Islamic insurance and foreign investment process: a basic analysis regarding takaful laws of the Arab states of the Persian gulf
Автор: Abadikhah M.
Журнал: Вестник Института права Башкирского государственного университета @vestnik-ip
Рубрика: Международное право
Статья в выпуске: 4 (24), 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The Arab states of the Persian Gulf (ASPG), i.e. Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Bahrain, Oman, Kuwait and the United Arab Emirates, have adopted different protection mechanisms in recent years to attract foreign investors. One of the most significant mechanisms in this regard is foreign investment insurance. The noteworthy point is that these Arab states are Islamic ones and the existing laws in these societies are based on Islamic doctrine.
Takaful, investment law, arab states, persian gulf, islamic insurance
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142243965
IDR: 142243965 | УДК: 34 | DOI: 10.33184/vest-law-bsu-2024.24.13
Текст научной статьи Islamic insurance and foreign investment process: a basic analysis regarding takaful laws of the Arab states of the Persian gulf
Ufa University of Science and Technologies, Ufa, Russia, ,
Уфимский университет науки и технологий, Уфа, Россия, ,
Introduction. Many capital-exporting countries use unilateral initiatives to further protect their investors when investing in developing countries in the form of government-sponsored insurance through export credit agencies and importexport banks. They provide an additional layer of protection against mainly political risks. These unilateral measures were followed by multilateral measures by a number of countries that decided to provide insurance through a multilateral agency called the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA). The functioning of these agencies as an insurance institution is the last solution in this regard, which means that investors are expected to seek the support of insurance companies in the first place, and if they do not get the required support Through these companies, they may seek the support of national insurance programs. At this stage, if companies and investors cannot find the protection they need through national insurance programs, only then can they resort to MIGA. The difference between the insurance programs provided by insurance companies on the one hand, and the programs provided by import and export banks and MIGA on the other hand, is that the list of political issues covered by MIGA and the banks is more expanded than what the insurance companies cover.
Therefore, insurance is another protective mechanism which investors try to buy and guarantee their investment. Access to insurance, as part of a broad range of essential financial services, is especially important for foreign investors in order to smooth investment process, build assets, absorb shocks, and manage risks associated with irregular and unpredictable conditions1. However, using insurance by Muslim investors or in Islamic states is considered in different way which is more cooperative and based on Islamic doctrine. In majority Islamic countries, accessing and using insurance products has been quite limited, as many Muslims avoid such services over concerns about Riba (interest), Gharar (uncertainty and ambiguity in contracts), and Maysir (speculative risk), among other factors. Takaful insurance products (Islamic Insurance) are emerging as a central part of the Shariah-compliant family of financial services, helping meet insurance needs in ways that are consistent with the Islamic norms and beliefs of majority Islamic countries. Takaful has been developing steadily since the first Shariah-compliant insurer was founded in 1979, based on a Shariah-compliant cooperative model resembling mu- tual insurance. This is based on a group of participants donating funds into a pool that members can then use in the event of specified unfavorable contingencies. While practitioners have applied varying business models and standardization remains a challenge, many policy makers recognize the potential of takaful to expand financial inclusion and have aimed to promote the industry with supportive legislation and effective regulation. The response has been strong, with premiums growing about 30 percent annually between 2007 and 2010, reaching US$8,3 billion21. In addition, the takaful market size has grown rapidly in recent years. It will grow from $29,54 billion in 2023 to $33.14 billion in 2024 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12,2 %. The expansion during the historical period can be credited to the growth of Islamic finance, increasing awareness of Islamic insurance, government backing and regulation, ethical and social responsibility, and partnerships in Islamic banking. This robust performance is expected to continue, based on substantial latent demand in Muslim majority countries and improvements in the industry, including better distribution capabilities. As, the takaful market size is expected to see rapid growth in the next few years. It will grow to $51,75 billion in 2028 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11,8 %32 and $126,8 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 15,2 %43.
