function among depressed patients with diabetes mellitus // Clinical and experimental pharmacology and physiology. 2014. V. 41. №9. P. 650-656.
- DOI: 10.1111/1440-1681.12265
- Herath P. M. et al. The effect of diabetes medication on cognitive function: evidence from the PATH through life study // BioMed research international. 2016. V. 2016.
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/7208429
- Moore E. M. et al. Increased risk of cognitive impairment in patients with diabetes is associated with metformin // Diabetes care. 2013. V. 36. №10. P. 2981-2987.
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-0229
- Osborne C. et al. Glimepiride protects neurons against amyloid-β-induced synapse damage // Neuropharmacology. 2016. V. 101. P. 225-236.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.09.030
- Alp H. et al. Protective effects of beta glucan and gliclazide on brain tissue and sciatic nerve of diabetic rats induced by streptozosin // Experimental diabetes research. 2012. V. 2012.
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/230342
- Esmaeili M. H., Bahari B., Salari A. A. ATP-sensitive potassium-channel inhibitor glibenclamide attenuates HPA axis hyperactivity, depression-and anxiety-related symptoms in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease // Brain research bulletin. 2018. V. 137. P. 265-276.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.01.001
- Hsu C. C. et al. Incidence of dementia is increased in type 2 diabetes and reduced by the use of sulfonylureas and metformin // Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2011. V. 24. №3. P. 485-493.
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-2011-101524
- Landreth G. Therapeutic use of agonists of the nuclear receptor PPARγ in Alzheimer's disease // Current Alzheimer Research. 2007. V. 4. №2. P. 159-164.
- DOI: 10.2174/156720507780362092
- Heneka M. T. et al. Acute treatment with the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone and ibuprofen reduces glial inflammation and Aβ1-42 levels in APPV717I transgenic mice // Brain. 2005. V. 128. №6. P. 1442-1453.
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awh452
- Yu Y. et al. Insulin sensitizers improve learning and attenuate tau hyperphosphorylation and neuroinflammation in 3xTg-AD mice // Journal of neural transmission. 2015. V. 122. №4. P. 593-606.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00702-014-1294-z
- Fernandez-Martos C. M. et al. Combination treatment with leptin and pioglitazone in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease // Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions. 2017. V. 3. №1. P. 92-106.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2016.11.002
- Sato T. et al. Efficacy of PPAR-γ agonist pioglitazone in mild Alzheimer disease // Neurobiology of aging. 2011. V. 32. №9. P. 1626-1633.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.10.009
- Cheng H. et al. The peroxisome proliferators activated receptor-gamma agonists as therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis // International Journal of Neuroscience. 2016. V. 126. №4. P. 299-307.
- DOI: 10.3109/00207454.2015.1015722
- Hölscher C. The role of GLP-1 in neuronal activity and neurodegeneration // Vitamins & Hormones. Academic Press, 2010. V. 84. P. 331-354.
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381517-0.00013-8
- Hunter K., Hölscher C. Drugs developed to treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis // BMC neuroscience. 2012. V. 13. №1. P. 33.
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-33
- McClean P. L., Hölscher C. Liraglutide can reverse memory impairment, synaptic loss and reduce plaque load in aged APP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer's disease // Neuropharmacology. 2014. V. 76. P. 57-67.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.005
- Hansen H. H. et al. The GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide reduces pathology-specific tau phosphorylation and improves motor function in a transgenic hTauP301L mouse model of tauopathy // Brain research. 2016. V. 1634. P. 158-170.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.052
- Gejl M. et al. In Alzheimer's disease, 6-month treatment with GLP-1 analog prevents decline of brain glucose metabolism: randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial // Frontiers in aging neuroscience. 2016. V. 8. P. 108.
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00108
- Kosaraju J. et al. Saxagliptin: a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor ameliorates streptozotocin induced Alzheimer's disease // Neuropharmacology. 2013. V. 72. P. 291-300.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.008
- Kosaraju J. et al. Vildagliptin: an anti-diabetes agent ameliorates cognitive deficits and pathology observed in streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer's disease // Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2013. V. 65. №12. P. 1773-1784.
