Intellectual agility: a toolkit of varied techniques for critical thinking
Автор: Oripova N., Rakhmatova D.
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Педагогические науки
Статья в выпуске: 5 т.10, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article describes the essence of critical thinking, the existence of various tools for developing critical thinking, and the need to use a set of techniques to deeply understand and learn these tools, as well as the ways and conditions of their implementation. Also, in this article, several practical examples and manuals are presented to further develop critical thinking, to be able to use a wide range of techniques, and to be able to appropriately use the various critical thinking tools cited as examples, some of which are presented in pictures and test views.
Critical, critical thinking, factors, techniques, guides, critical questions, tools, digital resources
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14130142
IDR: 14130142 | УДК: 372.3 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/102/78
Текст научной статьи Intellectual agility: a toolkit of varied techniques for critical thinking
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
UDC 372.3
In an era where information overload and rapid technological advancements characterize our daily lives, the ability to think critically has become an indispensable skill. Critical thinking enables individuals to navigate complex issues, discern truth from misinformation, and make well-informed decisions. However, the landscape of critical thinking is not static; it demands intellectual agility— the capacity to adapt and deploy a diverse array of techniques tailored to different contexts and challenges [1].
This article delves into the concept of intellectual agility as a cornerstone of effective critical thinking. It emphasizes the importance of embracing varied techniques to enhance cognitive flexibility, problem-solving abilities, and decision-making processes. By cultivating intellectual
(ос) ® agility, individuals can navigate the nuances of modern-day problems with confidence and creativity [2, 3].
Through a comprehensive exploration of diverse methodologies—from logical reasoning and analytical thinking to creative problem-solving and interdisciplinary approaches—this article illuminates the multifaceted nature of critical thinking. It underscores the importance of recognizing that no single approach suffices for all situations, advocating instead for a dynamic and adaptive mindset that embraces a spectrum of tools and strategies [4, 5].
As we embark on this journey of discovery, we invite readers to delve deeper into the realm of intellectual agility and critical thinking. By unpacking innovative techniques and practical insights, we aim to empower individuals to harness their cognitive potential and thrive in an increasingly complex and interconnected world [6, 7].
Material and research methods
This article synthesizes a comprehensive array of scholarly literature, practical resources, and empirical studies to explore the concept of intellectual agility within the framework of critical thinking. Drawing upon multidisciplinary perspectives from fields such as psychology, education, cognitive science, and philosophy, the research methodology employed herein encompasses a thorough review and analysis of existing literature, supplemented by practical insights and examples. A systematic search of academic databases, including but not limited to PubMed, PsycINFO, ERIC, and Google Scholar, was conducted to identify relevant peer-reviewed articles, books, and research papers. Keywords such as "intellectual agility," "critical thinking," "cognitive flexibility," "problem-solving," and "decision-making" were utilized to refine search parameters and ensure the inclusion of pertinent literature.
In addition to academic sources, this article also incorporates insights from reputable online resources, educational platforms, and expert opinions to provide a holistic perspective on the topic. Digital resources such as online courses, interactive tutorials, and cognitive assessment tools were evaluated for their relevance and applicability in fostering intellectual agility and enhancing critical thinking skills.
Furthermore, practical exercises and examples were curated from a diverse range of sources, including educational institutions, professional development programs, and industry publications. These exercises were selected based on their effectiveness in stimulating cognitive engagement, promoting analytical reasoning, and facilitating creative problem-solving. By synthesizing insights from diverse sources and disciplines, this article aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of intellectual agility and its role in cultivating critical thinking skills. Through a rigorous review of the literature and practical examples, this research methodology endeavours to elucidate the multifaceted nature of critical thinking and empower individuals to harness the power of intellectual agility in their personal and professional lives.
Critical thinking is a system of reasoning used to analyze things and information, interpret events, evaluate events, and then draw objective conclusions.
A person with developed critical thinking shows a whole set of necessary skills, namely: the ability to observe and justify one's point of view, to pay attention to the study of information, and to apply analytical skills in various situations [8, 9].
To acquire the above necessary skills, an individual can apply practical processes using various techniques and tools. It is not an exaggeration to say that several techniques will indirectly help in this. For example: Identify the topic under discussion and learn why the discussion is important; In the process of reasoning, errors are identified and evaluated with evidence; Inaccuracy is explained or understood and accounted for; Technologies are used; Clear, reliable, critical writing is carried out on the discussed topic.