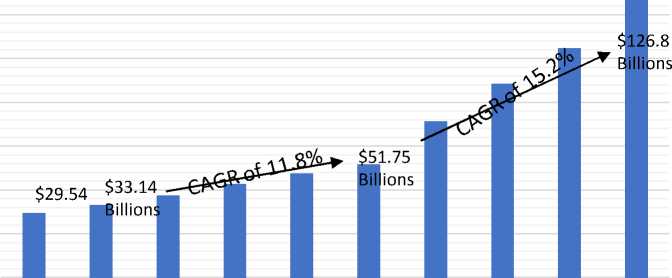
Takaful Global Market Size from 2023 to 2032 (source: investigation of author)
Considering the Global Market size of the takaful and its significant annual growth, it is necessary for Islamic states, whose goal is to attract more foreign investors, to pay attention to this commercial field by taking into consideration the legal framework. Therefore, in line with the basic question of this article, i.e. have the relevant laws regarding foreign investment insurance in the ASPG also paid attention to Islamic insurance or Takaful, five basic hypotheses are considered: first, Although the ASPG are Islamic ones, some countries such as Oman and Kuwait have enacted Islamic insurance laws in the last ten years (in 2016 and 2019, respectively). Second, Takaful activities started much earlier on the basis of Islamic fatwa, and years later, Arab states enacted Islamic insurance laws. Third, all ASPG have established Islamic insurance laws which including Takaful and conventional insurance at the same time. Fourth, some of these countries' insurance laws include Islamic and conventional insurance at the same time, like Qatar. Fifth, all six Arab states in this region believe that insurance laws should not contradict Islamic doctrine. In accordance with the hypotheses, the current article proceeds in four steps. Part 1, focuses on concept and definition of Takaful insurance; in this part, concept of Takaful has been considered from the point of view of laws. Part 2 ponders the main relevant laws which considered the Takaful insurance in Arab states. Part 3 makes a brief comparison between the Arab states of Persian Gulf through a table. The last part concludes.
The concept and definition of Takaful insurance. Takaful originates from the Arabic word Kafalah, which means “joint guarantee”. The concept is in line with the principle of compensation and shared responsibilities among the community. Takaful originated within the ancient Arab tribes as a pooled liability that obliged those who committed offences against members of a different tribe to pay compensation to the victims or their heirs. This principle later extended to many walks of life in Modern Islamic world, including maritime commercial relations, in which participants contributed to a fund to cover anyone in a group who suffered mishaps on sea voyages51. From the point of view of law, the concept can be seen within the Bahrani and UAE’s Takaful law. According to the Bahrani Takaful Modules, it is generally accepted by Muslim Jurists that the operation of conventional insurance does not conform to the rules and requirements of Shari’a. Takaful firms62 provide products and services corresponding to those offered by a conventional insurer to an insured (policyholder) but in a legitimate co-operative manner consistent with Islamic principles. Accordingly, takaful contracts are designed so as to be free of any gharar (uncertainty that would render them non-compliant with Shari’a), riba (interest) and other prohibitions71. Furthermore, the concept of takaful involves the payment of contributions that are wholly or partially donated to form an insurance portfolio. The pooled resources are then used to pay indemnity when the insured risk occurs. The pooling of donations and assisting those in need through indemnity payments does not contradict Shari’a but is in line with the principles of compensation and shared responsibilities among the community82.
In addition, according to the Takaful law of UAE, Takaful insurance means a collective contractual system aiming at attaining cooperation between a group of participants to face specific risks whereby each one of them pays a certain contribution that leads to formation of an account called the participants' account through which the due compensation will be paid to whomever the risks are realized in his respect. The Takaful operator will manage the account and invest the amounts collected therein against a specified remuneration9 3 .
Islamic Insurance Regulations of Arab States of Persian Gulf. Regarding insurance laws, three approaches can be observed among these six States: 1. Countries that have directly and transparently established Takaful insurance law, such as UAE, Bahrain and Oman 2. Sates which do not directly have a law under the title of Takaful, but their insurance law includes Takaful and conventional insurance such as Kuwait and Qatar. 3. Countries that do not have a law directly for takaful insurance, but their insurance law only includes Shariah doctrine. There is only one state in this approach i.e. Saudi Arabia.
Arab States with laws titled “Takaful law”. In exactly the same year that Saudi Arabia enacted its insurance law, Bahrain introduced the Islamic insurance model or takaful. However, the history of insurance in Bahrain can be seen in several stages. first, foreign insurance companies that provided conventional insurance in 1950; Second, national insurance companies that provided conventional insurance in 1960; Third, the national insurance companies that offered Islamic insurance for the first time in 1989. Fourth, approval of the Islamic insur- ance model under the Takaful model in 2005. The Bahraini Takaful module which has been provided by Central Bank of Bahrain includes 6 sections. The sections paved the foreign investors’ way by focusing on important elements of Takaful insurance in Bahrain like concept of Takaful, authorization, high level controls, general requirements, risk managements and liabilities10.