- DOI: 10.1111/jphp.12148
- Kornelius E. et al. DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin attenuates Aβ-induced cytotoxicity through activation of AMPK in neuronal cells // CNS neuroscience & therapeutics. 2015. V. 21. №7. P. 549-557.
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12404
- Rizzo M. R. et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors have protective effect on cognitive impairment in aged diabetic patients with mild cognitive impairment // Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2014. V. 69. №9. P. 1122-1131.
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glu032
- Kern W. et al. Improving influence of insulin on cognitive functions in humans // Neuroendocrinology. 2001. V. 74. №4. P. 270-280.
- DOI: 10.1159/000054694
- Freiherr J. et al. Intranasal insulin as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease: a review of basic research and clinical evidence // CNS drugs. 2013. V. 27. №7. P. 505-514.
- DOI: 10.1007/s40263-013-0076-8
- Plum L., Schubert M., Brüning J. C. The role of insulin receptor signaling in the brain // Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2005. V. 16. №2. P. 59-65.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2005.01.008
- Craft S. et al. Effects of regular and long-acting insulin on cognition and Alzheimer's disease biomarkers: a pilot clinical trial // Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2017. V. 57. №4. P. 1325-1334.
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-161256
- Łabuzek K. et al. Quantification of metformin by the HPLC method in brain regions, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of rats treated with lipopolysaccharide // Pharmacological Reports. 2010. V. 62. №5. P. 956-965.
- DOI: 10.1016/S1734-1140(10)70357-1
- Cheng C. et al. Type 2 diabetes and antidiabetic medications in relation to dementia diagnosis // Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2014. V. 69. №10. P. 1299-1305.
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glu073
- Luchsinger J. A. et al. Metformin in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: results of a pilot randomized placebo controlled clinical trial // Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2016. V. 51. №2. P. 501-514.
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-150493
- Luchsinger J. A. et al. Metformin, lifestyle intervention, and cognition in the diabetes prevention program outcomes study // Diabetes care. 2017. V. 40. №7. P. 958-965.
- DOI: 10.2337/dc16-2376
- Valencia W. M. et al. Metformin and ageing: improving ageing outcomes beyond glycaemic control // Diabetologia. 2017. V. 60. №9. P. 1630-1638.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4349-5
- Imfeld P. et al. Metformin, other antidiabetic drugs, and risk of Alzheimer's disease: a population-based case-control study // Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2012. V. 60. №5. P. 916-921.
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.03916.x
- Geldmacher D. S. et al. A randomized pilot clinical trial of the safety of pioglitazone in treatment of patients with Alzheimer disease // Archives of neurology. 2011. V. 68. №1. P. 45-50.
- DOI: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.229
- Femminella G. D. et al. Antidiabetic drugs in Alzheimer's disease: Mechanisms of action and future perspectives // Journal of diabetes research. 2017. V. 2017.
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7420796
- Nauck M. A. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in the treatment of diabetes // Hormone and metabolic research. 2004. V. 36. №11/12. P. 852-858.
- DOI: 10.1055/s-2004-826175
- Drucker D. J. et al. Incretin-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: evaluation of the risks and benefits // Diabetes care. 2010. V. 33. №2. P. 428-433.
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-1499
- Cork S. C. et al. Distribution and characterization of Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor expressing cells in the mouse brain // Molecular metabolism. 2015. V. 4. №10. P. 718-731.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.07.008
- Liu X. Y. et al. Liraglutide prevents beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells via a PI3K-dependent signaling pathway // Neurological research. 2016. V. 38. №4. P. 313-319.
- DOI: 10.1080/01616412.2016.1145914
- Cai H. Y. et al. Lixisenatide attenuates the detrimental effects of amyloid β protein on spatial working memory and hippocampal neurons in rats // Behavioural brain research. 2017. V. 318. P. 28-35.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.10.033
- Isik A. T. et al. The effects of sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, on cognitive functions in elderly diabetic patients with or without Alzheimer's disease // Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2017. V. 123. P. 192-198.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.12.010
- Shingo A. S. et al. Intracerebroventricular administration of an insulin analogue recovers STZ-induced cognitive decline in rats // Behavioural brain research. 2013. V. 241. P. 105-111.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.12.005