Several practical tasks such as BuzzFeed, ASMR video, Talk Critical Thinking test, and Smart Study can be used to implement these processes. Practical tools like these help us think critically and technically and enrich our productivity on the topic we are considering.
At this point, the question may arise: "Why do we need to engage in critical thinking and critical thinking?". We will answer this question instead. Guess we wouldn't get very far if we took everything at face value. In other words, if we believe everyone's lies or unproven conclusions as well as the truth, or if we react to events interpreted as fakes, we would be in a state of confusion, deception, and manipulation [10].
The art of critical thinking is not about changing human nature or pretending that we should always act rationally. It means learning to recognize ourselves and others, knowing our limitations and when to pause, think, and reach for the right questions to figure out what's going on. Critical thinking skills can be useful in any area of our lives - for children and teenagers as well as for adults. A person with critical thinking skills can: understand logical and causal relationships between different ideas and concepts; quickly analyze and evaluate the opinions of others; correctly form their arguments and communicate them to others; attention to inconsistencies and common errors in logic and argumentation; note the importance and relevance of ideas to the general context; evaluate in a way that reflects one's views and beliefs.
“Is it easy for you to make connections between ideas and notice inconsistencies in your interlocutor's arguments? If so, congratulations: you're a critical thinker. What is this and what does GLOBUC have to do with it," says Nikita Nepryakhin [4].
Nikita Nepryakhin explains what is the essence of critical thinking and "What is critical thinking?" To better answer that question, GLOBUC has developed a system of six requirements. G — flexible thinking; L — logical presentation; O — informed judgments; B — unbiased approach; U — ordered points; S — independent thinking.
It is no exaggeration to say that this GLOBUC system, designed for the development of critical thinking, is an encouraging guide to true critical thinking. We will get to know the GLOBUC system developed by Nikita Nepryakhin in more depth in our next articles.
In addition, there are several practical processes for identifying and developing critical thinking skills. For example:
Task 1: Look at the picture. What about the dimensions of the segments?

A) they are the same; B) the first one is longer; D) the second one is longer.
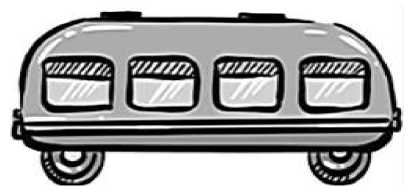
Task 2: Your friend drew a picture of a bus. Can you tell which direction it is going
A) To the right; B) To the left.
Task 3: What is missing from this list?
A) Throwing; B) Shooting; D) Kicking; E) Spread; F) Abandonment.
Task 4: A new chocolate ad will make you a series of offers. Which can be considered a noteworthy fact?
A) Great taste; B) Contains hazelnut, milk and caramel; D) Incomparable pleasure;E) Favorite chocolate of all top athletes.
Results and discussion
There are many such tasks. All of these are aimed at developing critical thinking and thinking, which can result in effective critical observation. Fostering intellectual agility within the realm of critical thinking yields a myriad of benefits, empowering individuals to navigate complex challenges, make sound decisions, and adapt to changing circumstances. Through the application of varied techniques and approaches, individuals develop a versatile toolkit that enhances their cognitive flexibility and problem-solving capabilities.
One of the key outcomes of cultivating intellectual agility is the ability to approach problems from multiple perspectives. By embracing diverse methodologies such as logical reasoning, creative thinking, and systems analysis, individuals gain a more comprehensive understanding of complex issues. This holistic perspective enables them to identify underlying patterns, anticipate potential obstacles, and devise innovative solutions.
Moreover, intellectual agility fosters adaptability in the face of uncertainty. In today's rapidly evolving world, the ability to pivot and adjust strategies is paramount. By honing skills such as critical reflection, adaptive thinking, and scenario planning, individuals become better equipped to navigate unforeseen challenges and seize emerging opportunities.