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) can be considered the first Arab country located in the Persian Gulf that has officially established the Islamic insurance law or takaful. However, before the adoption of a comprehensive law regarding Takaful insurance by the UAE, this country has gone through several stages. First. The presence of foreign insurance companies in the 1950s; Second, national insurance companies that paid attention to conventional insurance laws in the early 1970s; Third, national insurance companies that officially offered Islamic insurance or takaful in the late 70s. Fourth, the approval of a comprehensive law entitled "Takaful Regulations" which officially addresses the dimensions of Islamic insurance. This law consisted of seven sections which fully explained Takaful dimensions. The law clarifies the way of foreign investors by delving into the main issues like Takaful Insurance policy, liability in takaful insurance, risk management policy, membership contribution and so on11 2 .
Oman has paid attention to Islamic insurance in the last ten years. Insurance activities in this country include four stages: First, like other Arab states in this realm, insurance activities in Oman were started by foreign insurance companies in 1971. Second, twelve years later, in 1983, national insurance companies began to operate. It should be noted that insurance activities were based on conventional insurance. Third, the activities of national insurance companies in line with Islamic insurance rules have started in 2014. Fourth, the Islamic Insurance Law was approved in Oman in 2016. The law titled “Royal Decree 11/2016 Promulgating the Takaful Insurance law”, duly paid attention to the dimension of Takaful in Oman containing types of operations, liabilities, the rights of partners, risk management in investment and the like12 3 .
Arab states with laws titled “Insurance law”. Qatar is another state located in the Persian Gulf that has attracted the attention of many foreign investors. Qatar is another country located in the Persian Gulf that has attracted the attention of many foreign investors. The governing law in Qatar can be considered a mixed law of Islamic insurance and conventional insurance. Insurance activities in Qatar since its beginning in the 1960s until now include three stages: First, foreign insurance companies that started conventional insurance activities in 1964. Second, the national insurance companies that provided conventional insurance and Islamic insurance and their activities have been started in 1966. Third, the Qatar Insurance Law, only a small part of which deals with Islamic insurance or takaful. According to the Article 78 of the insurance law of Qatar Takaful is a type of Islamic businesses which the investors can involve in13 1 .
Kuwait can be considered as the last state in Persian Gulf that has officially established a law in line with takaful. The beginning of insurance activities in this country includes four stages: First, foreign insurance companies started their activities in 1949. it should be noted that the first company was an Arab company from Lebanon. So, it can be said that Kuwait is slightly different from other Arab countries because there were foreign companies from America or Britain in those countries. Second, local insurance companies that started their activities in 1960. Of course, it important to say that at this time, insurance activities were based on conventional insurance. Third, national insurance companies that paid attention to Islamic insurance in 2000. Fourth, the comprehensive Insurance Law which includes conventional and Takaful, and was approved in 2019. According to the title 5 of this law, the rights and duties of the Takaful insurance companies are determined14 2 .
Arab states with Laws titled “Insurance law” based on Shariah: There is only Saudi Arabia in this Approach. The Kingdome, as a state where Islam emerged, has been a leader in this regard15.3Before a comprehensive law regarding insurance in Saudi Arabia, insurance companies have started their activities. In other words, insurance activities in Saudi Arabia can be considered to contain four stages. First, foreign companies which started their activities in Saudi Arabia in 1950161. Second, local insurance companies like red sea company that started their activities in 1974. Third, national insurance companies like company for cooperative insurance which obtained the necessary licenses at the national level in 1986. Fourth, approval of the comprehensive national law for insurance activities. The comprehensive insurance law of Saudi Arabia under the title of “cooperative insurance companies control law” was approved in 2005. Since Saudi Arabia is an Islamic country, before the approval of this law, insurance activities were carried out on the basis of Islamic fatwas or Islamic orders of clerics27. This code includes 25 articles which provides good framework for insurance in Saudi Arabia and clarifies what is the Insurance, what kind of operations can be covered by insurance in the kingdom, what are the responsibilities and rights of both sides in an insurance contract and the like. The title of the Saudi Arabian insurance law does not officially refer to Islamic insurance or takaful. However, its regulations are based on Sharia law; as it states, Insurance in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia shall be provided by insurance companies registered in the Kingdom operating in accordance with the practice of cooperative insurance in line with the provisions of the Articles of Incorporation of the National Company for Cooperative Insurance issued by Royal Decree No (M/5) dated 17/4/1405 H, and not inconsistent with the provisions of Shari'ah183.
Comparison of the Arab States of the Persian Gulf at a glance. In general, it should be said that the approach of the United Arab Emirates, Oman and Bahrain has been better regarding the establishment of the Islamic Insurance Law; Because these states have strict laws under the title of Takaful insurance law and the exact framework of Islamic insurance is clear. Second, the approach of Saudi Arabia can be considered; because the country has not directly addressed Takaful, but in the first article of its insurance law, it has stated that all insurance operations in Saudi Arabia should not be contrary to Islamic doctrine. Thirdly, the approach of Kuwait and Qatar can be considered. The approach of these states is a little different and certainly such an approach has been adopted considering foreign investors. Because according to the laws of these two countries, both types of Islamic and con- ventional insurance are used. Of course, a foreign investor who does not like to apply takaful can use conventional insurance. In short, I mention the stages of insurance operations within the Arab states in the following table.
The table of Takaful regulation and stages of insurance in Arab states of Persian Gulf (source: the investigation of Author)
|
Arab States in Persian Gulf |
The Stages regarding conventional and Takaful |
The regulations on Takaful insurance |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Saudi Arabia |
|
Saudi Arabian Insurance law titled “cooperative insurance companies control law” was approved in 2005 |
|
Bahrain |
|
Islamic insurance model titled Takaful/Re-takaful Modul in 2005 |
|
UAE |
|
The approval of a comprehensive law entitled "Takaful Regulations" in 2010 |
|
Qatar |
|
The Qatari Insurance law titled “Law No. 13 of 2012” |
End of table
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Oman |
|
The Omani Islamic insurance law titled “Royal Decree 11/2016 Promulgating the Takaful Insurance law” approved in 2016 |
|
Kuwait |
|
The comprehensive Insurance Law which includes conventional and Takaful insurance, and was approved in 2019 |
Conclusion. In recent years, the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, namely Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Oman and Bahrain, have become one of the main destinations in international investment process. Therefore, the officials of these states are trying to attract more investors by considering specific investment protection mechanisms. One of these special mechanisms is foreign investment insurance. In this article, I clarified that the foreign investment insurance in these countries is different from other countries; Because the Arab states located in this geographical area are considered Islamic ones and the insurance laws governing them are also in accordance with Islamic doctrine. However, three processes can be observed in the direction of foreign investment insurance in these states: First, the beginning of insurance activities in the Arab states has been carried out by foreign insurance companies, and all foreign insurance companies have also involved in insurance operations based on conventional insurance. Therefore, no attention has been paid to Takaful in these countries from the very beginning. Second, Takaful activities have been started by national insurance companies. The activities of these companies were initially based on Islamic fatwas; because there were no governmental laws in this regard. Third, regarding insurance laws, three approaches can be observed among these six States: 1. Countries that have directly and transparently established Takaful insurance law, such as UAE, Bahrain and Oman 2. Sates which do not directly have a law under the title of Takaful, but their insurance law includes Takaful and conventional insurance such as Kuwait and Qatar. 3. Countries that do not have a law directly for takaful insurance, but their insurance law only includes takaful. There is only one state in this approach i.e. Saudi Arabia.
Список литературы Islamic insurance and foreign investment process: a basic analysis regarding takaful laws of the Arab states of the Persian gulf
- Alshammari A., Alhabshi S.M. and Saiti B. A Comparative Study of the Historical and Current Development of the GCC Insurance and Takaful Industry. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 2018, vol. 2, no. 9, pp. 356-369.
- Jason Chuah. Export Credit and Credit Guarantee Institutions - Balancing Values in the Regulatory Environment.International Trade Law and Regulation, 2010, vol. 155, pp 155-164.
- James Crawford and William Micheal Reisman, Foreign Investment Disputes. Wolters Law and Business, 2014. 1277 p.
- Hemrit W. Determinants Driving Takaful and Cooperative Insurance Financial Performance in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Accounting & Organizational Change, 2020, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 123-143. EDN: KSSWAJ
- Kathryn Gordon. Investment Guarantees and Political Risk Insurance Institutions, Incentives and Development. OECD Investment Policy Perspectives, 2008, 104 p.
- Various Authors. Approaches to Enterprise Risk Management. Bloomsbury USA, 2011, February 15, 146 p.
- Wael Saghir, Foreign Direct Investment Risks and Export Credit Agencies: A Practitioner's Guide. Wildy, Simmonds and Hill Publishing. 2018, December. 275 p.