Furthermore, fostering intellectual agility fosters resilience in the face of adversity. The ability to quickly assess situations, identify viable alternatives, and make informed decisions is essential for overcoming obstacles and achieving goals. By integrating techniques such as risk assessment, decision analysis, and problem-solving, individuals develop the resilience needed to persevere in the face of setbacks. Additionally, intellectual agility promotes continuous learning and growth. By embracing a mindset of curiosity, experimentation, and self-reflection, individuals expand their knowledge base, refine their skills, and adapt to evolving circumstances. This commitment to lifelong learning enables individuals to stay ahead of the curve in an ever-changing world.
Overall, fostering intellectual agility within the context of critical thinking is essential for success in today's dynamic environment. By equipping individuals with a diverse toolkit of techniques and approaches, intellectual agility empowers them to navigate complexity, seize opportunities, and achieve their full potential. As we continue to explore and cultivate intellectual agility, we pave the way for a more innovative, resilient, and adaptable future.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the amalgamation of digital resources and practical exercises presented in this discourse serves as a robust arsenal for honing critical thinking and writing skills, particularly in an era inundated with information. Whether embarking on a maiden academic journey or navigating the complexities of adult life on a global scale, the cultivation of critical thinking equips individuals with invaluable competencies, comprehension, and self-assurance essential for success.
In today's information-saturated landscape, where discerning truth from falsehood and navigating the deluge of data are paramount, the tools and techniques elucidated herein provide a beacon of guidance. By engaging with diverse digital resources and undertaking thought-provoking exercises, individuals can sharpen their analytical acumen, refine their communication prowess, and fortify their intellectual resilience.
Moreover, the significance of critical thinking transcends academic pursuits, permeating every facet of professional and personal life. Whether confronting complex challenges in the workplace, making informed decisions in daily endeavours, or engaging in civil discourse on societal issues, the ability to think critically empowers individuals to navigate ambiguity, evaluate evidence, and articulate reasoned perspectives.
As we reflect on the insights gleaned from this exploration, it becomes evident that critical thinking is not merely a skill set but a mindset—an ethos of inquiry, scepticism, and intellectual curiosity that transcends disciplinary boundaries and cultural contexts. By fostering a culture of critical inquiry and embracing lifelong learning, individuals can embark on a trajectory of continual growth, adaptability, and success in an ever-evolving world.
In essence, the journey of cultivating critical thinking is one of perpetual evolution — a journey marked by introspection, exploration, and transformation. As we harness the power of digital resources and exercises to sharpen our critical faculties, we fortify our cognitive armour, enabling us to navigate the complexities of the modern age with clarity, conviction, and confidence.
Список литературы Intellectual agility: a toolkit of varied techniques for critical thinking
- Abdukadirov A. A. Cases from "Pedagogy" and "Psychology" sciences and the methodology of their use // Science and technologies. 2015. 161 p.
- Непряхин Н., Пащенко Т. Критическое мышление: железная логика наbвсе случаи жизни. М.: Альпина Паблишер, 2020. 192 с.
- Чатфилд Т. Критическое мышление. Анализируй, сомневайся, формируй свое мнение. М.: Альпина Диджитал, 2018.
- Махошева М. Х. Критическое мышление // Моя профессиональная карьера. 2021. Т. 1. №28. С. 23-27. EDN: MAGPWP
- Brookfield S. D. Teaching for critical thinking: Tools and techniques to help students question their assumptions. John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
- Changwong K., Sukkamart A., Sisan B. Critical thinking skill development: Analysis of a new learning management model for Thai high schools // Journal of International studies. 2018. V. 11. №2.
- Saiz C., Rivas S. F. New teaching techniques to improve critical thinking. The Diaprove methodology // Educational Research Quarterly. 2016. V. 40. №1. P. 3-36.
- Орипова Н. Х., Ашурова С. Б. Аспекты формирования мировоззрения детей дошкольного возраста // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2018. Т. 4. №2. С. 409-413. EDN: YOQNAV
- Орипова Н. Х., Ашурова С. Б. Современные методы формирования мировозрения детей дошкольного возраста // Журнал научных публикаций аспирантов и докторантов. 2018. №7. С. 46-48. EDN: XUOLUD
- Орипова Н. Х., Келдиярова В. Б. Формирование образного мышления учеников начальных классов через интеграционное обучение // Журнал научных публикаций аспирантов и докторантов. 2018. №7. С. 43-45. EDN: XUOLTV


